An LC-MS Method to Quantify Rhein and Its Metabolites in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Method
2.2.1. UHPLC System
2.2.2. MS System
2.2.3. Biosynthesis of Rhein-G1 and Rhein-G2
2.2.4. Identification and Quantification of Rhein-G1 and Rhein-G2
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Calibration Curve and LLOQ (Lower Limit of Quantification)
2.3.2. Precision and Accuracy
2.3.3. Extraction Recovery and Matrix Effect
2.3.4. Stability
2.4. Pharmacokinetics Study
2.4.1. Animals
2.4.2. Pharmacokinetic Experimental Design
2.4.3. Data Analysis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Method Comparison
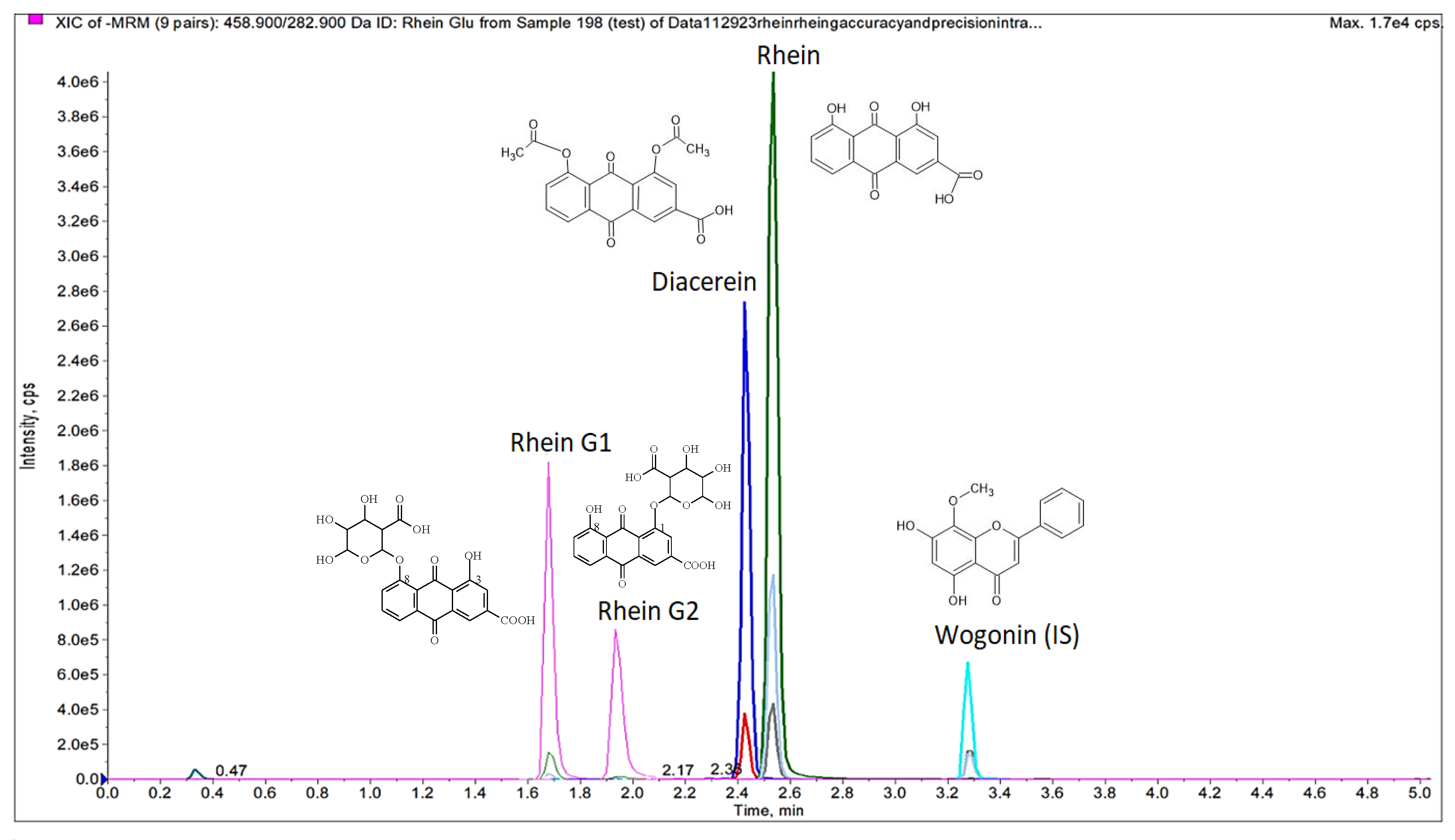
3.2. Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry
3.3. Identification and Quantification of Rhein-G1 and Rhein-G2
3.4. Method Validation
3.4.1. Linearity and Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
3.4.2. Accuracy and Precision
3.4.3. Matrix Effect and Stability
3.5. Application in Pharmacokinetic Studies in Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Mineau, F.; Jolicoeur, F.C.; Cloutier, J.M.; Pelletier, J.P. In vitro effects of diacerhein and rhein on interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha systems in human osteoarthritic synovium and chondrocytes. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, H.J.; Park, K.; Song, G.G.; Choi, S.J. A comparative pilot study of oral diacerein and locally treated diacerein-loaded nanoparticles in a model of osteoarthritis. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaid, A.G.; Spencer, K.B. Strategies for Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome in the Clinical and Preclinical Space. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Du, J.; Yin, Y.; Cao, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.; Han, J. Rhein for treating diabetes mellitus: A pharmacological and mechanistic overview. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.; Barakat, L.A.A.; Zakaria, M.M.; Khirallah, S.M. Diacerein ameliorates kidney injury induced by cisplatin in rats by activation of Nrf2/Ho-1 pathway and Bax down-regulation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 7219–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, N.S.; Elzaitony, A.S.; Abdel Baky, N.A. Diacerein attenuate LPS-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ER stress and apoptosis: Impact on the crosstalk between SphK1/S1P, TLR4/NFkappaB/STAT3, and NLRP3/IL-1beta signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2022, 308, 120915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, P.; Tod, M.; Padoin, C.; Petitjean, O. Clinical pharmacokinetics of diacerein. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 35, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Hu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Yan, R.; Wang, Y. In vitro glucuronidation of five rhubarb anthraquinones by intestinal and liver microsomes from humans and rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 219, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Mao, X.; Qin, B.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, J. In vitro and in vivo metabolic activation of Rhein and characterization of glutathione conjugates derived from Rhein. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 283, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, W. Pharmacokinetics of 14C-labelled Rhein in rats. Pharmacology 1988, 36, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layek, B.; Kumar, T.S.; Trivedi, R.K.; Mullangi, R.; Srinivas, N.R. Development and validation of a sensitive LC-MS/MS method with electrospray ionization for quantitation of Rhein in human plasma: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, T.P.; Tsai, T.H. Preclinical Pharmacokinetics of Scoparone, Geniposide and Rhein in an Herbal Medicine Using a Validated LC-MS/MS Method. Molecules 2018, 23, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Yang, G.; Ge, S.; Yin, T.; Hu, M.; Gao, S. Validated LC-MS/MS method for the determination of 3-hydroxflavone and its glucuronide in blood and bioequivalent buffers: Application to pharmacokinetic, absorption, and metabolism studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 85, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.F.; Zhou, L.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Gao, S.; Hu, M. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of flavonoid glucuronides (wogonoside, baicalin, and apigenin-glucuronide) in the bile and blood samples: Application to a portal vein infusion study. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 601, 113723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, T.; Sun, R.; Siddiqui, N.; Moatamed, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, D.; Hu, M.; Gao, S. A positive-negative switching LC-MS/MS method for quantification of fenoldopam and its phase II metabolites: Applications to a pharmacokinetic study in rats. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1179, 122854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry. 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/bioanalytical-method-validation-guidance-industry (accessed on 10 May 2018).
- Dahms, M.; Lotz, R.; Lang, W.; Renner, U.; Bayer, E.; Langguth, H.S. Elucidation of phase I and phase II metabolic pathways of Rhein: Species differences and their potential relevance. Drug. Metab. Dispos. 1997, 25, 442–452. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Wu, B.; Tang, L.; Liu, Z.; Hu, M. Identification of the position of mono-O-glucuronide of flavones and flavonols by analyzing shift in online UV spectrum (lambdamax) generated from an online diode array detector. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9384–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Laizure, S.C.; Herring, V.; Hu, Z.; Witbrodt, K.; Parker, R.B. The role of human carboxylesterases in drug metabolism: Have we overlooked their importance. Pharmacotherapy 2013, 33, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Y.; Yang, M.W.; Qian, W.; Lin, H.; Geng, Y.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Xiao, D.W. Quantitative determination of Rhein in human plasma by liquid chromatography-negative electrospray ionization tandem mass/mass spectrometry and the application in a pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 57, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Gao, J.W.; Shi, Z.; Zou, J.L.; Lu, Y.S.; Yuan, Y.M.; Yao, M.C. A novel UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of Rhein, emodin, berberine and baicalin in rat plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.L.; Chang, L.W.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, L.C.; Tsai, T.H. Determination of bioactive components in Chinese herbal formulae and pharmacokinetics of Rhein in rats by UPLC-MS/MS. Molecules 2014, 19, 4058–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Sun, C.; Fang, B.; Huo, X.; Ma, X. Simultaneous Determination of Ten Active Components from Jinhongtang Granule in Rat Plasma by LC-MS/MS and its Application to a Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study in Normal and Sepsis Rats In Vivo and In Vitro. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2023, 61, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Tong, X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Lv, K.; Li, X.; Cao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W.; et al. Comparative pharmacokinetics of six bioactive components of Shen-Wu-Yi-Shen tablets in normal and chronic renal failure rats based on UPLC-TSQ-MS/MS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 317, 116818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.D.; Han, Q.B.; Zhong, L.L.; Li, Y.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Ho, H.M.; Zhang, M.; Lin, S.H.; Zhao, L.; Huang, T.; et al. Simultaneous determination of ten compounds in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS: Application in the pharmacokinetic study of Ma-Zi-Ren-Wan. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 1000, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Q1 | Q3 | DP | CE | CXP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diacerein | 366.8 | 323.2 | −70.0 | −20.0 | −9.0 |
| Rhein | 282.9 | 238.5 | −65.0 | −19.0 | −9.0 |
| Rhein-G1 | 458.9 | 282.9 | −70.0 | −22.0 | −14.0 |
| Rhein-G2 | 458.9 | 282.9 | −140.0 | −22.0 | −11.0 |
| IS (wogonin) | 283.0 | 162.0 | −80.0 | −40.0 | −15.0 |
| Analyte | Concentration (nM) | LLOQ (nM) |
|---|---|---|
| Rhein | 2000.00 - 7.81 | 7.81 |
| Rhein-G1 | 2000.00 - 7.81 | 7.81 |
| Rhein-G2 | 2000.00 - 7.81 | 7.81 |
| Analyte | QC Samples (nM) | Intra-Day (n = 6) | Inter-Day (n = 18) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| Rhein | 7.81 | 8.83 | 96.90 | 7.86 | 98.70 |
| 15.62 | 5.81 | 92.00 | 5.77 | 97.91 | |
| 500.00 | 3.93 | 102.26 | 3.53 | 102.0 | |
| 1000.00 | 4.82 | 89.60 | 3.25 | 88.20 | |
| Rhein-G1 | 7.81 | 4.29 | 100.13 | 8.08 | 101.73 |
| 15.62 | 6.24 | 97.19 | 9.14 | 99.40 | |
| 500.00 | 4.29 | 102.83 | 5.11 | 103.51 | |
| 1000.00 | 3.76 | 96.21 | 4.45 | 94.22 | |
| Rhein-G2 | 7.81 | 5.45 | 96.20 | 6.48 | 80.1 |
| 15.62 | 4.32 | 97.51 | 3.40 | 97.90 | |
| 500.00 | 7.83 | 103.0 | 4.22 | 104.2 | |
| 1000.00 | 2.54 | 93.12 | 5.21 | 98.23 | |
| Analyte | Conc (nM) | Extraction Recovery | Matrix Effect | Matrix Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) | SD | Average ± SD (%) | ||
| Rhein | 7.81 | 103.27 | 5.40 | 83.07 ± 1.67 |
| 15.62 | 101.20 | 8.30 | 101.20 ± 3.36 | |
| 500.00 | 82.31 | 6.00 | 97.13 ± 2.58 | |
| 1000.00 | 90.78 | 12.60 | 87.24 ± 2.54 | |
| Rhein-G1 | 7.81 | 103.20 | 10.54 | 88.75 ± 3.31 |
| 15.62 | 86.41 | 7.50 | 102.94 ± 2.09 | |
| 500.00 | 91.40 | 9.05 | 95.03 ± 5.00 | |
| 1000.00 | 98.40 | 3.89 | 94.34 ± 0.61 | |
| Rhein-G2 | 7.81 | 93.20 | 4.54 | 98.75 ± 1.09 |
| 15.62 | 96.43 | 6.50 | 92.94 ± 1.79 | |
| 500.00 | 91.40 | 5.05 | 85.07 ± 1.18 | |
| 1000.00 | 88.40 | 2.89 | 84.30 ± 0.69 |
| Analyte | Conc (nM) | 25 °C for 6 h | Freeze Thaw | Long Term | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stability (%) | CV (%) | Stability (%) | CV (%) | Stability (%) | CV (%) | ||
| Rhein | 7.81 | 99.74 | 10.37 | 95.35 | 6.89 | 93.10 | 3.20 |
| 15.62 | 99.08 | 6.99 | 102.20 | 7.33 | 98.06 | 6.40 | |
| 500.00 | 99.40 | 1.75 | 102.10 | 6.18 | 92.12 | 8.20 | |
| 1000.00 | 97.32 | 2.97 | 96.21 | 1.72 | 96.30 | 4.80 | |
| Rhein-G1 | 7.81 | 104.60 | 7.22 | 104.76 | 6.44 | 83.19 | 4.54 |
| 15.62 | 97.70 | 6.37 | 106.91 | 5.69 | 85.60 | 5.57 | |
| 500.00 | 104.62 | 6.89 | 97.59 | 6.29 | 81.20 | 6.82 | |
| 1000.00 | 97.94 | 1.29 | 97.87 | 2.61 | 95.30 | 4.55 | |
| Rhein-G2 | 7.81 | 86.40 | 3.43 | 89.40 | 4.20 | 89.23 | 8.39 |
| 15.62 | 81.30 | 4.23 | 91.20 | 5.20 | 88.34 | 6.24 | |
| 500.00 | 88.40 | 5.32 | 89.30 | 5.10 | 81.40 | 7.12 | |
| 1000.00 | 97.31 | 1.86 | 97.75 | 1.94 | 95.75 | 1.98 | |
| Parameters | Rhein | Rhein-G1 | Rhein-G2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tmax (h) | 1.00 ± 0.14 | 2.30 ± 1.30 | 1.80 ± 0.84 |
| Cmax (nmol/L) | 1623.25 ± 334.06 | 1351.70 ± 574.46 | 800.74 ± 1007.24 |
| AUC0~t (h·nmol/L) | 4280.15 ± 1576.81 | 3849.045 ± 1983.15 | 2210.80 ± 2386.71 |
| MRT (h) | 2.63 ± 0.35 | 3.76 ± 0.60 | 4.91 ± 1.77 |
| T1/2 (h) | 2.34 ± 1.81 | 2.78 ± 0.39 | 5.95 ± 2.98 |
| CL (L/h/kg) | 144.9 ± 85.69 | 2.01 ± 1.29 | 4.082 ± 1.73 |
| Vz (L/kg) | 47.03 ± 33.44 | 43.08 ± 21.98 | 36.04 ± 18.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siddiqui, N.; Chen, Y.; Du, T.; Wang, Y.; Buck, C.; Gao, S. An LC-MS Method to Quantify Rhein and Its Metabolites in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats. Metabolites 2025, 15, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060407
Siddiqui N, Chen Y, Du T, Wang Y, Buck C, Gao S. An LC-MS Method to Quantify Rhein and Its Metabolites in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats. Metabolites. 2025; 15(6):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060407
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiddiqui, Nyma, Yuan Chen, Ting Du, Yang Wang, Charmeyce Buck, and Song Gao. 2025. "An LC-MS Method to Quantify Rhein and Its Metabolites in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats" Metabolites 15, no. 6: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060407
APA StyleSiddiqui, N., Chen, Y., Du, T., Wang, Y., Buck, C., & Gao, S. (2025). An LC-MS Method to Quantify Rhein and Its Metabolites in Plasma: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats. Metabolites, 15(6), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060407






