Abstract
Cyanobacteria have many defence strategies to overcome harmful ultraviolet (UV) stress including the production of secondary metabolites. Metabolomics can be used to investigate this altered metabolism via targeted and untargeted techniques. In this study we assessed the changes in the intra- and extracellular low molecular weight metabolite levels of Chlorogloeopsis fritschii (C. fritschii) during 48 h of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) supplemented with UV-B (15 µmol m−2 s−1 of PAR plus 3 µmol m−2 s−1 of UV-B) and intracellular levels during 48 h of PAR only (15 µmol m−2 s−1) with sampling points at 0, 2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) was used as a metabolite profiling tool to investigate the global changes in metabolite levels. The UV-B time series experiment showed an overall significant reduction in intracellular metabolites involved with carbon and nitrogen metabolism such as the amino acids tyrosine and phenylalanine which have a role in secondary metabolite production. Significant accumulation of proline was observed with a potential role in stress mitigation as seen in other photosynthetic organisms. 12 commonly identified metabolites were measured in both UV-B exposed (PAR + UV-B) and PAR only experiments with differences in significance observed. Extracellular metabolites (PAR + UV-B) showed accumulation of sugars as seen in other cyanobacterial species as a stress response to UV-B. In conclusion, a snapshot of the metabolome of C. fritschii was measured. Little work has been undertaken on C. fritschii, a novel candidate for use in industrial biotechnology, with, to our knowledge, no previous literature on combined intra- and extracellular analysis during a UV-B treatment time-series. This study is important to build on experimental data already available for cyanobacteria and other photosynthetic organisms exposed to UV-B.
Keywords:
cyanobacteria; C. fritschii; UV-B; PAR; time-series; intracellular; extracellular; metabolites; GC–MS 1. Introduction
Cyanobacteria are gram-negative bacteria with the ability to photosynthesise, assimilating CO2 into a variety of biochemical compounds through different metabolic pathways [1]. Cyanobacteria can thrive in a wide variety of extreme habitats such as high ultraviolet radiation (UVR) due to their adaptive capabilities such as the production of secondary metabolites [1]. Metabolomics can be used to determine changes at the metabolite level during varying environmental stimuli and is a useful tool in cyanobacterial research [2]. The metabolome provides information closely reflecting the interaction between an organism and its environment. Some metabolites produced by cyanobacteria under stress conditions are unique and are of increasing interest from a biotechnological perspective as sustainable sources of ingredients in a variety of industries [3,4].
The effect of UVR on cyanobacteria has been widely researched including the interaction with biomolecules, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which cause oxidative stress, impaired growth, partial inhibition of photosynthesis and decreased enzyme activity [5,6,7]. UVR also has a role as an activator of secondary metabolite production such as mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) [8] and other protective secondary metabolites [9]. Many studies have been conducted to identify these targeted intracellular metabolites during UV-B and UV-A exposure in Lyngbya sp. CU2555 [10], Nostoc commune [11], Anabaena variabilis PCC 7937 [12], Calothrix sp. [13] and Chlorogloeopsis fritschii (C. fritschii), PCC 6912, [14] to name a few. Other studies conducted have sought to evaluate changes at the protein level [15,16], targeted and untargeted metabolomic analysis using different intensities of UV-B [17] and combined metabolomic and proteomic analysis during UV-A exposure [18].
Cyanobacteria convert CO2 into reduced carbon which forms the backbone of metabolites and are central to life. Like many other microorganisms, cyanobacteria release these carbon-based primary and secondary metabolites into their surrounding area which drives carbon cycling within microbial communities [19,20]. These released metabolites are by-products of metabolism within cells and make up a small proportion of the dissolved organic matter (DOM) pool within freshwater and marine ecosystems [19]. Consisting of a variety of chemical compositions such as; polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, organic compounds or inorganic molecules, they are released for communication, structural organisation, and defence against biotic and abiotic factors [20,21,22]. The uptake and release of metabolites change with varying environments; examples include the release of exopolysaccharides during high light and UVR [11,23].
Monitoring industrially relevant metabolites released by microorganisms into their surroundings is a widely used technique in the fermentation industry. It can be used in bioprocess monitoring, fermentation biomarker identification, for monitoring metabolite levels in fermentation processes and microbial contamination [24,25].
Combining intracellular and extracellular analysis is useful in the study of cyanobacteria providing a more holistic picture of metabolite production during growth and its response to different environmental conditions [25,26].
Little work has been undertaken on monitoring both intracellular and extracellular metabolites in cyanobacteria especially C. fritschii, a potential candidate for use in industrial biotechnology due to its scalability [27] and tolerance to different growth conditions [28,29,30]. In this study, we observe the changes in metabolites produced by C. fritschii during 48 h of UV-B exposure as detected by untargeted gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS). We were able to identify metabolites with altered levels comparing UV-B treatment (PAR + UV-B) to cultures irradiated with PAR only.
2. Results
2.1. Intracellular and Extracellular Analysis of C. fritschii during UV-B Stress Response
The metabolite profiles of C. fritschii cultures (n = 3) were investigated during 48 h of UV-B exposure. At each time point (0, 2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h) intracellular and extracellular metabolites were analysed by untargeted GC–MS to evaluate the global changes in metabolite production during UV-B stress.
A total of 300 and 412 peaks were detected from the intracellular and extracellular time-series data respectively (Tables S1 and S2). Using a match factor of 60% or above, 135 and 218 peaks were putatively identified within the intracellular and extracellular data respectively (Tables S1 and S2). The identified chemical structures belonged to a variety of classes such as; acids, alcohols, amino acids, aromatics, fatty acids, heterocycles and sugars.
A Principle Component Analysis (PCA) model was used as an unsupervised multivariate statistical tool to plot and visualise the variance between UV-B exposed samples over time. A total variance of 37.2% for intracellular (Figure 1A, PC1 = 17%, PC2 = 11.1%, PC3 = 9.1%) and 36.4% for extracellular (Figure 1B, PC1 = 18.9%, PC2 = 9.2%, PC3 = 8.3%) was observed.
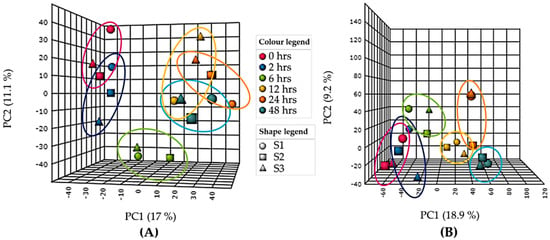
Figure 1.
Principle component analysis (PCA) of (A) intracellular and (B) extracellular gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS) data of UV-B exposed (PAR + UV-B) Chlorogloeopsis fritschii (C. fritschii) cultures showing PC1 vs PC2 only. Each ring represents distribution of biological replicates. S1 = replicate 1, S2 = replicate 2, S3 = replicate 3.
The results of the PCA for intracellular samples (Figure 1A) showed good separation over time between the control (0 h) and 6, 12, 24 and 48 h of UV-B. Less variation was observed between 0 and 2 h of UV-B with clustering seen between 12, 24 and 48 h of UV-B. This result was consistent with the two sample T-test results comparing control (0 h) with each time point where the number of significant features increases with length of UV-B exposure (Table S1). After a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repeated measures, 112 statistically significant peaks were observed with p ≤ 0.05 (Figure S1A), 10 of which remained significant after Bonferroni correction.
From the extracellular data PCA (Figure 1B) a similar pattern was observed with increasing variance with increasing length of UV-B exposure. Statistically significant changes between control (0 h) and each time point, measured using a two-sample T-test also showed increasing significance (p ≤ 0.05) with increasing length of UV-B up to 24 h (Table S2). A one-way ANOVA with repeated measures calculated 114 statistically significant peaks with p ≤ 0.05 (Figure S1B).
2.1.1. Intracellular Metabolites
28 metabolites (13 represented for simplicity, Figure 2), selected as being involved in the central carbon and nitrogen metabolism within cyanobacteria, were identified within the intracellular GC–MS results Table S3). Many changes in metabolite levels were observed comparing between time points. Glucose, pyruvate and lactate all decreased in abundance after UV-B exposure with significant reduction after 2 h (pyruvate p ≤ 0.05, 0 vs. 2 h), 6 h (glucose p ≤ 0.05, 2 vs. 6 h) and 12 h (lactate p ≤ 0.05, 0 vs. 12 h). Lactate was present during the whole time course whereas glucose and pyruvate were below detection limit after 6 h (p ≤ 0.05) and 24 h (p ≤ 0.001) respectively.
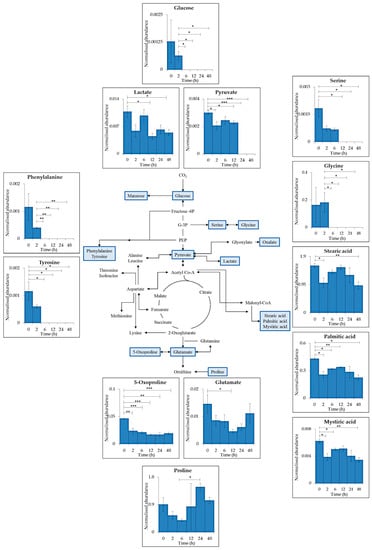
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of a generalised reduced carbon metabolism in the cyanobacterium C. fritschii showing glycolysis, the citric acid (TCA) cycle, amino acid and fatty acid biosynthesis. Primary metabolites identified in intracellular samples using GC–MS are highlighted in blue with each insert presenting mean values of normalised abundance (normalised to internal standard and dry weight) ± standard error of each metabolite during supplemented UV-B exposure PAR + UV-B). Statistical significance between control (0 h) and UV-B exposure (2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h) and between each treatment time point was measured using a two-sample T-test with equal variance; * = 0.05 ≥ p ≥ 0.01, ** = 0.01 ≥ p ≥ 0.001 and *** = p ≤ 0.001.
6 proteinogenic amino acids were detected; serine (ser), glycine (gly), glutamate (glu), proline (pro), tyrosine (tyr) and phenylalanine (phe). All detected amino acids decreased after 6 or 12 h of exposure with the exception of pro. A decrease in tyr, phe and gly was seen after 6 h (tyr p ≤ 0.05, 0 vs. 6 h; phe p ≤ 0.01, 2 vs. 6 h; gly p ≤ 0.05, 2 vs. 6 h) of UV-B followed by no detection at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h (tyr p ≤ 0.05; phe p ≤ 0.01; gly p ≤ 0.05). Ser and glu decreased significantly after 12 h of treatment (ser p ≤ 0.05, 0 vs. 12 h; glu p ≤ 0.05, 0 vs. 12 h), ser was below detection limit between 12 and 48 h (p ≤ 0.05) whereas glu was detected throughout the time series. Proline showed no significant decrease after UV-B exposure with a significant increase observed after 24 h (p ≤ 0.05, 6 vs. 24 h).
The fatty acids stearic acid, palmitic acid and mystiric acid all decreased significantly after 2 h of treatment (p ≤ 0.05) and their abundance remained lowered throughout the time series (stearic acid p ≤ 0.01, 0 vs. 48 h; palmitic acid p ≤ 0.05, 0 vs. 48 h; mystiric acid p ≤ 0.01, 0 vs. 48 h).
Carotenoid and MAA Analysis
Carotenoid concentration (Figure 3A) and MAA content (Figure 3B) were analysed by UV-visible spectroscopy and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) respectively. Total carotenoid concentration decreased after 2 h (p ≤ 0.05); with a steady significant increase up to 48 h with a final concentration of 2.59 μg/mg dry weight (p ≤ 0.05).
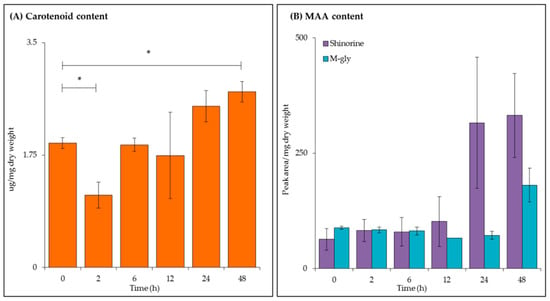
Figure 3.
Carotenoid and mycosporine-like amino acid (MAA) analysis of C. fritschii extracts during UV-B exposure. (A) Total carotenoid concentration as measured by UV-visible spectroscopy and (B) shinorine and mycosporine-glycine (m-gly) content measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis. All values are the mean of three biological replicates (normalised to dry weight) ± standard error. Statistical significance was measured using a two-sample T-test with equal variance; * = 0.05 ≥ p ≥ 0.01, ** = 0.01 ≥ p ≥ 0.001 and *** = p ≤ 0.001.
As described above, UV-B also induces the production of the photoprotective compounds, MAAs. The two forms found in C. fritschii are mycosporine-glycine (m-gly) and shinorine [29], both were detected during this experiment with peaks identified using their retention time and absorption maxima (λmax) values. As expected an increase in shinorine (retention time ~4.9 min, λmax = 334 nm) was observed with increasing length of UV-B exposure. No significance was observed with m-gly (retention time ~10.8 min, λmax = 310 nm) content during this experimental time series.
2.1.2. Extracellular Metabolites
29 biologically relevant dissolved metabolites (Table S3) were detected within the extracellular data set (13 represented for simplicity, Figure 4). Citrate, a component of BG-11 medium [31] and involved in the citric acid (TCA) cycle, was consistently detected throughout the time series (ANOVA, p ≤ 0.05) along with succinate. Other TCA substrates; malate and fumarate were also detected at 0 h with decreasing abundance after 2 h of UV-B (malate, p ≤ 0.001). Other metabolites detected at 0 h which decreased after UV-B exposure were leucine (p ≤ 0.01, 0 vs. 6 h), putrescine (p ≤ 0.05, 0 vs. 2 h) octanoic acid (p ≤ 0.001, 0 vs. 24 h) mystiric acid (p ≤ 0.01, 2 vs. 24 h) and fructose (p ≤ 0.01, 0 vs. 2 h). Accumulation of the sugars galactose, xylose, lyxose and arabinose was seen after 6 h (galactose p ≤ 0.01; arabinose p ≤ 0.01) 12 h (arabinose p ≤ 0.05), 24 h (arabinose p ≤ 0.05; xylose p ≤ 0.05; lyxose p ≤ 0.01) and 48 h (galactose p ≤ 0.05; arabinose p ≤ 0.001; lyxose p ≤ 0.01) of UV-B exposure. Trehalose was also identified throughout the time series with no significant changes.
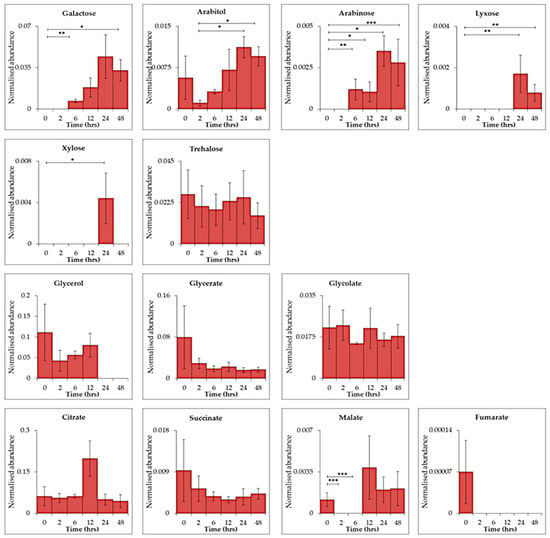
Figure 4.
Time-series exometabolomics data of C. fritschii over 48 h of UV-B exposure showing primary metabolites found in extracellular samples only. Statistical significance was measured using a two-sample T-test comparing control (0 h) and UV-B exposure (2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h) and between each treatment time point, * = 0.05 ≥ p ≥ 0.01, ** = 0.01 ≥ p ≥ 0.001 and *** = p ≤ 0.001.
2.2. Intracellular Analysis of C. fritschii (PAR Only)
Intracellular Metabolites
A time-series analysis of PAR only (without UV-B supplementation) over 48 h (Table S4) revealed 35 key primary intracellular metabolites (Table S3). 12 were commonly identified between PAR only conditions and during UV-B supplementation (nine represented for simplicity in pathway schematic, Figure 5).
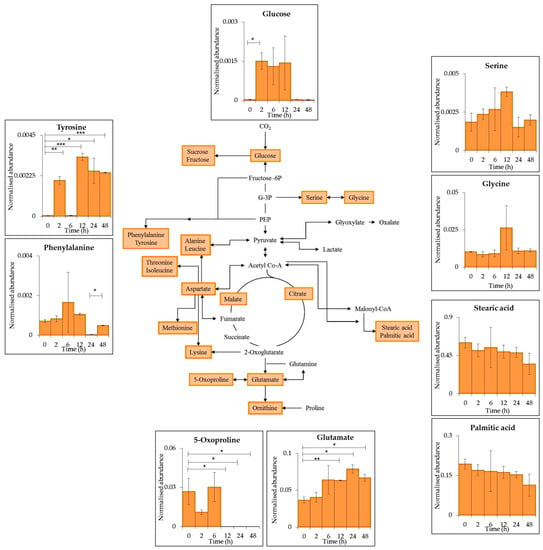
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of a generalised reduced carbon metabolism in the cyanobacterium C. fritschii showing glycolysis, TCA cycle, amino acid and fatty acid biosynthesis. Primary metabolites identified in intracellular samples using GC–MS are highlighted in orange with each insert presenting mean values of normalised abundance (normalised to internal standard and dry weight) ± standard error of common metabolites found during PAR only conditions and supplemented UV-B (Figure 2). Statistical significance between 0 h and each time point as well as between time points were measured using a two-sample T-test with equal variance; * = 0.05 ≥ p ≥ 0.01, ** = 0.01 ≥ p ≥ 0.001 and *** = p ≤ 0.001.
In general, comparing both supplement UV-B and PAR only, the nine common metabolites (Figure 6) showed differences in log2 fold change (FC). The metabolites detected during supplemented UV-B showed negative log2(FC) values which corresponds to reduced metabolite abundances compared to 0 h. Positive log2 (FC)) was generally observed for metabolites detected during PAR only indicating increased abundances compared to 0 h. The main exception is 5-oxoproline that reduced in both UV-B + PAR and PAR only experiments.
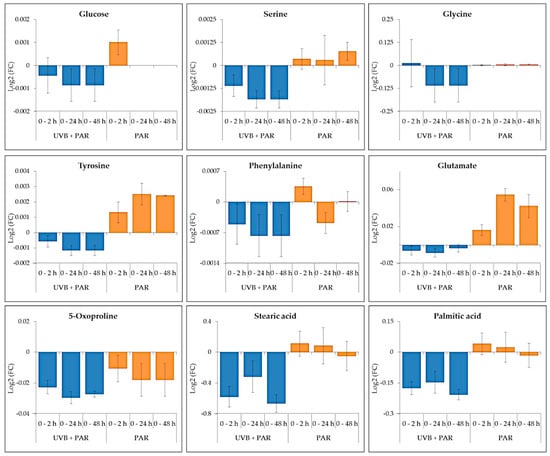
Figure 6.
The changes in common metabolites identified in both UV-B + PAR and PAR only experiments comparing 0 h with 2, 24 and 48 h. Data are presented as Log2 Fold Change (FC) ± standard error.
A significant accumulation of glu (p ≤ 0.01) was observed after 12 h of PAR only whereas a significant decrease was seen after 12 h of UV-B exposure. Tyr accumulation (p ≤ 0.001) was also seen after 2 and 12 h of PAR only conditions with a significant decrease during UV-B treatment. Palmitic and stearic acid remained relatively stable over time with a significant reduction during UV-B exposure observed. Gly and ser abundance remained consistent with significant decreases after 6 and 12 h respectively during UV-B exposure.
3. Discussion
3.1 Intracellular Metabolite Changes and Pathway Analysis
UV-B exposure is known to reduce growth, photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation in cells to divert energy from key primary pathways to adaptive mechanisms such as; the production of secondary metabolites, MAAs; antioxidant production and DNA/protein repair [32]. A reduction in average dry weight was measured over 24 h of UV-B exposure (Figure S2) with the recovery of the initial biomass concentration and further growth measured between 24 and 48 h. These results showed no significance (p ≥ 0.05) across the time series suggesting acclimation of cells to UV-B where damage to photosynthetic systems are counterbalanced by repair and mitigation strategies. A reduction in carotenoid concentration (Figure 3A) was observed after 2 h (p ≤ 0.05) due to damage to photosystems caused by UV-B. Accumulation of total carotenoids could be indicative of antioxidant activity as a response to ROS production [6,33].
A reduction in glucose, pyruvate and lactate (Figure 2) could indicate a reduction in CO2 fixation via photosynthesis and further biochemical processes. This could be due to the reduced production of ATP and NADPH2 from photosynthesis [34].
The 13 selected intracellular metabolites (Figure 2) were reduced across the UV-B time series indicating the reduction of cellular processes. A decrease in phe and tyr could be due to their role as precursors to many secondary metabolites such as aromatic nitrogen-containing alkaloids [13]. M-gly and shinorine are produced via a combination of the shikimate/pentose phosphate pathway which also involves the addition of gly and ser to form the final MAAs [9,35]. The reduction of these amino acids coincides with an increase in MAA levels (Figure 3B).
5-oxoproline and glu are involved in glutathione metabolism. 5-oxoproline reduction (p ≤ 0.01) could be due to its interconversion into glutamate which is further converted into the antioxidant glutathione [36]. Glu is also produced from the assimilation of nitrogen during nitrogen fixation which is reduced during UV-B exposure [34].
Pro has been studied in many UV-B experiments involving different photosynthetic organisms and its accumulation is thought to have a role in stress response by providing additional defence as a ROS scavenger and molecular chaperone [37,38,39]. Accumulation of proline has been observed in Nostoc punctiforme during 24 h of UV-A stress [18], in the model plant organism Arabidopsis after 24 h of UV-B treatment [40], and also in C. fritschii after 24 h of UV-B exposure within this study.
3.2 Extracellular Metabolite Changes
The movement of metabolites and substrates between cells and their surrounding environment (or vice versa) can occur via passive and active uptake and efflux systems. Reactions can also occur on cell surface membranes and as transformations of media components [41]. Identification of extracellular metabolite uptake and release from cyanobacteria is, therefore, a complex process due to the high turnover rates of intracellular processes [25]. Extracellular metabolites can be released during stress and as by-products of intracellular reactions [19]. Sugars such as galactose, arabinose, lyxose and xylose are actively released during UV-B stress [5] as seen in this experiment (Figure 4).
7 metabolites from the identified biologically relevant pool were found in both intra- and extracellular metabolite samples (Figure S3). The fatty acid mystiric acid shows a similar pattern of reduced abundance with increasing length of UV-B in both samples (intracellular p ≤ 0.05; extracellular p ≤ 0.05). Ethanolamine, involved in glycerophospholipid metabolism, and 2-oxobutanoate, involved in amino acid biosynthesis show opposite patterns with intracellular levels decreasing (p ≤ 0.05) and extracellular levels increasing (ethanolamine, p ≤ 0.01, 2-oxobutanoate, p ≤ 0.001) (S1: Figure 3). Further detailed analysis using a combination of -omic techniques and the application of isotopic labelling such as 13C flux balance analysis would be required to better understand the uptake and release of extracellular metabolites and their possible use within cyanobacterial metabolite production [42].
4. Conclusions
In summary, an untargeted GC–MS workflow was used to evaluate intra- and extracellular metabolites under supplemented UV-B exposure (PAR + UV-B). Most significantly we found a reduction of intracellular metabolites such as the amino acids, tyr, phe, ser, gly and glu and the accumulation of pro, which to our knowledge has not been previously reported in C. fritschii. Compared to PAR only, intracellular metabolites showed less significant changes with amino acids tyr, phe and glu accumulation observed.
Although a time series analysis was conducted, this only represents a minuscule proportion of the true changes within the metabolome. This study is important to build on experimental data already available for cyanobacteria and other photosynthetic organisms exposed to UV-B. To understand the changes in primary metabolites and metabolic process with increasing length of UVR exposure to help further understand secondary metabolite production and adaptation of cyanobacteria to UV stress. Further studies are needed to understand and verify these processes within cyanobacteria to aid in the understanding of UV stress adaptation at the metabolite level.
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Organism and Growth Conditions
The cyanobacterium C. fritschii, PCC 6912, was obtained from the Pasteur culture collection (PCC) and grown in autoclaved deionised water with filtered BG-11 growth medium (Sigma Aldrich). The strain was maintained in 50 mL BG-11 at a temperature of 27 ± 2 °C under continuous PAR illuminated at 15 µmol m−2 s−1 (measured using a PAR light sensor, Enviromonitors, West Sussex, UK). Experimental cultures were pre-grown in 300 mL BG-11 media under the same conditions with constant shaking at 80 rpm.
5.2. Experimental Setup
5.2.1. Supplemented UV-B Experiment (PAR + UV-B)
After 6 days of pre-growth, triplicate experimental C. fritschii cultures were transferred into three Quartz Erlenmeyer flasks (H.Baumbach & CO.LTD, Suffolk, UK) at an optical density at 750 nm (OD750nm) of approx. 0.14 to allow even UV-B exposure. The cultures were exposed to a total of 48 h of UV-B radiation using a UVB broadband (290–315 nm, centered at 310 nm) fluorescent tube (Philips TL 20W/12 RS SLV/25, Proflamps, Eindhoven, The Netherlands) emitting 3 µmol m−2 s−1 of UV-B radiation (measured using a UVR light sensor, Enviromonitors, West Sussex, UK). The experiment was carried out under continuous PAR at 15 µmol m−2 s−1 and shaking at 100 rpm for even UVB exposure of cells. For time course analysis samples were collected at no UV-B (0 h), 2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h for dry weight, pigment, MAA, and GC–MS analysis.
5.2.2. PAR Only Experiment (PAR only)
C. fritschii cultures were pre-grown for 6 days prior to experimental analysis. After 6 days of pre-growth, triplicate experimental C. fritschii cultures (OD750nm of approx. 0.13) were grown at a temperature of 27 ± 2 °C under continuous PAR illuminated at 15 µmol m−2 s−1 (measured using a PAR light sensor, Enviromonitors, West Sussex, UK) and continuous shaking at 100 rpm. For time course analysis samples were collected at 0, 2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h for dry weight and GC–MS analysis.
5.3. Sample Harvest and Growth Analysis
Forty mL volumes of UV-B exposed (n = 3) and PAR only cultures (n = 3) were harvested at each time point by centrifugation at 4400 rpm for 20 min to produce a pellet and supernatant. The supernatants (40 mL) were collected and freeze-dried (Edwards, super modulyo) for 72 h. The remaining pellets were transferred into pre-weighed Eppendorf’s and freeze-dried for 24 h (Scanvac, CoolSafeTM, LaboGeneTM, Vassingerød, Denmark) for dry weight measurements. Both pellets (PAR + UV-B and PAR only) and dried supernatant (PAR + UV-B only) were stored at −20 °C until analysis. OD was monitored using absorbance at 750 nm using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, UV-2550, Kyoto, Japan).
5.4. GC–MS Analysis
5.4.1. Sample Preparation
Polar and non-polar metabolites were extracted from UV-B exposed and PAR only dried cell pellets for GC–MS analysis. Briefly, approx. 0.5–1 mg (UV-B exposed) or 1.5–3 mg (PAR only) of dried biomass was re-suspended in 1 mL methanol:chloroform:water (2:2:1) and sonicated using a sonicator probe (Fisher Scientific, FB50) using 6 cycles of 20 s pulses at 40 Hz at 0 °C. After centrifugation (5 min at 12,000 rpm), 100 µL of each solvent layer (both methanolic and chloroform layers) were aliquoted into new Eppendorf’s and evaporate to dryness using a rotary vacuum concentrator (Eppendorf concentrator 5301).
Dried supernatant (PAR + UV-B) was re-suspended in 1 mL of methanol and centrifuged (4000 rpm, 5 min). Two hundred µL was aliquoted into new Eppendorf’s followed by evaporation to dryness and derivatisation as below.
5.4.2. Sample Derivatisation
To each 200 μL dried sample, 30 μL of methoxyamine hydrochloride (23 mg) in pyridine (1.5 mL) was added and samples were heated at 70 °C for 45 min. Once cooled to room temperature, 50 μL of MSTFA+TMCS (Thermo ScientificTM, product no: TS-48915) was added and samples heated for an additional 90 min at 40 °C. Once cooled to room temperature, 10 μL of tetracosane dissolved in hexane (2 mg/mL) was added as an internal standard. Derivatised samples were transferred into auto-sample vials ready for analysis.
5.4.3. GC–MS Analysis
Derivatised sample (1 µL) was loaded onto an Agilent HP-5MS capillary column (30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 um) in splitless mode at 250 °C. The GC was operated at a constant flow of 1 mL min−1 helium. The temperature program started at 60 °C for 1 min, followed by temperature ramping at 10 °C min−1 temp of to a final 180 °C, this was followed by a second temperature ramping at 4 °C min−1 to a final temp of 300 °C and held constant at 300 °C for 15 min. Data acquisition included a mass range of 50 to 650 and resulted in .D data files for analysis.
Chromatograms were deconvoluted using AMDIS (Automated Mass Spectral Deconvolution and Identification System) followed by alignments using the online portal SpectConnect, http://spectconnect.mit.edu/ [43], before identifying peaks using Golm metabolome database, www.gmd.mpimp-golm.mpg.de/, and the NIST 05 (National Institute of Standards and Technology) library [44]. MetaboAnalyst, www.metaboanalyst.ca/, was used for statistical analysis [45,46].
5.4.4. GC–MS Data Processing
GC–MS data sets need deconvolution of co-eluting compounds, the freely available software AMDIS was used to process the chromatograms (.D) and produce .ELU files for alignment and conservative component identification using SpectConnect [43,47]. Settings for AMDIS were as followed [18]; Resolution = medium, sensitivity = medium, shape requirement = medium and component width was 10. The resulting .ELU files were uploaded to SpectConnect to produce matrices for further analysis and processing in Excel 2010 (Microsoft, USA). The integrated signal (IS) matrix generated was used for relative quantification of peaks. Triplicate missing data points (within time points) were assumed to be lower than the detection limit and replaced with half of the minimum integrated signal within each data set. Data normalisation was carried out using the peak area of the internal standard tetracosane and dry weight of each sample (for intracellular data only; approx. 0.5–1 mg of UV-B exposed cells and 1.5–3 mg of PAR only cells). All duplicate retention times were removed before further analysis.
5.4.5. Identification
Identification of peaks was carried out in AMDIS by analysing each chromatogram using the Golm databases as a target library, followed by searching the NIST 05 library with a match factor of 60% or above. Reports were exported in .xls format from AMDIS with the first hit only included for further processing using Excel 2010 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). A true hit was considered when two or more biological replicates (within the same time-point) contained the peak. If none of the time points contained ‘true hits,’ the peaks were removed before further analysis. Metabolites reported belonged to level 2 (putatively annotated compounds) and level 4 (unknown compounds) identifications in accordance with the Metabolomics Standards Initiative [48].
5.4.6. Statistical Analysis
MetaboAnalyst was used to statistically analyse the IS peak lists (in .csv format) of the time series data using the time-series/two-factor module. Multivariate analysis was carried out using each column as a different time point and each row representing a metabolite (data type = peak intensity table; study design = time-series only; data format = samples in columns) [46]. Missing data points were uploaded as blanks and replaced with half of the minimum integrated signal within each data set. Peaks were normalised to total sum of peaks, log-transformed and mean centered prior to statistical analysis. PCA, a one-way repeated ANOVA (p ≤ 0.05) and hierarchical heat map clustering was used to evaluate the data. A two-sample T-test with equal variance was also used as a univariate statistical tool to evaluate data comparing 0 h with each treatment time point (2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h) as well as between each time points in Excel.
5.5. MAA analysis
5.5.1. Sample Preparation
0.5–1 mg of UV-B exposed dried biomass was re-suspended in 100% HPLC grade methanol (1 mL) and left in the dark at 4 °C overnight (24 h). After centrifugation (5 min at 12000 rpm), the supernatant was removed and evaporated to dryness using a rotary vacuum concentrator. The dried extract was re-dissolved in 600 µL of deionised water and transferred to autosample vials for HPLC analysis [49].
5.5.2. HPLC Analysis
HPLC analysis was performed using an Agilent 1100 system equipped with a binary pump (G1312A), an autosampler injector (ALS, G1313A), thermostatted column compartment (G1316A) and diode array detector (DAD, G1315A) connected via an interface module to a computer running ChemStation software. The stationary phase was an AlltimaTM AltechTM C18, 4.6 × 150 mm, 5 µm column heated to 35 °C. The mobile phases consisted of; Eluent A: Water (0.01% TFA, v/v) and Eluent B: 70% methanol (0.054% TFA, v/v) with a gradient of; 99% A for 10 min, to 80% A over 5 min, to 1% A over 5 min, held for 3 min and increased to 99% A over 2 min. The samples were injected at a volume of 100 µL and MAA’s were monitored at wavelengths of; 310, 320 and 330 nm, absorption spectra between 200–400 nm were stored in each detected peak.
5.6. Pigment Analysis
Sample Preparation
To approx. 0.5–1 mg of dried biomass, 100% HPLC grade methanol (1 mL) was added and vortexed to re-suspend. Samples were sonicated under low light conditions using a sonicator probe for 6 cycles of 20 s pulses at 40 Hz at 0 °C. After centrifugation (5 min at 12,000 rpm), the supernatant was removed and absorbance spectra measured using a UV-visible spectrophotometer between 400–800 nm with 100% methanol as a blank. Carotenoid concentration was calculated using the equations as described in [50,51].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2218-1989/9/4/74/s1, Figure S1: Hierarchical heatmap visualisation of the significant (A) intracellular and (B) extracellular peak intensities (p ≤ 0.05) during UV-B exposure using a one-way repeated measure ANOVA in MetaboAnalyst. Data is arranged in triplicate with increasing length of UV-B exposure from left to right (0–48 h). S1 = replicate 1, S2 = replicate 2, S3 = replicate 3; Figure S2: Dry weight measurements of C. fritschii cultures during 48 h of supplemented UV-B exposure. All values are the mean of three biological replicates ± standard error; Figure S3: Time-series metabolomics data of C. fritschii during 48 h of UV-B exposure showing primary metabolites found in both intra- and extracellular during GC–MS analysis. (A) Metabolites showing statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05) changes over time in intra- and extracellular data; (B) metabolites showing statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05) changes over time in intracellular samples only. Statistical significance was measured using a two-sample T-test comparing control (0 h) to each treatment time point (2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h) and between treatment time points, * = 0.05 ≥ p ≥ 0.01, ** = 0.01≥ p ≥ 0.001 and *** = p ≤ 0.001; Table S1: Intracellular compounds detected during UV-B exposure using GC–MS including; Retention time (RT), name, class, model (m/z), normalised mean abundance (n = 3) ± standard error (SE). T-test and ANOVA results showing statistical significant compounds, * = 0.05 ≥ p ≥ 0.01, ** = 0.01 ≥ p ≥ 0.001, *** = p ≤ 0.001; Table S2: Extracellular compounds detected during UV-B exposure using GC–MS including; Retention time (RT), name, class, model (m/z), normalised mean abundance (n = 3) ± standard error (SE). T-test and ANOVA results showing statistical significant compounds, * = 0.05 ≥ p ≥0.01, ** = 0.01 ≥ p ≥ 0.001, *** = p ≤ 0.001; Table S3: Biologically relevant metabolites detected during PAR + UV-B (intra- and extracellular metabolites) and PAR only (intracellular metabolites), including possible biosynthetic pathways; Table S4: Intracellular compounds detected during PAR only exposure using GC–MS including; Retention time (RT), name, class, model (m/z), normalised mean abundance (n = 3) ± standard error (SE). T-test and ANOVA results showing statistical significant compounds, * = 0.05 ≥ p ≥ 0.01, ** = 0.01 ≥ p ≥ 0.001, *** = p ≤ 0.001.
Author Contributions
Authors in this study contributed in the following areas: B.K. was responsible for the design of the experiment, execution of experimental work and data analysis. E.D. supported experimental and data acquisition. B.K. wrote the manuscript with input from C.A.L., E.D. and S.W. Supervision by C.A.L., E.D. and S.W.
Funding
This research was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC iCASE studentship), UK, grant number BB/N503630/1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gupta, V.; Ratha, S.K.; Sood, A.; Chaudhary, V.; Prasanna, R. New Insights into the Biodiversity and Applications of Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae)—Prospects and Challenges. Algal Res. 2013, 2, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.; Orf, I.; Kopka, J.; Hagemann, M. Recent Applications of Metabolomics Toward Cyanobacteria. Metabolites 2013, 3, 72–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijffels, R.H.; Kruse, O.; Hellingwerf, K.J. Potential of Industrial Biotechnology with Cyanobacteria and Eukaryotic Microalgae. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sinha, R.P. Biotechnological and Industrial Significance of Cyanobacterial Secondary Metabolites. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sinha, R.P.; Moh, S.H.; Lee, T.K.; Kottuparambil, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Rhee, J.S.; Choi, E.M.; Brown, M.T.; Häder, D.P.; et al. Ultraviolet Radiation and Cyanobacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 141, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P. UV-Induced Oxidative Stress in Cyanobacteria: How Life Is Able to Survive? Biochem. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 4, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, R.; Paris, D.; Melck, D.; Fulgentini, L.; Colombetti, G.; Motta, A. In Vivo NMR Metabolic Profiling of Fabrea Salina Reveals Sequential Defense Mechanisms against Ultraviolet Radiation. Biophys. J. 2011, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.P.; Häder, D.P. UV-Protectants in Cyanobacteria. Plant Sci. 2008, 174, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, N.; Sakamoto, T.; Matsugo, S. Multiple Roles of Photosynthetic and Sunscreen Pigments in Cyanobacteria Focusing on the Oxidative Stress. Metabolites 2013, 3, 463–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Incharoensakdi, A. Characterization of UV-Screening Compounds, Mycosporine-like Amino Acids, and Scytonemin in the Cyanobacterium Lyngbya Sp. CU2555. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Bilger, W.; Scherer, S. UV-B-Induced Synthesis of Photoprotective Pigments and Extracellular Polysaccharides in the Terrestrial Cyanobacterium Nostoc Commune. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 1940–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.P.; Klisch, M.; Sinha, R.P.; Hader, D.-P. Effects of Abiotic Stressors on Synthesis of the Mycosporine-like Amino Acid Shinorine in the Cyanobacterium Anabaena Variabilis PCC 7937. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.; Albert, A.; Ganzera, M. Effects of Elevated Ultraviolet Radiation on Primary Metabolites in Selected Alpine Algae and Cyanobacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 149, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Portwich, A.; Garcia-Pichel, F. A Novel Prokaryotic UVB Photoreceptor in the Cyanobacterium Chlorogloeopsis PCC 6912. Photochem. Photobiol. 2000, 71, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Schulz, S.; Wait, R.; Görg, A.; Scherer, S. The UV-B Stimulon of the Terrestrial Cyanobacterium Nostoc Commune Comprises Early Shock Proteins and Late Acclimation Proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 827–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.K.; Chatterjee, A.; Yadav, S.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, S.; Rai, L.C. UV-B Stress Induced Metabolic Rearrangements Explored with Comparative Proteomics in Three Anabaena Species. J. Proteomics 2015, 127, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.G.; Jia, S.R.; Yan, R.R.; Wu, Y.K.; Wang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Zhao, D.X.; Tan, Z.L.; Lv, H.X.; Han, P.P. The Physiological Responses of Terrestrial Cyanobacterium: Nostoc Flagelliforme to Different Intensities of Ultraviolet-B Radiation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21065–21074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wase, N.; Pham, T.K.; Ow, S.Y.; Wright, P.C. Quantitative Analysis of UV-A Shock and Short Term Stress Using ITRAQ, Pseudo Selective Reaction Monitoring (PSRM) and GC-MS Based Metabolite Analysis of the Cyanobacterium Nostoc Punctiforme ATCC 29133. J. Proteomics 2014, 109, 332–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, C.L.; Longnecker, K.; Kido Soule, M.C.; Kujawinski, E.B. Release of Ecologically Relevant Metabolites by the Cyanobacterium S Ynechococcus Elongatus CCMP 1631. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3949–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, R.K.; Mayali, X.; Lee, J.Z.; Craig Everroad, R.; Hwang, M.; Bebout, B.M.; Weber, P.K.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Thelen, M.P. Cyanobacterial Reuse of Extracellular Organic Carbon in Microbial Mats. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujawinski, E.B. The Impact of Microbial Metabolism on Marine Dissolved Organic Matter. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 567–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Sinha, R.P.; Tyagi, M.B.; Kumar, A. Cyanobacterial Secondary Metabolites. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2011, 2, 144–167. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, R.; Guimarães, R.; Büttel, Z.; Rossi, F.; Colica, G.; Silva, C.J.; Santos, C.; Gales, L.; Zille, A.; De Philippis, R.; et al. Production and Characterization of Extracellular Carbohydrate Polymer from Cyanothece Sp. CCY 0110. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sue, T.; Obolonkin, V.; Griffiths, H.; Villas-Bôas, S.G. An Exometabolomics Approach to Monitoring Microbial Contamination in Microalgal Fermentation Processes by Using Metabolic Footprint Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7605–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinu, F.; Villas-Boas, S. Extracellular Microbial Metabolomics: The State of the Art. Metabolites 2017, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granucci, N.; Pinu, F.R.; Han, T.-L.; Villas-Boas, S.G. Can We Predict the Intracellular Metabolic State of a Cell Based on Extracellular Metabolite Data? Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 3297–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasundaram, B.; Skill, S.C.; Llewellyn, C. a. A Low Energy Process for the Recovery of Bioproducts from Cyanobacteria Using a Ball Mill. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 69, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.H.; Foulds, I.; Carr, N.G. Environmental Conditions and Morphological Variation in the Blue-Green Alga Chlorogloea Fritschii. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1976, 92, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portwich, A.; Garcia-Pichel, F. Ultraviolet and Osmotic Stresses Induce and Regulate the Synthesis of Mycosporines in the Cyanobacterium Chlorogloeopsis PCC 6912. Arch. Microbiol. 1999, 172, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airs, R.L.; Temperton, B.; Sambles, C.; Farnham, G.; Skill, S.C.; Llewellyn, C.A. Chlorophyll f and Chlorophyll d Are Produced in the Cyanobacterium Chlorogloeopsis Fritschii When Cultured under Natural Light and Near-Infrared Radiation. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3770–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanier, R.Y.; Deruelles, J.; Rippka, R.; Herdman, M.; Waterbury, J.B. Generic Assignments, Strain Histories and Properties of Pure Cultures of Cyanobacteria. Microbiology 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.P.; Häder, D.P.; Sinha, R.P. Cyanobacteria and Ultraviolet Radiation (UVR) Stress: Mitigation Strategies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, A.; Ruiz, M.; Zhang, C.C. Oxidative Stress in Cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sinha, R.P.; Häder, D.-P. Effect of UV-B on Enzymes of Nitrogen Metabolism in the Cyanobacterium Nostoc Calcicola. J. Plant Physiol. 1996, 148, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kultschar, B.; Llewellyn, C. Secondary Metabolites in Cyanobacteria. In Secondary Metabolites—Sources and Applications; InTech: London, UK, 2018; Volume 2, p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, J.C.; Pakrasi, H.B. Essential Role of Glutathione in Acclimation to Environmental and Redox Perturbations in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis Sp. PCC 6803. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 1672–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Natarajan, S.K.; Becker, D.F. Proline Mechanisms of Stress Survival. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbruggen, N.; Hermans, C. Proline Accumulation in Plants: A Review. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chris, A.; Zeeshan, M.; Abraham, G.; Prasad, S.M. Proline Accumulation in Cylindrospermum sp. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusano, M.; Tohge, T.; Fukushima, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Hayashi, N.; Otsuki, H.; Kondou, Y.; Goto, H.; Kawashima, M.; Matsuda, F.; et al. Metabolomics Reveals Comprehensive Reprogramming Involving Two Independent Metabolic Responses of Arabidopsis to UV-B Light. Plant J. 2011, 67, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinu, F.R.; Granucci, N.; Daniell, J.; Han, T.-L.; Carneiro, S.; Rocha, I.; Nielsen, J.; Villas-Boas, S.G. Metabolite Secretion in Microorganisms: The Theory of Metabolic Overflow Put to the Test. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, A.A.; Morgan, J.A. A Transient Isotopic Labeling Methodology for 13C Metabolic Flux Analysis of Photoautotrophic Microorganisms. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2302–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styczynski, M.P.; Moxley, J.F.; Tong, L.V.; Walther, J.L.; Jensen, K.L.; Stephanopoulos, G.N. Systematic Identification of Conserved Metabolites in GC/MS Data for Metabolomics and Biomarker Discovery. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopka, J.; Schauer, N.; Krueger, S.; Birkemeyer, C.; Usadel, B.; Bergmüller, E.; Dörmann, P.; Weckwerth, W.; Gibon, Y.; Stitt, M.; et al. GMD@CSB.DB: The Golm Metabolome Database. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards More Transparent and Integrative Metabolomics Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Sinelnikov, I.V.; Wishart, D.S. MetATT: A Web-Based Metabolomics Tool for Analyzing Time-Series and Two-Factor Datasets. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2455–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Combined Targeted and Untargeted Profiling. In Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 131 A, pp. 30.4.1–30.4.32. [Google Scholar]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed Minimum Reporting Standards for Chemical Analysis: Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Madamwar, D.; Incharoensakdi, A. Sun-Screening Bioactive Compounds Mycosporine-like Amino Acids in Naturally Occurring Cyanobacterial Biofilms: Role in Photoprotection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, R.J. Consistent Sets of Spectrophotometric Chlorophyll Equations for Acetone, Methanol and Ethanol Solvents. Photosynth. Res. 2006, 89, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, M.; Silva, A.; Rocha, J. Extraction and Quantification of Pigments from a Marine Microalga: A Simple and Reproducible Method. Commun. Curr. Res. Educ. Top. Trends Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 2, 586–593. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).