Abstract
In the covariant averaging scheme of macroscopic gravity, the process of averaging breaks the metricity of geometry. We reinterpret the back-reaction within macroscopic gravity in terms of the non-metricity of averaged geometry. This interpretation extends the effect of back-reaction beyond mere dynamics to the kinematics of geodesic bundles. With a 1 + 3 decomposition of the spacetime, we analyse how geometric flows are modified by deriving the Raychaudhuri and Sachs equations. We also present the modified forms of Gauss and Codazzi equations. Finally, we derive an expression for the angular diameter distance in the Friedmann Lemaître Robertson Walker universe and show that non-metricity modifies it only through the Hubble parameter. Thus, we caution against overestimating the influence of back-reaction on the distances.
PACS:
98.80.-k; 04.50.Kd
MSC:
83D05; 83F05
1. Introduction
The universe is traditionally modelled by employing cosmological solutions to the Einstein field equations. In these models, the matter distribution is taken to be averaged over cosmological scales and hence, the Einstein tensor needs to be averaged as well [1,2]. However, averaging tensor fields on a differentiable manifold is not straightforward, and this is a well-known problem in relativistic cosmology [3,4]. The difficulty arises because of the lack of a mathematically rigorous integration operation on non-Euclidean geometries. The non-linearity of the Einstein field equations exacerbates the problem since the averaged dynamics of a given metric are different from the dynamics of an averaged metric, i.e., . This is referred to as the averaging problem in the literature. There is a long history of approaches to this problem (see [3,5,6] and the references within). In all the approaches, however, the problem is effectively addressed by modifying the dynamics of the averaged spacetime. This modification may take different forms in various approaches and is generically referred to as cosmological back-reaction [5,6]. One such approach is macroscopic gravity [7,8,9,10], which offers a non-perturbative and fully covariant solution to the averaging problem.
Macroscopic gravity calculates the spacetime averages of arbitrary tensor fields through averaging bi-vectors and Lie dragging of the averaging regions. When this averaging scheme is applied to general relativity (GR), the Riemannian1 structure of the geometry is broken. The averaged geometry (the geometry at the macroscopic scales) is equipped with a metric-incompatible but symmetric connection that arises from averaging. This leads to a non-vanishing non-metricity but a vanishing torsion. The dynamics of macroscopic gravity are given by taking a spacetime average of the Einstein field equations. The back-reaction in these dynamics is also given in terms of the non-metricity, as has been noted in [11,12].
The aim of this work is to analyse the effects of the non-metricity in macroscopic gravity on various aspects of relativistic cosmology. We achieve this by treating macroscopic gravity as a metric-affine theory. In such a theory, the geometry is endowed with a metric and an independent connection, which is precisely how macroscopic gravity proposes the averaged geometry to be. This means that the back-reaction (arising due to non-metricity) modifies the kinematics in the averaged universe. This work emphasises this by demonstrating its effects on geometric flows, which in turn affect the distance measures in cosmology.
We perform a 1 + 3 decomposition of the macroscopic geometry. This enables us to derive the kinematics of geodesic flows. We show that both the Raychaudhuri and Sachs optical equations have contributions from the non-metricity. In other words, back-reaction in macroscopic gravity modifies not only the dynamics but also the kinematics. However, it turns out that the non-metricity has no effect on the cross-sectional area of geodesic bundles. We use the Sachs equation to derive an expression for the angular distances in an arbitrary spacetime. As a quick application of this geometric setup, we present the case of a spatially flat Friedman–Lemaître-Robertson–Walker (FLRW) universe and discuss how the non-metricity affects the distance measurements. We also show that the spatial hypersurfaces have a non-Riemannian geometry and derive the modified Gauss and the Codazzi equations.
The organisation of the paper is as follows: in Section 2, we present the basic formalism of macroscopic gravity and reinterpret it as a metric-affine theory. In Section 3, we derive the structure equations for geometric flows. Then, in Section 4, we discuss the geometry of spatial hypersurfaces and derive the Gauss–Codazzi equations. In Section 5, we derive an expression for the angular distances. We show that the back-reaction affects the distances only through the dynamics (Hubble expansion). Finally, in Section 6, we discuss the results in this paper and provide a few concluding remarks.
The notation used is as follows: Greek indices run from 0 to 3 while Latin indices run from 1 to 3. The partial derivative is denoted by ∂, while ∇ and denote the covariant derivatives with respect to the non-Riemannian and the Levi–Civita connections, respectively. Averaged quantities are denoted using angular brackets, . The indices within and are symmetrised/anti-symmetrised and underlined indices are not included in (anti-)symmetrisation. The sign convention followed is the ‘Landau-Lifshitz Space-like Convention (LLSC)’ [13].
2. Averaging the (Pseudo-)Riemannian Geometry
2.1. Basics of Macroscopic Gravity Formalism
In this section, we briefly present the basic formalism of macroscopic gravity. We use the same terminology as used in [7,8,9,11]. We will reinterpret certain quantities within the macroscopic gravity formalism in terms of more familiar geometric objects in a metric-affine gravity. Macroscopic gravity employs a covariant averaging procedure to average out the (pseudo-)Riemannian geometry and the field equations of general relativity [7,8,9,10,11,14,15]. Given a geometric object, , defined on an n-dimensional differentiable metric manifold , the spacetime averaged value of this object is defined as:
where the average has been taken over a compact region around a supporting point ; is the volume () of the region and . The integration is carried out for all the points . The integrand is called the bilocal extension of the object and the objects and are called the bilocal averaging operators.
The average is taken over finite volume regions in the manifold (i.e., is finite). Hence, well defined microscopic objects average out without the integral diverging in Equation (1). In the limit of vanishing averaging volume, the average of the object is equal to the object itself [7,8,9]. Furthermore, there is freedom to choose these averaging operators according to the problem at hand. However, all these operators must have the following properties: coincidence limit, idempotency, the existence of an inverse, and factorisation (see [7,8] for details). Moreover, the averaging procedure is constructed in such a way that the average of a quantity is uniquely defined and does not depend on the choice of the averaging operators [7,8,9].
The average of the microscopic Riemann curvature tensor is written as and behaves like a curvature tensor [7,8,9,11]. Further, bilocal objects defined as behave as connection coefficients at x, and hence can be considered the bilocal extension of the microscopic connection coefficients, . They have the following coincidence limit:
The average of the connection coefficients, , are the macroscopic affine connection coefficients [7,8]. Then, one can construct a curvature tensor, , with these macroscopic connection coefficients. This will not be the same as the average of the microscopic curvature tensor, but rather is related to it through
The additional terms on the right hand side arise from the fact that the curvature is a non-linear function of the connection coefficients.
One can calculate another connection, , associated with the curvature tensor . Therefore, in the macroscopic spacetime, there are two connections associated with two curvature tensors, which are related to each other via Equation (3). An affine deformation tensor, , can be defined, which measures the difference between the two connections. This deformation tensor exists due to the metric incompatibility of the connection . That is, for macroscopic metric, , we have:
where | denotes the covariant derivative with respect to the connection .
Further, looking at the construction of both the curvature tensors in terms of their respective connections, Equation (3) takes the form:
where || denotes the covariant derivative with respect to the metric-compatible (Levi–Civita) connection, , of the macroscopic manifold. The tensor, , is dubbed the gravitational polarisation tensor [7], and is related to the the bilocal objects , as follows:
The tensor, , although not a curvature tensor, follows the algebraic and differential properties of one. From Equations (3) and (6), we can see the that it measures the difference between the two curvature tensors—a curvature deformation tensor:
Both the curvature tensors, and , follow the same algebraic identities and the differential Bianchi identities with respect to their corresponding connections. The former ensures that the connection, , although metric-incompatible, is symmetric. Moreover, the averaging of the differential Bianchi identities for the microscopic curvature tensor leads to the following relations:
In order to evaluate the above equations, a splitting rule is required for the products in the second and third terms. This is constructed using an object called the connection correlation, which is defined as [7,8]:
Using Equations (6) and (9), we see that,
In summary, when the averaging procedure of macroscopic gravity (1) is applied to the four-dimensional (pseudo-)Riemannian manifold of GR, one finds that, at macroscopic scales, the manifold is characterised by a metric, two symmetric affine connections2, two curvature tensors associated with these connections, and a correlation tensor that needs to be constructed in order to solve the differential Bianchi identities for these curvature tensors.
The Field Equations of Macroscopic Gravity
The average of Einstein field equations with a cosmological constant:
yields the field equations of macroscopic gravity, which are given by: [7,8],
where , , , , and is the averaged energy-momentum tensor (usually taken to be that of a perfect fluid in cosmology). Therefore, upon averaging, the field equations are modified and now include additional terms, given (partially) in terms of the non-metricity of the spacetime.
2.2. Non-Metricity of the Averaged Geometry
As discussed above, applying the averaging procedure of macroscopic gravity to GR leads to the interesting result that, at macroscopic scales, the manifold is non-Riemannian. That is, the manifold has a Riemannian structure only at small (microscopic) scales. At such scales, GR is a valid theory of gravity. However, when one is concerned with large scales (like in cosmology), an averaging has to be performed on the geometry, and in the process, the Riemannian structure of the manifold is broken. In other words, for cosmological analyses, one must work with a theory of gravity that employs a non-Riemannian geometrical framework. The theory of macroscopic gravity is precisely such a theory.
According to the macroscopic gravity formalism, the non-Riemannian (macroscopic) manifold is characterised by a symmetric but metric-incompatible connection, given by . The covariant derivative of the metric (of the macroscopic manifold) with respect to this connection is not zero. The non-metricity tensor is then defined as:
Using this, the general connection, , can be decomposed as:
where is the Riemannian part (Levi–Civita connection)3, and is the so-called disformation tensor that encapsulates the deviation from the Riemannian nature of geometry. The disformation is given in terms of the non-metricity as:
Further, the Ricci identity is given by:
where , is the Riemann curvature tensor defined in terms of the general connection of the non-Riemannian geometry:
Using Equation (14), it can be shown that:
where is the Riemannian part of the curvature tensor, which is the same as of the previous section, and is the covariant derivative both defined with the Levi–Civita connection. One can define a new quantity that captures the deviation of the curvature tensor from its Riemannian counterpart:
It is not difficult to see that the so-called affine deformation tensor, , and the polarisation tensor, , of macroscopic gravity are, respectively, the disformation tensor, , and the object, , of the metric–affine gravity literature. Henceforth, we will use these symbols to denote the affine deformation tensor and polarisation tensor since we are treating the theory of macroscopic gravity as a metric–affine theory.
3. Structure Equations for Geometric Flows
Since the geometry at the macroscopic scales is no longer Riemannian, determining the geodesic curves (curves with extremum length) is not trivial. In Riemannian geometry, the autoparallel curves with respect to the Levi-Civita connection are also the geodesic curves. Then, the geodesic equation is given by:
However, in general, autoparallel curves (of a non-Riemannian geometry) are not necessarily geodesics. In fact, since, in non-Riemannian geometry, there exist additional geometric fields (like non-metricity), the paths traced by freely moving physical particles (the geodesics) will depend on whether these particles interact with these ‘new’ geometric fields [18]. In cosmology, one takes the content of the universe to be a perfect fluid or dust. Since such matter does not interact with non-metricity, despite the averaged geometry being non-Riemannian, the path that is traced is taken to be the Riemannian geodesics given by Equation (21).
We will now derive equations governing the evolution of the congruences of geodesics on the averaged (non-Riemannian) geometry. These are sometimes called kinematic equations. Given a congruence, one can characterise its flow in terms of the evolution of the irreducible components of its velocity gradient. Physically, these equations characterise the flow of the fluid content of the Universe (for the timelike curves) and bundle of photons (for the null curves). We will derive (in detail) the equations for the trace part of the velocity gradient (also called expansion) for both the timelike and null curves. This will provide us with the macroscopic gravity analogue of the Raychaudhuri and Sachs equations [19,20].
3.1. The Raychaudhuri Equation
To derive the Raychaudhuri equation, we begin with considering a congruence of timelike geodesics. Let be the vector field tangent to the congruence (the velocity vector). In cosmology, this is simply the comoving velocity of the (fluid) content of the Universe, . The norm of such a velocity is normalised as [21]. We are interested in the transverse evolution of the congruence, and hence we define a transverse metric in the following manner [21]:
The 3-metric is completely transverse to the congruence, i.e., we have . It is easy to see that . This splits the spacetime into temporal and spatial parts, referred to as decomposition. All the quantities transverse to the congruence reside on a spatial hypersurface orthogonal to it. Here, we will investigate the transverse properties of the congruence while, in the next section, we present the properties of spatial hypersurfaces.
Using the 3-metric, one can separate the transverse and longitudinal parts of the velocity gradient, as follows:
where ∇ represents the covariant derivative with respect to the non-Riemannian connection, . It is easy to observe that . The transverse velocity gradient can be decomposed into its irreducible components as follows:
where is the trace part, known as expansion, is the anti-symmetric part, known as rotation or vorticity, and is the symmetric traceless part, known as shear.
Using the expression for the expansion scalar, we can write:
where we have used , which follows from Equation (21). One can decompose the first term on the right hand side of the above equation into a Riemannian and a non-Riemannian part. The Riemannian part would be the usual expansion scalar: . Then, we have:
Taking a derivative on both sides gives us the Raychaudhuri equation in the averaged geometry:
where the terms with a bar over them are Riemannian quantities. The last term on the right hand side is the contribution from averaging (the back-reaction), provided solely on terms of the non-metricity of the averaged spacetime.
3.2. The Sachs Optical Equation
The Sachs optical equation is the null counterpart of the Raychaudhuri equation. To derive this, we begin by considering a congruence of null geodesics with tangent vector . The norm of the tangent is, . In this case, the transverse metric is given by:
where is an auxiliary null vector satisfying the conditions and . Once again, one can check, , and .
The steps involved in deriving the Sachs equation are analogous to the previous section. We define the transverse part of the velocity gradient as:
This can be can be decomposed into irreducible components, as follows:
Using the definition of the expansion scalar, we can obtain:
where we used . The first term on the right hand side can again be decomposed into Riemannian and non-Riemannian parts. The Riemannian part is the usual null expansion scalar, . This gives us:
Taking a derivative on both sides leads to the Sachs optical equation in the averaged geometry:
Therefore, the expansion of both the timelike and null geodesics is affected by the non-metricity that arises due to averaging. The non-metricity in macroscopic gravity partially constitutes the cosmological back-reaction. Hence, we have shown here that the back-reaction modifies not only the dynamics but also the kinematics in the averaged Universe. This is expected since, in addition to the field equations, the process of averaging in macroscopic gravity also modifies the underlying geometric structure.
Expansion Scalar and Cross-Section of Null Bundles
It is useful (especially in cosmology) to show how the expansion scalar is related to the cross-sectional area of the congruence. A formal way of achieving this can be found in [22]. We will follow an analogous treatment here. Consider a cross-section around a point P on a curve in the congruence. This can be constructed by taking a set of points, , on the neighbouring curves that correspond to the same parameter value as that of P. Let this set of points be called . To see the change in the cross-section, we need to compare to a similar set of neighbouring points at some other point, Q, along the same curve. Let us call this . Since the points on (and ) are also points on neighbouring curves; they can be used to label the curves, thus providing us with a consistent coordinate system, , on the cross-section. Then, one can construct a 2-metric on the cross-section, as follows:
Using this, it can be shown that (see [22]) the fractional rate of the change in the cross-sectional area is:
Calculating the right hand side of the above equation, we can obtain:
Using Equation (37), this becomes:
Therefore, the fractional rate of change of the cross-sectional area of the null geodesic congruence in the averaged geometry is equal to the Riemannian part of the expansion scalar:
An important point to note here is that this is turning out to be the case since we are dealing with geodesic curves (). For non-geodesic curves, one should expect contributions from non-metricity4. The fractional rate of change in the cross-sectional area is closely related to the angular diameter distances in cosmology. The consequence of Equation (42) is that the non-metricity will contribute to the distances only through the dynamics.
4. The Geometry of Hypersurfaces
In this section, we will continue with the decomposition of the spacetime presented in the last section. However, here we will present the equations governing the geometric properties of the spatial hypersurfaces. This approach is commonly employed in GR to split the curvature and the field equations into temporal and spatial parts. This leads to the well-known Gauss-Codazzi equations and the definitions of the shift and lapse functions. Such a splitting is particularly useful in probing various physical situations in numerical relativity.
Let us consider a spacelike hypersurface normal to a timelike geodesic. The 3-metric, , in Equation (22) serves as the metric for this hypersurface. This is sometimes referred to as the induced metric. In the signature adapted in this paper, this is a positive, definite, non-Riemannian metric. To analyse the geometric properties of the hypersurface, one needs to take the spatial projection of the spacetime objects. This is achieved using the induced metric in a similar manner as equation (23).
4.1. The Non-Metricity of the Hypersurface
The spatial projection of the covariant derivative is defined as follows:
This serves as the covariant derivative on the hypersurface. Using this definition, we can write:
Therefore, we see that the spatial covariant derivative of the three-metric is not zero. In other words, the spatial connection is not metric-compatible5. This means that the hypersurface retains the non-Riemannian nature. We define the the non-metricity of the hypersurface as follows:
Similarly, one can evaluate that . Note, however, that .
The extrinsic curvature of the hypersurface is defined as follows:
where is a timelike vector normal to the hypersurface, i.e., . Due to the non-metricity of the hypersurface, we have:
where . Since the connection is torsion-less (and, hence, so is the connection on the hypersurface), we have .
4.2. The Gauss Equation
The Gauss equations arises from evaluations of the Ricci identity on the hypersurface. This provides an expression for the Riemannian curvature of the full spacetime in terms of the components projected onto its hypersurface. To derive the Gauss equation, we begin by defining the Riemann tensor on the hypersurface in the following manner:
where is some vector tangential to the hypersurface, i.e., . Evaluating the left side of the above equation, we can obtain:
4.3. The Codazzi Equation
The Gauss equation relates the Riemann curvature tensor with all components projected onto the hypersurface to the extrinsic curvature. Similar to this, one can project only three components of the Riemann tensor onto the hypersurface and one component along a timelike vector: . This quantity can also be written in terms of the extrinsic curvature. This is achieved through the Codazzi equation.
To derive the Codazzi equation, we start by evaluating the following:
By anti-symmetrising and , the first term in the brackets on the right hand side vanishes. The second term turns into the Ricci identity (17). Taking care of raising and lowering of the indices introduces a few non-metricity terms, finally leading to the following:
This is the Codazzi equation. Contracting the indices and in the above equation, we can obtain:
Using the covariant formalism presented here, it will be straightforward to decompose the four dimensional averaged geometry into foliations and fibrations, as is frequently done within GR. The definition of the lapse function and the shift vector remain the same and the decomposition of the metric retains the same form [24].
5. FLRW Cosmology in Macroscopic Gravity
The field equations of macroscopic gravity, obtained by averaging the Einstein field equations, contain different traces of the connection correlation and the non-Riemannian part of the curvature tensor. These additional terms in Equation (12) are the result of a change in the geometric structure of the spacetime due to averaging. These terms constitute precisely what is referred to as the cosmological back-reaction in the literature. Considering a particular averaged geometry (i.e., taking an ansatz on the metric of the averaged spacetime), one can find the back-reaction in terms of the metric coefficients. This was previously done for the FLRW cosmological model [25,26,27]. Here, we will build upon the analyses in [25,26,27] and discuss how the non-metricity affects the distance measurements in cosmology.
5.1. Dynamics and Expansion History
Let us begin by considering the metric at the macroscopic scales, which is the spatially flat FLRW metric:
Considering the averaged matter distribution to be a perfect fluid, we can obtain the following:
where and are the energy density and pressure for the averaged matter–energy content, respectively, and is the average four-velocity of the fluid. Then, writing Equation (12) explicitly provides us with the modified Friedmann equations [25,26]:
where is a constant coming from the back-reaction term and ‘dot’ represents the derivative with respect to the cosmological time, t. One can immediately notice that the back-reaction term evolves as a curvature.
The first equation above can be written in the form:
where is the Hubble parameter; we defined, and , and we added the subscript m to differentiate the matter density from other energy densities. Further, by defining the associated density parameters as, , we can write,
Multiplying both sides by a factor of , we can obtain:
where , is the ‘non-metricity density’ at present, and we have used . The above expression provides the expansion history of the universe, taking into account the effect due to non-metricity at the macroscopic scales. One can see that, depending on the sign of the constant, , a spatially flat FLRW universe may evolve identically to a spatially curved one.
5.2. Angular Diameter Distance
In observational cosmology, one deals with large amounts of photons, and therefore, it is the averaged photon paths that should be used to calculate distances. In the context of macroscopic gravity, this means that the paths of photon bundles (null geodesics) on the macroscopic geometry should be used to determine the distance measures in cosmology. The angular diameter distance, , is related to the cross-sectional area, A, of null congruence, as [28]:
Using this, one can write:
Using Equation (43), this becomes:
Taking a derivative on both sides, one can obtain:
where, in the second equality, we have used the Sachs Equation (38).
The above equation holds for arbitrary spacetimes. For a spatially flat FLRW spacetime, we have, , and the four-velocity of null geodesics is given by [29],
Using this, one can calculate:
Using this in Equation (67), we can obtain:
Using , the above equation becomes:
Writing in terms of the scale factor, a, this becomes:
Now, making a variable change, , we can obtain:
which can be reduced to:
Solving the above differential equation leads to an expression for the angular diameter distance in the FLRW geometry:
Therefore, we see that the non-metricity affects the distance measurements only through its presence in the Hubble parameter. That is, even though the cross-sectional area of null congruences only depends on the Riemannian part of the expansion scalar, since photon trajectories are also affected by the Hubble parameter (H), the distance measurements are modified by the non-metricity. In Figure 1, we plot the expansion history and the angular distance to show the modifications caused by the small values of the non-metricity parameter.
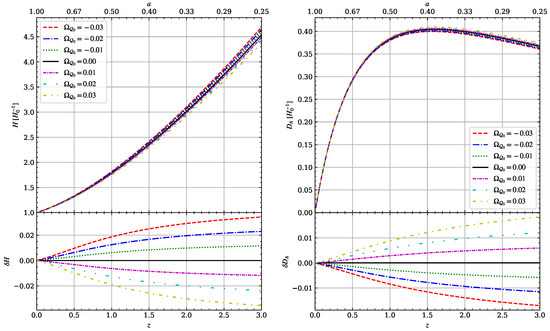
Figure 1.
Hubble parameter (left) and angular diameter distance (right) at later times () for small values of the non-metricity parameter (). The lower panel shows the relative difference between CDM values and the -CDM values.
The effects of the non-metricity (back-reaction) become more pronounced for large redshifts. For small, negative values of the non-metricity parameter, the Hubble parameter becomes larger than its CDM value. This could prove useful in the context of Hubble tension [30], in which the cosmic microwave data suggest a smaller value of the Hubble constant than the local observations. However, it is worth noting that the back-reaction parameter was previously constrained to have small positive values [31,32].
6. Summary and Discussion
In macroscopic gravity, the averaging procedure breaks the metricity of geometry, and the cosmological back-reaction can be provided in terms of the non-metricity of the spacetime. Since the non-metricity results from a change in the geometric structure of the spacetime, the effects of the back-reaction are not limited to dynamics. In this paper, we analysed the effects of non-metricity on the geometric properties of the averaged universe. The primary goal of this paper was to demonstrate how non-metricity modifies kinematics by deriving the Raychaudhuri and Sachs equations. To be able to do so, we first dealt with the questions the the non-Riemannian nature of spacetime raises about the trajectories of physical particles. It has been argued that only matter that possesses a ‘microstructure’ (properties like hypercharge and dilation) couples with the non-Riemannian geometric fields and thus will be affected by them [18]. In the metric-affine gravity literature, such matter has been termed a ‘hyperfluid’ [33,34]. Ordinary matter (e.g., the perfect fluid or dust used in cosmology) does not possess this microstructure. Hence, despite the averaged geometry being non-Riemannian, we took the paths traced by physical particles to be simply Riemannian geodesics.
Having clarified this issue, we presented a decomposition of the averaged spacetime geometry within macroscopic gravity. We started by deriving the Raychaudhuri and Sachs equations which govern the expansion of the geodesic flows. Physically, these equations characterise the flow of the cosmic fluid and photon bundles, respectively. Both of these equations were modified due to non-metricity. However, we found that only the Riemannian part of the expansion scalar was related to the fractional rate of change in the cross-sectional area of the geodesic bundles. Then, we presented the geometric properties of the spatial hypersurfaces orthogonal to these geodesics. Using a definition of the spatial covariant derivative, we showed that the spatial hypersurfaces are also non-Riemannian in nature. This became even more apparent in the expressions for the extrinsic curvature. Using the Ricci identity for hypersurfaces, we derived the Gauss–Codazzi equations. As expected, they showed us that non-metricity modifies the Riemann curvature projected onto the hypersurfaces.
Finally, we applied the results derived in this paper to observational cosmology. Using the Sachs optical equation, we derived the angular diameter distance formula. We showed that, despite the existence of a non-metricity, the angular diameter distances are not explicitly modified by it. This is a consequence of the cross-sectional area depending only on the Riemannian part of the expansion scalar. Therefore, one needs to be careful when using distances for observational cosmology within macroscopic gravity. Including the averaged Ricci tensor directly in the Sachs equation might result in an incorrect evaluation of the effects of back-reaction on distances in cosmology. However, it is important to note that the non-metricity does modify the distances implicitly through the dynamics (Hubble parameter). We plotted the expansion history and the angular distance formula to demonstrate the deviation from their CDM counterparts for small back-reaction values. We noted that a small negative value of the back-reaction parameter could help alleviate the Hubble tension. This warrants further investigations into the averaging problem.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.; methodology, A.A. and S.M.M.; formal analysis, A.A. and S.M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.; writing—review and editing, A.A. and S.M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mustapha Ishak for the useful comments. A.A. would also like to thank the anonymous reviewer of one of our previous manuscripts, whose comments were crucial in the conception of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Constraint on the Connection Correlation
To derive a solution to the averaged field Equation (12), we need to determine the form of connection correlation for a given macroscopic geometry. This is achieved by solving the following algebraic and differential constraints on the connection correlation [7,8],
where, is the unit time-like four-vector field and is the Riemannian part of the curvature tensor for the (assumed) macroscopic metric.
Equations (A1)–(A5) in Appendix A are algebraic constraints and do not depend on the macroscopic geometry. Solving these leaves one with 121 independent components in the connection correlation. Equations (A5)–(A7) ensure that the higher-order correlations are zero. One also assumes that the connection correlation is invariant under the same group of isometries as the macroscopic metric [35]. Given this, the connection correlation can be determined completely. A systematic way of deriving the above macroscopic gravity identities is presented in [26,27,35]. The disformation tensor can also be solved in a similar manner.
Notes
| 1 | The signature is implicitly assumed to be Lorentzian. Therefore, the term ‘Riemannian’ here is used to mean pseudo-Riemannian. |
| 2 | Gravity theories with multiple connections both in the Riemannian and non-Riemannian framework are already present in the literature [16,17]. |
| 3 | The Levi–Civita connection can be written in terms of metric as:
|
| 4 | In an even more general, metric-affine geometry, where the connection is not symmetric, one would have contributions from torsion even in the case of geodesic curves [23]. |
| 5 | This could mean that a covariant averaging, albeit over three-space, necessarily breaks the Riemannian nature of the space. One needs to be careful about this when comparing macroscopic gravity to spatial averaging schemes that deal only with scalars. |
References
- Ellis, G. Relativistic Cosmology: Its Nature, Aims and Problems. Fundam. Theor. Phys. 1984, 9, 215–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G.; Stoeger, W. The ’fitting problem’ in cosmology. Class. Quantum Gravity 1987, 4, 1697–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G.F.; Buchert, T. The Universe seen at different scales. Phys. Lett. A 2005, 347, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, R. Averaging Spacetime: Where do we go from here? In Proceedings of the 12th Marcel Grossmann Meeting on General Relativity, Paris, France, 12–18 July 2009; Volume 3, pp. 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, T. Back-Reaction in Relativistic Cosmology. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2013, 22, 1330004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchert, T.; Räsänen, S. Backreaction in Late-Time Cosmology. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2012, 62, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalaletdinov, R.M. Averaging out the Einstein equations. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1992, 24, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalaletdinov, R. Towards a theory of macroscopic gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1993, 25, 673–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, M.; Zalaletdinov, R.M. Space–time averages in macroscopic gravity and volume-preserving coordinates. J. Math. Phys. 1997, 38, 4741–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalaletdinov, R.M. Averaged Lagrangians and MacCallum–Taub’s Limit in Macroscopic Gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1996, 28, 953–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalaletdinov, R.M. Space-time Averages of Classical Physical Fields. Ann. Eur. Acad. Sci. 2004, 344–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Hoogen, R.J. Towards a covariant smoothing procedure for gravitational theories. J. Math. Phys. 2017, 58, 122501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misner, C.W.; Thorne, K.; Wheeler, J. Gravitation; W. H. Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Zalaletdinov, R. The averaging problem in cosmology and macroscopic gravity. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2008, 23, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalaletdinov, R.M. Averaging problem in general relativity, macroscopic gravity and using Einstein’s equations in cosmology. Bull. Astron. Soc. India 1997, 25, 401–416. [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi, N. Geometric massive gravity in multiconnection framework. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosifidis, D.; Pallikaris, K. Biconnection gravity as a statistical manifold. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 044026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukhov, Y.N.; Puetzfeld, D. Demystifying autoparallels in alternative gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 044031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, A. Relativistic cosmology. 1. Phys. Rev. 1955, 98, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, R.; Bondi, H. Gravitational waves in general relativity. VI. The outgoing radiation condition. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1961, 264, 309–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosifidis, D.; Vogiatzis, I.G.; Tsagas, C.G. Friedmann-like universes with non-metricity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, E. A Relativist’s Toolkit: The Mathematics of Black-Hole Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agashe, A. Kinematics in metric-affine geometry. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Finch, A.; Said, J.L.; Magro, A. The 3 + 1 formalism in teleparallel and symmetric teleparallel gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, A.A.; Pelavas, N.; Zalaletdinov, R.M. Cosmological Solutions in Macroscopic Gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 151102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, R.J. A complete cosmological solution to the averaged Einstein field equations as found in macroscopic gravity. J. Math. Phys. 2009, 50, 082503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijenayake, T.; Ishak, M. Expansion and Growth of Structure Observables in a Macroscopic Gravity Averaged Universe. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 063534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, P. Principles of Physical Cosmology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 99. [Google Scholar]
- Plebanski, J.; Krasinski, A. An Introduction to General Relativity and Cosmology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Di Valentino, E.; Mena, O.; Pan, S.; Visinelli, L.; Yang, W.; Melchiorri, A.; Mota, D.F.; Riess, A.G.; Silk, J. In the realm of the Hubble tension—A review of solutions. Class. Quantum Gravity 2021, 38, 153001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.; Clifton, T.; Coley, A.; Sung, R. Observational Constraints on the Averaged Universe. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 043506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijenayake, T.; Lin, W.; Ishak, M. Averaged universe confronted with cosmological observations: A fully covariant approach. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 083501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukhov, Y.N.; Tresguerres, R. Hyperfluid: A Model of classical matter with hypermomentum. Phys. Lett. A 1993, 184, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosifidis, D. The Perfect Hyperfluid of Metric-Affine Gravity: The Foundation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Hoogen, R. Spherically Symmetric Solutions in Macroscopic Gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2008, 40, 2213–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).