The Impact of Uranium-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis on Gut Microbiota and Related Metabolites in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal, Fibrotic Models, and Sample Collection
2.2. Pathological Analysis and Hydroxyproline Quantification
2.3. Metagenomics Sequencing
2.4. Gene Prediction and Abundance Information
2.5. LefSe Analysis of Different Gut Microbiota
2.6. Targeted Metabolomics Profiling
2.7. Analysis of Targeted Metabolomics Profiling Data
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Alterations of Uranium Content in Rat Tissue
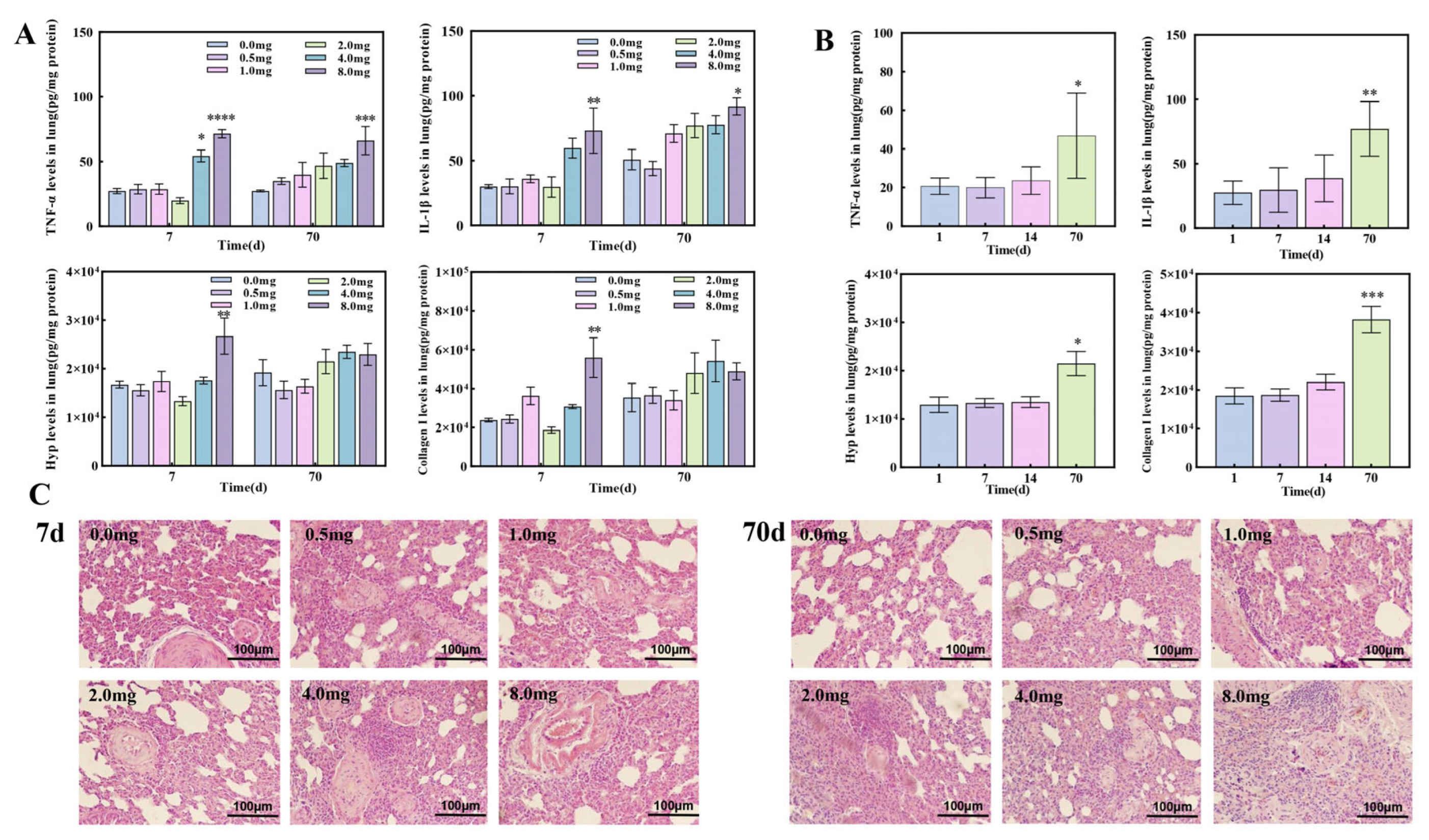
3.2. The Establishment of Pulmonary Fibrosis Rat Models Induced by UO2
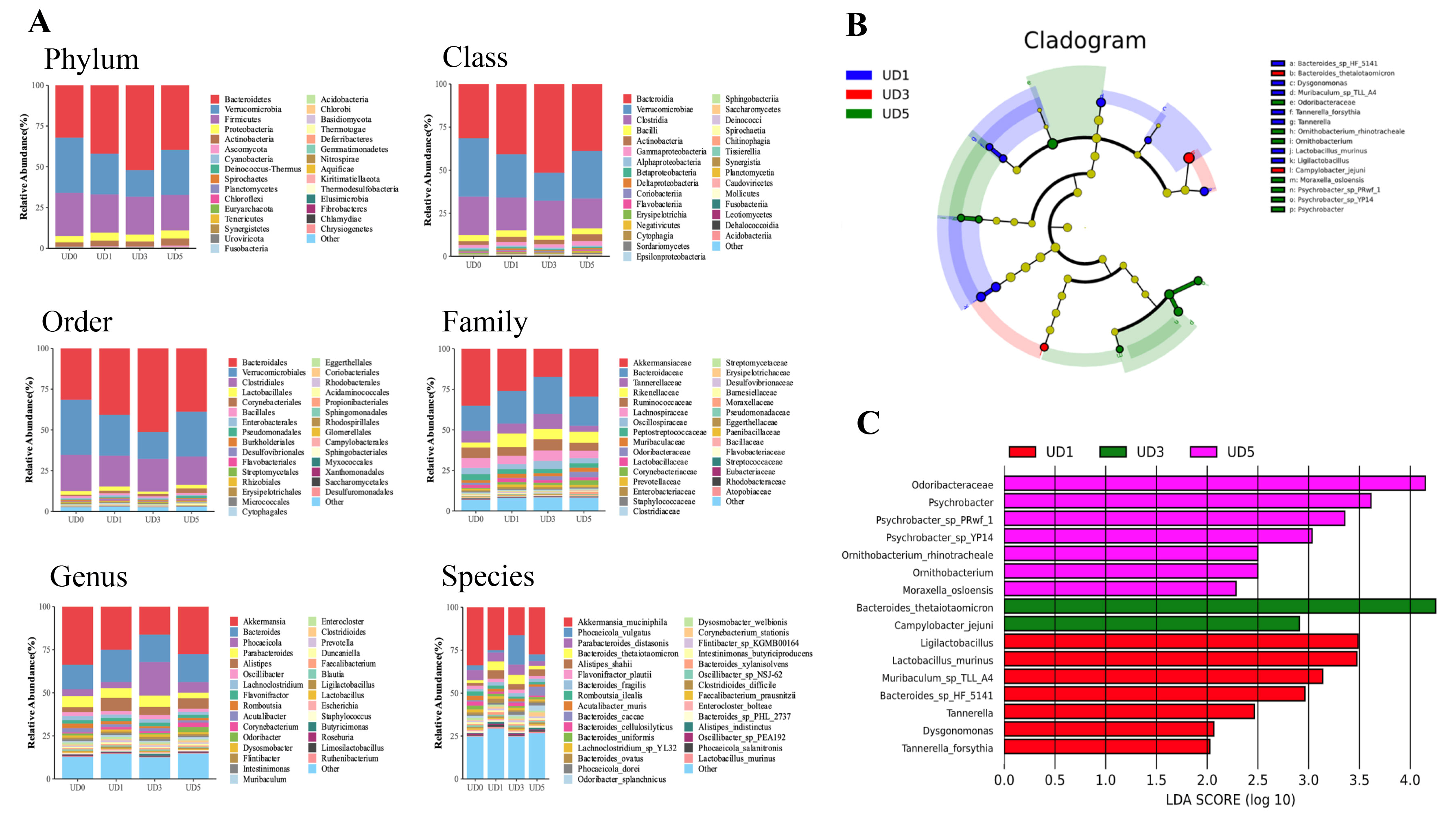
3.3. Alterations of Rats’ Gut Microbiota upon Induction of Pulmonary Fibrosis
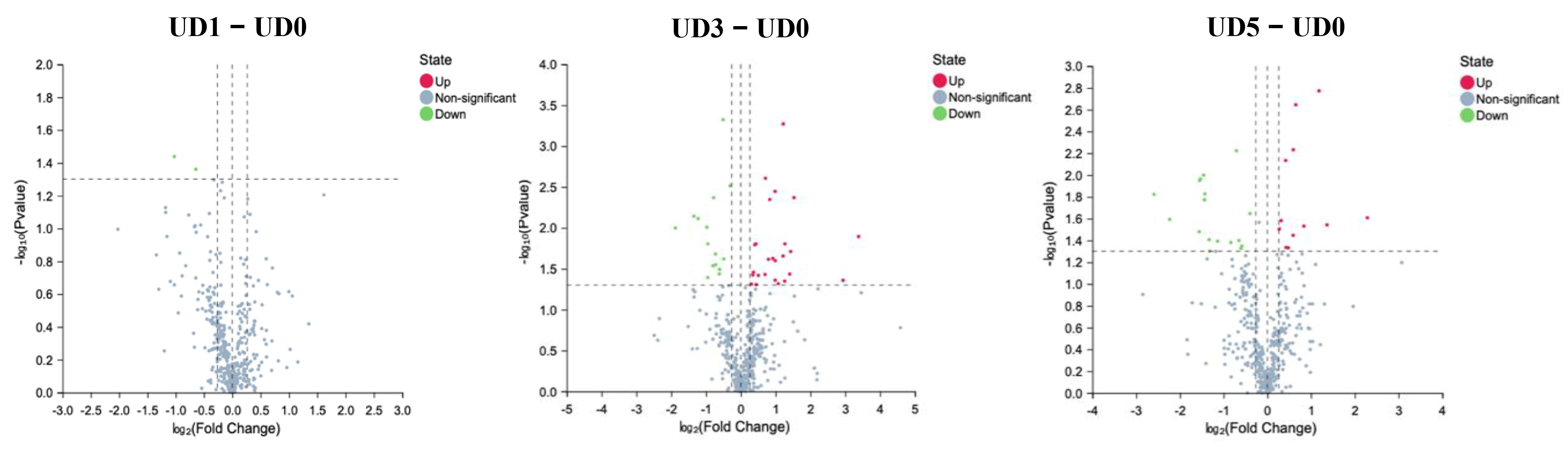
3.4. Alterations of Metabolites in Enteric Canal of Pulmonary Fibrosis
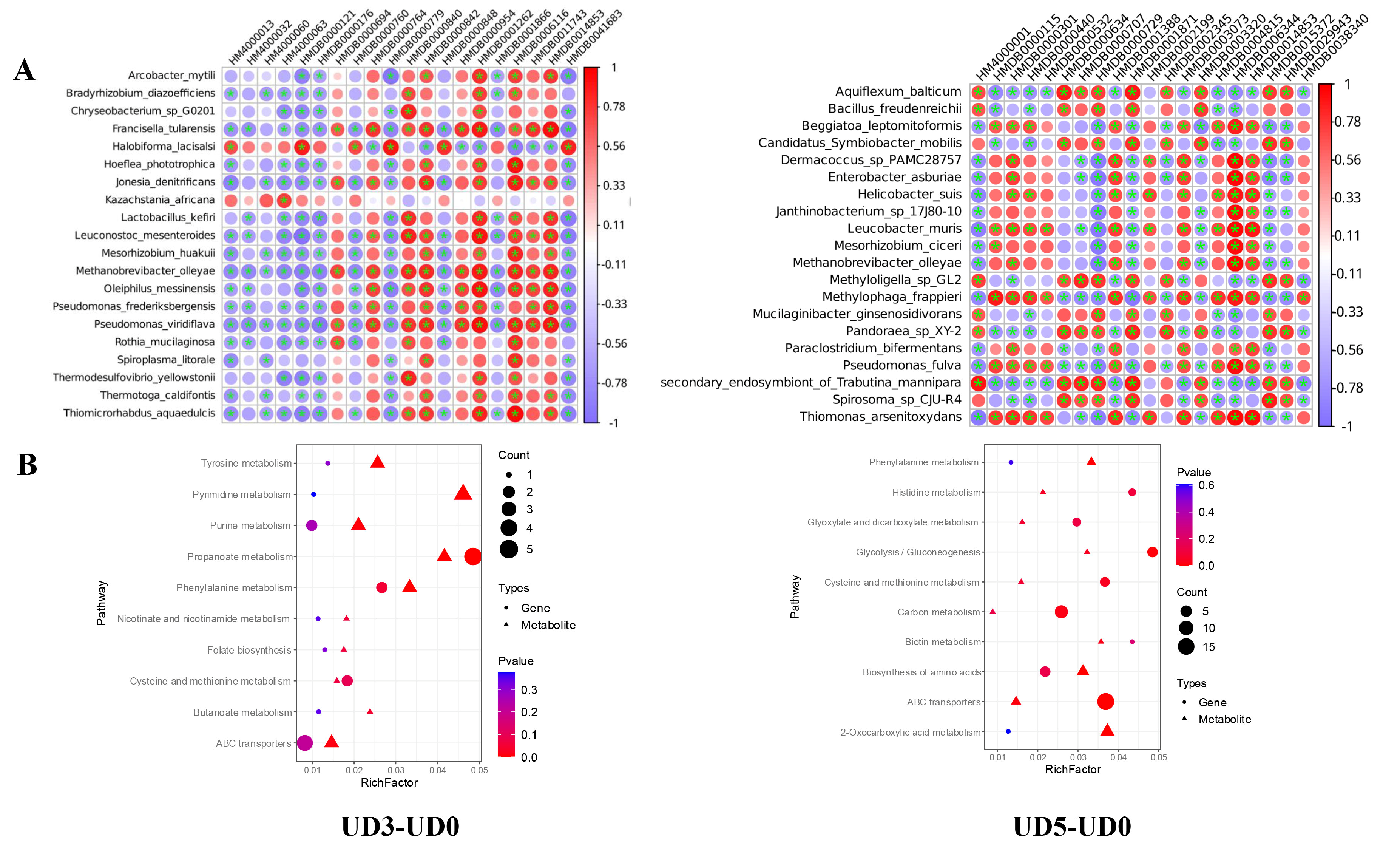
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Gut Microbiota and Metabolite
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKK | Akkermansia muciniphila |
| FC | Fold Change |
| Hyp | Hydroxyproline |
| ICP-MS | Inductively coupled plasma-Mass Spectrometry |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal Partial Least-Squares Discrimination Analysis |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor-β |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| UPLC-MS | Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography- Mass Spectrometry |
| VIP | Variable Important for the Projection |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size |
References
- Zhang, L.; Chu, J.; Xia, B.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Tang, W. Health Effects of Particulate Uranium Exposure. Toxics 2022, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wei, Z.; Jiang, X.; Wei, C.; Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, R.; Nie, J.; Shi, Y.; Qin, X. A comprehensive retrospect on the current perspectives and future prospects of pneumoconiosis. Front. Public Health 2025, 12, 1435840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitot, F.; Lestaevel, P.; Tourlonias, E.; Mazzucco, C.; Jacquinot, S.; Dhieux, B.; Delissen, O.; Tournier, B.B.; Gensdarmes, F.; Beaunier, P.; et al. Inhalation of uranium nanoparticles: Respiratory tract deposition and translocation to secondary target organs in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 217, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Yang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Li, P.; Liu, G.; Cheng, Z.; Wei, H.; Zhu, M. Distribution of uranium in rats inhaled with depleted uranium aerosols. Chin. J. Radiol. Med. Prot. 2009, 29, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Koudstaal, T.; Funke-Chambour, M.; Kreuter, M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Wijsenbeek, M.S. Pulmonary fibrosis: From pathogenesis to clinical decision-making. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savin, I.A.; Zenkova, M.A.; Sen’kova, A.V. Pulmonary Fibrosis as a Result of Acute Lung Inflammation: Molecular Mechanisms, Relevant In Vivo Models, Prognostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Liu, X.; Peng, C.; Meng, X.; Jia, Q. Silicosis: From pathogenesis to therapeutics. Front Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1516200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, J.; Lei, H.; Zhai, X. Development of potent indole-3-carboxamide autotaxin inhibitors with preferred lipophilicity for in vivo treatment of pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 288, 117398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Lu, F.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, S. Respiratory diseases and gut microbiota: Relevance, pathogenesis, and treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1358597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, U.C.; Singh, D.P.; Choudhari, O.K.; Gothi, D.; Singh, S. Correlation of Severity of Functional Gastrointestinal Disease Symptoms with that of Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Multicenter Study. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2018, 8, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; He, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, F.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. The mechanism of gut-lung axis in pulmonary fibrosis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1258246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alswat, A.S. The Influence of the Gut Microbiota on Host Health: A Focus on the Gut-Lung Axis and Therapeutic Approaches. Life 2024, 14, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioma, O.S.; Hesse, L.E.; Chapman, A.; Drake, W.P. Role of the Microbiome in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 595522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Yang, L. Regulation effect of the intestinal flora and intervention strategies targeting the intestinal flora in alleviation of pulmonary fibrosis development. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2024, 43, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioma, O.S.; Mallott, E.K.; Chapman, A.; Van Amburg, J.C.; Wu, H.; Shah-Gandhi, B.; Dey, N.; Kirkland, M.E.; Blanca Piazuelo, M.; Johnson, J.; et al. Gut microbiota modulates lung fibrosis severity following acute lung injury in mice. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.C.; Song, S.R.; Su, J. Pulmonary fibrosis alters gut microbiota and associated metabolites in mice: An integrated 16S and metabolomics analysis. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lu, L.; Liu, B.; Qin, S. Effects of phycocyanin on pulmonary and gut microbiota in a radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Li, L.; Yi, M.; Qin, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, F.; Wu, B.; Yuan, X. The Intestinal Microbiota Plays as a Protective Regulator Against Radiation Pneumonitis. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Z.; An, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Lu, D.; Zhong, J.; et al. Subchronic exposure to concentrated ambient PM2.5 perturbs gut and lung microbiota as well as metabolic profiles in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Huang, R. Alterations in the gut microbiota of patients with silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2019, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, I.; Crescenzi, O.; Esposito, S. Gut Dysbiosis in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: Development, Features and the Role of Gut-Lung Axis on Disease Progression. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; De Rubis, G.; Sirohi, E.; Mishra, N.; Rihan, M.; Garg, A.; Reyes, R.J.; Manandhar, B.; Bhatt, S.; Jha, N.K.; et al. Short Chain Fatty Acids: Fundamental mediators of the gut-lung axis and their involvement in pulmonary diseases. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 368, 110231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Wu, X.; Wen, W.; Lan, P. Gut Microbiome Alterations in COVID-19. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, W.; Kong, X.; Yang, X.; Li, K.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zou, J.; Liang, Y. Roles of gut microbiome-associated metabolites in pulmonary fibrosis by integrated analysis. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albedewi, H.; Bindayel, I.; Albarrag, A.; Banjar, H. Correlation of Gut Microbiota, Vitamin D Status, and Pulmonary Function Tests in Children With Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 884104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Shen, X.; Xie, Y.; Ge, A.; Lu, H.; Gu, S.; Kong, L.; Narayana, J.K.; Mattner, J.; Chotirmall, S.H.; et al. A gut Eggerthella lenta-derived metabolite impairs neutrophil function to aggravate bacterial lung infection. Sci Transl Med. 2025, 17, eadq4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Xin, J.; Xu, X.; Ding, Q.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; Wei, X.; Wei, Y.; et al. Cryptotanshinone alleviates radiation-induced lung fibrosis via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 4557–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, Y.; Feng, W.; Peng, C. Interactions between gut microbiota and polyphenols: A mechanistic and metabolomic review. Phytomedicine 2023, 119, 154979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, J.; Chen, L.; Liang, X.; Wu, T.; Tan, C.; Liu, Y. Gut microbiome and metabolites: The potential key roles in pulmonary fibrosis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 943791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmes, P.; Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Ostaszewski, M.; Aho, V.T.E.; Novikova, P.V.; Laczny, C.C.; Schneider, J.G. The gut microbiome molecular complex in human health and disease. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautkramer, K.A.; Fan, J.; Bäckhed, F. Gut microbial metabolites as multi-kingdom intermediates. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunxi, L.; Haiyue, L.; Yanxia, L.; Jianbing, P.; Jin, S. The Gut Microbiota and Respiratory Diseases: New Evidence. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 2340670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, G. Roles of dietary glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in collagen synthesis and animal growth. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C. Detection and Analysis of Lung and Gut Microbiota in Experimental Silicosis Mice. Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Honggang, Y.; Dahai, F.; Lisheng, Y.; Chao, S.; Junfeng, T.; Xiaojuan, Q. Fuming decoction inhibits the activation of lung fibroblast and lung epithelial injury to alleviate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis through regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway. Tianjin J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 37, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Zhu, M.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, Y. Characteristic Pathological Changes of Main Organs of Rats after Inhalation of Depleted Uranium Aerosol. Chin. J. Radiol. Health 2005, 2, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Pan, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L.; Lu, A.; Xiong, S.; Li, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M. Clearance of insoluble depleted uranium particles in lungs by citric acid and ambroxol. Mil. Med. Sci. 2014, 38, 775–779. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoli, G. Effect of Citric Acid Atomization Inhalation on Toxicity of Depleted Uranium Instillation in Rat Lung. Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dublineau, I.; Souidi, M.; Gueguen, Y.; Lestaevel, P.; Bertho, J.M.; Manens, L.; Delissen, O.; Grison, S.; Paulard, A.; Monin, A.; et al. Unexpected lack of deleterious effects of uranium on physiological systems following a chronic oral intake in adult rat. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 181989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monleau, M.; De Méo, M.; Paquet, F.; Chazel, V.; Duménil, G.; Donnadieu-Claraz, M. Genotoxic and inflammatory effects of depleted uranium particles inhaled by rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 89, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zeng, F.; Fu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, M. Effects of a Modified Chitosan Compound Combined with Lung Lavage after Inhalation of Depleted Uranium Dust. Health Phys. 2022, 122, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zeng, F.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, M. Features of early injuries in canine model of high dose depleted uranium exposure through bronchial spraying. J. Third Mil. Med. Univ. 2021, 43, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Song, Z.-G.; Liu, C.; Tan, S.; Lin, S.; Zhu, J.; Dai, F.-H.; Gao, J.; She, J.-L.; Mei, Z.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations and gut barrier dysfunction are associated with host immune homeostasis in COVID-19 patients. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, Y.K.; Zuo, T.; Lui, G.C.-Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, A.Y.; Chung, A.C.; Cheung, C.P.; Tso, E.Y.; Fung, K.S.; et al. Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19. Gut 2021, 70, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wan, Y.; Zuo, T.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, H.; Lu, W.; Xu, W.; Lui, G.C.; et al. Prolonged Impairment of Short-Chain Fatty Acid and L-Isoleucine Biosynthesis in Gut Microbiome in Patients With COVID-19. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 548–561.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Ye, W.; Zhao, T.; Li, Z. Rhubarb Alleviates Acute Lung Injury by Modulating Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Mice. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 116, Erratum in Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02885-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H. Study of Efficacy of Wine-Processed Scutellaria Baicalensis on LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury Based on Gut Microbiota and Related Metabolomics. Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Li, T.; Yu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Feng, S.; Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Effects of subchronic oral toxic metal exposure on the intestinal microbiota of mice. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Lee, S.C.; Chen, S.; Li, F. Akkermansia muciniphila: Promises and pitfallsfor next-generation beneficial microorganisms. Arch. Microbiol. 2025, 207, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, P.; Yang, S.; Xue, W.; Xu, B.; Zhang, S.; Tang, B.; Xu, D. Akkermansia muciniphila: A promising probiotic against inflammation and metabolic disorders. Virulence 2024, 15, 2375555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsiedel, R.; Hahn, D.; Ossig, R.; Ritz, S.; Sauer, L.; Buesen, R.; Rehm, S.; Wohlleben, W.; Groeters, S.; Strauss, V.; et al. Gut microbiome and plasma metabolome changes in rats after oral gavage of nanoparticles: Sensitive indicators of possible adverse health effects. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Sun, H.; Lu, C.; He, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q. Kuqin ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 and Akkermansia muciniphila. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz Aziziraftar, S.; Bahrami, R.; Hashemi, D.; Shahryari, A.; Ramezani, A.; Ashrafian, F.; Siadat, S.D. The beneficial effects of Akkermansia muciniphila and its derivatives on pulmonary fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 180, 117571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; He, H.; Qin, L.; Xu, W.; Tian, H.; Liu, R.; Lian, X.; Li, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. Low-dose radiation ameliorates PM2.5-induced lung injury through non-canonical TLR1/TLR2-like receptor pathways modulated by Akkermansia muciniphila. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 289, 117625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberman, Y.; Kamer, I.; Amir, A.; Goldenberg, S.; Efroni, G.; Daniel-Meshulam, I.; Lobachov, A.; Daher, S.; Hadar, R.; Gantz-Sorotsky, H.; et al. Gut microbial signature in lung cancer patients highlights specific taxa as predictors for durable clinical benefit. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akk Abundance Alters Survival in Patients with NSCLC on ICIs. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, OF8. [CrossRef]
- Derosa, L.; Routy, B.; Thomas, A.M.; Iebba, V.; Zalcman, G.; Friard, S.; Mazieres, J.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Goldwasser, F.; et al. Intestinal Akkermansia muciniphila predicts clinical response to PD-1 blockade in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, T.; Chelvanambi, M.; Wargo, J.A. Immunotherapy response-associated Akkermansia: Canary in a coal mine? Trends Immunol. 2022, 43, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y. The Cross-Talk Between Gut Microbiota and Lungs in Common Lung Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, W.; Zeng, Y. The role of the microbiota and metabolites in the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis with UC-MSCs: Integrating fecal metabolomics and 16S rDNA analysis. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0313989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyarov, S.; Kotlyarova, A. Anti-Inflammatory Function of Fatty Acids and Involvement of Their Metabolites in the Resolution of Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ameliorate PM2.5 exposure induced lung injury in mice through remodeling the gut microbiota and modulating the lung metabolism. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 40490–40506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Zou, Y.; Li, J. Alpha-linolenic acid protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative pathways. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Q.; Zhou, H.B.; Bai, W.F.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Fan, L.Y.; Chang, H.; Shi, S.L. Assessment of progression of pulmonary fibrosis based on metabonomics and analysis of intestinal microbiota. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2024, 52, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, K.; Zhuang, S.; Ma, N.; Nan, S.; Li, Q.; Ding, M.; Ding, Y. Astragalus polysaccharides alleviates lipopolysaccharides-induced inflammatory lung injury by altering intestinal microbiota in mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1033875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Xia, H.; Han, S.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhuge, A.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Lv, L.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by modulating the gut microbiota and SCFAs in mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10401–10417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, R.; Gu, X.; Su, L.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Liang, H.; Xue, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhan, J. The Impact of Uranium-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis on Gut Microbiota and Related Metabolites in Rats. Metabolites 2025, 15, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080492
Dong R, Gu X, Su L, Wu Q, Tang Y, Liang H, Xue X, Zhang T, Zhan J. The Impact of Uranium-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis on Gut Microbiota and Related Metabolites in Rats. Metabolites. 2025; 15(8):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080492
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Ruifeng, Xiaona Gu, Lixia Su, Qingdong Wu, Yufu Tang, Hongying Liang, Xiangming Xue, Teng Zhang, and Jingming Zhan. 2025. "The Impact of Uranium-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis on Gut Microbiota and Related Metabolites in Rats" Metabolites 15, no. 8: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080492
APA StyleDong, R., Gu, X., Su, L., Wu, Q., Tang, Y., Liang, H., Xue, X., Zhang, T., & Zhan, J. (2025). The Impact of Uranium-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis on Gut Microbiota and Related Metabolites in Rats. Metabolites, 15(8), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080492





