Unravelling the Dynamic Physiological and Metabolome Responses of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Saline–Alkaline Stress at the Seedling Stage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Plant Growth Conditions
2.2. Evaluation of Physiological Parameters
2.3. Extraction of Samples for Metabolomics Analysis
2.4. UPLC and ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS Conditions
- Starting conditions: 95% A, 5% B; within 9 min, a linear gradient to 5% A, 95% B; and a composition of 5% A, 95% B was kept for 1 min;
- Then, a composition of 95% A and 5.0% B was adjusted within 1.1 min and kept for 2.9 min;
- The flow velocity was set as 0.35 mL/min;
- The column oven was set to 40 °C;
- The injection volume was 2 μL;
- The effluent was alternatively connected to an ESI-triple quadrupole-linear ion trap (QTRAP)-MS.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
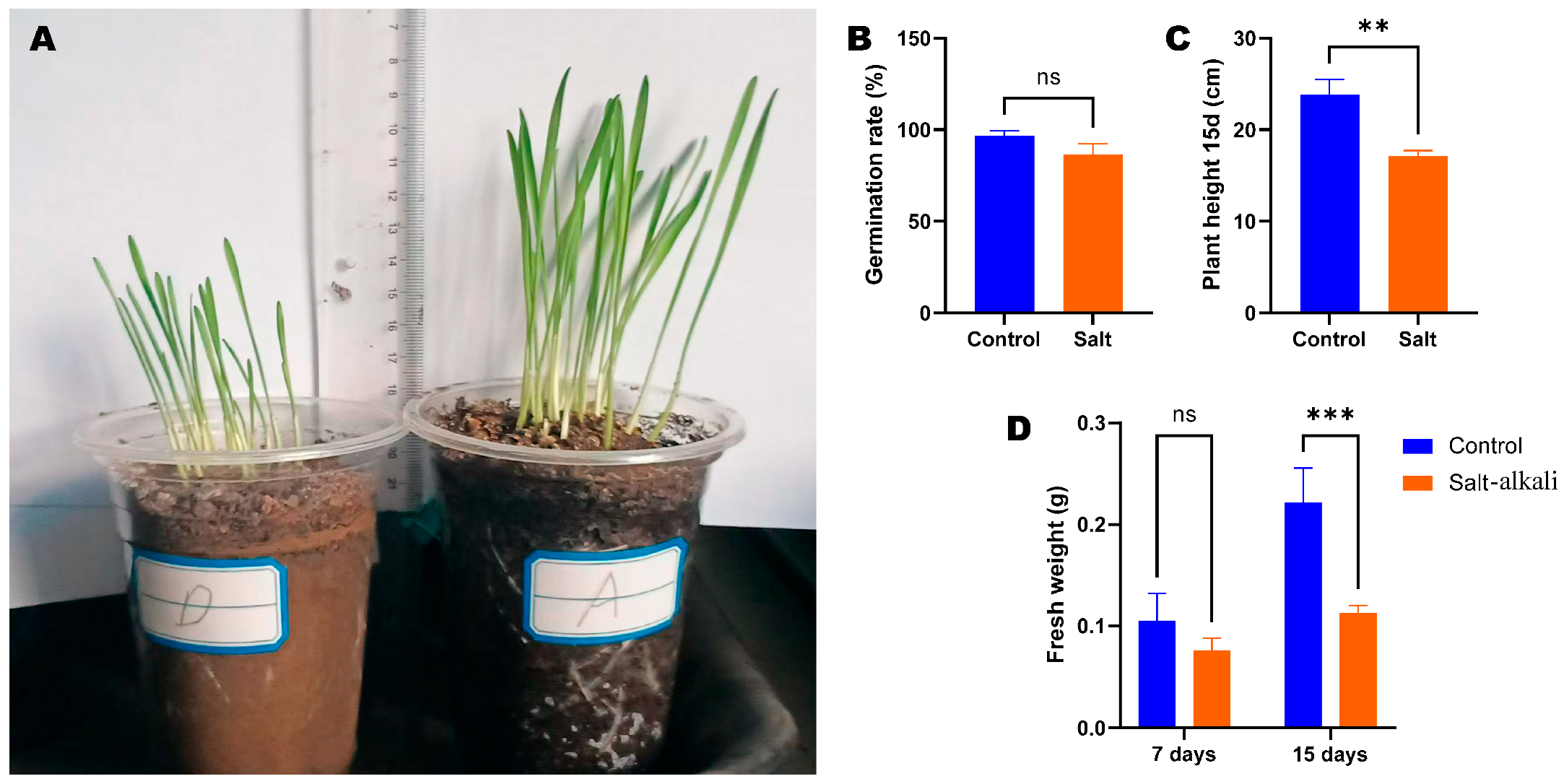
3.1. Effect of Salt Stress on Wheat Seed Germination and Growth
3.2. Dynamic Physiological Responses of Wheat Seedlings to Salt Stress
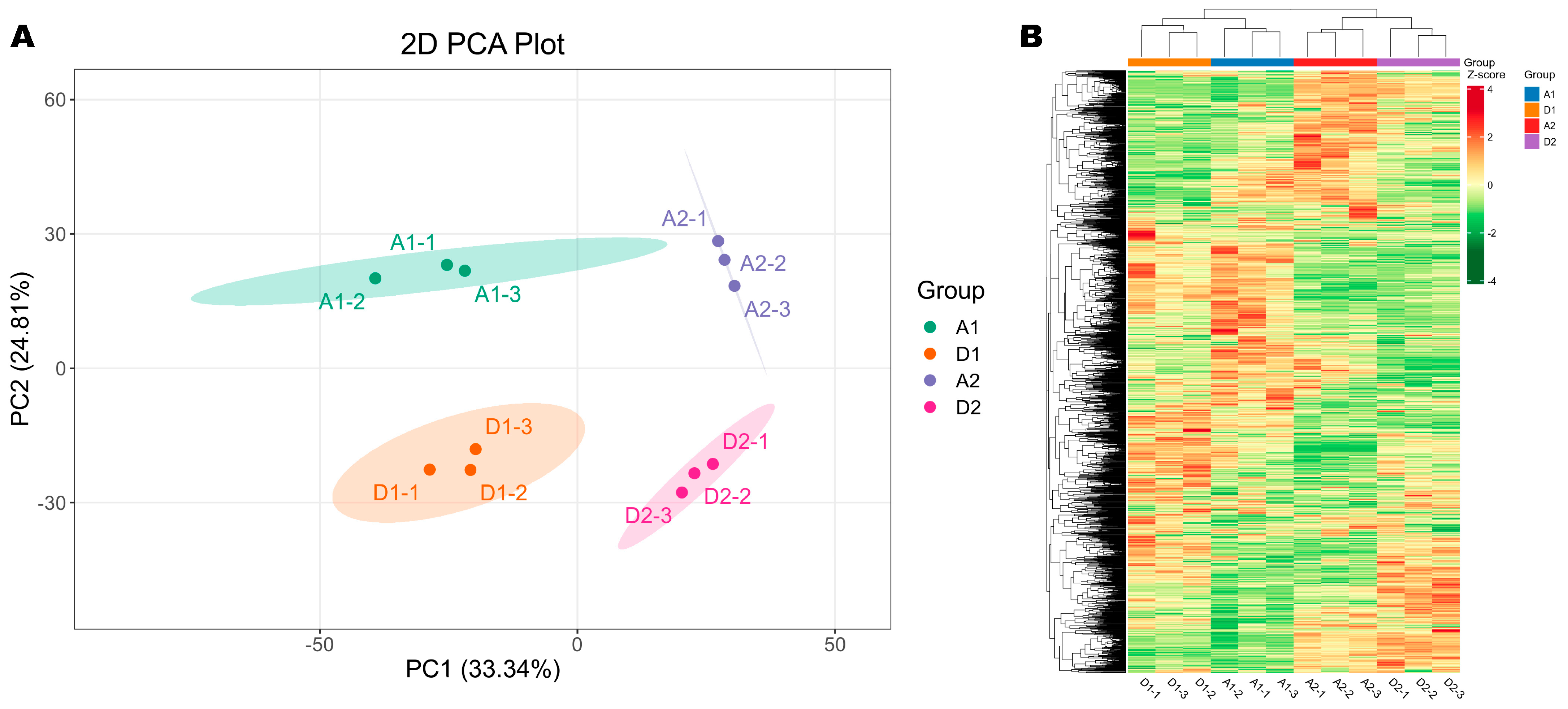
3.3. Metabolome Plasticity of Wheat Seedlings Under Salt Stress
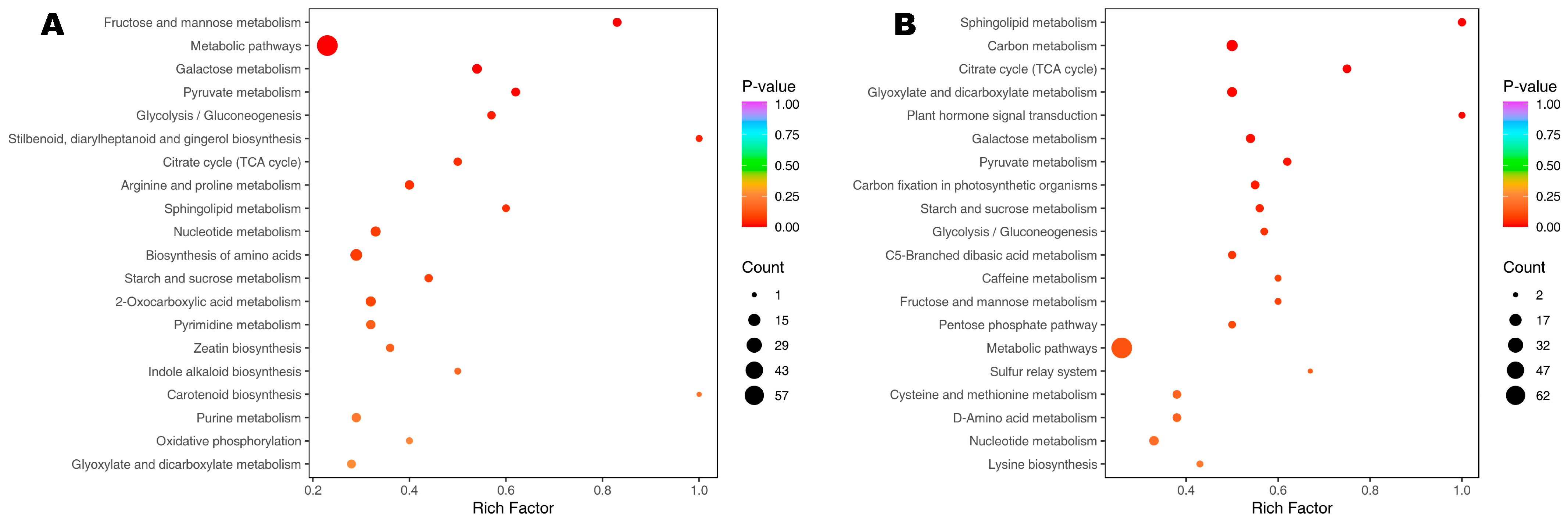
3.4. Differential Metabolites (DMs) and Key Responsive Metabolic Pathways
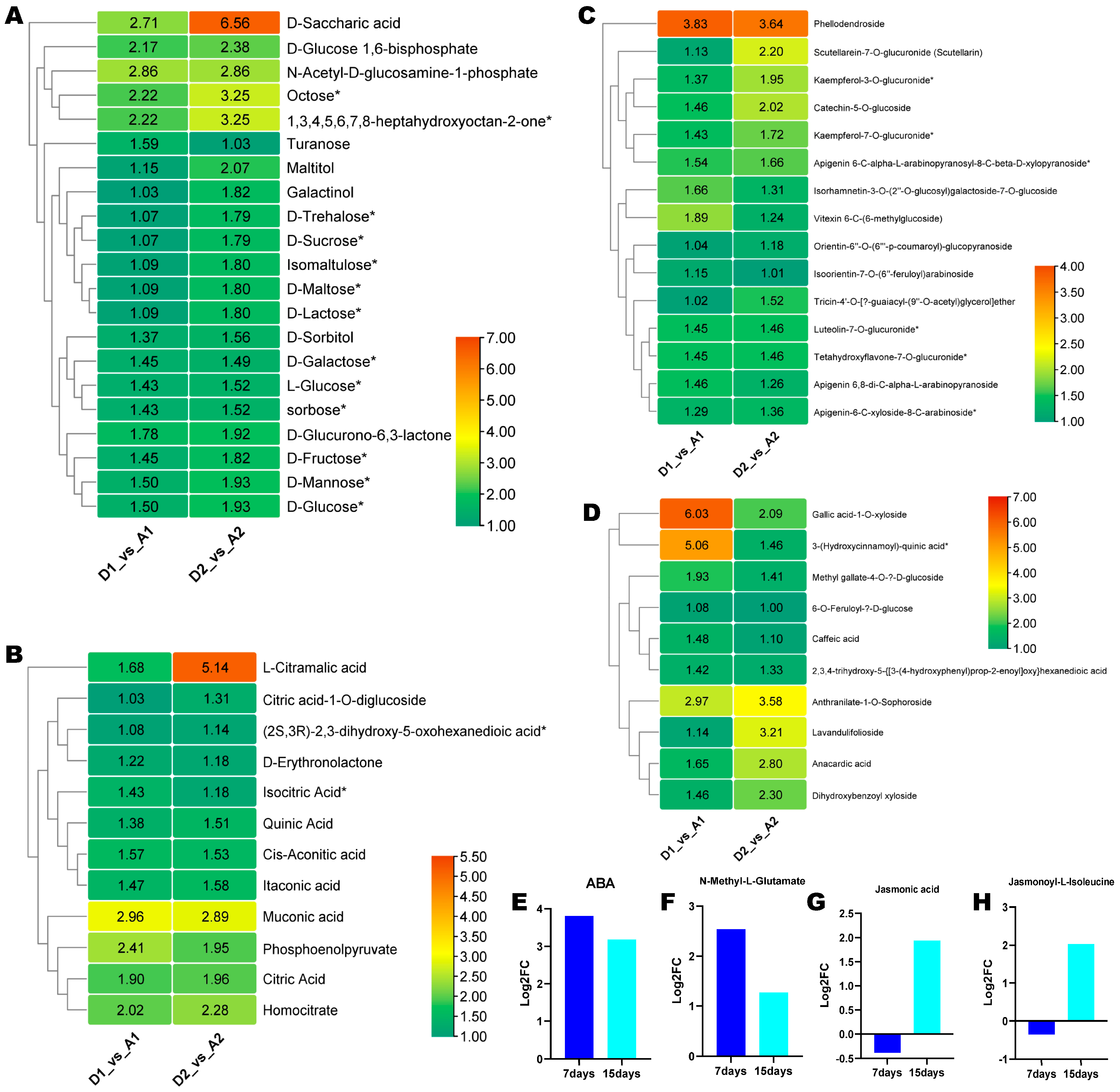
3.5. Potential Salt–Alkali Stress Alleviating Metabolites in Wheat
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Sarkar, B.; Jat, H.S.; Sharma, P.C.; Bolan, N.S. Soil Salinity under Climate Change: Challenges for Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.; Shao, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Feng, X.; Lv, X.; Ding, Q.; Cai, B.; Altan, O. Evolution of Soil Salinization under the Background of Landscape Patterns in the Irrigated Northern Slopes of Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, China. Catena 2021, 206, 105561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Peng, T.; Xue, S. Mechanisms of Plant Saline–Alkaline Tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 281, 153916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, T.; He, X.-L.; Yang, L.-L.; Xu, X.; Feng, Y. Mechanism of Saline–Alkali Land Improvement Using Subsurface Pipe and Vertical Well Drainage Measures and Its Response to Agricultural Soil Ecosystem. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Qian, H.; Fang, Y. Assessment of Soil Salinization Based on a Low-Cost Method and Its Influencing Factors in a Semi-Arid Agricultural Area, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3465–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, A.L.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Tao, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, J. Current Status, Challenges, and Opportunities for Sustainable Crop Production in Xinjiang. iScience 2025, 28, 112114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahri, G.; Alyamani, A.A.; Badran, A.; Hijazi, A.; Nasser, M.; Maresca, M.; Baydoun, E. Enhancing Essential Grains Yield for Sustainable Food Security and Bio-Safe Agriculture through Latest Innovative Approaches. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohra, A.; Choudhary, M.; Bennett, D.; Joshi, R.; Mir, R.R.; Varshney, R.K. Drought-Tolerant Wheat for Enhancing Global Food Security. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2024, 24, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, C.; Ge, S.; Chen, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Sun, T.; Xu, W. Wide-Narrow Row Planting and Limited Irrigation Improve Grain Filling and Spike Traits in Winter Wheat in Arid Regions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Hou, X.; Liang, X. Response Mechanisms of Plants Under Saline–Alkali Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 667458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Y.; Singh, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Salinity Induced Physiological and Biochemical Changes in Plants: An Omic Approach towards Salt Stress Tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chang, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, K. Metabolic and Photosynthesis Analysis of Compound-Material-Mediated Saline and Alkaline Stress Tolerance in Cotton Leaves. Plants 2025, 14, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Kang, H.; Zeng, J. The Tolerance to Saline–Alkaline Stress Was Dependent on the Roots in Wheat. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants Int. J. Funct. Plant Biol. 2020, 26, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifikalhor, M.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Shomali, A.; Azad, N.; Hassani, B.; Lastochkina, O.; Li, T. Calcium Signaling and Salt Tolerance Are Diversely Entwined in Plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2019, 14, 1665455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzyz, P. Decoding the Ca2+ Signal for Salt Tolerance. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 642–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J. Salinity-Alkalinity Tolerance in Wheat: Seed Germination, Early Seedling Growth, Ion Relations and Solute Accumulation. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.M.I.; Farghly, K.A.; Börner, A.; Moursi, Y.S. Candidate Genes Controlling Alkaline-Saline Tolerance in Two Different Growing Stages of Wheat Life Cycle. Plant Soil 2023, 493, 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lian, Y.; Li, S.; Fahim, A.M.; Hou, X.; Liu, L.; Pu, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; et al. Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis Revealed Molecular Regulatory Mechanism of Saline–Alkali Stress Tolerance and Identified BHLH142 in Winter Rapeseed (Brassica rapa). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 139542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Tisarum, R.; Kohli, R.K.; Batish, D.R.; Cha-um, S.; Singh, H.P. Inroads into Saline–Alkaline Stress Response in Plants: Unravelling Morphological, Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Mechanisms. Planta 2024, 259, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luoa, J. A Novel Integrated Method for Large-Scale Detection, Identification, and Quantification of Widely Targeted Metabolites: Application in the Study of Rice Metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossou, S.S.K.; Xu, F.; You, J.; Zhou, R.; Li, D.; Wang, L. Widely Targeted Metabolome Profiling of Different Colored Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) Seeds Provides New Insight into Their Antioxidant Activities. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Khattab, A.R.; Maamoun, A.A.; Kropf, M.; Heiss, A.G. UPLC-MS Metabolome Based Classification of Lupinus and Lens Seeds: A Prospect for Phyto-Equivalency of Its Different Accessions. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgerton, M.D. Increasing Crop Productivity to Meet Global Needs for Feed, Food, and Fuel. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Du, X.; Liu, C. Enhancing Crop Yields to Ensure Food Security by Optimizing Photosynthesis. J. Genet. Genom. 2025, in press, corrected proof. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Moradkhani, H.; Mekonnen, M.; Moftakhari, H.; Magliocca, N. Towards Strategic Interventions for Global Food Security in 2050. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, T.; Neelapu, N.R.R.; Wani, S.H.; Surekha, C. Chapter 30—Role and Regulation of Osmolytes as Signaling Molecules to Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Khan, M.I.R., Reddy, P.S., Ferrante, A., Khan, N.A.B.T.-P.S.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 459–477. ISBN 978-0-12-816451-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Kumari, A. Chapter 9—Role of Compatible Osmolytes in Plant Stress Tolerance under the Influence of Phytohormones and Mineral Elements; Ahanger, M.A., Bhat, J.A., Ahmad, P., John, R.B.T.-I.S.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 165–201. ISBN 978-0-443-18927-2. [Google Scholar]
- Elhakem, H.A. Exogenous Proline Enhances Salt Tolerance in Wheat: Regulating Osmolytes, Hormonal Balance, Antioxidant Defence, and Yield Performance. Plant Soil Environ. 2025, 71, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Yao, Y.-T.; Wang, B.-B.; Li, Y.-M.; Li, L.; Bao, A.-K. Flavonoids Are Involved in Salt Tolerance through ROS Scavenging in the Halophyte Atriplex Canescens. Plant Cell Rep. 2023, 43, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eh, T.-J.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Li, J.; Lei, P.; Ji, X.; Kim, H.-I.; Zhao, X.; Meng, F. The Role of Trehalose Metabolism in Plant Stress Tolerance. J. Adv. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangola, M.P.; Ramadoss, B.R. Chapter 2—Sugars Play a Critical Role in Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. In Biochemical, Physiological and Molecular Avenues for Combating Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants; Wani, S.H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 17–38. ISBN 978-0-12-813066-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Ye, W.; Chen, X.; Ma, X.; Xiong, X.; Hu, G. A Large-Scale Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Glutamate Dehydrogenase 2 (GhGDH2_D03) as a Hub Regulator of Salt and Salt-Alkali Tolerance in Cotton. Plant Mol. Biol. 2025, 115, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Park, Y.; Hwang, I. Abscisic Acid: Biosynthesis, Inactivation, Homoeostasis and Signalling. Essays Biochem. 2015, 58, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Shi, L.; Lv, G.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. Jasmonate Signaling Pathway Confers Salt Tolerance through a NUCLEAR FACTOR-Y Trimeric Transcription Factor Complex in Arabidopsis. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 113825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Song, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Pang, Q. Salt-Alkali-Tolerant Growth-Promoting Streptomyces Sp. Jrh8-9 Enhances Alfalfa Growth and Resilience under Saline–Alkali Stress through Integrated Modulation of Photosynthesis, Antioxidant Defense, and Hormone Signaling. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 296, 128158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, D.; Lin, X. Interlinked Regulator Loops of ABA and JA Respond to Salt and Drought Stress in Caragana korshinskii. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 225, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | pH | Cl− mg/g | SO42− mg/g | Ca2+ mg/g | K+ mg/g | Mg2+ mg/g | Na+ mg/g | CO32− mg/g | HCO3− mg/g | Total Salt mg/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7.21 ± 0.026 | 2.162 ± 0.103 | 2.179 ± 0.085 | 0.026 ± 0.003 | 0.021 ± 0.001 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 4.694 ± 0.125 | 0.069 ± 0.015 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 9.79 ± 0.115 |
| SAS | 10.43 ± 0.021 | 3.457 ± 0.096 | 3.428 ± 0.12 | 0.019 ± 0.002 | 0.029 ± 0.004 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 7.459 ± 0.201 | 0.136 ± 0.013 | 0.055 ± 0.004 | 15.94 ± 0.137 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, W.; Chen, L. Unravelling the Dynamic Physiological and Metabolome Responses of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Saline–Alkaline Stress at the Seedling Stage. Metabolites 2025, 15, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070430
Ren W, Chen L. Unravelling the Dynamic Physiological and Metabolome Responses of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Saline–Alkaline Stress at the Seedling Stage. Metabolites. 2025; 15(7):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070430
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Wei, and Li Chen. 2025. "Unravelling the Dynamic Physiological and Metabolome Responses of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Saline–Alkaline Stress at the Seedling Stage" Metabolites 15, no. 7: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070430
APA StyleRen, W., & Chen, L. (2025). Unravelling the Dynamic Physiological and Metabolome Responses of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Saline–Alkaline Stress at the Seedling Stage. Metabolites, 15(7), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070430





