PLS2 in Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
Notation
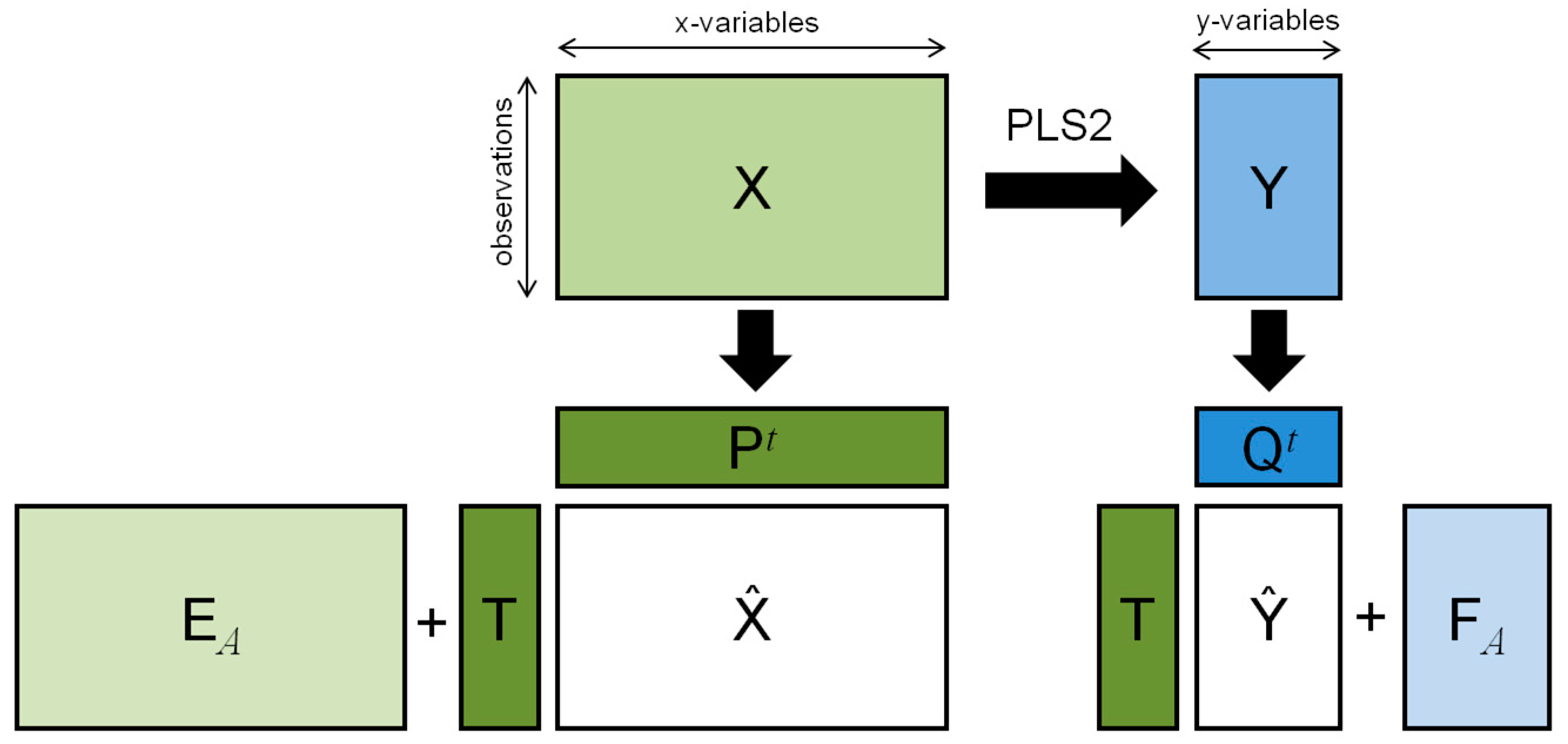
2. The PLS2 Algorithm
- two matrices and ;
- the integer number of latent variables.
Let For (1) EndFor
2.1. Main Properties
- -
- the score vectors of the X-block are a set of mutually orthogonal vectors;
- -
- the weight vectors are a set of mutually orthonormal vectors; and
- -
- the matrix is an upper triangular matrix with determinant equal to 1 [11].
2.2. Structured Noise and Post-Transformation of PLS2 (ptPLS2)
2.3. Orthogonally-Constrained PLS2 (oCPLS2)
2.4. Non-Linear Problems: Kernel-PLS (KPLS2)
3. Model Interpretation
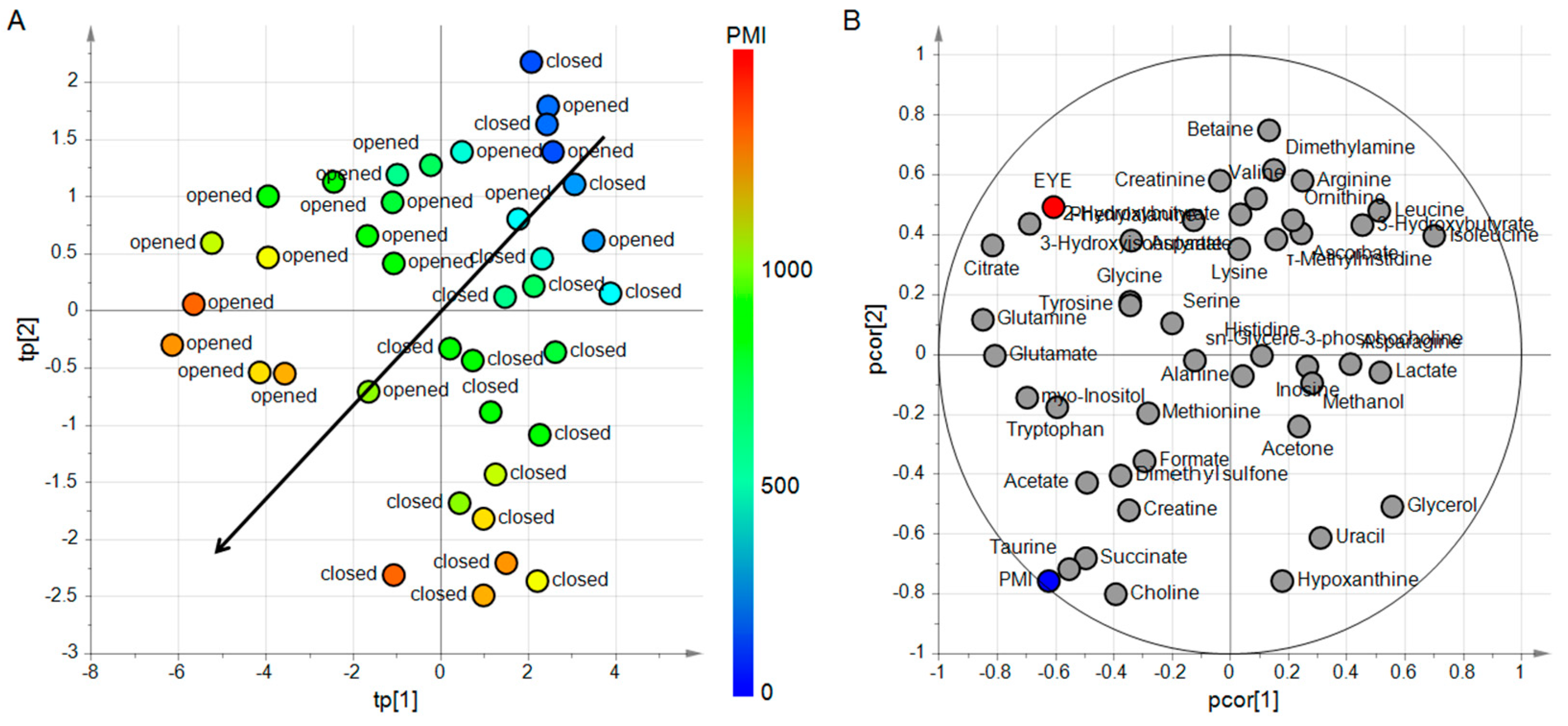
3.1. Which are the Relationships Between Predictors and Responses?
3.2. How is it Possible to Interpret the Latent Variables in Terms of Single Metabolites?
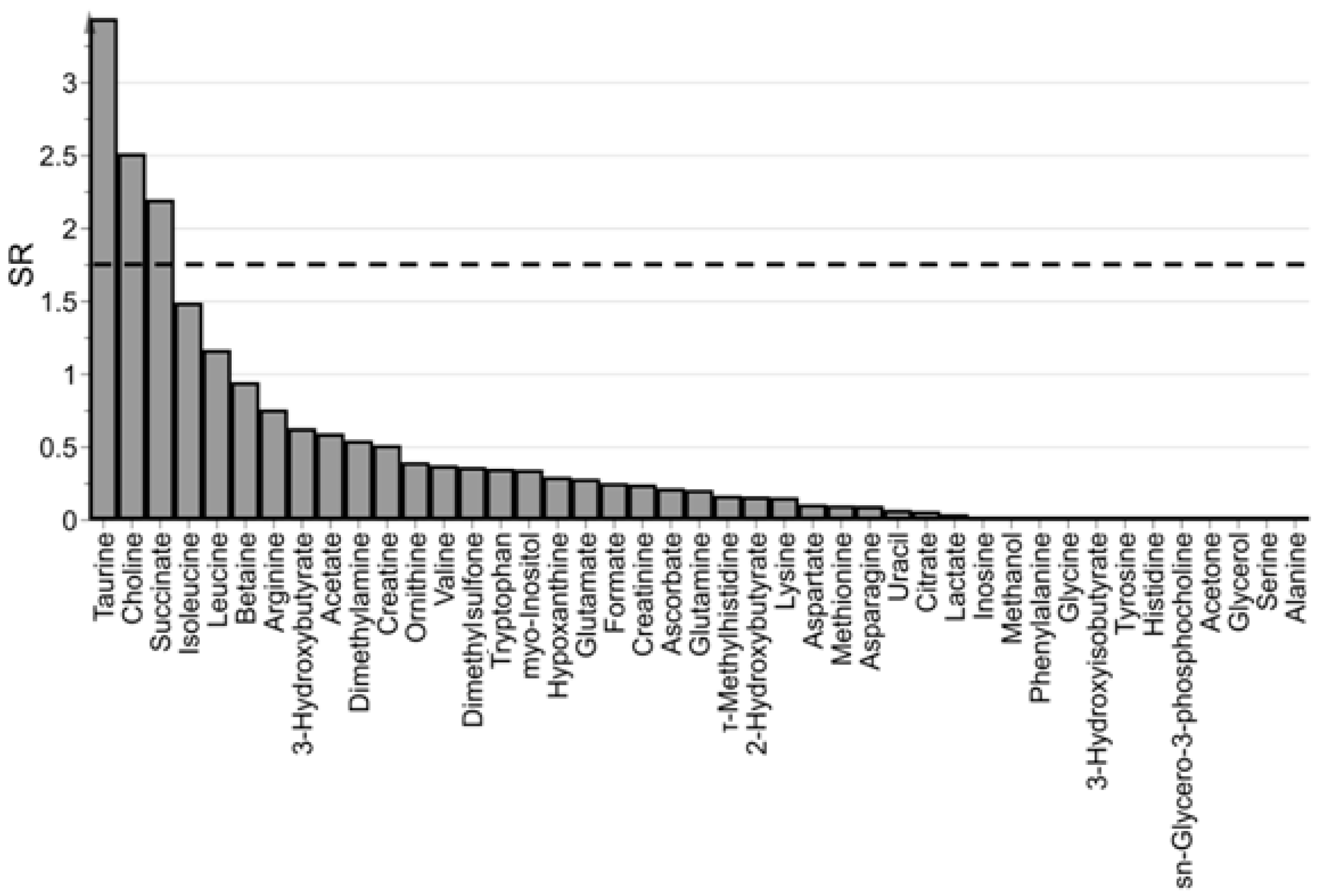
3.3. Which are the Most Important Metabolites in the Model?
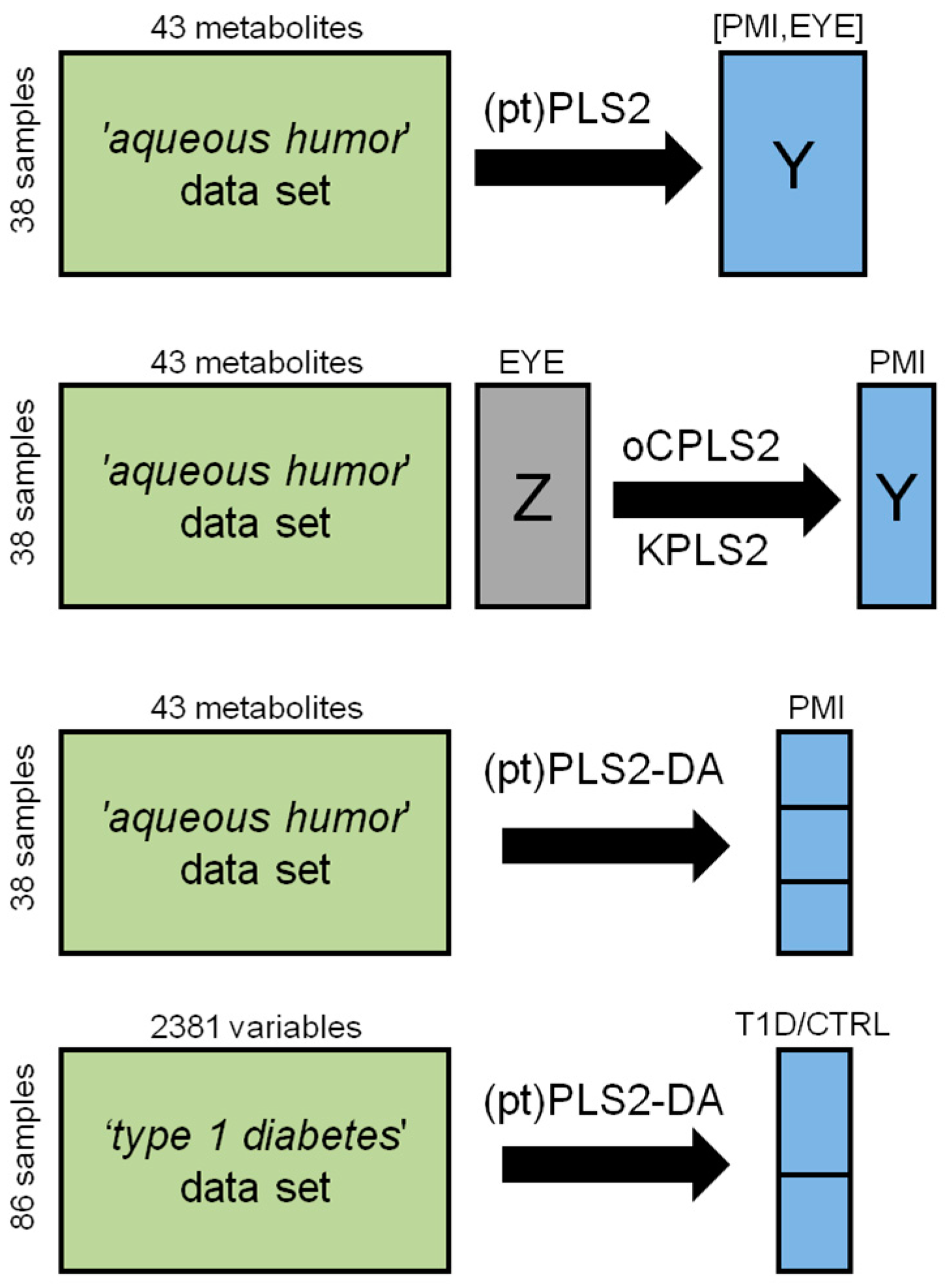
4. Applications to Metabolomics
4.1. Data Pre-Processing and Data Pre-Treatment
4.2. Mulivariate Calibration Problems: PLS2
4.3. The ‘Aqueous Humor’ Dataset
4.3.1. Design of Experiment and PLS2
4.3.2. Predicting PMI by oCPLS2
4.4. Classification Problems: PLS2-DA
4.4.1. Dummy Y-Response and Scaling
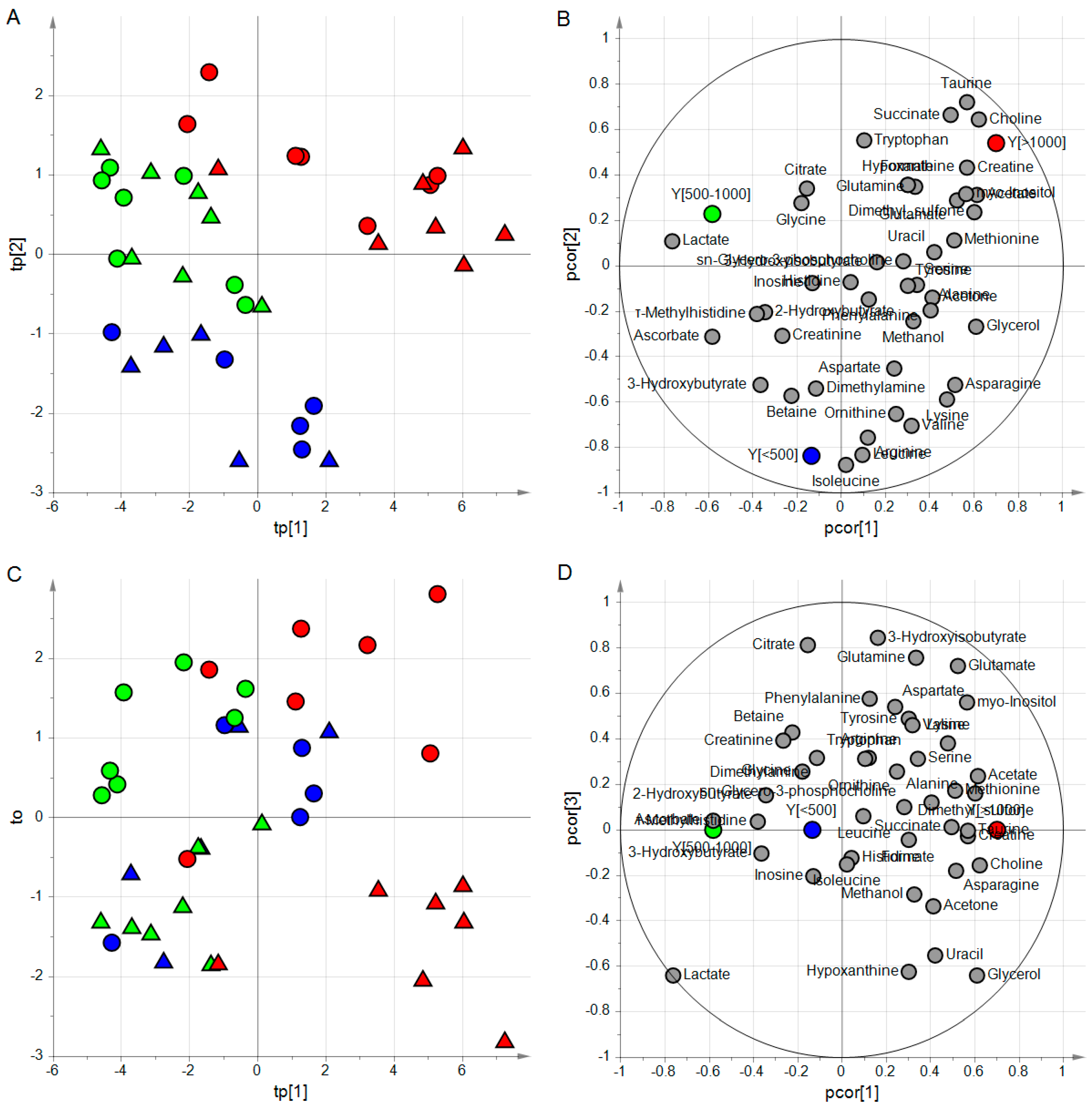
4.4.2. Application to the ‘Aqueous Humor’ Dataset
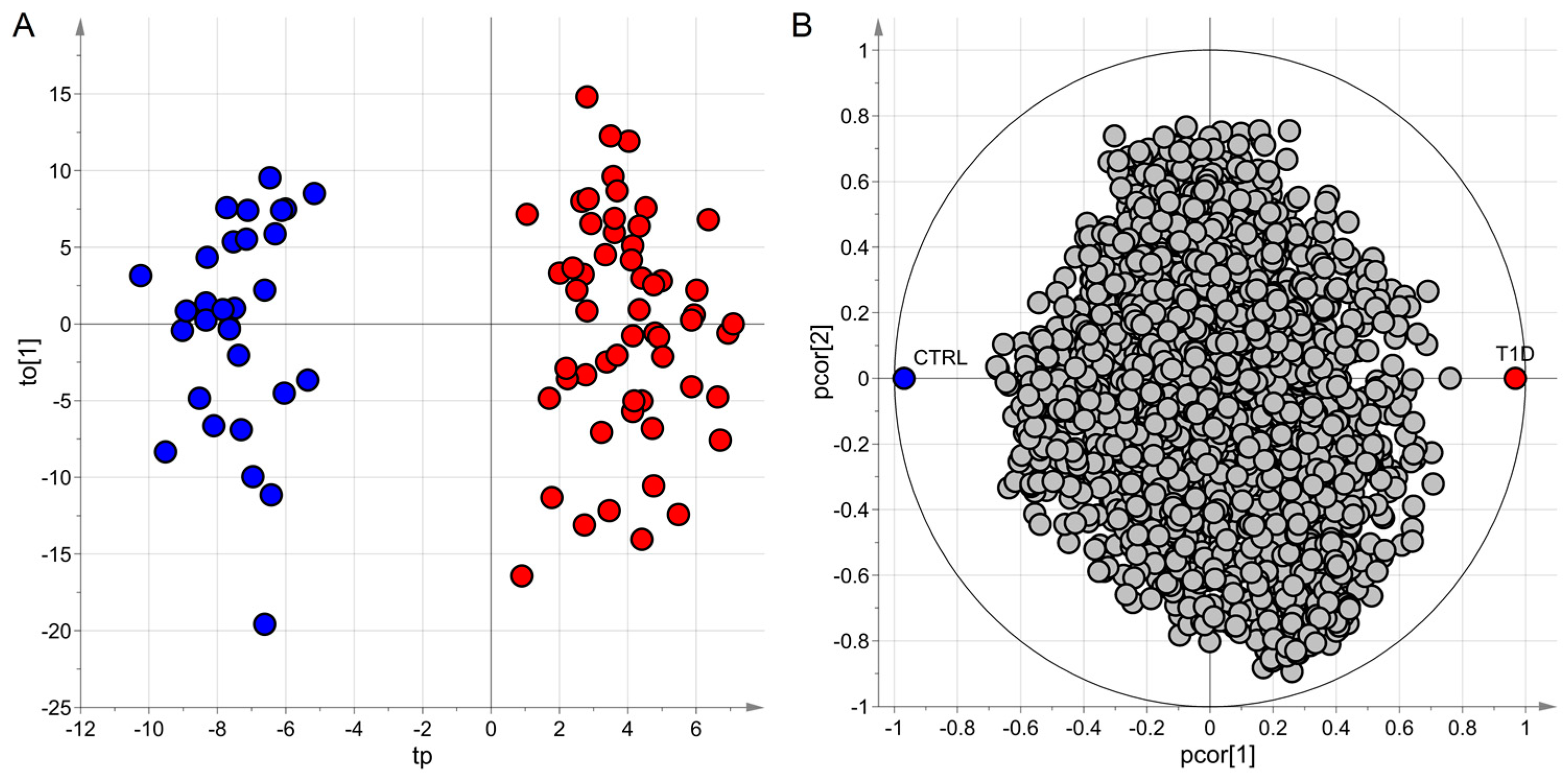
4.4.3. Application to the ‘Type 1 Diabetes’ Dataset
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wold, S.; Martens, H.; Wold, H. The multivariate calibration method in chemistry solved by the PLS method. In Proceedings of the Conference on Matrix Pencils, Lecture Notes in Mathematics; Ruhe, A., Kågström, B., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; pp. 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S. Personal memories of the early PLS development. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, H. Reliable and relevant modelling of real world data: A personal account of the development of PLS Regression. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, S. SIMPLS: An alternative approach to partial least squares regression. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1993, 18, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, A.J.; Viveros, R.; MacGregor, J.F. Frameworks for latent variable multivariate regression. J. Chemom. 1996, 10, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeniay, Ö.; Göktaş, A. A comparison of Partial Least Squares regression with other prediction methods. Hacet. J. Math. Stat. 2002, 31, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Vigneau, E.; Devaux, M.F.; Qannari, E.M.; Robert, P. Principal component regression, ridge regression and ridge principal component regression in spectroscopy calibration. J. Chemom. 1997, 11, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchero, M.; Paris, D. Post-transformation of PLS2 (ptPLS2) by orthogonal matrix: A new approach for generating predictive and orthogonal latent variables. J. Chemom. 2016, 30, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchero, M. Exploring the latent variable space of PLS2 by post-transformation of the score matrix (ptLV). J. Chemom. 2018, e3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchero, M.; Riccadonna, S.; Franceschi, P. Projection to latent structures with orthogonal constraints: Versatile tools for the analysis of metabolomics data. J. Chemom. 2018, 32, e2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, R. Analysis of two partial-least-squares algorithms for multivariate calibration. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1987, 2, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland, I.S. On the structure of partial least squares regression. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 1988, 17, 581–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ruscio, D. Weighted view on the partial least-squares algorithm. Automatica 2000, 36, 831–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.; Byrne, T.; Johansson, E.; Trygg, J.; Wikström, C. Multi- and Megavariate Data Analysis Basic Principles and Applications. In Umetrics Academy, 3rd ed.; MKS Umetrics AB: Malmö, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Höskuldsson, A. PLS regression methods. J. Chemom. 1988, 2, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phatak, A.; de Jong, S. The geometry of partial least squares. J. Chemom. 1997, 11, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trygg, J.; Wold, S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J. Chemom. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvalheim, O.M.; Rajalahti, T.; Arneberg, R. X-tended target projection (XTP)—Comparison with orthogonal partial least squares (OPLS) and PLS post-processing by similarity transformation (PLS+ST). J. Chemom. 2009, 23, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergon, R. PLS post-processing by similarity transformation (PLS+ST): A simple alternative to OPLS. J. Chemom. 2005, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilde, A.K.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Westerhuis, J.A. The geometry of ASCA. J. Chemom. 2008, 22, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, A.; Wold, S. INLR, Implicit Non-linear Latent Variable Regression. J. Chemom. 1997, 11, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, A.; Kettaneh, N.; Uppgård, L.T.; Wold, S.; Bendwell, N.; Cameron, D.R. The GIFI approach to non-linear PLS modeling. J. Chemom. 2001, 15, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, F.; Geladi, P.; Wold, S. The kernel algorithm for PLS. J Chemom. 1993, 7, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, R.; Palací-López, D.; Kerkenaar, H.H.M.; Postma, G.J.; Buydens, L.M.C.; Ferrer, A. Kernel-Partial Least Squares regression coupled to pseudo-sample trajectories for the analysis of mixture designs of experiments. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2018, 175, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantalainen, M.; Bylesjö, M.; Cloarec, O.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Trygg, J. Kernel-based orthogonal projections to latent structures (K-OPLS). J. Chemom. 2007, 21, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Statistical modelling: The two cultures. Stat. Sci. 2001, 16, 199–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvalheim, O.M. Interpretation of partial least squares regression models by means of target projection and selectivity ratio plots. J. Chemom. 2010, 24, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalahti, T.; Arneberg, R.; Kroksveen, A.C.; Berle, M.; Myhr, K.-M.; Kvalheim, O.M. Discriminating variable test and selectivity ratio plot: Quantitative tools for interpretation and variable (biomarker) selection in complex spectral or chromatographic profiles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2581–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, S.; Johansson, E.; Cocchi, M. 3D QSAR in Drug Design; Theory, Methods, and Applications; ESCOM: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 523–550. [Google Scholar]
- Arredouani, A.; Stocchero, M.; Culeddu, N.; Moustafa, J.E.; Tichet, J.; Balkau, B.; Brousseau, T.; Manca, M.; Falchi, M.; DESIR Study Group. Metabolomic Profile of Low–Copy Number Carriers at the Salivary α-Amylase Gene Suggests a Metabolic Shift Toward Lipid-Based Energy Production. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3362–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centner, V.; Massart, D.L.; de Noord, O.E.; de Jong, S.; Vandeginste, B.M.; Sterna, C. Elimination of Uninformative Variables for Multivariate Calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 68, 3851–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodacre, R.; Broadhurst, D.; Smilde, A.K.; Kristal, B.S.; Baker, J.D.; Beger, R.; Bessant, C.; Connor, S.; Capuani, G.; Craig, A.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for data analysis in metabolomics. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euceda, L.R.; Giskeødegård, G.F.; Bathen, T.F. Preprocessing of NMR metabolomics data. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2015, 75, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharias, H.U.; Altenbuchinger, M.; Gronwald, W. Statistical analysis of NMR metabolic fingerprints: established methods and recent advances. Metabolites 2018, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Wang, J.; Su, M.; Jia, E.; Chen, S.; Chen, T.; Ni, Y. Missing value imputation approach for Mass Spectrometry-based metabolomics data. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccenti, E. Correlation patterns in experimental data are affected by normalization procedures: Consequences for data analysis and network inference. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locci, E.; Stocchero, M.; Noto, A.; Chighine, A.; Natali, L.; Caria, R.; De-Giorgio, F.; Nioi, M.; d’Aloja, E. A 1H NMR metabolomic approach for the estimation of the time since death using aqueous humour: An animal model. Metabolomics. submitted.
- Ballabio, D.; Consonni, V. Classification tools in chemistry. Part 1: Linear models. PLS-DA. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.; Rayens, W. Partial least squares for discrimination. J. Chemom. 2003, 17, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galderisi, A.; Pirillo, P.; Moret, V.; Stocchero, M.; Gucciardi, A.; Perilongo, G.; Moretti, C.; Monciotti, C.; Giordano, G.; Baraldi, E. Metabolomics reveals new metabolic perturbations in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 19, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stocchero, M.; Locci, E.; d’Aloja, E.; Nioi, M.; Baraldi, E.; Giordano, G. PLS2 in Metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9030051
Stocchero M, Locci E, d’Aloja E, Nioi M, Baraldi E, Giordano G. PLS2 in Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2019; 9(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleStocchero, Matteo, Emanuela Locci, Ernesto d’Aloja, Matteo Nioi, Eugenio Baraldi, and Giuseppe Giordano. 2019. "PLS2 in Metabolomics" Metabolites 9, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9030051
APA StyleStocchero, M., Locci, E., d’Aloja, E., Nioi, M., Baraldi, E., & Giordano, G. (2019). PLS2 in Metabolomics. Metabolites, 9(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9030051





