Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted MR Imaging and Signal Variations in a Rat Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
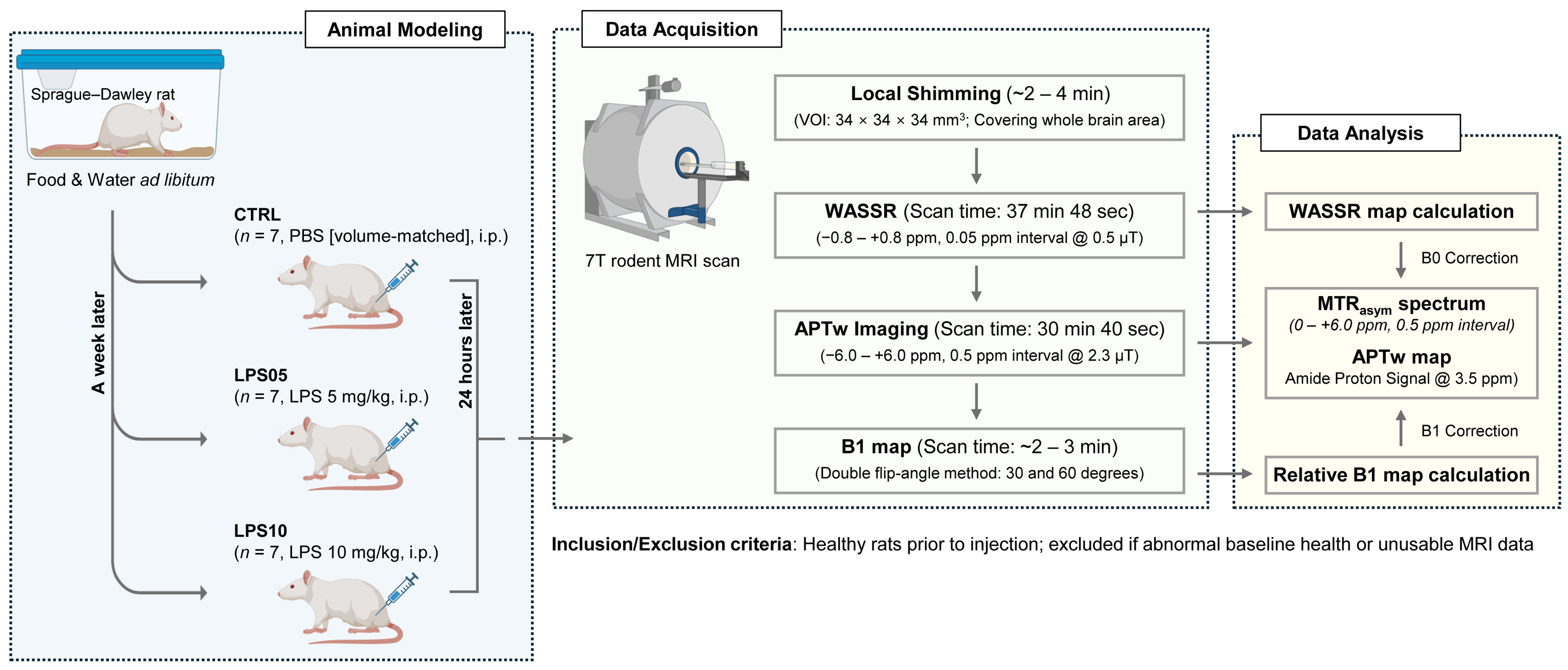
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. LPS-Induced Sepsis Modeling
2.3. Clinically Informed Observations in LPS-Treated Rats
2.4. In Vivo APTw CEST Imaging
2.5. Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
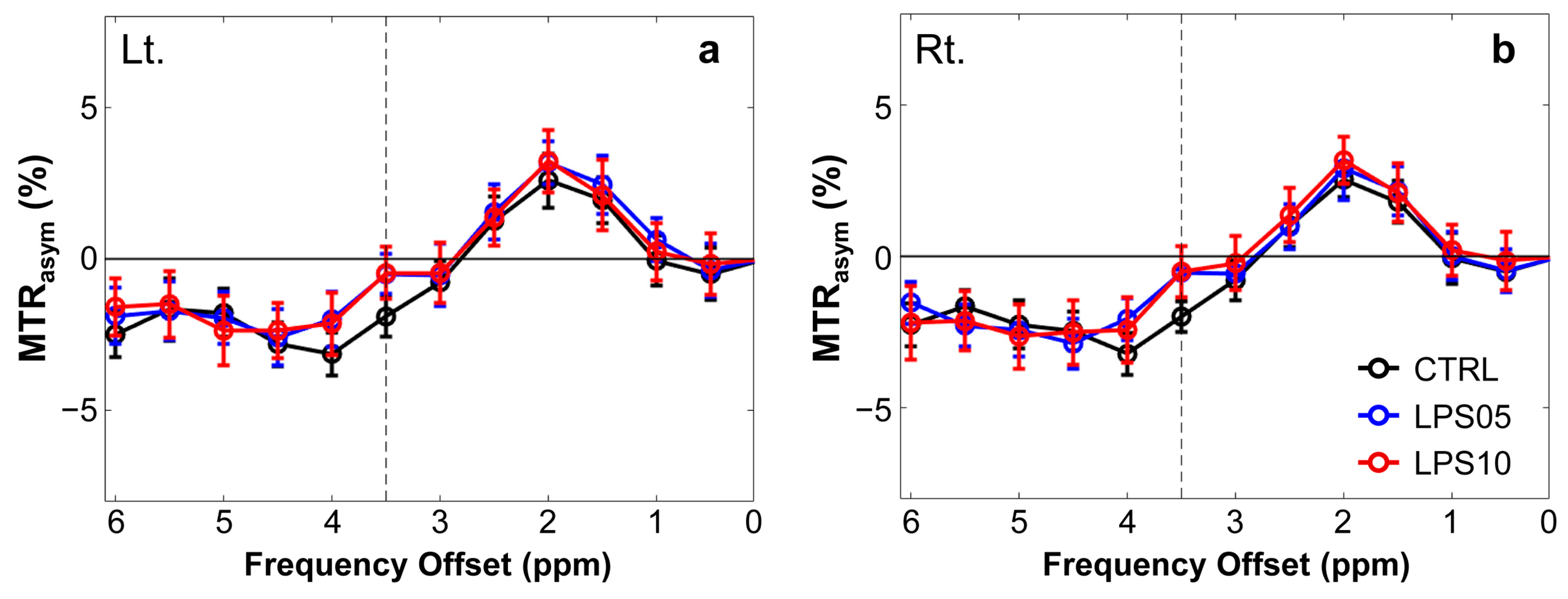
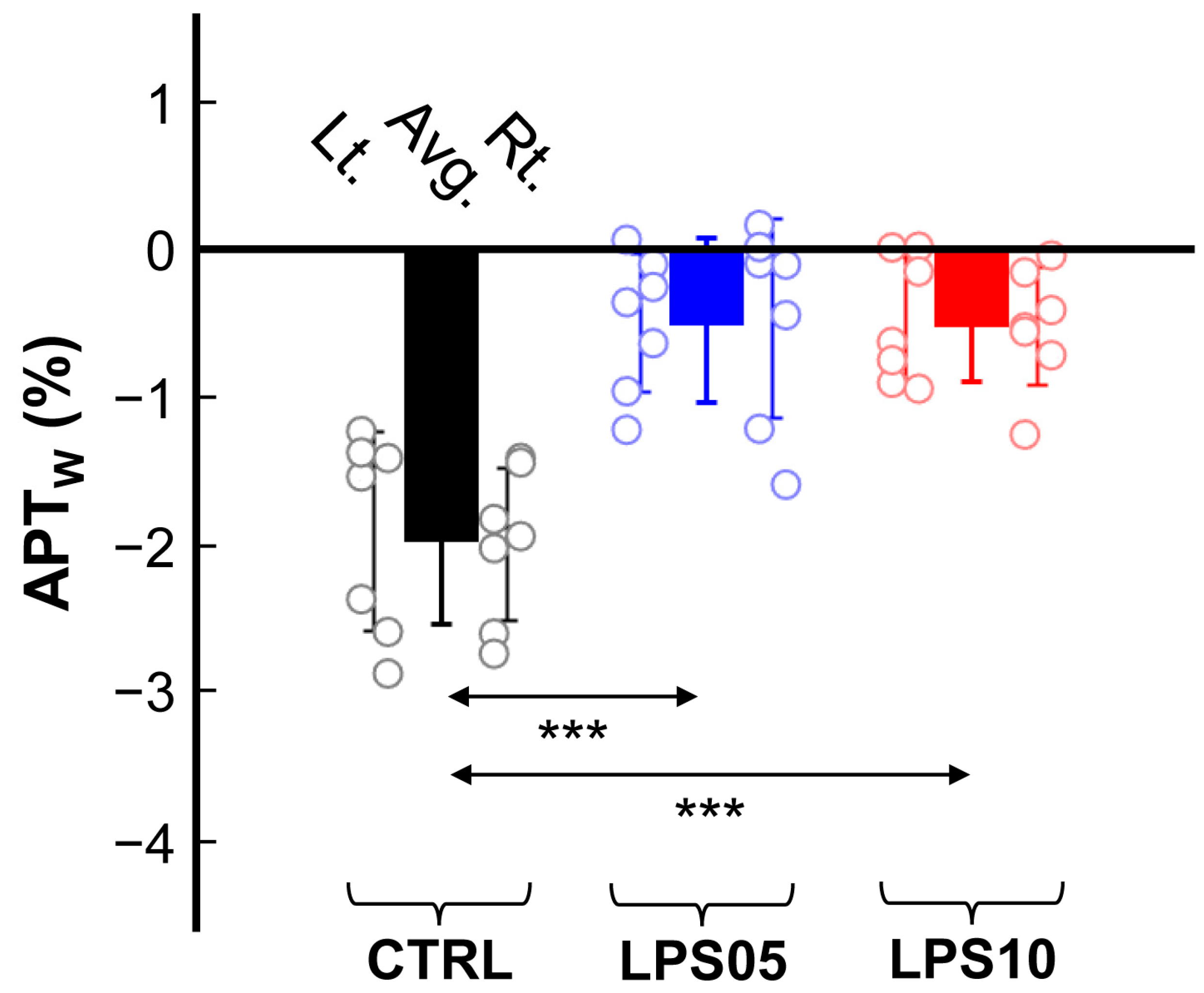
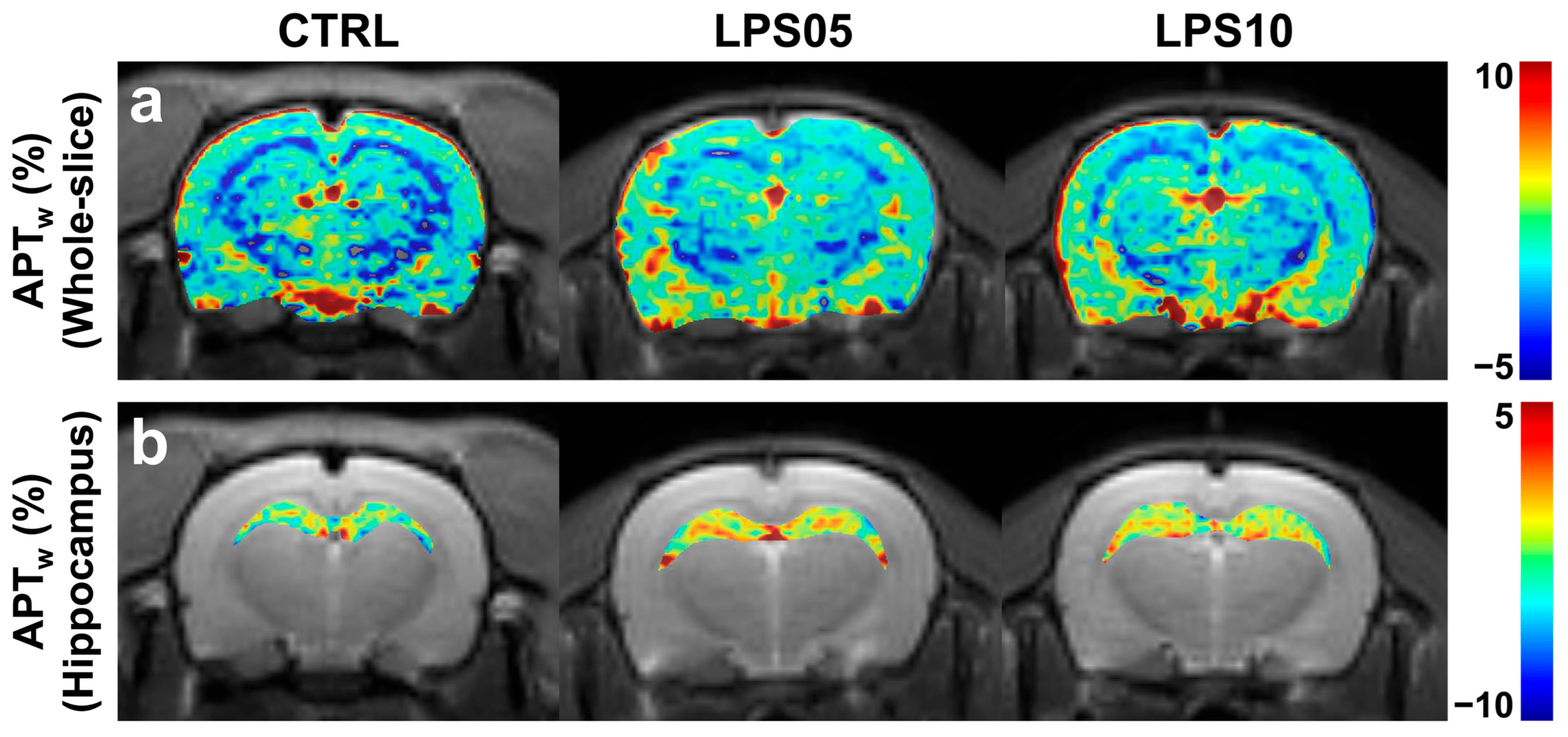
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catarina, A.V.; Branchini, G.; Bettoni, L.; De Oliveira, J.R.; Nunes, F.B. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: From pathophysiology to progress in experimental studies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 2770–2779. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, S.; Geng, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Cao, Y.; Li, R.; Gao, G.; Li, L. Development of a nomogram to predict 30-day mortality of patients with sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A retrospective cohort study. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Shi, X.; Diao, M.; Jin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, W.; Xi, S. A retrospective study of sepsis-associated encephalopathy: Epidemiology, clinical features and adverse outcomes. BMC Emerg. Med. 2020, 20, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Barichello, T.; Generoso, J.S.; Collodel, A.; Petronilho, F.; Dal-Pizzol, F. The blood-brain barrier dysfunction in sepsis. Tissue Barriers 2021, 9, 1840912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielski, L.G.; Giustina, A.D.; Badawy, M.; Barichello, T.; Quevedo, J.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Petronilho, F. Brain Barrier Breakdown as a Cause and Consequence of Neuroinflammation in Sepsis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buras, J.A.; Holzmann, B.; Sitkovsky, M. Animal models of sepsis: Setting the stage. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 854–865. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, M.; Gerlach, H.; Vogelmann, T.; Preissing, F.; Stiefel, J.; Adam, D. Mortality in sepsis and septic shock in Europe, North America and Australia between 2009 and 2019—Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 239. [Google Scholar]
- Bircak-Kuchtova, B.; Chung, H.-Y.; Wickel, J.; Ehler, J.; Geis, C. Neurofilament light chains to assess sepsis-associated encephalopathy: Are we on the track toward clinical implementation? Crit. Care 2023, 27, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sonneville, R.; Verdonk, F.; Rauturier, C.; Klein, I.F.; Wolff, M.; Annane, D.; Chretien, F.; Sharshar, T. Understanding brain dysfunction in sepsis. Ann. Intensive Care 2013, 3, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Netea, M.G.; Van Der Meer, J.W.; Van Deuren, M.; Kullberg, B.J. Proinflammatory cytokines and sepsis syndrome: Not enough, or too much of a good thing? Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- James, M.L.; Gambhir, S.S. A molecular imaging primer: Modalities, imaging agents, and applications. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 897–965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, D.J.; Yamamoto, A.K.; Menon, D.K. Imaging in sepsis-associated encephalopathy—Insights and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Nakaso, K.; Horikoshi, Y.; Morimoto, M.; Omotani, T.; Otsuki, A.; Inagaki, Y.; Sato, H.; Matsura, T. System xc− in microglia is a novel therapeutic target for post-septic neurological and psychiatric illness. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7562. [Google Scholar]
- Osborn, E.A.; Jaffer, F.A. Advances in molecular imaging of atherosclerotic vascular disease. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2008, 23, 620–628. [Google Scholar]
- Weissleder, R.; Pittet, M.J. Imaging in the era of molecular oncology. Nature 2008, 452, 580–589. [Google Scholar]
- Dumbuya, J.S.; Li, S.; Liang, L.; Zeng, Q. Paediatric sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE): A comprehensive review. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Reed, J.L.; Wang, F.; Yan, X.; Lu, M.; Gore, J.C.; Chen, L.M. Validation of qMT and CEST MRI as Biomarkers of Response to Treatment After Lumbar Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. NMR Biomed. 2025, 38, e70015. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.-W.; Kwon, J.-I.; Heo, H.; Woo, C.-W.; Yu, N.H.; Kim, K.W.; Woo, D.-C. Cerebral Glutamate Alterations Using Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Imaging in a Rat Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis. Metabolites 2023, 13, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Heo, H.; Woo, C.-W.; Chae, Y.J.; Choi, M.Y.; Min, J.; Woo, D.-C.; Lee, D.-W. In Vivo Assessment of Cerebral Functional Changes in a Rat Model of Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy Using Multi-Parametric MR Imaging. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2025, 56, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liao, H.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, S.; Li, Q.; Si, Y.; Bao, H. Disrupted metabolic and spontaneous neuronal activity of hippocampus in sepsis associated encephalopathy rats: A study combining magnetic resonance spectroscopy and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1032098. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wu, G.; Ye, H.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, S. Assessment of sepsis-associated encephalopathy by quantitative magnetic resonance spectroscopy in a rat model of cecal ligation and puncture. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wen, M.; Lian, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhu, S.; Hu, B.; Han, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zeng, H. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy for assessment of brain injury in the rat model of sepsis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4118–4124. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Zhu, T.; Jiang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, D.; Liang, Z.; Bi, L.; Yang, M.; Liang, M.; Li, D.; Lin, Y. Early Diagnosis of Murine Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy Using Dynamic PET/CT Imaging and Multiparametric MRI. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szöllősi, D.; Hegedűs, N.; Veres, D.S.; Futó, I.; Horváth, I.; Kovács, N.; Martinecz, B.; Dénes, Á.; Seifert, D.; Bergmann, R.; et al. Evaluation of Brain Nuclear Medicine Imaging Tracers in a Murine Model of Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 20, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zijl, P.C.; Yadav, N.N. Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST): What is in a name and what isn’t? Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 927–948. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Payen, J.-F.; Wilson, D.A.; Traystman, R.J.; Van Zijl, P.C.M. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Tryggestad, E.; Wen, Z.; Lal, B.; Zhou, T.; Grossman, R.; Wang, S.; Yan, K.; Fu, D.-X.; Ford, E.; et al. Differentiation between glioma and radiation necrosis using molecular magnetic resonance imaging of endogenous proteins and peptides. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Lee, D.-W.; Kwon, J.-I.; Kim, S.-T.; Woo, C.-W.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, C.G.; Suh, J.-Y. Changes to gamma-aminobutyric acid levels during short-term epileptiform activity in a kainic acid-induced rat model of status epilepticus: A chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging study. Brain Res. 2019, 1717, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.-H.; Lee, D.-W.; Kwon, J.-I.; Woo, C.-W.; Kim, S.-T.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, C.G.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, J.K.; Woo, D.-C. In Vivo Mapping and Quantification of Creatine Using Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Imaging in Rat Models of Epileptic Seizure. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-W.; Woo, D.-C.; Heo, H.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, D.-H. Signal alterations of glutamate-weighted chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI in lysophosphatidylcholine-induced demyelination in the rat brain. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 164, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Heo, H.; Woo, C.W.; Woo, D.C.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, D.H. Temporal changes in in vivo glutamate signal during demyelination and remyelination in the corpus callosum: A glutamate-weighted chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Woo, C.-W.; Heo, H.; Ko, Y.; Jang, J.S.; Na, S.; Kim, N.; Woo, D.-C.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, D.-W. Mapping Changes in Glutamate with Glutamate-Weighted MRI in Forced Swim Test Model of Depression in Rats. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, K.; Li, H.; Tao, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, H.; Wei, J.; Wang, A. Glutamate chemical exchange saturation transfer (GluCEST) MRI to evaluate the relationship between demyelination and glutamate content in depressed mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2025, 476, 115247. [Google Scholar]
- Foo, L.S.; Harston, G.; Mehndiratta, A.; Yap, W.-S.; Hum, Y.C.; Lai, K.W.; Mukari, S.A.M.; Zaki, F.M.; Tee, Y.K. Clinical translation of amide proton transfer (APT) MRI for ischemic stroke: A systematic review (2003–2020). Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 3797. [Google Scholar]
- Cronin, A.E.; Liebig, P.; Detombe, S.A.; Duggal, N.; Bartha, R. Reproducibility of 3D chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) contrasts in the healthy brain at 3T. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25637. [Google Scholar]
- Hamon, G.; Lecler, A.; Ferré, J.-C.; Bourdillon, P.; Duron, L.; Savatovsky, J. 3-Tesla amide proton transfer-weighted imaging (APT-WI): Elevated signal also in tumor mimics. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 35, 3558–3567. [Google Scholar]
- By, S.; Barry, R.L.; Smith, A.K.; Lyttle, B.D.; Box, B.A.; Bagnato, F.R.; Pawate, S.; Smith, S.A. Amide proton transfer CEST of the cervical spinal cord in multiple sclerosis patients at 3T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 806–814. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Luo, H.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, D.; Wu, Y. Mitigation of T1 impact for unbiased tumor magnetic resonance amide proton transfer imaging at 3T. Radiol. Adv. 2025, 2, umaf011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.-P.; Yu, X.-Y.; Pan, Q.-Q.; Ren, J.-J.; Han, Y.-X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ban, T. Multi-Omics and Network-Based Drug Repurposing for Septic Cardiomyopathy. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Peek, V.; Harden, L.M.; Damm, J.; Aslani, F.; Leisengang, S.; Roth, J.; Gerstberger, R.; Meurer, M.; von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Schulz, S. LPS primes brain responsiveness to high mobility group box-1 protein. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-W.; Heo, H.; Woo, D.-C.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, D.-H. Amide proton transfer-weighted 7-T MRI contrast of myelination after cuprizone administration. Radiology 2021, 299, 428–434. [Google Scholar]
- Sagiyama, K.; Mashimo, T.; Togao, O.; Vemireddy, V.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Maher, E.A.; Mickey, B.E.; Pan, E.; Sherry, A.D.; Bachoo, R.M. In vivo chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging allows early detection of a therapeutic response in glioblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4542–4547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Gillen, J.; Landman, B.A.; Zhou, J.; Van Zijl, P.C. Water saturation shift referencing (WASSR) for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) experiments. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 61, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Heo, H.Y.; Knutsson, L.; van Zijl, P.C.; Jiang, S. APT-weighted MRI: Techniques, current neuro applications, and challenging issues. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lal, B.; Wilson, D.A.; Laterra, J.; Van Zijl, P.C. Amide proton transfer (APT) contrast for imaging of brain tumors. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 50, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.H.; Heo, H.Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J. Quantitative assessment of the effects of water proton concentration and water T1 changes on amide proton transfer (APT) and nuclear overhauser enhancement (NOE) MRI: The origin of the APT imaging signal in brain tumor. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 855–863. [Google Scholar]
- Furtmann, J.K.; Sichtermann, T.; Oros-Peusquens, A.-M.; Dekeyzer, S.; Shah, N.J.; Wiesmann, M.; Nikoubashman, O. MRI Analysis Of the Water Content Change In the Brain During Acute Ethanol Consumption Via Quantitative Water Mapping. Alcohol Alcohol. 2022, 57, 429–436. [Google Scholar]
- Nishioku, T.; Dohgu, S.; Takata, F.; Eto, T.; Ishikawa, N.; Kodama, K.B.; Nakagawa, S.; Yamauchi, A.; Kataoka, Y. Detachment of brain pericytes from the basal lamina is involved in disruption of the blood–brain barrier caused by lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in mice. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2009, 29, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Weimer, J.; Jones, S.; Frontera, J. Acute cytotoxic and vasogenic edema after subarachnoid hemorrhage: A quantitative MRI study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gofton, T.E.; Young, G.B. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heming, N.; Mazeraud, A.; Verdonk, F.; Bozza, F.A.; Chrétien, F.; Sharshar, T. Neuroanatomy of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Ziaja, M. Sepsis and septic encephalopathy: Characteristics and experimental models. Folia Neuropathol. 2012, 50, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Ryu, H.; Chae, Y.J.; Binjaffar, H.; Woo, C.-W.; Woo, D.-C.; Lee, D.-W. Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted MR Imaging and Signal Variations in a Rat Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy. Metabolites 2025, 15, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070465
Lee D, Ryu H, Chae YJ, Binjaffar H, Woo C-W, Woo D-C, Lee D-W. Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted MR Imaging and Signal Variations in a Rat Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy. Metabolites. 2025; 15(7):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070465
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Donghoon, HyunJu Ryu, Yeon Ji Chae, Hind Binjaffar, Chul-Woong Woo, Dong-Cheol Woo, and Do-Wan Lee. 2025. "Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted MR Imaging and Signal Variations in a Rat Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy" Metabolites 15, no. 7: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070465
APA StyleLee, D., Ryu, H., Chae, Y. J., Binjaffar, H., Woo, C.-W., Woo, D.-C., & Lee, D.-W. (2025). Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted MR Imaging and Signal Variations in a Rat Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy. Metabolites, 15(7), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070465





