Investigating the Utility of Dopamine in Agricultural Practices: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Dopamine Effects and Its Role in Plans
3. Dopamine Biosynthesis and Regulation in Plants
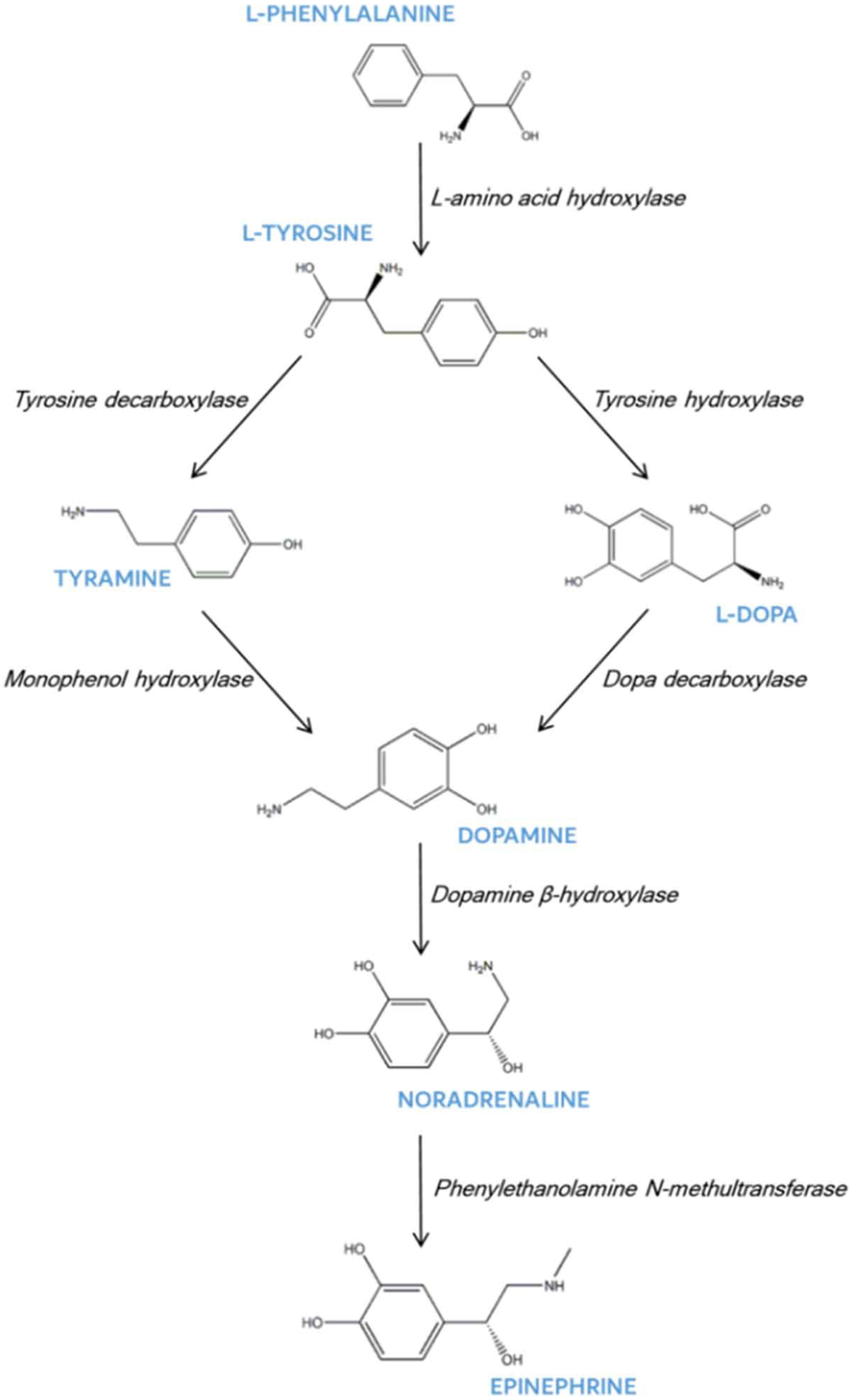
4. Physiological Effects of Dopamine in Plants
5. Growth and Developmental Processes
6. The Agricultural Applications of Dopamine
| Method and Rate of Dopamine Application | Study Objectives | Outcomes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
| [36] |
|
|
| [38] |
|
|
| [10] |
6.1. Salinity Stress
6.2. Drought Stress
6.3. Nutrient Stress
7. Dopamine and Environmental Pollutants
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Semida, W.M.; Abdelkhalik, A.; Rady, M.O.A.; Marey, R.A.; El-mageed, T.A.A. Exogenously applied proline enhances growth and productivity of drought stressed onion by improving photosynthetic efficiency, water use efficiency and up-regulating osmoprotectants. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semida, W.M.; Abdelkhalik, A.; Mohamed, G.F.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Abd El-Mageed, S.A.; Rady, M.M.; Ali, E.F. Foliar Application of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Promotes Drought Stress Tolerance in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Plants 2021, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkhalik, A.; Gyushi, M.A.H.; Howladar, S.M.; Kutby, A.M.; Asiri, N.A.; Baeshen, A.A.; Nahari, A.M.; Alsamadany, H.; Semida, W.M. Synergistic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Moringa Leaf Extracts on Drought Tolerance and Productivity of Cucurbita pepo L. Under Saline Conditions. Plants 2025, 14, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Gao, T.T.; Zhang, Z.J.; Tan, K.X.; Jin, Y.B.; Zhao, Y.J.; Ma, F.W.; Li, C. The mitigation effects of exogenous dopamine on low nitrogen stress in Malus hupehensis. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2709–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulma, A.; Szopa, J. Catecholamines are active compounds in plants. Plant Sci. 2007, 172, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerzemowska, G. Hypothalamic and Midbrain Cells, Tyrosine Hydroxylase, and Implications for Drug Addiction. In Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse Volume 3: General Processes and Mechanisms, Prescription Medications, Caffeine and Areca, Polydrug Misuse, Emerging Addictions and Non-Drug Addictions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 71–81. ISBN 9780128006771. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, W.U.; Shah, A.A.; Yasin, N.A.; Ali, A.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S. Dopamine Alleviates Hydrocarbon Stress in Brassica oleracea through Modulation of Physio-Biochemical Attributes and Antioxidant Defense Systems. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Gao, T.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, C.; Chen, Q.; Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Ma, F. Effects of exogenous dopamine on the uptake, transport, and resorption of apple ionome under moderate drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Ding, K.; Li, C.; Zou, Y.; Ma, F. Overexpression of tyrosine decarboxylase (MdTYDC) enhances drought tolerance in Malus domestica. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 289, 110425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G.; Jiao, C.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y. Effects of dopamine on growth, carbon metabolism, and nitrogen metabolism in cucumber under nitrate stress. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 260, 108790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklin, A.I.; Conger, B.V. Catecholamines in Plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 1995, 14, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamel, K. Prabhavathi Dopamine in Plant Development and Redox Signaling. In Neurotransmitters in Plant Signaling and Communication; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 123–139. [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa, K.; Sakakibara, H. High content of dopamine, a strong antioxidant, in Cavendish banana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini, P.J.; Yu, M.; Penzes-Yost, C. Decreased Cell Wall Digestibility in Canola Transformed with Chimeric Tyrosine Decarboxylase Genes from Opium Poppy 1. Am. Soc. Plant Physiol. 1999, 120, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, Y.; Tae, G.S.; Kang, B.G. Antioxidant responses of cucumber (Cucumis satius) to photoinhibition and oxidative stress induced by norflurazon under high and low PPFDs. Plant Sci. 2000, 153, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Che, T.; Levit, A.; Shoichet, B.K.; Wacker, D.; Roth, B.L. Structure of the D2 dopamine receptor bound to the atypical antipsychotic drug risperidone. Nature 2018, 555, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Q.; Mercier, R.W.; Yao, W.; Berkowitz, G.A. Cloning and First Functional Characterization of a Plant Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Cation Channel 1. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applewhite, P.B.; Bcxsdanski, D.F.; Pletscher, A.; Brodie, B.B.; Udenfriend, S.; Pbarm Exper, I.; Clark, G.; FENsrER, E.D.; Towne, J.C. Serotonin and Norepinephrine in Plant Tissues. Phytochemistry 1973, 12, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.M.R.; Vuille-Dit-Bille, R.N.; Mariotta, L.; Ramadan, T.; Huggel, K.; Singer, D.; Götze, O.; Verrey, F. The molecular mechanism of intestinal levodopa absorption and its possible implications for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 351, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Qidwai, T.; Shukla, R.K.; Gupta, V. Alkaloids derived from tyrosine: Modified benzyltetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids. In Natural Products: Phytochemistry, Botany and Metabolism of Alkaloids, Phenolics and Terpenes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 405–460. ISBN 9783642221446. [Google Scholar]
- Sourkes, T.L. Actions of Levodopa and Dopamine in the Central Nervous System. JAMA 1971, 218, 1909–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosei, M.A.; Blarzino, C.; Foppoli, C.; Mosca, L.; Coccia, R. Lipoxygenase-catalyzed oxidation of catecholamines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 200, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, U.; Schliemann, W.; Strack, D. Assay for tyrosine hydroxylation activity of tyrosinase from betalain-forming plants and cell cultures. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 238, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.; Lee, J.; Park, H.; Cho, S. Purification and characterization of the tyrosinase isozymes of pine needles. IUBMB Life 1998, 45, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundström, J. Biosynthesis of mescaline and tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids in Lophophora williamsii (Lem.) Coult. Occurrence and biosynthesis of catecholamine and other intermediates. Acta Chem. Scand. 1971, 25, 3489–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, T.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Ding, K.; Ma, F.; Li, C. Functions of dopamine in plants: A review. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1827782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshchina, V.V. Biogenic amines in plant cell at norma and stress: Probes for dopamine and histamine. In Emerging Plant Growth Regulators in Agriculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 357–376. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q.; van Nocker, S.; Ma, F.; Li, C. Physiological and transcriptome analyses of the effects of exogenous dopamine on drought tolerance in apple. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sun, X.; Chang, C.; Jia, D.; Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Ma, F. Dopamine alleviates salt-induced stress in Malus hupehensis. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 153, 584–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahammed, G.J.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Wu, M.; Yan, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, A.; Chen, S. Dopamine alleviates bisphenol A-induced phytotoxicity by enhancing antioxidant and detoxification potential in cucumber. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shull, T.E.; Kurepa, J.; Smalle, J.A. Dopamine Inhibits Arabidopsis Growth through Increased Oxidative Stress and Auxin Activity. Stresses 2023, 3, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Shanab, W.A.; Diab, R.H. Dopamine Hydrochloride Alleviates the Salt-induced Stress in Glycine max (L.) Merr. plant. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 3474–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcay, U.C.; Gencay, R.; Koc, F.Z. Effect of dopamine and progesterone on the physiological and molecular responses of tomato seedlings to drought and salt stress. Cogent Food Agric. 2024, 10, 2321308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, E.; Ekinci, M.; Turan, M.; Yuce, M.; Ors, S.; Araz, O.; Torun, U.; Argin, S. Exogenous dopamine mitigates the effects of salinity stress in tomato seedlings by alleviating the oxidative stress and regulating phytohormones. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2024, 46, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Lan, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y. Dopamine Alleviates Chilling Stress in Watermelon Seedlings via Modulation of Proline Content, Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, and Polyamine Metabolism. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, S.; El-Hady, M.A.M.A.; El-Sherpiny, M.A.; Hassan, M.M.; Alamer, K.H.; Al-Robai, S.A.; Ali, E.F.; El-Bauome, H.A. Effect of Dopamine on Growth, Some Biochemical Attributes, and the Yield of Crisphead Lettuce under Nitrogen Deficiency. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulmajeed, A.M.; Alharbi, B.M.; Alharby, H.F.; Abualresh, A.M.; Badawy, G.A.; Semida, W.M.; Rady, M.M. Simultaneous Action of Silymarin and Dopamine Enhances Defense Mechanisms Related to Antioxidants, Polyamine Metabolic Enzymes, and Tolerance to Cadmium Stress in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plants 2022, 11, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.W.; Li, C.Y.; Ma, C.Q.; Wei, Z.W.; Wang, Q.; Huang, D. Dopamine alleviates nutrient deficiency-induced stress in Malus hupehensis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 119, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopa, J.; Wilczyn´ski, G.W.; Fiehn, O.; Wenczel, A.; Willmitzer, L. Identification and quantification of catecholamines in potato plants (Solanum tuberosum) by GC-MS. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świȩdrych, A.; Lorenc-Kukuła, K.; Skirycz, A.; Szopa, J. The catecholamine biosynthesis route in potato is affected by stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Du, P.; Yin, B.; Zhou, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Liang, B. Melatonin and dopamine enhance waterlogging tolerance by modulating ROS scavenging, nitrogen uptake, and the rhizosphere microbial community in Malus hupehensis. Plant Soil 2023, 483, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Hu, D.; Yu, J.; Liu, H. Effect of green, yellow and purple radiation on biomass, photosynthesis, morphology and soluble sugar content of leafy lettuce via spectral wavebands “knock out”. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 236, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-mageed, S.A.; Sayed, A.A.S.; Shaaban, A.; Hemida, K.A.; Abdelkhalik, A.; Semida, W.M.; Mohamed, I.A.A.; Gyushi, M.A.; Elmohsen, Y.H.A.; Abd El Mageed, T.A. Integrative application of licorice root extract and melatonin improves faba bean growth and production in Cd-contaminated saline soil. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.J.; Kumar, R. Bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soil to combat toxicity on Withania somnifera through seed priming with biosurfactant producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 174, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odukoya, J.; Lambert, R.; Sakrabani, R. Understanding the impacts of crude oil and its induced abiotic stresses on agrifood production: A review. Horticulturae 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed, G.J.; Li, X. Dopamine-induced abiotic stress tolerance in horticultural plants. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 307, 111506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Schmitt, S.; Neeb, A.; Karl, S.; Linder, M.; Schubert, S. The biochemical reaction of maize (Zea mays L.) to salt stress is characterized by a mitigation of symptoms and not by a specific adaptation. Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semida, W.M.; Abdeltawab, K.K.; Osman, A.S.; Roby, M.H.H. Investigating the Utility of Dopamine in Agricultural Practices: A Review. Metabolites 2025, 15, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090586
Semida WM, Abdeltawab KK, Osman AS, Roby MHH. Investigating the Utility of Dopamine in Agricultural Practices: A Review. Metabolites. 2025; 15(9):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090586
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemida, Wael M., Kareem Khalafallah Abdeltawab, Ashraf Sh. Osman, and Mohamed H. H. Roby. 2025. "Investigating the Utility of Dopamine in Agricultural Practices: A Review" Metabolites 15, no. 9: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090586
APA StyleSemida, W. M., Abdeltawab, K. K., Osman, A. S., & Roby, M. H. H. (2025). Investigating the Utility of Dopamine in Agricultural Practices: A Review. Metabolites, 15(9), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090586








