Detecting Pulmonary Oxygen Toxicity Using eNose Technology and Associations between Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. eNose
2.2. Associating eNose and GC–MS Data
3. Discussion
Direction of Future Research
4. Materials and Methods
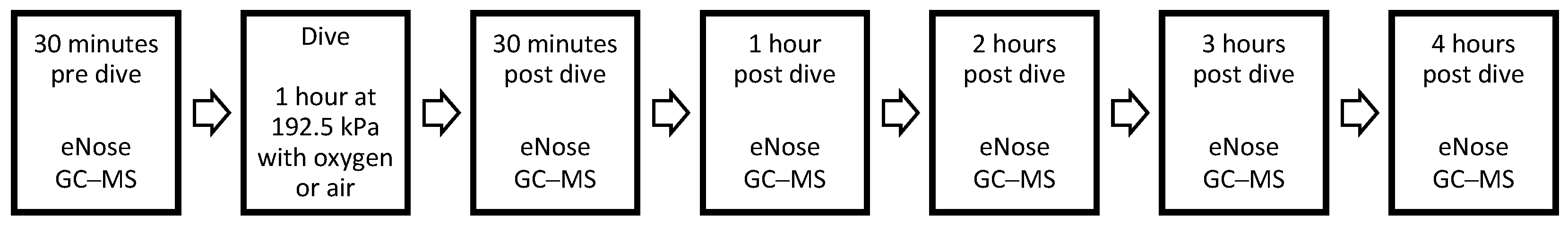
4.1. Study Design
4.2. eNose
4.3. GC–MS Dataset
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Associating eNose and GC–MS Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorrain, S.J. The pathological effects due to increase of oxygen tension in the air breathed. J. Physiol. 1899, 24, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J. Normobaric pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Anesth. Analg. 1990, 70, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ooij, P.J.A.M.; Hollmann, M.W.; van Hulst, R.A.; Sterk, P.J. Assessment of pulmonary oxygen toxicity: Relevance to professional diving; a review. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 189, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.M.; Lambertsen, C.J. Pulmonary Oxygen Tolerance in Man and Derivation of Pulmonary Oxygen Tolerance Curves; Institute for Environmental Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Bardin, H.; Lambertsen, C.J. A Quantitative Method for Calculating Pulmonary Toxicity: Use of the Unit Pulmonary Toxicity Dose (UPTD); Institute for Environmental Medicine, University of Pennsylvania: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ooij, P.J.A.M.; Sterk, P.J.; van Hulst, R.A. Oxygen, the lung and the diver: Friends and foes? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2016, 25, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingelaar, T.T.; van Ooij, P.J.A.M.; van Hulst, R.A. Oxygen Toxicity and Special Operations Forces Diving: Hidden and Dangerous. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ooij, P.J.A.M.; van Hulst, R.A.; Kulik, W.; Brinkman, P.; Houtkooper, A.; Sterk, P.J. Hyperbaric oxygen diving affects exhaled molecular profiles in men. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2014, 198, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingelaar, T.T.; Brinkman, P.; van Ooij, P.J.A.M.; Hoencamp, R.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H.; Hollmann, M.W.; van Hulst, R.A. Markers of Pulmonary Oxygen Toxicity in Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Using Exhaled Breath Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingelaar, T.T.; Ooij, P.J.A.M.; Brinkman, P.; Van Hulst, R.A. Pulmonary Oxygen Toxicity in Navy Divers: A Crossover Study Using Exhaled Breath Analysis After a One-Hour Air or Oxygen Dive at Nine Meters of Sea Water. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, L.D.; Sterk, P.J.; Fowler, S.J. Breathomics in the setting of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boots, A.W.; Bos, L.D.; van der Schee, M.P.; van Schooten, F.J.; Sterk, P.J. Exhaled Molecular Fingerprinting in Diagnosis and Monitoring: Validating Volatile Promises. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, P.; Zee, A.M.; Wagener, A.H. Breathomics and treatable traits for chronic airway diseases. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2019, 25, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fens, N.; van der Schee, M.P.; Brinkman, P.; Sterk, P.J. Exhaled breath analysis by electronic nose in airways disease. Established issues and key questions. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusselmans, L.; Arnouts, L.; Millevert, C.; Vandersnickt, J.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Lamote, K. Breath analysis as a diagnostic and screening tool for malignant pleural mesothelioma: A systematic review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.D. Advances in electronic-nose technologies for the detection of volatile biomarker metabolites in the human breath. Metabolites 2015, 5, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, P.; van de Pol, M.A.; Gerritsen, M.G.; Bos, L.D.; Dekker, T.; Smids, B.S.; Sinha, A.; Majoor, C.J.; Sneeboer, M.M.; Knobel, H.H.; et al. Exhaled breath profiles in the monitoring of loss of control and clinical recovery in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamote, K.; Brinkman, P.; Vandermeersch, L.; Vynck, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Van Langenhove, H.; Thas, O.; van Cleemput, J.; Nackaert, K.; van Meerbeeck, J.P. Breath analysis by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and electronic nose to screen for pleural mesothelioma: A cross-sectional case-control study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91593–91602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W. Issues and opinions on structural equation modeling. MIS Q. 1998, 22, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhaddani, S.E.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.; Salo, P.; Perola, M.; Jongbloed, G.; Uh, H.W. Evaluation of O2PLS in Omics data integration. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, I.; Cao, K.A.; Davis, M.J.; Dejean, S. Visualising associations between paired omics data sets. BioData Min. 2012, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Bergmann, A.; Steffens, M.; Trefz, P.; Ziller, M.; Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.S.; Köhler, H.; Reinhold, P. Impact of food intake on in vivo VOC concentrations in exhaled breath assessed in a caprine animal model. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 047113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.; Brinkman, P.; van der Schee, M.P.; Fens, N.; Dijkers, E.; Bootsma, S.K.; de Jongh, F.H.C.; Sterk, P.J. Integration of electronic nose technology with spirometry: Validation of a new approach for exhaled breath analysis. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 046001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, R.; Dagelet, Y.W.F.; Spoor, P.; Snoey, E.; Jak, P.M.C.; Brinkman, P.; Dijkers, E.; Bootsma, S.K.; Elskamp, F.; de Jongh, F.H.C.; et al. Clinical and inflammatory phenotyping by breathomics in chronic airway diseases irrespective of the diagnostic label. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
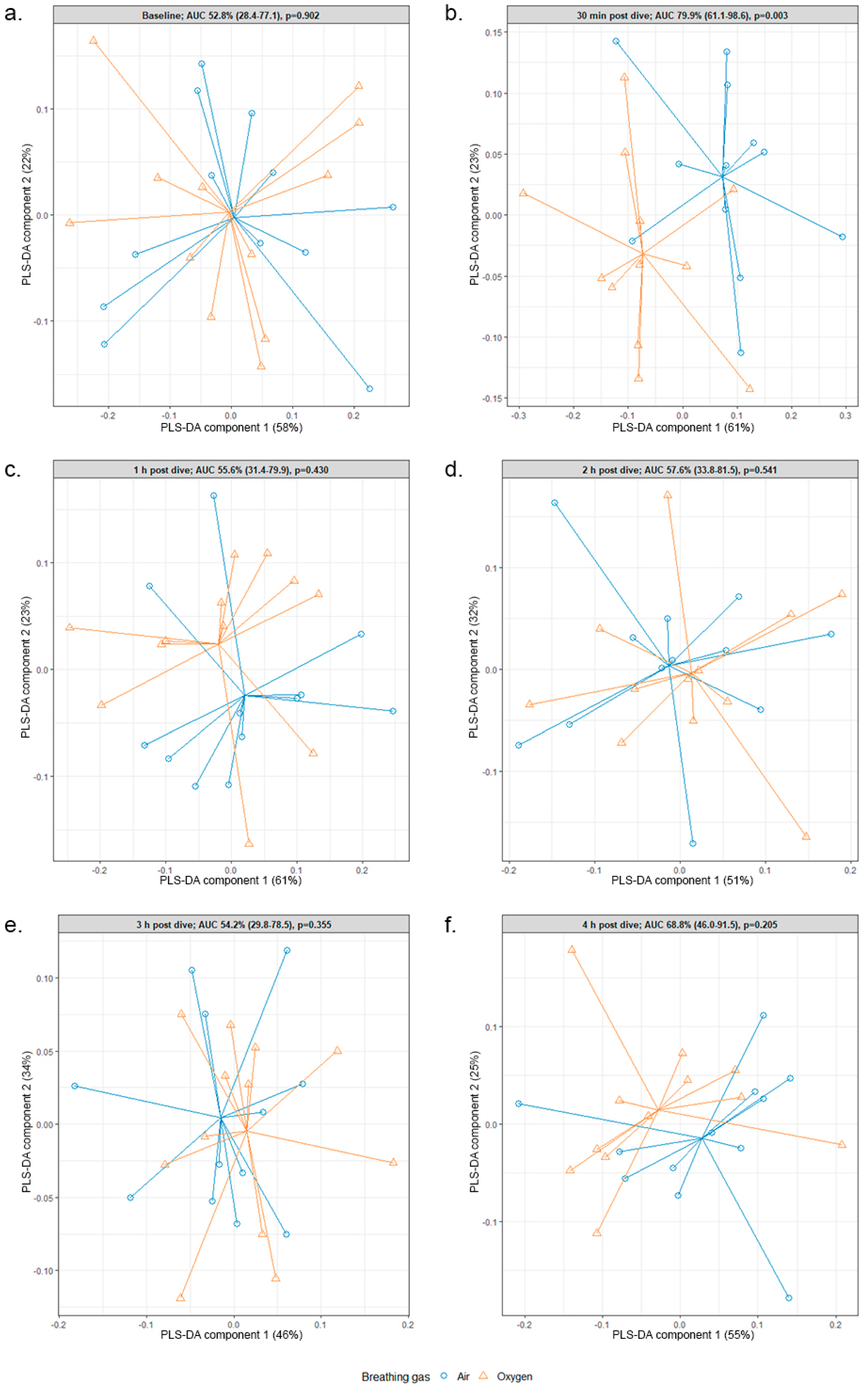
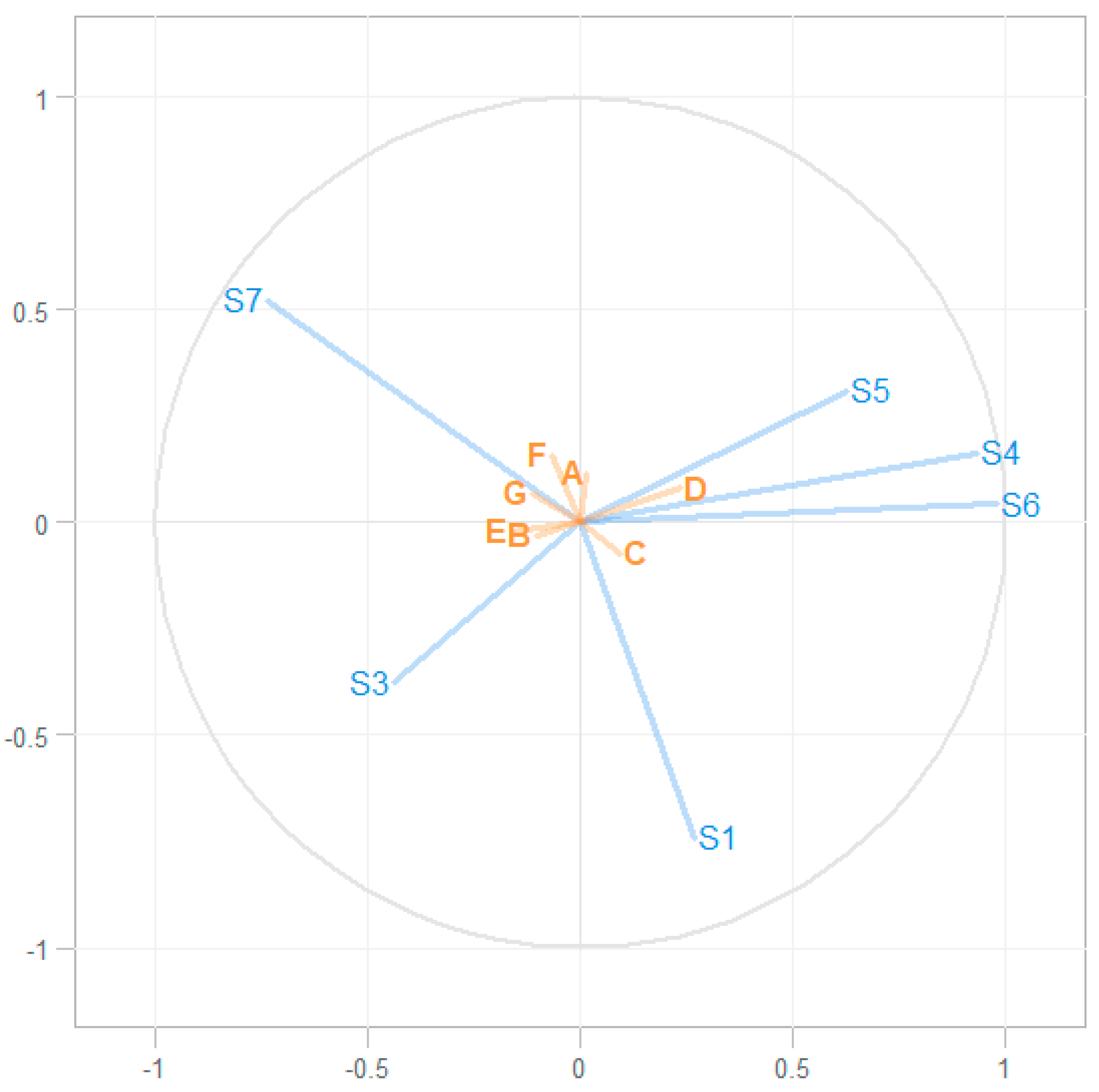
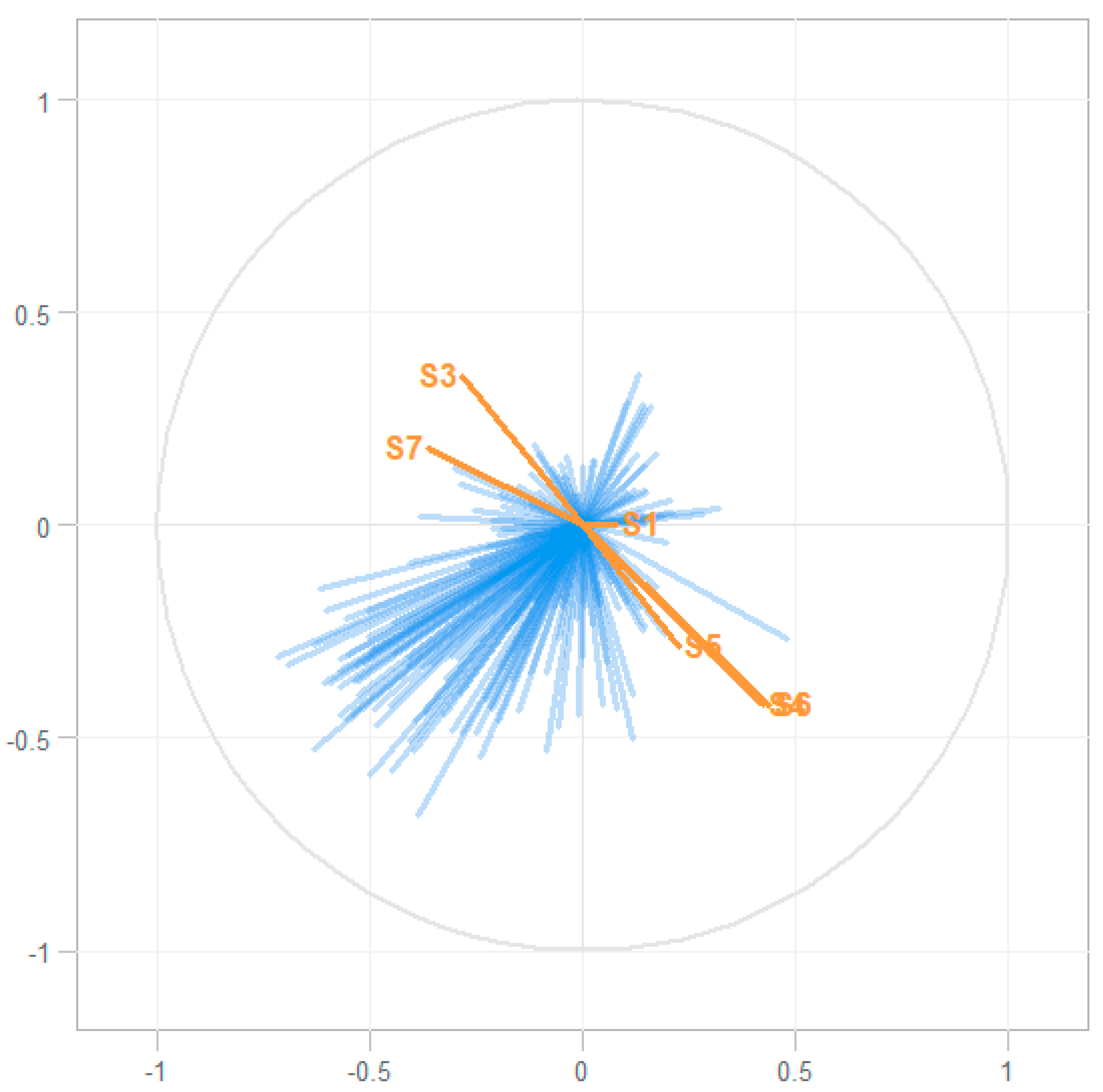
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | −0.065 | 0.010 | 0.048 | −0.029 | 0.001 | −0.092 | −0.046 |
| S3 | −0.056 | 0.031 | 0.018 | −0.076 | 0.037 | −0.060 | −0.012 |
| S4 | 0.013 | −0.035 | 0.024 | 0.080 | −0.053 | −0.011 | −0.031 |
| S5 | 0.050 | −0.032 | −0.012 | 0.077 | −0.039 | 0.051 | 0.006 |
| S6 | 0.007 | −0.031 | 0.026 | 0.072 | −0.049 | −0.016 | −0.032 |
| S7 | 0.057 | 0.011 | −0.063 | −0.020 | 0.032 | 0.099 | 0.066 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wingelaar, T.T.; Brinkman, P.; de Vries, R.; van Ooij, P.-J.A.M.; Hoencamp, R.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.-H.; Hollmann, M.W.; van Hulst, R.A. Detecting Pulmonary Oxygen Toxicity Using eNose Technology and Associations between Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Data. Metabolites 2019, 9, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9120286
Wingelaar TT, Brinkman P, de Vries R, van Ooij P-JAM, Hoencamp R, Maitland-van der Zee A-H, Hollmann MW, van Hulst RA. Detecting Pulmonary Oxygen Toxicity Using eNose Technology and Associations between Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Data. Metabolites. 2019; 9(12):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9120286
Chicago/Turabian StyleWingelaar, Thijs T., Paul Brinkman, Rianne de Vries, Pieter-Jan A.M. van Ooij, Rigo Hoencamp, Anke-Hilse Maitland-van der Zee, Markus W. Hollmann, and Rob A. van Hulst. 2019. "Detecting Pulmonary Oxygen Toxicity Using eNose Technology and Associations between Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Data" Metabolites 9, no. 12: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9120286
APA StyleWingelaar, T. T., Brinkman, P., de Vries, R., van Ooij, P.-J. A. M., Hoencamp, R., Maitland-van der Zee, A.-H., Hollmann, M. W., & van Hulst, R. A. (2019). Detecting Pulmonary Oxygen Toxicity Using eNose Technology and Associations between Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Data. Metabolites, 9(12), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9120286








