Compositional Differences and Similarities between Typical Chinese Baijiu and Western Liquor as Revealed by Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics
Abstract
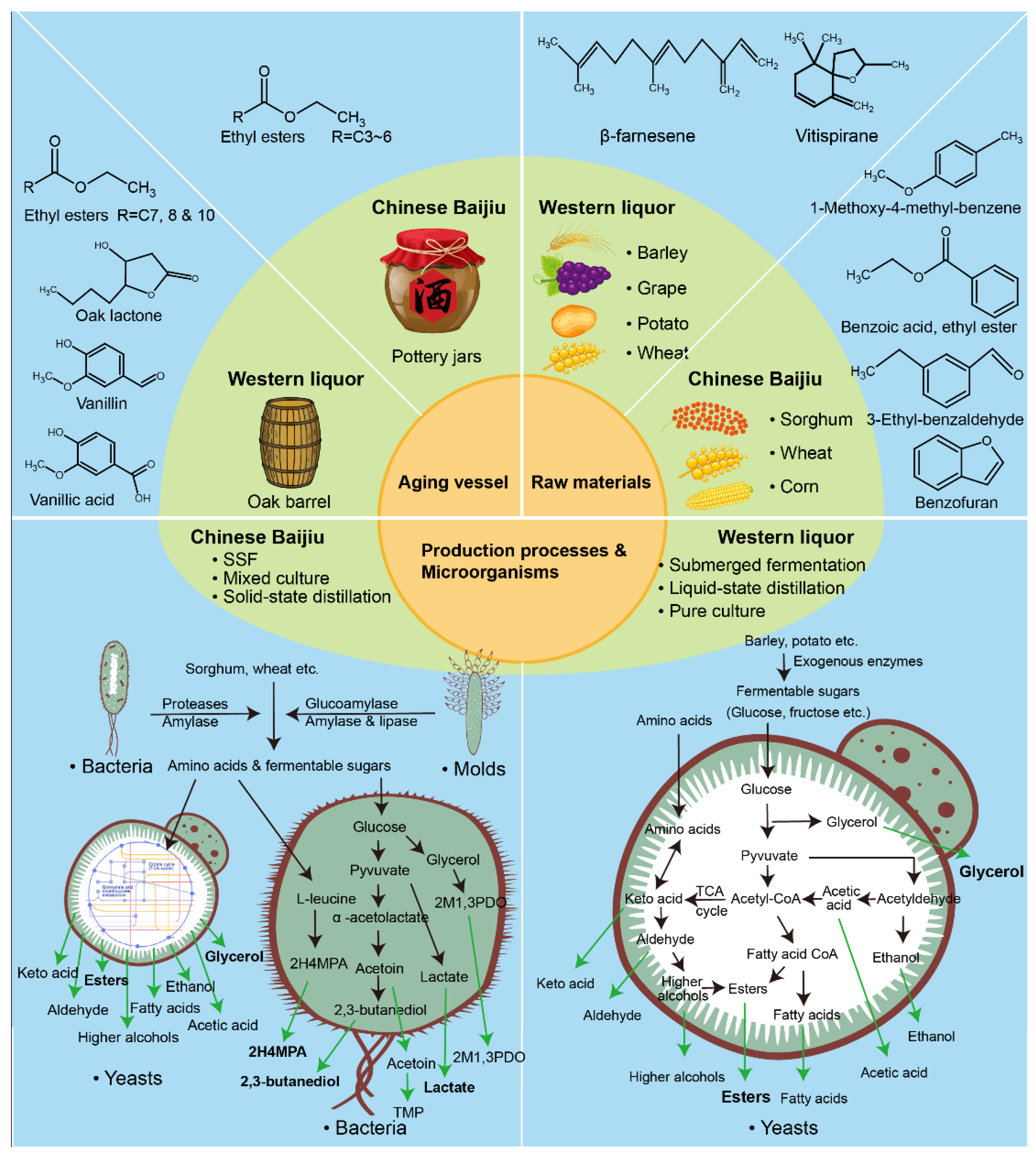
1. Introduction
2. Results
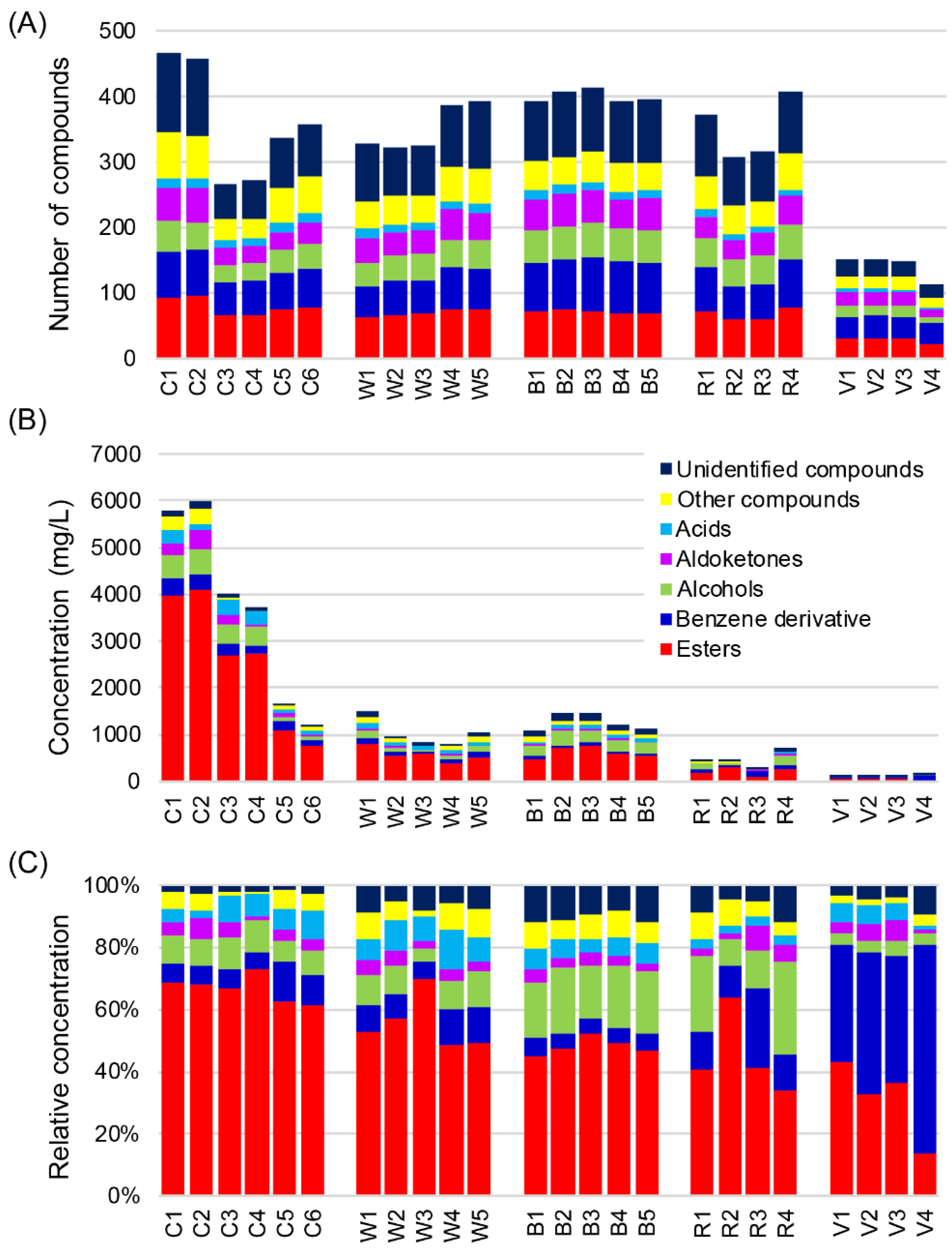
2.1. VOCs Detected by HS-SPME-GC-TOFMS
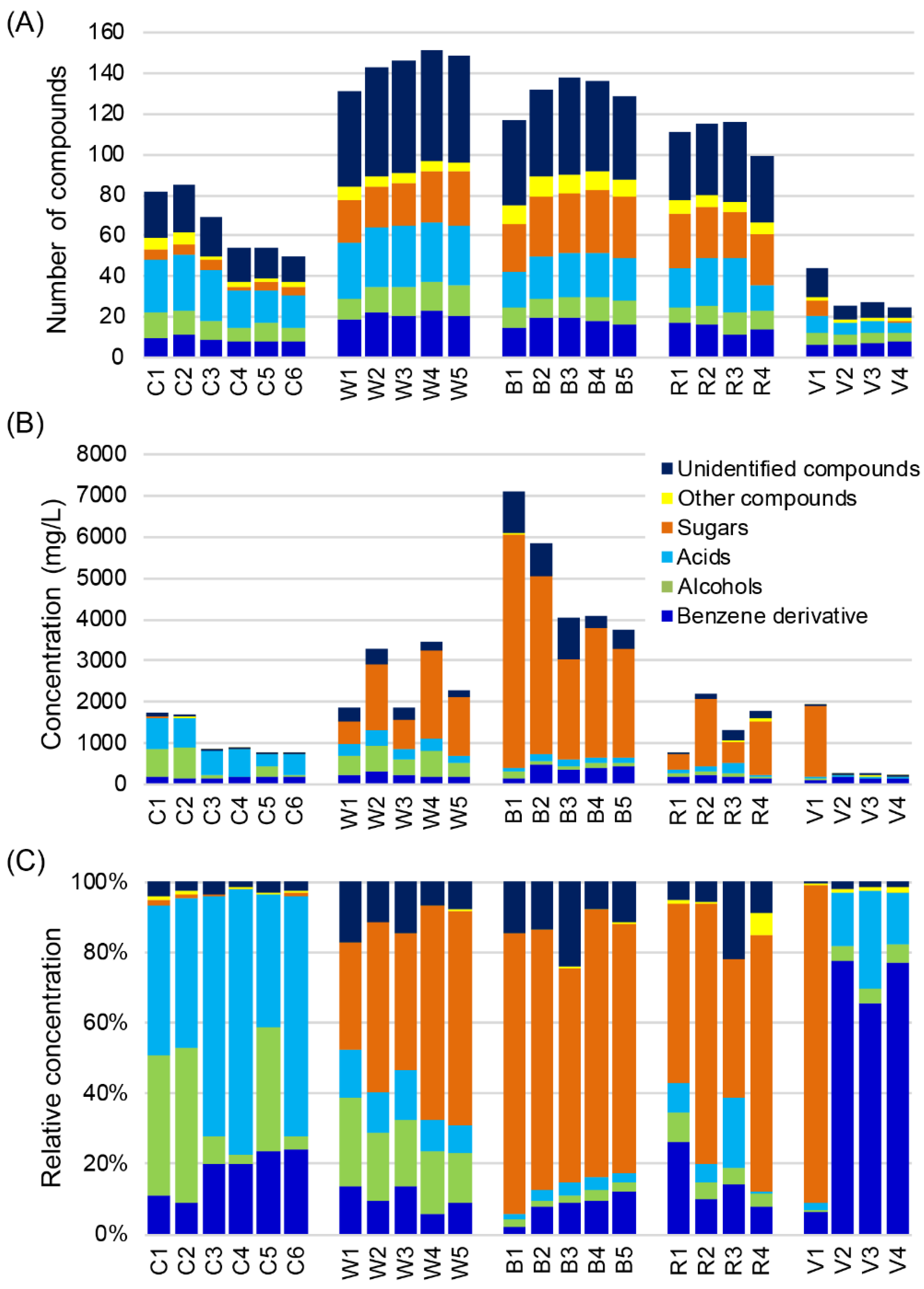
2.2. Non-VOCs Detected by GC-TOFMS
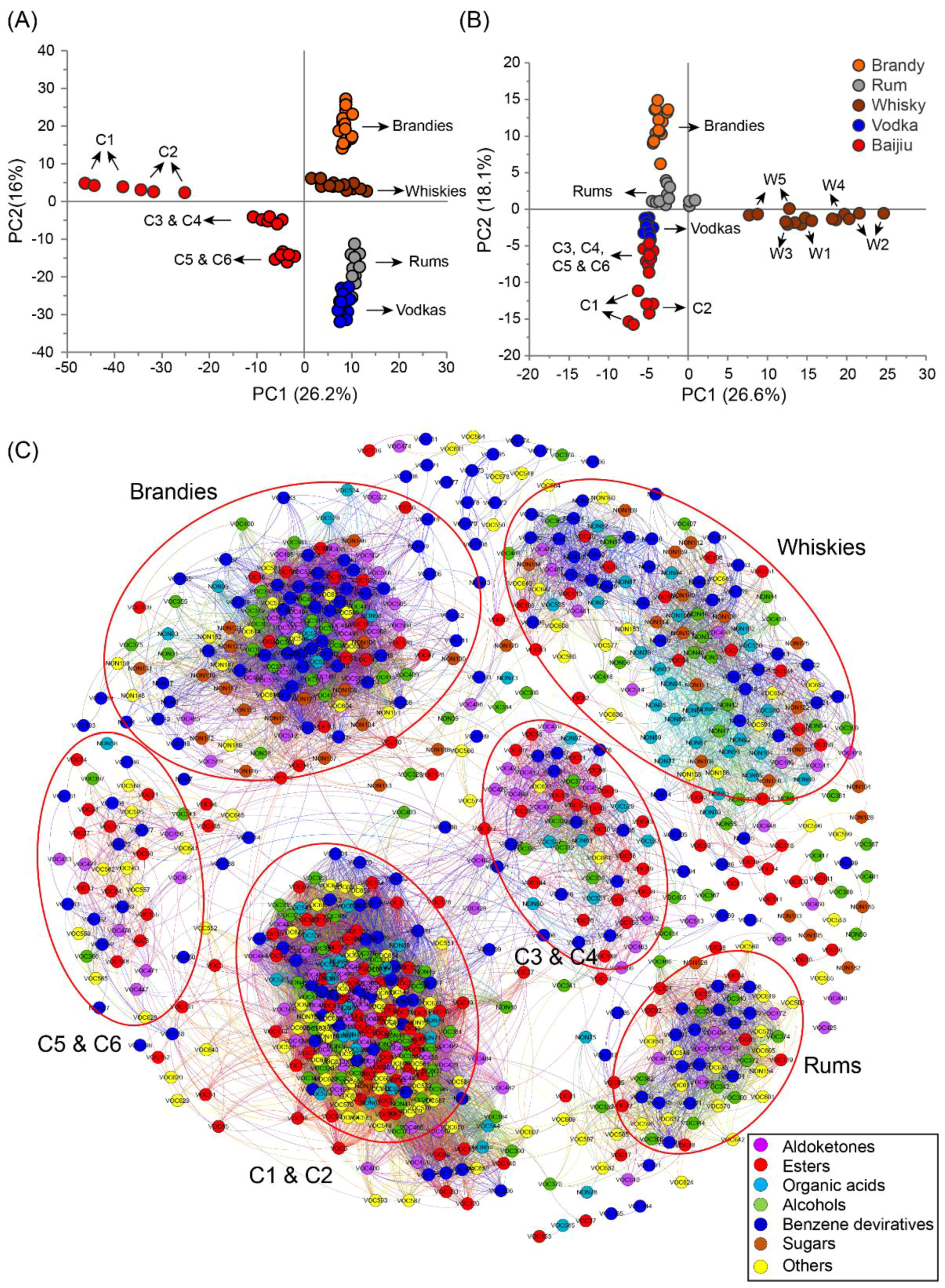
2.3. Characterization of Differences and Similarities of Chinese Baijius and Western Liquors by PCA and Correlation Network
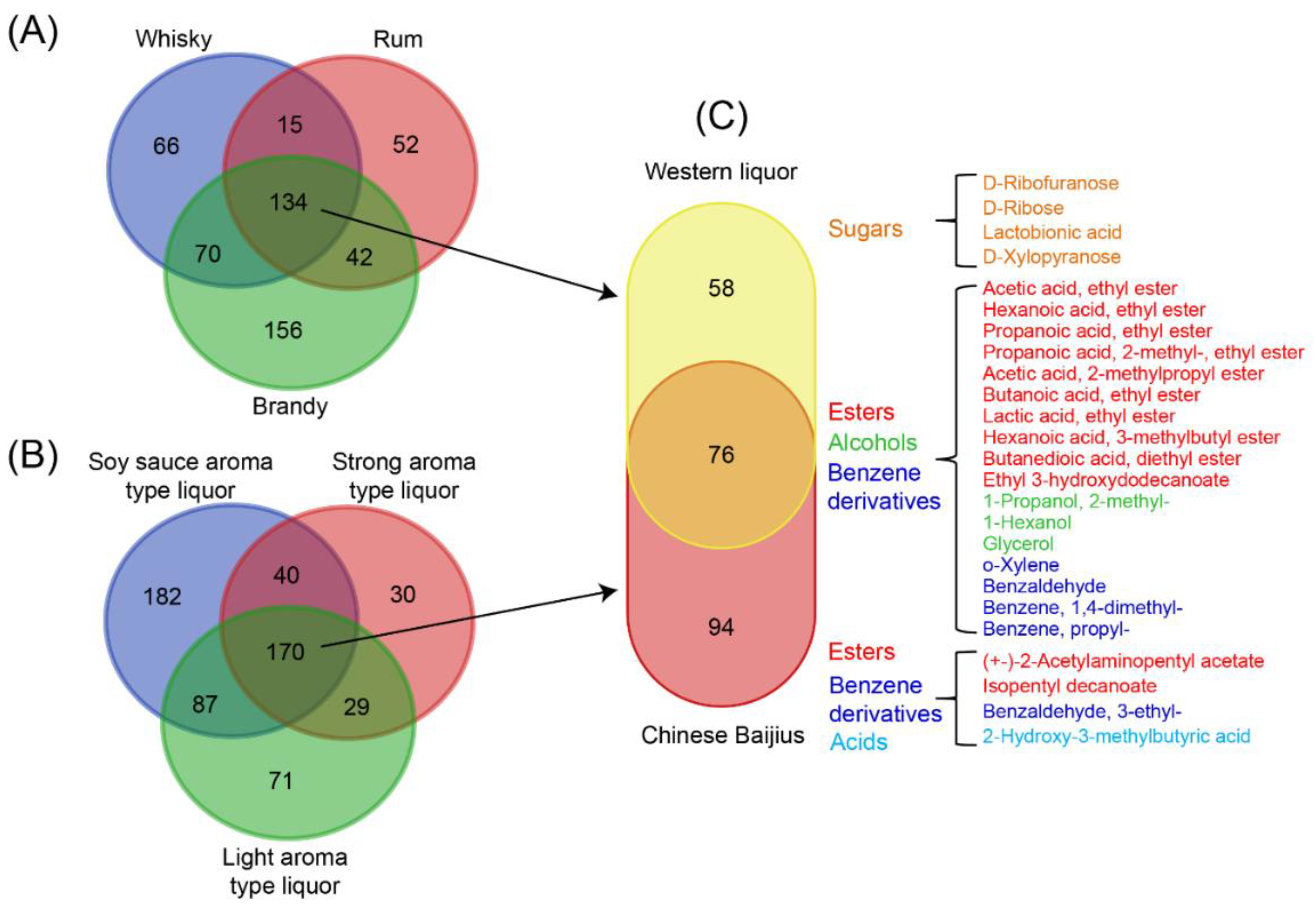
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents
5.2. Distilled Liquors
5.3. Sample Preparation
5.3.1. VOC Extraction
5.3.2. Extraction, Oximation, and Derivatization of Non-VOCs
5.4. Metabolomics Analyses
5.5. GC–MS Data Pretreatment, Compound Identification, and Quantification
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lapsley, J. History of the hard stuff. Nature 2009, 461, 1213–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, W.; Goodall, I.; Clarke, D.; Uhrin, D. Chemical Diversity and Complexity of Scotch Whisky as Revealed by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y. Mystery behind Chinese liquor fermentation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrera, R.R.; Gomis, D.B.; Alonso, J.J. Influence of distillation system, oak wood type, and aging time on volatile compounds of cider brandy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5709–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, J.A. Characterization of rum using solid-phase microextraction with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, J.S.; Marques, J.C.; Perestrelo, R.M.; Rodrigues, F.; Oliveira, L.; Andrade, P.; Caldeira, M. Comparative study of the whisky aroma profile based on headspace solid phase microextraction using different fibre coatings. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1150, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelen, H.H.; Ziolkowska, A.; Kaczmarek, A. Identification of the botanical origin of raw spirits produced from rye, potato, and corn based on volatile compounds analysis using a SPME-MS method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12585–12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Qian, M.C. Headspace solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography-olfactometry dilution analysis of young and aged Chinese “Yanghe Daqu” liquors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7931–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Qian, M.C. Isolation, identification, and quantification of lichenysin, a novel nonvolatile compound in Chinese distilled spirits. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C1907–C1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y. Lichenysin, a cyclooctapeptide occurring in Chinese liquor jiannanchun reduced the headspace concentration of phenolic off-flavors via hydrogen-bond interactions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8302–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, A.; Kallithraka, S.; Kourkoutas, Y. Grape brandy production, composition and sensory evaluation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics-the link between genotypes and phenotypes. In Functional Genomics; Town, C., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 155–171. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla, R.; Narasimhan, K.; Swarup, S. Metabolomics and its role in understanding cellular responses in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2005, 24, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.X.; Xu, G.W. Mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics analysis for foodomics. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 52, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Metabolomics: Applications to food science and nutrition research. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.; Simo, C.; Garcia-Canas, V.; Ibanez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Foodomics: MS-based strategies in modern food science and nutrition. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2012, 31, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Fan, W.L.; Xu, Y. Characterization of Geosmin as Source of Earthy Odor in Different Aroma Type Chinese Liquors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8331–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Xu, Y. Determination of the Microbial Origin of Geosmin in Chinese Liquor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2288–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Lu, H.; Xu, Y.; Du, X.W. Community of Environmental Streptomyces Related to Geosmin Development in Chinese Liquors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Lu, H.; Xu, Y. Influence of Geosmin-Producing Streptomyces on the Growth and Volatile Metabolites of Yeasts during Chinese Liquor Fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.L.; Yu, Y.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Zhu, S.M. Characterization of Chinese liquor aroma components during aging process and liquor age discrimination using gas chromatography combined with multivariable statistics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.M.; Xu, M.L.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Yang, M.Y.; Yu, Y. Effect of high pressure treatment on the aging characteristics of Chinese liquor as evaluated by electronic nose and chemical analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, G.M.; Hill, A.E. Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the production of whisk (e) y. Beverages 2016, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinas, P.; Martinez-Castillo, N.; Campillo, N.; Hernandez-Cordoba, M. Directly suspended droplet microextraction with in injection-port derivatization coupled to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the analysis of polyphenols in herbal infusions, fruits and functional foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Nouri, N.; Khorram, P. Derivatization and microextraction methods for determination of organic compounds by gas chromatography. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 55, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakimov, B.; Mongi, R.J.; Sorensen, K.M.; Ndabikunze, B.K.; Chove, B.E.; Engelsen, S.B. A comprehensive and comparative GC-MS metabolomics study of non-volatiles in Tanzanian grown mango, pineapple, jackfruit, baobab and tamarind fruits. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, N.; Isogai, A.; Iwashita, K.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry based component profiling and quality prediction for Japanese sake. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 118, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, F.; Torres, P.; Oomah, B.D.; de Alencar, S.M.; Massarioli, A.P.; Martin-Venegas, R.; Albarral-Avila, V.; Burgos-Diaz, C.; Ferrer, R.; Rubilar, M. Volatile and non-volatile/semi-volatile compounds and in vitro bioactive properties of Chilean Ulmo (Eucryphia cordifolia Cav.) honey. Food Res. Int. 2017, 94, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Rasheed, D.M.; Kamal, I.M. Volatiles and primary metabolites profiling in two Hibiscus sabdariffa (roselle) cultivars via headspace SPME-GC-MS and chemometrics. Food Res. Int. 2015, 78, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, G.; Lablanquie, O.; Cantagrel, R.; Ledauphin, J.; Payot, T.; Fournier, N.; Guichard, E. Determination of key odorant compounds in freshly distilled cognac using GC-O, GC-MS, and sensory evaluation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5670–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Wang, H.; Cui, T.; Chen, A.; Han, P.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, P.; Wang, L.; Guo, K. Researching development of Maotai microorganisms. Liquor-Mak. Sci. Technol. 2006, 10, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, P.; Lin, J.; Huang, L.; Xu, Y. Synergistic Effect in Core Microbiota Associated with Sulfur Metabolism in Spontaneous Chinese Liquor Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agati, G.; Azzarello, E.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Flavonoids as antioxidants in plants: Location and functional significance. Plant Sci. 2012, 196, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B.; Gunaratne, A.; Sui, Z.Q.; Corke, H. Effects of Fermented Edible Seeds and Their Products on Human Health: Bioactive Components and Bioactivities. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 489–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, N.T.; Van Camp, J.; Smagghe, G.; Raes, K. Improved Release and Metabolism of Flavonoids by Steered Fermentation Processes: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19369–19388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Xu, Y.; Qian, M.C. Identification of Aroma Compounds in Chinese “Moutai” and “Langjiu” Liquors by Normal Phase Liquid Chromatography Fractionation Followed by Gas Chromatography/Olfactometry. In Flavor Chemistry of Wine and Other Alcoholic Beverages; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 1104, pp. 303–338. [Google Scholar]
- Sakko, M.; Moore, C.; Novak-Frazer, L.; Rautemaa, V.; Sorsa, T.; Hietala, P.; Jarvinen, A.; Bowyer, P.; Tjaderhane, L.; Rautemaa, R. 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid is fungicidal for Candida and Aspergillus species. Mycoses 2014, 57, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.J.; Huang, H.; Ouyang, P.K. Microbial 2,3-butanediol production: A state-of-the-art review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, Y. Transcriptome profiling of heat-resistant strain Bacillus licheniformis CGMCC3962 producing Maotai flavor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2033–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xu, Y.; Fan, W. High-yield fermentative preparation of tetramethylpyrazine by Bacillus sp using an endogenous precursor approach. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saerens, S.M.; Delvaux, F.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Van Dijck, P.; Thevelein, J.M.; Delvaux, F.R. Parameters affecting ethyl ester production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garde-Cerdan, T.; Ancin-Azpilicueta, C. Review of quality factors on wine ageing in oak barrels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, P.P.; Resende, A.M.; Augusti, D.V.; Badotti, F.; Gomes Fde, C.; Catharino, R.R.; Eberlin, M.N.; Augusti, R. Artificially-aged cachaca samples characterised by direct infusion electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintea, A.M. Food colorants derived from natural sources by processing. In Food Colorants: Chemical and Functional Properties; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 303–426. [Google Scholar]
- Abid, A.; Taha, O.; Nseir, W.; Farah, R.; Grosovski, M.; Assy, N. Soft drink consumption is associated with fatty liver disease independent of metabolic syndrome. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Yi, B.; Shen, C.; Tao, F.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xu, P. Chemical analysis of the Chinese liquor Luzhoulaojiao by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G. Gut-liver axis in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lu, X.; Ji, K.; Guo, K.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Xu, G. Characterization of flavor compounds in Chinese liquor Moutai by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagimoto, K.; Lee, K.G.; Ochi, H.; Shibamoto, T. Antioxidative activity of heterocyclic compounds found in coffee volatiles produced by Maillard reaction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5480–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, A.; Mathurin, P. Alcoholic liver disease: Mechanisms of injury and targeted treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, S.; Chen, S.; Qian, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y. Characterization of the typical potent odorants in Chinese roasted sesame-like flavor type liquor by headspace solid phase microextraction–aroma extract dilution analysis, with special emphasis on sulfur-containing odorants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 65, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Cai, G.; Su, M.; Chen, T.; Zheng, X.; Xu, Y.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, A.; Xu, L.X.; Cai, S. Serum metabolite profiling of human colorectal cancer using GC− TOFMS and UPLC−QTOFMS. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 4844–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; Johansson, A.I.; Gullberg, J.; Trygg, J.; Grung, B.; Marklund, S.; Sjöström, M.; Antti, H.; Moritz, T. High-throughput data analysis for detecting and identifying differences between samples in GC/MS-based metabolomic analyses. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5635–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Lee, D.Y.; Lu, Y.; Palazoglu, M.; Shahbaz, S.; Fiehn, O. FiehnLib: Mass Spectral and Retention Index Libraries for Metabolomics Based on Quadrupole and Time-of-Flight Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 10038–10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. Characterization of the Key Odorants in Light Aroma Type Chinese Liquor by Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry, Quantitative Measurements, Aroma Recombination, and Omission Studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5796–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. ICWSM 2009, 8, 361–362. [Google Scholar]
| Type of Distillate | Abbreviation | Place of Origin | Raw Material | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese baijius | Soy sauce aroma type liquor | C1 | Guizhou, China | Sorghum, wheat |
| Soy sauce aroma type liquor | C2 | Guizhou, China | Sorghum, wheat | |
| Strong aroma type liquor | C3 | Sichuan, China | Sorghum, wheat, corn | |
| Strong aroma type liquor | C4 | Anhui, China | Sorghum, wheat, corn | |
| Light aroma type liquor | C5 | Shanxi, China | Sorghum, barley, pea | |
| Light aroma type liquor | C6 | Beijing, China | Sorghum, barley, pea | |
| Western liquors | Whisky | W1 | Kentucky, America | Barley malt, corn, caramel |
| Whisky | W2 | Speyside, Scotland | Barley malt, caramel | |
| Whisky | W3 | Ireland | Barley malt, corn, caramel | |
| Whisky | W4 | Scotland | Barley malt, corn, caramel | |
| Whisky | W5 | Scotland | Barley malt, caramel | |
| Brandy | B1 | France | Grape, caramel | |
| Brandy | B2 | France | Grape, caramel | |
| Brandy | B3 | France | Grape, caramel | |
| Brandy | B4 | France | Grape, caramel | |
| Brandy | B5 | France | Grape, caramel | |
| Rum | R1 | Puerto Rico | Sugar cane, caramel | |
| Rum | R2 | U.S. | Sugar cane, caramel | |
| Rum | R3 | France | Sugar cane, caramel | |
| Rum | R4 | Cuba | Sugar cane, caramel | |
| Vodka | V1 | Britain | Wheat, barley malt | |
| Vodka | V2 | Sweden | Wheat | |
| Vodka | V3 | France | Wheat | |
| Vodka | V4 | Poland | Wheat, potato |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, C.; Du, H.; Jia, W.; Xu, Y. Compositional Differences and Similarities between Typical Chinese Baijiu and Western Liquor as Revealed by Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9010002
Fang C, Du H, Jia W, Xu Y. Compositional Differences and Similarities between Typical Chinese Baijiu and Western Liquor as Revealed by Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2019; 9(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Cheng, Hai Du, Wei Jia, and Yan Xu. 2019. "Compositional Differences and Similarities between Typical Chinese Baijiu and Western Liquor as Revealed by Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics" Metabolites 9, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9010002
APA StyleFang, C., Du, H., Jia, W., & Xu, Y. (2019). Compositional Differences and Similarities between Typical Chinese Baijiu and Western Liquor as Revealed by Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites, 9(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9010002





