Cosmological Test of an Ultraviolet Origin of Dark Energy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Basic Idea
3. The Press–Schechter Formalism
4. The Revised Friedmann Equation
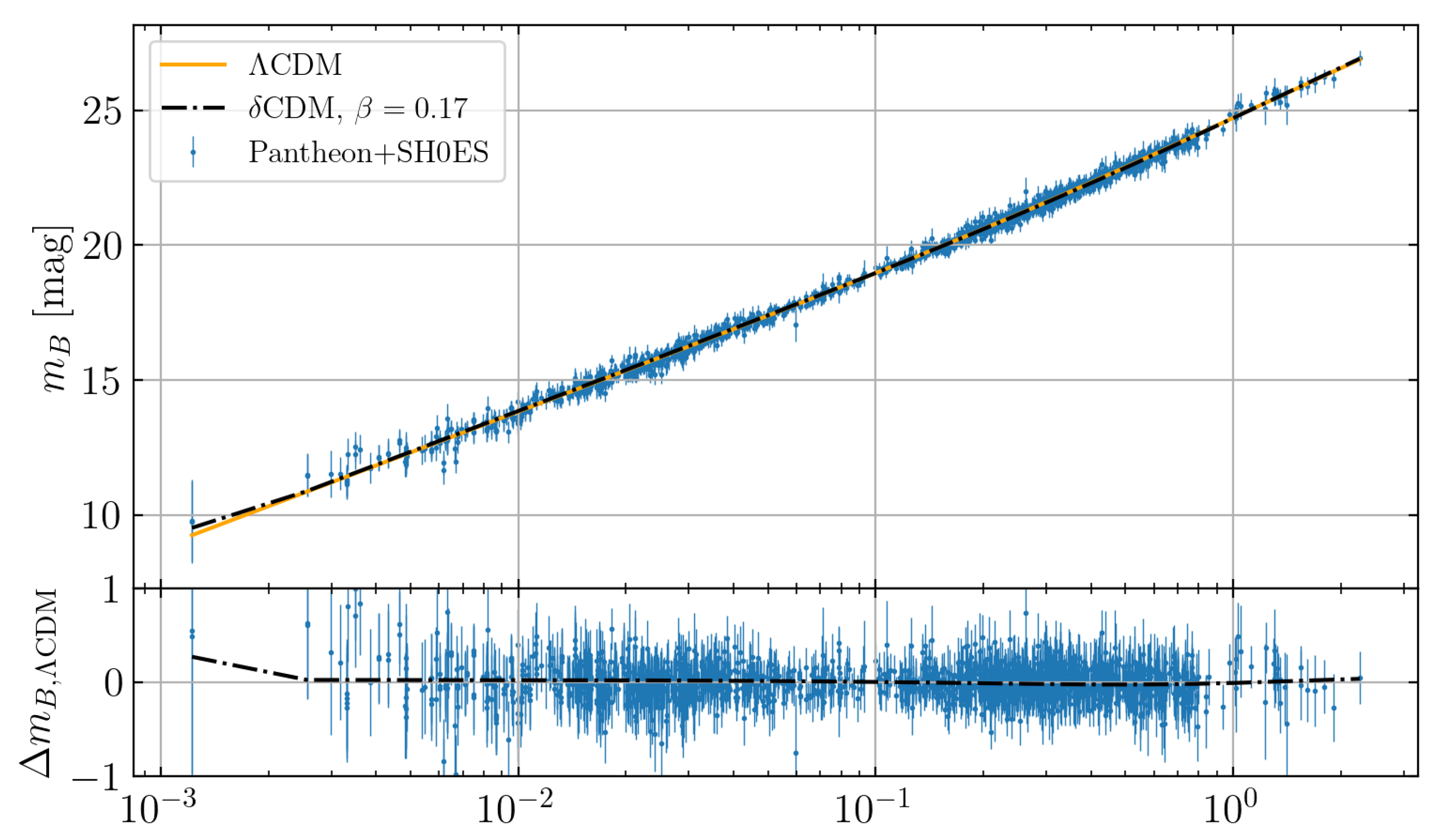
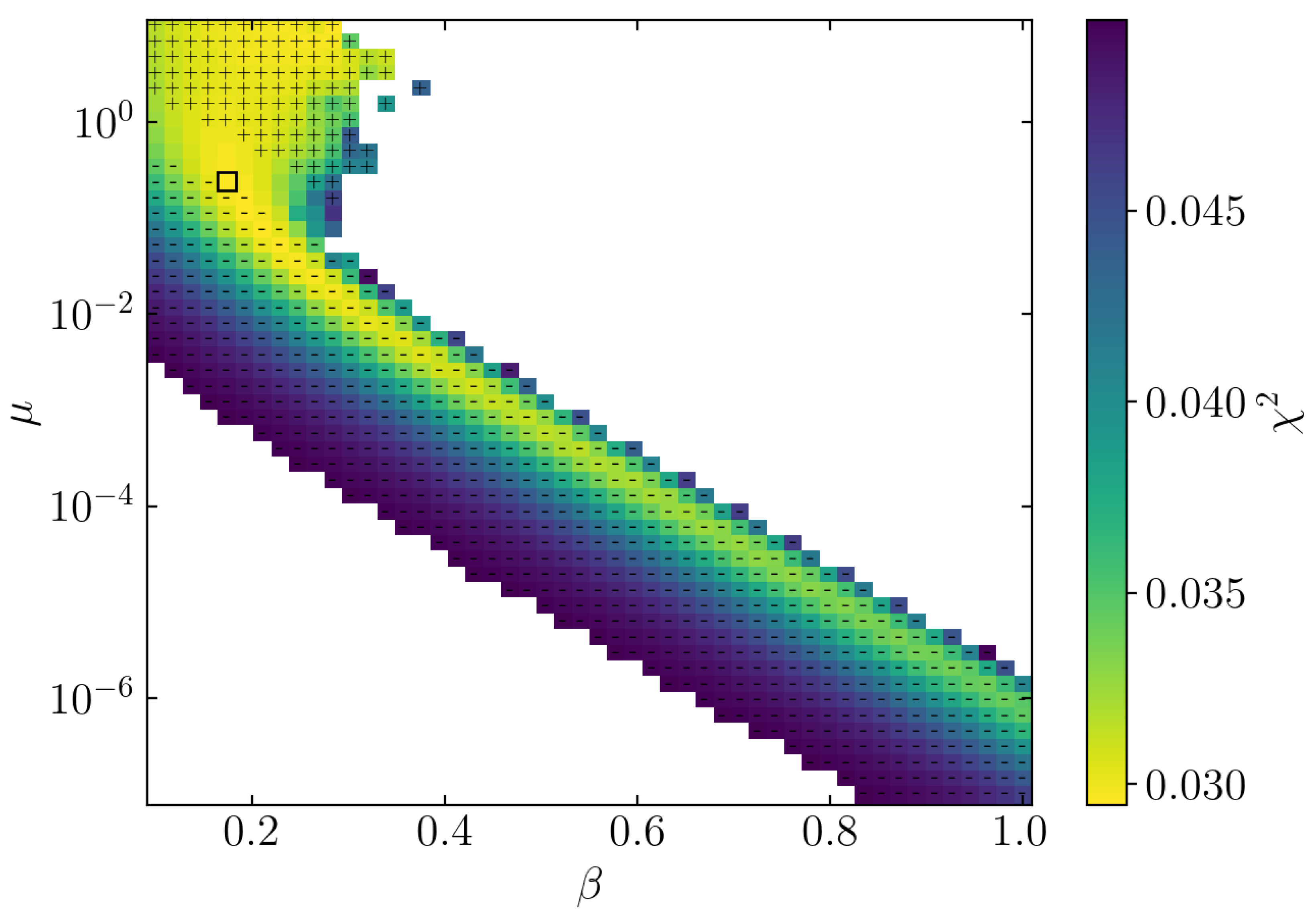
5. Supernova Data
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Goldhaber, G.; Knop, R.A.; Nugent, P.; Castro, P.G.; Deustua, S.; Fabbro, S.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 High-Redshift Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1999, 517, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, E.; Dunkley, J.; Nolta, M.R.; Bennett, C.L.; Gold, B.; Hinshaw, G.; Jarosik, N.; Larson, D.; Limon, M.; Page, L.E.A.; et al. Seven-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Cosmological Interpretation. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2011, 192, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, W.J.; Reid, B.A.; Eisenstein, D.J.; Bahcall, N.A.; Budavari, T.; Frieman, J.A.; Fukugita, M.; Gunn, J.E.; Ivezić, Ž.; Knapp, G.R.; et al. Baryon acoustic oscillations in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 galaxy sample. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 401, 2148–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.; Brough, S.; Colless, M.; Contreras, C.; Couch, W.; Croom, S.; Davis, T.; Drinkwater, M.J.; Forster, K.; Gilbank, D.; et al. The WiggleZ Dark Energy Survey: The growth rate of cosmic structure since redshift z = 0.9. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 2876–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, D.; Dunkley, J.; Hinshaw, G.; Komatsu, E.; Nolta, M.R.; Bennett, C.L.; Gold, B.; Halpern, M.; Hill, R.S.; Jarosik, N.; et al. Seven-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Power Spectra and WMAP-derived Parameters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2011, 192, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicken, M.; Wood-Vasey, W.M.; Blondin, S.; Challis, P.; Jha, S.; Kelly, P.L.; Rest, A.; Kirshner, R.P. Improved Dark Energy Constraints from 100 New CfA Supernova Type Ia Light Curves. Astrophys. J. 2009, 700, 1097–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.; Glazebrook, K.; Davis, T.M.; Brough, S.; Colless, M.; Contreras, C.; Couch, W.; Croom, S.; Drinkwater, M.J.; Forster, K.; et al. The WiggleZ Dark Energy Survey: Measuring the cosmic expansion history using the Alcock-Paczynski test and distant supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 418, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. The cosmological constant problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1989, 61, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, P.J.; Ratra, B. The cosmological constant and dark energy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 559–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, G.F. The Dawn of the Post-Naturalness Era. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.07663. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.G.; Kaplan, D.B.; Nelson, A.E. Effective Field Theory, Black Holes, and the Cosmological Constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 4971–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekenstein, J.D. Black Holes and Entropy. Phys. Rev. D 1973, 7, 2333–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekenstein, J.D. Universal upper bound on the entropy-to-energy ratio for bounded systems. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, N.; Draper, P. Densities of states and the Cohen-Kaplan-Nelson bound. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 076024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Dienes, K.R. Calculating the Higgs mass in string theory. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 126032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, N.; Koren, S. IR dynamics from UV divergences: UV/IR mixing, NCFT, and the hierarchy problem. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeve, K.; Nielsen, K.S.; Hansen, S.H. Consistency Analysis of a Dark Matter Velocity-dependent Force as an Alternative to the Cosmological Constant. Astrophys. J. 2021, 910, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.H. A force proportional to velocity squared derived from spacetime algebra. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 506, L16–L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Schechter, P. Formation of Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies by Self-Similar Gravitational Condensation. Astrophys. J. 1974, 187, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.V.; Jenkins, A. Cosmic structure growth and dark energy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 346, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Cosmology; Weinberg, S., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; ISBN 978-0-19-852682-7. [Google Scholar]
- Binney, J.; Tremaine, S. Galactic Dynamics, 2nd ed.; Binney, J., Tremaine, S., Eds.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-691-13026-2. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, D.J. The growth of density perturbations in zero pressure Friedmann-Lemaître universes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M.; Press, W.H.; Turner, E.L. The cosmological constant. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 30, 499–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longair, M.S. Galaxy Formation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-73477-2. [Google Scholar]
- Riess, A.G.; Strolger, L.G.; Tonry, J.; Casertano, S.; Ferguson, H.C.; Mobasher, B.; Challis, P.; Filippenko, A.V.; Jha, S.; Li, W.; et al. Type Ia supernova discoveries at z > 1 from the Hubble Space Telescope: Evidence for past deceleration and constraints on dark energy evolution. Astrophys. J. 2004, 607, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolnic, D.; Brout, D.; Carr, A.; Riess, A.G.; Davis, T.M.; Dwomoh, A.; Jones, D.O.; Ali, N.; Charvu, P.; Chen, R.; et al. The Pantheon+ Analysis: The Full Data Set and Light-curve Release. Astrophys. J. 2022, 938, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.M. The Absolute Magnitudes of Type IA Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1993, 413, L105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Li, W.; Treffers, R.R.; Schmidt, B.P.; Qiu, Y.; Hu, J.; Armstrong, M.; Faranda, C.; Thouvenot, E.; et al. The Rise Time of Nearby Type IA Supernovae. Astron. J. 1999, 118, 2675–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarese, L.; Merritt, D. A Fundamental Relation between Supermassive Black Holes and Their Host Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2000, 539, L9–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, K.; Bender, R.; Bower, G.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Filippenko, A.V.; Green, R.; Grillmair, C.; Ho, L.C.; Kormendy, J.; et al. A Relationship between Nuclear Black Hole Mass and Galaxy Velocity Dispersion. Astrophys. J. 2000, 539, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado-Barahona, A.; Rubiño-Martín, J.A.; Ferragamo, A.; Barrena, R.; Streblyanska, A.; Tramonte, D. Velocity dispersion and dynamical masses for 388 galaxy clusters and groups. Calibrating the MSZ - Mdyn scaling relation for the PSZ2 sample. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 659, A126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Steinhardt, P.J. Cluster abundance constraints for cosmological models with a time-varying, spatially inhomogeneous energy component with negative pressure. Astrophys. J. 1998, 508, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainotti, M.G.; De Simone, B.; Schiavone, T.; Montani, G.; Rinaldi, E. and Lambiase, G. On the Hubble Constant Tension in the SNe Ia Pantheon Sample. Astrophys. J. 2021, 912, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.-P.; Lee, W.; Ng, K.-W. Constraining the dark-energy equation of state with cosmological data. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 083519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krolewski, A.; Ferraro, S.; White, M. Cosmological constraints from unWISE and Planck CMB lensing tomography. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 2021, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrah, D.; Croker, K.S.; Zevin, M.; Tarlé, G.; Faraoni, V.; Petty, S.; Afonso, J.; Fernandez, N.; Nishimura, K.A.; Pearson, C.; et al. Observational Evidence for Cosmological Coupling of Black Holes and its Implications for an Astrophysical Source of Dark Energy. Astrophys. J. 2023, 944, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, R.K.; Tormen, G. An excursion set model of hierarchical clustering: Ellipsoidal collapse and the moving barrier. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 329, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinker, J.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Klypin, A.; Abazajian, K.; Warren, M.; Yepes, G.; Gottlöber, S.; Holz, D.E. Toward a halo mass function for precision cosmology: The Limits of universality. Astrophys. J. 2008, 688, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasaki, M.; Ishiyama, T.; Ando, S. Virial halo mass function in the Planck cosmology. Astrophys. J. 2021, 922, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, B.; Davis, A.J.; Khochfar, S.; Natarajan, P.; Dunlop, J.S. Unravelling obese black holes in the first galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 3438–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, P.; Rossi, E.M.; Shiralilou, B.; Piana, O.; Choudhury, T.R.; Volonteri, M. The hierarchical assembly of galaxies and black holes in the first billion years: Predictions for the era of gravitational wave astronomy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 486, 2336–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habouzit, M.; Onoue, M.; Banados, E.; Neeleman, M.; Anglés-Alcázar, D.; Walter, F.; Pillepich, A.; Davé, R.; Jahnke, K.; Dubois, Y. Co-evolution of massive black holes and their host galaxies at high redshift: Discrepancies from six cosmological simulations and the key role of JWST. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 511, 3751–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulding, A.D.; Greene, J.E.; Setton, D.J.; Labbe, I.; Bezanson, R.; Miller, T.B.; Atek, H.; Bogdán, Á.; Brammer, G.; Chemerynska, I.; et al. UNCOVER: The Growth of the First Massive Black Holes from JWST/NIRSpec-Spectroscopic Redshift Confirmation of an X-ray Luminous AGN at z = 10.1. Astrophys. J. 2023, 955, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christiansen, H.; Takács, B.; Hansen, S.H. Cosmological Test of an Ultraviolet Origin of Dark Energy. Universe 2024, 10, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10050193
Christiansen H, Takács B, Hansen SH. Cosmological Test of an Ultraviolet Origin of Dark Energy. Universe. 2024; 10(5):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10050193
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristiansen, Hans, Bence Takács, and Steen H. Hansen. 2024. "Cosmological Test of an Ultraviolet Origin of Dark Energy" Universe 10, no. 5: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10050193
APA StyleChristiansen, H., Takács, B., & Hansen, S. H. (2024). Cosmological Test of an Ultraviolet Origin of Dark Energy. Universe, 10(5), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10050193






