A Comparative Analysis of Raw and Bran-Fried Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma Based on the Intelligent Sensory Evaluation System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Raw and Bran-Fried ATR
2.3. Preparation of Test Samples
2.4. Establishment of the Odor Detection Method for Raw and Bran-Fried Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma
2.4.1. Optimization of Incubation Temperature
2.4.2. Optimization of Incubation Time
2.4.3. Optimization of Sample Amount
2.4.4. Optimization of Injection Volume
2.5. Determination of Detection Conditions
2.6. Analysis of Ultra-Fast Gas-Phase Electronic Nose Detection
2.7. E-Eye Analysis
2.8. E-Tongue Analysis
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
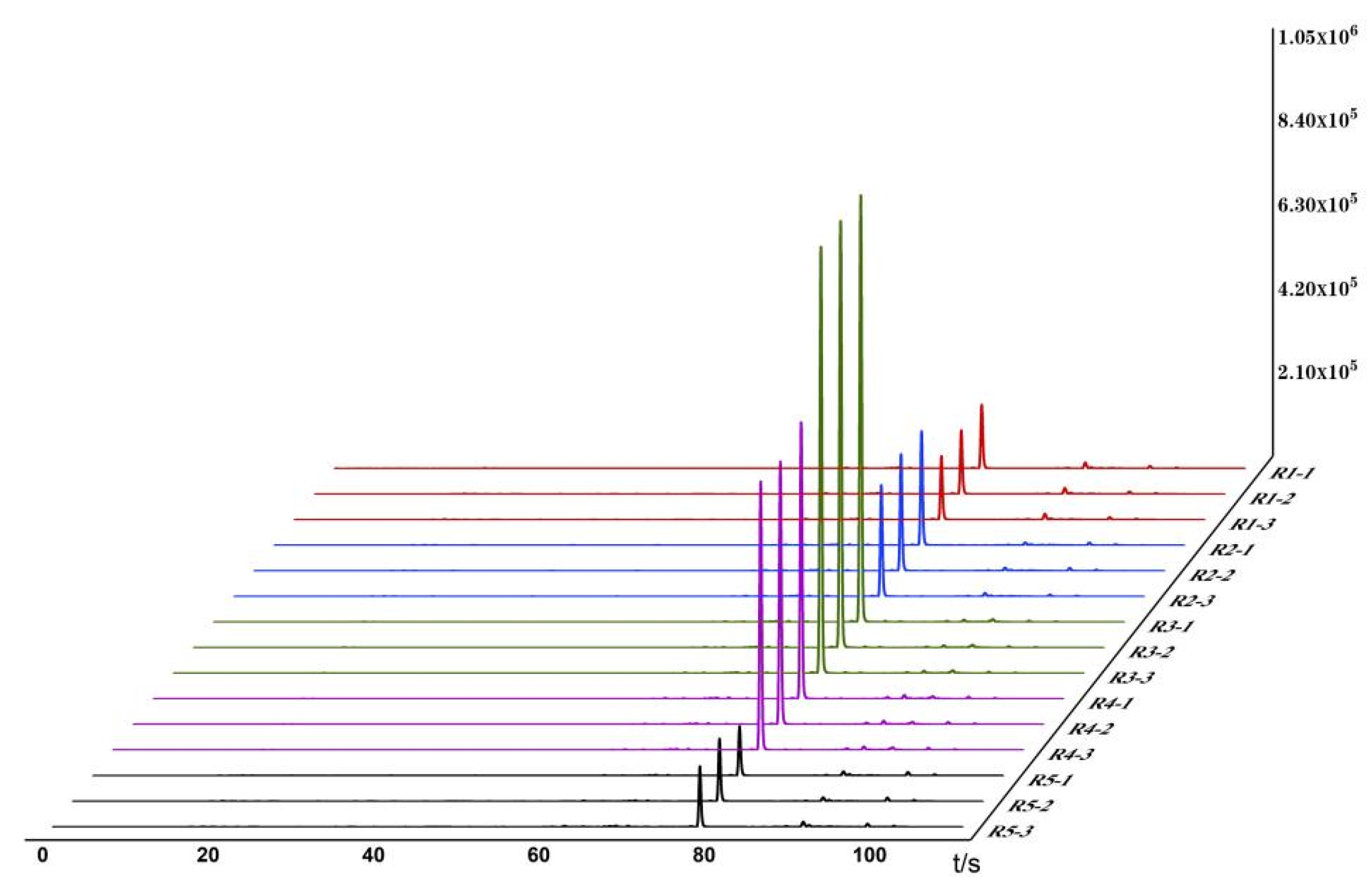
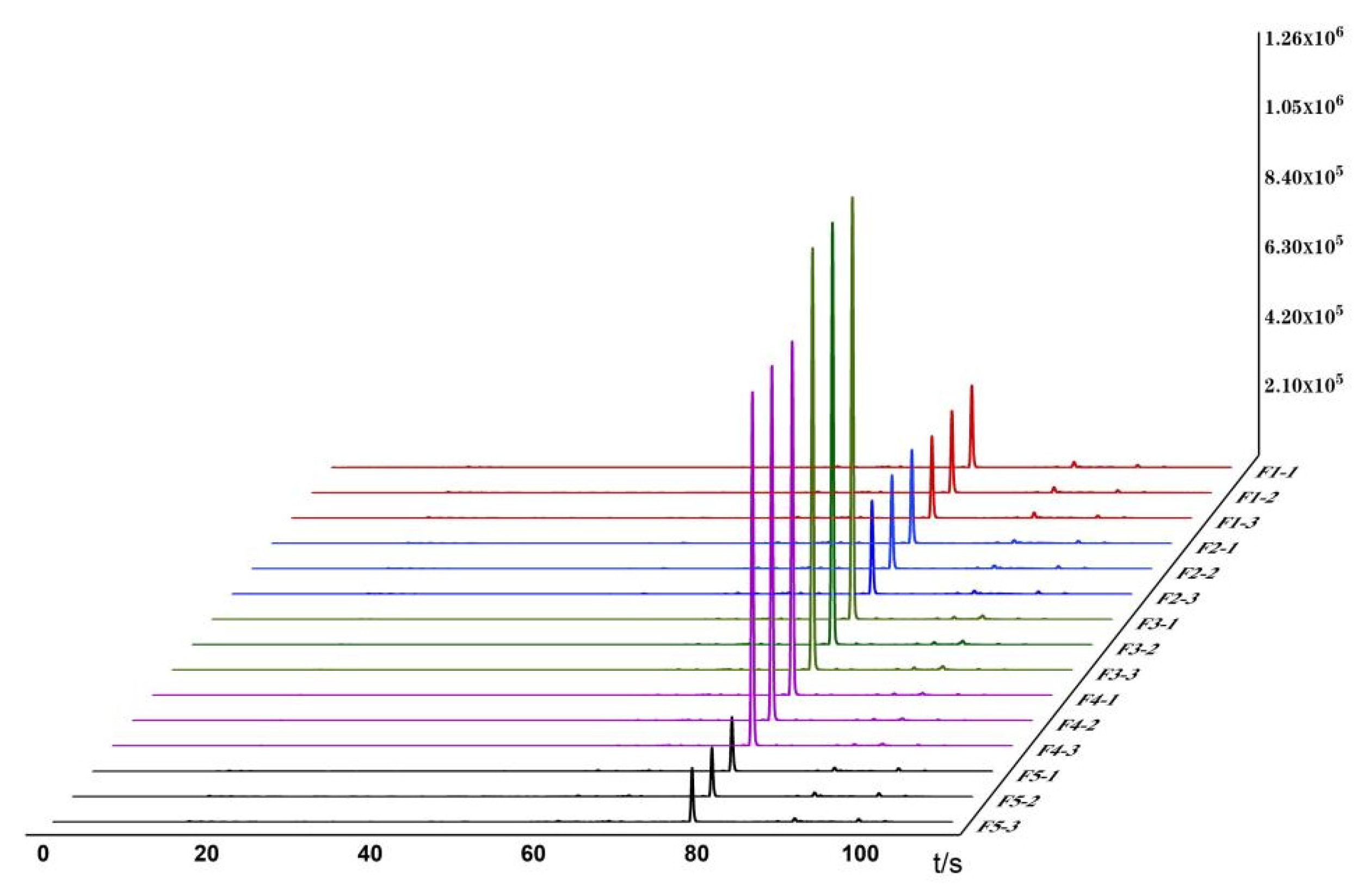
3.1. Establishment of Odor Fingerprint Spectra
3.2. Analysis of Odor Changes
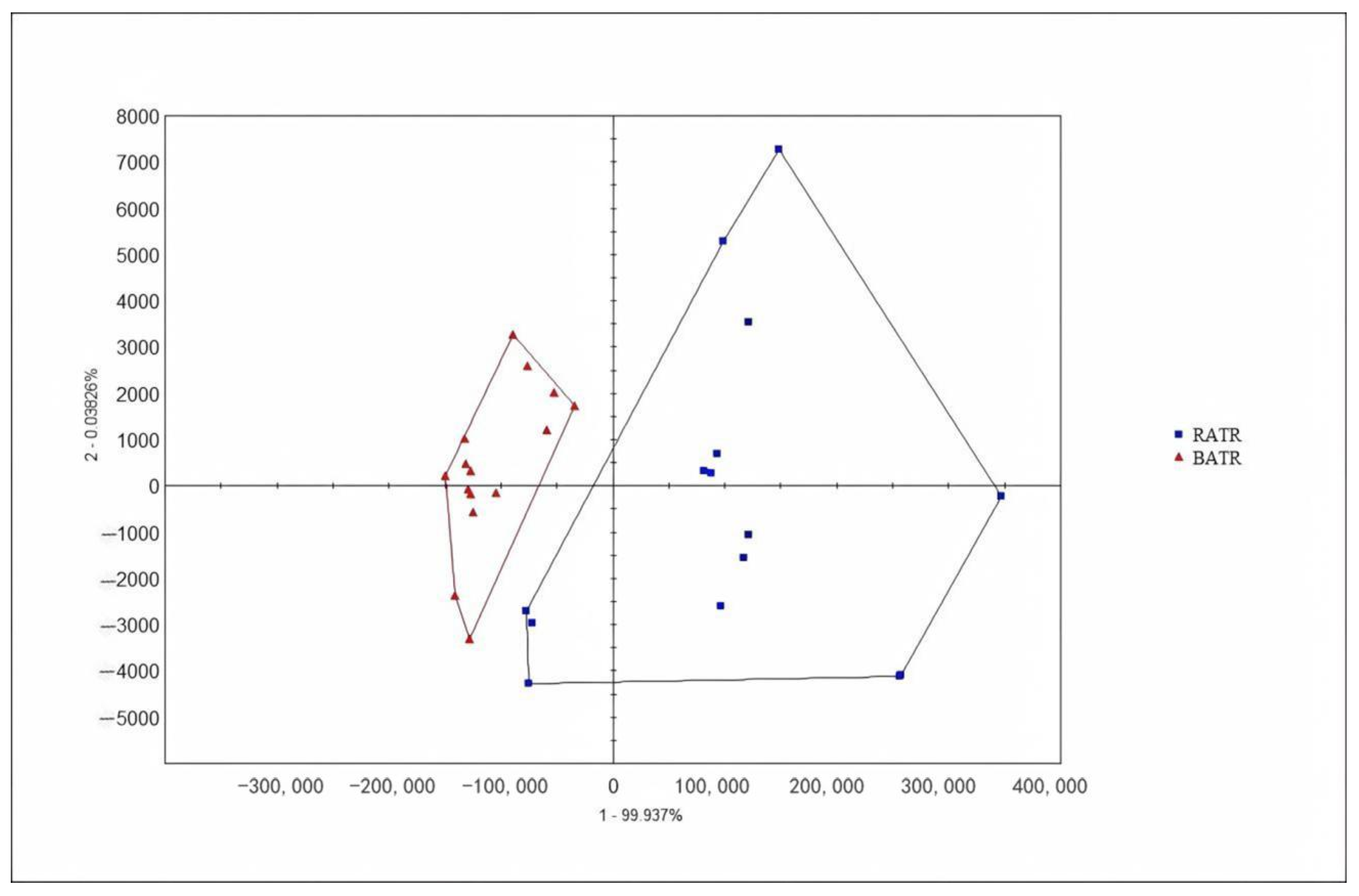
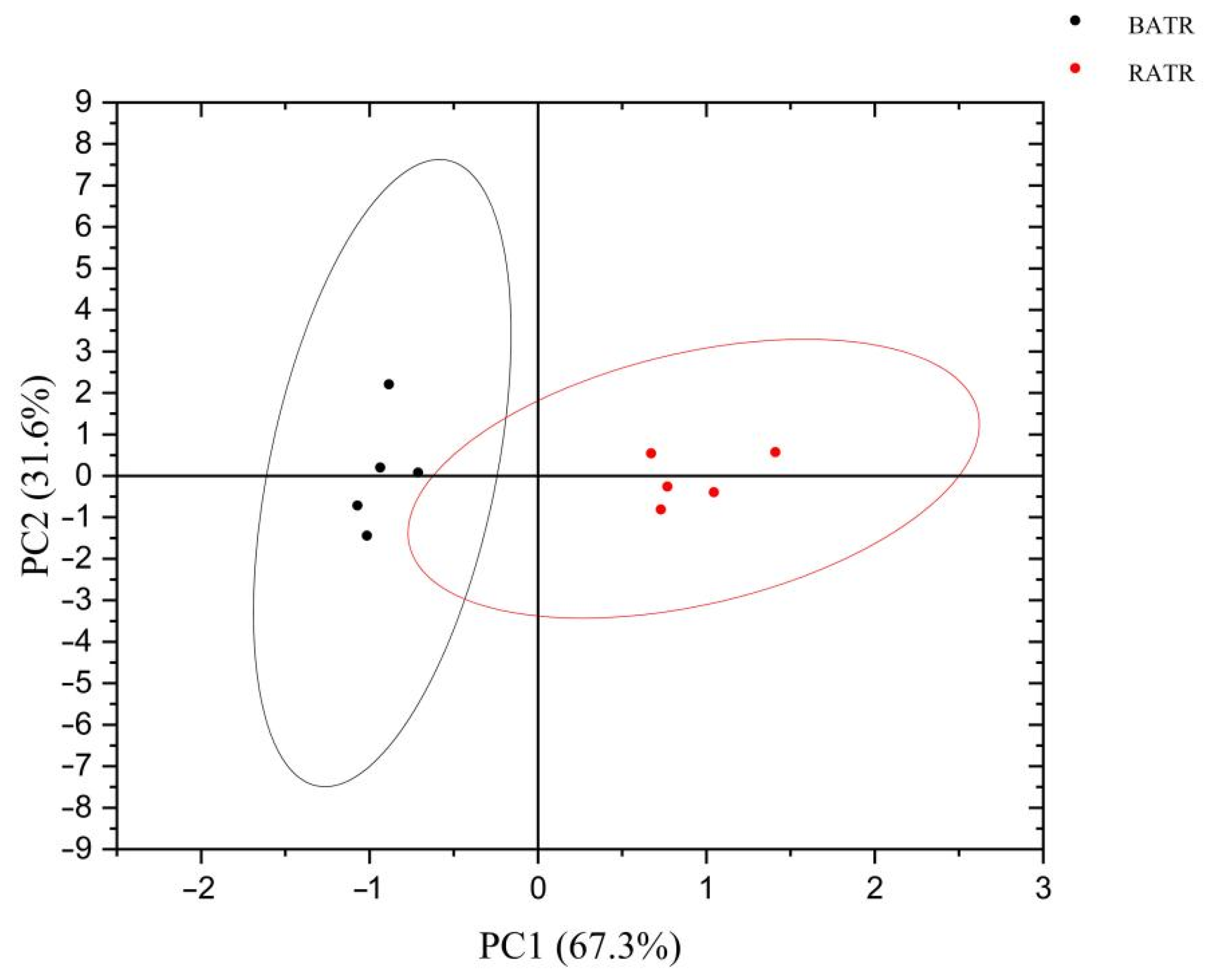
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of the Heracles NEO Electronic Nose
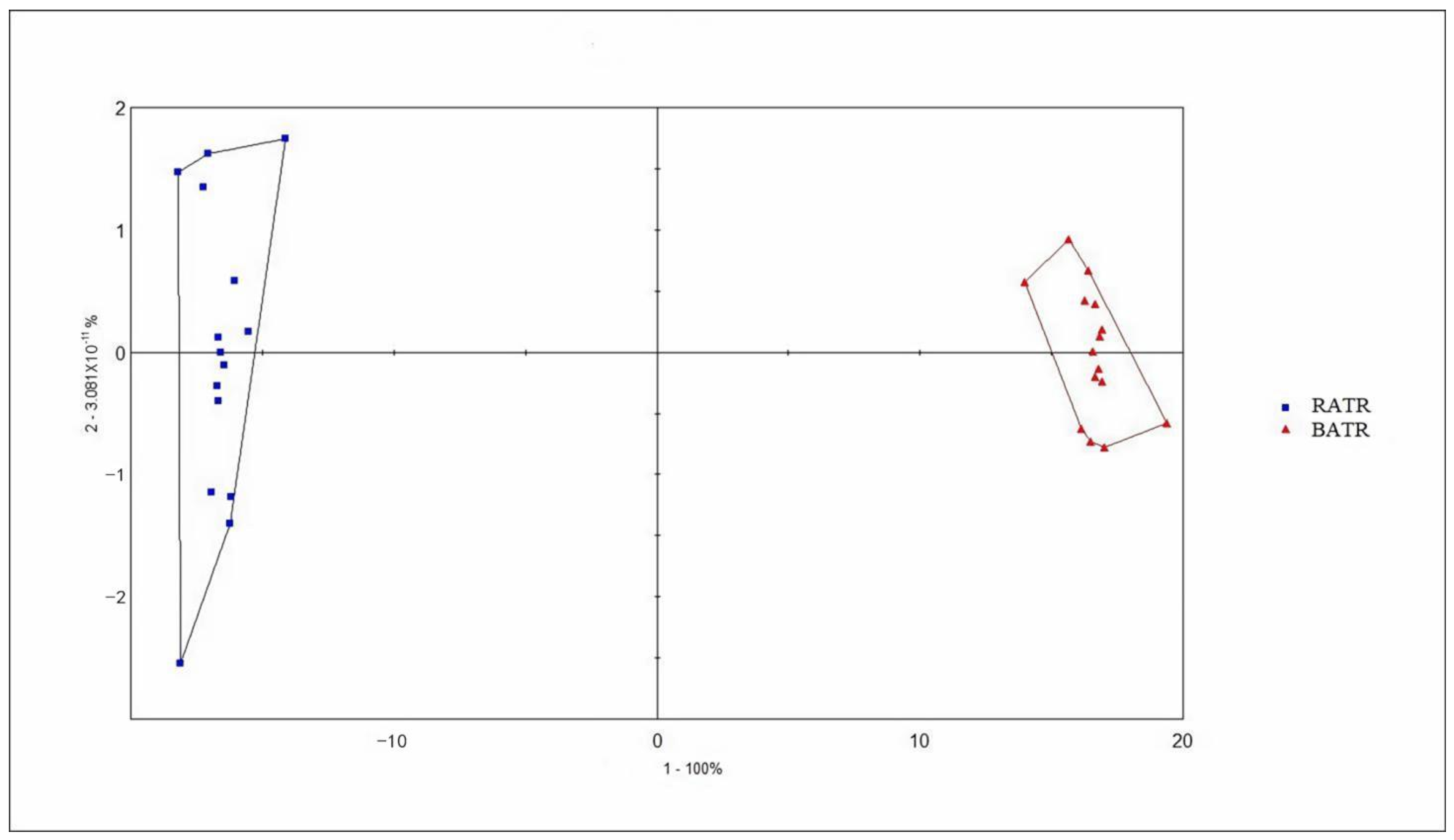
3.4. Discriminant Factor Analysis (DFA) of the Heracles NEO Electronic Nose
3.5. E-Eye Analysis
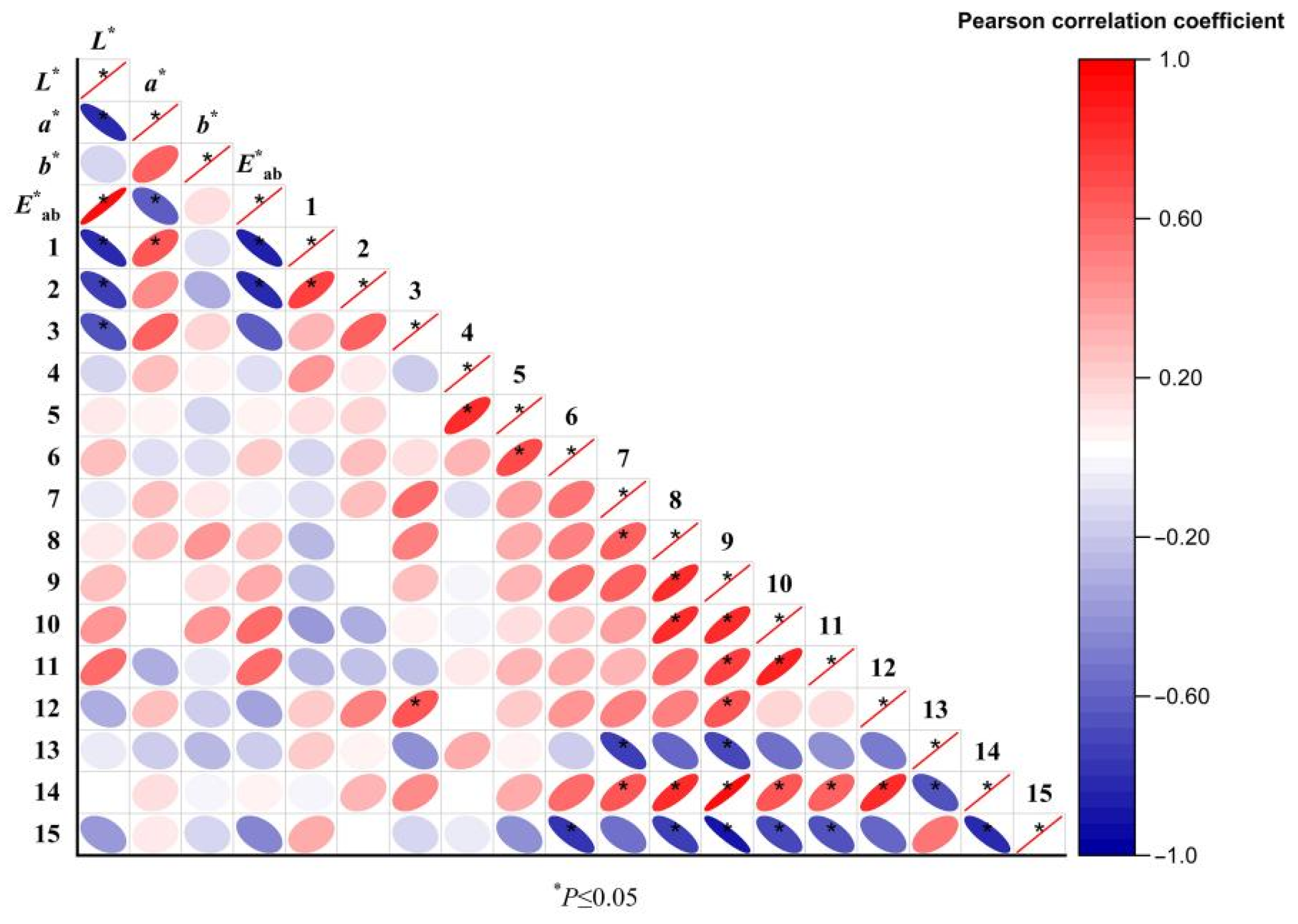
3.6. Correlation Analysis of E-Nose and E-Eye
3.7. E-Tongue Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATR | Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma |
| VOCs | Volatile organic compounds |
| BATR | Bran-fried Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma |
| RATR | Raw Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma |
References
- Sichuan Provincial Food and Drug Administration. Sichuan Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Decoction Pieces Processing Standards; Sichuan Science and Technology Press: Chengdu, China, 2015; p. 372.
- Qiu, L.Y.; Yang, G.; Jin, Q.; Luo, X.D.; Liu, Y.P.; Wang, Y.F. Chemical constituents and anti-inflammatory activity of Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma rhizomes. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 4617–4624. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.H.; Sun, Y.; Feng, X.L.; Tao, X.R.; Gong, N.C.; Cai, Y.; Peng, Y.M. Prediction and analysis of quality markers of Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma based on fingerprint, chemical pattern recognition, and network pharmacology. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2024, 33, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Henan Provincial Food and Drug Administration. Henan Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Decoction Pieces Processing Standards; Henan People’s Publishing House: Zhengzhou, China, 2005; p. 36.
- Shuba, A.; Umarkhanov, R.; Bogdanova, E.; Anokhina, E.; Burakova, I. Possibilities of an electronic nose on piezoelectric sensors with polycomposite coatings to investigate the microbiological indicators of milk. Sensors 2024, 11, 3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.T.; Feng, T.; Song, S.Q.; Yao, L.Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, H.T.; Yu, C.; Liu, Q. Research progress of machine learning in predicting food flavor. Food Sci. 2024, 12, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, S.H.; Wang, J.L.; Zhou, S.Y.; Jiang, S.H.; Zhang, H. Rapid identification of American ginseng originated from varied places based on Heracles ultra-fast gas phase electronic nose. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- Nai, G.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Yue, Y.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Zhang, X.Y. Influences of different aging containers on the wine quality analyzed by electronic nose and HS-SPME-GC-MS. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2024, 51, 152–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sipos, L.; Végh, R.; Bodor, Z.; Zaukuu, J.L.Z.; Hitka, G.; Bázár, G.; Kovacs, Z. Classification of bee pollen and prediction of sensory and colorimetric attributes-A sensometric fusion approach by e-nose, e-tongue, and NIR. Sensors 2020, 20, 6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Cai, Y.; Wu, X.; Gai, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, D. Characterization of selected commercially available grilled lamb shashliks based on flavor profiles using GC-MS, GC × GC-TOF-MS, GC-IMS, E-nose, and E-tongue combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Yue, N.; Shao, H.; Wang, J.; Jin, F. Discrimination and characterization of volatile flavor compounds in fresh oriental melon after forchlorfenuron application using electronic nose (E-nose) and headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS). Foods 2023, 12, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Dan, M.; Zhao, G.; Wang, D. Recent advances in chromatography-mass spectrometry and electronic nose technology in food flavor analysis and detection. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.R.D.; Leone, F.; Cheli, F.; Chiofalo, V. Fusion of electronic nose, electronic tongue and computer vision for animal source food authentication and quality assessment-a review. J. Food Eng. 2017, 210, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.L.; Xu, L.Y.; Yang, G.S.; Wang, B.; Chen, D.D. Research progress of intelligent sensory analysis technology in food flavor. J. Food Saf. Qual. Insp. 2023, 14, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J.W.; Chen, Q.S. Instrumental intelligent test of food sensory quality as mimic of human panel test combining multiple cross-perception sensors and data fusion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 841, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikri, N.A.; Adom, A.H.; Shakaff, A.Y.M.; Ahmad, M.N.; Abdullah, A.H.; Zakaria, A.; Markom, M.A. Development of human sensory mimicking system. Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti, M.; Mohtasebi, S.S.; Siadat, M. Biomimetic-based odor and taste sensing systems to food quality and safety characterization: An overview on basic principles and recent achievements. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Fan, X.; Zhu, G.; Lu, T.; Xue, R. Discrimination between raw and gingerjuice processed Magnoliae officinalis cortex based on HPLC and Hera-cles NEO ultra—Fast gas phase electronic nose. Phytochem. Anal. 2022, 33, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Jiang, M.R.; Yue, Z.Z.; Wang, Z.C.; Chen, M.Y.; Wei, X.T.; Shi, S.H.; Wang, M.L.; Wang, Y.Z. Correlation between morphological characteristics and chemical composition of honey-processed Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2022, 40, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yang, S.L.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhong, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Ai, L. E-tongue analysis of taste changes during Crataegi Fructus processing. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2015, 37, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Qin, Y.W.; Fei, C.H.; Su, L.L.; Ji, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.-Y.; Mao, C.-Q.; Lu, T.-L. Rapid identification of odor difference markers in Curcuma wenyujin before and after vinegar processing based on Heracles NEO ultra-fast gas chromatography electronic nose. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Yimenu, S.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, B.S. Prediction of egg freshness during storage using electronic nose. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 3733–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Q.; Mao, Y.N.; Li, H.; Huang, X.X.; Liu, Y. Identification of the quality of Lonicera japonica powder using Heracles II ultra-fast gas phase electronic nose. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2019, 44, 5129–5133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.Y.; Dai, Y.J.; Wang, Q.H.; Ma, Y.L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Lv, T.T.; et al. Dynamic correlation study between HPLC fingerprint changes and appearance color during the stir-frying process of Gardeniae Fructus Praeparatus. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2018, 49, 4029–4037. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, X.L.; Qiu, B. Correlation between color characteristics and anthraquinone components in Knoxia valerianoides based on “color-quality discrimination” theory. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Medica Res. 2023, 34, 2288–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Zhu, Y.W.; Peng, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. Characterization of stewed beef by sensory evaluation and multiple intelligent sensory technologies combined with chemometrics methods. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 135193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.W.; Zhou, X.R.; Chen, Y.P.; Liu, Z.Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, G.L.; Liu, Y. Exploring the relationships between perceived umami intensity, umami components and electronic tongue responses in food matrices. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Du, H.; Wan, W.; Li, W. Analysis of volatile components in Acorus tatarinowii before and after bran-frying by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Guizhou Sci. 2021, 39, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gong, J.W.; Fei, C.H.; Su, L.L.; Ji, D.; Bian, Z.H.; Zhang, W.; Qin, Y.W.; Mao, C.Q.; Lu, T.L. Rapid identification and odor difference markers of three Schisandra medicinal pieces using fast gas phase electronic nose combined with artificial neural network. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Fei, C.; Su, L.L.; Mao, C.Q.; Wang, X.C.; Xu, J.G.; Lu, T.L. Rapid identification of raw and sulfur-fumigated Paeoniae Radix Alba based on Heracles NEO ultra-fast gas phase electronic nose. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2022, 47, 3781–3787. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Cao, G.S.; Zhao, D.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Yan, M. Ethnic, botanic, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of the Acorus L. genus: A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Kuang, D.; Wang, J.; Long, Q.; Huang, D. An Exploratory Study on the Rapid Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds in Gardenia Fruit Using the Heracles NEO Ultra-Fast Gas Phase Electronic Nose. Metabolites 2024, 14, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Sun, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yin, F.; Liu, J.; Lu, T.; et al. Rapid Evaluation of Qingpi Products Using E-Eye, Fast GC e-Nose, and FT-NIR. Phytochem. Anal. 2025; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, A.; Kumar, N. Electronic panel for sensory assessment of food: A review on technologies integration and their benefits. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Serial | Origin | Serial | Origin | Batch |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Hunan | B1 | Hunan | 20231024004 |
| R2 | Sichuan | B2 | Sichuan | 20231024013 |
| R3 | Jiangxi | B3 | Jiangxi | 20231024001 |
| R4 | Guizhou | B4 | Guizhou | 20231024010 |
| R5 | Hubei | B5 | Hubei | 20231024007 |
| Condition | Parameter | Condition | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample vial | 20 mL | Trap temperature | 40 °C |
| Sample amount | 0.25 g | Column front pressure | 57 kPa |
| Injection volume | 500 μL | Trap time | 14 s |
| Incubation temperature | 45 °C | Valve temperature | 250 °C |
| Incubation time | 5 min | Initial column oven temperature | 50 °C |
| Injection speed | 125 μL/s | Column temperature program | 3.0 °C/s |
| Injection time | 9 s | Acquisition time | 110 s |
| Inlet temperature | 200 °C | FID gain | 12 |
| Inlet pressure | 10 kPa | FID offset | 1000 |
| No. | Relative Peak Area | No. | Relative Peak Area | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | (1.47 ± 0.05) × 105 | B1 | (3.86 ± 0.12) × 105 *** | Hunan |
| R2 | (2.87 ± 0.08) × 105 | B2 | (3.22 ± 0.09) × 105 * | Sichuan |
| R3 | (7.59 ± 0.15) × 105 | B3 | (12.78 ± 0.25) × 105 *** | Jiangxi |
| R4 | (6.94 ± 0.12) × 105 | B4 | (7.49 ± 0.13) × 105 | Guizhou |
| R5 | (1.24 ± 0.03) × 105 | B5 | (1.64 ± 0.04) × 105 * | Hubei |
| No. | Molecular Formula | tR/s | RI | Possible Compound | Similarity Index | Odor Information | RATR | BATR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CH4O | 16.63 | 436 | Methanol | 91.06 | Alcoholic; spicy, etc. | − | + |
| 2 | C3H8O | 19.25 | 489 | 2-Propanol | 89.63 | Acetone; alcohol; ethanol, etc. | − | + |
| 3 | C5H6O | 50.28 | 842 | 2-Cyclopentenone | 74.89 | / | − | + |
| 4 | C7H6O | 61.84 | 968 | Benzaldehyde | 91.21 | Almond; bitter, etc. | + | + |
| 5 | C6H4Cl2 | 67.68 | 1041 | o-Dichlorobenzene | 88.15 | Aromatic; aromatic hydrocarbon odor | + | + |
| 6 | C10H16 | 68.04 | 1051 | L-Limonene | 91.13 | Orange; mint, etc. | + | + |
| 7 | C11H24 | 71.72 | 1106 | Undecane | 81.56 | Alkane; fusel alcohol, etc. | + | + |
| 8 | C8H10O3 | 77.15 | 1197 | 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol | 87.03 | Sesame oil; phenol, etc. | + | + |
| 9 | C10H20O | 78.30 | 1219 | Decanal | 98.35 | Aldehyde; candle, etc. | + | + |
| 10 | C10H16O | 81.23 | 1274 | Geranial | 96.69 | Orange; mint, etc. | + | + |
| 11 | C9H12O3 | 83.02 | 1310 | Methyl eugenol | 85.42 | Aromatic; spicy odor | + | + |
| 12 | C12H26O | 88.67 | 1427 | 2-Dodecanol | 93.53 | Coconut; candle, etc. | + | + |
| 13 | C13H26O2 | 92.97 | 1521 | Methyl dodecanoate | 95.87 | Coconut; cream, etc. | + | + |
| 14 | C11H20O2 | 94.93 | 1562 | 4-Undecanolide | 92.79 | Apricot; coconut; peach, etc. | + | + |
| 15 | C12H27O4P | 98.61 | 1639 | Tributyl phosphate | 80.19 | Odorless | + | + |
| No. | Chromatic Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | E*ab | |
| R1 | 61.01 ± 0.12 | 5.83 ± 0.05 | 14.17 ± 0.08 | 81.01 ± 0.15 |
| R2 | 59.97 ± 0.09 | 6.41 ± 0.07 * | 15.22 ± 0.11 * | 81.60 ± 0.13 |
| R3 | 64.85 ± 0.15 ** | 6.20 ± 0.04 * | 14.69 ± 0.09 | 85.74 ± 0.17 ** |
| R4 | 60.11 ± 0.11 | 6.33 ± 0.06 * | 14.24 ± 0.07 | 80.68 ± 0.12 |
| R5 | 58.65 ± 0.08 | 5.88 ± 0.03 | 13.95 ± 0.05 | 78.48 ± 0.10 |
| B1 | 52.19 ± 0.18 ** | 7.59 ± 0.12 *** | 15.16 ± 0.15 | 74.94 ± 0.22 *** |
| B2 | 49.69 ± 0.15 *** | 7.82 ± 0.10 *** | 14.41 ± 0.13 * | 71.92 ± 0.19 *** |
| B3 | 53.50 ± 0.20 *** | 8.34 ± 0.14 *** | 17.29 ± 0.18 *** | 79.13 ± 0.25 ** |
| B4 | 48.91 ± 0.14 *** | 7.41 ± 0.09 *** | 13.79 ± 0.12 | 70.11 ± 0.17 *** |
| B5 | 51.23 ± 0.16 *** | 7.88 ± 0.11 *** | 15.31 ± 0.14 | 74.42 ± 0.20 *** |
| NO. | Type | Sourness | Bitterness | Astringency | Aftertaste-B | Aftertaste-A | Umami | Richness | Saltiness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Tastless | −13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −6 |
| 1 | R1 | −22.68 ± 0.85 * | 2.23 ± 0.12 | −2.65 ± 0.08 | −0.44 ± 0.05 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 5.53 ± 0.25 ** | 0.17 ± 0.01 | −2.31 ± 0.15 |
| 2 | R2 | −26.31 ± 1.10 ** | 2.95 ± 0.15 * | −2.58 ± 0.07 | 0.46 ± 0.04 * | 0.63 ± 0.05 ** | 7.05 ± 0.35 *** | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 2.64 ± 0.20 |
| 3 | R3 | −25.72 ± 1.05 ** | 2.89 ± 0.14 * | −2.41 ± 0.06 * | 0.33 ± 0.03 * | 0.78 ± 0.06 *** | 7.06 ± 0.30 *** | 0.22 ± 0.02 * | 4.07 ± 0.25 ** |
| 4 | R4 | −25.27 ± 0.95 ** | 2.33 ± 0.10 | −2.75 ± 0.09 | −0.39 ± 0.04 | 0.51 ± 0.04 ** | 6.55 ± 0.28 *** | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 1.72 ± 0.12 |
| 5 | R5 | −18.65 ± 0.75 * | 2.35 ± 0.11 | −2.39 ± 0.05 * | −0.20 ± 0.02 | 0.56 ± 0.04 ** | 4.28 ± 0.20 ** | 0.14 ± 0.01 | −1.11 ± 0.08 |
| 6 | B1 | −20.42 ± 0.92 * | 2.65 ± 0.13 * | −2.47 ± 0.12 | 0.19 ± 0.02 * | 0.80 ± 0.06 *** | 5.25 ± 0.26 ** | 0.25 ± 0.02 ** | 1.02 ± 0.08 * |
| 7 | B2 | −19.27 ± 0.87 * | 2.94 ± 0.15 * | −2.61 ± 0.13 | 0.49 ± 0.04 ** | 0.82 ± 0.06 *** | 4.99 ± 0.25 ** | 0.36 ± 0.03 *** | 0.76 ± 0.06 * |
| 8 | B3 | −20.60 ± 0.93 * | 3.47 ± 0.17 ** | −2.19 ± 0.11 * | 0.87 ± 0.07 *** | 0.85 ± 0.06 *** | 5.61 ± 0.28 ** | 0.40 ± 0.03 *** | 2.33 ± 0.17 ** |
| 9 | B4 | −23.09 ± 1.04 ** | 3.73 ± 0.19 ** | −1.91 ± 0.10 ** | 1.11 ± 0.09 *** | 1.21 ± 0.09 *** | 6.89 ± 0.34 *** | 0.49 ± 0.04 *** | 5.35 ± 0.38 *** |
| 10 | B5 | −20.21 ± 0.91 * | 2.14 ± 0.11 | −3.14 ± 0.16 | −0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.03 * | 4.89 ± 0.24 ** | 0.23 ± 0.02 ** | −1.69 ± 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, R.; Ma, S.; Cui, Y.; Shi, K.; Xin, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, L. A Comparative Analysis of Raw and Bran-Fried Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma Based on the Intelligent Sensory Evaluation System. Metabolites 2025, 15, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050338
Le Y, Yang Z, Wang R, Ma S, Cui Y, Shi K, Xin L, Zhang J, Zhong L. A Comparative Analysis of Raw and Bran-Fried Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma Based on the Intelligent Sensory Evaluation System. Metabolites. 2025; 15(5):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050338
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Yingna, Zhongjian Yang, Ruiping Wang, Shaolong Ma, Yang Cui, Kun Shi, Li Xin, Jinlian Zhang, and Lingyun Zhong. 2025. "A Comparative Analysis of Raw and Bran-Fried Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma Based on the Intelligent Sensory Evaluation System" Metabolites 15, no. 5: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050338
APA StyleLe, Y., Yang, Z., Wang, R., Ma, S., Cui, Y., Shi, K., Xin, L., Zhang, J., & Zhong, L. (2025). A Comparative Analysis of Raw and Bran-Fried Acori tatarinowii Rhizoma Based on the Intelligent Sensory Evaluation System. Metabolites, 15(5), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050338






