Synergistic Impact of Aerobic Exercise and Resveratrol on White Adipose Tissue Browning in Obese Rats: Mechanistic Exploration and Biological Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Main Reagents and Detection Methods
2.2. Animals and Treatments
2.3. Exercise Training
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
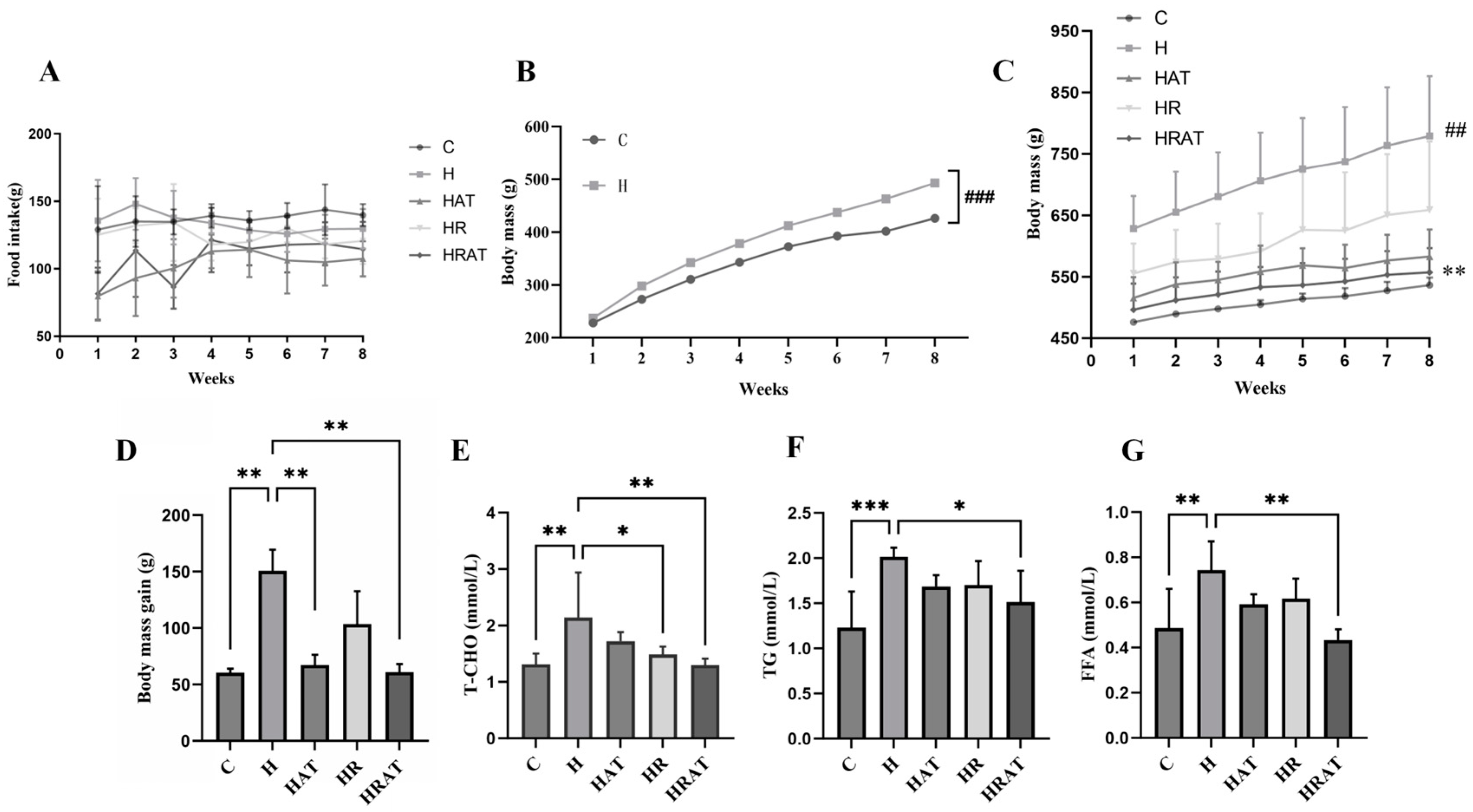
3.1. Effects of Aerobic Exercise Combined with RES on Body Weight and Fat Metabolism in Rats
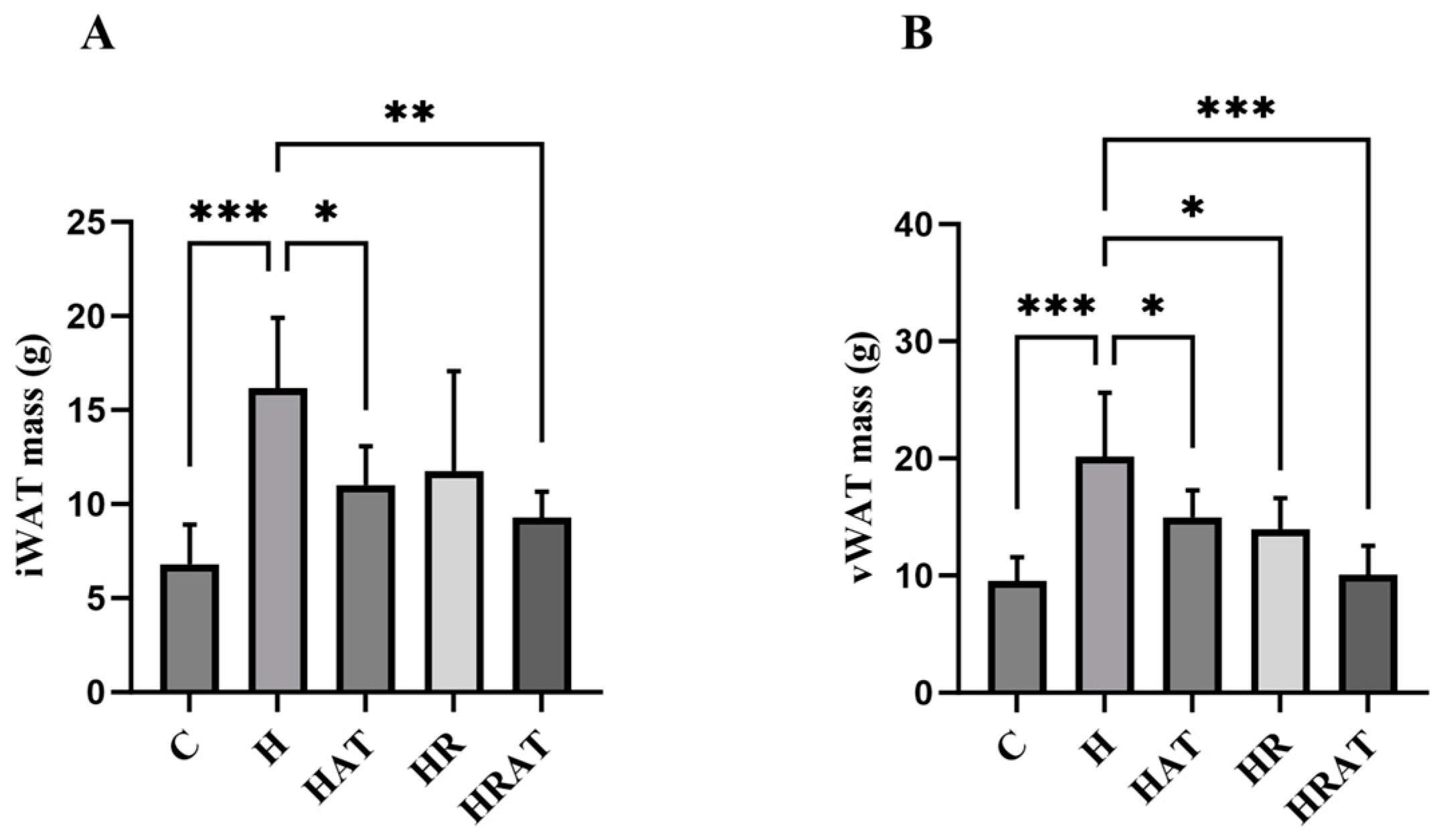
3.2. Aerobic Exercise Combined with RES Inhibits the Increase in Adipose Tissue Content and Enhances Lipolysis in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet
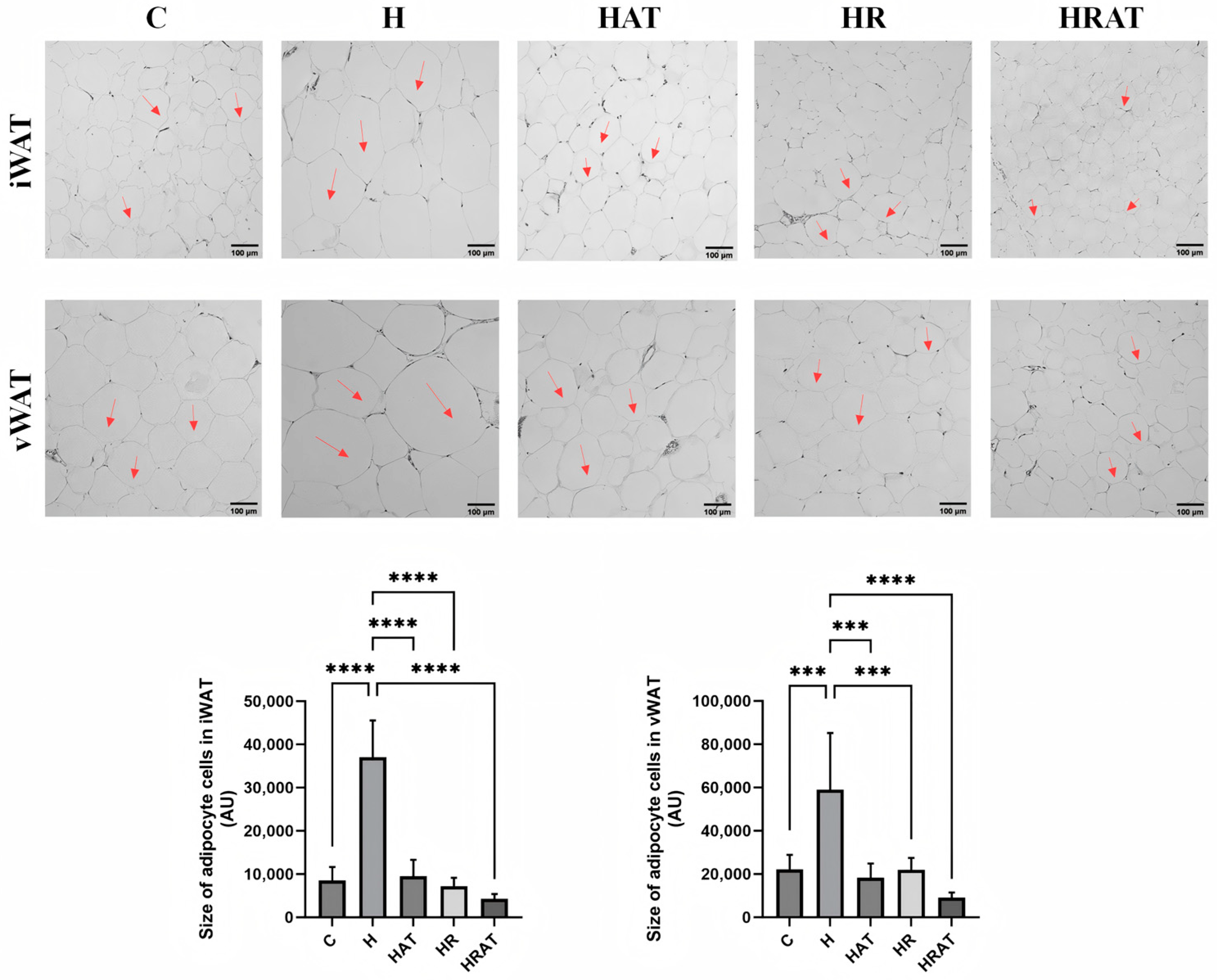
3.3. Aerobic Exercise Combined with RES Triggers the Browning of WAT and Enhances Thermogenesis in BAT
3.4. Aerobic Exercise Combined with RES Promotes White Adipose Tissue Mitochondrial Biogenesis Through a Multidimensional Mechanism
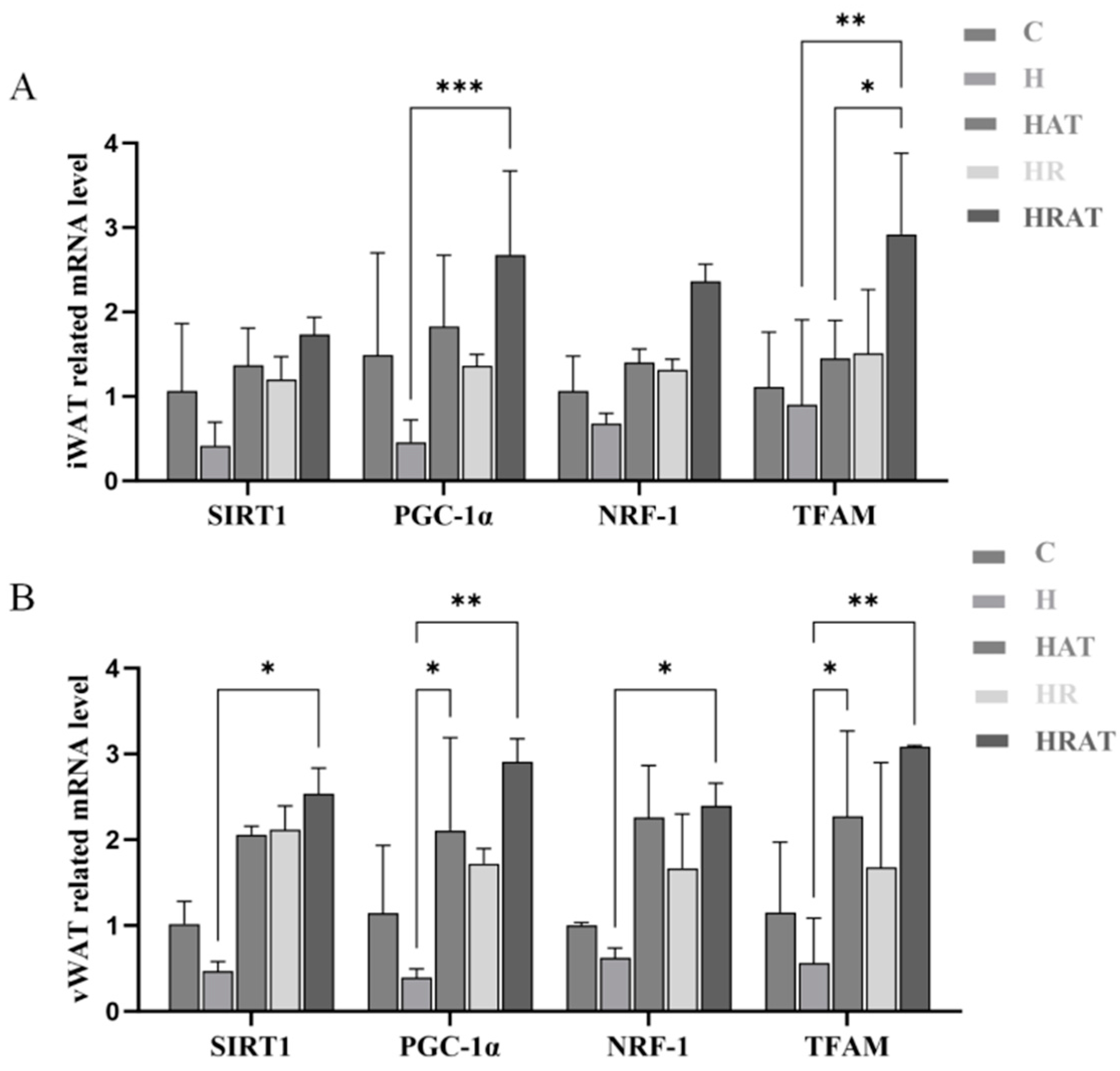
3.5. Aerobic Exercise Combined with RES Promotes Mitochondrial Biogenesis Through the SIRT1-PGC-1α-NRF-1-TFAM Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RES | Resveratrol |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
| BAT | Brown adipose tissue |
| iWAT | Inguinal adipose tissue |
| vWAT | Visceral adipose tissue |
| T-CHO | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| FFA | Free fatty acid |
| COX | Cytochrome c Oxidase |
| SDH | Succinate dehydrogenase |
| mtDNA | Mitochondrial DNA |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling protein 1 |
| Cidea | Cell Death-Inducing DNA Fragmentation Factor Alpha-like Effector A |
| Tbx1 | T-Box Transcription Factor 1 |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| PGC-1α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha |
| NRF-1 | Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 |
| TFAM | Mitochondrial Transcription Factor A |
References
- Stroh, A.M.; Stanford, K.I. Exercise-induced regulation of adipose tissue. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2023, 81, 102058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Dai, H.; Duan, Y.; An, Y.; Shi, L.; Lv, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, Q.; et al. Brown and beige adipose tissue: A novel therapeutic strategy for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, M.J.; Du, M. Prevention of obesity by dietary resveratrol: How strong is the evidence? Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 10, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lagouge, M.; Argmann, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Meziane, H.; Lerin, C.; Daussin, F.; Messadeq, N.; Milne, J.; Lambert, P.; Elliott, P.; et al. Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 2006, 127, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.A.; Hou, X.; Hao, S. Mitochondrial biogenesis in neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 2025–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liang, X.; Yang, Q.; Fu, X.; Rogers, C.J.; Zhu, M.; Rodgers, B.D.; Jiang, Q.; Dodson, M.V.; Du, M. Resveratrol induces brown-like adipocyte formation in white fat through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) α1. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, Z.; Puigserver, P.; Andersson, U.; Zhang, C.; Adelmant, G.; Mootha, V.; Troy, A.; Cinti, S.; Lowell, B.; Scarpulla, R.C.; et al. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 1999, 98, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.; Hu, Y.; Ruan, R.; Jin, Q. Resveratrol promotes mitochondrial energy metabolism in exercise-induced fatigued rats. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2023, 17, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, M.O. Determination of the surface area of the white rat with its application to the expression of metabolic results. Am. J. Physiol.-Leg. Content 1929, 89, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safahani, M.; Aligholi, H.; Noorbakhsh, F.; Djalali, M.; Pishva, H.; Mousavi, S.M.M.; Alipour, F.; Gorji, A.; Koohdani, F. Resveratrol promotes the arcuate nucleus architecture remodeling to produce more anorexigenic neurons in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Nutrition 2018, 50, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, M.; Moco, S. Resveratrol and Its Human Metabolites-Effects on Metabolic Health and Obesity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gollisch, K.S.; Brandauer, J.; Jessen, N.; Toyoda, T.; Nayer, A.; Hirshman, M.F.; Goodyear, L.J. Effects of exercise training on subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in normal- and high-fat diet-fed rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E495–E504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ziqubu, K.; Dludla, P.V.; Mthembu, S.X.H.; Nkambule, B.B.; Mabhida, S.E.; Jack, B.U.; Nyambuya, T.M.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E. An insight into brown/beige adipose tissue whitening, a metabolic complication of obesity with the multifactorial origin. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1114767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ross, J.M. Visualization of mitochondrial respiratory function using cytochrome c oxidase/succinate dehydrogenase (COX/SDH) double-labeling histochemistry. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 57, e3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Handschin, C.; Spiegelman, B.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 coactivators, energy homeostasis, and metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.; Theofanous, D.; Britton, R.G.; Aburido, G.; Pepper, C.; Sri Undru, S.; Howells, L. Resveratrol for the Management of Human Health: How Far Have We Come? A Systematic Review of Resveratrol Clinical Trials to Highlight Gaps and Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Méndez-del Villar, M.; González-Ortiz, M.; Martínez-Abundis, E.; Pérez-Rubio, K.G.; Lizárraga-Valdez, R. Effect of resveratrol administration on metabolic syndrome, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2014, 12, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konings, E.; Timmers, S.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Goossens, G.H.; Jocken, J.W.; Afman, L.A.; Müller, M.; Schrauwen, P.; Mariman, E.C.; Blaak, E.E. The effects of 30 days resveratrol supplementation on adipose tissue morphology and gene expression patterns in obese men. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitterberger, M.C.; Zwerschke, W. Mechanisms of resveratrol-induced inhibition of clonal expansion and terminal adipogenic differentiation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 1356–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Most, J.; Timmers, S.; Warnke, I.; Jocken, J.W.; van Boekschoten, M.; de Groot, P.; Bendik, I.; Schrauwen, P.; Goossens, G.H.; Blaak, E.E. Combined epigallocatechin-3-gallate and resveratrol supplementation for 12 wk increases mitochondrial capacity and fat oxidation, but not insulin sensitivity, in obese humans: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Seale, P. Control of brown and beige fat development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stanford, K.I.; Middelbeek, R.J.; Goodyear, L.J. Exercise Effects on White Adipose Tissue: Beiging and Metabolic Adaptations. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2361–2368, Erratum in Diabetes 2015, 64, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kang, N.E.; Ha, A.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.K. Resveratrol inhibits the protein expression of transcription factors related adipocyte differentiation and the activity of matrix metalloproteinase in mouse fibroblast 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2012, 6, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pilkington, A.C.; Paz, H.A.; Wankhade, U.D. Beige Adipose Tissue Identification and Marker Specificity-Overview. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 599134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Diaz, M.B.; Herzig, S.; Vegiopoulos, A. Thermogenic adipocytes: From cells to physiology and medicine. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Guo, Z.; Yang, N.; Bai, G.; Zhao, J.; Xu, D. The Mitochondrial Blueprint: Unlocking Secondary Metabolite Production. Metabolites 2024, 14, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pardo, R.; Velilla, M.; Herrero, L.; Cervela, L.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Simó, R.; Villena, J.A. Calorie Restriction and SIRT1 Overexpression Induce Different Gene Expression Profiles in White Adipose Tissue in Association with Metabolic Improvement. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2000672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.M.; Frade, A.C.; Guimarães, J.B.; Freitas, K.M.; Lopes, M.T.; Guimarães, A.L.; de Paula, A.M.; Coimbra, C.C.; Santos, S.H. Resveratrol increases brown adipose tissue thermogenesis markers by increasing SIRT1 and energy expenditure and decreasing fat accumulation in adipose tissue of mice fed a standard diet. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.B.; Ai, H.Y.; Yuan, S.H.; Cao, H.Y.; Liang, H.; Weng, J.P.; Xu, F. Effect of SIRT1 deficiency on function of brown adipose tissue in obese mice. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 96, 1859–1862. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nøhr, M.K.; Bobba, N.; Richelsen, B.; Lund, S.; Pedersen, S.B. Inflammation Downregulates UCP1 Expression in Brown Adipocytes Potentially via SIRT1 and DBC1 Interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Houtkooper, R.H.; Pirinen, E.; Auwerx, J. Sirtuins as regulators of metabolism and healthspan. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, W.C.; Hsu, Y.J.; Wei, L.; Chen, Y.J.; Huang, C.C. Association of physical performance and biochemical profile of mice with intrinsic endurance swimming. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Bi, Z.; Lan, T.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Y.; Mo, F.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; He, X.; et al. TFAM deficiency in dendritic cells leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and enhanced antitumor immunity through cGAS-STING pathway. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e005430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]


| Gene Name | Forward Sequences (5′-3′) | Reverse Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | 5′-TGCCACTCAGAAGACTGTGG-3′ | 5′-TTCAGCTCTGGGATGACCTT-3′ |
| UCP1 | 5′-GGGCTGATTCCTTTTGGTCTCT-3′ | 5′-GGGTTGCACTTCGGAAGTTGT-3′ |
| Cidea | 5′-TGTTAAGGAGTCTGCTGCGGTTC-3′ | 5′-ATGGCTGCTCTTCTGTGTCACC-3′ |
| Cited | 5′-AAGCCAACCAGGAGAGGATGAG-3′ | 5′-GGGCACCAGCAGGAGAGAC-3′ |
| Tbx1 | 5′-GGCAGGCAGACGAATGTTCCC-3′ | 5′-CAGCCACCAGCCAGGAGGAG-3′ |
| SIRT1 | 5′-ATTTATGCTCGCCTTGCTGTG-3′ | 5′-CAGAGCTGCTCATGAATGCTG-3′ |
| PGC-1α | 5′-TATTCATTGTTCGATGTGTCGC-3′ | 5′-TGTCTGTAGTGGCTTGATTCAT-3′ |
| NRF-1 | 5′-TCTGCTGTGGCTGATGGAGAGG-3′ | 5′-GATGCTTGCGTCGTCTGGATGG-3′ |
| TFAM | 5′-GCAGAAACGCCTAAAGAAGAAAGC-3′ | 5′-ACTCATCCTTAGCCTCCTGGAAG-3′ |
| MT-ND1 | 5′-CAGGACCATTCGCCCTATTCT-3′ | 5′-ATAGGAGGTGCATTAGTTGGTCAT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Jin, Q.; Chen, X. Synergistic Impact of Aerobic Exercise and Resveratrol on White Adipose Tissue Browning in Obese Rats: Mechanistic Exploration and Biological Insights. Metabolites 2025, 15, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050331
Hu Y, Wu Y, Wang C, Jin Q, Chen X. Synergistic Impact of Aerobic Exercise and Resveratrol on White Adipose Tissue Browning in Obese Rats: Mechanistic Exploration and Biological Insights. Metabolites. 2025; 15(5):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050331
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yulong, Yihan Wu, Chunlong Wang, Qiguan Jin, and Xianghe Chen. 2025. "Synergistic Impact of Aerobic Exercise and Resveratrol on White Adipose Tissue Browning in Obese Rats: Mechanistic Exploration and Biological Insights" Metabolites 15, no. 5: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050331
APA StyleHu, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, C., Jin, Q., & Chen, X. (2025). Synergistic Impact of Aerobic Exercise and Resveratrol on White Adipose Tissue Browning in Obese Rats: Mechanistic Exploration and Biological Insights. Metabolites, 15(5), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050331





