Simultaneous Quantification of Main Saponins in Panax vietnamensis by HPLC-PDA/ELSD Using the Quantitative Analysis of Multi-Components by Single-Marker Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
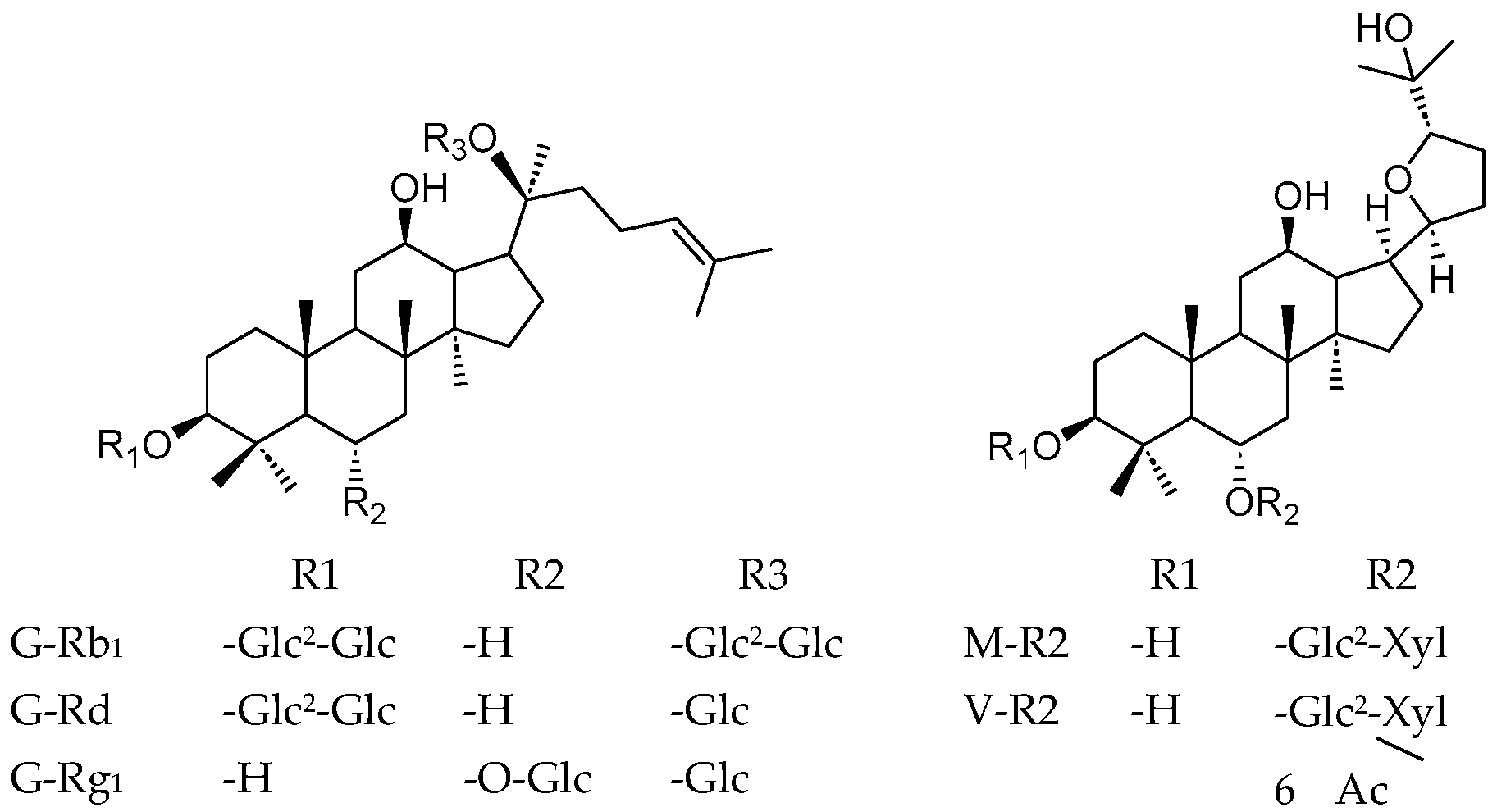
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Sample Solutions
2.3. Preparation of Ginsenoside Standard Solutions
2.4. HPLC-PDA/ELSD Parameters
2.5. HPLC-PDA/ELSD QAMS Method Establishment
3. Results
3.1. Relative Conversion Factor Calculation
3.2. Method Validation of HPLC-PDA/ELSD Methods
3.2.1. Specificity

3.2.2. Linearity, Linear Range, Limit of Detection, and Limit of Quantification
3.2.3. Precision
3.2.4. Accuracy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDA | Photodiode Array; |
| ELSD | Evaporative Light Scattering Detector; |
| QAMS | Quantitative Analysis of Multi-components by Single-marker; |
| VG | Vietnamese Ginseng; |
| OT | Ocotillol; |
| EMS | External Standards Method; |
| Eq. | Equation. |
References
- Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Nguyen, H.T.; Van Le, T.H.; Ma, C.T.; Lee, G.J.; Kwon, S.W.; Park, J.H.; Nguyen, M.D. Accumulation of Saponins in Underground Parts of Panax vietnamensis at Different Ages Analyzed by HPLC-UV/ELSD. Molecules 2020, 25, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlietinck, A.; Pieters, L.; Apers, S. Legal requirements for the quality of herbal substances and herbal preparations for the manufacturing of herbal medicinal products in the European union. Planta Medica 2009, 75, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.M.; Gao, H.M.; Fu, X.T.; Wang, W.H. Multi-components quantitation by one marker new method for quality evaluation of Chinese herbal medicine. J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2006, 31, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar]
- The United States Pharmacopoeial Convention. United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary (USP 2024); United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare. The European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) Supplement 11.2; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Da, J.; Cheng, C.R.; Yao, S.; Long, H.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Khan, I.A.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, Q.R.; Cai, L.Y.; Jiang, B.H.; et al. A reproducible analytical system based on the multi-component analysis of triterpene acids in Ganoderma lucidum. Phytochemistry 2015, 114, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Guo, Q.; Liu, J.; Ma, X. Simultaneous determination of seven phenylethanoid glycosides in Cistanches Herba by a single marker using a new calculation of relative correction factor. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Q.; Ma, N. A quantitative method using one marker for simultaneous assay of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng and P. notoginseng. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2008, 43, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Q.; Jia, X.-H.; Zhu, S.; Komatsu, K.; Wang, X.; Cai, S.-Q. A systematic study on the influencing parameters and improvement of quantitative analysis of multi-component with single marker method using notoginseng as research subject. Talanta 2015, 134, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavrianidi, A.; Stekolshchikova, E.; Porotova, A.; Rodin, I.; Shpigun, O. Combination of HPLC–MS and QAMS as a new analytical approach for determination of saponins in ginseng containing products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 132, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Sun, X.-G.; Dong, R.; Xie, J.-H.; Wang, Y.-L.; Yang, X.-N. Simultaneous quantitative analyses of six components in Astragalus membranaceus based on HPLC-CAD and quantitative analysis of multi-components with a single-marker. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2021, 56, 557–564. [Google Scholar]
- Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Le, T.H.V.; Ngo, T.M.D.; Tran, M.K.; Nguyen, M.D. Quantitative analysis of Saponin in Vietnamese Ginseng (Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv.) cultivated in Lam Dong province by HPLC-UV-ELSD. J. Med. Mater. 2021, 26, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, W.; Liu, J.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Yang, J. Systematic Study on a Quantitative Analysis of Multicomponents by Single Marker (QAMS) Method for Simultaneous Determination of Eight Constituents in Pneumonia Mixture by UPLC-MS/MS. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2021, 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wu, H.; Sun, L.L.; Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Li, S.P.; Wang, W.Y.; Dai, L.; Zhang, Z.R.; Fu, J.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of Multi-components by Single Marker and Fingerprint Analysis of Achyranthes bidentata Blume. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2018, 56, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Hu, C.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, Y. Simultaneous Determination of 25 Ginsenosides by UPLC-HRMS via Quantitative Analysis of Multicomponents by Single Marker. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 2021, 9986793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Q2(R2): Validation of Analytical Procedures; International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Appendix K: Guidelines for Dietary Supplements and Botanicals; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.-L.; Wan, J.; Xiong, J.; Yang, G.-X.; Hu, J.-F. Simultaneous Identification of Characteristic Components in HPLC-PDA-ELSD Fingerprint Profile of Ginkgo biloba Leaves Extract. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19857902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimadzu Scientific Instruments. ELSD and UV—Complementary Detectors for the HPLC Analysis of Commercial Stevia Sweeteners; Application Note, S.C.; Shimadzu Scientific Instruments: Columbia, MD, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.ssi.shimadzu.com (accessed on 1 June 2025).
| The Regression Equation and Fx | Calculate Cx (mg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC-PDA | |||
| Ax = ax × Cx + bx | (1) | Cx = | (4) |
| (2) | Cx = | (5) | |
| (3) | Cx = | (6) | |
| HPLC-ELSD | |||
| log (Ax) = ax × log (Cx) + bx | (7) | Cx = | (10) |
| (8) | Cx = | (11) | |
| (9) | Cx = | (12) | |
| Compound | Average Relative Conversion Factor (Fx) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC-PDA | HPLC-ELSD | ||||
| Fx (2) | Fx (3) | Fx (8) | Fx (9) | ||
| Single marker G-Rb1 | G-Rb1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| G-Rg1 | 1.42 | 1.32 | 0.94 | 0.95 | |
| G-Rd | 1.08 | 1.08 | N.D | N.D | |
| M-R2 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.93 | 0.92 | |
| V-R2 | N.D | N.D | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| Single marker M-R2 | M-R2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| V-R2 | N.D | N.D | 1.04 | 1.05 | |
| Compound | Linearity (n = 3) | R | Linear Range (mg/mL) | LOD (mg/mL) | LOQ (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC-PDA | |||||
| G-Rg1 | y = 13,426 x + 846,186 | 0.9998 | 0.33–1.39 | 0.055 | 0.167 |
| M-R2 | y = 374 x + 14,146 | 0.9999 | 0.55–2.30 | 0.065 | 0.197 |
| V-R2 | N.D | N.D | N.D | N.D | N.D |
| G-Rb1 | y = 10,175 x + 50,838 | 0.9999 | 0.09–0.36 | 0.010 | 0.030 |
| G-Rd | y = 11,035 x + 17,292 | 1.0000 | 0.04–0.17 | 0.007 | 0.022 |
| HPLC-ELSD | |||||
| G-Rg1 | y = 1.3722 x + 1.0728 | 0.9999 | 0.33–1.39 | 0.002 | 0.010 |
| M-R2 | y = 1.3223 x + 1.2472 | 0.9996 | 0.55–2.30 | 0.003 | 0.018 |
| V-R2 | y = 1.3942 x + 1.0544 | 0.9999 | 0.19–0.81 | 0.002 | 0.007 |
| G-Rb1 | y = 1.4371 x + 0.9450 | 0.9998 | 0.09–0.36 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| G-Rd | y = 1.1121 x + 1.3828 | 0.9937 | 0.04–0.17 | 0.014 | 2.804 |
| Compound | %RSD (n = 6) Shimadzu and Agilent HPLC-PDA Systems | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESM (Equation (4)) | QAMS (Equation (5)) | QAMS (Equation (6)) | ||||||
| Shimadzu HPLC System | Agilent HPLC System | Shimadzu HPLC System | Agilent HPLC System | Shimadzu HPLC System | Agilent HPLC System | |||
| Single marker G-Rb1 | G-Rb1 | Intra-day | 1.10 | 1.89 | 1.10 | 1.89 | 1.10 | 1.89 |
| Inter-laboratory | 1.89 | 1.89 | 1.89 | |||||
| G-Rg1 | Intra-day | 0.88 | 1.97 | 0.80 | 1.81 | 0.88 | 1.97 | |
| Inter-laboratory | 2.86 | 3.95 | 2.86 | |||||
| G-Rd | Intra-day | 1.62 | 1.68 | 1.61 | 1.64 | 1.62 | 1.68 | |
| Inter-laboratory | 6.48 | 6.81 | 6.47 | |||||
| M-R2 | Intra-day | 0.96 | 0.26 | 0.92 | 0.20 | 0.96 | 0.26 | |
| Inter-laboratory | 1.89 | 0.65 | 1.94 | |||||
| V-R2 | Intra-day | N.D | N.D | N.D | ||||
| Inter-laboratory | N.D | N.D | N.D | |||||
| Single marker M-R2 | M-R2 | Intra-day | 0.96 | 0.26 | 0.96 | 0.26 | 0.96 | 0.26 |
| Inter-laboratory | 1.89 | 1.89 | 1.89 | |||||
| V-R2 | Intra-day | N.D | N.D | N.D | ||||
| Inter-laboratory | N.D | N.D | N.D | |||||
| Compound | Intra-Day and Inter-Day Precision (%RSD) (n = 6), Shimadzu HPLC-ELSD System | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESM (Equation (10)) | QAMS (Equation (11)) | QAMS (Equation (12)) | ||||||
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 1 | Day 2 | |||
| Single marker G-Rb1 | G-Rb1 | Intra-day | 2.70 | 1.89 | 2.70 | 1.89 | 2.70 | 1.89 |
| Inter-day | 2.83 | 2.83 | 2.83 | |||||
| G-Rg1 | Intra-day | 1.76 | 2.87 | 1.87 | 2.64 | 1.76 | 2.87 | |
| Inter-day | 2.49 | 2.53 | 2.49 | |||||
| G-Rd | Intra-day | N.D | N.D | N.D | ||||
| Inter-day | N.D | N.D | N.D | |||||
| M-R2 | Intra-day | 2.44 | 3.05 | 2.48 | 2.80 | 2.44 | 3.05 | |
| Inter-day | 2.67 | 2.65 | 2.67 | |||||
| V-R2 | Intra-day | 2.72 | 1.44 | 2.40 | 1.23 | 2.72 | 1.44 | |
| Inter-day | 2.12 | 1.97 | 2.12 | |||||
| Single marker M-R2 | M-R2 | Intra-day | 2.44 | 3.05 | 2.44 | 3.05 | 2.44 | 3.05 |
| Inter-day | 2.67 | 2.67 | 2.67 | |||||
| V-R2 | Intra-day | 2.72 | 1.44 | 2.50 | 1.19 | 2.72 | 1.56 | |
| Inter-day | 2.12 | 1.90 | 2.15 | |||||
| Compound | Recovery (%) (n = 9) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC-PDA | HPLC-ELSD | ||||||
| ESM (Equation (4)) | QAMS (Equation (5)) | QAMS (Equation (6)) | ESM (Equation (10)) | QAMS (Equation (11)) | QAMS (Equation (12)) | ||
| Single marker G-Rb1 | G-Rb1 | 80.04–95.30 | 80.04–95.30 | 80.04–95.30 | 90.44–101.56 | 90.44–101.56 | 90.44–101.56 |
| G-Rg1 | 85.98–108.45 | 86.40–108.92 | 85.98–108.45 | 92.95–111.62 | 113.75–134.21 | 92.95–111.62 | |
| G-Rd | 79.37–97.46 | 73.95–90.78 | 79.37–97.46 | N.D | N.D | N.D | |
| M-R2 | 81.75–99.90 | 81.35–99.45 | 81.75–99.90 | 87.69–110.59 | 160.90–191.90 | 87.69–110.59 | |
| V-R2 | N.D | N.D | N.D | 89.07–111.30 | 103.05–125.74 | 89.07–111.30 | |
| Single marker M-R2 | M-R2 | 81.75–99.90 | 81.75–99.90 | 81.75–99.90 | 87.69–110.59 | 87.69–110.59 | 87.69–110.59 |
| V-R2 | N.D | N.D | N.D | 89.07–111.30 | 74.13–92.84 | 89.07–111.30 | |
| Method | The Mean Saponin Content Was Calculated from a Dried Herb (%)with Fx Values According to G-Rb1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-Rb1 | G-Rd | G-Rg1 | M-R2 | |
| ESM (Equation (4)) | 1.46 0.11 | 0.96 0.03 | 3.96 0.26 | 5.51 0.43 |
| QAMS (Equation (5)) | 1.46 0.11 | 0.96 0.03 | 3.95 0.24 | 5.56 0.43 |
| QAMS (Equation (6)) | 1.46 0.11 | 0.96 0.03 | 3.96 0.26 | 5.51 0.43 |
| %SMD (Equations (4) and (5)) | 0.00 0.00 | 0.77 0.18 | 0.34 0.75 | 0.79 0.28 |
| %SMD (Equation (4) and (6)) | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 |
| Method | The Mean Saponin Content Was Calculated from a Dried Herb (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| with Fx Values According to G-Rb1 | with Fx Values According to M-R2 | |||||
| G-Rb1 | G-Rg1 | M-R2 | V-R2 | M-R2 | V-R2 | |
| ESM (Equation (10)) | 1.62 0.11 | 3.99 0.27 | 5.71 0.38 | 2.67 0.16 | 5.71 0.38 | 2.67 0.16 |
| QAMS (Equation (11)) | 1.62 0.11 | 4.55 0.33 | 6.79 0.47 | 2.93 0.19 | 5.71 0.38 | 2.52 0.15 |
| QAMS (Equation (12)) | 1.62 0.11 | 3.99 0.27 | 4.13 0.26 | 2.68 0.16 | 5.71 0.38 | 2.67 0.16 |
| %SMD (Equations (10) and (11)) | 0.00 0.00 | 13.98 1.05 | 18.92 0.90 | 9.80 1.04 | 0.00 0.00 | 5.77 0.69 |
| %SMD (Equations (10) and (12)) | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 27.65 0.48 | 0.51 0.01 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 |
| Method | The Mean Saponin Content Was Calculated from a Dried Herb (%)with Fx Values According to G-Rb1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-Rb1 | G-Rd | G-Rg1 | M-R2 | |
| ESM (Equation (4)) | 1.41 0.24 | 0.94 0.07 | 3.78 0.22 | 5.69 0.40 |
| QAMS (Equation (5)) | 1.41 0.24 | 0.93 0.07 | 3.76 0.21 | 5.71 0.39 |
| QAMS (Equation (6)) | 1.41 0.24 | 0.94 0.07 | 3.78 0.22 | 5.70 0.40 |
| %SMD (Equations (4) and (5)) | 0.00 0.00 | 0.63 0.25 | 0.42 0.88 | 0.40 0.30 |
| %SMD (Equations (4) and (6)) | 0.00 0.00 | 0.01 0.00 | 0.01 0.00 | 0.11 0.00 |
| Method | The Mean Saponin Content Was Calculated from a Dried Herb (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| with Fx Values According to G-Rb1 | with Fx Values According to M-R2 | |||||
| G-Rb1 | G-Rg1 | M-R2 | V-R2 | M-R2 | V-R2 | |
| ESM (Equation (10)) | 1.58 0.10 | 3.91 0.24 | 6.00 0.34 | 2.75 0.15 | 6.00 0.34 | 2.75 0.15 |
| QAMS (Equation (1)) | 1.58 0.10 | 4.46 0.29 | 7.02 0.34 | 2.97 0.19 | 6.00 0.34 | 3.31 0.15 |
| QAMS (Equation (2)) | 1.58 0.10 | 3.91 0.24 | 6.00 0.34 | 2.75 0.15 | 6.00 0.34 | 2.75 0.15 |
| %SMD (Equations (10) and (1)) | 0.00 0.00 | 14.20 0.25 | 17.01 1.07 | 8.32 0.42 | 0.00 0.00 | 20.55 0.45 |
| %SMD (Equations (10) and (2)) | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.01 0.00 | 0.03 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.28 0.71 |
| HPLC-PDA | Fx | The mean saponin content was calculated on a dried herb (%) | |||
| with Fx-Slope values according to G-Rb1 | |||||
| G-Rb1 | G-Rd | G-Rg1 | M-R2 | ||
| Intra-day (n = 3) | 1.46 0.24 | 0.96 0,07 | 3.96 0,56 | 5.51 0,95 | |
| Inter-day (n = 3) | 1.41 0.11 | 0.94 0,07 | 3.78 0,25 | 5.69 0,45 | |
| %SMD | 3.71 0.48 | 1.87 1.07 | 4.66 0.42 | 3.31 0.14 | |
| HPLC-ELSD | Fx | With Fx-Slope values according to G-Rb1 | With Fx-Slope values according to M-R2 | ||
| G-Rb1 | G-Rg1 | M-R2 | V-R2 | ||
| Intra-day (n = 3) | 1.62 0.25 | 3.99 0.60 | 5.71 0.83 | 2.67 0.35 | |
| Inter-day (n = 3) | 1.58 0.25 | 3.91 0.59 | 6.00 0.86 | 2.75 0.36 | |
| %SMD | 2.44 0.17 | 2.01 0.24 | 5.00 0.37 | 3.13 0.90 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ngo, T.-M.-D.; Tran, T.K.N.; Le, T.M.T.; Tran, M.K.; Nguyen, H.S.; Nguyen, H.T.; Vu-Huynh, K.L. Simultaneous Quantification of Main Saponins in Panax vietnamensis by HPLC-PDA/ELSD Using the Quantitative Analysis of Multi-Components by Single-Marker Method. Metabolites 2025, 15, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070419
Ngo T-M-D, Tran TKN, Le TMT, Tran MK, Nguyen HS, Nguyen HT, Vu-Huynh KL. Simultaneous Quantification of Main Saponins in Panax vietnamensis by HPLC-PDA/ELSD Using the Quantitative Analysis of Multi-Components by Single-Marker Method. Metabolites. 2025; 15(7):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070419
Chicago/Turabian StyleNgo, Thi-My-Duyen, Thi Kim Ngan Tran, Thi Minh Thu Le, Mong Kha Tran, Huu Son Nguyen, Huy Truong Nguyen, and Kim Long Vu-Huynh. 2025. "Simultaneous Quantification of Main Saponins in Panax vietnamensis by HPLC-PDA/ELSD Using the Quantitative Analysis of Multi-Components by Single-Marker Method" Metabolites 15, no. 7: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070419
APA StyleNgo, T.-M.-D., Tran, T. K. N., Le, T. M. T., Tran, M. K., Nguyen, H. S., Nguyen, H. T., & Vu-Huynh, K. L. (2025). Simultaneous Quantification of Main Saponins in Panax vietnamensis by HPLC-PDA/ELSD Using the Quantitative Analysis of Multi-Components by Single-Marker Method. Metabolites, 15(7), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070419






