Mitochondrial Metabolomics in Cancer: Mass Spectrometry-Based Approaches for Metabolic Rewiring Analysis and Therapeutic Discovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Collection and Storage of Mitochondrial Samples
2.1. Collection
2.1.1. Centrifugation
2.1.2. Laser-Based Techniques
2.1.3. Nanoprobe-Based Techniques
2.1.4. Post-Centrifugation Purification
| Isolation Method | Timing | Yield | Purity | Advantages | Limitations | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC | Moderate | High | Moderate | Reliable for large-scale isolation | Time-consuming and resource-intensive | [28,30,31] |
| DGC | Long | Low | High | Higher purity of mitochondrial fractions | Low yield; complex procedure | [28,30,32] |
| Laser-based techniques | Short | Variable | Variable | Effective for single-cell isolation | Potential damage to mitochondria and mtDNA | [34,35,36,37,38,39,40] |
| Nanoprobe-based techniques | Real-time | Variable | Variable | Precise and non-invasive | Challenges in sample isolation | [41,42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| AP | Short | High | High | High specificity and purity | Higher reagent costs | [48,49,50,51] |
| FAOS | Real-time | High | High | Effective for high-throughput applications | Cytotoxicity of fluorescent labels | [52,53,54,55] |
| CE | Variable | Low | High | Good signal-to-noise ratio | Lower throughput; requires smaller samples | [58] |
| FFE | Variable | High | Moderate | Rapid separation for high-throughput studies | Trade-off with purity | [57] |
| FFF | Variable | High | High | Rapid and effective | Trade-off with purity | [59] |
| Microfluidics | Variable | Low | High | Minimal damage to organelles | Limited information on mitochondrial subsets | [40,60,61,62,63] |
| FluidFM | Real-time | Variable | Variable | High-resolution sampling with minimal effects | Challenges in targeting specific locations | [64,65] |
2.2. Quantity and Quality Control of Mitochondrial Samples
2.3. Storage
3. Mass Spectrometry-Based Analysis for Mitochondrial Metabolomics
3.1. Sample Pretreatment
3.2. Chromatography-Based Separation Techniques
3.3. Detection Method and Data Analysis
3.4. Novel Breakthroughs and Applications
4. Mitochondrial Metabolism and Cancer
4.1. Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
4.2. Redox Homeostasis
4.3. Ion Metabolism
4.4. One Carbon Metabolism
4.5. Fatty Acid Metabolism
4.6. Amino Acid Metabolism
| Cancer Type | Metabolite | Change | Association | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AML | 2-HG | Accumulation | IDH1/IDH2 mutations: 2-HG accumulation inhibits TET/HDMs, causing DNA hypermethylation and differentiation block; promotes redox imbalance and leukemogenesis. | [83,99,100,101,102,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121] |
| Glutamine | Increased | GLS1 upregulation supports TCA cycle anaplerosis via α-KG. | [213,214,215,216,217,218,219,220,221] | |
| Glioma | 2-HG | Accumulation | IDH1 mutations: Chromatin remodeling impairs differentiation, driving oncogenesis via epigenetic dysregulation. | [83,98,99,117] |
| NAD+/NADH Ratio | Decreased | Enhanced glycolysis and suppressed OXPHOS. | [73,123] | |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | 2-HG | Accumulation | IDH1 mutations: Epigenetic dysregulation drives chemoresistance and tumor progression. | [101,120] |
| Fatty Acid | Upregulated | CD36—mediated lipid uptake fuels energy production and metastasis. | [186,187] | |
| Paraganglioma | Succinate | Accumulation | SDHB/SDHD mutations: HIF-1α stabilization activates VEGF, promoting angiogenesis. | [104,105,106] |
| ROS | Increased | Succinate accumulation inhibits prolyl hydroxylases, enhancing HIF-1α-mediated survival. | [104,127] | |
| RCC | Fumarate | Accumulation | FH mutations: DNA alkylation and NRF2 activation promote antioxidant defense; fumarate accumulation induces DNA damage and tumorigenesis. | [111,164] |
| Glutathione | Increased | Enhanced GSH synthesis compensates for oxidative stress from fumarate accumulation. | [124,126] | |
| NSCLC | Glutamine | Increased uptake | GLS1 overexpression fuels α-KG production for TCA cycle and nucleotide synthesis, supporting proliferation. | [149,150,219,222] |
| Aspartate | Increased | ASNS upregulation supports mTORC1-driven proliferation and metastasis. | [225,226,227] | |
| HCC | Glutamine | Increased uptake | Glutaminolysis supports ATP production and redox balance via GSH synthesis. | [215,251] |
| Acetyl-CoA | Accumulation | FASN overexpression drives de novo lipogenesis for membrane biosynthesis. | [192,193,194] | |
| Breast Cancer | Serine/Glycine | Increased synthesis | SHMT2/MTHFD2 overexpression supports nucleotide synthesis and redox homeostasis. | [160,162] |
| Fatty Acid | Upregulated | ACC/FASN upregulation provides lipids for rapid proliferation. | [191,192,193] | |
| CRC | Aspartate | Increased uptake | ASNS-mediated aspartate synthesis supports mTORC1 activation and EMT, promoting metastasis. | [225,226,227] |
| Butyrate | Decreased | Dysbiosis reduces butyrate levels, impairing colonocyte metabolism and promoting inflammation. | [179,202] | |
| PDAC | Mitochondrial Ca2+ | Increased influx | MCU overexpression activates ROS/NF-κB signaling, driving metastasis. | [145] |
| Ketone Bodies | Increased | β-Hydroxybutyrate: Alternative energy source under hypoxia. | [81,172] | |
| CLL | Mitochondrial K+ | Dysregulated flux | MitoKv1.3 upregulation inhibits apoptosis, promoting survival. | [147,148] |
| ATP/ADP Ratio | Decreased | OXPHOS suppression shifts energy reliance to glycolysis. | [74,145] | |
| Ovarian Cancer | Folate Cycle Intermediates | Increased | MTHFD2 overexpression supports purine synthesis and chemoresistance. | [167] |
| Proline | Accumulation | PYCR1-driven proline synthesis supports redox balance and tumor growth. | [245,246] | |
| Melanoma | Glutamine | Increased uptake | GLS1 inhibition reduces α-KG levels, suppressing TCA cycle and proliferation. | [218] |
| Lactate | Accumulation | Warburg effect: Dominant glycolysis with suppressed mitochondrial respiration. | [22,81] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Name |
| mtDNA | Mitochondrial DNA |
| OM | Outer Membrane |
| IMS | Intermembrane Space |
| MPTP | Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore |
| IM | Inner Membrane |
| ETC | Electron Transport Chain |
| OXPHOS | Oxidative Phosphorylation |
| NADH | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide |
| FADH2 | Flavine Adenine Dinucleotide |
| α-KG | Alpha-Ketoglutarate |
| 2-HG | 2-Hydroxyglutarate |
| IDH | Isocitrate Dehydrogenase |
| SDH | Succinate Dehydrogenase |
| FH | Fumarate Hydratase |
| TET | Ten-Eleven Translocation |
| FAO | Fatty Acid Oxidation |
| GLS1 | Glutaminase 1 |
| ASCT | Alanine–Serine–Cysteine Transporter |
| SNAT | Sodium-Coupled Neutral Amino Acid Transporter |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| GPx | Glutathione Peroxidase |
| HSL | Hormone-Sensitive Lipase |
| FAS | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| ACC | Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase |
| DHFR | Dihydrofolate Reductase |
| TYMS | Thymidylate Synthase |
| ALDH | Aldehyde Dehydrogenase |
| SHMT | Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase |
| MTHFD | Methylenetetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase |
| DNMT | DNA Methyltransferase |
| KCa | Calcium-Activated Potassium Channel |
| KV | Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel |
| VDAC | Voltage-Dependent Anion Channel |
| MCU | Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter |
| NCLX | Sodium/Calcium Exchanger |
| LETM1 | Calcium/Hydrogen Exchanger |
| FFE | Free-Flow Electrophoresis |
| CE | Capillary Electrophoresis |
| FFF | Field-Flow Fractionation |
| FAOS | Fluorescence-Activated Organelle Sorting |
| AP | Affinity Purification |
| LCM | Laser Capture Microdissection |
| OTs | Optical Tweezers |
| FluidFM | Fluid-Force Microscopy |
| OCR | Oxygen Consumption Rate |
| ECAR | Extracellular Acidification Rate |
| mtROS | Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species |
| PDAC | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| RCC | Renal Cell Carcinoma |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| SCC | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscope |
References
- Suomalainen, A.; Nunnari, J. Mitochondria at the crossroads of health and disease. Cell 2024, 187, 2601–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focusing on mitochondrial form and function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 735. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, U.; Bostwick, A.M.; Das, K.; Dittenhafer-Reed, K.E.; Patel, S.S. Structure, mechanism, and regulation of mitochondrial DNA transcription initiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 18406–18425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomello, M.; Pyakurel, A.; Glytsou, C.; Scorrano, L. The cell biology of mitochondrial membrane dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 204–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, E.L.; Ludlam, A.V.; Tan, Z.; Cianfrocco, M.A. Miro: A molecular switch at the center of mitochondrial regulation. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.E. The ATP synthase: The understood, the uncertain and the unknown. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikström, M.; Pecorilla, C.; Sharma, V. The mitochondrial respiratory chain. Enzymes 2023, 54, 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, S.; Bankier, A.T.; Barrell, B.G.; de Bruijn, M.H.; Coulson, A.R.; Drouin, J.; Eperon, I.C.; Nierlich, D.P.; Roe, B.A.; Sanger, F.; et al. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 1981, 290, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sampath, H. Mitochondrial DNA Integrity: Role in Health and Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzi, A.; Manganas, P.; Tokatlidis, K. Oxidative folding in the mitochondrial intermembrane space: A regulated process important for cell physiology and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellino, I.; Sazanov, L.A. The assembly, regulation and function of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowinski, S.M.; Van Vranken, J.G.; Dove, K.K.; Rutter, J. Impact of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Synthesis on Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R1212–R1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowinski, S.M.; Solmonson, A.; Rusin, S.F.; Maschek, J.A.; Bensard, C.L.; Fogarty, S.; Jeong, M.Y.; Lettlova, S.; Berg, J.A.; Morgan, J.T.; et al. Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis coordinates oxidative metabolism in mammalian mitochondria. eLife 2020, 9, e58041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucadyil, T.J.; Chipuk, J.E.; Liu, Y.; O’Neill, L.; Chen, Q. The multifaceted roles of mitochondria. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensvold, J.W.; Shishkova, E.; Sverchkov, Y.; Miller, I.J.; Cetinkaya, A.; Pyle, A.; Manicki, M.; Brademan, D.R.; Alanay, Y.; Raiman, J.; et al. Defining mitochondrial protein functions through deep multiomic profiling. Nature 2022, 606, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazier, A.E.; Thorburn, D.R.; Compton, A.G. Mitochondrial energy generation disorders: Genes, mechanisms, and clues to pathology. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 5386–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijas, C.; Montenegro-Burke, J.R.; Warth, B.; Spilker, M.E.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics activity screening for identifying metabolites that modulate phenotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Heyman, H.M. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1775, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Alseekh, S.; Aharoni, A.; Brotman, Y.; Contrepois, K.; D’Auria, J.; Ewald, J.; C. Ewald, J.; Fraser, P.D.; Giavalisco, P.; Hall, R.D.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: A guide for annotation, quantification and best reporting practices. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainero-Alcolado, L.; Liaño-Pons, J.; Ruiz-Pérez, M.V.; Arsenian-Henriksson, M. Targeting mitochondrial metabolism for precision medicine in cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 1304–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porporato, P.E.; Filigheddu, N.; Pedro, J.M.B.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappler, L.; Li, J.; Häring, H.U.; Weigert, C.; Lehmann, R.; Xu, G.; Hoene, M. Purity matters: A workflow for the valid high-resolution lipid profiling of mitochondria from cell culture samples. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vögtle, F.N.; Burkhart, J.M.; Gonczarowska-Jorge, H.; Kücükköse, C.; Taskin, A.A.; Kopczynski, D.; Ahrends, R.; Mossmann, D.; Sickmann, A.; Zahedi, R.P.; et al. Landscape of submitochondrial protein distribution. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebiedzinska-Arciszewska, M.; Wojtczak, L.; Wieckowski, M.R. An Update on Isolation of Functional Mitochondria from Cells for Bioenergetics Studies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2310, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Roede, J.R.; Park, Y.; Li, S.; Strobel, F.H.; Jones, D.P. Detailed mitochondrial phenotyping by high resolution metabolomics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, W.W.; Freinkman, E.; Wang, T.; Birsoy, K.; Sabatini, D.M. Absolute Quantification of Matrix Metabolites Reveals the Dynamics of Mitochondrial Metabolism. Cell 2016, 166, 1324–1337.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, N.; Kummitha, C.M.; Rosca, M.G.; Fujioka, H.; Tandler, B.; Hoppel, C.L. Isolation of mitochondrial subpopulations from skeletal muscle: Optimizing recovery and preserving integrity. Acta Physiol. 2019, 225, e13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.C.; Bergamini, C.; Fato, R.; Pon, L.A.; Pallotti, F. Isolation of mitochondria from cells and tissues. Methods Cell Biol. 2020, 155, 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhang, P. Subcellular metabolomics: Isolation, measurement, and applications. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 210, 114557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaigoub, H.; Tirichen, H.; Xin, X.; Shi, S.; Wu, C.; Li, R.; Li, Y. Isolation of Viable Single Cells With High Yield and Purity Using a Small Amount of Human Kidney Tissue Biopsy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 822275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, D.A.; Shadel, G.S. Purification of mitochondria by sucrose step density gradient centrifugation. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 2014, pdb.prot080028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickles, S.; Vigié, P.; Youle, R.J. Mitophagy and Quality Control Mechanisms in Mitochondrial Maintenance. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R170–R185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horneffer, V.; Linz, N.; Vogel, A. Principles of laser-induced separation and transport of living cells. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 054016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifunov, S.; Pyle, A.; Valentino, M.L.; Liguori, R.; Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Burté, F.; Duff, J.; Kleinle, S.; Diebold, I.; Rugolo, M.; et al. Clonal expansion of mtDNA deletions: Different disease models assessed by digital droplet PCR in single muscle cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.C.; Rosa, H.S.; Grady, J.P.; Blakely, E.L.; He, L.; Romain, N.; Haller, R.G.; Newman, J.; McFarland, R.; Ng, Y.S.; et al. Pathological mechanisms underlying single large-scale mitochondrial DNA deletions. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, J.E.; Kishore, R.B.; Levin, B.C.; Albanetti, T.; Boire, N.; Knipe, A.; Helmerson, K.; Deckman, K.H. Detection of heteroplasmic mitochondrial DNA in single mitochondria. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.E.; Rosa, H.S.; Pabis, K.; Lawless, C.; Chen, C.; Grünewald, A.; Rygiel, K.A.; Rocha, M.C.; Reeve, A.K.; Falkous, G.; et al. Subcellular origin of mitochondrial DNA deletions in human skeletal muscle. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keloth, A.; Anderson, O.; Risbridger, D.; Paterson, L. Single Cell Isolation Using Optical Tweezers. Micromachines 2018, 9, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutaux, E.; Christaller, W.; Scaramuzzino, C.; Genoux, A.; Charlot, B.; Cazorla, M.; Saudou, F. Neuronal network maturation differently affects secretory vesicles and mitochondria transport in axons. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforge, F.O.; Carpino, J.; Rotenberg, S.A.; Mirkin, M.V. Electrochemical attosyringe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11895–11900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Noël, J.M.; Mirkin, M.V.; Gao, Y.; Mashtalir, O.; Friedman, G.; Gogotsi, Y. Carbon pipette-based electrochemical nanosampler. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3365–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Guggilla, R.R.; Gansemans, Y.; Van der Jeught, M.; Boel, A.; Popovic, M.; Stamatiadis, P.; Ferrer-Buitrago, M.; Thys, V.; Van Coster, R.; et al. Comparative analysis of different nuclear transfer techniques to prevent the transmission of mitochondrial DNA variants. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 25, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Li, L.; Shi, J.; Sheng, Y.; Lu, W.; Gallego-Perez, D.; Lee, L.J. Micro-/nanoscale electroporation. Lab. Chip 2016, 16, 4047–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, Y. Microfluidic Exponential Rolling Circle Amplification for Sensitive microRNA Detection Directly from Biological Samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 279, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, A.; Gabi, M.; Behr, P.; Studer, P.; Vörös, J.; Niedermann, P.; Bitterli, J.; Polesel-Maris, J.; Liley, M.; Heinzelmann, H.; et al. FluidFM: Combining atomic force microscopy and nanofluidics in a universal liquid delivery system for single cell applications and beyond. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2501–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Actis, P.; Maalouf, M.M.; Kim, H.J.; Lohith, A.; Vilozny, B.; Seger, R.A.; Pourmand, N. Compartmental genomics in living cells revealed by single-cell nanobiopsy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, Y.; Yin, L.; Sun, H.; Yin, S.; Pan, Q.; Wei, H.; Wu, L.; Liu, S. A micropreparation of mitochondria from cells using magnetic beads with immunoaffinity. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 421, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahier, A.; Dai, C.Y.; Tweedie, A.; Bezawork-Geleta, A.; Kirmes, I.; Zuryn, S. Affinity purification of cell-specific mitochondria from whole animals resolves patterns of genetic mosaicism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, W.B.; Harwood, C.L.; Prajapati, P.; Springer, J.E.; Saatman, K.E.; Sullivan, P.G. Fractionated mitochondrial magnetic separation for isolation of synaptic mitochondria from brain tissue. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afanasyeva, M.A.; Ustiugova, A.S.; Golyshev, S.A.; Kopylov, A.T.; Bogolyubova, A.V.; Demin, D.E.; Belousov, P.V.; Schwartz, A.M. Isolation of Large Amounts of Highly Pure Mitochondria for “Omics” Studies. Biochemistry 2018, 83, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floros, V.I.; Pyle, A.; Dietmann, S.; Wei, W.; Tang, W.C.W.; Irie, N.; Payne, B.; Capalbo, A.; Noli, L.; Coxhead, J.; et al. Segregation of mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy through a developmental genetic bottleneck in human embryos. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barteneva, N.S.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Tsytsykova, A.; Armant, M.; Vorobjev, I.A. Mitochondrial staining allows robust elimination of apoptotic and damaged cells during cell sorting. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflugradt, R.; Schmidt, U.; Landenberger, B.; Sänger, T.; Lutz-Bonengel, S. A novel and effective separation method for single mitochondria analysis. Mitochondrion 2011, 11, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poe, B.G.; Navratil, M.; Arriaga, E.A. Analysis of subcellular sized particles. Capillary electrophoresis with post-column laser-induced fluorescence detection versus flow cytometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1137, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zischka, H.; Braun, R.J.; Marantidis, E.P.; Büringer, D.; Bornhövd, C.; Hauck, S.M.; Demmer, O.; Gloeckner, C.J.; Reichert, A.S.; Madeo, F.; et al. Differential analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria by free flow electrophoresis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2006, 5, 2185–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Islinger, M.; Wildgruber, R.; Völkl, A. Preparative free-flow electrophoresis, a versatile technology complementing gradient centrifugation in the isolation of highly purified cell organelles. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2288–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostal, V.; Fonslow, B.R.; Arriaga, E.A.; Bowser, M.T. Fast determination of mitochondria electrophoretic mobility using micro free-flow electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9267–9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Moon, M.H. High Speed Size Sorting of Subcellular Organelles by Flow Field-Flow Fractionation. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6342–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Wolken, G.G.; Wittenberg, N.J.; Arriaga, E.A.; Oh, S.-H. Nanohole Array-Directed Trapping of Mammalian Mitochondria Enabling Single Organelle Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11973–11977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; McNaughton, R.L.; Espinosa, H.D. Micro- and Nanoscale Technologies for Delivery into Adherent Cells. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, B.; Askins, B.W.; Dhar, S. Mito-magneto: A tool for nanoparticle mediated mitochondria isolation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 19581–19591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarjanli, Z.; Ghaedi, K.; Esmaeili, A.; Rahgozar, S.; Zarrabi, A. Iron oxide nanoparticles may damage to the neural tissue through iron accumulation, oxidative stress, and protein aggregation. BMC Neurosci. 2017, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbiest, G.J.; Rost, M.J. Resonance frequencies of AFM cantilevers in contact with a surface. Ultramicroscopy 2016, 171, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäbelein, C.G.; Feng, Q.; Sarajlic, E.; Zambelli, T.; Guillaume-Gentil, O.; Kornmann, B.; Vorholt, J.A. Mitochondria transplantation between living cells. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, S.; Feckler, C.; Lehr, S.; Wallbrecht, K.; Wolgast, H.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Kotzka, J. A critical comparison between two classical and a kit-based method for mitochondria isolation. Proteomics 2009, 9, 3209–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuthner, T.C.; Hartman, J.H.; Ryde, I.T.; Meyer, J.N. PCR-Based Determination of Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number in Multiple Species. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2310, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chutipongtanate, S.; Watcharatanyatip, K.; Homvises, T.; Jaturongkakul, K.; Thongboonkerd, V. Systematic comparisons of various spectrophotometric and colorimetric methods to measure concentrations of protein, peptide and amino acid: Detectable limits, linear dynamic ranges, interferences, practicality and unit costs. Talanta 2012, 98, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, V.; Wang, J.; Dimmock, D.; Wong, L.J. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of mitochondrial DNA content. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2011, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micakovic, T.; Banczyk, W.Z.; Clark, E.; Kränzlin, B.; Peters, J.; Hoffmann, S.C. Isolation of Pure Mitochondria from Rat Kidneys and Western Blot of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Complexes. Bio Protoc. 2019, 9, e3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neikirk, K.; Lopez, E.G.; Marshall, A.G.; Alghanem, A.; Krystofiak, E.; Kula, B.; Smith, N.; Shao, J.; Katti, P.; Hinton, A., Jr. Call to action to properly utilize electron microscopy to measure organelles to monitor disease. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2023, 102, 151365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmann, M.; Benavides, G.A.; Wani, W.Y.; Berryhill, T.F.; Ouyang, X.; Johnson, M.S.; Ravi, S.; Mitra, K.; Barnes, S.; Darley-Usmar, V.M.; et al. Methods for assessing mitochondrial quality control mechanisms and cellular consequences in cell culture. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolfi-Donegan, D.; Braganza, A.; Shiva, S. Mitochondrial electron transport chain: Oxidative phosphorylation, oxidant production, and methods of measurement. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinazzi, M.; Casarin, A.; Pertegato, V.; Salviati, L.; Angelini, C. Assessment of mitochondrial respiratory chain enzymatic activities on tissues and cultured cells. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmusson, A.G.; Hao, M.; Møller, I.M. Integrity Assessment of Isolated Plant Mitochondria. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2363, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Degli Esposti, M. Assessing functional integrity of mitochondria in vitro and in vivo. Methods Cell Biol. 2001, 65, 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- Eubel, H.; Heazlewood, J.L.; Millar, A.H. Isolation and subfractionation of plant mitochondria for proteomic analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 355, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pallotti, F.; Lenaz, G. Isolation and subfractionation of mitochondria from animal cells and tissue culture lines. Methods Cell Biol. 2007, 80, 3–44. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, A.H.; Liddell, A.; Leaver, C.J. Isolation and subfractionation of mitochondria from plants. Methods Cell Biol. 2007, 80, 65–90. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Reyes, I.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial TCA cycle metabolites control physiology and disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.L.; Shockcor, J.P. Metabolic profiles of cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elpa, D.P.; Prabhu, G.R.D.; Wu, S.-P.; Tay, K.S.; Urban, P.L. Automation of mass spectrometric detection of analytes and related workflows: A review. Talanta 2020, 208, 120304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Combined Targeted and Untargeted Profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 30.4.1–30.4.32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmer, P.O.; Wienken, C.M.; Korf, A.; Hayen, H. Mass spectrometric investigation of cardiolipins and their oxidation products after two-dimensional heart-cut liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1619, 460918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Taylor, M.C.; Shrestha, P.; Singh, S.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhou, X.R. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry based approach for rapid comparison of lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase activity on multiple substrates. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1572, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagura, L.; Dumoulin, P.C.; Ellis, C.C.; Mendes, M.T.; Estevao, I.L.; Almeida, I.C.; Burleigh, B.A. Fatty acid elongases 1-3 have distinct roles in mitochondrial function, growth, and lipid homeostasis in Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, A.; Nagornov, K.O.; Kozhinov, A.N.; Michael, J.A.; Anthony, I.G.M.; Tsybin, Y.O.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Ellis, S.R. Ultrahigh-Mass Resolution Mass Spectrometry Imaging with an Orbitrap Externally Coupled to a High-Performance Data Acquisition System. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourceau, P.; Geier, B.; Suerdieck, V.; Bien, T.; Soltwisch, J.; Dreisewerd, K.; Liebeke, M. Visualization of metabolites and microbes at high spatial resolution using MALDI mass spectrometry imaging and in situ fluorescence labeling. Nat. Protoc. 2023, 18, 3050–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.P.; Antoniewicz, M.R. High-resolution (13)C metabolic flux analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2856–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Sun, F.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z. Metabolomics, metabolic flux analysis and cancer pharmacology. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 224, 107827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, F.K.; Pandey, P.; Meitei, R.; Cardona, D.; Gujar, A.C.; Shulaev, V. GC-MS/MS Profiling of Plant Metabolites. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2396, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Menger, K.E.; Nicholls, T.J. Isolating Mitochondria, Mitoplasts, and mtDNA from Cultured Mammalian Cells. Mitochondrial DNA Methods Protoc. 2023, 2615, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, D.; Lindau, C.; Lagies, S.; Wiedemann, N.; Kammerer, B. Metabolic profiling of isolated mitochondria and cytoplasm reveals compartment-specific metabolic responses. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, W.; Xu, Y.; Edom, R.W.; Weng, N. Analysis of polar metabolites by hydrophilic interaction chromatography—MS/MS. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kremer, D.M.; Sajjakulnukit, P.; Zhang, L.; Lyssiotis, C.A. A large-scale analysis of targeted metabolomics data from heterogeneous biological samples provides insights into metabolite dynamics. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.M.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Chua, G.H.; Li, B.; Shui, G. A robust, integrated platform for comprehensive analyses of acyl-coenzyme As and acyl-carnitines revealed chain length-dependent disparity in fatty acyl metabolic fates across Drosophila development. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Jian, W.; Zhang, D.; Aubry, A.F.; Arnold, M.E. Application of a stabilizer cocktail of N-ethylmaleimide and phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride to concurrently stabilize the disulfide and ester containing compounds in a plasma LC-MS/MS assay. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 88, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, M.; Fröbel, D.; Helm, J.; Chavakis, T.; Peitzsch, M.; Bechmann, N. Accurate redox state indication by in situ derivatization with N-ethylmaleimide—Profiling of transsulfuration and glutathione pathway metabolites by UPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2024, 1236, 124062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiz, B.; Sriram, G.; Clyne, A.M. Interpreting metabolic complexity via isotope-assisted metabolic flux analysis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2023, 48, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvatam, R.; Singh, R.; Sharma, R. Comparison of different derivatising reagents in identification of milk metabolites using GC–MS. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 138, 105535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaženović, I.; Kind, T.; Sa, M.R.; Ji, J.; Vaniya, A.; Wancewicz, B.; Roberts, B.S.; Torbašinović, H.; Lee, T.; Mehta, S.S.; et al. Structure Annotation of All Mass Spectra in Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Fiehn, O. Mass spectral fragmentation of trimethylsilylated small molecules. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, A.P.; Abzalimov, R.R.; Shvartsburg, A.A. Broad Separation of Isomeric Lipids by High-Resolution Differential Ion Mobility Spectrometry with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrieder, E.M.; Kretschmer, F.; Böcker, S.; Witting, M. Current state-of-the-art of separation methods used in LC-MS based metabolomics and lipidomics. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2022, 1188, 123069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, Q.F.; Wang, Q.; Hussain, D.; Feng, Y.Q. Derivatization for liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry analysis of small-molecular weight compounds. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.H.J.; Chan, L.Y.; Fitzner, L.; Keppler, J.K.; Ismail, S.M.; Hird, S.; Hancock, P.; Karin, S.; Tobias, D. A novel screening method for free non-standard amino acids in human plasma samples using AccQ·Tag reagents and LC-MS/MS. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.; Chen, L.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Metabolomics and Isotope Tracing. Cell 2018, 173, 822–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeArmond, P.D.; Bunch, D.R. Quantitation of non-derivatized free amino acids for detecting inborn errors of metabolism by incorporating mixed-mode chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. Adv. Clin. Lab. 2022, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.L.J.; Welbourne, E.N.; Evans, C.A.; Dickman, M.J. Characterisation and analysis of mRNA critical quality attributes using liquid. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1745, 465724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajka, T.; Hricko, J.; Rudl Kulhava, L.; Paucova, M.; Novakova, M.; Fiehn, O.; Kuda, O. Exploring the Impact of Organic Solvent Quality and Unusual Adduct Formation during LC-MS-Based Lipidomic Profiling. Metabolites 2023, 13, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisz, J.A.; D’Alessandro, A. Measurement of metabolic fluxes using stable isotope tracers in whole animals and human patients. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Sevillano, M.A.; García-Barrera, T.; Navarro, F.; Montero-Lobato, Z.; Gómez-Ariza, J.L. Shotgun metabolomic approach based on mass spectrometry for hepatic mitochondria of mice under arsenic exposure. Biometals 2015, 28, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, L.; Lv, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, G. Development of a plasma pseudotargeted metabolomics method based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2519–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Dai, W.; Yin, P.; Zeng, Z.; Kong, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Lu, X.; Xu, G. Multiple reaction monitoring-ion pair finder: A systematic approach to transform nontargeted mode to pseudotargeted mode for metabolomics study based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5050–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Su, B.; Zeng, Z.; Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Lv, W.; Xuan, Q.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yin, P.; et al. Ion-Pair Selection Method for Pseudotargeted Metabolomics Based on SWATH MS Acquisition and Its Application in Differential Metabolite Discovery of Type 2 Diabetes. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11401–11408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, H.; Cai, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Zhu, Z.J. SWATHtoMRM: Development of High-Coverage Targeted Metabolomics Method Using SWATH Technology for Biomarker Discovery. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, E.C.; Baudrier, L.; Özerdem, C.; Lewis, C.A.; Chan, S.H.; Kunchok, T.; Abu-Remaileh, M.; Cangelosi, A.L.; Sabatini, D.M.; Birsoy, K.; et al. MITO-Tag Mice enable rapid isolation and multimodal profiling of mitochondria from specific cell types in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurekten, O.; Payne, T.; Tejera, N.; Amaladoss, F.X.; Martin, C.; Williams, M.; O’Donovan, C. MetaboLights: Open data repository for metabolomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D640–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, M.; Fahy, E.; Cotter, D.; Azam, K.; Vadivelu, I.; Burant, C.; Edison, A.; Fiehn, O.; Higashi, R.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Metabolomics Workbench: An international repository for metabolomics data and metadata, metabolite standards, protocols, tutorials and training, and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D463–D470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSI Board Members; Sansone, S.A.; Fan, T.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; Hardy, N.W.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Kristal, B.S.; Lindon, J.; Mendes, P.; et al. The metabolomics standards initiative. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Ko, J. Single-cell and spatially resolved omics: Advances and limitations. J Pharm Anal. 2023, 13, 833–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughton, B.A.; Hamilton, B. Spatial Metabolite Profiling by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 965, 291–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ru, Y.; Xie, P.; Han, J.; Chai, X.; Wang, J.; Cai, Z. Optimized MALDI2-Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Stable Isotope Tracing of Tissue-Specific Metabolic Pathways in Mice. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, W.; Huo, M.; He, B.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.; Li, W.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Xia, J.; et al. Spatial-resolved metabolomics reveals tissue-specific metabolic reprogramming in diabetic nephropathy by using mass spectrometry imaging. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3665–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xing, X.; Zeng, X.; Jackson, S.R.; TeSlaa, T.; Al-Dalahmah, O.; Samarah, L.Z.; Goodwin, K.; Yang, L.; McReynolds, M.R.; et al. Spatially resolved isotope tracing reveals tissue metabolic activity. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Xia, D.; Xu, M.; Gao, Y.; Tong, L.; Lu, C.; Li, W.; Xie, R.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, D.; et al. Single-Cell Simultaneous Metabolome and Transcriptome Profiling Revealing Metabolite-Gene Correlation Network. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2411276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Yao, Q.J.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, W.; Qian, K.; Wan, J.J.; Zhou, B.O. Deciphering the metabolic heterogeneity of hematopoietic stem cells with single-cell resolution. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, S.; He, Q.; Shen, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. iNAP: An integrated network analysis pipeline for microbiome studies. iMeta 2022, 1, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Feng, K.; Yang, X.; He, Q.; Zhao, B.; Li, T.; Wang, S.; Deng, Y. iNAP 2.0: Harnessing metabolic complementarity in microbial network analysis. iMeta 2024, 3, e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Feng, K.; He, Q.; Yang, X.; Hou, W.; Li, F.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, B.; et al. Metabolic interdependencies in thermophilic communities are revealed using co-occurrence and complementarity networks. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, P.; Khan, S.; Hemrom, A.J.; Open Source Drug Discovery Consortium; Lynn, A.M. MetaNET--a web-accessible interactive platform for biological metabolic network analysis. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töpfer, N.; Kleessen, S.; Nikoloski, Z. Integration of metabolomics data into metabolic networks. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Zheng, M.; Yang, T. An integrated bioinformatics and machine learning approach to identifying biomarkers connecting parkinson’s disease with purine metabolism-related genes. BMC Neurol. 2025, 25, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Badur, M.G.; Luebeck, J.; Magaña, J.H.; Birmingham, A.; Sasik, R.; Ahn, C.S.; Ideker, T.; Metallo, C.M.; Mali, P.; et al. Combinatorial CRISPR-Cas9 Metabolic Screens Reveal Critical Redox Control Points Dependent on the KEAP1-NRF2 Regulatory Axis. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drapal, M.; Enfissi, E.M.A.; Almeida, J.; Rapacz, E.; Nogueira, M.; Fraser, P.D. The potential of metabolomics in assessing global compositional changes resulting from the application of CRISPR/Cas9 technologies. Transgenic Res. 2023, 32, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Jiao, N. Development of a CRISPR/Cas9n-based tool for metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas putida for ferulic acid-to-polyhydroxyalkanoate bioconversion. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, A.; Singh, S.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Kaur, J.; Bari, V.K. Integration of CRISPR/Cas9 with multi-omics technologies to engineer secondary metabolite productions in medicinal plant: Challenges and Prospects. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2024, 24, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Shin, J.; Cho, B.K. Applications of CRISPR/Cas System to Bacterial Metabolic Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Huang, T.W.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Wang, Y.F.; Yen, C.C.; Lee, G.L.; Yeh, C.C.; Peng, Y.J.; Kuo, Y.Y.; Wen, H.T.; et al. Cancer-Derived Succinate Promotes Macrophage Polarization and Cancer Metastasis via Succinate Receptor. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Succinate-loaded tumor cell-derived microparticles reprogram tumor-associated macrophage metabolism. Sci. Transl. Med. 2025, 17, eadr4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowerison, M.R.; Sekaran, N.V.C.; Dong, Z.; Chen, X.; You, Q.; Llano, D.A.; Song, P. Super-Resolution Ultrasound Reveals Cerebrovascular Impairment in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2024, 44, e1251232024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Ryan, D.G.; Prag, H.A.; Dikovskaya, D.; Menon, D.; Zaslona, Z.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Costa, A.S.H.; Higgins, M.; Hams, E.; et al. Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 2018, 556, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhen, S.; Ping, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Metabolomic biomarkers in liquid biopsy: Accurate cancer diagnosis and prognosis monitoring. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1331215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.; Moret, M.; Salvy, P.; Weilandt, D.; Hatzimanikatis, V.; Miskovic, L. Reconstructing Kinetic Models for Dynamical Studies of Metabolism using Generative Adversarial Networks. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.; York, E.M.; Stopka, S.A.; Martínez-François, J.R.; Hossain, M.A.; Baquer, G.; Regan, M.S.; Agar, N.Y.R.; Yellen, G. Spatially resolved metabolomics and isotope tracing reveal dynamic metabolic responses of dentate granule neurons with acute stimulation. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 1820–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Dong, D.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, X.D.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, G.; Yin, Y. Single cell atlas reveals multilayered metabolic heterogeneity across tumour types. eBioMedicine 2024, 109, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Allam, M.; Cai, S.; Henderson, W.; Yueh, B.; Garipcan, A.; Ievlev, A.V.; Afkarian, M.; Beyaz, S.; Coskun, A.F. Single-cell spatial metabolomics with cell-type specific protein profiling for tissue systems biology. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Hu, Z. Metabolic orchestration of drug-tolerant persister cells in cancer. Life Med. 2024, 3, lnae040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, H.; Wang, A.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Zou, Y.; Shi, M.; Liu, R.; Su, N.; et al. Genetically encoded fluorescent sensors reveal dynamic regulation of NADPH metabolism. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, N.; Llabrés, M.; Reyes-Prieto, M.; Simeoni, M. MetNet: A two-level approach to reconstructing and comparing metabolic networks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, J.L.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Shen, L.; Long, Q. Deep learning-based approaches for multi-omics data integration and analysis. BioData Min. 2024, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidley, C.; Darnell, A.M.; Gaudio, B.L.; Lien, E.C.; Barbeau, A.M.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Sorger, P.K. A CRISPRi/a screening platform to study cellular nutrient transport in diverse microenvironments. Nat. Cell Biol. 2024, 26, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Bai, H.; Cao, L.; Peng, B.; Li, L. Development of a Microfluidic System for Mitochondrial Extraction, Purification, and Analysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 20487–20500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böken, D.; Cox, D.; Burke, M.; Lam, J.Y.L.; Katsinelos, T.; Danial, J.S.H.; Fertan, E.; McEwan, W.A.; Rowe, J.B.; Klenerman, D. Single-Molecule Characterization and Super-Resolution Imaging of Alzheimer’s Disease-Relevant Tau Aggregates in Human Samples. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2024, 63, e202317756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Morcelle, C.; Cheng, Z.L.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Smith, M.D.; Shi, M.; et al. Itaconate inhibits TET DNA dioxygenases to dampen inflammatory responses. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliola, A.; Mainini, F.; Cardaci, S. The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle at the Crossroad Between Cancer and Immunity. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 834–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Sun, D.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Chen, L. The regulatory mechanisms and inhibitors of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 in cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 1438–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Dooling, D.J.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; Delehaunty, K.D.; McGrath, S.D.; et al. Recurring mutations found by sequencing an acute myeloid leukemia genome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.L.; Holmen, S.L.; Colman, H. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amary, M.F.; Bacsi, K.; Maggiani, F.; Damato, S.; Halai, D.; Berisha, F.; Pollock, R.; O’Donnell, P.; Grigoriadis, A.; Diss, T.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations are frequent events in central chondrosarcoma and central and periosteal chondromas but not in other mesenchymal tumours. J. Pathol. 2011, 224, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borger, D.R.; Tanabe, K.K.; Fan, K.C.; Lopez, H.U.; Fantin, V.R.; Straley, K.S.; Schenkein, D.P.; Hezel, A.F.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Liebman, H.M.; et al. Frequent mutation of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)1 and IDH2 in cholangiocarcinoma identified through broad-based tumor genotyping. Oncologist 2012, 17, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruchtman, H.; Avigan, Z.M.; Waksal, J.A.; Brennan, N.; Mascarenhas, J.O. Management of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1/2 mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2024, 38, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Z.; Duan, Z.; Yin, D.; Zhou, Y. Biological Roles and Therapeutic Applications of IDH2 Mutations in Human Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 644857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, D.; Latif, F.; Dallol, A.; Dahia, P.L.; Douglas, F.; George, E.; Sköldberg, F.; Husebye, E.S.; Eng, C.; Maher, E.R. Gene mutations in the succinate dehydrogenase subunit SDHB cause susceptibility to familial pheochromocytoma and to familial paraganglioma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayley, J.P.; Kunst, H.P.; Cascon, A.; Sampietro, M.L.; Gaal, J.; Korpershoek, E.; Hinojar-Gutierrez, A.; Timmers, H.J.; Hoefsloot, L.H.; Hermsen, M.A.; et al. SDHAF2 mutations in familial and sporadic paraganglioma and phaeochromocytoma. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanharanta, S.; Buchta, M.; McWhinney, S.R.; Virta, S.K.; Peçzkowska, M.; Morrison, C.D.; Lehtonen, R.; Januszewicz, A.; Järvinen, H.; Juhola, M.; et al. Early-onset renal cell carcinoma as a novel extraparaganglial component of SDHB-associated heritable paraganglioma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiano, A.; Chen, C.L.; Sung, Y.S.; Singer, S.; DeMatteo, R.P.; LaQuaglia, M.P.; Besmer, P.; Socci, N.; Antonescu, C.R. SDHA loss of function mutations in a subset of young adult wild-type gastrointestinal stromal tumors. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Seballos, S.; Ganapathi, S.; Gurin, D.; Fletcher, B.; Ngeow, J.; Nagy, R.; Kloos, R.T.; Ringel, M.D.; LaFramboise, T.; et al. Germline and somatic SDHx alterations in apparently sporadic differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galera-Ruiz, H.; Gonzalez-Campora, R.; Rey-Barrera, M.; Rollón-Mayordomo, A.; Garcia-Escudero, A.; Fernández-Santos, J.M.; DeMiguel, M.; Galera-Davidson, H. W43X SDHD mutation in sporadic head and neck paraganglioma. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 2008, 30, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schimke, R.N.; Collins, D.L.; Stolle, C.A. Paraganglioma, neuroblastoma, and a SDHB mutation: Resolution of a 30-year-old mystery. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, I.P.; Alam, N.A.; Rowan, A.J.; Barclay, E.; Jaeger, E.E.; Kelsell, D.; Leigh, I.; Gorman, P.; Lamlum, H.; Rahman, S.; et al. Germline mutations in FH predispose to dominantly inherited uterine fibroids, skin leiomyomata and papillary renal cell cancer. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal-Carmona, L.G.; Alam, N.A.; Pollard, P.J.; Jones, A.M.; Barclay, E.; Wortham, N.; Pignatelli, M.; Freeman, A.; Pomplun, S.; Ellis, I.; et al. Adult leydig cell tumors of the testis caused by germline fumarate hydratase mutations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3071–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoube, P.; Cutano, V.; González-Morena, J.M.; Keckesova, Z. Mitochondrial Tumor Suppressors-The Energetic Enemies of Tumor Progression. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 4652–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S. Enasidenib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsworthy, K.J.; Luo, L.; Hsu, V.; Gudi, R.; Dorff, S.E.; Przepiorka, D.; Deisseroth, A.; Shen, Y.L.; Sheth, C.M.; Charlab, R.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Ivosidenib for Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia with an Isocitrate Dehydrogenase-1 Mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3205–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C. Olutasidenib: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. FDA approves IDH1 and IDH2 inhibitor for brain cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Sun, F.; Li, C.; Nan, P.; Song, Y.; Wan, X.; Mo, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Y.; et al. MTA1, a Novel ATP Synthase Complex Modulator, Enhances Colon Cancer Liver Metastasis by Driving Mitochondrial Metabolism Reprogramming. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoerger, B.; Schiff, M.; Penard-Lacronique, V.; Darin, N.; Saad, S.M.; Duchon, C.; Lamazière, A.; Desmons, A.; Pontoizeau, C.; Berlanga, P.; et al. Enasidenib treatment in two individuals with D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria carrying a germline IDH2 mutation. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xia, Y.K.; Li, C.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Yi, W.; Qin, Z.Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, Z.F.; Quan, K.; et al. Rapid diagnosis of IDH1-mutated gliomas by 2-HG detection with gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.M. Enasidenib, a targeted inhibitor of mutant IDH2 proteins for treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, A.; Norsworthy, K.J.; Wang, X.; Vallejo, J.; Chiu Yuen Chow, E.; Li, R.J.; Sun, J.; Charlab, R.; Jiang, X.; Pazdur, R.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Ivosidenib in Combination with Azacitidine for Treatment of Patients with Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia with an IDH1 Mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uson Junior, P.L.S.; Borad, M.J. Clinical Utility of Ivosidenib in the Treatment of IDH1-Mutant Cholangiocarcinoma: Evidence To Date. Cancer Manag. Res. 2023, 15, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E. Olutasidenib: A novel mutant IDH1 inhibitor for the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Expert. Rev. Hematol. 2024, 17, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennicke, C.; Cochemé, H.M. Redox metabolism: ROS as specific molecular regulators of cell signaling and function. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3691–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.B. Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Giménez, J.L.; Pallardó, F.V. Maintenance of glutathione levels and its importance in epigenetic regulation. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichmann, D.; Voth, W.; Jakob, U. Maintaining a Healthy Proteome during Oxidative Stress. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Gutierrez, C.; Bonora, N.; Bobo-Jimenez, V.; Jimenez-Blasco, D.; Lopez-Fabuel, I.; Fernandez, E.; Josephine, C.; Bonvento, G.; Enriquez, J.A.; Almeida, A.; et al. Astrocytic mitochondrial ROS modulate brain metabolism and mouse behaviour. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scialò, F.; Fernández-Ayala, D.J.; Sanz, A. Role of Mitochondrial Reverse Electron Transport in ROS Signaling: Potential Roles in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Boiti, A.; Vallone, D.; Foulkes, N.S. Reactive Oxygen Species Signaling and Oxidative Stress: Transcriptional Regulation and Evolution. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onukwufor, J.O.; Berry, B.J.; Wojtovich, A.P. Physiologic Implications of Reactive Oxygen Species Production by Mitochondrial Complex I Reverse Electron Transport. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldon, S.; Fernández-Vizarra, E.; Tokatlidis, K. Redox-Mediated Regulation of Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Dynamics, and Respiratory Chain Assembly in Yeast and Human Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 720656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, L.; Riemer, J. Maintenance of small molecule redox homeostasis in mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 2023, 597, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Wang, D.; Zhou, M.; Bae, J.H.; Yu, Y.; Xin, H.; Mirkin, M.V. Ultrasensitive Detection of Dopamine with Carbon Nanopipets. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12935–12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Gong, L.; Qi, R.; Qing, W.; Zou, M.; Ke, Q.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Nie, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. Oxidative stress-induced KLF4 activates inflammatory response through IL17RA and its downstream targets in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 147, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Wang, M.; Zhou, W.; Mao, M.X.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, N.; Peng, X.C.; Cai, J.; Cai, Z.Q. ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Biology, diagnostics, therapeutics and resistance. J. Drug Target. 2022, 30, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, F.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Ma, T.; Feng, J. Novel insights into molecular patterns of ROS1 fusions in a large Chinese NSCLC cohort: A multicenter study. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 2200–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Aredo, J.V.; Feng, J.; Shepherd, F.; Xu, C.; Kaldas, D.; Gray, J.E.; Dilling, T.J.; Neal, J.W.; et al. Consolidation Osimertinib Versus Durvalumab Versus Observation After Concurrent Chemoradiation in Unresectable EGFR-Mutant NSCLC: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, M.; Wufuer, R.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Nrf1 is an indispensable redox-determining factor for mitochondrial homeostasis by integrating multi-hierarchical regulatory networks. Redox Biol. 2022, 57, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellanti, F.; Mangieri, D.; di Bello, G.; Lo Buglio, A.; Pannone, G.; Pedicillo, M.C.; Fersini, A.; Dobrakowski, M.; Kasperczyk, A.; Kasperczyk, S.; et al. Redox-Dependent Modulation of Human Liver Progenitor Cell Line Fate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.W.; Leggett, A.; Bruschweiler-Li, L.; Brüschweiler, R. COLMARq: A Web Server for 2D NMR Peak Picking and Quantitative Comparative Analysis of Cohorts of Metabolomics Samples. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8674–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Deja, S.; Kucejova, B.; Duarte, J.A.G.; McDonald, J.G.; Burgess, S.C. Targeted Determination of Tissue Energy Status by LC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5881–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Bermúdez, A.; Laza-Briviesca, R.; Vicente-Blanco, R.J.; García-Grande, A.; Coronado, M.J.; Laine-Menéndez, S.; Palacios-Zambrano, S.; Moreno-Villa, M.R.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas, A.M.; Lendinez, C.; et al. Cisplatin resistance involves a metabolic reprogramming through ROS and PGC-1α in NSCLC which can be overcome by OXPHOS inhibition. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 135, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleih, M.; Böpple, K.; Dong, M.; Gaißler, A.; Heine, S.; Olayioye, M.A.; Aulitzky, W.E.; Essmann, F. Direct impact of cisplatin on mitochondria induces ROS production that dictates cell fate of ovarian cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnalagu, D.; Singh, H. Anion Channels of Mitochondria. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 240, 71–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.; Costa, R.; Peruzzo, R.; Prosdocimi, E.; Checchetto, V.; Leanza, L. Targeting Mitochondrial Ion Channels to Fight Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; An, P.; Gu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J. Mitochondrial Metal Ion Transport in Cell Metabolism and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Pizzo, P.; Filadi, R. Calcium, mitochondria and cell metabolism: A functional triangle in bioenergetics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, C.; Marchi, S.; Pinton, P. The machineries, regulation and cellular functions of mitochondrial calcium. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alevriadou, B.R.; Patel, A.; Noble, M.; Ghosh, S.; Gohil, V.M.; Stathopulos, P.B.; Madesh, M. Molecular nature and physiological role of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter channel. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C465–C482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, I.; Szewczyk, A. Mitochondrial Ion Channels. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2023, 52, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbincius, J.F.; Elrod, J.W. Mitochondrial calcium exchange in physiology and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 893–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.X.; Cui, S.M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Ren, J. Mitochondrial Ca2+ regulation in the etiology of heart failure: Physiological and pathophysiological implications. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioretti, C.; Zanetti, G.; Pirazzini, M.; Gherardi, G.; Nogara, L.; Andreotti, R.; Martini, P.; Marcucci, L.; Canato, M.; Nath, S.R.; et al. Defective excitation-contraction coupling and mitochondrial respiration precede mitochondrial Ca2+ accumulation in spinobulbar muscular atrophy skeletal muscle. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadiya, P.; Kolmetzky, D.W.; Tomar, D.; Di Meco, A.; Lombardi, A.A.; Lambert, J.P.; Luongo, T.S.; Ludtmann, M.H.; Praticò, D.; Elrod, J.W. Impaired mitochondrial calcium efflux contributes to disease progression in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Lan, C.; Wu, L.; Sun, D.; Huang, C.; et al. Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter Drives Metastasis and Confers a Targetable Cystine Dependency in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2254–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, K.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, H.; Yao, J.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. The mitochondrial calcium uniporter engages UCP1 to form a thermoporter that promotes thermogenesis. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Si, W.; Xia, L.; Yin, D.; Wei, T.; Tao, M.; Cui, X.; Yang, J.; Hong, T.; Wei, R. Positive feedback regulation between glycolysis and histone lactylation drives oncogenesis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tan, R.; Zhao, J.; Ji, X.; Jin, C.; Jia, Y.; Ren, T.; et al. MCU-induced mitochondrial calcium uptake promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and colorectal cancer growth. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, F.; Gao, Y.; Pang, Y.; Xie, C.; Jiang, C. An Integrated LC-MS/MS Strategy for Quantifying the Oxidative-Redox Metabolome in Multiple Biological Samples. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8810–8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Yonemura, A.; Yasuda-Yoshihara, N.; Umemoto, T.; Zhang, J.; Yasuda, T.; Uchihara, T.; Akiyama, T.; Kitamura, F.; Yamashita, K.; et al. Intracellular MUC20 variant 2 maintains mitochondrial calcium homeostasis and enhances drug resistance in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2022, 25, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, I.; Trentin, L.; Trimarco, V.; Semenzato, G.; Leanza, L. Biophysical characterization and expression analysis of Kv1.3 potassium channel in primary human leukemic B cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severin, F.; Urbani, A.; Varanita, T.; Bachmann, M.; Azzolini, M.; Martini, V.; Pizzi, M.; Tos, A.P.D.; Frezzato, F.; Mattarei, A.; et al. Pharmacological modulation of Kv1.3 potassium channel selectively triggers pathological B lymphocyte apoptosis in vivo in a genetic CLL model. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulk, E.; Todesca, L.M.; Bachmann, M.; Szabo, I.; Rieke, M.; Schwab, A. Functional expression of mitochondrial KCa3.1 channels in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Pflug. Arch. 2022, 474, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, F.; Hundehege, P.; Bulk, E.; Todesca, L.M.; Schimmelpfennig, S.; Nass, E.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Schwab, A. KCa channel blockers increase effectiveness of the EGF receptor TK inhibitor erlotinib in non-small cell lung cancer cells (A549). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Xie, E.; Xu, H.; Cheng, H.; Li, G. One-carbon metabolism shapes T cell immunity in cancer. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbetts, A.S.; Appling, D.R. Compartmentalization of Mammalian folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 30, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, B.; Maynard, A.G.; Wang, P.; Kanarek, N. Regulatory mechanisms of one-carbon metabolism enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kuno, S.; Ota, T.; Mochidome, K.; Saito, Y.; Sugihara, F.; Takakusagi, Y.; Aoki, I.; Nagatoishi, S.; et al. Design strategy for serine hydroxymethyltransferase probes based on retro-aldol-type reaction. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, R.; Nicolaidou, V.; Koufaris, C. Mitochondrial MTHFD isozymes display distinct expression, regulation, and association with cancer. Gene 2019, 716, 144032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, T.; Gao, B.; Mackowiak, B. Alcohol metabolism in alcohol use disorder: A potential therapeutic. Alcohol Alcohol. 2024, 59, agad077, Erratum in Alcohol Alcohol. 2024, 59, agae064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Unveiling the oncogenic significance of thymidylate synthase in human cancers. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2024, 16, 5228–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abali, E.E.; Skacel, N.E.; Celikkaya, H.; Hsieh, Y.C. Regulation of human dihydrofolate reductase activity and expression. Vitam. Horm. 2008, 79, 267–292. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; He, Z.; Jin, G.; Jin, S.; Du, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, J. Targeting DNA methyltransferases for cancer therapy. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 151, 107652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, R.; Jain, M.; Madhusudhan, N.; Sheppard, N.G.; Strittmatter, L.; Kampf, C.; Huang, J.; Asplund, A.; Mootha, V.K. Metabolic enzyme expression highlights a key role for MTHFD2 and the mitochondrial folate pathway in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, M.; Kami, K. Cancer. Systems biology, metabolomics, and cancer metabolism. Science 2012, 336, 990–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; He, C.; Tao, L.; He, X.; Song, H.; Zhang, G. Increased MTHFD2 expression is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Tumour. Biol. 2014, 35, 8685–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Q.Q.; Wu, Q.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.J.; Fu, J.K.; Chen, N.Z. Clinical significance of circ-MTHFD2 in diagnosis, pathological staging and prognosis of NSCLC. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 9473–9479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Huang, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Hong, Y.; Qiu, S.; Zheng, J. MTHFD2 Overexpression Predicts Poor Prognosis in Renal Cell Carcinoma and is Associated with Cell Proliferation and Vimentin-Modulated Migration and Invasion. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ou, H.; Guo, B.; Liao, H.; Li, X.; Yang, D. Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2 overexpression is associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Li, P.C.; Jia, W.; Hu, B.; Ji, C.S. High Expression of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase 2 (MTHFD2) in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and its Clinical Prognostic Significance. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e920259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Su, H.; Yang, J.; Wu, X.; Huo, K.; Jing, X.; Zhang, S. Up-regulation of MTHFD2 is associated with clinicopathological characteristics and poor survival in ovarian cancer, possibly by regulating MOB1A signaling. J. Ovarian Res. 2022, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyo, M.; Konno, M.; Colvin, H.; Nishida, N.; Koseki, J.; Kawamoto, K.; Tsunekuni, K.; Nishimura, J.; Hata, T.; Takemasa, I.; et al. The importance of mitochondrial folate enzymes in human colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.J.; Tsai, E.M.; Hou, M.F.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, T.N. Global untargeted and individual targeted plasma metabolomics of breast cancer recurrence modified by hormone receptors. Breast Cancer. 2024, 31, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machover, D.; Almohamad, W.; Castagné, V.; Desterke, C.; Gomez, L.; Gaston-Mathé, Y.; Boucheix, C.; Goldschmidt, E. Pharmacologic modulation of 5-fluorouracil by folinic acid and high-dose pyridoxine for treatment of patients with digestive tract carcinomas. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machover, D.; Goldschmidt, E.; Almohamad, W.; Castagné, V.; Dairou, J.; Desterke, C.; Gomez, L.; Gaston-Mathé, Y.; Boucheix, C. Pharmacologic modulation of 5-fluorouracil by folinic acid and pyridoxine for treatment of patients with advanced breast carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.M.; Danenberg, P.V.; Johnston, P.G.; Lenz, H.J.; Ladner, R.D. Standing the test of time: Targeting thymidylate biosynthesis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, R.; Rathee, P.; Khatkar, S.; Akkol, E.; Khayatkashani, M.; Nabavi, S.M.; Khatkar, A. Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR) Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 31, 799–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, H.Q.; Liu, F. DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors and their Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikalov, S.; Panov, A.; Dikalova, A. Critical Role of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Metabolism in Normal Cell Function and Pathological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, C.; Caramujo, M.J. The Various Roles of Fatty Acids. Molecules 2018, 23, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Zheng, L.F.; Li, P.; Zhao, T.J. Context-specific fatty acid uptake is a finely-tuned multi-level effort. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 36, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althaher, A.R. An Overview of Hormone-Sensitive Lipase (HSL). Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 1964684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, G.F.; Xie, H.; Schweiger, M.; Zechner, R. Lipolysis: Cellular mechanisms for lipid mobilization from fat stores. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1445–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günenc, A.N.; Graf, B.; Stark, H.; Chari, A. Fatty Acid Synthase: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Subcell. Biochem. 2022, 99, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wedan, R.J.; Longenecker, J.Z.; Nowinski, S.M. Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis is an emergent central regulator of mammalian oxidative metabolism. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Sun, W.; Balaz, M.; He, A.; Klug, M.; Wieland, S.; Caiazzo, R.; Raverdy, V.; Pattou, F.; Lefebvre, P.; et al. Peroxisomal β-oxidation acts as a sensor for intracellular fatty acids and regulates lipolysis. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1648–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Shen, Y.; Wang, C.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, D.; Wu, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation as the target for blocking therapy-resistance and inhibiting tumor recurrence: The proof-of-principle model demonstrated for ovarian cancer cells. J. Adv. Res. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Quanico, J.; Hauberg-Lotte, L.; Devaux, S.; Laouby, Z.; Meriaux, C.; Raffo-Romero, A.; Rose, M.; Westerheide, L.; Vehmeyer, J.; Rodet, F.; et al. 3D MALDI mass spectrometry imaging reveals specific localization of long-chain acylcarnitines within a 10-day time window of spinal cord injury. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desousa, B.R.; Kim, K.K.; Jones, A.E.; Ball, A.B.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Swain, P.; Morrow, D.H.; Brownstein, A.J.; Ferrick, D.A.; Shirihai, O.S.; et al. Calculation of ATP production rates using the Seahorse XF Analyzer. EMBO Rep. 2023, 24, e56380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drover, V.A.; Nguyen, D.V.; Bastie, C.C.; Darlington, Y.F.; Abumrad, N.A.; Pessin, J.E.; London, E.; Sahoo, D.; Phillips, M.C. CD36 mediates both cellular uptake of very long chain fatty acids and their intestinal absorption in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13108–13115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisiger, R.A. Mechanisms of intracellular fatty acid transport: Role of cytoplasmic-binding proteins. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2007, 33, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.W.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Sun, H.H.; Li, Y.F.; Lai, X.Y.; Zhao, N.; Wang, X.; Xie, C.; et al. CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation-regulated endocytosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, J.J.; Hellmich, C.; Moore, J.A.; Jibril, A.; Macaulay, I.; Moreno-Gonzalez, M.; Di Palma, F.; Beraza, N.; Bowles, K.M.; Rushworth, S.A. Free fatty-acid transport via CD36 drives β-oxidation-mediated hematopoietic stem cell response to infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhong, S.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, P.; Tang, R.; et al. CD36 palmitoylation disrupts free fatty acid metabolism and promotes tissue inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, P.; González-Rodríguez, Á.; García-Monzón, C.; Valverde, Á.M. Understanding lipotoxicity in NAFLD pathogenesis: Is CD36 a key driver? Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladanyi, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Kenny, H.A.; Johnson, A.; Mitra, A.K.; Sundaresan, S.; Nieman, K.M.; Pascual, G.; Benitah, S.A.; Montag, A.; et al. Adipocyte-induced CD36 expression drives ovarian cancer progression and metastasis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2285–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Meng, Y.; Song, H. CD36: An emerging therapeutic target for cancer and its molecular mechanisms. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recazens, E.; Mouisel, E.; Langin, D. Hormone-sensitive lipase: Sixty years later. Prog. Lipid Res. 2021, 82, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnotta, P.; Gantov, M.; Fletcher, S.; Lombardi, A.; Crosbie, M.L.; Santiso, N.; Ursino, A.; Frascarolli, C.; Amato, A.; Dreszman, R.; et al. Peritumoral adipose tissue promotes lipolysis and white adipocytes browning by paracrine action. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1144016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Song, N.Y.; Yim, H. Targeting dysregulated lipid metabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2023, 46, 855–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, Q.; Li, X. Acetyl-CoA regulates lipid metabolism and histone acetylation modification in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beld, J.; Lee, D.J.; Burkart, M.D. Fatty acid biosynthesis revisited: Structure elucidation and metabolic engineering. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, T. Recent development in acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors and their potential as novel drugs. Future Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 533–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozolewska, P.; Duzowska, K.; Pakiet, A.; Mika, A.; ŚledziŃski, T. Inhibitors of Fatty Acid Synthesis and Oxidation as Potential Anticancer Agents in Colorectal Cancer Treatment. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 4843–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, S.; Ou, K. Metabolic reprogramming of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1195500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koundouros, N.; Poulogiannis, G. Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Nenkov, M.; Chen, Y.; Press, A.T.; Kaemmerer, E.; Gassler, N. Fatty acid metabolism and acyl-CoA synthetases in the liver-gut axis. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1512–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Bode, A.M.; Luo, X. ACSL family: The regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic implications in cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 909, 174397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi Sebastiano, M.; Konstantinidou, G. Targeting Long Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetases for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanders, R.J.A.; Vaz, F.M.; Waterham, H.R.; Ferdinandusse, S. Fatty Acid Oxidation in Peroxisomes: Enzymology, Metabolic Crosstalk with Other Organelles and Peroxisomal Disorders. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1299, 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hama, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hayama, T.; Ozawa, T.; Nozawa, K.; Matsuda, K.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Yokoyama, K. Very long-chain fatty acids are accumulated in triacylglycerol and nonesterified forms in colorectal cancer tissues. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, G.; Majem, B.; Benitah, S.A. Targeting lipid metabolism in cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.; Jiang, C.H.; Li, N. Altered metabolism in cancer: Insights into energy pathways and therapeutic targets. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiliro, C.; Firestein, B.L. Mechanisms of Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer Cells Supporting Enhanced Growth and Proliferation. Cells 2021, 10, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.N.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ru, J.N.; Lu, J.H.; Ding, B.; Wu, J. Amino acid metabolism in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Lu, S.; Xu, S. Amino acid metabolism in tumor biology and therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.H.; Coloff, J.L. The Diverse Functions of Non-Essential Amino Acids in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.J.; Mohiuddin, S.S. Biochemistry, Essential Amino Acids. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, H.C.; Yu, Y.C.; Sung, Y.; Han, J.M. Glutamine reliance in cell metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1496–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Byun, J.K.; Choi, Y.K.; Park, K.G. Targeting glutamine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Kim, E.S.; Koo, J.S. Amino Acid Transporters and Glutamine Metabolism in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sniegowski, T.; Korac, K.; Bhutia, Y.D.; Ganapathy, V. SLC6A14 and SLC38A5 Drive the Glutaminolysis and Serine-Glycine-One-Carbon Pathways in Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyton, K.J.; Liu, X.M.; Yu, Y.; Yates, B.; Behnammanesh, G.; Durante, W. Glutaminase-1 stimulates the proliferation, migration, and survival of human endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 156, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, D.; Son, J.; Hong, K.M.; Song, J.; Kim, S.Y. Dual targeting of glutaminase 1 and thymidylate synthase elicits death synergistically in NSCLC. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, E.H.; Dahabieh, M.S.; DeCamp, L.M.; Kaymak, I.; Kitchen-Goosen, S.M.; Oswald, B.M.; Longo, J.; Roy, D.G.; Verway, M.J.; Johnson, R.M.; et al. 13C metabolite tracing reveals glutamine and acetate as critical in vivo fuels for CD8 T cells. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadj1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Kirk, K.; Shurubor, Y.I.; Zhao, D.; Arreguin, A.J.; Shahi, I.; Valsecchi, F.; Primiano, G.; Calder, E.L.; Carelli, V.; et al. Rewiring of Glutamine Metabolism Is a Bioenergetic Adaptation of Human Cells with Mitochondrial DNA Mutations. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1007–1025.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Tian, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, S.; Zhou, M.; Wu, L.; et al. Gankyrin drives metabolic reprogramming to promote tumorigenesis, metastasis and drug resistance through activating β-catenin/c-Myc signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 443, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, S.; Zaal, E.A.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Bosma, A.; Jochems, F.; Isima, N.; Jin, G.; Lieftink, C.; et al. A powerful drug combination strategy targeting glutamine addiction for the treatment of human liver cancer. eLife 2020, 9, e56749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.N.; Ngwa, V.M.; Raybuck, A.L.; Wang, S.; Hwang, Y.; Kim, L.C.; Cho, S.H.; Paik, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; et al. Selective glutamine metabolism inhibition in tumor cells improves antitumor T lymphocyte activity in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e140100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Pathria, G.; Heynen-Genel, S.; Jackson, M.; James, B.; Yin, J.; Scott, D.A.; Ronai, Z.A. Identification and Characterization of IMD-0354 as a Glutamine Carrier Protein Inhibitor in Melanoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 816–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Heuvel, A.P.; Jing, J.; Wooster, R.F.; Bachman, K.E. Analysis of glutamine dependency in non-small cell lung cancer: GLS1 splice variant GAC is essential for cancer cell growth. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2012, 13, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, M.; Oshikawa, K.; Shimizu, H.; Yoshioka, S.; Takahashi, M.; Izumi, Y.; Bamba, T.; Tateishi, C.; Tomonaga, T.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. A shift in glutamine nitrogen metabolism contributes to the malignant progression of cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Hui, S.; Ghergurovich, J.M.; Fan, J.; Intlekofer, A.M.; White, R.M.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Thompson, C.B.; Zhang, J. As Extracellular Glutamine Levels Decline, Asparagine Becomes an Essential Amino Acid. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 428–438.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajaj, E.; Sciacovelli, M.; Frezza, C.; Erez, A. The context-specific roles of urea cycle enzymes in tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3749–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radadiya, A.; Zhu, W.; Coricello, A.; Alcaro, S.; Richards, N.G.J. Improving the Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 3193–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Sakai, K.; Hirano, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Hattori, A.; Dohmae, N.; Nishio, K.; Kakeya, H. Bisabosqual A: A novel asparagine synthetase inhibitor suppressing the proliferation and migration of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 960, 176156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, K.; Kawada, K.; Nishikawa, G.; Toda, K.; Maekawa, H.; Nishikawa, Y.; Masui, H.; Hirata, W.; Okamoto, M.; Kiyasu, Y.; et al. Dual blockade of macropinocytosis and asparagine bioavailability shows synergistic anti-tumor effects on KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 522, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, S.R.V.; Wagenblast, E.; Khan, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Soto, M.; Wagner, M.; Turgeon, M.O.; Fish, L.; Erard, N.; Gable, A.L.; et al. Asparagine bioavailability governs metastasis in a model of breast cancer. Nature 2018, 554, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwinn, D.M.; Lee, A.G.; Briones-Martin-Del-Campo, M.; Conn, C.S.; Simpson, D.R.; Scott, A.I.; Le, A.; Cowan, T.M.; Ruggero, D.; Sweet-Cordero, E.A. Oncogenic KRAS Regulates Amino Acid Homeostasis and Asparagine Biosynthesis via ATF4 and Alters Sensitivity to L-Asparaginase. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 91–107.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Meininger, C.J.; McNeal, C.J.; Bazer, F.W.; Rhoads, J.M. Role of L-Arginine in Nitric Oxide Synthesis and Health in Humans. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1332, 167–187. [Google Scholar]
- You, S.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Q. Research progress on the role of cationic amino acid transporter (CAT) family members in malignant tumors and immune microenvironment. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closs, E.I.; Simon, A.; Vékony, N.; Rotmann, A. Plasma membrane transporters for arginine. J. Nutr. 2004, 134 (Suppl. S10), 2752S–2759S; discussion 2765S–2767S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.T.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Chi, K.K.; Chung, Y.; Ouyang, C.; Chen, Y.R.; Oh, M.E.; Sheng, X.; Tang, Y.; et al. Arginine starvation kills tumor cells through aspartate exhaustion and mitochondrial dysfunction. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunxi, W.; Xiaoxue, Y.; Guanbin, S.; Li, Y.; Junyu, J.; Wanqian, L. Serine Metabolic Reprogramming in Tumorigenesis, Tumor Immunity, and Clinical Treatment. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 1050–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.; Zubedat, S.; Radzishevsky, I.; Valenta, A.C.; Rechnitz, O.; Sason, H.; Sajrawi, C.; Bodner, O.; Konno, K.; Esaki, K.; et al. ASCT1 (Slc1a4) transporter is a physiologic regulator of brain d-serine and neurodevelopment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9628–9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conger, K.O.; Chidley, C.; Ozgurses, M.E.; Zhao, H.; Kim, Y.; Semina, S.E.; Burns, P.; Rawat, V.; Lietuvninkas, L.; Sheldon, R.; et al. ASCT2 is a major contributor to serine uptake in cancer cells. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, F.F.; Lewis, C.A.; Fiske, B.P.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Cellular redox state constrains serine synthesis and nucleotide production to impact cell proliferation. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrose, D.C.; Saha, S.; Foronda, M.; McNally, E.M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.K.; Ha, T.; Krumsiek, J.; Buyukozkan, M.; Verma, A.; et al. Exogenous and Endogenous Sources of Serine Contribute to Colon Cancer Metabolism, Growth, and Resistance to 5-Fluorouracil. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2275–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajan, M.; Hennequart, M.; Cheung, E.C.; Zani, F.; Hock, A.K.; Legrave, N.; Maddocks, O.D.K.; Ridgway, R.A.; Athineos, D.; Suárez-Bonnet, A.; et al. Serine synthesis pathway inhibition cooperates with dietary serine and glycine limitation for cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassone-Corsi, P. Physiology. When metabolism and epigenetics converge. Science 2013, 339, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.; Agostini, M.; Morello, M.; Minieri, M.; Melino, G.; Amelio, I. Bioinformatics analysis of the serine and glycine pathway in cancer cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11004–11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Yang, H.; Yang, R.; Chen, T.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; et al. The folate cycle enzyme MTHFD2 induces cancer immune evasion through PD-L1 up-regulation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.E.; Savouré, A.; Szabados, L. Proline metabolism as regulatory hub. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanaga, H.; Mackenzie, B.; Suzuki, Y.; Hediger, M.A. Identification of mammalian proline transporter SIT1 (SLC6A20) with characteristics of classical system imino. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 8974–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhu, S.; Lim, R.R.; Chao, J.R. Proline metabolism and transport in retinal health and disease. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 1789–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Shang, W.; Liu, Y.; Ji, J.F.; Liu, J.P.; Tong, C. Pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase senses cellular stress and modulates metabolism by regulating mitochondrial respiration. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.; Dela Cruz, D.; Gao, M.; Sandoval, W.; Haverty, P.M.; Liu, J.; Stephan, J.P.; Haley, B.; Classon, M.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; et al. Proline Starvation Induces Unresolved ER Stress and Hinders mTORC1-Dependent Tumorigenesis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipanuk, M.H. Metabolism of Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids: How the Body Copes with Excess Methionine, Cysteine, and Sulfide. J. Nutr. 2020, 150 (Suppl. S1), 2494s–2505s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, A.A.; Marshall, E.A.; Noonan, A.J.C.; Filho, F.S.L.; Yang, J.; Stewart, G.L.; Johnson, F.D.; Vucic, E.A.; Pewarchuk, M.E.; Shah, P.P.; et al. Methionine-producing tumor micro(be) environment fuels growth of solid tumors. Cell. Oncol. 2023, 46, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassinari, V.; Jia, W.; Chen, W.L.; Candi, E.; Melino, G. The methionine cycle and its cancer implications. Oncogene 2024, 43, 3483–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.M.; Stern, P.H.; Coalson, D.W.; Douglas Wallace, C.; Erbe, R.W. Altered Methionine Metabolism in Cancer Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1866, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, M.H.; Lee, J.S.; Ma, C.; Diggs, L.P.; Heinrich, S.; Chang, C.W.; Ma, L.; Forgues, M.; Budhu, A.; Chaisaingmongkol, J.; et al. Tumor methionine metabolism drives T-cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zuo, D.; Wang, J.; Tao, Y.; Li, Z.; He, X.; Meng, H.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; et al. Methionine intervention induces PD-L1 expression to enhance the immune checkpoint therapy response in MTAP-deleted osteosarcoma. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 101977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fan, T.W.M.; Brandon, J.A.; Lane, A.N.; Higashi, R.M. Rapid analysis of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) isotopologues in stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM) using direct infusion nanoelectrospray ultra-high-resolution Fourier transform mass spectrometry (DI-nESI-UHR-FTMS). Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1181, 338873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Han, Q.; Sugisawa, N.; Yamamoto, J.; Yamamoto, N.; Hayashi, K.; Kimura, H.; Miwa, S.; Igarashi, K.; Bouvet, M.; et al. Combination Methionine-methylation-axis Blockade: A Novel Approach to Target the Methionine Addiction of Cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2021, 18, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröer, S. Amino Acid Transporters as Targets for Cancer Therapy: Why, Where, When, and How. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Peng, H.F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.S. Comprehensive review of amino acid transporters as therapeutic targets. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260 Pt 2, 129646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.; van der Meer, L.T.; van Leeuwen, F.N. Amino Acid Depletion Therapies: Starving Cancer Cells to Death. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
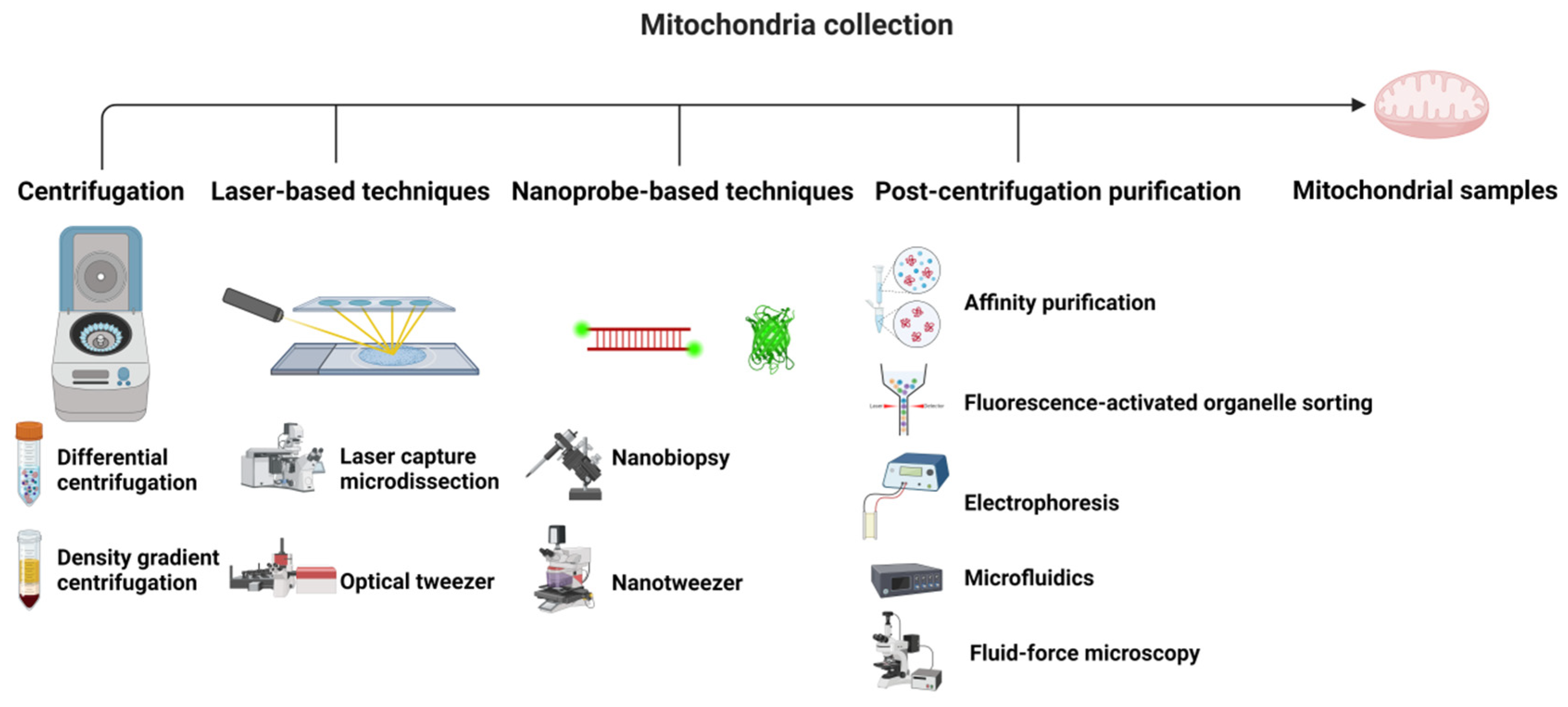
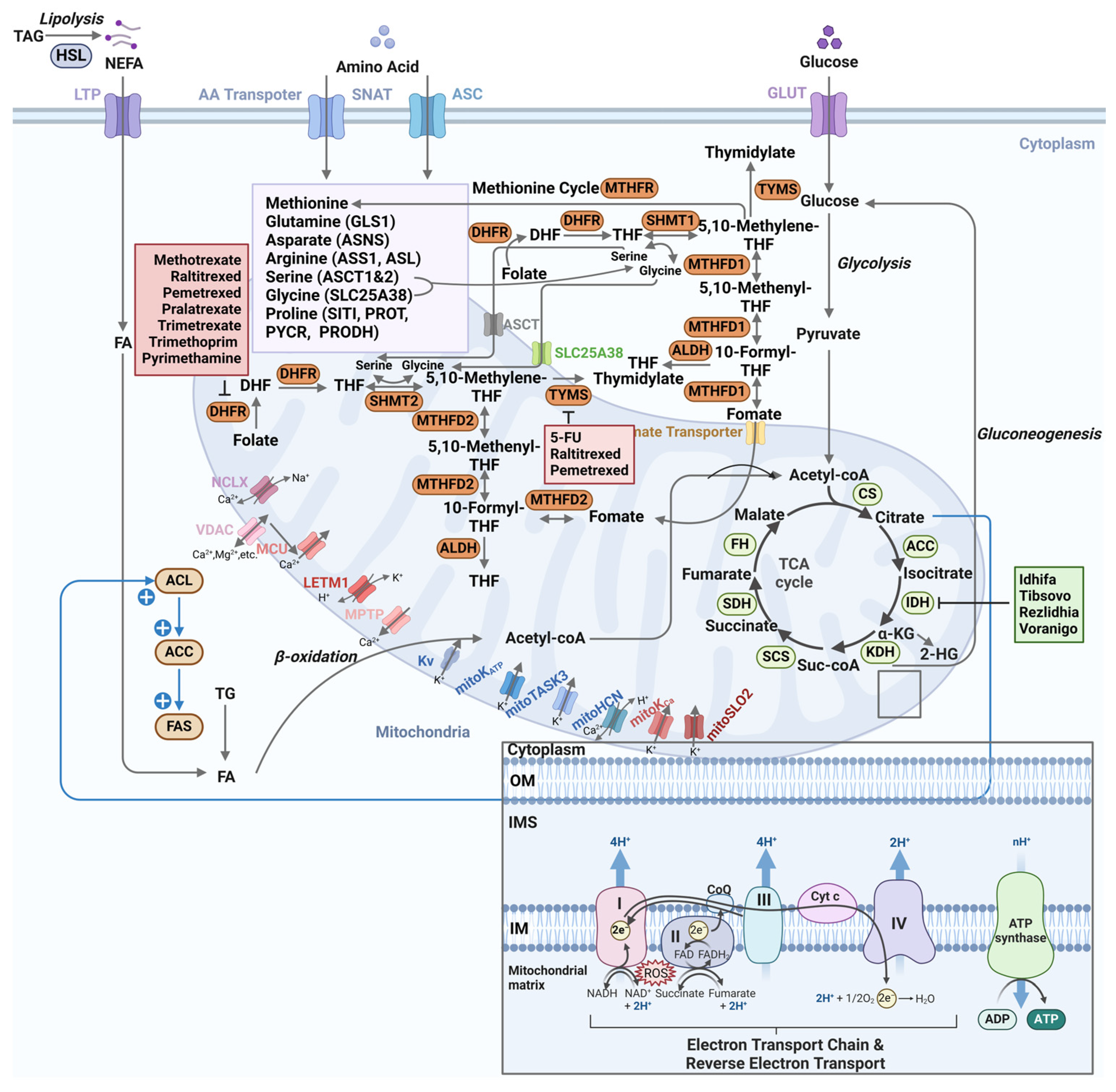
| Metabolite Class | Sample Preparation | Chromatography | Ionization | Key Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCA intermediates | Methanol/water (8:2) | HILIC (BEH Amide) | ESI(−) | Redox ratio (NAD+/NADH) | [82] |
| Amino acids | Methanol/water (9:1) | GC (DB-5MS) | EI | Isotopomer flux (U-13C-glutamine) | [91] |
| Cardiolipins | Chloroform/methanol (2:1) | RP-C18 | APCI(+) | Cristae membrane dynamics | [109] |
| Acylcarnitines | Acetonitrile precipitation | HILIC (ZIC-HILIC) | ESI(+) | β-oxidation disorders | [104] |
| Nucleotides | Perchloric acid (0.3 M) | Ion-pairing RP (C18) | ESI(−) | ATP/ADP energy charge | [106] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Wei, X. Mitochondrial Metabolomics in Cancer: Mass Spectrometry-Based Approaches for Metabolic Rewiring Analysis and Therapeutic Discovery. Metabolites 2025, 15, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080513
Gao Y, Xiong Z, Wei X. Mitochondrial Metabolomics in Cancer: Mass Spectrometry-Based Approaches for Metabolic Rewiring Analysis and Therapeutic Discovery. Metabolites. 2025; 15(8):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080513
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yuqing, Zhirou Xiong, and Xinyi Wei. 2025. "Mitochondrial Metabolomics in Cancer: Mass Spectrometry-Based Approaches for Metabolic Rewiring Analysis and Therapeutic Discovery" Metabolites 15, no. 8: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080513
APA StyleGao, Y., Xiong, Z., & Wei, X. (2025). Mitochondrial Metabolomics in Cancer: Mass Spectrometry-Based Approaches for Metabolic Rewiring Analysis and Therapeutic Discovery. Metabolites, 15(8), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080513






