Dietary Tea Polyphenols Alleviate Acute-Heat-Stress-Induced Death of Hybrid Crucian Carp HCC2: Involvement of Modified Lipid Metabolisms in Liver
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TPs and Experimental Diets
2.2. Fish and Experimental Conditions
2.3. Heat Stress Experiment and Sample Collection
2.4. Stress Indicators
2.5. Antioxidant Capacity
2.6. Metabolomic Method
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
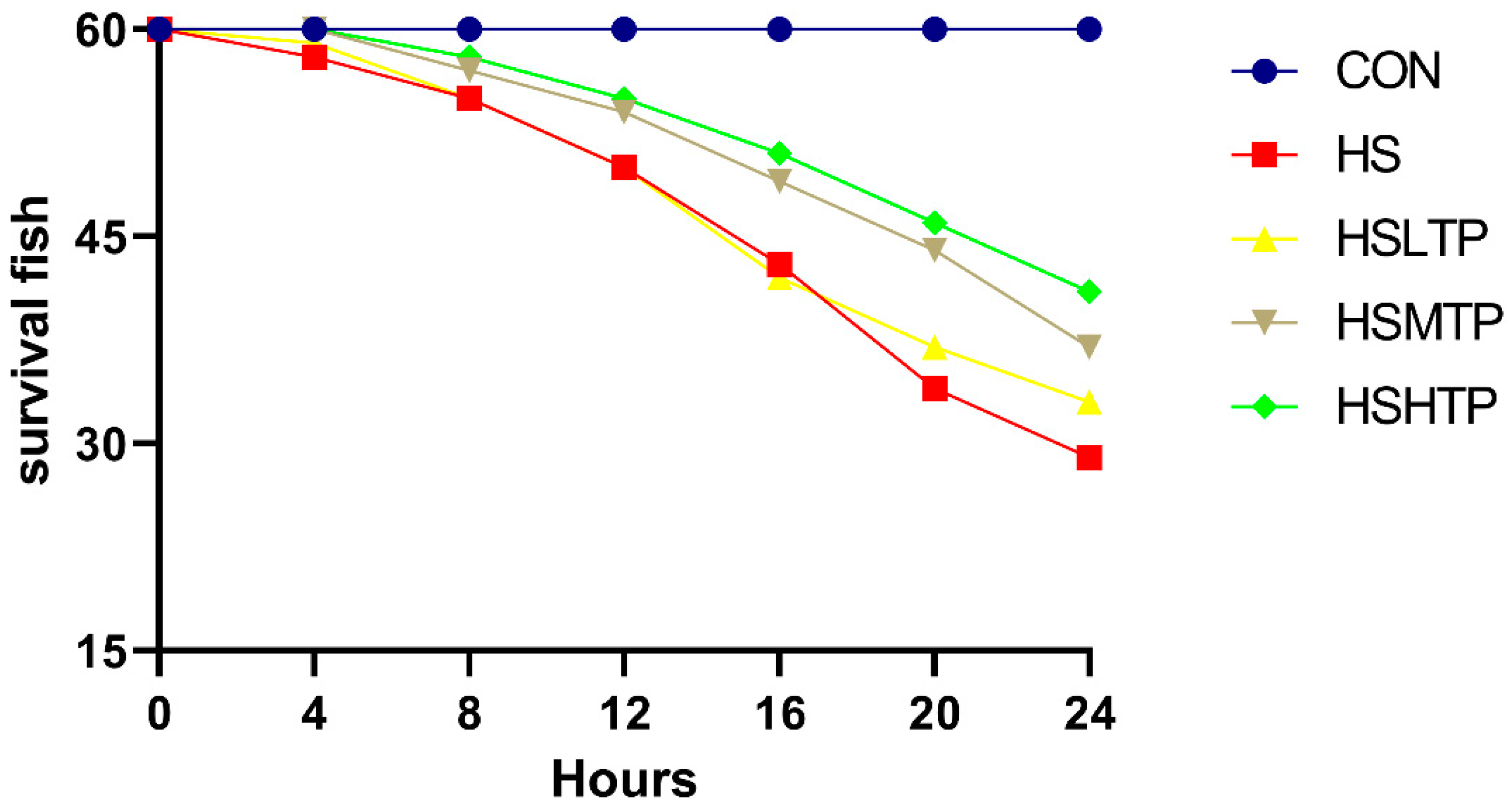
3.1. Effects of TPs Supplementation on Survival Rate
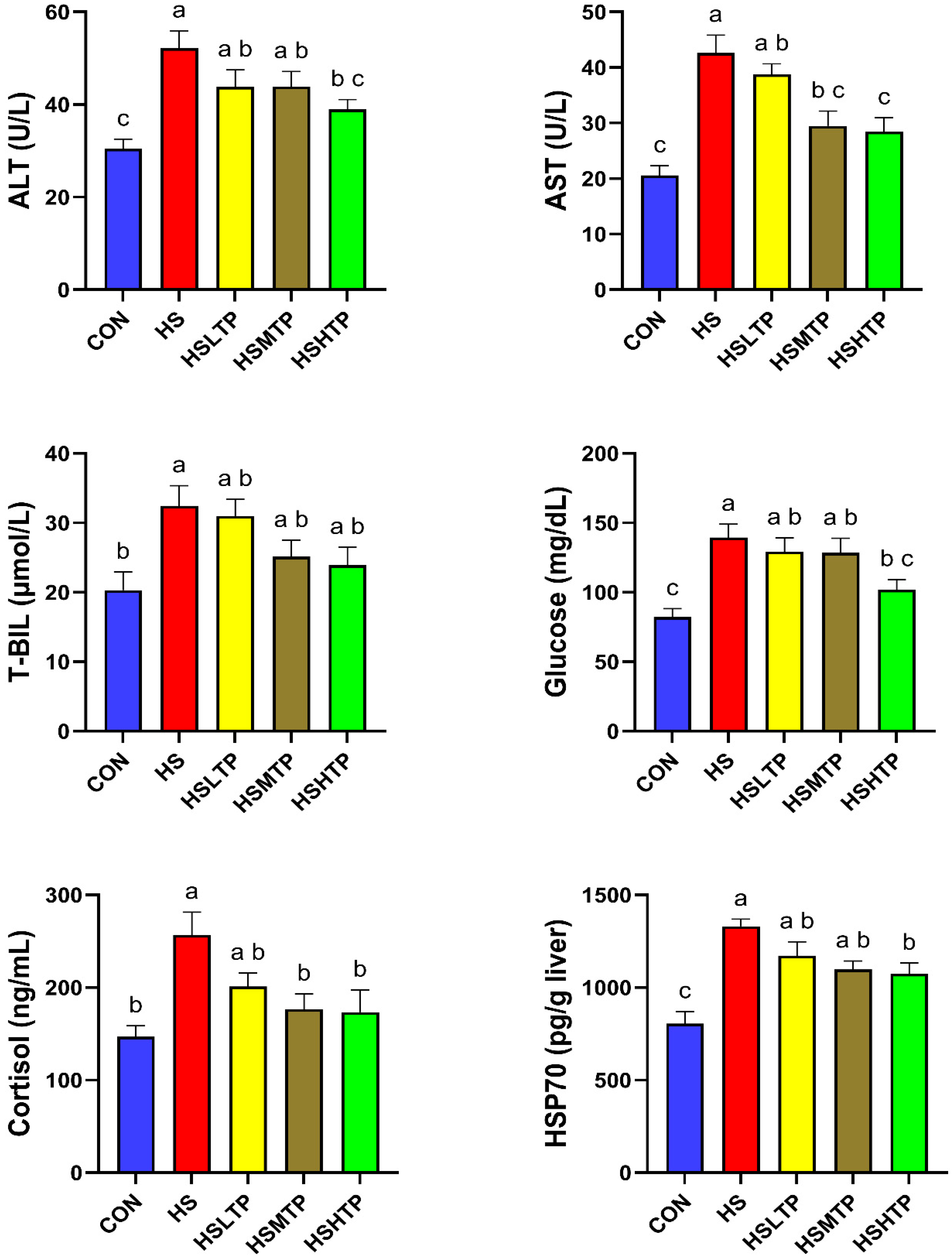
3.2. Effects of TPs Supplementation on Stress Indicators
3.3. Effects of TPs Supplementation on Antioxidant Capacity
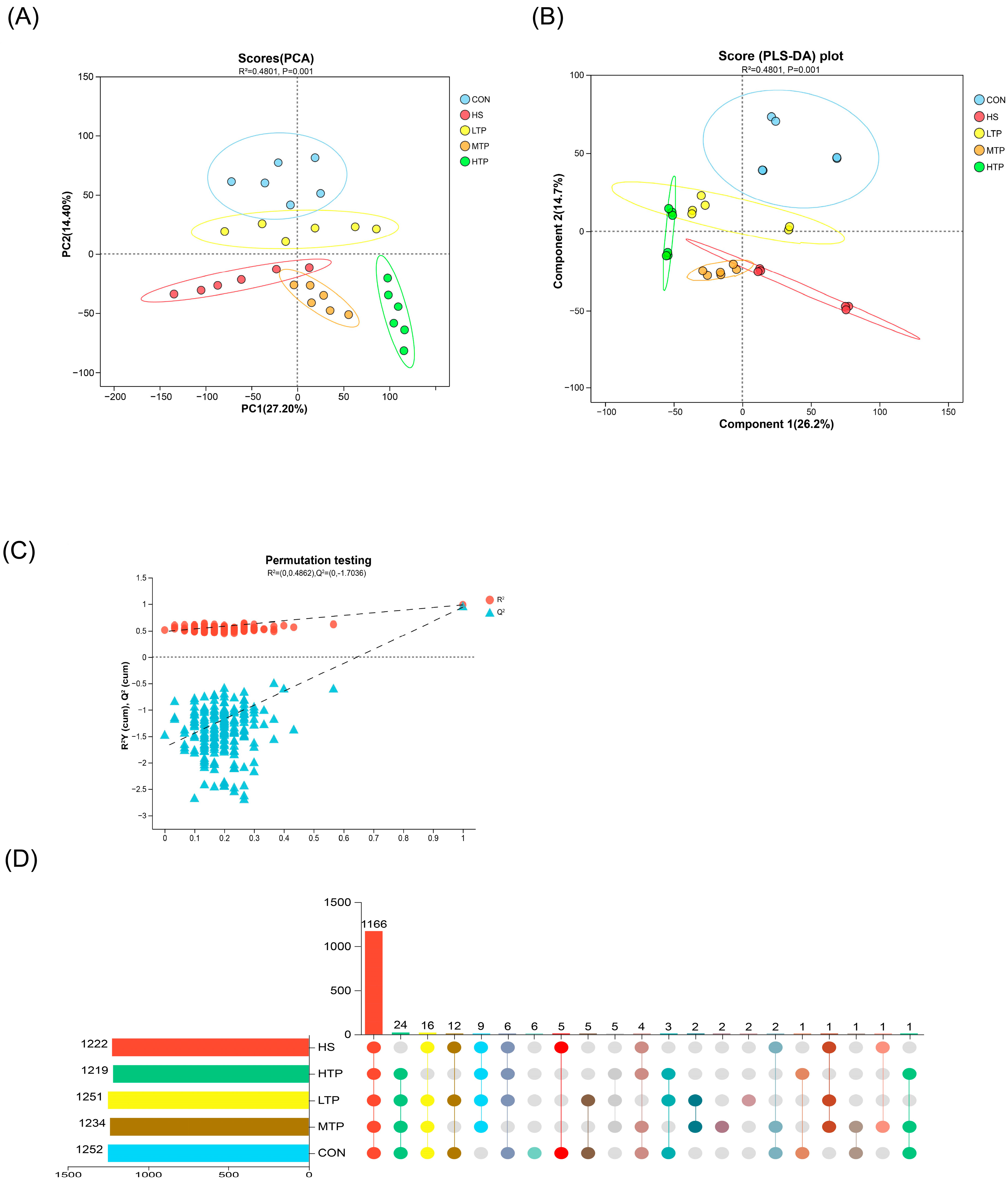
3.4. Sample Information and Comparative Analysis
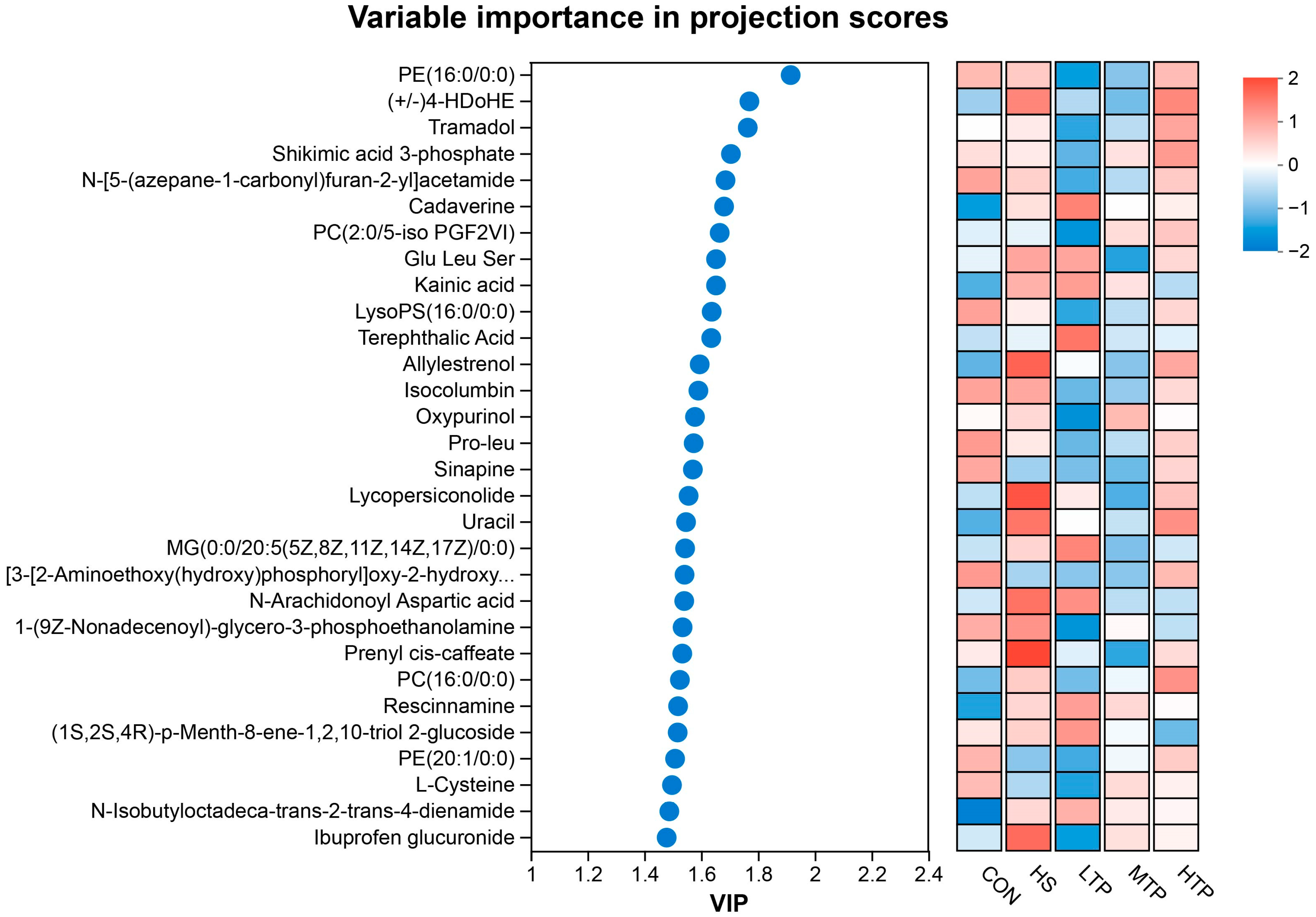
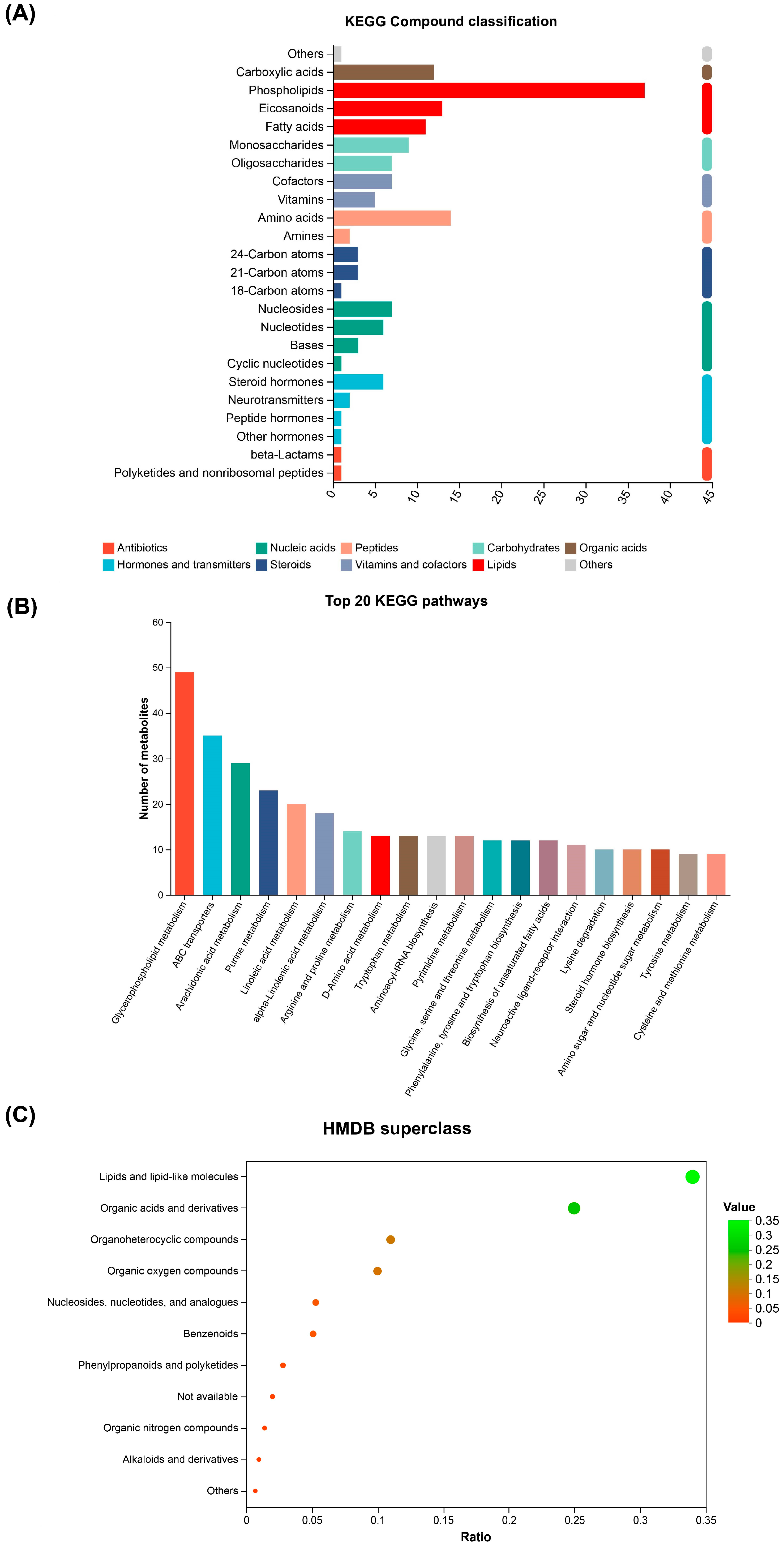
3.5. Metabolite Annotation and Pathway Analysis
3.6. Metabolite Clustering Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feldman, D.R.; Collins, W.D.; Gero, P.J.; Torn, M.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shippert, T.R. Observational determination of surface radiative forcing by CO2 from 2000 to 2010. Nature 2015, 519, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miranda, L.E.; Coppola, G.; Boxrucker, J. Reservoir fish habitats: A perspective on coping with climate change. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 478–498. [Google Scholar]
- Esam, F.; Khalafalla, M.M.; Gewaily, M.S.; Abdo, S.; Hassan, A.M.; Dawood, M.A.O. Acute ammonia exposure combined with heat stress impaired the histological features of gills and liver tissues and the expression responses of immune and antioxidative related genes in nile tilapia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, J.L.; Shen, Y.B. Transcriptomic analysis of the liver and brain in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) under heat stress. Mar. Biotechnol. 2022, 24, 856–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.Z.; Wang, S.; Tang, C.C.; Tao, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, Q.B.; Luo, K.K.; Wu, C.; Hu, F.Z.; et al. The research advances in distant hybridization and gynogenesis in fish. Rev. Aquac. 2025, 17, e12972. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.F.; Liu, J.M.; Liang, Q.L.; Qi, Y.H.; Tao, M.; Zhang, C.; Qin, Q.B.; Zhao, R.R.; Chen, B.; Liu, S.J. A hybrid lineage derived from hybridization of Carassius cuvieri and Carassius auratus red var. And a new type of improved fish obtained by backcrossing. Aquaculture 2019, 505, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Sikorska, J.; Kondera, E.; Kaminski, R.; Lugowska, K.; Witeska, M.; Wolnicki, J. Effect of four rearing water temperatures on some performance parameters of larval and juvenile crucian carp, Carassius carassius, under controlled conditions. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 3874–3880. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Feng, W.H.; Gao, G.L.; Li, M.G.; Zheng, G.W. Causes of the severe drought in southwest china during the summer of 2022. Atmos. Res. 2024, 303, 107320. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Tea polyphenols for health promotion. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 519–533. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.M.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Duan, Y.H.; Chen, Q.H.; Li, F.N. Antioxidant mechanism of tea polyphenols and its impact on health benefits. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Z.; Li, Z.L.; Ma, Y.T.; Liu, Y.; Lin, C.C.; Li, S.M.; Zhan, J.F.; Ho, C.T. Immunomodulatory effects of green tea polyphenols. Molecules 2021, 26, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.; Choudhary, S.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, S.S.; Lohan, S.; Bhardwaj, V.; Syan, N.; Jyoti, S. Tea: A native source of antimicrobial agents. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 568–584. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Y.; Gao, X.; Lou, Y.J. Interactions of tea polyphenols with intestinal microbiota and their implication for cellular signal conditioning mechanism. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Qiu, P.X.; Shen, J.Y.; Wang, H.X.; Shao, Y.; Song, H.L.; Shen, L.D.; Zhang, S. Tea polyphenols postpone the evolution of multidrug tolerance in escherichia coli under the stress of antibiotic in water. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 457, 142467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.F.; Han, S.; Zha, X.N.; Cheng, J.R.; Song, J.Y.; Jiao, Z. Response surface optimization of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of tea polyphenols from green tea scraps. J. Aoac Int. 2019, 102, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakakibara, H.; Shimoi, K. Anti-stress effects of polyphenols: Animal models and human trials. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5702–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, X.C.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Geng, Z.Y.; Zhang, C. Effects of dietary supplementation with epigallocatechin gallate on meat quality and muscle antioxidant capacity of broilers subjected to acute heat stress. Animals 2021, 11, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.D.; An, Y.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.W.; Shao, Q.; Dou, M.Y.; He, L.; Zhang, C. Tea polyphenols protect bovine intestinal epithelial cells from the adverse effects of heat-stress in vitro. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.H.; Lin, W.; Wang, L.K.; Zhang, D.N.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, L.; Li, D.P.; Tang, R.; Yang, L.P.; Qiu, Y.M. The supplementation of dietary selenium yeast and green tea-derived polyphenols improves antioxidant capacity and immune response in juvenile wuchang bream under ammonia stress. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 3790–3803. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Zhou, S.S.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, Y.D.; Luo, W.T.; Zhao, Y.T.; Huang, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.B.; Li, Z.B. Effects of oxidized fish oil diet supplemented with tea polyphenols on intestinal health and liver metabolism of spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Aquac. Rep. 2024, 37, 102201. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.L.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.J.; Jiang, S.J.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, X.S. Evaluation of a transgenic tg(hspa8b: Gfp) nile tilapia for monitoring of stress and anti-stress effects of the influence of temperature and vibration. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T.; Alfaro, A.C. Metabolomic strategies for aquaculture research: A primer. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 26–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.L.; Li, D.; Cui, X.J.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.J.; Sun, Y.D. The impact of rutin on heat stress response of hybrid fish (Carassius auratus cuvieri ♀ x Carassius auratus red var. ♂). Fishes 2024, 9, 509. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.Z.; Luo, J.R.; Fu, D.B.; Zhao, X.H.; Bunlue, K.; Xu, Z.S.; Qu, M.R. Traditional chinese medicine prescriptions enhance growth performance of heat stressed beef cattle by relieving heat stress responses and increasing apparent nutrient digestibility. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.B.; Yoon, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, I.; Lim, H.K. A comparison of the physiological responses to heat stress of juvenile and adult starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2021, 73, 1546029. [Google Scholar]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Eweedah, N.M.; Elbialy, Z.I.; Abdelhamid, A.I. Dietary sodium butyrate ameliorated the blood stress biomarkers, heat shock proteins, and immune response of nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to heat stress. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 88, 102500. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, D.N.; Qin, J.G.; Harris, J.O.; Hoang, T.H.; Bansemer, M.S.; Currie, K.L.; Phan-Thien, K.Y.; Dowell, A.; Stone, D.A.J. Effects of dietary grape seed extract, green tea extract, peanut extract and vitamin c supplementation on metabolism and survival of greenlip abalone (Haliotis laevigata donovan) cultured at high temperature. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 364–373. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Mao, W.J.; Lin, Z.J.; Ling, Q.F. Heat stress induced hepatocyte apoptosis in largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides via ire1α/traf2/ask1/jnk pathway. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 988–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.D.; Li, M.; Chu, G.S.; Liu, H.J.; Shan, X.F.; Wang, G.Q.; Han, G.H. The positive effects of single or conjoint administration of lactic acid bacteria on Channa argus: Digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant capacity, intestinal microbiota and morphology. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735852. [Google Scholar]
- Khieokhajonkhet, A.; Phoprakot, M.; Aeksiri, N.; Kaneko, G.; Phromkunthong, W. Effects of thermal stress responses in goldfish (carassius auratus): Growth performance, total carotenoids and coloration, hematology, liver histology, and critical thermal maximum. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 49, 1391–1407. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, H.J.; Fazio, A.; Faggio, C.; Blust, R.; De Boeck, G. Cortisol affects metabolic and ionoregulatory responses to a different extent depending on feeding ration in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A-Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 189, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.L.; Liu, F.Q.; Jin, H.M.; Li, R.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, W.Q.; Wang, H.C.; Chen, W.Q. Involvement of pkcα and erk1/2 signaling pathways in egcg’s protection against stress-induced neural injuries in wistar rats. Neuroscience 2017, 346, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, X.L.; Jin, S.H.; Shou, C.Y.; Han, Z.Q. Hsp70 gene family in Sebastiscus marmoratus: The genome-wide identification and transcriptome analysis under thermal stress. Genes 2023, 14, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Xie, H.Y.; Pan, P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, B.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.Y.; Sun, Y.J.; Wei, Y.R.; Jiang, Q.Y.; et al. Egcg alleviates heat-stress-induced fat deposition by targeting hsp70 through activation of ampk-sirt1-pgc-1α in porcine subcutaneous preadipocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 225, 116250. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.W.; Cai, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.N. Functional analysis of a dietary recombinant fatty acid binding protein 10 (fasp10) on the Epinephelus coioides in response to acute low temperature challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 475–484. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj, V.; Yeager-Armstead, M.; Murray, E. Protective and antioxidant role of selenium on arsenic trioxide-induced oxidative stress and genotoxicity in the fish hepatoma cell line plhc-1. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar]
- Faizan, M.; Stubhaug, I.; Menoyo, D.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Wagner, A.E.; Struksnæs, G.; Koppe, W.; Rimbach, G. Dietary alpha-tocopherol affects tissue vitamin e and malondialdehyde levels but does not change antioxidant enzymes and fatty acid composition in farmed atlantic salmon (Salmo solar L.). Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2013, 83, 238–245. [Google Scholar]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Maiorino, M. Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 3289–3303. [Google Scholar]
- Yusefi, M.; Mohammadiazarm, H.; Salati, A.P. Effects of dietary sodium diformate on growth performance, immunological and biochemical blood indices, antioxidant capacity, and thermal stress tolerance of juvenile common carp (Cprinus carpio). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 22, 100963. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Lu, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, J. Acute thermal stress reduces skeletal muscle growth and quality in gibel carp (Carassius gibelio). Water 2023, 15, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Hu, Y.J.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.L.; Tian, Y.A.; Chen, J.S.; Ai, Q.H.; Xiao, T.Y. Effects of dietary tea polyphenols on growth, immunity and lipid metabolism of juvenile black carp Mylopharyngodon piceus. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.Z.; He, Y.J.; Arowolo, M.A.; Wu, S.S.; He, J. Polyphenols as potential attenuators of heat stress in poultry production. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechmann, L.P.; Hannivoort, R.A.; Gerken, G.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Trauner, M.; Canbay, A. The interaction of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.W.; Qiang, J.; Tao, Y.F.; Li, H.X.; He, J.; Xu, P.; Chen, D.J. Responses of blood biochemistry, fatty acid composition and expression of micrornas to heat stress in genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Therm. Biol. 2018, 73, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulijwa, R.; Alfaro, A.C.; Young, T. Metabolomics in salmonid aquaculture research: Applications and future perspectives. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 547–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, K.; Nie, H.T.; Yan, X.W. Revealing the potential regulatory relationship between Hsp70, Hsp90 and Hsf genes under temperature stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 134, 108607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Shin, M.; Choi, W.; Kim, K.H. Comparative metabolite profiling of wild type and thermo-tolerant mutant of saccharomyces cerevisiae. Process Biochem. 2021, 111, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chiou, Y.S.; Pan, M.H.; Shahidi, F. Anti-inflammatory activity of lipophilic epigallocatechin gallate (egcg) derivatives in lps-stimulated murine macrophages. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, M.; Choi, M.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, N.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, S.; Kim, J.; Ryu, D.H.; Hwang, G.S. Effect of green tea on hepatic lipid metabolism in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.W.; Du, J.X.; Li, S.J.; Lei, C.X.; Zhu, T.; Han, L.Q.; Song, H.M. Chronic heat stress is capable of reducing the growth performance, causing damage to the liver structure, and altering the liver glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides L). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 51, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredients | CON | HS | HSLTP | HSMTP | HSHTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat Flour | 29.7 | 29.7 | 29.69 | 29.68 | 29.66 |
| Soybean Meal | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 |
| Rapeseed Meal | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Peanut Hulls | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Fish Meal | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Fish Oil | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Soybean Oil | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Additive Premixes b | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Choline Chloride | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Antimicrobial Agents | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Antioxidants | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Tea Polyphenols c | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Proximate Composition (%) | |||||
| Crude Protein | 35.01 | 35.01 | 35.01 | 35.01 | 35.00 |
| Crude Fat | 5.38 | 5.38 | 5.38 | 5.38 | 5.38 |
| Moisture | 6.09 | 6.09 | 6.09 | 6.09 | 6.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Tao, J.; Yu, Q.; Sun, G.; Liu, X.; Tang, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z. Dietary Tea Polyphenols Alleviate Acute-Heat-Stress-Induced Death of Hybrid Crucian Carp HCC2: Involvement of Modified Lipid Metabolisms in Liver. Metabolites 2025, 15, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040229
Zhang N, Tao J, Yu Q, Sun G, Liu X, Tang W, Zhang L, Yang Z. Dietary Tea Polyphenols Alleviate Acute-Heat-Stress-Induced Death of Hybrid Crucian Carp HCC2: Involvement of Modified Lipid Metabolisms in Liver. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040229
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Na, Jinsheng Tao, Qifang Yu, Gege Sun, Xiaopeng Liu, Weirong Tang, Lina Zhang, and Zhe Yang. 2025. "Dietary Tea Polyphenols Alleviate Acute-Heat-Stress-Induced Death of Hybrid Crucian Carp HCC2: Involvement of Modified Lipid Metabolisms in Liver" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040229
APA StyleZhang, N., Tao, J., Yu, Q., Sun, G., Liu, X., Tang, W., Zhang, L., & Yang, Z. (2025). Dietary Tea Polyphenols Alleviate Acute-Heat-Stress-Induced Death of Hybrid Crucian Carp HCC2: Involvement of Modified Lipid Metabolisms in Liver. Metabolites, 15(4), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040229






