Hepatic Metabolic Profile Reveals the Adaptive Mechanisms of Ewes to Severe Undernutrition during Late Gestation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
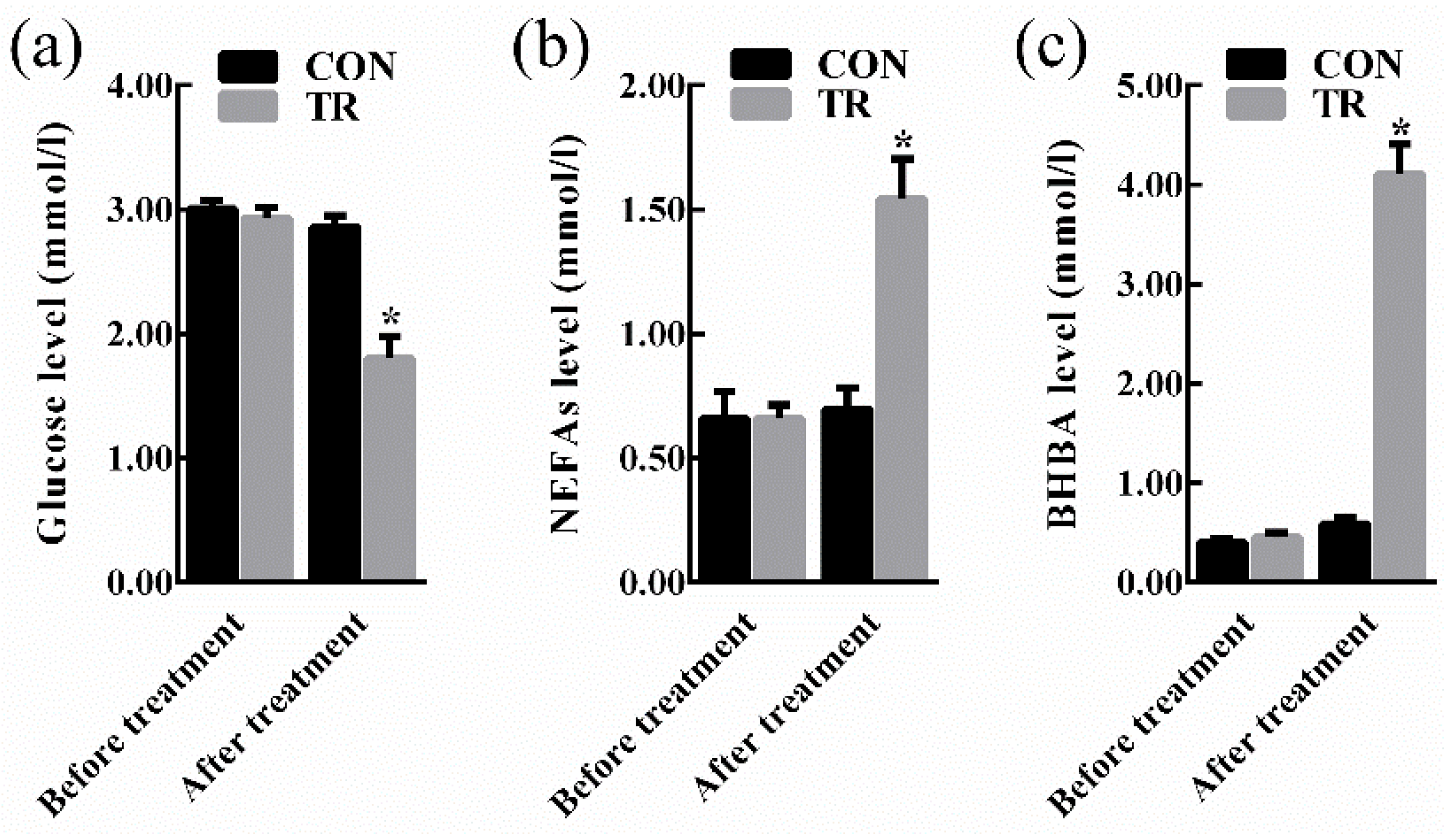
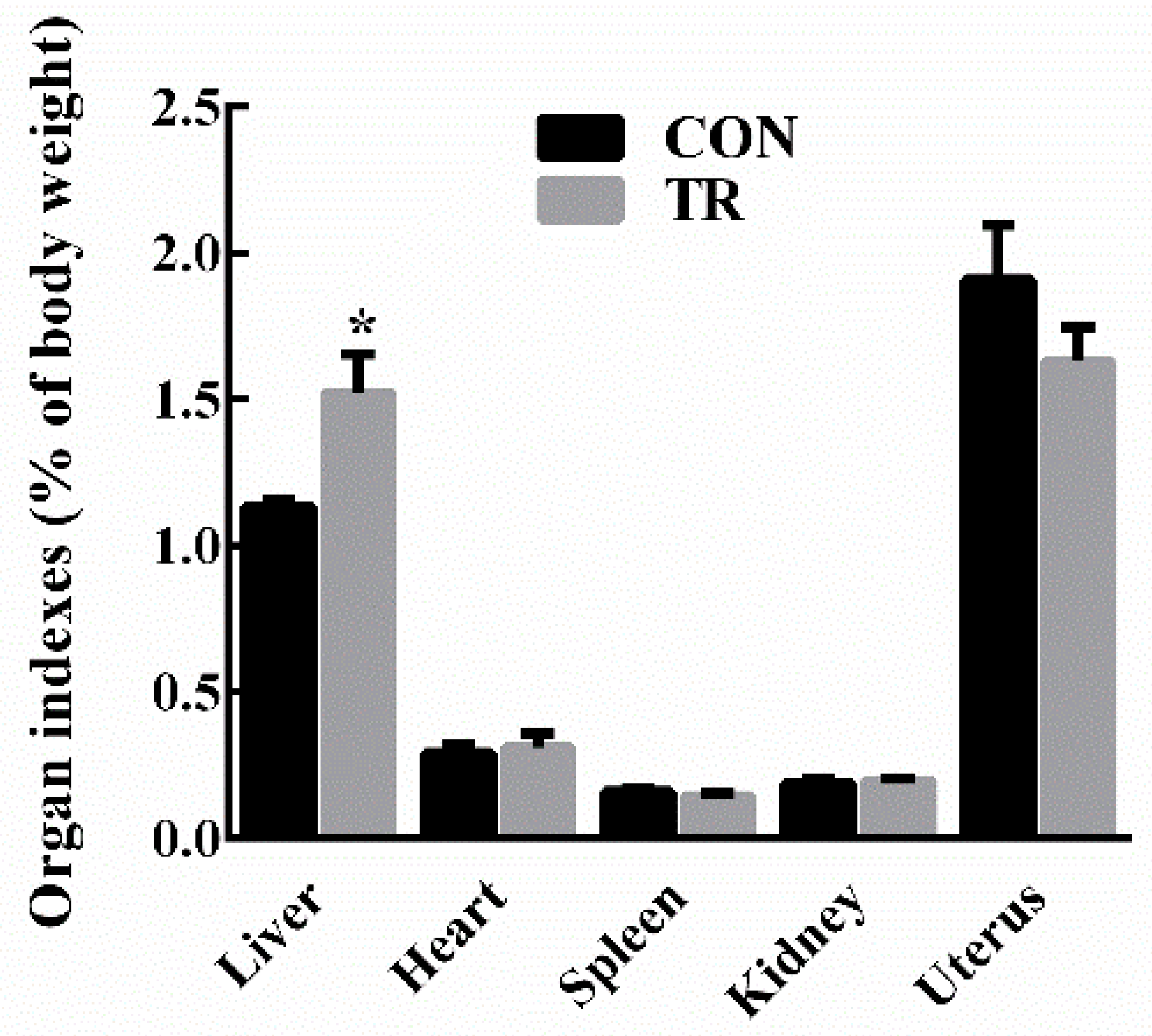
2.1. Performance and Indicators
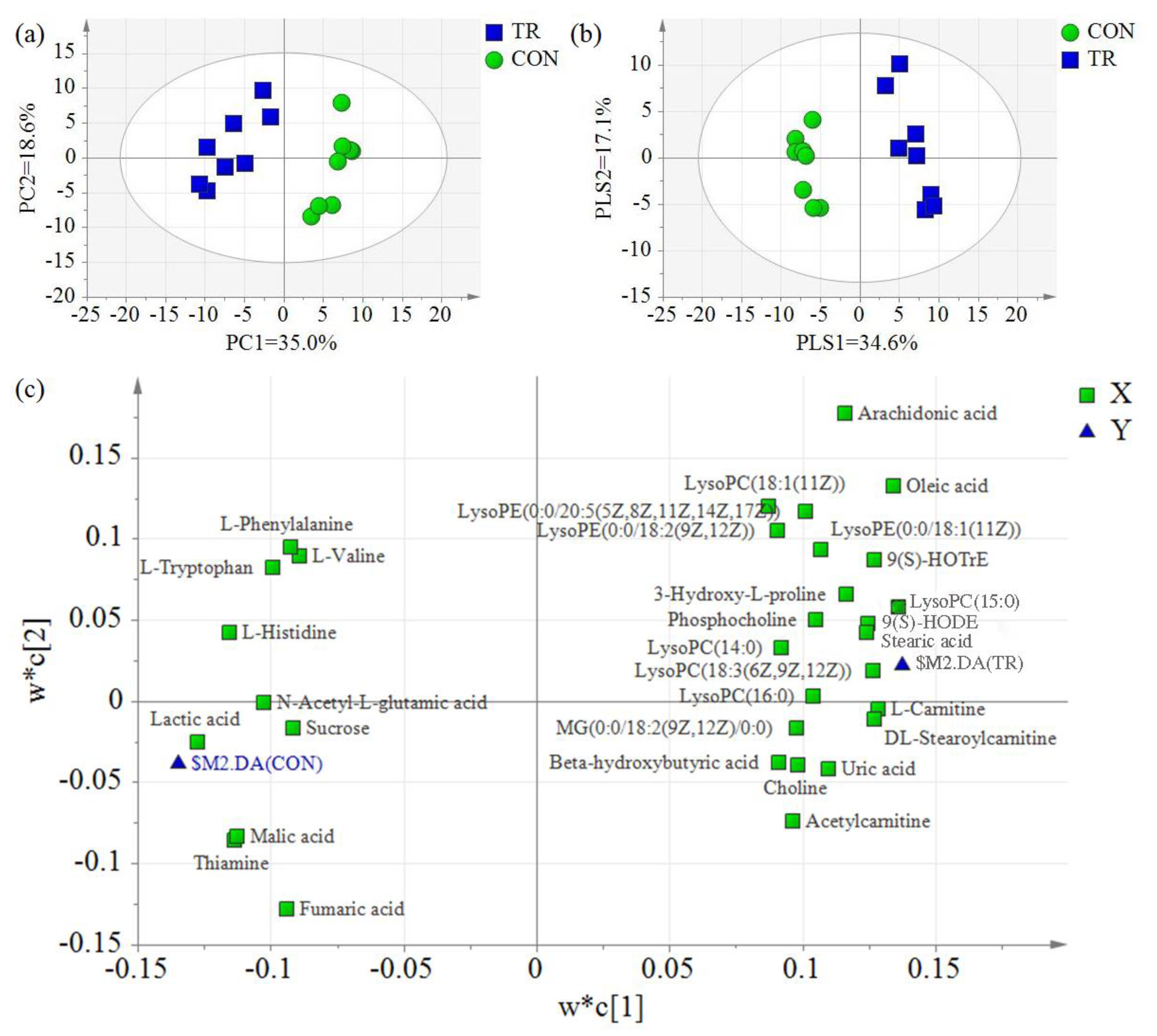
2.2. Identification and Quantification of Compounds
2.3. Differential Hepatic Metabolites
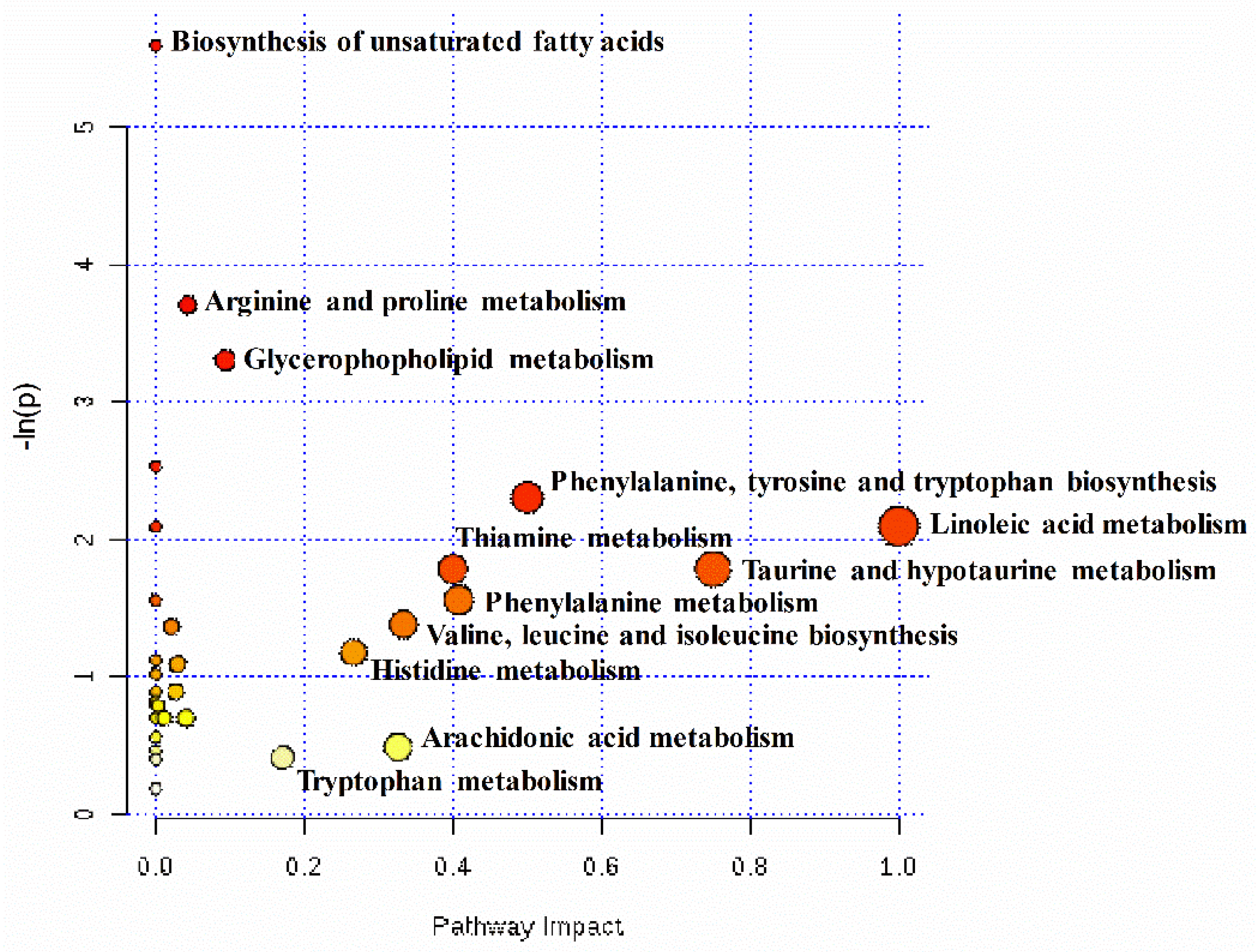
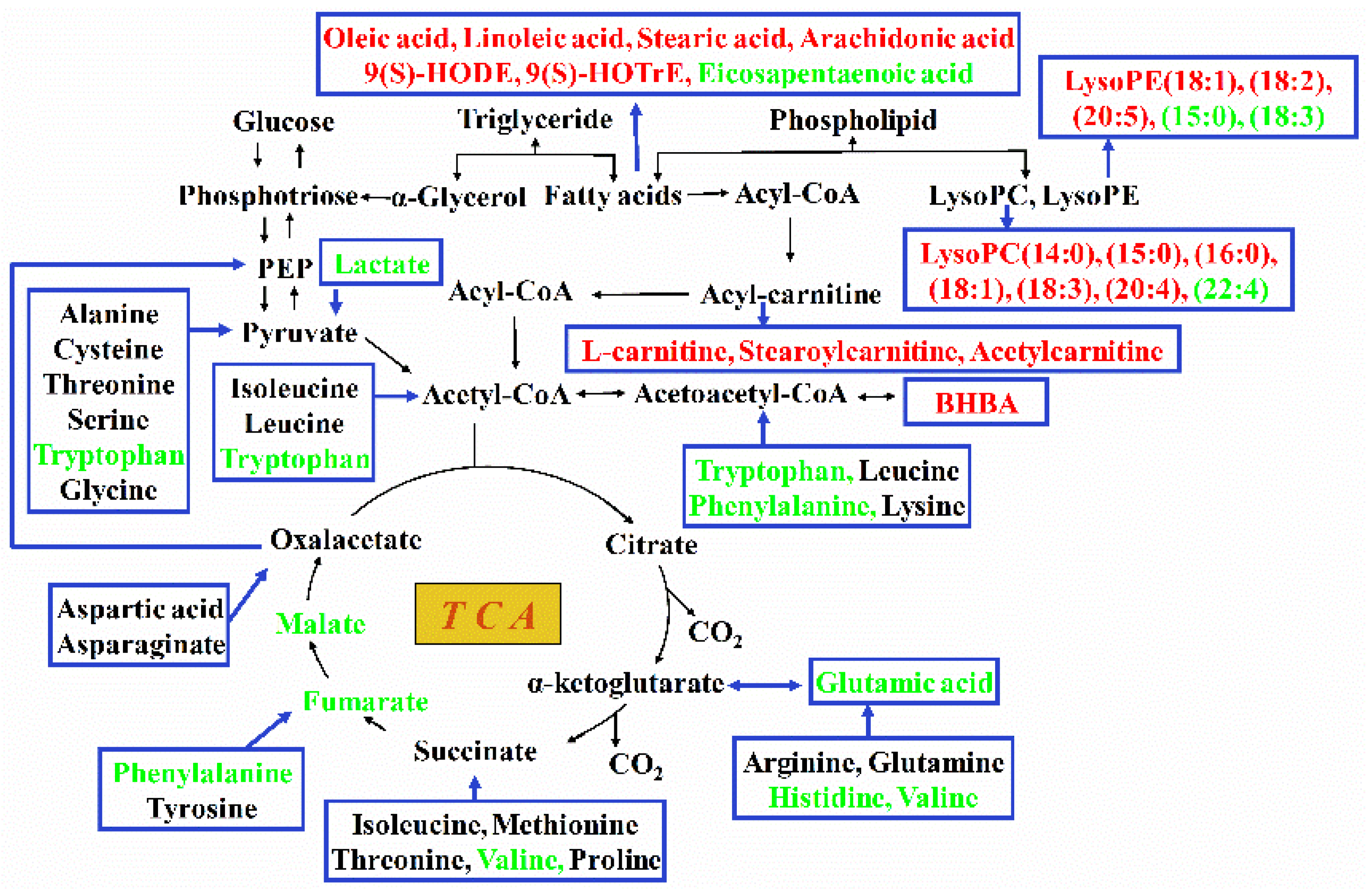
2.4. Pathway Analysis of Differential Hepatic Metabolites
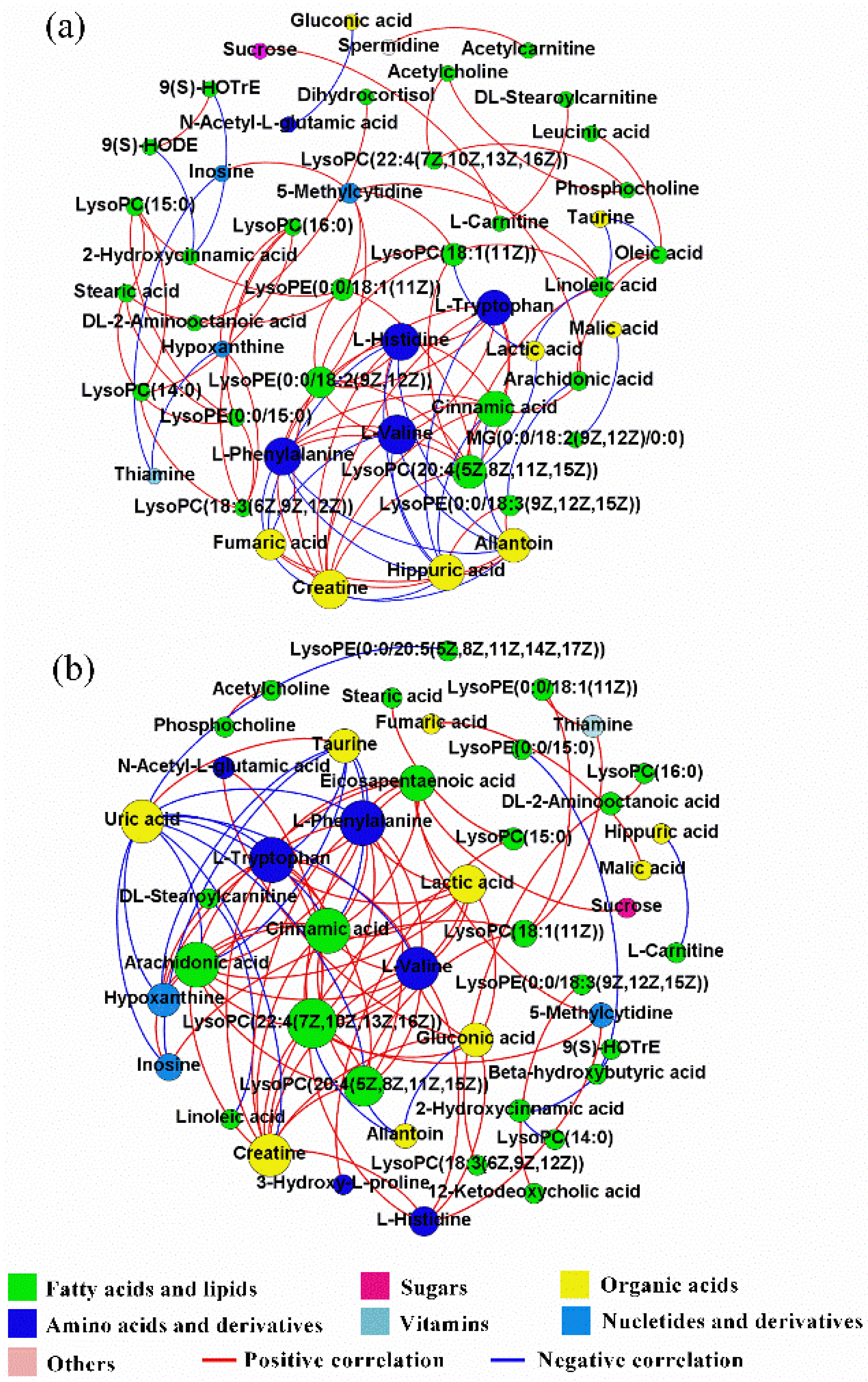
2.5. Correlation Networks of Hepatic Metabolites
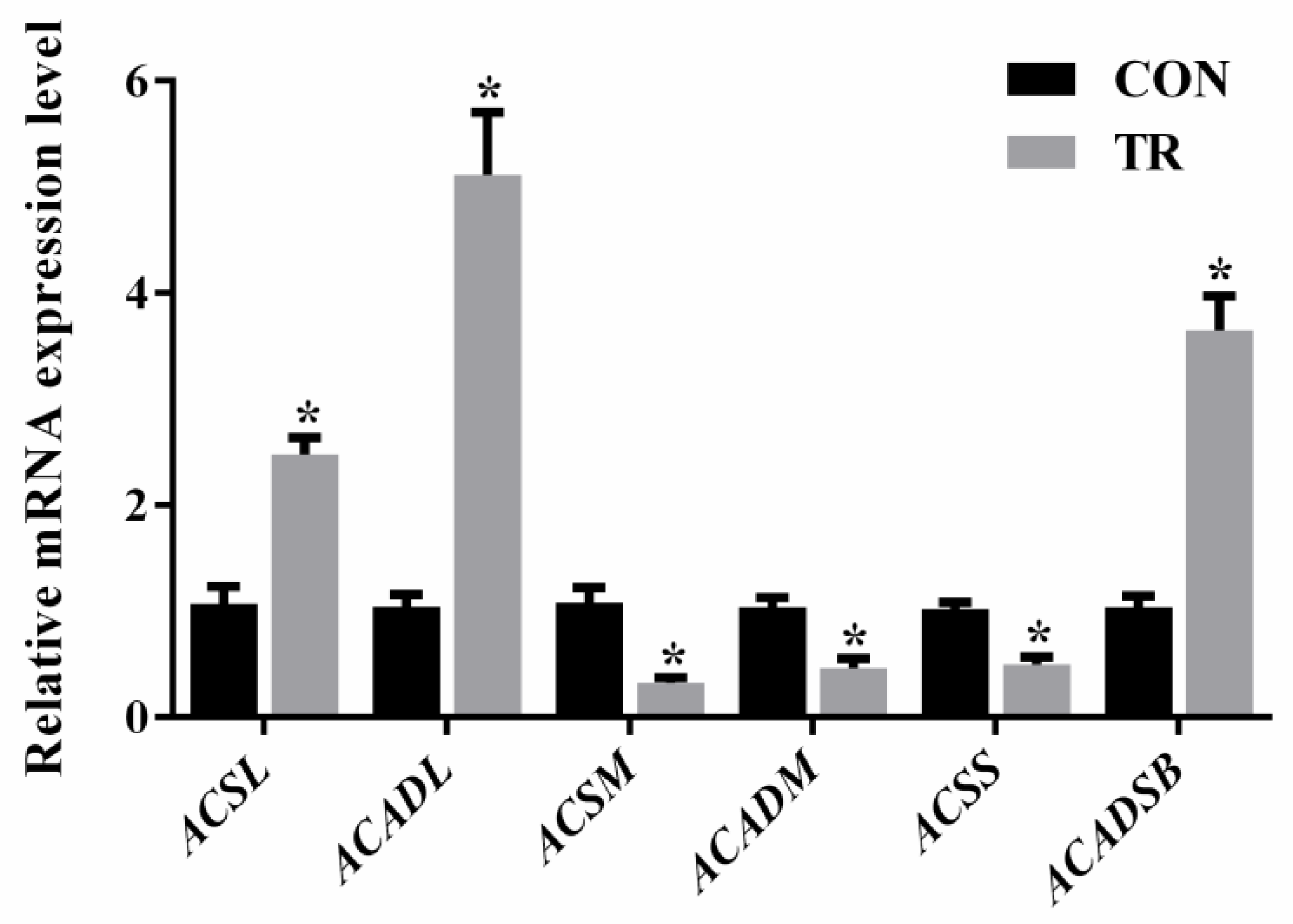
2.6. Expression of Genes Involved in Long-, Medium-, and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Metabolism
3. Discussion
3.1. Mobilization of Body Fat to Provide Energy
3.2. Utilization of Free Amino Acids to Provide Energy
3.3. Metabolic Dysfunction of Nucleotides and Derivatives, Vitamins, and Organic Acids
3.4. The Change in the General Metabolic Pattern
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal and Experimental Design
4.2. Collection of Blood and Hepatic Tissue Samples
4.3. Analysis of Biochemical Indicators in Blood
4.4. Histological Analysis of the Livers
4.5. Sample Preparation for LC/MS Detection
4.6. LC/MS-Based Hepatic Metabolic Profiling
4.7. RNA Extraction, Purification, and Complementary DNA Synthesis
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.9. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cal-Pereyra, L.; Acosta-Dibarrat, J.; Benech, A.; Silva, S.D.; Martín, A.; González-Montańa, J.R. Ewe pregnancy toxemia. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2012, 3, 247–264. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, A. Pregnancy toxemia in ewe. Practice 1997, 19, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Hou, X.Z.; Liu, Y.C. Effect of hormonal status and metabolic changes of restricted ewes during late pregnancy on their fetal growth and development. Sci. China 2007, 50, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Cutfield, W.; Hofman, P.; Hanson, M.A. The fetal, neonatal, and infant environments-the long-term consequences for disease risk. Early Hum. Dev. 2005, 81, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargison, N.D.; Scott, P.R.; Penny, C.D.; Pirie, R.S.; Kelly, J.M. Plasma enzymes and metabolites as potential prognostic indices of ovine pregnancy toxaemia—A preliminary study. Br. Vet. J. 1994, 150, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, J.S.; Herdt, T.H. Pregnancy toxemia of ewes, does, and beef cows. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pr. 2000, 16, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Saun, R.J. Pregnancy toxemia in a flock of sheep. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 217, 1536–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, M.S.; Pascoal, R.A.; Stilwell, G.T. Glycaemia as a sign of the viability of the foetuses in the last days of gestation in dairy goats with pregnancy toxaemia. Ir. Vet. J. 2012, 65, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, L.P.; Caton, J.S.; Redmer, D.A.; Grazul-Bilska, A.T.; Vonnahme, K.A.; Borowicz, P.P.; Luther, J.S.; Wallace, J.M.; Wu, G.; Spencer, T.E. Evidence for altered placental blood flow and vascularity in compromised pregnancies. J. Physiol. 2006, 572, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pethick, D.W.; Lindsay, D.B. Metabolism of ketone bodies in pregnant sheep. Br. J. Nutr. 1982, 48, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacetera, N.; Bernabucci, U.; Ronchi, B.; Nardone, A. Effects of subclinical pregnancy toxemia on immune responses in sheep. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cal-Pereyra, L.; Benech, A.; González-Montaña, J.; Acosta-Dibarrat, J.; Da-Silva, S.; Martín, A. Changes in the metabolic profile of pregnant ewes to an acute feed restriction in late gestation. N. Z. Vet. J. 2015, 63, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.X.; Dhahbi, J.M.; Mote, P.L.; Spindler, S.R. Genomic profiling of short- and long-term caloric restriction effects in the liver of aging mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10630–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Bruno, J.; Easlon, E.; Lin, S.J.; Cheng, H.L.; Alt, F.W.; Guarente, L. Tissue-specific regulation of SIRT1 by calorie restriction. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1753–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Dhahbi, J.M.; Cui, X.; Mote, P.L.; Bartke, A.; Spindler, S.R. Additive regulation of hepatic gene expression by dwarfism and caloric restriction. Physiol. Genom. 2004, 17, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dann, H.M.; Drackley, J.K. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I in liver of periparturient dairy cows: Effects of prepartum intake, postpartum induction of ketosis, and periparturient disorders. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3851–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Kersten, S. Nutrigenomics: Goals and strategies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Gamble, J. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase: An important regulator of fatty acid oxidation in the heart. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1994, 72, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiens, B. Skeletal muscle lipid metabolism in exercise and insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 205–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, F.B.; Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Greenhaff, P.L. New insights concerning the role of carnitine in the regulation of fuel metabolism in skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2007, 581, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carman, G.M. Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins, and Membranes; Vance, D.E., Vance, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 310, pp. 95–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wellner, N.; Diep, T.A.; Janfelt, C.; Hansen, H.S. N-acylation of phosphatidylethanolamine and its biological functions in mammals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkonen, T.; Taponen, J.; Anttila, T.; Syrjäläqvist, L.; Delavaud, C.; Chilliard, Y.; Tuori, M.; Tesfa, A.T. Effect of body fatness and glucogenic supplement on lipid and protein mobilization and plasma leptin in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Shibasaki, T.; Yano, K.; Ozaki, A. Purification and cloning of a proline 3-hydroxylase, a novel enzyme which hydroxylates free l-proline to cis-3-hydroxy-l-proline. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5677–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, A.W. Regulation of organic nutrient metabolism during transition from late pregnancy to early lactation. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 2804–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angstadt, C.N. Purines and Pyrimidine Metabolism. Purine catabolism. NetBiochem 1997, 3, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, D.W. The enzymes, regulation, and genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 137–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shefer, S.; Hauser, S.; Lapar, V.; Mosbach, E.H. Regulatory effects of sterols and bile acids on hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase and cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase in the rat. J. Lipid Res. 1973, 14, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.D.; Klaassen, C.D. Increased bile acids in enterohepatic circulation by short-term calorie restriction in male mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 273, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.F.; Guo, C.Z.; Hu, F.; Sun, D.M.; Liu, J.H.; Mao, S.Y. Molecular mechanisms of lipid metabolism disorder in livers of ewes with pregnancy toxemia. Animal 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odongo, N.; AlZahal, O.; Lindinger, M.; Duffield, T.; Valdes, E.; Terrell, S.; McBride, B. Effects of mild heat stress and grain challenge on acid-base balance and rumen tissue histology in lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the Third International ICWSM Conference, Paris, France, 28 June–10 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
| Name | Mass | VIP | FDR | FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty acids and lipids | - | - | - | - |
| BHBA | 104.04213 | 1.126 | 0.033 | 1.593 |
| dl-2-Aminooctanoic acid | 159.12537 | 1.364 | 0.004 | 0.534 |
| Cinnamic acid | 148.05241 | 1.162 | 0.018 | 0.608 |
| 2-Hydroxycinnamic acid | 163.06326 | 1.337 | 0.005 | 0.591 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid | 302.22404 | 1.346 | 0.005 | 0.482 |
| 9(S)-HODE | 296.23475 | 1.685 | <0.001 | 6.530 |
| 9(S)-HOTrE | 294.21894 | 1.569 | 0.002 | 10.016 |
| Oleic acid | 282.25560 | 1.661 | <0.001 | 3.807 |
| Linoleic acid | 280.23921 | 1.661 | <0.001 | 3.418 |
| Stearic acid | 284.27116 | 1.539 | <0.001 | 1.778 |
| Arachidonic acid | 304.23997 | 1.434 | 0.002 | 2.589 |
| Acetylcarnitine | 203.11522 | 1.192 | 0.027 | 135.264 |
| l-Carnitine | 161.10419 | 1.589 | 0.001 | 7.205 |
| dl-Stearoylcarnitine | 427.36354 | 1.571 | 0.002 | 14.803 |
| Acetylcholine | 145.10966 | 1.300 | 0.013 | 1.997 |
| Phosphocholine | 183.06569 | 1.301 | 0.013 | 2.002 |
| LysoPC(14:0) | 467.29894 | 1.141 | 0.021 | 1.629 |
| LysoPC(15:0) | 481.31638 | 1.540 | <0.001 | 1.611 |
| LysoPC(16:0) | 495.32976 | 1.287 | 0.007 | 1.685 |
| LysoPC(18:1(11Z)) | 521.34465 | 1.078 | 0.028 | 1.750 |
| LysoPC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | 517.31108 | 1.564 | <0.001 | 2.017 |
| LysoPC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,15Z)) | 544.33000 | 1.383 | 0.003 | 2.043 |
| LysoPC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) | 571.36009 | 1.071 | 0.035 | 0.484 |
| LysoPE(0:0/15:0) | 439.26760 | 1.184 | 0.025 | 0.261 |
| LysoPE(0:0/18:1(11Z)) | 479.29875 | 1.322 | 0.006 | 2.119 |
| LysoPE(0:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | 477.28301 | 1.121 | 0.024 | 1.527 |
| LysoPE(0:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) | 474.24544 | 1.190 | 0.015 | 0.503 |
| LysoPE(0:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) | 499.26766 | 1.250 | 0.015 | 1.736 |
| MG(0:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)/0:0) | 354.27562 | 1.211 | 0.013 | 3.078 |
| Chenodeoxycholic acid | 392.29152 | 1.375 | 0.006 | 1.983 |
| 12-Ketodeoxycholic acid | 390.23747 | 1.087 | 0.027 | 0.304 |
| Dihydrocortisol | 364.21602 | 1.068 | 0.030 | 0.576 |
| Leucinic acid | 132.07866 | 1.213 | 0.024 | 0.598 |
| Amino acids and derivatives | - | - | - | - |
| l-Histidine | 155.06909 | 1.429 | 0.002 | 0.540 |
| l-Valine | 117.07830 | 1.105 | 0.025 | 0.561 |
| l-Tryptophan | 204.08893 | 1.226 | 0.013 | 0.575 |
| l-Phenylalanine | 165.07807 | 1.146 | 0.020 | 0.639 |
| N-Acetyl-l-glutamic acid | 189.05966 | 1.269 | 0.008 | 0.330 |
| 3-Hydroxy-l-proline | 131.05827 | 1.441 | 0.007 | 4.862 |
| Sugars | - | - | - | - |
| Sucrose | 342.11511 | 1.134 | 0.028 | 0.120 |
| Organic acids | - | - | - | - |
| Malic acid | 134.02162 | 1.392 | 0.006 | 0.567 |
| Fumaric acid | 116.01103 | 1.165 | 0.018 | 0.594 |
| Lactic acid | 90.03218 | 1.574 | <0.001 | 0.570 |
| Gluconic acid | 196.05829 | 1.464 | 0.001 | 0.366 |
| Creatine | 131.07292 | 1.047 | 0.033 | 0.470 |
| Hippuric acid | 179.05806 | 1.107 | 0.025 | 0.582 |
| Taurine | 125.01437 | 1.088 | 0.028 | 2.566 |
| Uric acid | 168.02820 | 1.356 | 0.004 | 1.777 |
| Allantoin | 158.04402 | 1.137 | 0.033 | 3.428 |
| Nucleosides and nucleotides | - | - | - | - |
| Hypoxanthine | 136.03803 | 1.405 | 0.007 | 0.413 |
| 5-Methylcytidine | 257.10237 | 1.504 | <0.001 | 0.426 |
| Inosine | 268.08027 | 1.259 | 0.011 | 0.432 |
| Vitamins | - | - | - | - |
| Thiamine | 264.06179 | 1.405 | 0.008 | 0.255 |
| Others | - | - | - | - |
| Spermidine | 145.15767 | 1.151 | 0.020 | 2.380 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Y.; Guo, C.; Hu, F.; Liu, J.; Mao, S. Hepatic Metabolic Profile Reveals the Adaptive Mechanisms of Ewes to Severe Undernutrition during Late Gestation. Metabolites 2018, 8, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040085
Xue Y, Guo C, Hu F, Liu J, Mao S. Hepatic Metabolic Profile Reveals the Adaptive Mechanisms of Ewes to Severe Undernutrition during Late Gestation. Metabolites. 2018; 8(4):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040085
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Yanfeng, Changzheng Guo, Fan Hu, Junhua Liu, and Shengyong Mao. 2018. "Hepatic Metabolic Profile Reveals the Adaptive Mechanisms of Ewes to Severe Undernutrition during Late Gestation" Metabolites 8, no. 4: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040085
APA StyleXue, Y., Guo, C., Hu, F., Liu, J., & Mao, S. (2018). Hepatic Metabolic Profile Reveals the Adaptive Mechanisms of Ewes to Severe Undernutrition during Late Gestation. Metabolites, 8(4), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040085






