Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: A Focus on Puberty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG)
3. SHBG Gene Expression
4. Ontogeny of SHBG Production
5. Hormonal and Metabolic Regulation of SHBG Production
6. Direct Effects of SHBG
7. SHBG, a Biomarker of Metabolic Disease in Children and Adolescents
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, R.; Dziura, J.; Burgert, T.S.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Taksali, S.E.; Yeckel, C.W.; Allen, K.; Lopes, M.; Savoye, M.; Morrison, J.; et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2362–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.A.; Friedman, L.A.; Wang, P.; Glueck, C.J. Metabolic syndrome in childhood predicts adult metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus 25 to 30 years later. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, B.; Winters, S.J. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin in Children and Adolescents. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2016, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, W.; Hryb, D.J.; Khan, M.S.; Nakhla, A.M.; Romas, N.A. Sex hormone-binding globulin: Anatomy and physiology of a new regulatory system. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1991, 40, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, G.L. Plasma steroid-binding proteins: Primary gatekeepers of steroid hormone action. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, R13–R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.F.; Nisula, B.C.; Rodbard, D. Transport of steroid hormones: Binding of 21 endogenous steroids to both testosterone-binding globulin and corticosteroid-binding globulin in human plasma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1981, 53, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, D.M.; Hogeveen, K.N.; Innis, S.M.; Hammond, G.L. Monosaccharide-induced lipogenesis regulates the human hepatic sex hormone–binding globulin gene. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3979–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
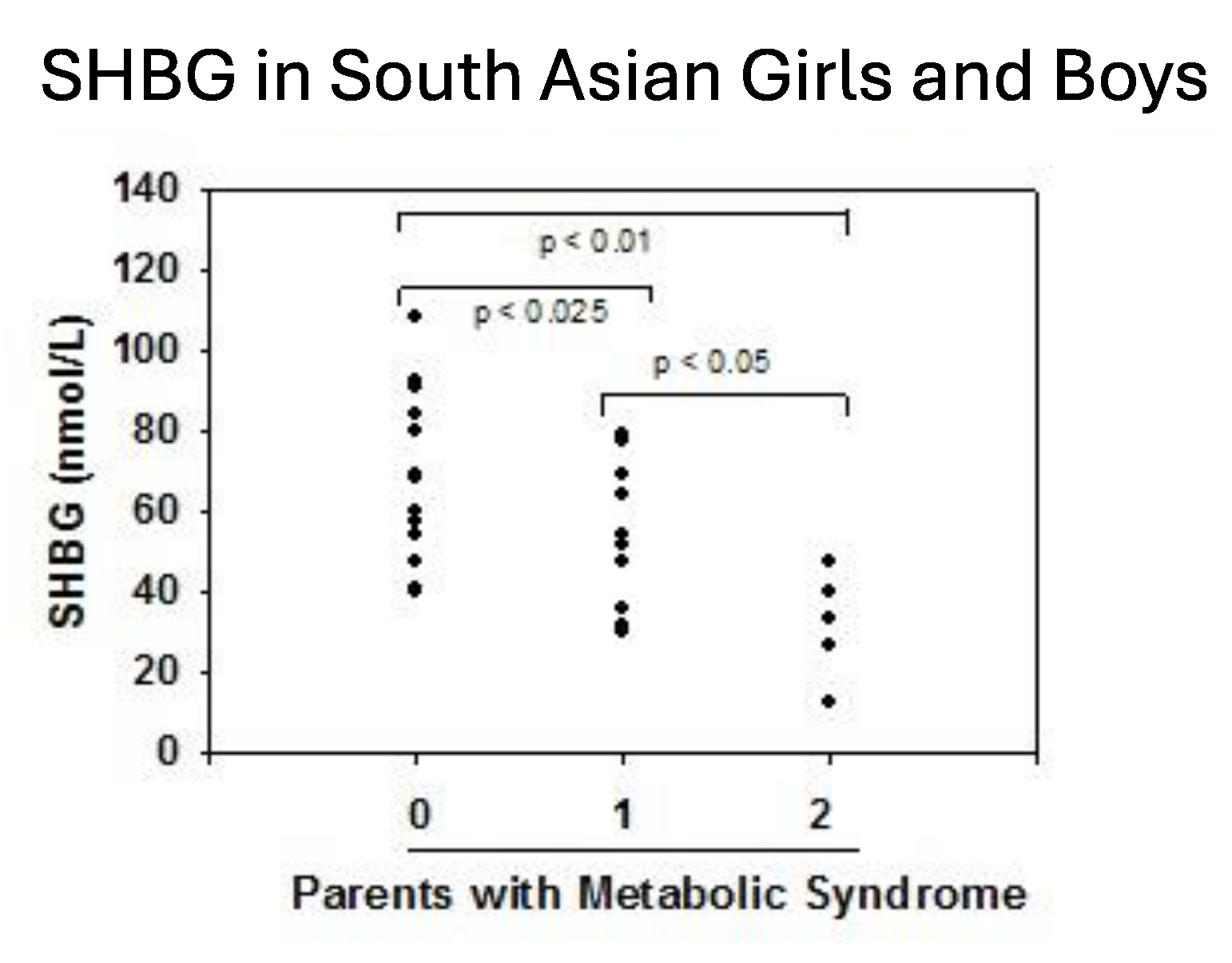
- Krishnasamy, S.S.; Chang, C.; Wang, C.; Chandiramani, R.; Winters, S.J. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and The Risk for Metabolic Syndrome in Children of South Asian Indian Origin. Endocr. Pract. 2012, 18, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oya, I.; Schoppen, S.; Lasunción, M.A.; Lopez-Simón, L.; Riestra, P.; de Oya, M.; Garcés, C. Sex hormone-binding globulin levels and metabolic syndrome and its features in adolescents. Pediatr. Diabetes 2010, 11, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano, F.; Chiarito, M.; Lattanzio, C.; Messa, A.; Ferrante, M.; Francavilla, M.; Mehmeti, I.; Lassandro, G.; Giordano, P.; Faienza, M.F. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG) Reduction: The Alarm Bell for the Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Adolescents with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Children 2022, 9, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Lopez, C.; Barbosa-Desongles, A.; Hernandez, C.; Dyer, R.A.; Innis, S.M.; Simó, R.; Selva, D.M. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Reduction in Metabolic Disorders May Play a Role in NAFLD Development. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, B.K.; Stenlid, R.; Ciba, I.; Cerenius, S.Y.; Dahlbom, M.; Bergsten, P.; Nergårdh, R.; Forslund, A. High levels of FSH before puberty are associated with increased risk of metabolic syndrome during pubertal transition. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogol, A.D.; Roemmich, J.N.; Clark, P.A. Growth at puberty. J. Adolesc. Health Off. Publ. Soc. Adolesc. Med. 2002, 31 (Suppl. S6), 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brufani, C.; Tozzi, A.; Fintini, D.; Ciampalini, P.; Grossi, A.; Fiori, R.; Kiepe, D.; Manco, M.; Schiaffini, R.; Porzio, O.; et al. Sexual dimorphism of body composition and insulin sensitivity across pubertal development in obese Caucasian subjects. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasik, C.B.; Lustig, R.H. Adolescent obesity and puberty: The “perfect storm”. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008, 1135, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, G.L.; Underhill, D.A.; Smith, C.L.; Goping, I.S.; Harley, M.J.; Musto, N.A.; Cheng, C.Y.; Bardin, C.W. The cDNA-deduced primary structure of human sex hormone-binding globulin and location of its steroid-binding domain. FEBS Lett. 1987, 215, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avvakumov, G.V.; Muller, Y.A.; Hammond, G.L. Steroid-binding specificity of human sex hormone-binding globulin is influenced by occupancy of a zinc-binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25920–25925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, D.R. Structure, function, and regulation of androgen-binding protein/sex hormone-binding globulin. Vitam. Horm. 1994, 49, 197–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, D.M.; Hammond, G.L. Human sex hormone-binding globulin is expressed in testicular germ cells and not in sertoli cells. Horm. Metab. Res. Horm. Stoffwechselforschung Horm. Metab. 2006, 38, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhla, A.M.; Hryb, D.J.; Rosner, W.; Romas, N.A.; Xiang, Z.; Kahn, S.M. Human sex hormone-binding globulin gene expression- multiple promoters and complex alternative splicing. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, A.; Kaufman, J.M.; Giagulli, V.A. Influence of some biological indexes on sex hormone-binding globulin and androgen levels in aging or obese males. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 1821–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Winters, S.J. SHBG and total testosterone levels in men with adult onset hypogonadism: What are we overlooking? Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ronde, W.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Pierik, F.H.; Pols, H.A.P.; Muller, M.; Grobbee, D.E.; Gooren, L.J.G.; Weber, R.F.A.; de Jong, F.H. Serum levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) are not associated with lower levels of non-SHBG-bound testosterone in male newborns and healthy adult men. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 62, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, G.L.; Bocchinfuso, W.P. Sex hormone-binding globulin: Gene organization and structure/function analyses. Horm. Res. 1996, 45, 97–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogeveen, K.N.; Cousin, P.; Pugeat, M.; Dewailly, D.; Soudan, B.; Hammond, G.L. Human sex hormone-binding globulin variants associated with hyperandrogenism and ovarian dysfunction. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, M.J.; Mijnhout, G.S.; Rondeel, J.M.M.; Baron, W.; Groeneveld, P.H.P. Sex hormone binding globulin deficiency due to a homozygous missense mutation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1798–E1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriessen, V.C.; Lightbourne, M.; Flippo, C.; Faucz, F.R.; Delaney, A.; Hannah-Shmouni, F.; Hammond, G.L.; Stratakis, C.A. Homozygous SHBG Variant (rs6258) Linked to Gonadotropin-Independent Precocious Puberty in a Young Girl. J. Endocr. Soc. 2021, 5, bvab125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, C.; Wallaschofski, H.; Lunetta, K.L.; Stolk, L.; Perry, J.R.B.; Koster, A.; Petersen, A.K.; Eriksson, J.; Lehtimäki, T.; Huhtaniemi, I.T.; et al. Genetic determinants of serum testosterone concentrations in men. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.S.; Hammond, G.L. Naturally occurring mutants inform SHBG structure and function. Mol. Endocrinol. Baltim. Md. 2014, 28, 1026–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walravens, J.; Sleumer, B.; Vos, M.J.; Snaterse, G.; Narinx, N.; Antonio, L.; Reyns, T.; Fiers, T.; Kema, I.P.; Kaufman, J.-M.; et al. SHBG Gene Polymorphisms and Their Influence on Serum SHBG, Total and Free Testosterone Concentrations in Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, e641–e649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, S.G.; Bocchinfuso, W.P.; Pallesen, M.; Warmels-Rodenhiser, S.; Van Baelen, H.; Hammond, G.L. Molecular analyses of a human sex hormone-binding globulin variant: Evidence for an additional carbohydrate chain. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 75, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, P.; Déchaud, H.; Grenot, C.; Lejeune, H.; Pugeat, M. Human variant sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) with an additional carbohydrate chain has a reduced clearance rate in rabbit. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, E.L.; Song, Y.; Manson, J.E.; Hunter, D.J.; Lee, C.C.; Rifai, N.; Buring, J.E.; Gaziano, J.M.; Liu, S. Sex hormone-binding globulin and risk of type 2 diabetes in women and men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.R.B.; Weedon, M.N.; Langenberg, C.; Jackson, A.U.; Lyssenko, V.; Sparsø, T.; Thorleifsson, G.; Grallert, H.; Ferrucci, L.; Maggio, M.; et al. Genetic evidence that raised sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) levels reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, A.L.; Lorentzon, M.; Mellström, D.; Vandenput, L.; Swanson, C.; Andersson, N.; Hammond, G.L.; Jakobsson, J.; Rane, A.; Orwoll, E.S.; et al. SHBG gene promoter polymorphisms in men are associated with serum sex hormone-binding globulin, androgen and androgen metabolite levels, and hip bone mineral density. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 5029–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svartberg, J.; Schirmer, H.; Wilsgaard, T.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Njølstad, I.; Løchen, M.-L.; Jorde, R. Single-nucleotide polymorphism, rs1799941 in the Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG) gene, related to both serum testosterone and SHBG levels and the risk of myocardial infarction, type 2 diabetes, cancer and mortality in men: The Tromsø Study. Andrology 2014, 2, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangl, T.A.; Wiepjes, C.M.; Smit, R.A.J.; van Hylckama Vlieg, A.V.; Lamb, H.J.; van der Velde, J.H.P.M.; Winters-van Eekelen, E.; Boone, S.C.; Brouwers, M.C.G.J.; Rosendaal, F.R.; et al. Association Between Low Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Is Mediated by Increased Visceral and Liver Fat: Results from Observational and Mendelian Randomization Analyses. Diabetes 2024, 73, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.J.; Eren, F.; Agirbasli, D.; Williams, S.M.; Agirbasli, M. SHBG gene polymorphism (rs1799941) associates with metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogeveen, K.N.; Talikka, M.; Hammond, G.L. Human sex hormone-binding globulin promoter activity is influenced by a (TAAAA)n repeat element within an Alu sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36383–36390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbillemont, G.; Bogaert, V.; De Bacquer, D.; Lapauw, B.; Goemaere, S.; Toye, K.; Van Steen, K.; Taes, Y.; Kaufman, J.-M. Polymorphisms of the SHBG gene contribute to the interindividual variation of sex steroid hormone blood levels in young, middle-aged and elderly men. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 70, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fang, L.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Jia, Q.; Cheng, J.-C.; Sun, Y.-P. Association between human SHBG gene polymorphisms and risk of PCOS: A meta-analysis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2021, 42, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrea, F.; Díaz, L.; Cariño, C.; Larriva-Sahd, J.; Carrillo, L.; Orozco, H.; Ulloa-Aguirre, A. Evidence that human placenta is a site of sex hormone-binding globulin gene expression. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1993, 46, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Guan, X.; Gao, H.; Shang, L.; Gao, M.; Su, D.; Li, W. The change in sex hormone binding globulin and the influence by gestational diabetes mellitus in fetal period. Gynecol. Endocrinol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2009, 25, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundell, A.C.; Ryberg, H.; Vandenput, L.; Rudin, A.; Ohlsson, C.; Tivesten, Å. Umbilical cord blood androgen levels in girls and boys assessed by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 171, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, B.K.; Yasa, B.; Moore, J.P.; Yasa, C.; Poyrazoglu, S.; Bas, F.; Coban, A.; Darendeliler, F.; Winters, S.J. Impact of Smoking, Obesity and Maternal Diabetes on SHBG Levels in Newborns. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Off. J. Ger. Soc. Endocrinol. Ger. Diabetes Assoc. 2022, 130, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, N.J.; Tapanainen, J.; Koivisto, M.; Vihko, R. Circulating sex hormone-binding globulin and testosterone in newborns and infants. Clin. Endocrinol. 1989, 31, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmlinger, M.W.; Kühnel, W.; Wormstall, H.; Döller, P.C. Reference intervals for testosterone, androstenedione and SHBG levels in healthy females and males from birth until old age. Clin. Lab. 2005, 51, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, A.K.; Sjöbom, U.; Landin, A.; Andersson, M.X.; Ryberg, H.; Pivodic, A.; Löfqvist, C.; Sävman, K.; Poutanen, M.; Ohlsson, C.; et al. Postnatal Dysregulation of Androgens in Extremely Preterm Male Infants. J. Endocr. Soc. 2024, 8, bvae179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, J.; Forest, M.G.; Czernichow, P. Thyroid hormones influences sex steroid binding protein levels in infancy: Study in congenital hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 71, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huhtaniemi, I.; Dunkel, L.; Perheentupa, J. Transient increase in postnatal testicular activity is not revealed by longitudinal measurements of salivary testosterone. Pediatr. Res. 1986, 20, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, M.; Raisingani, M.; Chandler, D.W.; Curtin, W.D.; Barillas, J.; Brar, P.C.; Prasad, K.; Shah, B.; David, R. Salivary Testosterone during the Minipuberty of Infancy. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2017, 87, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, A.; Almås, B.; Bruserud, I.S.; Oehme, N.H.B.; Nielsen, C.S.; Roelants, M.; Hundhausen, T.; Ljubicic, M.L.; Bjerknes, R.; Mellgren, G.; et al. Reference Curves for Pediatric Endocrinology: Leveraging Biomarker Z-Scores for Clinical Classifications. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2004–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkney, J.; Streeter, A.; Hosking, J.; Mostazir, M.; Jeffery, A.; Wilkin, T. Adiposity, chronic inflammation, and the prepubertal decline of sex hormone binding globulin in children: Evidence for associations with the timing of puberty (Earlybird 58). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 3224–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelsman, D.J.; Sikaris, K.; Ly, L.P. Estimating age-specific trends in circulating testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin in males and females across the lifespan. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 53 Pt 3, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcés, C.; Oya Ide Lasunción, M.A.; López-Simón, L.; Cano, B.; de Oya, M. Sex hormone-binding globulin and lipid profile in pubertal children. Metabolism 2010, 59, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgorosky, A.; Martinez, A.; Domene, H.; Heinrich, J.J.; Bergada, C.; Rivarola, M.A. High serum sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and low serum non-SHBG-bound testosterone in boys with idiopathic hypopituitarism: Effect of recombinant human growth hormone treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987, 65, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, S.K.; Loughlin, T.; Culliton, M.; McKenna, T.J. Plasma sex hormone-binding globulin levels decrease during the second decade of life irrespective of pubertal status. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1984, 58, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, H.G.; Dudley, E.C.; Cui, J.; Dennerstein, L.; Hopper, J.L. A prospective longitudinal study of serum testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, and sex hormone-binding globulin levels through the menopause transition. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 2832–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aribas, E.; Roeters van Lennep, J.E.; De Rijke, Y.B.; Laven, J.S.E.; Ikram, M.A.; Peeters, R.P.; Kavousi, M. Sex steroids and sex steroid-binding globulin levels amongst middle-aged and elderly men and women from general population. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Definition, Prevalence, and Risk Factors of Low Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin in US Adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e3946–e3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.; Cropp, C.S.; Smith, B.S.; Burkman, R.T.; Zacur, H.A. Effect of low-dose oral contraceptive on gonadotropins, androgens, and sex hormone binding globulin in nonhirsute women. Fertil. Steril. 1990, 53, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, M.P. Are all estrogens created equal? A review of oral vs. transdermal therapy. J. Womens Health 2012, 21, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, S.J.; Gogineni, J.; Karegar, M.; Scoggins, C.; Wunderlich, C.A.; Baumgartner, R.; Ghooray, D.T. Sex hormone-binding globulin gene expression and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2780–E2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, S.J.; Atkinson, L. Serum LH concentrations in hypogonadal men during transdermal testosterone replacement through scrotal skin: Further evidence that ageing enhances testosterone negative feedback. The Testoderm Study Group. Clin. Endocrinol. 1997, 47, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaii, T.; Gustafsson, T.P.; Axelson, M.; Zamani, L.; Ernberg, M.; Hirschberg, A.L.; Carlström, K.A.M. Circulating androgens and SHBG during the normal menstrual cycle in two ethnic populations. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2017, 77, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, P.; Boyne, P.; Flett, P.; Beilby, J.; James, I. Longitudinal assessment of changes in reproductive hormones during normal pregnancy. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.W.; Tajar, A.; Pye, S.R.; Silman, A.J.; Finn, J.D.; O’Neill, T.W.; Bartfai, G.; Casanueva, F.; Forti, G.; Giwercman, A.; et al. Hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis disruptions in older men are differentially linked to age and modifiable risk factors: The European Male Aging Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman, R.P.; Tepper, P.G.; Crawford, S.; Finkelstein, J.S.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; Thurston, R.C.; Santoro, N.; Sternfeld, B.; Greendale, G.A. Do changes in sex steroid hormones precede or follow increases in body weight during the menopause transition? Results from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1695–E1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aribas, E.; Kavousi, M.; Laven, J.S.E.; Ikram, M.A.; Roeters van Lennep, J.E. Aging, Cardiovascular Risk, and SHBG Levels in Men and Women From the General Population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 2890–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizman, J.E.; Quinn, F.; Armbruster, D.A.; Adeli, K. Pediatric reference intervals for calculated free testosterone, bioavailable testosterone and free androgen index in the CALIPER cohort. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, e239–e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakowsky, Y.; Conners, W.; Morgentaler, A. Serum Concentrations of Sex Hormone-binding Globulin Vary Widely in Younger and Older Men: Clinical Data from a Men’s Health Practice. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayagopal, V.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Jennings, P.E.; Hepburn, D.A.; Atkin, S.L. The biological variation of testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) in polycystic ovarian syndrome: Implications for SHBG as a surrogate marker of insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, K.; Aksglaede, L.; Munch-Andersen, T.; Aachmann-Andersen, N.J.; Petersen, J.H.; Hilsted, L.; Helge, J.W.; Juul, A. Sex Hormone–Binding Globulin Levels Predict Insulin Sensitivity, Disposition Index, and Cardiovascular Risk During Puberty. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijper, E.A.M.; Lambalk, C.B.; Boomsma, D.I.; van der Sluis, S.; Blankenstein, M.A.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Posthuma, D. Heritability of reproductive hormones in adult male twins. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, A.W.; Bishop, D.T.; Stringham, J.D.; West, D.W. Quantitating genetic and nongenetic factors that determine plasma sex steroid variation in normal male twins. Metabolism 1986, 35, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coviello, A.D.; Haring, R.; Wellons, M.; Vaidya, D.; Lehtimäki, T.; Keildson, S.; Lunetta, K.L.; He, C.; Fornage, M.; Lagou, V.; et al. A genome-wide association meta-analysis of circulating sex hormone-binding globulin reveals multiple Loci implicated in sex steroid hormone regulation. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruth, K.S.; Day, F.R.; Tyrrell, J.; Thompson, D.J.; Wood, A.R.; Mahajan, A.; Beaumont, R.N.; Wittemans, L.; Martin, S.; Busch, A.S.; et al. Using human genetics to understand the disease impacts of testosterone in men and women. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, A.S.; Ljubicic, M.L.; Upners, E.N.; Fischer, M.B.; Odroniec, A.; Hagen, C.P.; Juul, A. Polygenic Scores for Adult Testosterone and SHBG Levels Are Associated with Reproductive Hormone Levels in Male Infants. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 2343–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, Y.; Liang, J.M.; Voss, C.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Sheng, W.-Y.; Sun, Y.-H.; Wang, Z.-L. Intrauterine insulin resistance in fetuses of overweight mothers. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2013, 39, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, Z. β-Carotene regulates glucose transport and insulin resistance in gestational diabetes mellitus by increasing the expression of SHBG. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2022, 49, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanem, L.G.E.; Salvesen, Ø.; Madsen, A.; Sagen, J.V.; Mellgren, G.; Juliusson, P.B.; Carlsen, S.M.; Vanky, E.; Ødegård, R. Maternal PCOS status and metformin in pregnancy: Steroid hormones in 5-10 years old children from the PregMet randomized controlled study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirbasli, M.; Agaoglu, N.B.; Orak, N.; Caglioz, H.; Ocek, T.; Poci, N.; Salaj, A.; Maya, S. Sex hormones and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Metabolism 2009, 58, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, A.R.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Bray, G.A.; Dahms, W.T.; Atkinson, R.L. Low serum testosterone and sex-hormone-binding-globulin in massively obese men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1977, 45, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vignera, S.; Condorelli, R.A.; Calogero, A.E.; Cannarella, R.; Aversa, A. Sexual and Reproductive Outcomes in Obese Fertile Men with Functional Hypogonadism after Treatment with Liraglutide: Preliminary Results. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzick, D.S.; Wing, R.; Smith, D.; Berga, S.L.; Winters, S.J. Endocrine consequences of weight loss in obese, hyperandrogenic, anovulatory women. Fertil. Steril. 1994, 61, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubb, S.A.P.; Hyde, Z.; Almeida, O.P.; Flicker, L.; Norman, P.E.; Jamrozik, K.; Hankey, G.J.; Yeap, B.B. Lower sex hormone-binding globulin is more strongly associated with metabolic syndrome than lower total testosterone in older men: The Health in Men Study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 158, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Muller, D.C.; Metter, E.J.; Maggio, M.; Harman, S.M.; Blackman, M.R.; Andres, R. Aging, androgens, and the metabolic syndrome in a longitudinal study of aging. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3568–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajamor, S.; Després, J.P.; Couillard, C.; Lemieux, S.; Tremblay, A.; Prud’homme, D.; Tchernof, A. Relationship between sex hormone-binding globulin levels and features of the metabolic syndrome. Metabolism 2003, 52, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaei, S.; Mohseni, H. Correlation between Hormonal Statuses and Metabolic Syndrome in Postmenopausal Women. J. Fam. Reprod. Health 2013, 7, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Nyante, S.J.; Graubard, B.I.; Li, Y.; McQuillan, G.M.; Platz, E.A.; Rohrmann, S.; Bradwin, G.; McGlynn, K.A. Trends in sex hormone concentrations in U.S. males: 1988–1991 to 1999–2004. Int. J. Androl. 2012, 35, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahaman, E.; Raghavan, S.; Baker, L.; Weinrich, M.; Winters, S.J. Racial difference in circulating sex hormone-binding globulin levels in prepubertal boys. Metabolism 2005, 54, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrisse, S.; Garcia-Reyes, Y.; Pyle, L.; Kelsey, M.M.; Nadeau, K.J.; Cree-Green, M. Racial and Ethnic Differences in Metabolic Disease in Adolescents with Obesity and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J Endocr Soc. 2021, 5, bvab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Harlow, S.D.; Karvonen-Gutierrez, C.A.; Randolph, J.F., Jr.; Helmuth, M.; Kong, S.; Nan, B.; Carlos, R. Racial/ethnic differences in hepatic steatosis in a population-based cohort of post-menopausal women: The Michigan Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2013, 30, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; Wildman, R.P.; Matthews, K.A.; Chae, C.; Lasley, B.L.; Brockwell, S.; Pasternak, R.C.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; Sowers, M.F.; Torréns, J.I.; et al. Sex-hormone-binding globulin and the free androgen index are related to cardiovascular risk factors in multiethnic premenopausal and perimenopausal women enrolled in the Study of Women Across the Nation (SWAN). Circulation 2005, 111, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, S.P.; Holmes, M.D.; Pollak, M.N.; Barbieri, R.L.; Hankinson, S.E. Racial differences in premenopausal endogenous hormones. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2005, 14, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.S.; Peskoe, S.B.; Joshu, C.E.; Dobs, A.; Feinleib, M.; Kanarek, N.; Nelson, W.G.; Selvin, E.; Rohrmann, S.; Platz, E.A. Racial/ethnic differences in serum sex steroid hormone concentrations in US adolescent males. Cancer Causes Control CCC 2013, 24, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, S.M.; Shaten, J.; Stern, M.P.; Smith, G.D.; Kuller, L. Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin and testosterone predict the development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in men. MRFIT Research Group. Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 143, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engmann, L.; Jin, S.; Sun, F.; Legro, R.S.; Polotsky, A.J.; Hansen, K.R.; Coutifaris, C.; Diamond, M.P.; Eisenberg, E.; Zhang, H.; et al. Racial and ethnic differences in the polycystic ovary syndrome metabolic phenotype. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 216, 493.e1–e493.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, A.H.; Anderson, S.G.; Ivison, F.; Riste, L.; Laing, I.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Gibson, J.M. Low sex hormone binding globulin is a potential marker for the metabolic syndrome in different ethnic groups. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Off. J. Ger. Soc. Endocrinol. Ger. Diabetes Assoc. 2005, 113, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeyaratne, C.N.; Balen, A.H.; Barth, J.H.; Belchetz, P.E. Clinical manifestations and insulin resistance (IR) in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) among South Asians and Caucasians: Is there a difference? Clin. Endocrinol. 2002, 57, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.L.; Kim, C.; Mukherjee, B.; Bagchi, P.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Kanaya, A.M. Endogenous sex steroid hormones and glucose in a South-Asian population without diabetes: The Metabolic Syndrome and Atherosclerosis in South-Asians Living in America pilot study. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2015, 32, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, H.J.; Bhasin, S.; Link, C.L.; Araujo, A.B.; McKinlay, J.B. Serum androgen levels in black, Hispanic, and white men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4326–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkeland, K.I.; Hanssen, K.F.; Torjesen, P.A.; Vaaler, S. Level of sex hormone-binding globulin is positively correlated with insulin sensitivity in men with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, I.R.; McKinley, M.C.; Bell, P.M.; Hunter, S.J. Sex hormone binding globulin and insulin resistance. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 78, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugeat, M.; Crave, J.C.; Elmidani, M.; Nicolas, M.H.; Garoscio-Cholet, M.; Lejeune, H.; Déchaud, H.; Tourniaire, J. Pathophysiology of sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG): Relation to insulin. J Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1991, 40, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascón, F.; Valle, M.; Martos, R.; Ruz, F.J.; Ríos, R.; Montilla, P.; Cañete, R. Sex hormone-binding globulin as a marker for hyperinsulinemia and/or insulin resistance in obese children. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 143, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, P.J.; Donaldson, M.D.; Wallace, A.M. Sex hormone binding globulin concentration as a prepubertal marker for hyperinsulinaemia in obesity. Arch. Dis. Child. 2001, 85, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano, V.; Balducci, R.; Bianchi, P.; Guglielmi, R.; Mangiantini, A.; Sciarra, F. Steroidal and non-steroidal factors in plasma sex hormone binding globulin regulation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 43, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, A.; Sumida, Y.; Murashima, S.; Fujii, M.; Ito, K.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Murata, K.; Yano, Y.; Shima, T. Acute and chronic regulation of serum sex hormone-binding globulin levels by plasma insulin concentrations in male noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 2515–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pasquali, R.; Vicennati, V.; Scopinaro, N.; Marinari, G.; Simonelli, A.; Flamia, R.; Casimirri, F.; Gagliardi, L. Achievement of near-normal body weight as the prerequisite to normalize sex hormone-binding globulin concentrations in massively obese men. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 1997, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.K.; Croymans, D.M.; Aziz, N.; Butch, A.W.; Lee, C.C. Resistance training increases SHBG in overweight/obese, young men. Metabolism 2013, 62, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, J.E.; Powers, L.P.; Matt, D.W.; Steingold, K.A.; Plymate, S.R.; Rittmaster, R.S.; Clore, J.N.; Blackard, W.G. A direct effect of hyperinsulinemia on serum sex hormone-binding globulin levels in obese women with the polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 72, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukovaara, M.; Carson, M.; Adlercreutz, H. Regulation of production and secretion of sex hormone-binding globulin in HepG2 cell cultures by hormones and growth factors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plymate, S.R.; Matej, L.A.; Jones, R.E.; Friedl, K.E. Inhibition of sex hormone-binding globulin production in the human hepatoma (Hep G2) cell line by insulin and prolactin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 67, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, D.M.; Hammond, G.L. Peroxisome-proliferator receptor gamma represses hepatic sex hormone-binding globulin expression. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, K.K.; Drum, M.L.; Lipton, R.B. Sex hormone-binding globulin and testosterone in individuals with childhood diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.; Channer, K.S.; Jones, T.H. Rosiglitazone increases bioactive testosterone and reduces waist circumference in hypogonadal men with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2008, 5, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tang, Y.; Wu, L.; Mo, F.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Qi, R.; Zhang, H.; Srivastava, A.; Ling, C. The hepatocyte-specific HNF4α/miR-122 pathway contributes to iron overload-mediated hepatic inflammation. Blood 2017, 130, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H. Crosstalk of HNF4α with extracellular and intracellular signaling pathways in the regulation of hepatic metabolism of drugs and lipids. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baciu, C.; Pasini, E.; Angeli, M.; Schwenger, K.; Afrin, J.; Humar, A.; Fischer, S.; Patel, K.; Allard, J.; Bhat, M. Systematic integrative analysis of gene expression identifies HNF4A as the central gene in pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, M.; Hammond, G.L. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 controls transcription from a TATA-less human sex hormone-binding globulin gene promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 34105–34114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Liao, H.; Dang, H.; Pang, W.; Guan, Y.; Wang, X.; Shyy, J.Y.-J.; Zhu, Y.; Sladek, F.M. Down-regulation of hepatic HNF4alpha gene expression during hyperinsulinemia via SREBPs. Mol. Endocrinol. Baltim. Md. 2009, 23, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Kantartzis, K.; Häring, H.U. Causes and metabolic consequences of Fatty liver. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 939–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Feng, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Hu, Y. Low serum sex hormone-binding globulin is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetic patients. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 80, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, M.; Zeb, I.; Nasir, K.; Tracy, R.P.; Budoff, M.J.; Ouyang, P.; Vaidya, D. Association Between Endogenous Sex Hormones and Liver Fat in a Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2015, 13, 1686–1693.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Schick, F.; Häring, H.U. Sex hormone-binding globulin and risk of type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2675–2676, author reply 2677–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackey, D.E.; Olefsky, J.M. Regulation of metabolism by the innate immune system. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó, R.; Barbosa-Desongles, A.; Lecube, A.; Hernandez, C.; Selva, D.M. Potential role of tumor necrosis factor-α in downregulating sex hormone-binding globulin. Diabetes 2012, 61, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó, R.; Barbosa-Desongles, A.; Hernandez, C.; Selva, D.M. IL1β down-regulation of sex hormone-binding globulin production by decreasing HNF-4α via MEK-1/2 and JNK MAPK pathways. Mol. Endocrinol. Baltim. Md. 2012, 26, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, G.L. Diverse roles for sex hormone-binding globulin in reproduction. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 85, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsas, G.A.; Korbonits, M.; Isidori, A.M.; Webb, J.A.; Trainer, P.J.; Monson, J.P.; Besser, G.M.; Grossman, A.B. How common are polycystic ovaries and the polycystic ovarian syndrome in women with Cushing’s syndrome? Clin. Endocrinol. 2000, 53, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.M.; Tucker, P.; Williams, D.M.; Hughes, I.A.; Ahmed, S.F. Short-term effects of prednisolone and dexamethasone on circulating concentrations of leptin and sex hormone-binding globulin in children being treated for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Clin. Endocrinol. 2003, 58, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamrazilová, L.; Dvořáková, M.; Lisá, L.; Stárka, L.; Hampl, R. Sex hormone-binding globulin in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2010, 1, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paizoni, L.; Auer, M.K.; Schmidt, H.; Hübner, A.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Reisch, N. Effect of androgen excess and glucocorticoid exposure on metabolic risk profiles in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 197, 105540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, M.; Salvatori, R.; Melo, L.D.; Rocha, Í.E.S.; Oliveira, C.R.P.; Pereira, R.M.C.; Souza, A.H.O.; Valença, E.H.O.; Melo, E.V.; Campos, V.C.; et al. Prolactin and sex steroids levels in congenital lifetime isolated GH deficiency. Endocrine 2013, 44, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscarsson, J.; Wiklund, O.; Jakobsson, K.E.; Petruson, B.; Bengtsson, B.A. Serum lipoproteins in acromegaly before and 6-15 months after transsphenoidal adenomectomy. Clin. Endocrinol. 1994, 41, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selva, D.M.; Hammond, G.L. Thyroid hormones act indirectly to increase sex hormone-binding globulin production by liver via hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 43, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.; Jensen, R.B.; Juul, A. Increased sex hormone-binding globulin levels in children and adolescents with thyrotoxicosis. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2013, 79, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, I.J. Gonadal steroids and gonadotropins in hyperthyroidism. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1975, 59, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, H.C.; Cooke, R.R.; Keightley, E.A.; Feek, C.M. Serum levels of free and bound testosterone in hyperthyroidism. Clin. Endocrinol. 1992, 36, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, R.W.; Edwards, A.L. Testicular function in hyperthyroidism. J. Androl. 1992, 13, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaya Kumar, B.; Khurana, M.L.; Ammini, A.C.; Karmarkar, M.G.; Ahuja, M.M. Reproductive endocrine functions in men with primary hypothyroidism: Effect of thyroxine replacement. Horm. Res. 1990, 34, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thiel, D.H.; Loriaux, D.L. Evidence for an adrenal origin of plasma estrogens in alcoholic men. Metabolism 1979, 28, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Klein, M.; Zanger, U.M.; Mohammad, M.K.; Cave, M.C.; Gaikwad, N.W.; Dias, N.J.; Selcer, K.W.; Guo, Y.; He, J.; et al. Inflammatory regulation of steroid sulfatase: A novel mechanism to control estrogen homeostasis and inflammation in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.; Danoff, A.; Bini, E.J. Elevated sex hormone binding globulin levels may contribute to sexual dysfunction in men with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 43, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, N.K.; Koo, H.S.; Haam, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Park, K.-C.; Park, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-S. Prediction of prevalent but not incident non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by levels of serum testosterone. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.; VanWagner, L.B.; Terry, J.G.; Carr, J.J.; Rinella, M.; Schreiner, P.J.; Lewis, C.E.; Terrault, N. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Levels in Young Men Are Associated With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Midlife. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Pang, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, Q.; Ma, J.; Xu, X.; et al. Serum SHBG Is Associated With the Development and Regression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Prospective Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, dgz244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, W.; Hryb, D.J.; Khan, M.S.; Nakhla, A.M.; Romas, N.A. Sex hormone-binding globulin mediates steroid hormone signal transduction at the plasma membrane. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 69, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Toni, L.; Guidolin, D.; De Filippis, V.; Tescari, S.; Strapazzon, G.; Rocca, M.S.; Ferlin, A.; Plebani, M.; Foresta, C. Osteocalcin and Sex Hormone Binding Globulin Compete on a Specific Binding Site of GPRC6A. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4473–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, M.; Chen, L.; Huang, M.Z.; Zhu, W.; Ringhofer, B.; Luo, J.; Christenson, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Jackson, P.D.; et al. GPRC6A null mice exhibit osteopenia, feminization and metabolic syndrome. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Kushiyama, A.; Sakoda, H.; Fujishiro, M.; Yamamotoya, T.; Nakatsu, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Kaneko, S.; Tanaka, H.; Asano, T. Protective Effect of Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin against Metabolic Syndrome: In Vitro Evidence Showing Anti-Inflammatory and Lipolytic Effects on Adipocytes and Macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3062319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourebaba, L.; Kępska, M.; Qasem, B.; Zyzak, M.; Łyczko, J.; Klemens, M.; Mularczyk, M.; Marycz, K. Sex hormone-binding globulin improves lipid metabolism and reduces inflammation in subcutaneous adipose tissue of metabolic syndrome-affected horses. Front Mol Biosci. 2023, 10, 1214961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saez-Lopez, C.; Villena, J.A.; Simó, R.; Selva, D.M. Sex hormone-binding globulin overexpression protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity in transgenic male mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 85, 108480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, S.; Hosojima, M.; Kabasawa, H.; Saito, A. The endocytosis receptor megalin: From bench to bedside. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2023, 157, 106393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, A.; Andreassen, T.K.; Spoelgen, R.; Raila, J.; Hubner, N.; Schulz, H.; Metzger, J.; Schweigert, F.J.; Luppa, P.B.; Nykjaer, A.; et al. Role of endocytosis in cellular uptake of sex steroids. Cell 2005, 122, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Krieger, K.D.; Loitz, C.; Perez, L.M.; Richards, Z.A.; Helou, Y.; Kregel, S.; Celada, S.; Mesaros, C.A.; Bosland, M.; et al. Regulation of Prostate Androgens by Megalin and 25-hydroxyvitamin D Status: Mechanism for High Prostate Androgens in African American Men. Cancer Res. Commun. 2023, 3, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, P.I.H.G.; Valkenburg, O.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Brouwers, M.C.G.J. Sex hormone-binding globulin: Biomarker and hepatokine? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2021, 32, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, M.; Deol, H.K.; Power, S.G.; Yee, S.P.; Hammond, G.L. Human sex hormone-binding globulin gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol. Endocrinol. Baltim. Md. 1998, 12, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saéz-López, C.; Rivera-Giménez, M.; Hernández, C.; Simó, R.; Selva, D.M. SHBG-C57BL/ksJ-db/db: A New Mouse Model to Study SHBG Expression and Regulation During Obesity Development. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 4571–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Niu, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y. Downregulation of leptin receptor and kisspeptin/GPR54 in the murine hypothalamus contributes to male hypogonadism caused by high-fat diet-induced obesity. Endocrine 2018, 62, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofer, Y.; Nevo, N.; Vechoropoulos, M.; Shefer, G.; Osher, E.; Landis, N.; Tordjman, K.; Hammond, G.L.; Stern, N. Human sex hormone-binding globulin does not provide metabolic protection against diet-induced obesity and dysglycemia in mice. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, C.; Danielsson, P.; Hagman, E. Pediatric obesity—Long-term consequences and effect of weight loss. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 870–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, N.H.; Singleton, R.K.; Zhou, B.; Heap, R.A.; Mishra, A.; Bennett, J.E.; Paciorek, C.J.; Lhoste, V.P.F.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Stevens, G.A.; et al. Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2024, 403, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciba, I.; Dahlbom, M.; Manell, H.; Mörwald, K.; Roomp, K.; Weghuber, D.; Bergsten, P.; Forslund, A. Studies in children with obesity in two European treatment centres show a high prevalence of impaired glucose metabolism in the Swedish cohort. Acta Paediatr. 2024, 113, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iafusco, D.; Franceschi, R.; Maguolo, A.; Guercio Nuzio, S.; Crinò, A.; Delvecchio, M.; Iughetti, L.; Maffeis, C.; Calcaterra, V.; Manco, M. From Metabolic Syndrome to Type 2 Diabetes in Youth. Children 2023, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Alkhouri, N.; Vajro, P.; Baumann, U.; Weiss, R.; Socha, P.; Marcus, C.; Lee, W.S.; Kelly, D.; Porta, G.; et al. Defining paediatric metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julian, V.; Bergsten, P.; Forslund, A.; Ahlstrom, H.; Ciba, I.; Dahlbom, M.; Furthner, D.; Gomahr, J.; Kullberg, J.; Maruszczak, K.; et al. Sedentary time has a stronger impact on metabolic health than moderate to vigorous physical activity in adolescents with obesity: A cross-sectional analysis of the Beta-JUDO study. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Lee, D.K.; Liu, M.; Portincasa, P.; Wang, D.Q.H. Novel Insights into the Pathogenesis and Management of the Metabolic Syndrome. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2020, 23, 189–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinehr, T.; Wolters, B.; Knop, C.; Lass, N.; Holl, R.W. Strong effect of pubertal status on metabolic health in obese children: A longitudinal study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon-Krauel, M.; Leal-Witt, M.J.; Osorio-Conles, Ó.; Amat-Bou, M.; Lerin, C.; Selva, D.M. Relationship between adiponectin, TNFα, and SHBG in prepubertal children with obesity. Mol. Cell. Pediatr. 2021, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glueck, C.J.; Morrison, J.A.; Daniels, S.; Wang, P.; Stroop, D. Sex hormone-binding globulin, oligomenorrhea, polycystic ovary syndrome, and childhood insulin at age 14 years predict metabolic syndrome and class III obesity at age 24 years. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 308–313.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, M.M.; Zeitler, P.S. Insulin Resistance of Puberty. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, K.; Andersson, A.M.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Juul, A. Serum sex hormone-binding globulin levels in healthy children and girls with precocious puberty before and during gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3189–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandewalle, S.; Taes, Y.; Fiers, T.; Van Helvoirt, M.; Debode, P.; Herregods, N.; Ernst, C.; Van Caenegem, E.; Roggen, I.; Verhelle, F.; et al. Sex steroids in relation to sexual and skeletal maturation in obese male adolescents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 2977–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandewalle, S.; De Schepper, J.; Kaufman, J.M. Androgens and obesity in male adolescents. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2015, 22, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Vosberg, D.E.; Pausova, Z.; Paus, T. A Shifting Relationship Between Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Total Testosterone Across Puberty in Boys. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e4187–e4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Tiainen, M.; Tynkkynen, T.; Puukka, K.; Ruokonen, A.; Viikari, J.; Kähönen, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; et al. Sex hormone-binding globulin associations with circulating lipids and metabolites and the risk for type 2 diabetes: Observational and causal effect estimates. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, R.M.; Lakshminarayanan, S.; Deepa, M.; Farooq, S.; Pradeepa, R.; Mohan, V. Parental history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and cardiometabolic risk factors in Asian Indian adolescents. Metabolism 2009, 58, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, R.A.; Deepa, M.; Deepa, R.; Wilson, A.F.; Mohan, V. Heritability of quantitative traits associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in large multiplex families from South India. Metabolism 2009, 58, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirbasli, M.; Ciliv, G.; Cakir, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Berenson, G.S.; Ozme, S. Body mass index and lipid levels in children from Ankara, Turkey versus Bogalusa, Louisiana. Prev. Med. 2005, 41, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, B.S.; Poh, B.K.; Bulgiba, A.; Ismail, M.N.; Ruzita, A.T.; Hills, A.P. Risk of metabolic syndrome among children living in metropolitan Kuala Lumpur: A case control study. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolsgaard, M.L.P.; Andersen, L.F.; Tonstad, S.; Brunborg, C.; Wangensteen, T.; Joner, G. Ethnic differences in metabolic syndrome among overweight and obese children and adolescents: The Oslo Adiposity Intervention Study. Acta Paediatr. 2008, 97, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batey, L.S.; Goff, D.C.; Tortolero, S.R.; Nichaman, M.Z.; Chan, W.; Chan, F.A.; Grunbaum, J.; Hanis, C.L.; Labarthe, D.R. Summary measures of the insulin resistance syndrome are adverse among Mexican-American versus non-Hispanic white children: The Corpus Christi Child Heart Study. Circulation 1997, 96, 4319–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirbasli, M.; Eren, F.; Agirbasli, D.; White, M.J.; Williams, S.M. Multi-locus candidate gene analyses of lipid levels in a pediatric Turkish cohort: Lessons learned on LPL, CETP, LIPC, ABCA1, and SHBG. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2013, 17, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
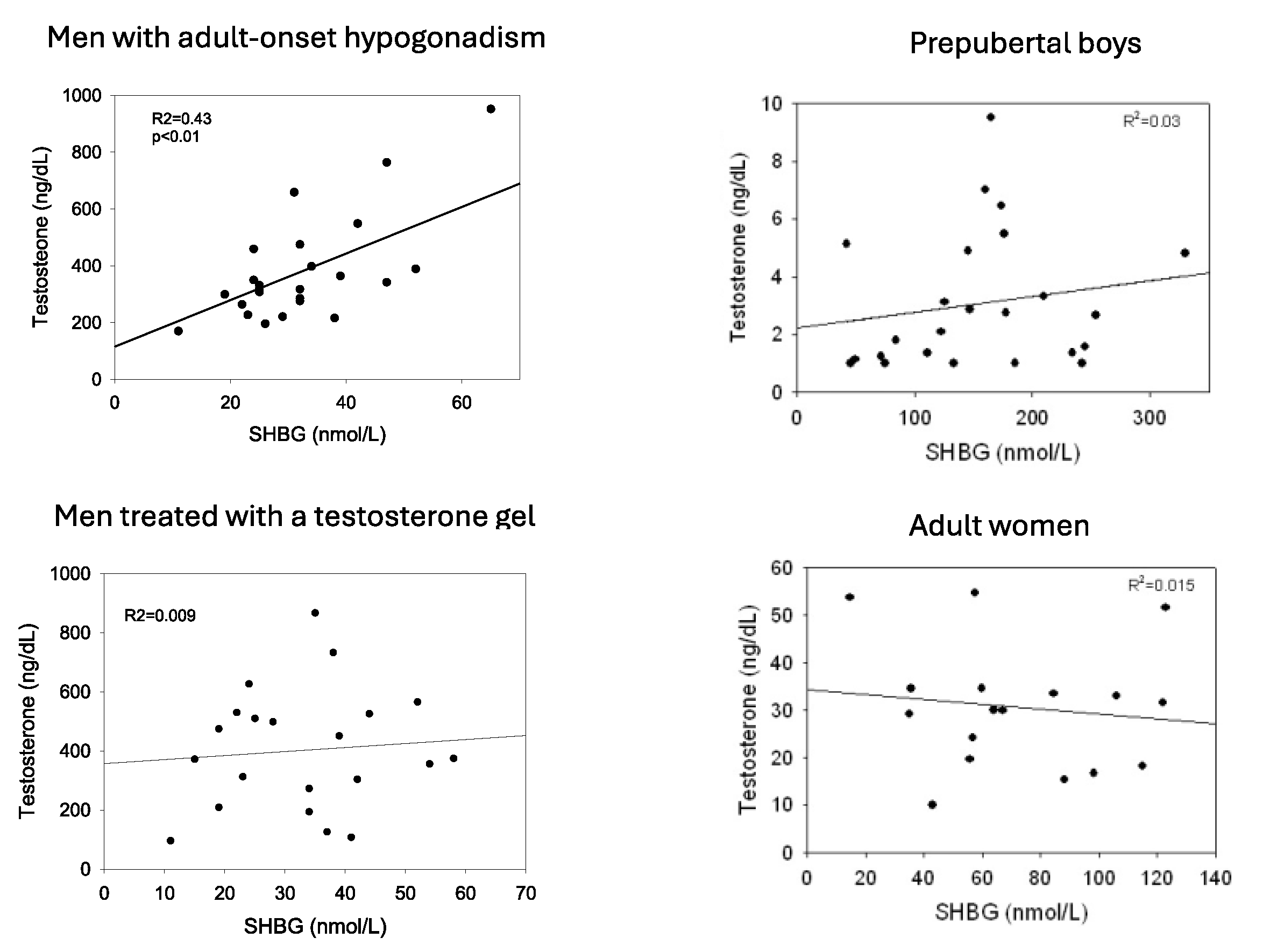
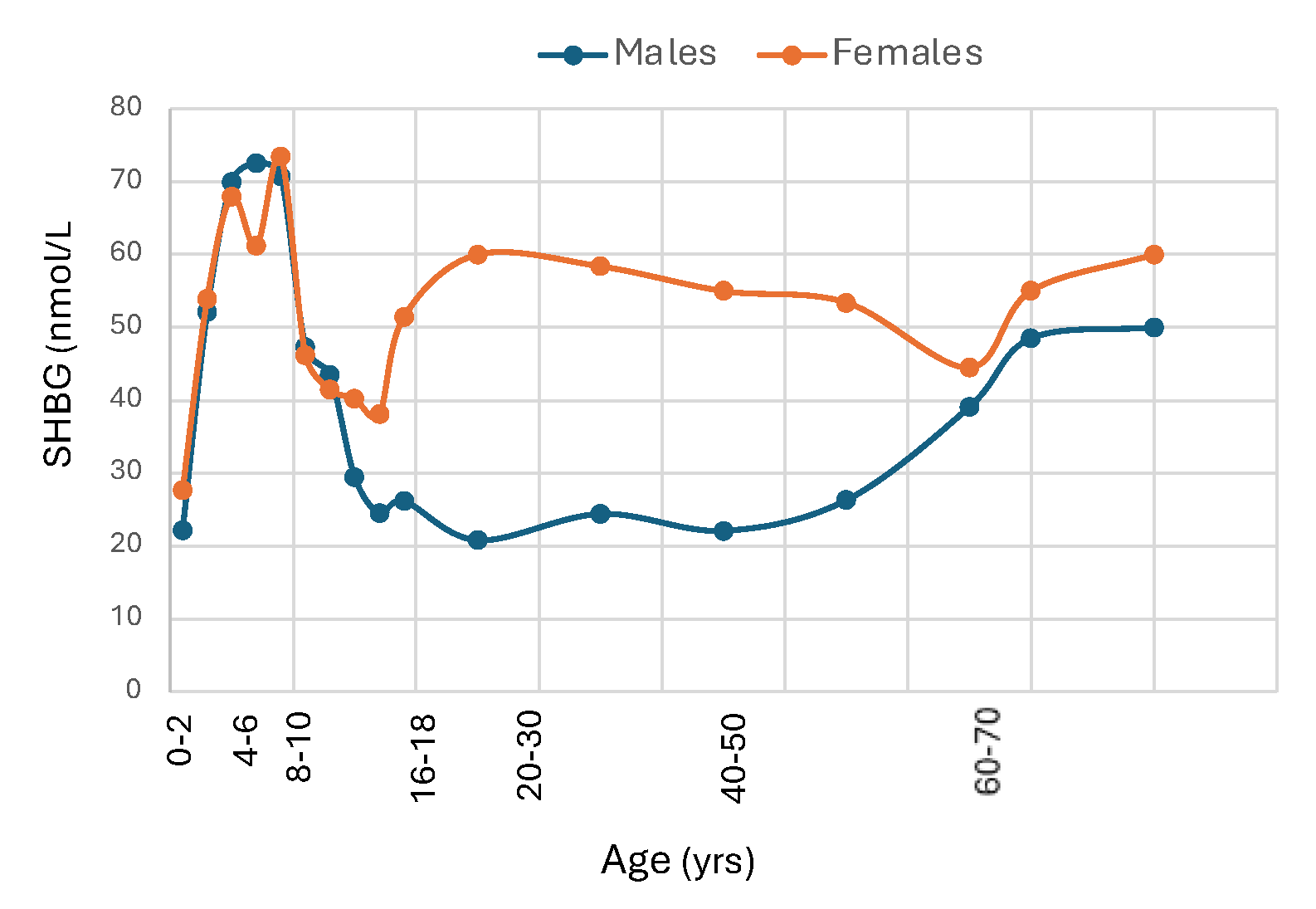
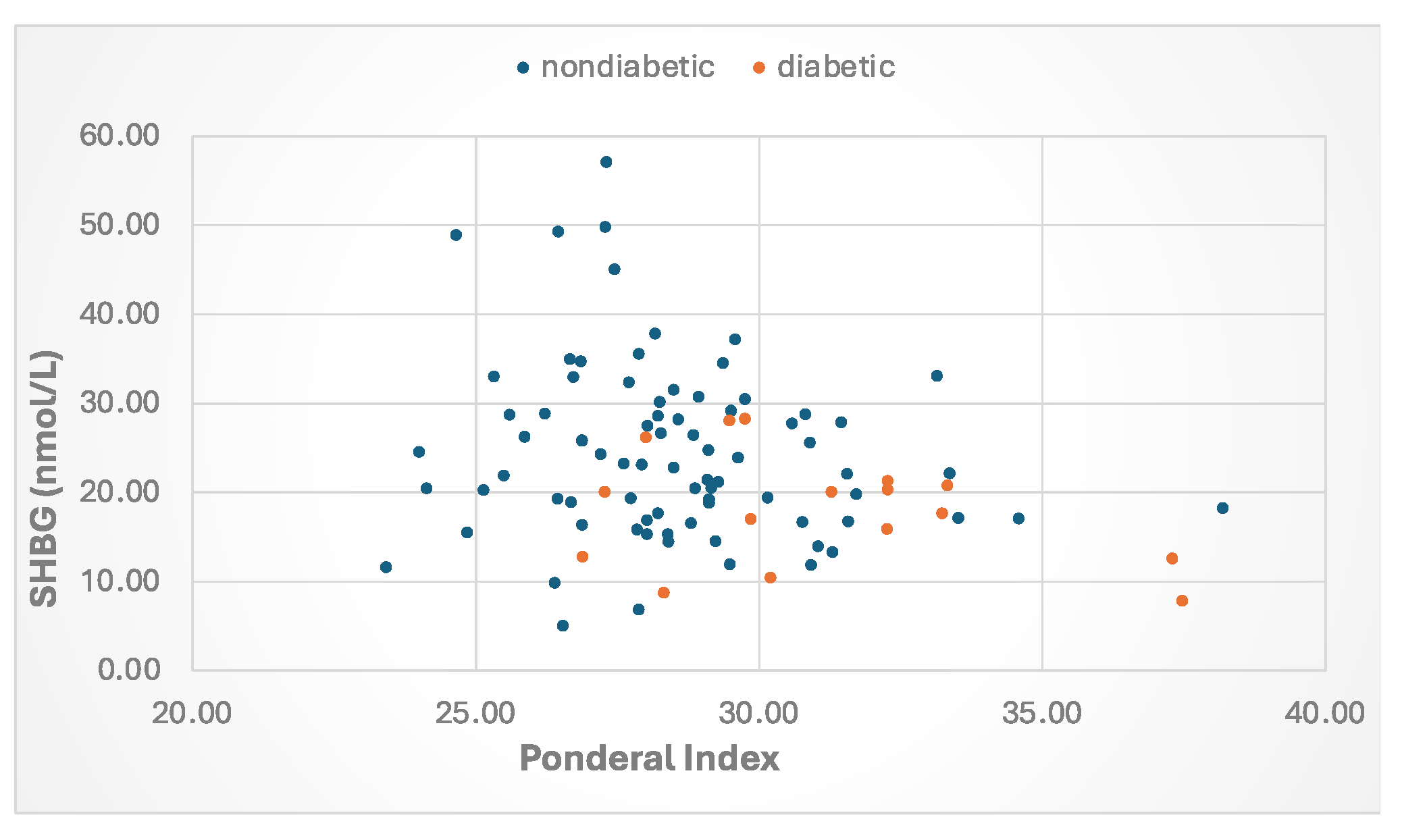
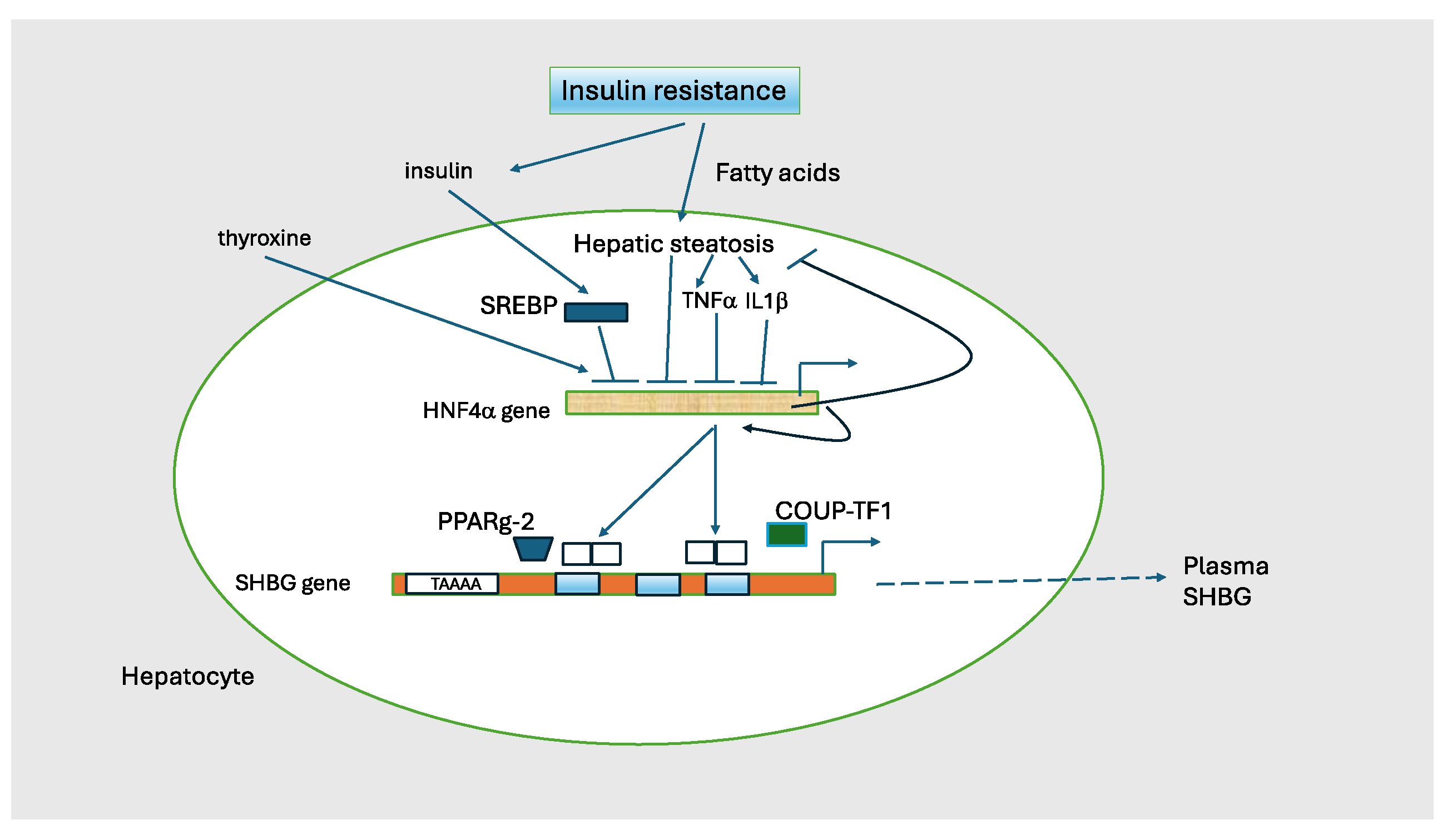
| Decrease | Increase |
|---|---|
| Androgens | Estrogens |
| Obesity | Pregnancy |
| Insulin resistance | SERMs * |
| Metabolic syndrome | Thinness |
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus | Weight loss |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | Alcoholic liver disease |
| Polycystic ovary syndrome | Hepatitis-B and hepatitis-C infection |
| Metabolic fatty liver disease | Hyperthyroidism |
| Acromegaly | Thyroid hormone receptor-b agonists |
| Cushing syndrome | Growth hormone deficiency |
| Congenital adrenal hyperplasia | Hemochromatosis |
| Hyperprolactinemia | Acute intermittent porphyria |
| Tumor necrosis factor alpha | First generation anticonvulsants |
| Interleukin-1 beta | Mitotane |
| Genetic polymorphisms | Genetic polymorphisms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aydin, B.; Winters, S.J. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: A Focus on Puberty. Metabolites 2025, 15, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080494
Aydin B, Winters SJ. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: A Focus on Puberty. Metabolites. 2025; 15(8):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080494
Chicago/Turabian StyleAydin, Banu, and Stephen J. Winters. 2025. "Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: A Focus on Puberty" Metabolites 15, no. 8: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080494
APA StyleAydin, B., & Winters, S. J. (2025). Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: A Focus on Puberty. Metabolites, 15(8), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080494






