Evaluation of the Metabolomics Profile in Charcot–Marie–Tooth (CMT) Patients: Novel Potential Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and 1H-NMR Acquisition
2.2. Data Processing and Multivariate and Univariate Statistical Analysis
2.3. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
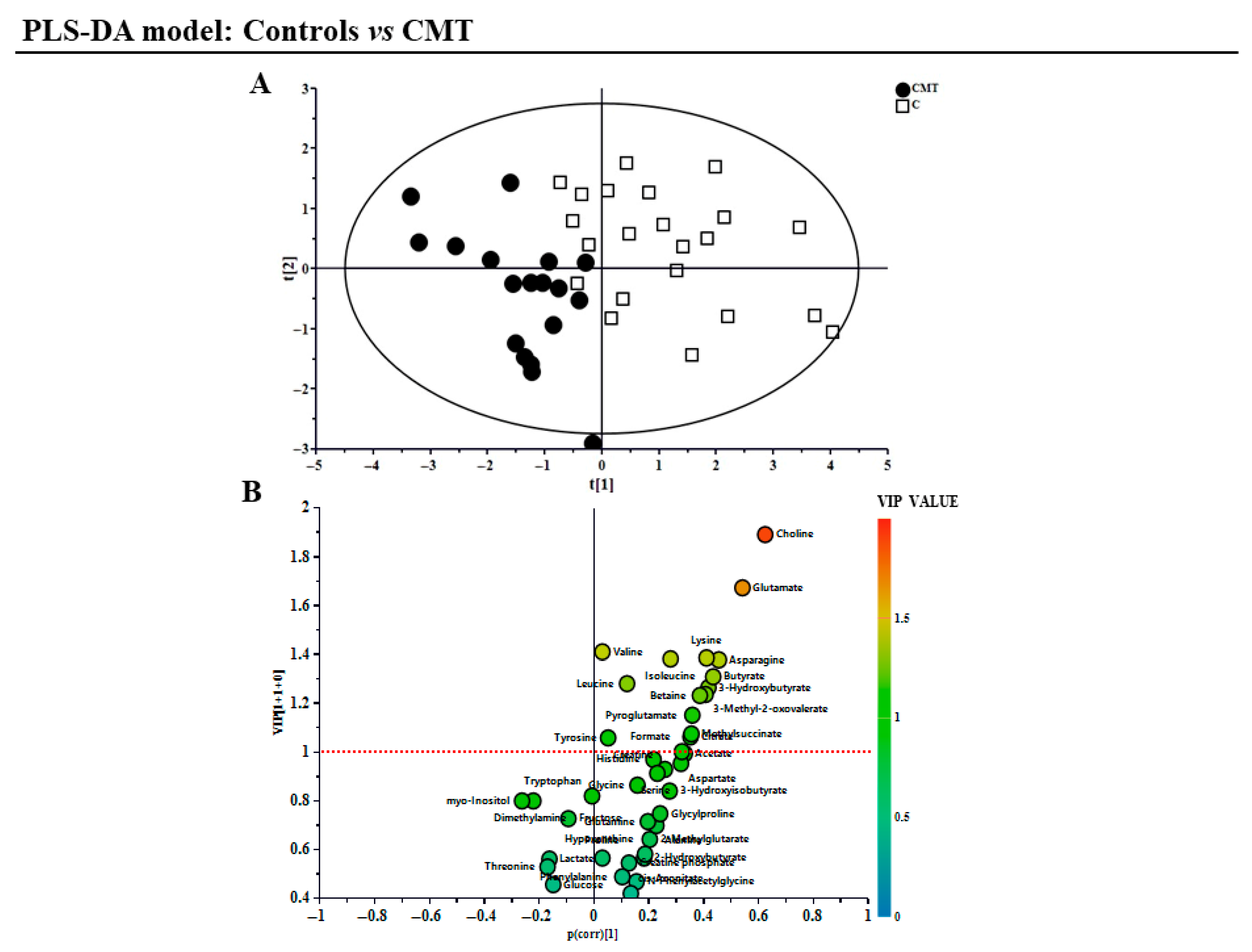
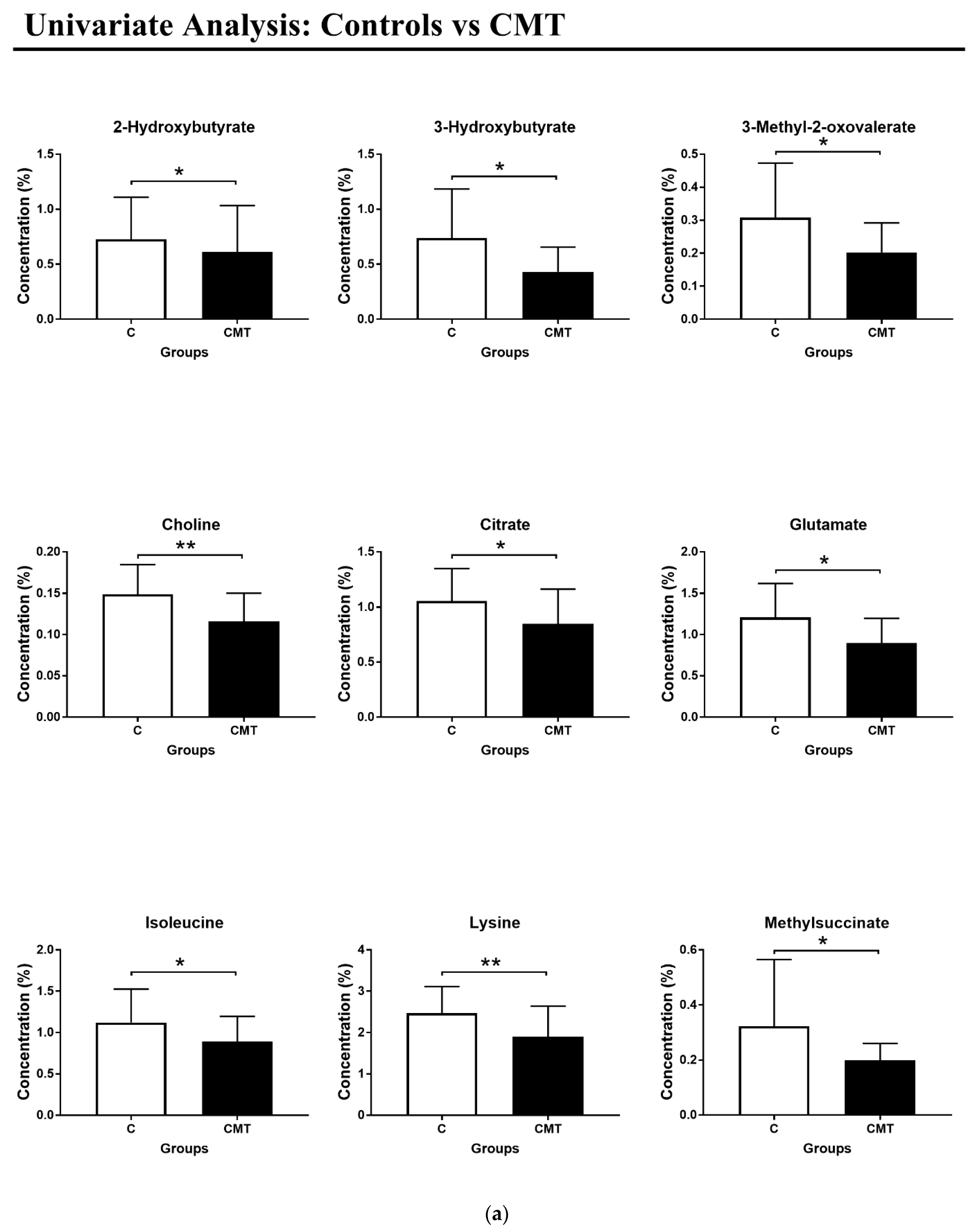
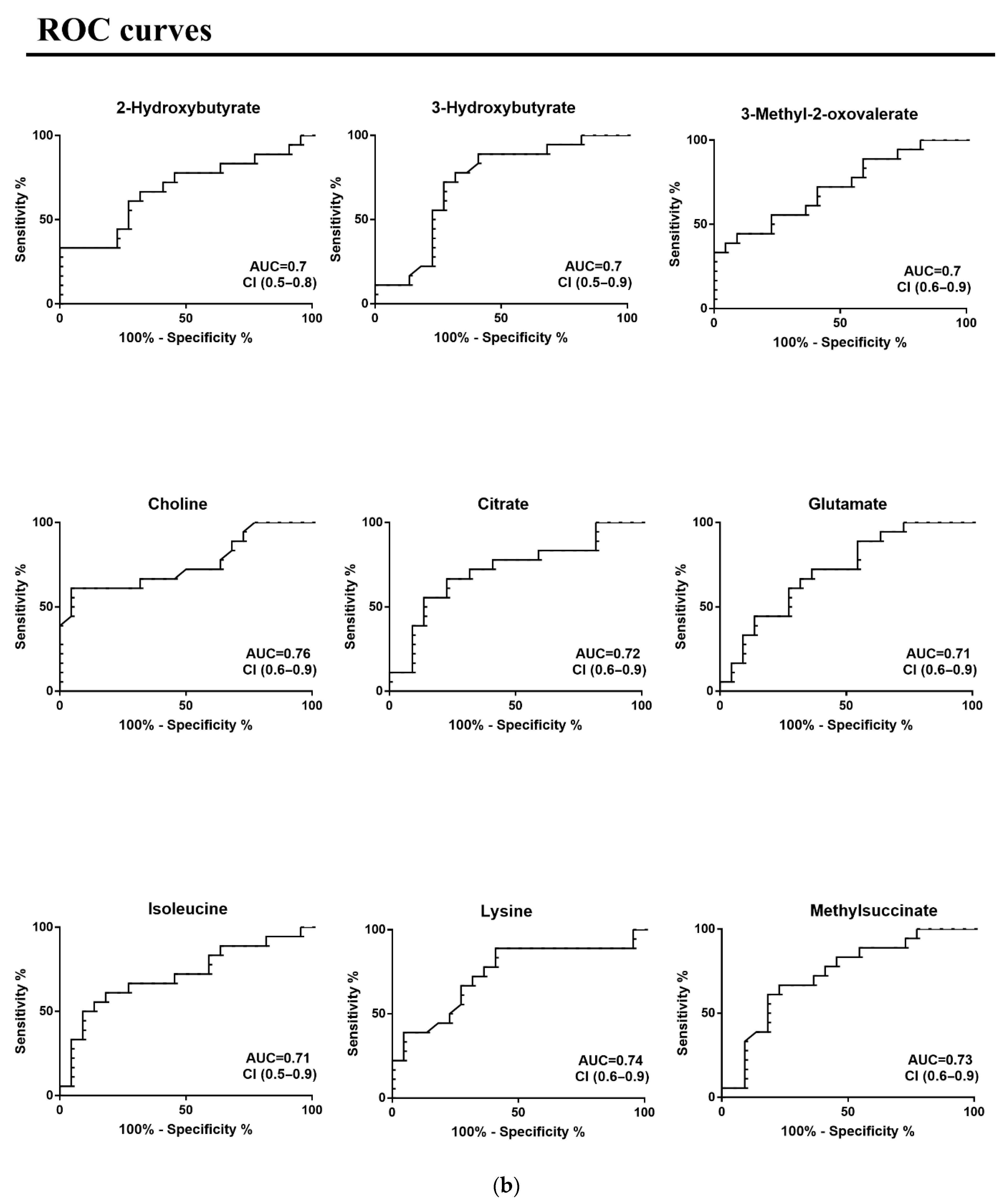
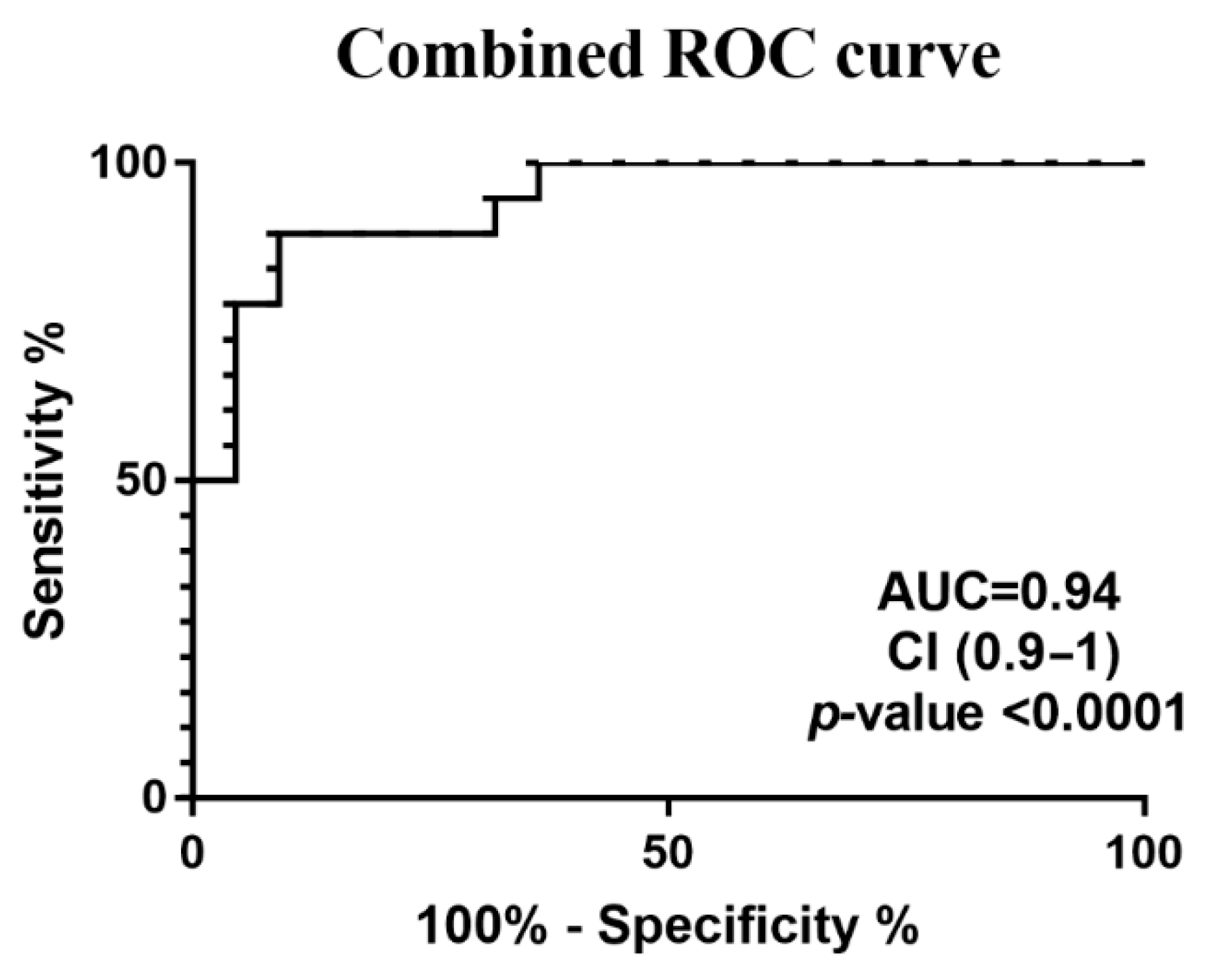
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reilly, M.M.; Murphy, S.M.; Laurá, M. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2011, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorefice, L.; Murru, M.R.; Coghe, G.; Fenu, G.; Corongiu, D.; Frau, J.; Tranquilli, S.; Tacconi, P.; Vannelli, A.; Marrosu, G.; et al. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: Genetic subtypes in the Sardinian population. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareyson, D.; Marchesi, C. Diagnosis, natural history, and management of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, G.; Wicklein, E.M.; Ratusinski, T.; Schmitt, L.; Kunze, K. Disability and quality of life in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisic, N.; Claeys, K.G.; Sirotković-Skerlev, M.; Löfgren, A.; Nelis, E.; De Jonghe, P.; Timmerman, V. Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: A Clinico-genetic Confrontation. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2008, 72, 416–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, K.J.; Grierson, A.J.; Ackerley, S.; Miller, C.C. Role of axonal transport in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 151–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandis, M.; Shy, M.E. Current Therapy for Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2005, 7, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisciotta, C.; Saveri, P.; Pareyson, D. Challenges in Treating Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease and Related Neuropathies: Current Management and Future Perspectives. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villoslada, P.; Alonso, C.; Agirrezabal, I.; Kotelnikova, E.; Zubizarreta, I.; Pulido-Valdeolivas, I.; Saiz, A.; Comabella, M.; Montalban, X.; Villar, L.; et al. Metabolomic signatures associated with disease severity in multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollywood, K.; Brison, D.R.; Goodacre, R. Metabolomics: Current technologies and future trends. Proteomics 2006, 17, 4716–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, P.; Calabresi, P.A. Metabolomics in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2016, 22, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Metabolomics. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddighe, S.; Murgia, F.; Lorefice, L.; Liggi, S.; Cocco, E.; Marrosu, M.G.; Atzori, L. Metabolomic analysis identifies altered metabolic pathways in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 93, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, F.; Lorefice, L.; Poddighe, S.; Fenu, G.; Secci, M.A.; Marrosu, M.G.; Cocco, E.; Atzori, L. Multi-Platform Characterization of Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum Metabolome of Patients Affected by Relapsing-Remitting and Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudetti, A.M.; Guerra, F.; Longo, S.; Beli, R.; Romano, R.; Manganelli, F.; Nolano, M.; Mangini, V.; Santoro, L.; Bucci, C. An altered lipid metabolism characterizes Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2B peripheral neuropathy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldevilla, B.; Cuevas-Martín, C.; Ibáñez, C.; Santacatterina, F.; Alberti, M.A.; Simó, C.; Casasnovas, C.; Márquez-Infante, C.; Sevilla, T.; Pascual, S.I.; et al. Plasma metabolome and skin proteins in Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1A patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setlere, S.; Schiemer, T.; Vaska, A.; Gailite, L.; Rots, D.; Kenina, V.; Klavins, K. Metabolomics insights into Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease: Toward biomarker discovery. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1543547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, E.; Murgia, F.; Lorefice, L.; Barberini, L.; Poddighe, S.; Frau, J.; Fenu, G.; Coghe, G.; Murru, M.R.; Murru, R.; et al. (1)H-NMR analysis provides a metabolomic profile of patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 3, e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, A.; Murgia, F.; Capodiferro, A.M.; Tanca, M.G.; Hendren, A.; Falqui, S.G.; Aresti, M.; Comini, M.; Carucci, S.; Cocco, E.; et al. 1H-NMR-Based Metabolomics in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorefice, L.; Murgia, F.; Fenu, G.; Frau, J.; Coghe, G.; Murru, M.R.; Tranquilli, S.; Visconti, A.; Marrosu, M.G.; Atzori, L.; et al. Assessing the Metabolomic Profile of Multiple Sclerosis Patients Treated with Interferon Beta 1a by 1H-NMR Spectroscopy. Neurotherapeutics. 2019, 16, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Eriksson, L. PLS_regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. J. Chemom. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Weljie, A.M.; Newton, J.; Mercier, P.; Carlson, E.; Slupsky, C.M. Targeted profiling: Quantitative analysis of 1H NMR metabolomics data. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4430–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Using MetaboAnalyst 3.0 for Comprehensive Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 55, 14.10.1–14.10.91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.Q.; Li, J. Ketogenic diets and protective mechanisms in epilepsy, metabolic disorders, cancer, neuronal loss, and muscle and nerve degeneration. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, M.; Blázquez, C. Ketone body synthesis in the brain: Possible neuroprotective effects. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2004, 70, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Multi-dimensional Roles of Ketone Bodies in Fuel Metabolism, Signaling, and Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 262–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, P.; Xiao, W. β-hydroxybutyrate as an Anti-Aging Metabolite. Nutrients 2021, 28, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toprak, İ.; Güler, H.; Genç, A.S.; Erbaş, O. Effects of ketone bodies on the brain. J. Exp. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 3, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, N.J.; Wodschow, H.Z.; Nilsson, M.; Rungby, J. Effects of Ketone Bodies on Brain Metabolism and Function in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shan, W.; Zhu, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, Q. Ketone Bodies in Neurological Diseases: Focus on Neuroprotection and Underlying Mechanisms. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabadu, D.; Agrawal, N.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, S. Mitochondrial metabolism: A common link between neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Behav. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T. Regulatory Mechanism of Peripheral Nerve Myelination by Glutamate-Induced Signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1190, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh, F.; Araki, T. Proteasomal degradation of glutamine synthetase regulates schwann cell differentiation. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, J.O.; Forstner, R.; Sperl, W. 2-Methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: Impaired catabolism of isoleucine presenting as neurodegenerative disease. Brain Dev. 2004, 26, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschocke, J.; Ruiter, J.P.; Brand, J.; Lindner, M.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Wanders, R.J.; Mayatepek, E. Progressive infantile neurodegeneration caused by 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: A novel inborn error of branched-chain fatty acid and isoleucine metabolism. Pediatr. Res. 2000, 48, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekdash, R.A. Choline and the Brain: An Epigenetic Perspective. Adv. Neurobiol. 2016, 12, 381–399. [Google Scholar]
- Barwick, K.E.; Wright, J.; Al-Turki, S.; McEntagart, M.M.; Nair, A.; Chioza, B.; Al-Memar, A.; Modarres, H.; Reilly, M.M.; Dick, K.J.; et al. Defective presynaptic choline transport underlies hereditary motor neuropathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Demographic Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CMT (n = 22) | C (n = 26) | p-Value | |
| Male/Female | 8/14 | 14/12 | >0.05 * (ns) |
| Mean age (years) ± SD | 49.3 ± 11.6 | 52.4 ± 9.6 | >0.05 ** (ns) |
| Age range (years) | 32–75 | 22–73 | |
| CMT diagnosis | CMT1 = 4 CMT2 = 11 CMTX = 2 | ||
| Metabolites | CMT | Effect Size Cohen’s D * | p-Value | ROC Curve | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Standard Error | 95% CI | p-Value | ||||
| 2-Hydroxybutyrate | - | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.68 | 0.09 | 0.5–0.8 | 0.05 |
| 3-Hydroxybutyrate | - | 0.86 | 0.02 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 0.5–0.9 | 0.02 |
| 3-Methyl-2-oxovalerate | - | 0.84 | 0.02 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 0.6–0.9 | 0.02 |
| Choline | - | 1.33 | 0.005 | 0.76 | 0.08 | 0.6–0.9 | 0.01 |
| Citrate | - | 0.69 | 0.02 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 0.5–0.9 | 0.02 |
| Glutamate | - | 0.87 | 0.02 | 0.71 | 0.08 | 0.5–0.9 | 0.02 |
| Isoleucine | - | 0.64 | 0.02 | 0.71 | 0.09 | 0.5–0.9 | 0.02 |
| Lysine | - | 0.93 | 0.01 | 0.74 | 0.08 | 0.6–0.9 | 0.01 |
| Methylsuccinate | - | 0.66 | 0.01 | 0.73 | 0.08 | 0.6–0.9 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murgia, F.; Cadeddu, M.; Frau, J.; Coghe, G.; Lorena, L.; Vannelli, A.; Murru, M.R.; Spada, M.; Noto, A.; Atzori, L.; et al. Evaluation of the Metabolomics Profile in Charcot–Marie–Tooth (CMT) Patients: Novel Potential Biomarkers. Metabolites 2025, 15, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080520
Murgia F, Cadeddu M, Frau J, Coghe G, Lorena L, Vannelli A, Murru MR, Spada M, Noto A, Atzori L, et al. Evaluation of the Metabolomics Profile in Charcot–Marie–Tooth (CMT) Patients: Novel Potential Biomarkers. Metabolites. 2025; 15(8):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080520
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurgia, Federica, Martina Cadeddu, Jessica Frau, Giancarlo Coghe, Lorefice Lorena, Alessandro Vannelli, Maria Rita Murru, Martina Spada, Antonio Noto, Luigi Atzori, and et al. 2025. "Evaluation of the Metabolomics Profile in Charcot–Marie–Tooth (CMT) Patients: Novel Potential Biomarkers" Metabolites 15, no. 8: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080520
APA StyleMurgia, F., Cadeddu, M., Frau, J., Coghe, G., Lorena, L., Vannelli, A., Murru, M. R., Spada, M., Noto, A., Atzori, L., & Cocco, E. (2025). Evaluation of the Metabolomics Profile in Charcot–Marie–Tooth (CMT) Patients: Novel Potential Biomarkers. Metabolites, 15(8), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080520









