Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and the Underlying Altered Fatty Acid Metabolism, Reveals Brain Hypoperfusion and Contributes to the Cognitive Decline in APP/PS1 Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
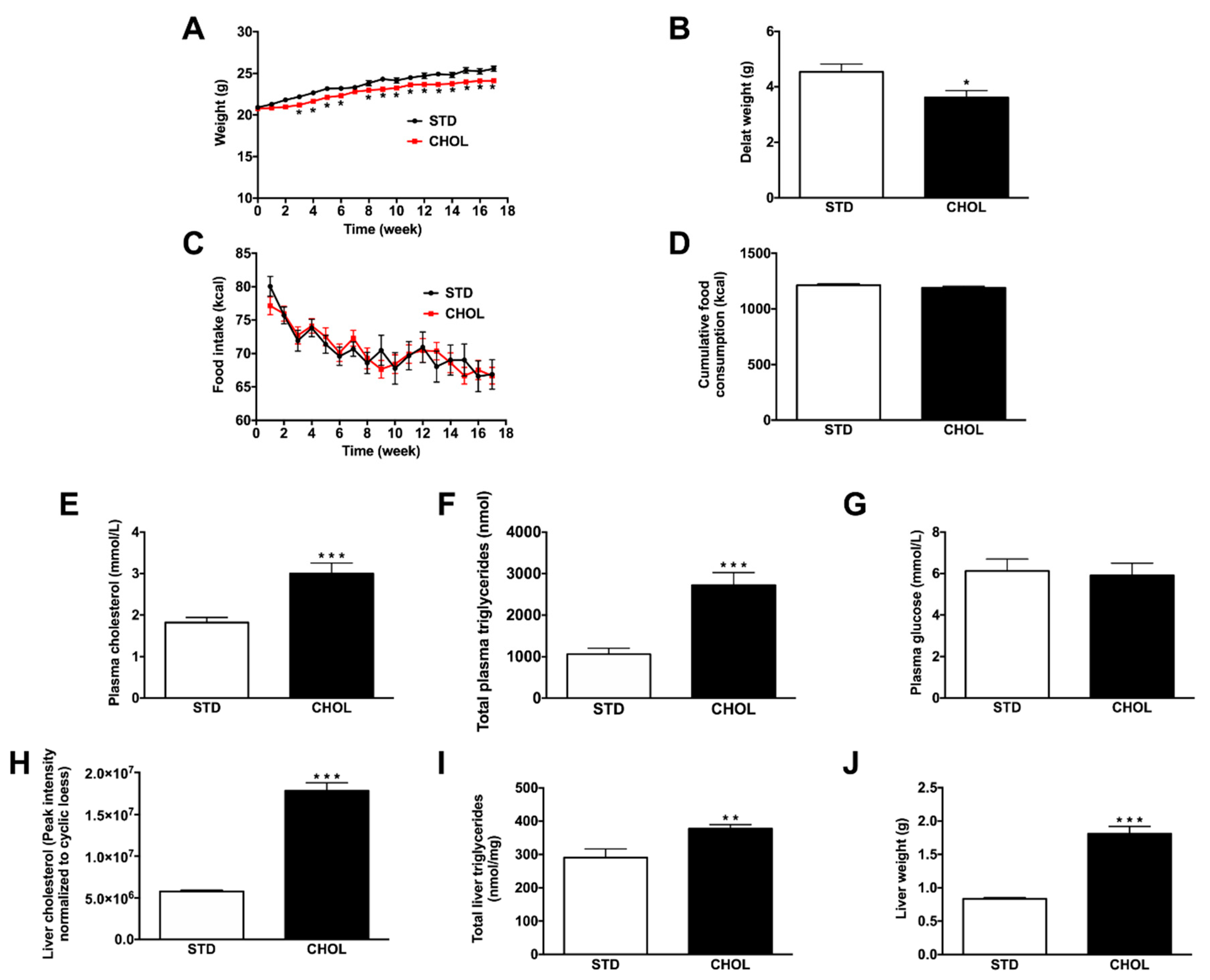
2.1. CHOL Diet Induces the Phenotype of NAFLD without Obesity in APP/PS1 Mice
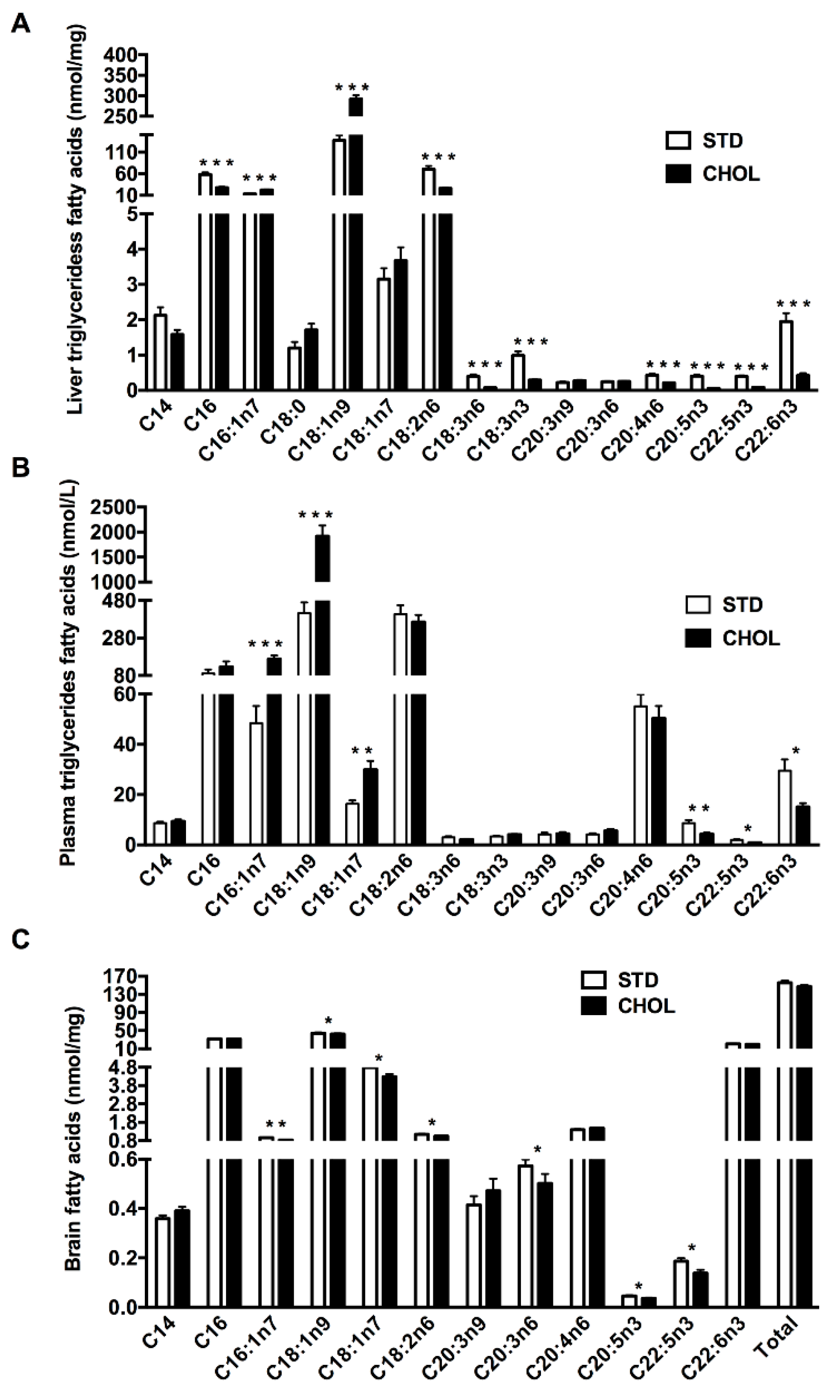
2.2. NAFLD is Associated with n-3 PUFAs Deficiency in the Triglyceride Fraction of the Plasma and the Liver
2.3. NAFLD is Associated with a Dysregulated Brain Lipid Metabolism Particularly MUFAs and PUFAs Deficiency
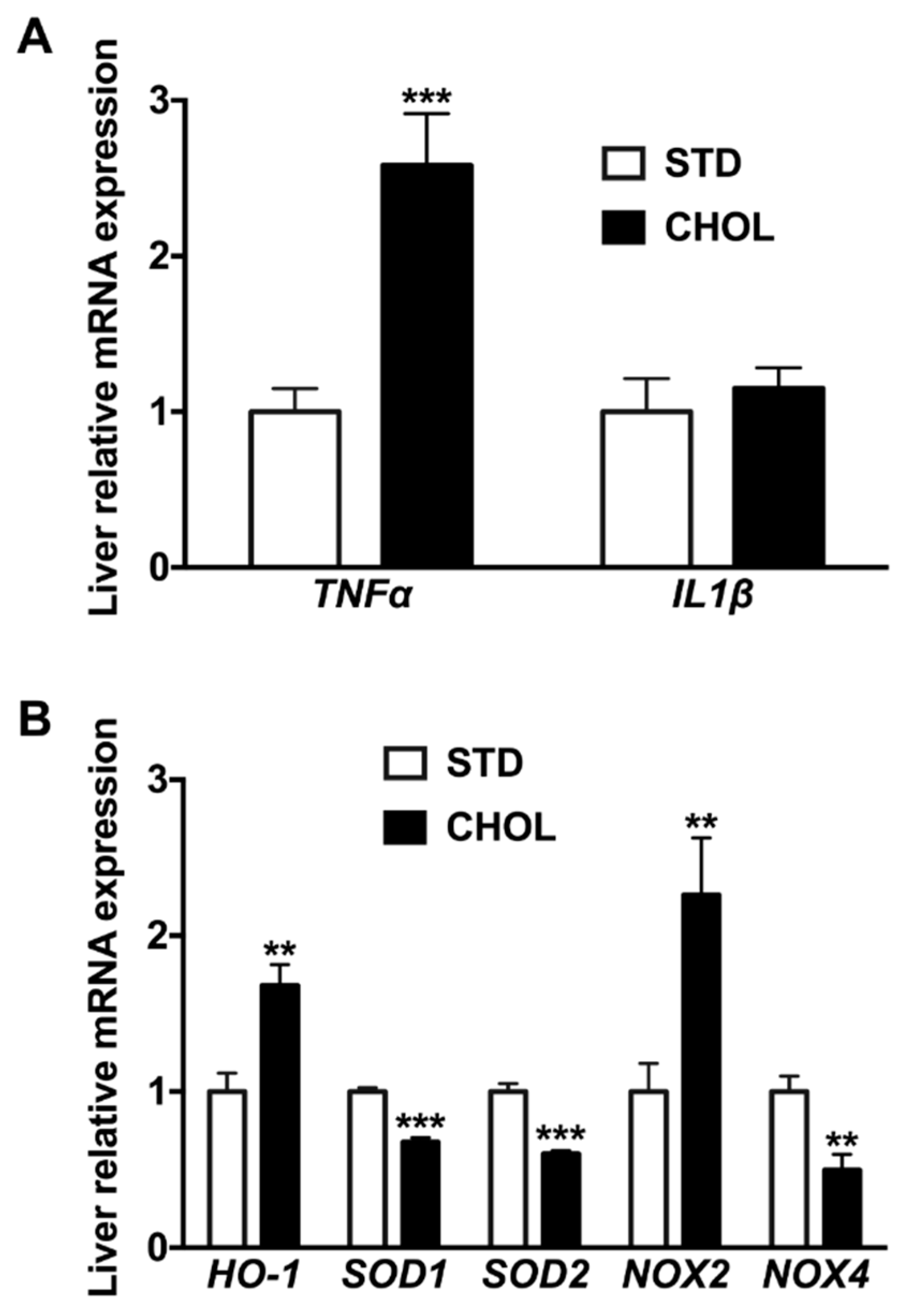
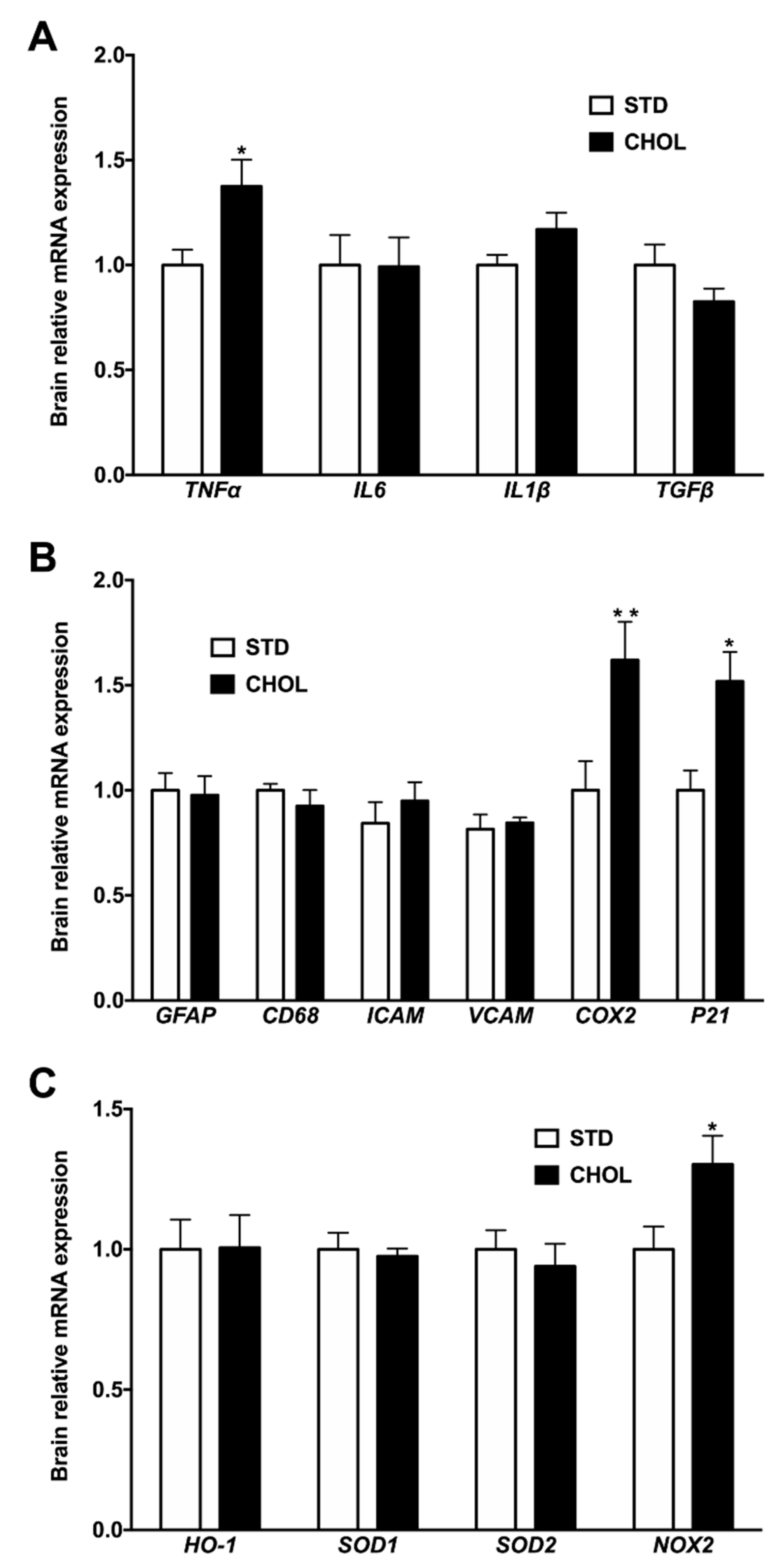
2.4. NAFLD Induces a Gene Expression Remodeling Reminiscent of Brain Inflammation, Cellular Senescence, and Oxidative Stress
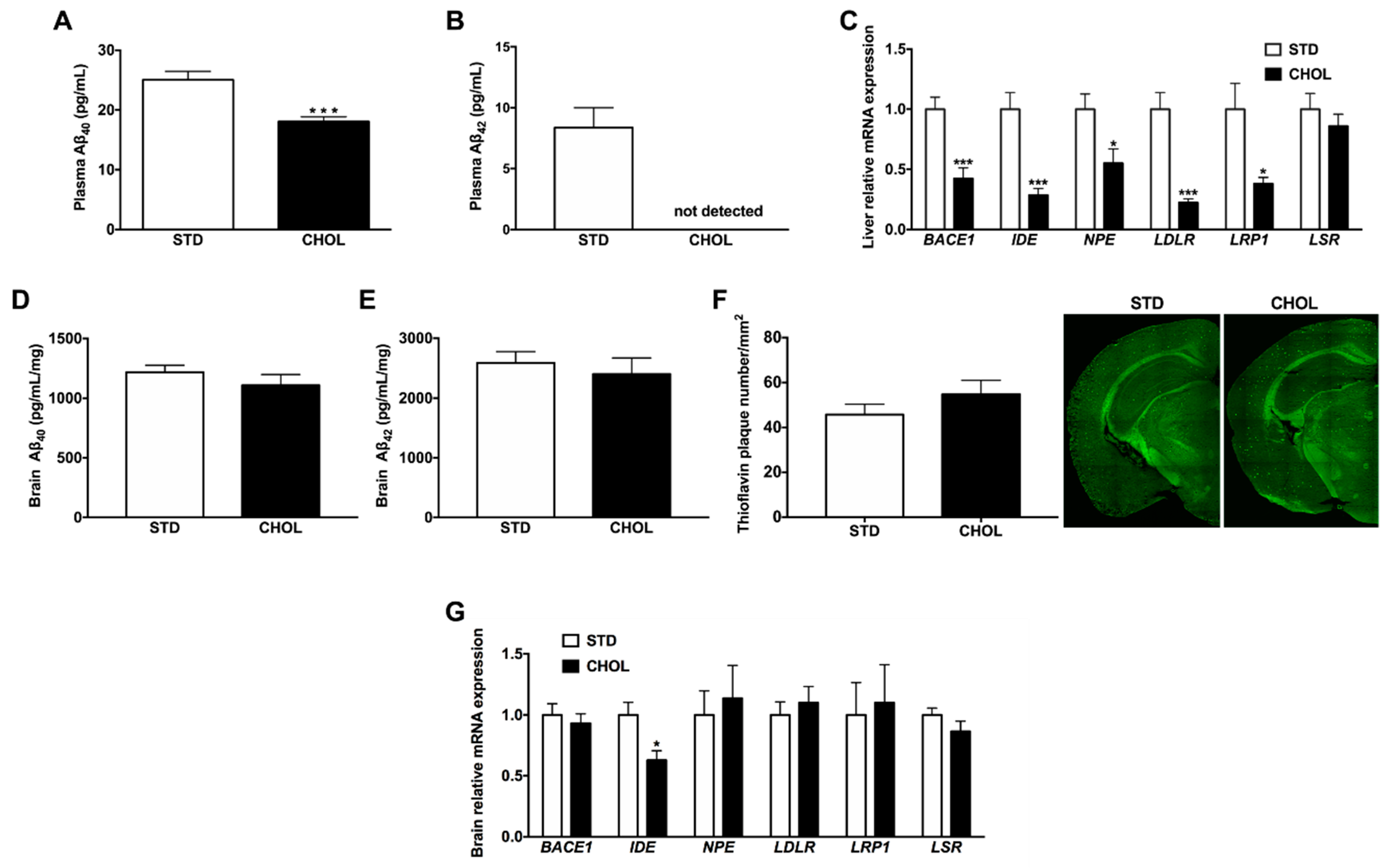
2.5. NAFLD is Associated with Dysregulated Hepatic and Plasma Aβ Metabolism
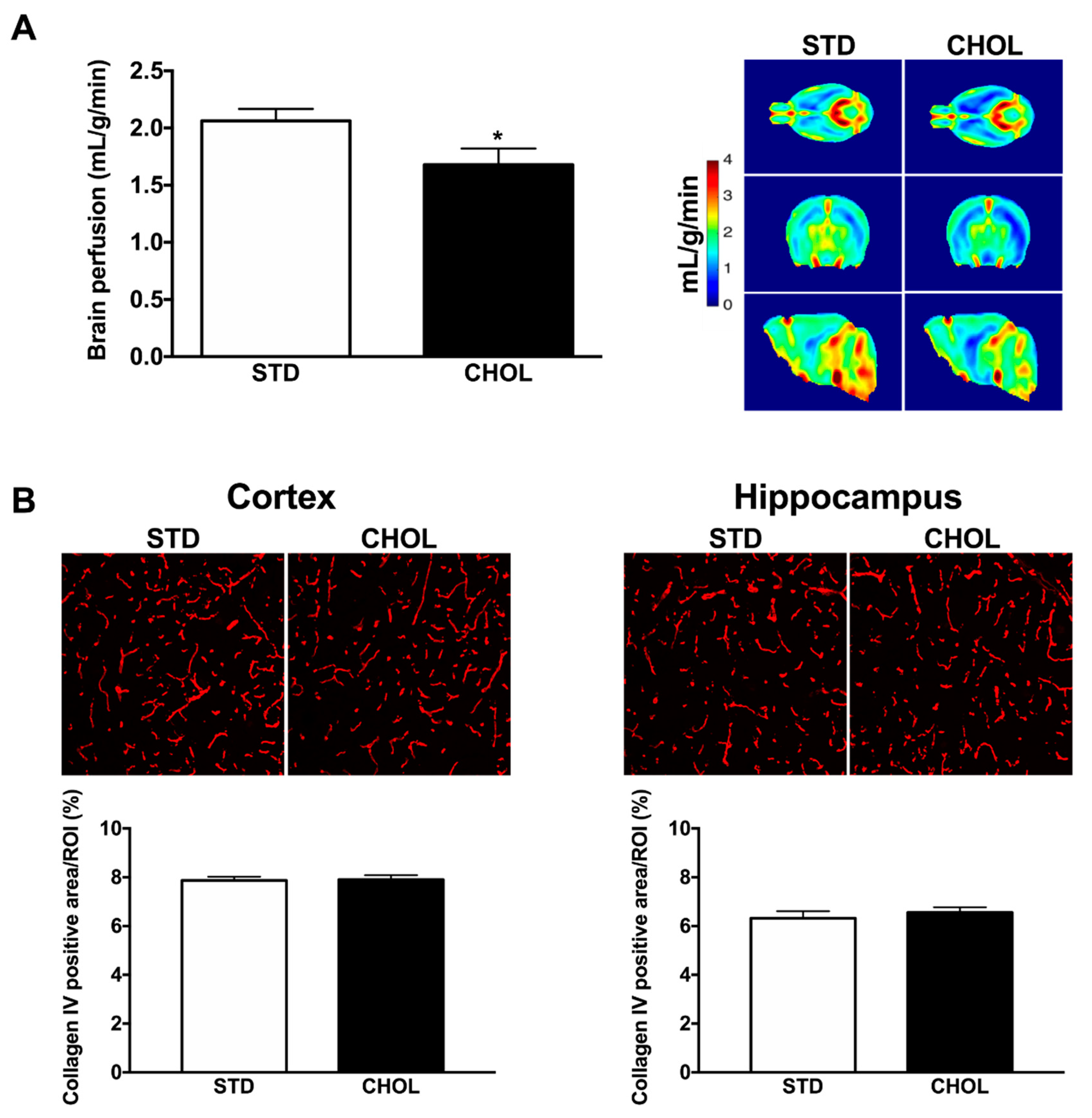
2.6. NAFLD is Associated with Brain Hypoperfusion
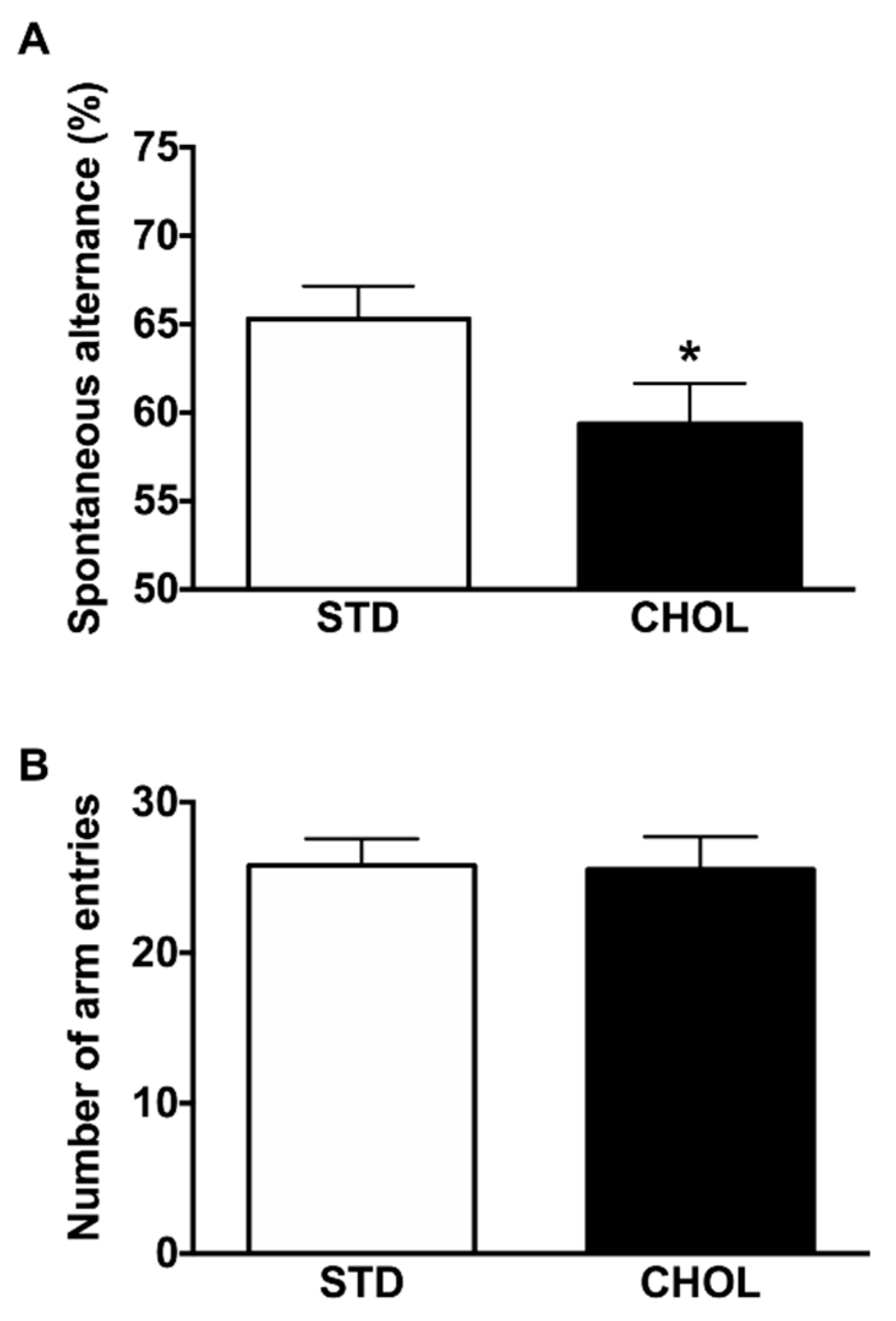
2.7. NAFLD Reduces Cognitive Performance
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animal Experiments
4.2. Lipids Analyses
4.2.1. Untargeted Lipidomics Analysis Using LC-MS
4.2.2. Targeted Fatty Acids Analysis Using GC-MS
4.3. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.4. Biochemical Analysis
4.5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Methods
4.6. MRI Data Analysis
4.7. Y-Maze
4.8. Amyloid Deposits Staining
4.9. Cerebral Microvessel Density Staining
4.10. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamilton, J.A.; Hillard, C.J.; Spector, A.A.; Watkins, P.A. Brain uptake and utilization of fatty acids, lipids and lipoproteins: Application to neurological disorders. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2007, 33, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goritz, C.; Mauch, D.H.; Pfrieger, F.W. Multiple mechanisms mediate cholesterol-induced synaptogenesis in a CNS neuron. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2005, 29, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.E.; Campenot, R.B.; Vance, D.E. The synthesis and transport of lipids for axonal growth and nerve regeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1486, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, P.; Fratangeli, A. Cholesterol and synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2010, 3, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Koudinov, A.R.; Koudinova, N.V. Essential role for cholesterol in synaptic plasticity and neuronal degeneration. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1858–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpech, J.C.; Madore, C.; Joffre, C.; Aubert, A.; Kang, J.X.; Nadjar, A.; Laye, S. Transgenic increase in n-3/n-6 fatty acid ratio protects against cognitive deficits induced by an immune challenge through decrease of neuroinflammation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Phillips, A.G.; Leonard, B.E.; Horrobin, D.F. Ethyl-eicosapentaenoic acid ingestion prevents corticosterone-mediated memory impairment induced by central administration of interleukin-1beta in rats. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lalancette-Hebert, M.; Julien, C.; Cordeau, P.; Bohacek, I.; Weng, Y.C.; Calon, F.; Kriz, J. Accumulation of dietary docosahexaenoic acid in the brain attenuates acute immune response and development of postischemic neuronal damage. Stroke 2011, 42, 2903–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, G.R.; Howarth, C.; MacVicar, B.A. Bidirectional control of arteriole diameter by astrocytes. Exp. Physiol. 2011, 96, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, F.; Kim, H.Y. Docosahexaenoic acid promotes neurite growth in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifferi, F.; Roux, F.; Langelier, B.; Alessandri, J.M.; Vancassel, S.; Jouin, M.; Lavialle, M.; Guesnet, P. (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency reduces the expression of both isoforms of the brain glucose transporter GLUT1 in rats. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 2241–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pifferi, F.; Jouin, M.; Alessandri, J.M.; Haedke, U.; Roux, F.; Perriere, N.; Denis, I.; Lavialle, M.; Guesnet, P. n-3 Fatty acids modulate brain glucose transport in endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2007, 77, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, I.; Hussein, N.; Di Martino, C.; Moriguchi, T.; Hoshiba, J.; Majchrzak, S.; Salem, N., Jr. An n-3 fatty acid deficient diet affects mouse spatial learning in the Barnes circular maze. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2007, 77, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R.P.; Shoemaker, W.J.; Shajenko, L.; Chambers, T.E.; Herbette, L.G. Evidence for changes in the Alzheimer’s disease brain cortical membrane structure mediated by cholesterol. Neurobiol. Aging 1992, 13, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L. Coronary artery disease, hypertension, ApoE, and cholesterol: A link to Alzheimer’s disease? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 826, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunnane, S.C.; Schneider, J.A.; Tangney, C.; Tremblay-Mercier, J.; Fortier, M.; Bennett, D.A.; Morris, M.C. Plasma and brain fatty acid profiles in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 29, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, S.G.; Ebshiana, A.A.; Hye, A.; An, Y.; Pletnikova, O.; O’Brien, R.; Troncoso, J.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Thambisetty, M. Association between fatty acid metabolism in the brain and Alzheimer disease neuropathology and cognitive performance: A nontargeted metabolomic study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Perez, E.J.; Sepulveda, F.J.; Peters, C.; Bascunan, D.; Riffo-Lepe, N.O.; Gonzalez-Sanmiguel, J.; Sanchez, S.A.; Peoples, R.W.; Vicente, B.; Aguayo, L.G. Effect of Cholesterol on Membrane Fluidity and Association of Abeta Oligomers and Subsequent Neuronal Damage: A Double-Edged Sword. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Callaghan, D.; Jones, A.; Walker, D.G.; Lue, L.F.; Beach, T.G.; Sue, L.I.; Woulfe, J.; Xu, H.; Stanimirovic, D.B.; et al. Cholesterol retention in Alzheimer’s brain is responsible for high beta- and gamma-secretase activities and Abeta production. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 29, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Luo, C.; Feng, Y.; Yao, X.; Shi, Z.; Liang, F.; Kang, J.X.; Wan, J.B.; Pei, Z.; Su, H. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids promote amyloid-beta clearance from the brain through mediating the function of the glymphatic system. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopperton, K.E.; Trepanier, M.O.; Giuliano, V.; Bazinet, R.P. Brain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids modulate microglia cell number and morphology in response to intracerebroventricular amyloid-beta 1-40 in mice. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amtul, Z.; Uhrig, M.; Rozmahel, R.F.; Beyreuther, K. Structural insight into the differential effects of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids on the production of Abeta peptides and amyloid plaques. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 6100–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amtul, Z.; Westaway, D.; Cechetto, D.F.; Rozmahel, R.F. Oleic acid ameliorates amyloidosis in cellular and mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2011, 21, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascoul-Colombo, C.; Guschina, I.A.; Maskrey, B.H.; Good, M.; O’Donnell, V.B.; Harwood, J.L. Dietary DHA supplementation causes selective changes in phospholipids from different brain regions in both wild type mice and the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.P.; Brickman, A.M. An Inflammation-related Nutrient Pattern is Associated with Both Brain and Cognitive Measures in a Multiethnic Elderly Population. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Gao, X.; Shi, B.; Chen, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Gan, Y.; Cui, L.; Kang, J.X.; Li, W.; et al. Enriched endogenous n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids alleviate cognitive and behavioral deficits in a mice model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 2016, 333, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otaegui-Arrazola, A.; Amiano, P.; Elbusto, A.; Urdaneta, E.; Martinez-Lage, P. Diet, cognition, and Alzheimer’s disease: Food for thought. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, C.; Wirth, M.; Gerischer, L.; Grittner, U.; Witte, A.V.; Kobe, T.; Floel, A. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Resting Cerebral Perfusion in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 5, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amen, D.G.; Harris, W.S.; Kidd, P.M.; Meysami, S.; Raji, C.A. Quantitative Erythrocyte Omega-3 EPA Plus DHA Levels are Related to Higher Regional Cerebral Blood Flow on Brain SPECT. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 58, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.; Bhalla, V.; El Regal, M.E.; HH, A.K. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comprehensive review of a growing epidemic. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12082–12101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.W.; Gottesman, R.F.; Clark, J.M.; Hernaez, R.; Chang, Y.; Kim, C.; Ha, K.H.; Guallar, E.; Lazo, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with cognitive function in adults. Neurology 2016, 86, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astarita, G.; Jung, K.M.; Berchtold, N.C.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Gillen, D.L.; Head, E.; Cotman, C.W.; Piomelli, D. Deficient liver biosynthesis of docosahexaenoic acid correlates with cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, D.; Poittevin, M.; Dere, E.; Broqueres-You, D.; Bonnin, P.; Benessiano, J.; Pocard, M.; Mariani, J.; Kubis, N.; Merkulova-Rainon, T.; et al. Hypertension accelerates the progression of Alzheimer-like pathology in a mouse model of the disease. Hypertension 2015, 65, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.; Miners, J.S. Cerebral Hypoperfusion and the Energy Deficit in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, F.; Sezer, S.; Erdogan, S.; Akyol, S.; Armutcu, F.; Akyol, O. The relationship between oxidative stress and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Its effects on the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Redox Rep. 2013, 18, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Montgolfier, O.; Pinçon, A.; Pouliot, M.-A.; Bishop, J.; Sled, J.; Villeneuve, L.; Ferland, G.; Levy, B.; Lesage, F.; Thorin-Trescases, N.; et al. Mechanical pulsatile pressure targets the cerebral circulation and induces microvascular endothelial dysfunction, neurovascular unit damage and cognitive decline in mice. Hypertension 2018, (in press).
- Bieghs, V.; Van Gorp, P.J.; Wouters, K.; Hendrikx, T.; Gijbels, M.J.; van Bilsen, M.; Bakker, J.; Binder, C.J.; Lutjohann, D.; Staels, B.; et al. LDL receptor knock-out mice are a physiological model particularly vulnerable to study the onset of inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierwagen, R.; Maybuchen, L.; Zimmer, S.; Hittatiya, K.; Back, C.; Klein, S.; Uschner, F.E.; Reul, W.; Boor, P.; Nickenig, G.; et al. Seven weeks of Western diet in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice induce metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with liver fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, S.; Pietrzik, C.U. Functional role of lipoprotein receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2008, 5, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, F.; Yoon, H.; Kim, J. Apolipoprotein E metabolism and functions in brain and its role in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2017, 28, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincon, A.; Thomas, M.H.; Huguet, M.; Allouche, A.; Colin, J.C.; Georges, A.; Derrien, A.; Lanhers, M.C.; Malaplate-Armand, C.; Oster, T.; et al. Increased susceptibility of dyslipidemic LSR+/- mice to amyloid stress is associated with changes in cortical cholesterol levels. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 45, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharpour, A.; Cazanave, S.C.; Pacana, T.; Seneshaw, M.; Vincent, R.; Banini, B.A.; Kumar, D.P.; Daita, K.; Min, H.K.; Mirshahi, F.; et al. A diet-induced animal model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular cancer. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaemers, I.C.; Stallen, J.M.; Kunne, C.; Wallner, C.; van Werven, J.; Nederveen, A.; Lamers, W.H. Lipotoxicity and steatohepatitis in an overfed mouse model for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, N.; Takamura, T.; Kurita, S.; Misu, H.; Ota, T.; Ando, H.; Yokoyama, M.; Honda, M.; Zen, Y.; Nakanuma, Y.; et al. Lipid-induced oxidative stress causes steatohepatitis in mice fed an atherogenic diet. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, P.M.; Verstuyft, J.; Paigen, B. Synthetic low and high fat diets for the study of atherosclerosis in the mouse. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 859–869. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.G.; Krenz, A.; Toussaint, L.E.; Maurer, K.J.; Robinson, S.A.; Yan, A.; Torres, L.; Bynoe, M.S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induces signs of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in wild-type mice and accelerates pathological signs of AD in an AD model. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelis-Pereira, M.C.; Barcelos, M.F.P.; Pereira, J.A.R.; Pereira, R.C.; Souza, R.V. Effect of different commercial fat sources on brain, liver and blood lipid profiles of rats in growth phase. Acta Cir. Bras. 2017, 32, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Park, S.M.; Kim, I.Y.; Sung, H.; Seong, J.K.; Moon, M.H. High-fat diet-induced lipidome perturbations in the cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and olfactory bulb of mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, C.; Masi, A.; Sansone, A.; Giacometti, G.; Larocca, A.V.; Menounou, G.; Scanferlato, R.; Tortorella, S.; Rota, D.; Conti, M.; et al. Fatty Acids in Membranes as Homeostatic, Metabolic and Nutritional Biomarkers: Recent Advancements in Analytics and Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.S.; Lonergan, P.E.; Boland, B.; Fogarty, M.P.; Brady, M.; Horrobin, D.F.; Campbell, V.A.; Lynch, M.A. Apoptotic changes in the aged brain are triggered by interleukin-1beta-induced activation of p38 and reversed by treatment with eicosapentaenoic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 34239–34246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, L.; Grehan, B.; Chiesa, A.D.; O’Mara, S.M.; Downer, E.; Sahyoun, G.; Massey, K.A.; Nicolaou, A.; Lynch, M.A. The polyunsaturated fatty acids, EPA and DPA exert a protective effect in the hippocampus of the aged rat. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 2318.e1–2318.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minogue, A.M.; Lynch, A.M.; Loane, D.J.; Herron, C.E.; Lynch, M.A. Modulation of amyloid-beta-induced and age-associated changes in rat hippocampus by eicosapentaenoic acid. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 914–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, A.M.; Loane, D.J.; Minogue, A.M.; Clarke, R.M.; Kilroy, D.; Nally, R.E.; Roche, O.J.; O’Connell, F.; Lynch, M.A. Eicosapentaenoic acid confers neuroprotection in the amyloid-beta challenged aged hippocampus. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, T.; Toben, C.; Jaehne, E.J.; Corrigan, F.; Baune, B.T. Long-term omega-3 supplementation modulates behavior, hippocampal fatty acid concentration, neuronal progenitor proliferation and central TNF-alpha expression in 7 month old unchallenged mice. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, Y.; Nagaki, M.; Banno, Y.; Brenner, D.A.; Asano, T.; Nozawa, Y.; Moriwaki, H.; Nakashima, S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced interleukin-8 production via NF-kappaB and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathways inhibits cell apoptosis in human hepatocytes. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 6294–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Takada, Y.; Hachiya, M.; Ando, K.; Nakajima, N.; Akashi, M. TNF-alpha induced p21(WAF1) but not Bax in colon cancer cells WiDr with mutated p53: Important role of protein stabilization. Cytokine 2000, 12, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussian, T.J.; Aziz, A.; Meyer, C.F.; Swenson, B.L.; van Deursen, J.M.; Baker, D.J. Clearance of senescent glial cells prevents tau-dependent pathology and cognitive decline. Nature 2018, 562, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leijenaar, J.F.; van Maurik, I.S.; Kuijer, J.P.A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Prins, N.D. Lower cerebral blood flow in subjects with Alzheimer’s dementia, mild cognitive impairment, and subjective cognitive decline using two-dimensional phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 9, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roher, A.E.; Debbins, J.P.; Malek-Ahmadi, M.; Chen, K.; Pipe, J.G.; Maze, S.; Belden, C.; Maarouf, C.L.; Thiyyagura, P.; Mo, H.; et al. Cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2012, 8, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ances, B.M.; Liang, C.L.; Leontiev, O.; Perthen, J.E.; Fleisher, A.S.; Lansing, A.E.; Buxton, R.B. Effects of aging on cerebral blood flow, oxygen metabolism, and blood oxygenation level dependent responses to visual stimulation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.K.; Jones, P.B.; Garcia-Alloza, M.; Borrelli, L.; Greenberg, S.M.; Bacskai, B.J.; Frosch, M.P.; Hyman, B.T.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Ayata, C. Age-dependent cerebrovascular dysfunction in a transgenic mouse model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Brain 2007, 130, 2310–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, K.; Porter, V.A.; Kazama, K.; Cornfield, D.; Carlson, G.A.; Iadecola, C. A beta-peptides enhance vasoconstriction in cerebral circulation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 281, H2417–H2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.E.; Greenberg, S.M. Beta-amyloid, blood vessels, and brain function. Stroke 2009, 40, 2601–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Todd, S.; Yaqoob, P. Fish-oil supplementation alters numbers of circulating endothelial progenitor cells and microparticles independently of eNOS genotype. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Christoph, M.; Hoffmann, G. Effects of Olive Oil on Markers of Inflammation and Endothelial Function-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7651–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Pieroni, C.; Winger, D.; Purohit, D.P.; Aisen, P.S.; Pasinetti, G.M. Regional distribution of cyclooxygenase-2 in the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 57, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanov, S.; Bernard, D.; Debacq-Chainiaux, F.; Martien, S.; Gosselin, K.; Vercamer, C.; Chelli, F.; Toussaint, O.; Abbadie, C. Normal or stress-induced fibroblast senescence involves COX-2 activity. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 3046–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Role of thromboxane A2 signaling in endothelium-dependent contractions of arteries. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018, 134, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwell, D.; Buchan, A.M.; Charpak, S.; Lauritzen, M.; Macvicar, B.A.; Newman, E.A. Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature 2010, 468, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Nakayama, N.; Ishida, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Kamata, K. Eicosapentaenoic acid improves imbalance between vasodilator and vasoconstrictor actions of endothelium-derived factors in mesenteric arteries from rats at chronic stage of type 2 diabetes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 329, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.W.; Kang, B.Y.; Hwang, O.; Choi, H.J. Cyclooxygenase-2 is involved in oxidative damage and alpha-synuclein accumulation in dopaminergic cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 436, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, L.; Zhou, P.; Pitstick, R.; Capone, C.; Anrather, J.; Norris, E.H.; Younkin, L.; Younkin, S.; Carlson, G.; McEwen, B.S.; et al. Nox2-derived radicals contribute to neurovascular and behavioral dysfunction in mice overexpressing the amyloid precursor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, F.H.; Grant, C.; Morris, A.C.; Horgan, G.W.; Polanski, A.J.; Allan, K.; Campbell, F.M.; Langston, R.F.; Williams, L.M. Rapid and reversible impairment of episodic memory by a high-fat diet in mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyward, F.D.; Walton, R.G.; Carle, M.S.; Coleman, M.A.; Garvey, W.T.; Sweatt, J.D. Adult mice maintained on a high-fat diet exhibit object location memory deficits and reduced hippocampal SIRT1 gene expression. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2012, 98, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistell, P.J.; Morrison, C.D.; Gupta, S.; Knight, A.G.; Keller, J.N.; Ingram, D.K.; Bruce-Keller, A.J. Cognitive impairment following high fat diet consumption is associated with brain inflammation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 219, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, A.; Ruiz, M.; Bouchard, B.; Boucher, G.; Gingras, O.; Daneault, C.; Robillard Frayne, I.; Rhainds, D.; Consortium, T.I.; Genetics Consortium, T.N.I.; et al. A Comprehensive and Reproducible Untargeted Lipidomic Workflow Using LC-QTOF Validated for Human Plasma Analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson Legault, J.; Strittmatter, L.; Tardif, J.; Sharma, R.; Tremblay-Vaillancourt, V.; Aubut, C.; Boucher, G.; Clish, C.B.; Cyr, D.; Daneault, C.; et al. A Metabolic Signature of Mitochondrial Dysfunction Revealed through a Monogenic Form of Leigh Syndrome. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelinas, R.; Thompson-Legault, J.; Bouchard, B.; Daneault, C.; Mansour, A.; Gillis, M.A.; Charron, G.; Gavino, V.; Labarthe, F.; Des Rosiers, C. Prolonged QT interval and lipid alterations beyond beta-oxidation in very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase null mouse hearts. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H813–H823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, C.V.; Gati, J.S.; Menon, R.S. Robust prescan calibration for multiple spin-echo sequences: Application to FSE and b-SSFP. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, B.P.; Bishop, J.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wu, J.; Henkelman, R.M.; Sled, J.G. Robust method for 3D arterial spin labeling in mice. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avants, B.B.; Tustison, N.J.; Song, G.; Cook, P.A.; Klein, A.; Gee, J.C. A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenger, C.; Pincon, A.; Hanse, M.; Royer, L.; Comte, A.; Koziel, V.; Olivier, J.L.; Pillot, T.; Yen, F.T. Brain region-specific immunolocalization of the lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor (LSR) and altered cholesterol distribution in aged LSR+/− mice. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinçon, A.; De Montgolfier, O.; Akkoyunlu, N.; Daneault, C.; Pouliot, P.; Villeneuve, L.; Lesage, F.; Levy, B.I.; Thorin-Trescases, N.; Thorin, É.; et al. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and the Underlying Altered Fatty Acid Metabolism, Reveals Brain Hypoperfusion and Contributes to the Cognitive Decline in APP/PS1 Mice. Metabolites 2019, 9, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050104
Pinçon A, De Montgolfier O, Akkoyunlu N, Daneault C, Pouliot P, Villeneuve L, Lesage F, Levy BI, Thorin-Trescases N, Thorin É, et al. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and the Underlying Altered Fatty Acid Metabolism, Reveals Brain Hypoperfusion and Contributes to the Cognitive Decline in APP/PS1 Mice. Metabolites. 2019; 9(5):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050104
Chicago/Turabian StylePinçon, Anthony, Olivia De Montgolfier, Nilay Akkoyunlu, Caroline Daneault, Philippe Pouliot, Louis Villeneuve, Frédéric Lesage, Bernard I. Levy, Nathalie Thorin-Trescases, Éric Thorin, and et al. 2019. "Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and the Underlying Altered Fatty Acid Metabolism, Reveals Brain Hypoperfusion and Contributes to the Cognitive Decline in APP/PS1 Mice" Metabolites 9, no. 5: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050104
APA StylePinçon, A., De Montgolfier, O., Akkoyunlu, N., Daneault, C., Pouliot, P., Villeneuve, L., Lesage, F., Levy, B. I., Thorin-Trescases, N., Thorin, É., & Ruiz, M. (2019). Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and the Underlying Altered Fatty Acid Metabolism, Reveals Brain Hypoperfusion and Contributes to the Cognitive Decline in APP/PS1 Mice. Metabolites, 9(5), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050104




