Metabolomics Signatures of a Respiratory Tract Infection During an Altitude Training Camp in Elite Rowers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample 1H NMR Acquisition and Data Processing
2.4. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
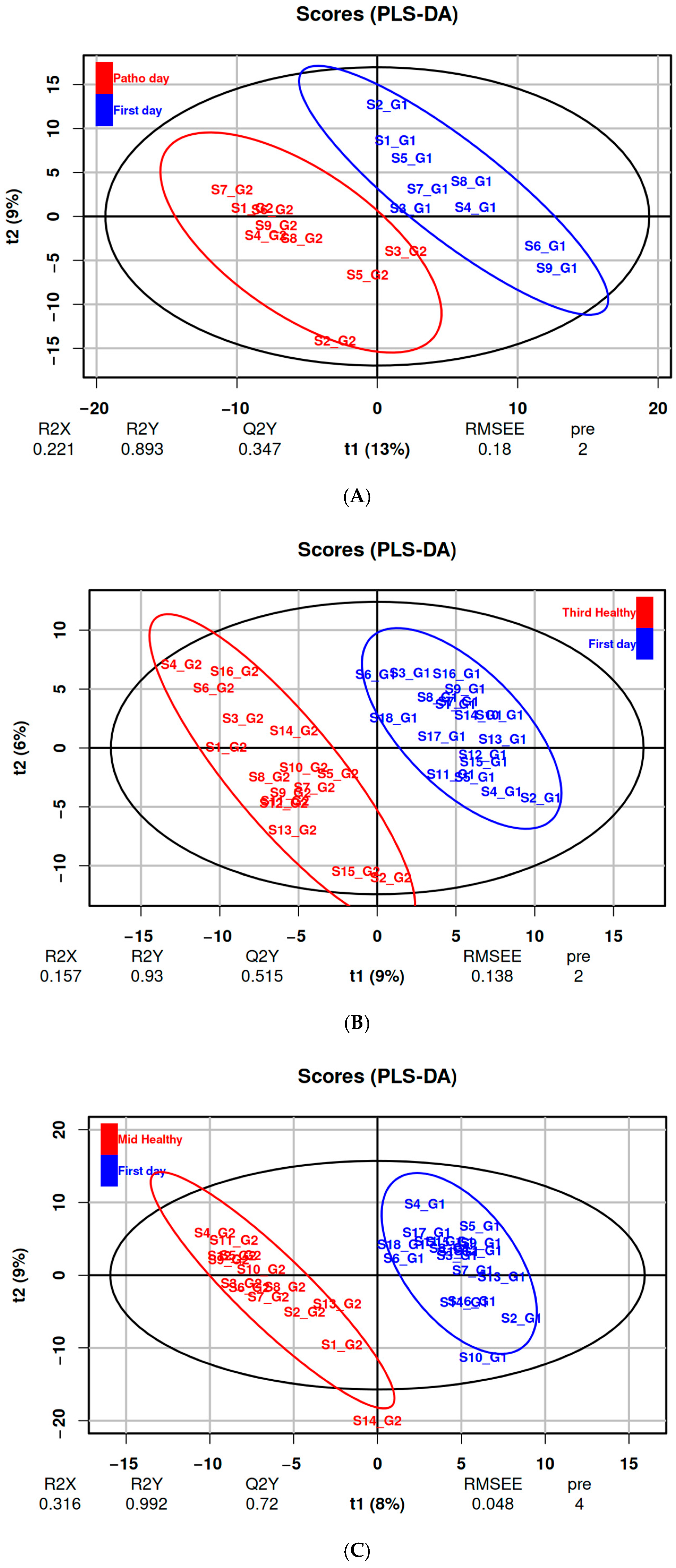
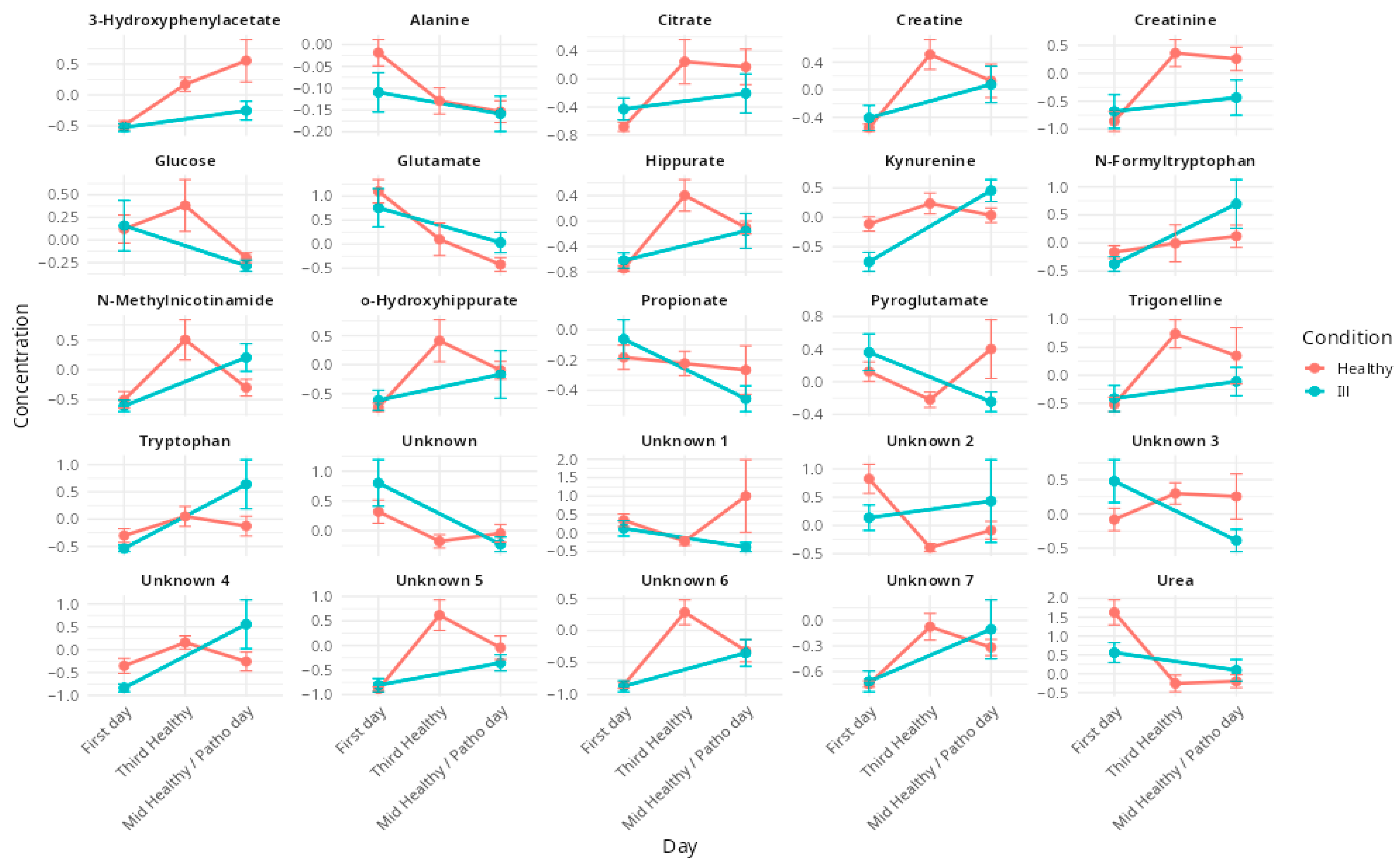
3.2. Effects of Respiratory Illnesses on Metabolic Profiles (DS1)
3.3. Effects of Altitude Training on Metabolic Profiles (DS2 & DS3)
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolic Impact of Altitude Training in Elite Rowers
4.2. Respiratory Pathologies and Their Metabolic Impact During an Altitude Training Camp
4.3. The Complex Interactions of Pathologies and Hypoxia
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1H NMR | Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| TMSP | 3-(trimethylsilyl)propionic-2,2,3,3-d4 acid sodium salt |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PC | Principal Component |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least-Square Discriminant Analysis |
| VIP | Variable Importance in Projection |
| LOOCV | Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation |
| R2 | Goodness of fit |
| Q2 | Ability of prediction |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
References
- Mitchell, J.H.; Haskell, W.; Snell, P.; Van Camp, S.P. Task Force 8: Classification of Sports. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 1364–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volianitis, S.; Yoshiga, C.C.; Secher, N.H. The Physiology of Rowing with Perspective on Training and Health. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 1943–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtscher, M.; Niedermeier, M.; Burtscher, J.; Pesta, D.; Suchy, J.; Strasser, B. Preparation for Endurance Competitions at Altitude: Physiological, Psychological, Dietary and Coaching Aspects. A Narrative Review. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.A.; Iglesias, X.; Feriche, B.; Calderón-Soto, C.; Chaverri, D.; Wachsmuth, N.B.; Schmidt, W.; Levine, B.D. Altitude Training in Elite Swimmers for Sea Level Performance (Altitude Project). Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, G.P.; Roels, B.; Schmitt, L.; Woorons, X.; Richalet, J.P. Combining Hypoxic Methods for Peak Performance. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, J.A.; La Gerche, A.; Hull, J.H. Is the Healthy Respiratory System Built Just Right, Overbuilt, or Underbuilt to Meet the Demands Imposed by Exercise? J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 129, 1235–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, G.; O’Connor, R.; Johnston, N. Altitude Training for Elite Endurance Athletes: A Review for the Travel Medicine Practitioner. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2016, 14, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogo, A. The Lung at High Altitude. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2011, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, L.; Brown, W.J.; Pyne, D.B.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P.; Mccormack, J.G.; Locke, A.S.; Fricker, P.A. Incidence, Etiology, and Symptomatology of Upper Respiratory Illness in Elite Athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujika, I.; Sharma, A.P.; Stellingwerff, T. Contemporary Periodization of Altitude Training for Elite Endurance Athletes: A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 1651–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, M.K.; Finch, C.F. The Relationship Between Training Load and Injury, Illness and Soreness: A Systematic and Literature Review. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 861–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessner, U.; Bowne, J. What Is Metabolomics All About? BioTechniques 2009, 46, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics—The Link between Genotypes and Phenotypes. In Functional Genomics; Town, C., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 155–171. ISBN 978-94-010-0448-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. “Metabonomics”: Understanding the Metabolic Responses of Living Systems to Pathophysiological Stimuli via Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Biological NMR Spectroscopic Data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: The Apogee of the Omics Trilogy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Wentz, L.M. The Compelling Link between Physical Activity and the Body’s Defense System. J. Sport. Health Sci. 2019, 8, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.A.; Pereira, T.C.S.; Souza, A.R.; Ribeiro, P.R. 1H NMR-Based Metabolite Profiling for Biomarker Identification. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 502, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, J.L.; Brüschweiler, R.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Powers, R.; Raftery, D.; Wishart, D.S. The Future of NMR-Based Metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.F.; Diaz, S.O.; Gil, A.M. NMR Metabolomics of Human Blood and Urine in Disease Research. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 93, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, I.J.; Peters, S.R.; Overmyer, K.A.; Paulson, B.R.; Westphall, M.S.; Coon, J.J. Real-Time Health Monitoring through Urine Metabolomics. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamko, D.J.; Nair, P.; Mayers, I.; Tsuyuki, R.T.; Regush, S.; Rowe, B.H. Metabolomic Profiling of Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Pilot Study Differentiating Diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 571–580.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slupsky, C.M. NMR-Based Analysis of Metabolites in Urine Provides Rapid Diagnosis and Etiology of Pneumonia. Biomark. Med. 2010, 4, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bester, R.; Stander, Z.; Mason, S.; Keane, K.M.; Howatson, G.; Clifford, T.; Stevenson, E.J.; Loots, D.T. Characterizing Marathon-Induced Metabolic Changes Using 1H-NMR Metabolomics. Metabolites 2021, 11, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechlivanis, A.; Kostidis, S.; Saraslanidis, P.; Petridou, A.; Tsalis, G.; Mougios, V.; Gika, H.G.; Mikros, E.; Theodoridis, G.A. 1H NMR-Based Metabonomic Investigation of the Effect of Two Different Exercise Sessions on the Metabolic Fingerprint of Human Urine. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6405–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miccheli, A.; Marini, F.; Capuani, G.; Miccheli, A.T.; Delfini, M.; Di Cocco, M.E.; Puccetti, C.; Paci, M.; Rizzo, M.; Spataro, A. The Influence of a Sports Drink on the Postexercise Metabolism of Elite Athletes as Investigated by NMR-Based Metabolomics. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2009, 28, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dünnwald, T.; Paglia, G.; Weiss, G.; Denti, V.; Faulhaber, M.; Schobersberger, W.; Wackerhage, H. High Intensity Concentric-Eccentric Exercise Under Hypoxia Changes the Blood Metabolome of Trained Athletes. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 904618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messier, F.M.; Le Moyec, L.; Santi, C.; Gaston, A.-F.; Triba, M.N.; Roca, E.; Durand, F. The Impact of Moderate Altitude on Exercise Metabolism in Recreational Sportsmen: A Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Metabolomic Approach. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.; Deborde, C.; Lefebvre, M.; Maucourt, M.; Moing, A. NMRProcFlow: A Graphical and Interactive Tool Dedicated to 1D Spectra Processing for NMR-Based Metabolomics. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2024; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Chinnadurai, V.; Bhadra, K.; Gupta, I.; Kanwar, R.S. Urinary Metabolic Modulation in Human Participants Residing in Siachen: A 1H NMR Metabolomics Approach. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibomana, I.; Foose, D.P.; Raymer, M.L.; Reo, N.V.; Karl, J.P.; Berryman, C.E.; Young, A.J.; Pasiakos, S.M.; Mauzy, C.A. Urinary Metabolites as Predictors of Acute Mountain Sickness Severity. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 709804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H.J. Altitude Acclimatization, Training and Performance. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2000, 3, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, G.F. Metabolic Role of Muscle. In Muscle Metabolism During Exercise: Proceedings of a Karolinska Institutet Symposium Held in Stockholm, Sweden, September 6–9, 1970 Honorary Guest: E Hohwü Christensen; Pernow, B., Saltin, B., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1971; pp. 103–109. ISBN 978-1-4613-4609-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, B.-S.; Wu, P.-S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.-S. Effects of Acute Systematic Hypoxia on Human Urinary Metabolites Using LC-MS-Based Metabolomics. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2014, 15, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enea, C.; Seguin, F.; Petitpas-Mulliez, J.; Boildieu, N.; Boisseau, N.; Delpech, N.; Diaz, V.; Eugène, M.; Dugué, B. 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics Approach for Exploring Urinary Metabolome Modifications after Acute and Chronic Physical Exercise. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.M.; Hunter, A.M.; Brennan, L.; O’Sullivan, A.; Hamilton, D.L.; DeVito, G.; Galloway, S.D.R. Six Weeks of a Polarized Training-Intensity Distribution Leads to Greater Physiological and Performance Adaptations than a Threshold Model in Trained Cyclists. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 114, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Castro, L.; Durán, R.E.; Méndez, V.; Dorochesi, F.; Zühlke, D.; Riedel, K.; Seeger, M. The Long-Chain Flavodoxin FldX1 Improves the Biodegradation of 4-Hydroxyphenylacetate and 3-Hydroxyphenylacetate and Counteracts the Oxidative Stress Associated to Aromatic Catabolism in Paraburkholderia Xenovorans. Biol. Res. 2024, 57, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, J.-D.; Lee, Y.-H.; Seo, S.-W.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.-B. Urinary Metabolomics in Young Soccer Players after Winter Training Season. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parstorfer, M.; Poschet, G.; Kronsteiner, D.; Brüning, K.; Friedmann-Bette, B. Targeted Metabolomics in High Performance Sports: Differences between the Resting Metabolic Profile of Endurance- and Strength-Trained Athletes in Comparison with Sedentary Subjects over the Course of a Training Year. Metabolites 2023, 13, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.S.; Kelly, M.P.; Kelly, P. Metabolomics, Physical Activity, Exercise and Health: A Review of the Current Evidence. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, G.; Vinaixa, M.; McGovern, R.; Beltran, A.; Novials, A.; Correig, X.; McClean, C. Metabolomic Response to Acute Hypoxic Exercise and Recovery in Adult Males. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.D.; Farrell, L.; Wood, M.J.; Martinovic, M.; Arany, Z.; Rowe, G.C.; Souza, A.; Cheng, S.; McCabe, E.L.; Yang, E.; et al. Metabolic Signatures of Exercise in Human Plasma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 33ra37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Narro-Serrano, J.; Shalabi-Benavent, M.J.; Álamo-Marzo, J.M.; Amador-Prous, C.; Algado-Rabasa, J.T.; Garijo-Saiz, A.M.; Marco-Escoto, M. A Metabolic Readout of the Urine Metabolome of COVID-19 Patients. Metabolomics 2023, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almulla, A.F.; Supasitthumrong, T.; Tunvirachaisakul, C.; Algon, A.A.A.; Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Maes, M. The Tryptophan Catabolite or Kynurenine Pathway in COVID-19 and Critical COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrábano, R.J.; Wipper, B.; Pencina, K.M.; Migaud, M.; Shang, Y.V.; Latham, N.K.; Montano, M.; Cunningham, J.M.; Wilson, L.; Peng, L.; et al. Dysregulated Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Metabolome in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, V.I. Glutathione Homeostasis and Functions: Potential Targets for Medical Interventions. J. Amino Acids 2012, 2012, 736837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonikov, A. Endogenous Deficiency of Glutathione as the Most Likely Cause of Serious Manifestations and Death in COVID-19 Patients. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1558–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wan, Y.; Zuo, T.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, H.; Lu, W.; Xu, W.; Lui, G.C.Y.; et al. Prolonged Impairment of Short-Chain Fatty Acid and L-Isoleucine Biosynthesis in Gut Microbiome in Patients With COVID-19. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 548–561.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.J. Energy Metabolism and the High-Altitude Environment. Exp. Physiol. 2016, 101, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.S.; Azzolini, M.; Lira Ruas, J. The Kynurenine Connection: How Exercise Shifts Muscle Tryptophan Metabolism and Affects Energy Homeostasis, the Immune System, and the Brain. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C818–C830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, B.; Geiger, D.; Schauer, M.; Gatterer, H.; Burtscher, M.; Fuchs, D. Effects of Exhaustive Aerobic Exercise on Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolism in Trained Athletes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, T.; Yin, M.O.L.; Heaney, L.M. The Athlete and Gut Microbiome: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Potential Ergogenic Aids for Exercise and Training. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, X.; Yue, X.; Hao, F.; Wang, H.; Duan, L.; Han, C.; Zhu, L. Metabolomic Analysis of Human Plasma Sample after Exposed to High Altitude and Return to Sea Level. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Men ♂ (n = 15) Women ♀ (n = 12) | Mean ± SD | Median | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ♂ | 26.4 ± 4.3 | 26.0 | 21.0 | 34.0 |
| ♀ | 24.5 ± 2.5 | 24.0 | 20.0 | 29.0 | |
| Height (cm) | ♂ | 191 ± 5.8 * | 193.5 | 179.0 | 196.0 |
| ♀ | 179.4 ± 7.8 | 177.0 | 168.0 | 197.0 | |
| Weight (kg) | ♂ | 88.8 ± 7.7 * | 90.0 | 70.0 | 97.0 |
| ♀ | 71.5 ± 7.0 | 73.0 | 60.0 | 81.0 | |
| BMI | ♂ | 24.1 ± 1.1 | 23.9 | 21.8 | 25.5 |
| ♀ | 22.3 ± 2.4 | 21.9 | 18.0 | 25.4 |
| Buckets | Mean | SD | p-Value | Metabolite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1_1239 | −0.39 | 0.13 | 0.0314685 | Propionate |
| B1_1539 | −0.51 | 0.25 | 0.0625257 | Unknown 1 |
| B2_4381 | −0.61 | 0.31 | 0.0244344 | Pyroglutamate |
| B4_1758 | 1.22 | 0.34 | 0.0141917 | Kynurenine |
| B4_4010 | −0.87 | 0.45 | 0.0399835 | Unknown 3 |
| B4_6451 | −0.44 | 0.65 | 0.4894282 | Glucose |
| B7_2429 | 1.07 | 0.91 | 0.0399835 | N-Formyltryptophan |
| B7_3101 | 1.18 | 1.17 | 0.0770053 | Tryptophan |
| B7_3634 | 1.39 | 1.35 | 0.0399835 | Unknown 4 |
| B9_2733 | 0.81 | 0.41 | 0.0187577 | N-Methylnicotinamide |
| Buckets | Mean | SD | p-Value | Metabolite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3_0612 | 1.22 | 0.22 | 0.0002649 | Creatinine |
| B3_7065 | −1.22 | 0.8 | 0.0000024 | Unknown 2 |
| B3_9187 | 1.06 | 0.65 | 0.0000103 | Creatine |
| B5_7836 | −1.88 | 0.53 | 0.0000650 | Urea |
| B6_7557 | 0.67 | 0.2 | 0.0000082 | 3-Hydroxyphenylacetate |
| B8_5324 | 1.51 | 1.06 | 0.0000000 | Unknown 5 |
| B8_5510 | 1.14 | 0.56 | 0.0000000 | Unknown 6 |
| B8_5647 | 0.67 | 0.47 | 0.0000103 | Unknown 7 |
| B8_8263 | 1.27 | 0.47 | 0.0000024 | Trigonelline |
| B1_4223 | −0.14 | 0.04 | 0.0020369 | Alanine |
| B2_3688 | −1.52 | 0.5 | 0.0000039 | Glutamate |
| B2_5771 | 0.86 | 0.68 | 0.0000718 | Citrate |
| B3_4768 | 1.76 | 2.22 | 0.0000029 | 3-Hydroxyphenylacetate |
| B7_5531 | 0.65 | 0.28 | 0.0002836 | Hippurate |
| B7_8284 | 0.64 | 0.26 | 0.0002358 | o-Hydroxyhippurate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boudry, F.; Durand, F.; Goossens, C. Metabolomics Signatures of a Respiratory Tract Infection During an Altitude Training Camp in Elite Rowers. Metabolites 2025, 15, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060408
Boudry F, Durand F, Goossens C. Metabolomics Signatures of a Respiratory Tract Infection During an Altitude Training Camp in Elite Rowers. Metabolites. 2025; 15(6):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060408
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoudry, Félix, Fabienne Durand, and Corentine Goossens. 2025. "Metabolomics Signatures of a Respiratory Tract Infection During an Altitude Training Camp in Elite Rowers" Metabolites 15, no. 6: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060408
APA StyleBoudry, F., Durand, F., & Goossens, C. (2025). Metabolomics Signatures of a Respiratory Tract Infection During an Altitude Training Camp in Elite Rowers. Metabolites, 15(6), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060408







