Optimized Method for Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
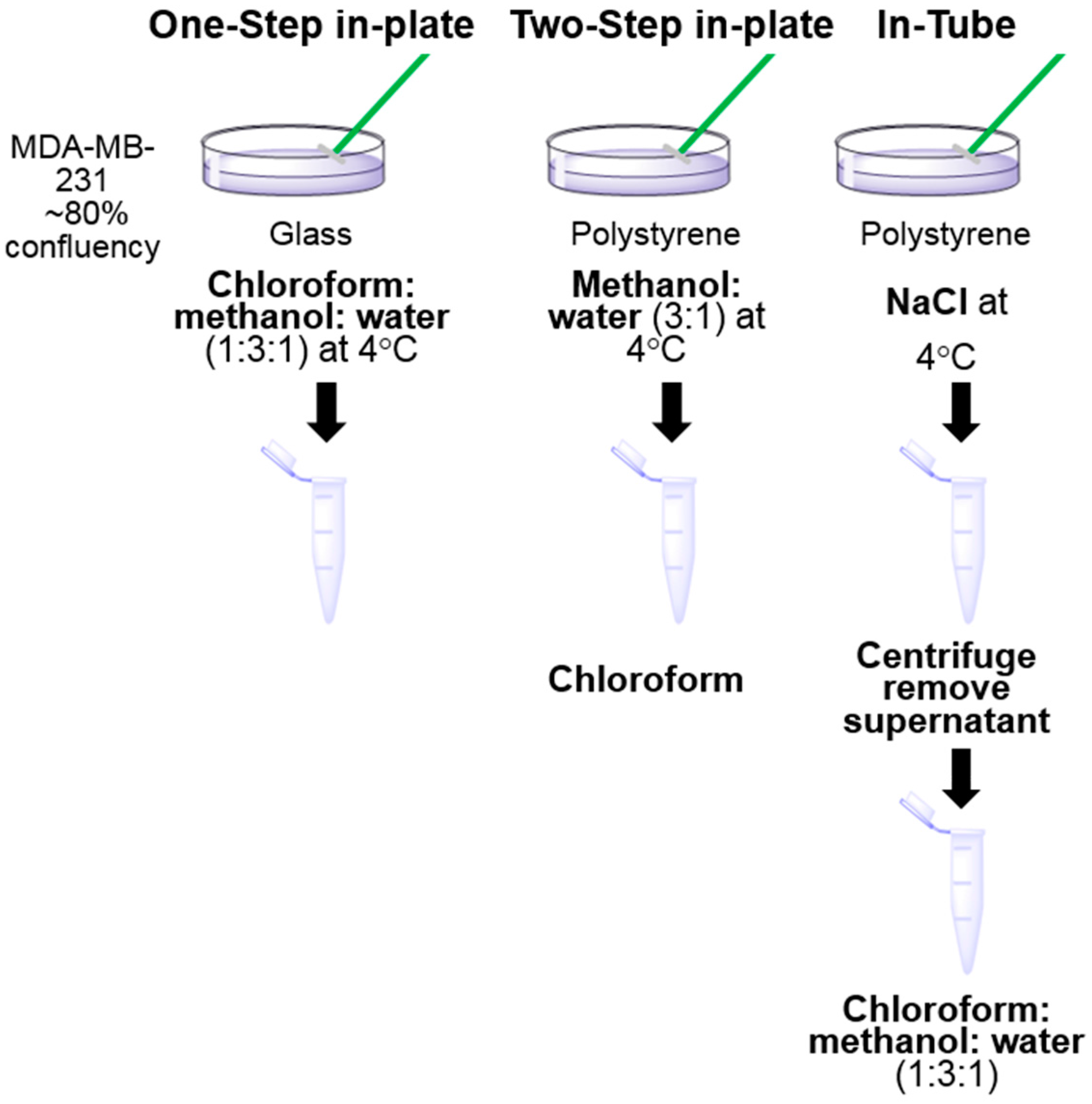
2.3. Sample Preparation for LC-MS Analysis
2.4. Stable Isotope Labelling and Drug Treatment
2.5. LC-MS Analysis
2.6. LC-MS Data Processing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
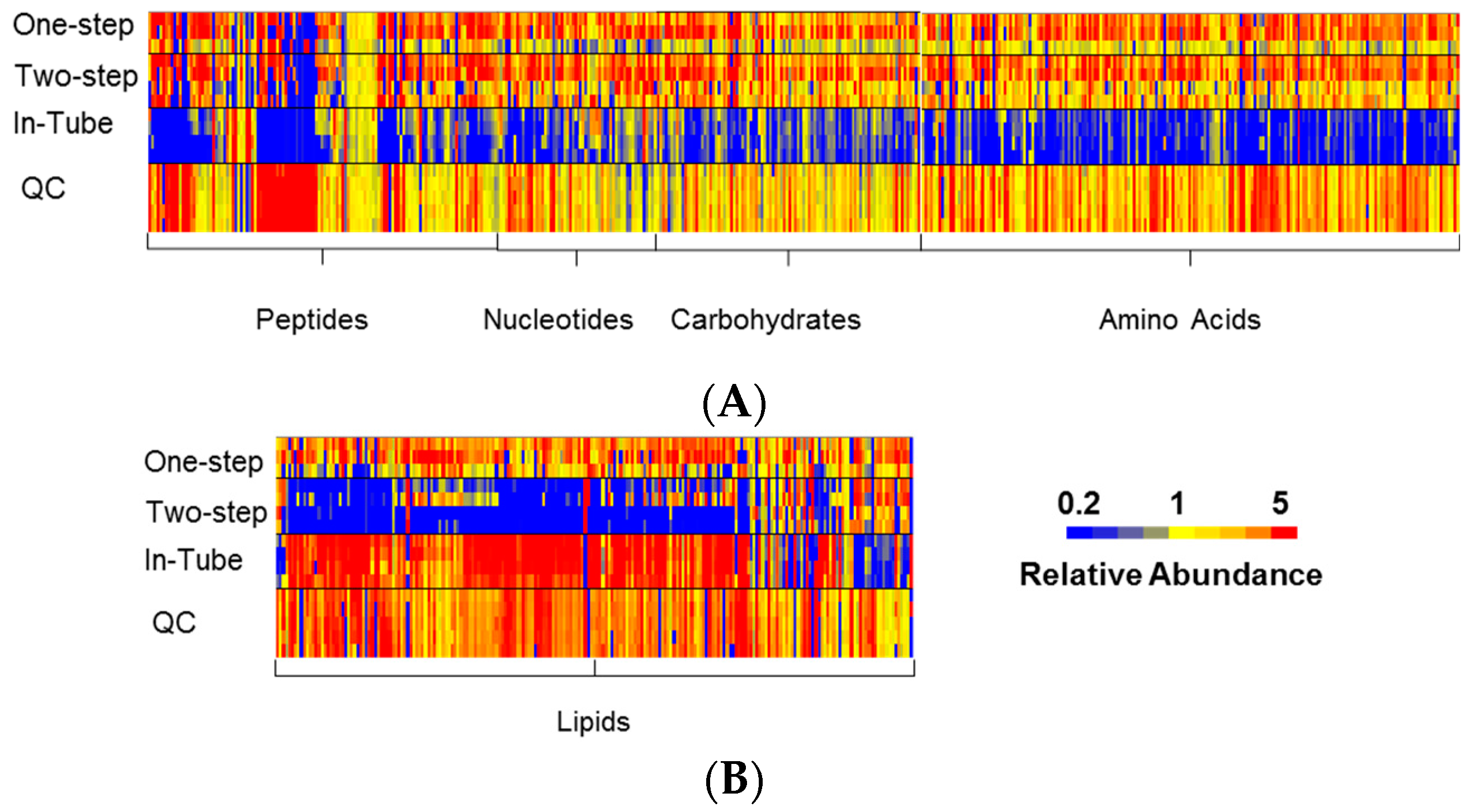
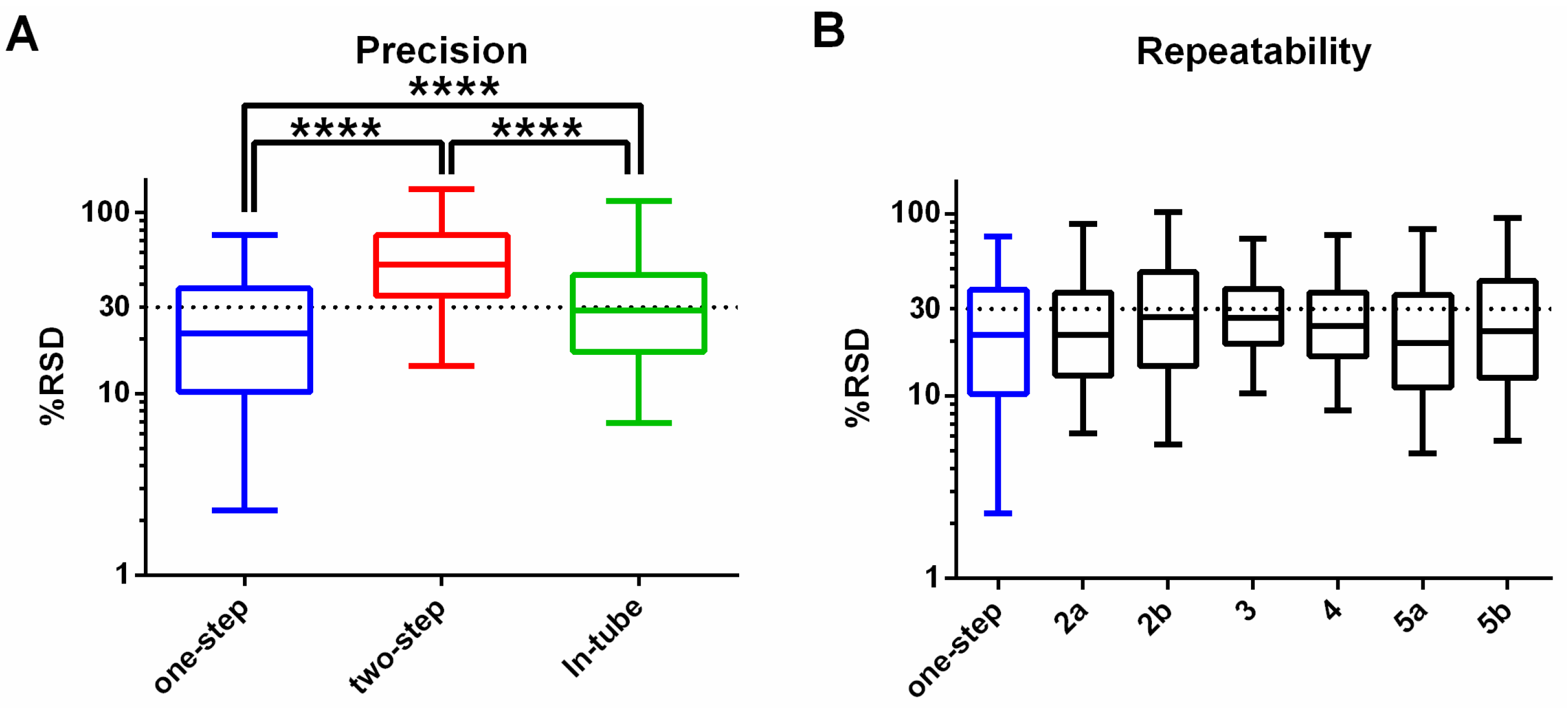
3.1. One-Step In-Plate Extraction Method Is Optimal for MDA-MB-231 Untargeted Metabolomics
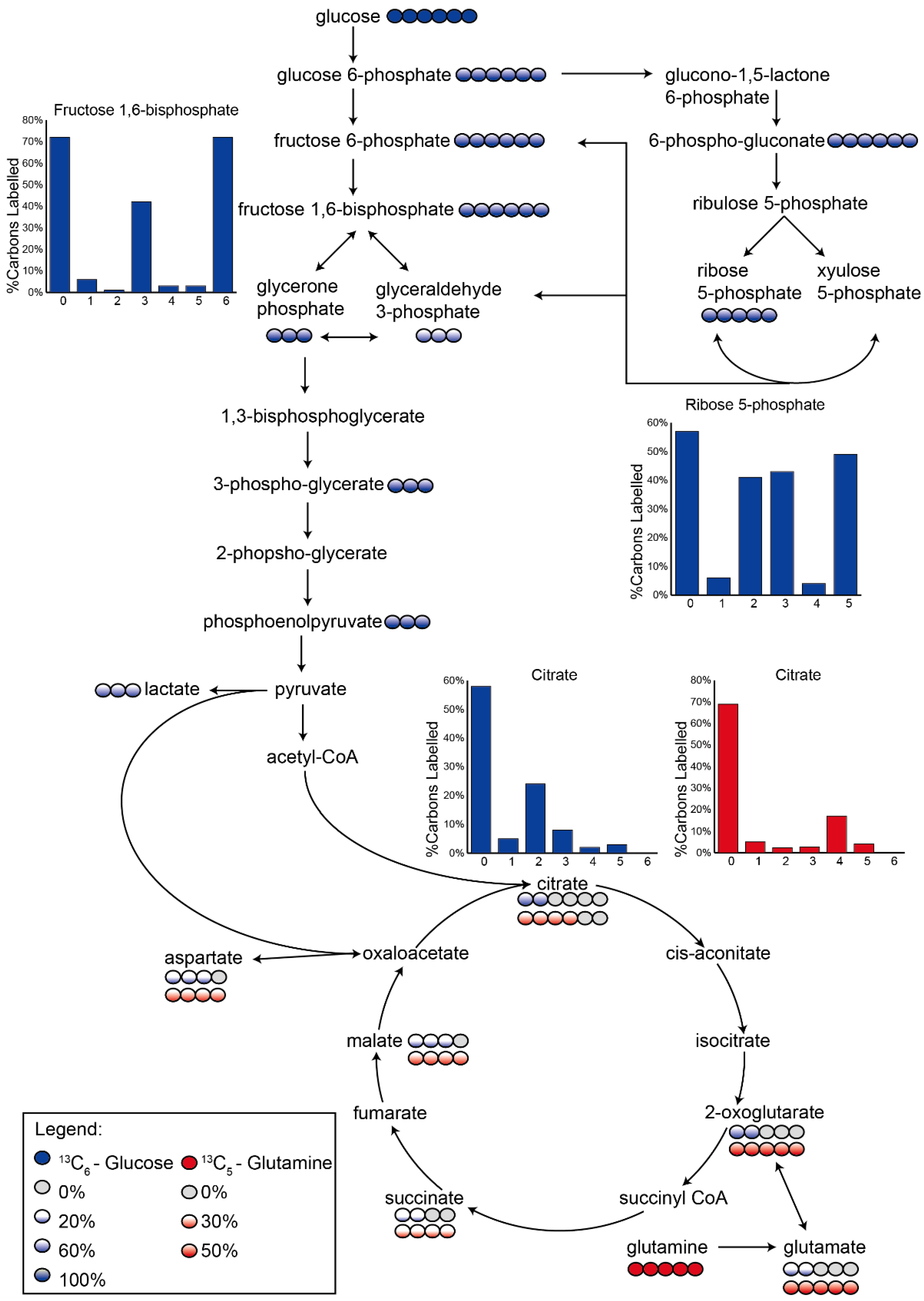
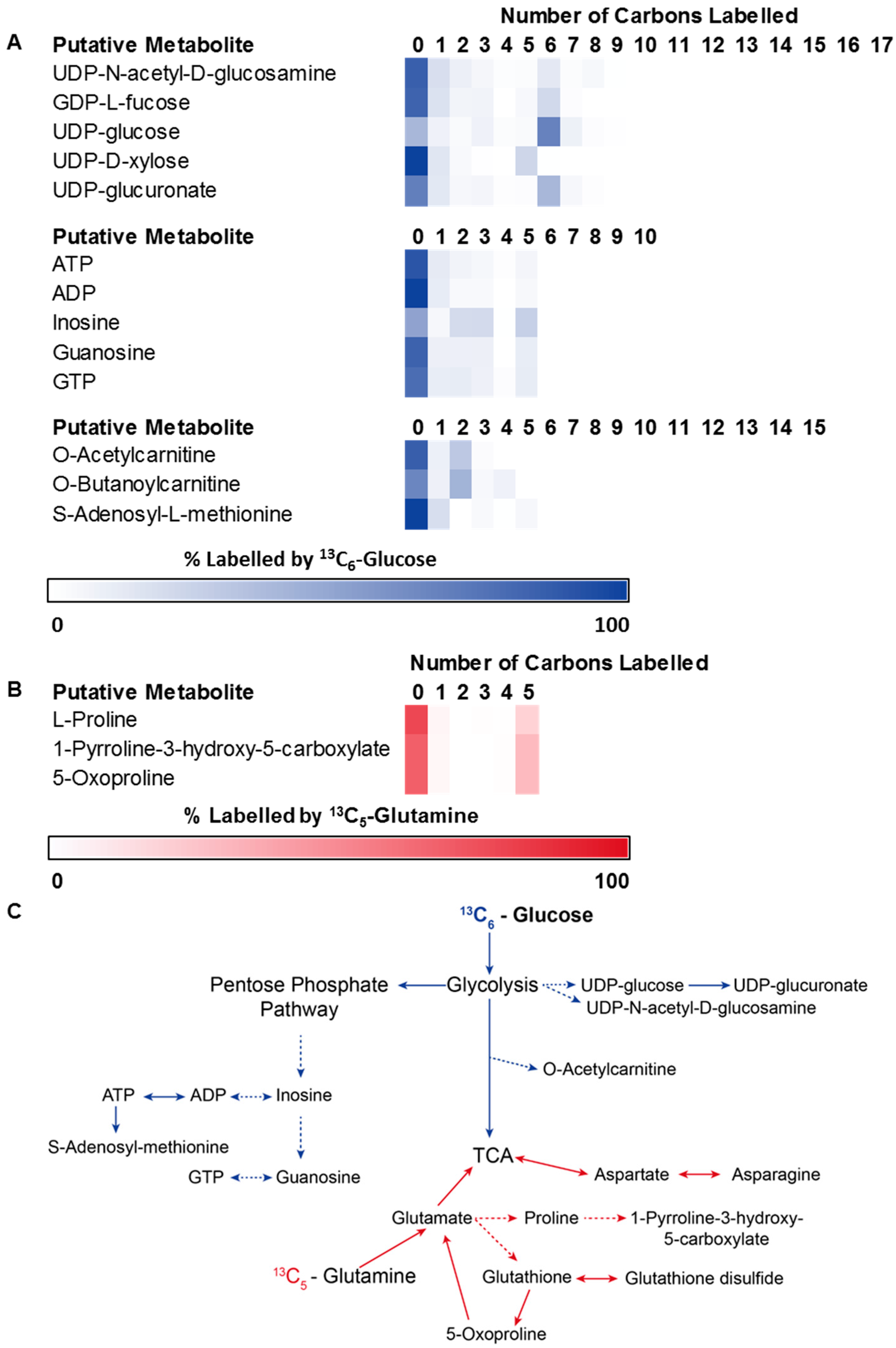
3.2. Application 1: Determination of Metabolic Flux with Isotope Labelling
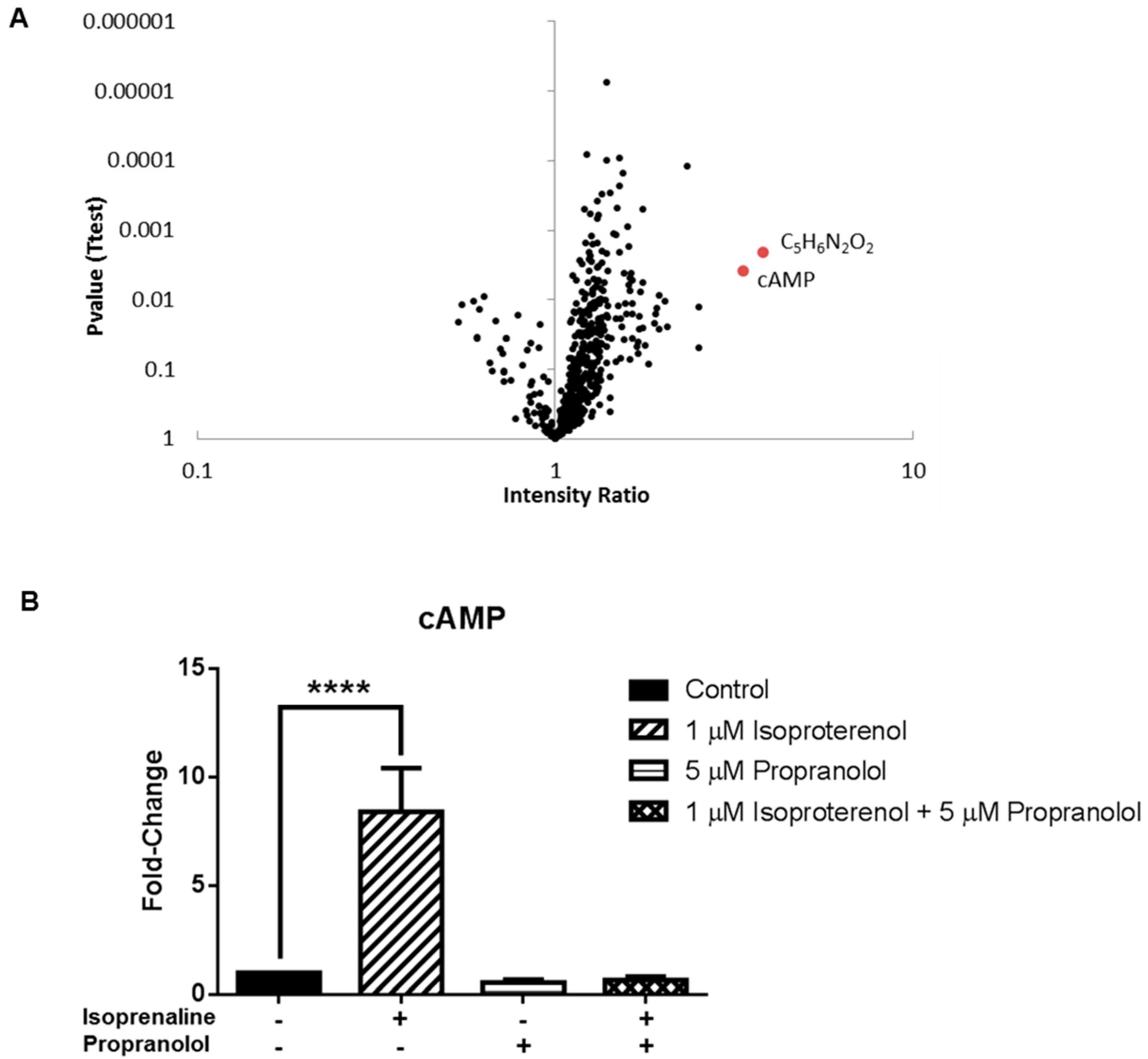
3.3. Application 2: Metabolic Impact of Isoproterenol Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| βAR | β-adrenergic receptor |
| µL | microliter |
| µM | micromolar |
| µm | micrometer |
| ACN | acetonitrile |
| ADP | adenosine diphosphate |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| cAMP | 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| CoA | coenzyme A |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| g | g-force |
| GC-MS | gas chromatography mass spectrometry |
| KV | kilovolt |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography mass spectroscopy |
| mL | milliliter |
| mm | millimeter |
| mM | millimolar |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| m/z | mass to charge ratio |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| ppm | parts per million |
| PPP | Pentose Phosphate Pathway |
| QC | quality control |
| Rpm | revolutions per minute |
| TCA cycle | tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| UDP | uridine diphosphate |
| V | volt |
References
- Ngo, H.; Tortorella, S.; Ververis, K.; Karagiannis, T. The warburg effect: Molecular aspects and therapeutic possibilities. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justus, C.; Sanderlin, E.; Yang, L. Molecular connections between cancer cell metabolism and the tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, R.A.; Harris, I.S.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Cheng, T. Q’s next: The diverse functions of glutamine in metabolism, cell biology and cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, D.R.; Thompson, C.B. Glutamine addiction: A new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Sahra, I.; Hoxhaj, G.; Ricoult, S.J.H.; Asara, J.M.; Manning, B.D. Mtorc1 induces purine synthesis through control of the mitochondrial tetrahydrofolate cycle. Science 2016, 351, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yecies, J.L.; Manning, B.D. Mtor links oncogenic signaling to tumor cell metabolism. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddocks, O.D.K.; Berkers, C.R.; Mason, S.M.; Zheng, L.; Blyth, K.; Gottlieb, E.; Vousden, K.H. Serine starvation induces stress and p53-dependent metabolic remodelling in cancer cells. Nature 2013, 493, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloribi-Djefaflia, S.; Vasseur, S.; Guillaumond, F. Lipid metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Holst, J. L-type amino acid transport and cancer: Targeting the mtorc1 pathway to inhibit neoplasia. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wang, P.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Modern analytical techniques in metabolomics analysis. Analyst 2012, 137, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Erban, A.; Weber, R.J.; Creek, D.J.; Brown, M.; Breitling, R.; Hankemeier, T.; Goodacre, R.; Neumann, S.; Kopka, J. Mass appeal: Metabolite identification in mass spectrometry-focused untargeted metabolomics. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 2005, 365, 1687–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Dent, R.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Hanna, W.M.; Kahn, H.K.; Sawka, C.A.; Lickley, L.A.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, F.; Zielinski, C.C. Optimal strategies for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer with currently approved agents. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, vi46–vi51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliday, D.L.; Speirs, V. Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, R.M.; Altei, W.F.; Andricopulo, A.D.; Becceneri, A.B.; Cominetti, M.R.; Venâncio, T.; Colnago, L.A. Characterization of metabolic profile of intact non-tumor and tumor breast cells by high-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 488, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmann, L.; Schlimpert, M.; Halbach, S.; Erbes, T.; Stickeler, E.; Kammerer, B. Metabolic profiling of breast cancer: Differences in central metabolism between subtypes of breast cancer cell lines. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1000, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, I.-L.; Kuo, T.-C.; Ho, T.-J.; Harn, Y.-C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Fu, W.-M.; Kuo, C.-H.; Tseng, Y. Metabolomic dynamic analysis of hypoxia in MDA-MB-231 and the comparison with inferred metabolites from transcriptomics data. Cancers 2013, 5, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, N.; Brown, A.; Lloyd, V.; Ouellette, R.; Touaibia, M.; Culf, A.S.; Cuperlovic-Culf, M. 1h nmr metabolomics analysis of the effect of dichloroacetate and allopurinol on breast cancers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 93, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayet-Robert, M.; Morvan, D. Metabolomics reveals metabolic targets and biphasic responses in breast cancer cells treated by curcumin alone and in association with docetaxel. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weljie, A.M.; Bondareva, A.; Zang, P.; Jirik, F.R. 1h nmr metabolomics identification of markers of hypoxia-induced metabolic shifts in a breast cancer model system. J. Biomol. NMR 2011, 49, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Q.; Huang, W.; Collette, T.W.; Ekman, D.R.; Tan, C. A direct cell quenching method for cell-culture based metabolomics. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Krausz, K.W.; Manna, S.K.; Li, F.; Johnson, C.H.; Gonzalez, F.J. Optimization of harvesting, extraction, and analytical protocols for uplc-esi-ms-based metabolomic analysis of adherent mammalian cancer cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5279–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettmer, K.; Nürnberger, N.; Kaspar, H.; Gruber, M.A.; Almstetter, M.F.; Oefner, P.J. Metabolite extraction from adherently growing mammalian cells for metabolomics studies: Optimization of harvesting and extraction protocols. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmann, L.; Schlimpert, M.; Hirschfeld, M.; Erbes, T.; Neubauer, H.; Stickeler, E.; Kammerer, B. Alterations of the exo- and endometabolite profiles in breast cancer cell lines: A mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approach. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 925, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, W.; Gruber, A.; Giessrigl, B.; Krupitza, G.; Szekeres, T.; Sonntag, D. Metabolomic analysis of resveratrol-induced effects in the human breast cancer cell lines mcf-7 and mda-mb-231. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2011, 15, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, M.A.; Burant, C.F.; Kennedy, R.T. Reducing time and increasing sensitivity in sample preparation for adherent mammalian cell metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.Q.; Wang, L.; Fei, F.; Hou, Y.F.; Luo, J.M.; Zeng, R.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.S.; Di, G.H.; Ou, Z.L. Identification of breast cancer metastasis-associated proteins in an isogenic tumor metastasis model using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and liquid chromatography-ion trap-mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2006, 6, 3352–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.-Z.; Li, D.-Q.; Hou, Y.-F.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.-S.; Di, G.-H.; Jin, W.; Ou, Z.-L.; Shen, Z.-Z.; Shao, Z.-M. Identification of the functional role of AF1Q in the progression of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 111, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Li, L.; Ou, Z.; Kong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, H.; Shao, Z.; Huang, B.; et al. Foxc1, a target of polycomb, inhibits metastasis of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 131, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creek, D.J.; Jankevics, A.; Breitling, R.; Watson, D.G.; Barrett, M.P.; Burgess, K.E.V. Toward global metabolomics analysis with hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry: Improved metabolite identification by retention time prediction. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8703–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creek, D.J.; Jankevics, A.; Burgess, K.E.; Breitling, R.; Barrett, M.P. Ideom: An excel interface for analysis of lc–ms-based metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1048–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chokkathukalam, A.; Jankevics, A.; Creek, D.J.; Achcar, F.; Barrett, M.P.; Breitling, R. Mzmatch–iso: An r tool for the annotation and relative quantification of isotope-labelled mass spectrometry data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creek, D.J.; Mazet, M.; Achcar, F.; Anderson, J.; Kim, D.-H.; Kamour, R.; Morand, P.; Millerioux, Y.; Biran, M.; Kerkhoven, E.J. Probing the metabolic network in bloodstream-form trypanosoma brucei using untargeted metabolomics with stable isotope labelled glucose. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phannasil, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Warnnissorn, M.; Wallace, J.C.; MacDonald, M.J.; Jitrapakdee, S. Pyruvate carboxylase is up-regulated in breast cancer and essential to support growth and invasion of mda-mb-231 cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creed, S.J.; Le, C.P.; Hassan, M.; Pon, C.K.; Albold, S.; Chan, K.T.; Berginski, M.E.; Huang, Z.; Bear, J.E.; Lane, J.R.; et al. β2-adrenoceptor signaling regulates invadopodia formation to enhance tumor cell invasion. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.; Le, C.P.; Walker, A.K.; Creed, S.J.; Pon, C.K.; Albold, S.; Carroll, D.; Halls, M.L.; Lane, J.R.; Riedel, B.; et al. β2-adrenoceptors on tumor cells play a critical role in stress-enhanced metastasis in a mouse model of breast cancer. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 57, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pon, C.K.; Lane, J.R.; Sloan, E.K.; Halls, M.L. The β2-adrenoceptor activates a positive camp-calcium feedforward loop to drive breast cancer cell invasion. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creek, D.J.; Chokkathukalam, A.; Jankevics, A.; Burgess, K.E.; Breitling, R.; Barrett, M.P. Stable isotope-assisted metabolomics for network-wide metabolic pathway elucidation. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8442–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatenby, R.A.; Gillies, R.J. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, K.C.; Hay, N. The pentose phosphate pathway and cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boros, L.G.; Puigjaner, J.; Cascante, M.; Lee, W.-N.P.; Brandes, J.L.; Bassilian, S.; Yusuf, F.I.; Williams, R.D.; Muscarella, P.; Melvin, W.S. Oxythiamine and dehydroepiandrosterone inhibit the nonoxidative synthesis of ribose and tumor cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4242–4248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Lum, J.J.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Thompson, C.B. The biology of cancer: Metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.-P.; Li, X.-N.; Zhang, F. Targeting metabolism in breast cancer: How far we can go? World J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 7, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, C.T.; Wasti, A.T.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Glutamine and cancer: Cell biology, physiology, and clinical opportunities. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, G.W.; Smollich, M.; Götte, M. Therapeutic value of glycosaminoglycans in cancer. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2006, 5, 2139–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego, S.L.; Fahrmann, J.; Datta, R.; Stringari, C.; Grapov, D.; Zeller, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; Baldi, P.; Gratton, E.; et al. Metabolic changes associated with methionine stress sensitivity in mda-mb-468 breast cancer cells. Cancer Metab. 2016, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daaka, Y.; Luttrell, L.M.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Switching of the coupling of the β2-adrenergic receptor to different g proteins by protein kinase A. Nature 1997, 390, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peterson, A.L.; Walker, A.K.; Sloan, E.K.; Creek, D.J. Optimized Method for Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Metabolites 2016, 6, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6040030
Peterson AL, Walker AK, Sloan EK, Creek DJ. Optimized Method for Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Metabolites. 2016; 6(4):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6040030
Chicago/Turabian StylePeterson, Amanda L., Adam K. Walker, Erica K. Sloan, and Darren J. Creek. 2016. "Optimized Method for Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells" Metabolites 6, no. 4: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6040030
APA StylePeterson, A. L., Walker, A. K., Sloan, E. K., & Creek, D. J. (2016). Optimized Method for Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Metabolites, 6(4), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6040030





