Identification and Evaluation of Colour Change in Rosemary and Biluochun Tea Infusions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Tea Infusions
2.2. Determination of the Total Contents of Theabrownin, Theaflavin and Thearubigin
2.3. pH Value Detection
2.4. Metabolomics Analysis Using Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC–MS)
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the Colour, Tea Pigment, and pH Value of the Infusions
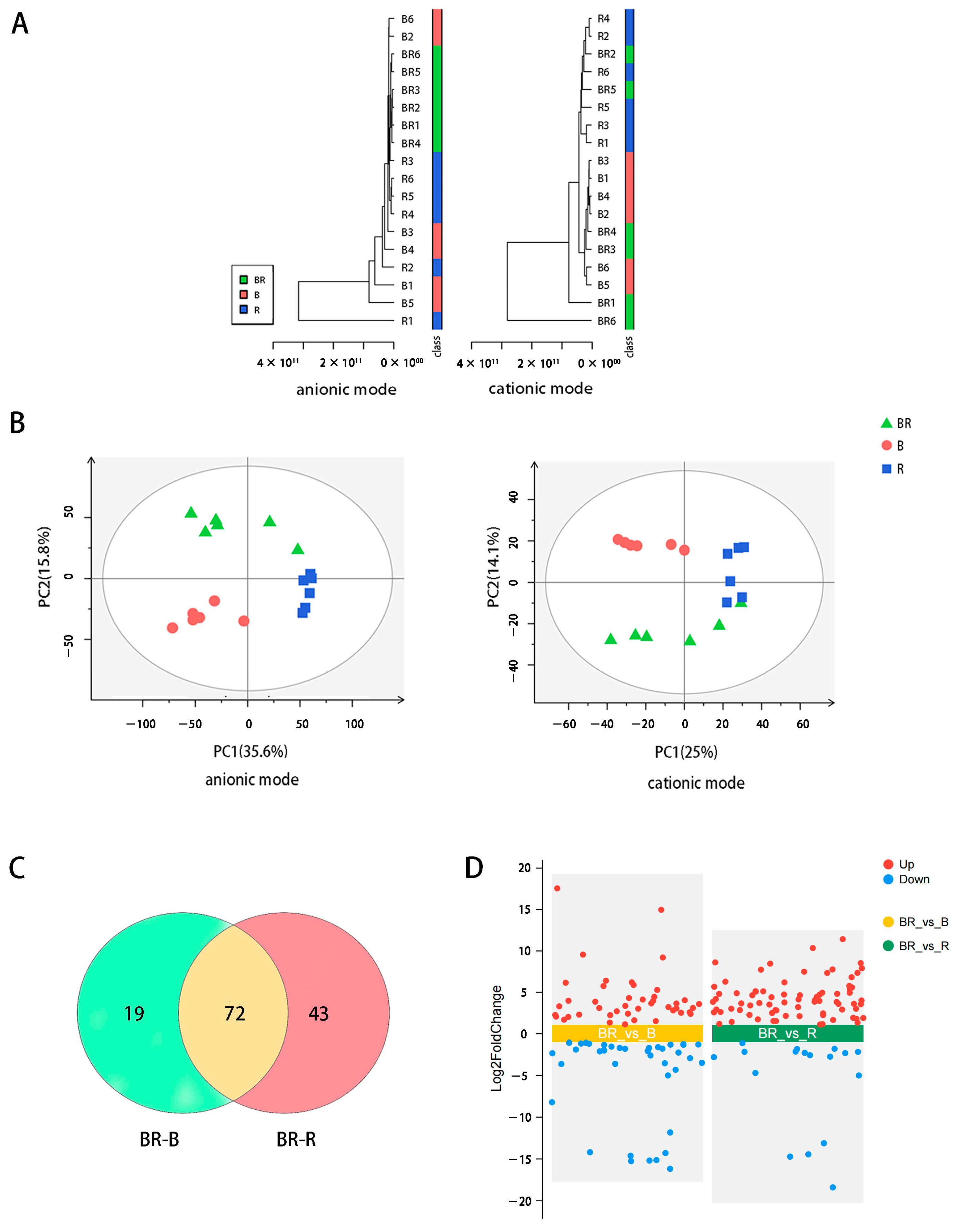
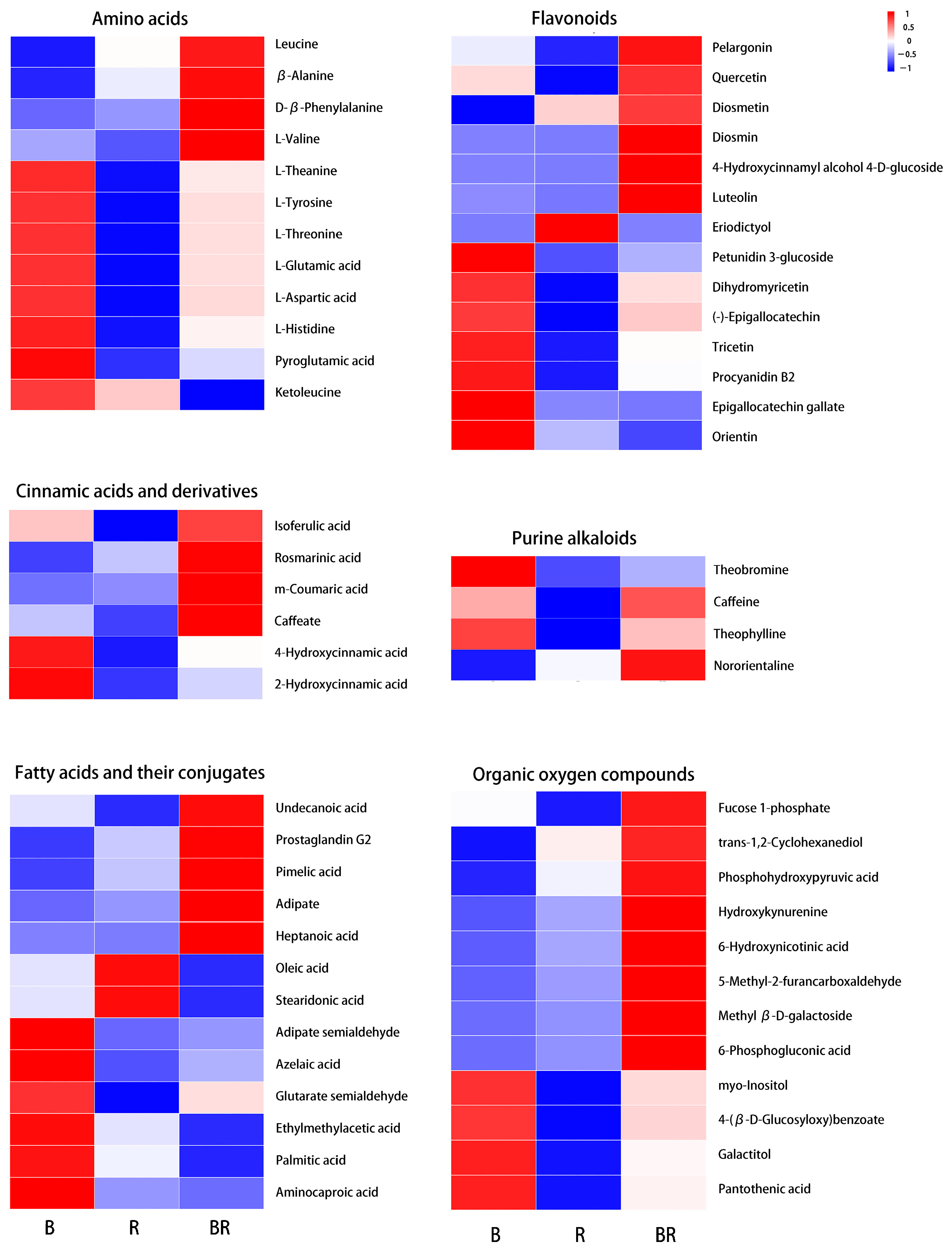
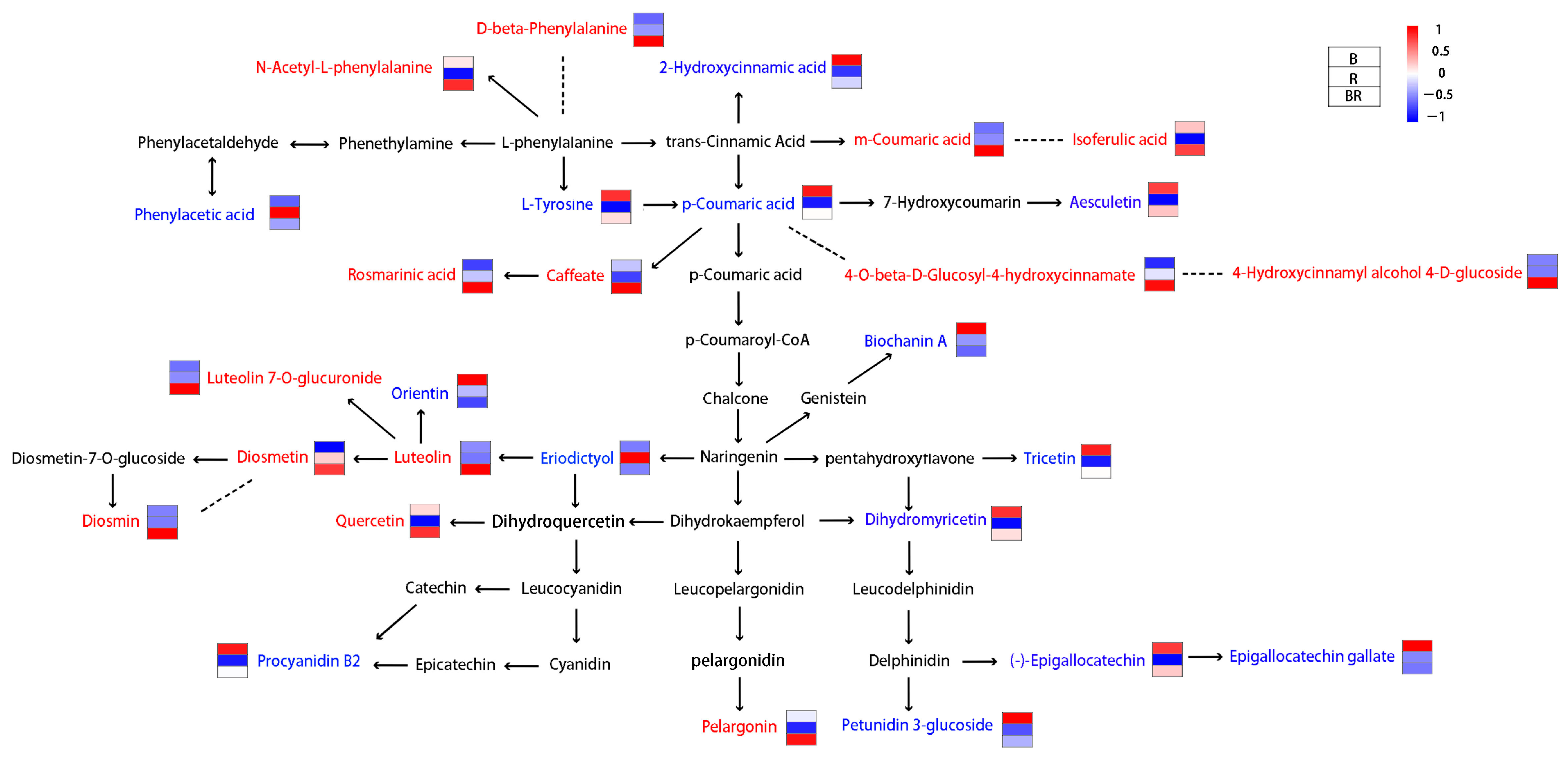
3.2. Metabolomic Analysis of the Tea Infusions
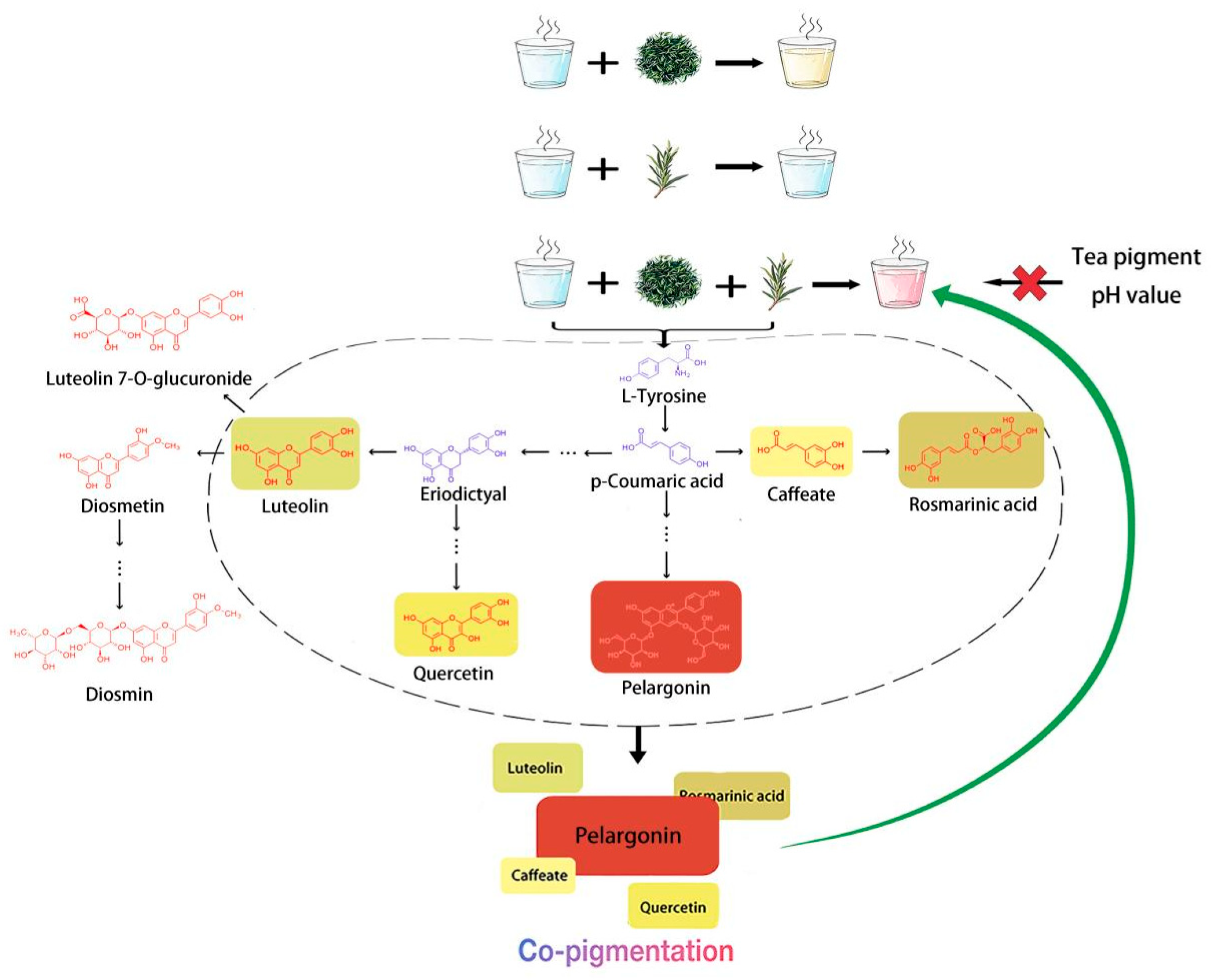
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Proteomic analysis of young leaves at three developmental stages in an albino tea cultivar. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedula, V.S.P.; Prakash, I. The aroma, taste, color and bioactive constituents of tea. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 2110–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Ding, Z.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xu, M. The identification and evaluation of two different color variations of tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4951–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wan, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, H. Oxidation Mechanism of Tea Catechins. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2006, 018, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q. The Mechanism and Adjustment of Sediment Formationand Color Distortion in Green Tea Extraction. Ph.D. Thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, R.; Gulati, A. Fractionation and identification of minor and aroma-active constituents in Kangra orthodox black tea. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Huang, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Shi, J.; Kong, Q.; Sun, S.; Jiang, X.; Chen, D.; Yan, S. GC–MS-based metabolomic study reveals dynamic changes of chemical compositions during black tea processing. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X. Tea Biochemistry; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.S.; Maliakal, P.; Meng, X. Inhibition of carcinogenesis by tea. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gong, J.; Chisti, Y.; Sirisansaneeyakul, S. Production of theabrownins using a crude fungal enzyme concentrate. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 231, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X. Distinct changes of metabolic profile and sensory quality during Qingzhuan tea processing revealed by LC-MS-based metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4955–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.; Peng, J.; Tang, G. Optimization the extraction of total flavonoids from Biluochun tea by orthogonal test. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2017, 46, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; An, Q.; Li, Q. Research progress on chemical components and biological effects of rosemary. Today Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2022, 38, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Yang, J.; Zeng, J.; Liu, X. Study on HPLC Characteristics of Rosemary Extract. Feed Ind. 2024, 45, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbardar, M.G.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Therapeutic effects of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its active constituents on nervous system disorders. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, C.; Gong, J. Effects of enzymatic action on the formation of theabrownin during solid state fermentation of Pu-erh tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2412–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Clowers, B.H.; Moore, R.J.; Zink, E.M. Signature-discovery approach for sample matching of a nerve-agent precursor using liquid chromatography−mass spectrometry, XCMS, and chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W. Forming Mechanism and Preparation of Tea RedPigment. J. Tea Sci. 1997, 17, 8. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=lwcs1eIaudgTWsAYHkh5aAkmrvpIn4SxHieKCC-4M4D0hj5NF9TnU2hYFDTxVcY9kT1mv9dI3lJIaVSOP2Xt_XLcBsbRKFsFXVD-UNqFs84GA85JF2TFPlBcZzKsm0I-YDgnYn3ZNxsZJJq1yVGa6_2DcKcTz8Jfr2yQjfqOPSX7H14_6LbWlnoBO6NTtWOQ&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Kim, S.H.; Park, J.D.; Lee, L.S.; Han, D.S. Effect of pH on the green tea extraction. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 31, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Hirono, H.; Yamashita, S.; Hirono, Y. Influence of steaming duration, chlorophyll-a and-b content and ratio, and pH on the color of green tea processed from multiple tea (Camellia sinensis L.) cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 9410–9422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, C.; Xu, H.; Yuan, K.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, G. Metabolic profiling of transgenic rice with cryIAc and sck genes: An evaluation of unintended effects at metabolic level by using GC-FID and GC–MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yang, Z. Understanding different regulatory mechanisms of proteinaceous and non-proteinaceous amino acid formation in tea (Camellia sinensis) provides new insights into the safe and effective alteration of tea flavor and function. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2020, 60, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P.C.; Aslam, S.N. The chemistry of the genus Cicer L. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2006, 33, 905–956. [Google Scholar]
- Alappat, B.; Alappat, J. Anthocyanin pigments: Beyond aesthetics. Molecules 2020, 25, 5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, I.; Du, J.; Nawaz, A.; Li, C. Multiple co-pigments of quercetin and chlorogenic acid blends intensify the color of mulberry anthocyanins: Insights from hyperchromicity, kinetics, and molecular modeling investigations. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Li-Beisson, Y. Lipids in Plant and Algae Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 86. [Google Scholar]
- Le Moigne, D.; Guéguen, N.; Salvaing, J. Lipid droplets in plants: More than a simple fat storage. Adv. Bot. Res. 2022, 101, 191–223. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.F.; Yang, P.D.; Bai, S.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, J.; Huang, J.A.; Xiong, L.G. Lipids: A noteworthy role in better tea quality. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jin, J.; Chen, J.; Ercisli, S.; Chen, L. Purine alkaloids in tea plants: Component, biosynthetic mechanism and genetic variation. Beverage Plant Res. 2022, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Ma, M.; Li, C.; Luo, L. Stability of tea polyphenols solution with different pH at different temperatures. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liang, Y.R.; Wang, K.R.; Ye, J.H.; Lu, J.L.; Zheng, X.Q. Anthocyanin metabolism and its differential regulation in purple tea (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 201, 107875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayesh, E.; Shangguan, L.; Korir, N.K.; Sun, X.; Bilkish, N.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Fang, J. Fruit skin color and the role of anthocyanin. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 2879–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.E.; Prasad, K.N.; Kong, K.W.; Jiang, Y.; Ismail, A. Carotenoids and their isomers: Color pigments in fruits and vegetables. Molecules 2011, 16, 1710–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandía-Herrero, F.; García-Carmona, F. Biosynthesis of betalains: Yellow and violet plant pigments. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swami, S.B.; Ghgare, S.N.; Swami, S.S.; Shinde, K.J.; Kalse, S.B.; Pardeshi, I.L. Natural pigments from plant sources: A review. Pharma Innov. J. 2020, 9, 56. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Mu, L.; Yan, G.L.; Liang, N.N.; Pan, Q.H.; Wang, J.; Reeves, M.J.; Duan, C.Q. Biosynthesis of anthocyanins and their regulation in colored grapes. Molecules 2010, 15, 9057–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroni, K.; Tonelli, C. Recent advances on the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in reproductive organs. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhao, X.D.; Zhong, Y. Research Progress on Regulation of Plant Flavonoids Biosynthesis. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhong, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Fan, H. Combinatorial preparation and structural characterization of anthocyanins and aglycones from Purple-heart Radish for evaluation of physicochemical stability and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Yu, C.; Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Luo, L.; Pan, H.; Zheng, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. Determination of flavonoids and carotenoids and their contributions to various colors of rose cultivars (Rosa spp.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, J.; Zhao, L. Research Progress on the Stability andFunction of Anthocyanins. Hans J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2018, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.P.; Dai, W.D.; Tan, J.F.; Guo, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, Z. Identification of the anthocyanins from the purple leaf coloured tea cultivar Zijuan (Camellia sinensis var. assamica) and characterization of their antioxidant activities. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.S.; Li, S.; Tang, Q.; Li, H.X.; Chen, S.X.; Li, P.W.; Xu, J.Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, X. The dark-purple tea cultivar ‘Ziyan’accumulates a large amount of delphinidin-related anthocyanins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2719–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendri, N.; Singh, S.; Sharma, B.; Purohit, R.; Bhandari, P. Effect of co-pigments on anthocyanins of Rhododendron arboreum and insights into interaction mechanism. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouillas, P.; Sancho-García, J.C.; De Freitas, V.; Gierschner, J.; Otyepka, M.; Dangles, O. Stabilizing and modulating color by copigmentation: Insights from theory and experiment. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4937–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klisurova, D.; Petrova, I.; Ognyanov, M.; Georgiev, Y.; Kratchanova, M.; Denev, P. Co-pigmentation of black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) anthocyanins with phenolic co-pigments and herbal extracts. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Shokri, S.; Gao, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. Improving effects of three selected co-pigments on fermentation, color stability, and anthocyanins content of blueberry wine. LWT 2022, 156, 113070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gençdağ, E.; Özdemir, E.E.; Demirci, K.; Görgüç, A.; Yılmaz, F.M. Copigmentation and stabilization of anthocyanins using organic molecules and encapsulation techniques. Curr. Plant Biol. 2022, 29, 100238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erşan, S.; Müller, M.; Reuter, L.; Carle, R.; Müller-Maatsch, J. Co-pigmentation of strawberry anthocyanins with phenolic compounds from rooibos. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2022, 4, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huwait, E.; Mobashir, M. Potential and therapeutic roles of diosmin in human diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Feng, L.; Shi, W.; Peng, Q.; Ding, L.; Tan, X.; Zhan, R.; et al. Genomic insights into the evolution of flavonoid biosynthesis and O-methyltransferase and glucosyltransferase in Chrysanthemum indicum. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 113725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xie, H.; Ding, Z.; Ding, S.; Wang, H. The quality evaluation of tea (Camellia sinensis) varieties based on the metabolomics. HortScience 2019, 54, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Fang, C.; Li, C.; You, J.; Ma, K. Identification and Evaluation of Colour Change in Rosemary and Biluochun Tea Infusions. Metabolites 2025, 15, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040265
Yuan Y, Fang C, Li C, You J, Ma K. Identification and Evaluation of Colour Change in Rosemary and Biluochun Tea Infusions. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040265
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yuan, Caochuang Fang, Chaohan Li, Jiaqi You, and Kun Ma. 2025. "Identification and Evaluation of Colour Change in Rosemary and Biluochun Tea Infusions" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040265
APA StyleYuan, Y., Fang, C., Li, C., You, J., & Ma, K. (2025). Identification and Evaluation of Colour Change in Rosemary and Biluochun Tea Infusions. Metabolites, 15(4), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040265





