Green Extraction Method: Microwave-Assisted Water Extraction Followed by HILIC-HRMS Analysis to Quantify Hydrophilic Compounds in Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Leaf Samples
2.3. Microcopy Analysis
2.4. Preparation of Leaf Samples
2.5. Optimizing Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
2.6. HILIC-HRMS
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Validation of the Method
2.9. Linearity for Amino Acids, Organic Acids and Sugars Analysis
2.10. Selectivity, Sensitivity and Reproducibility of the Method
3. Results
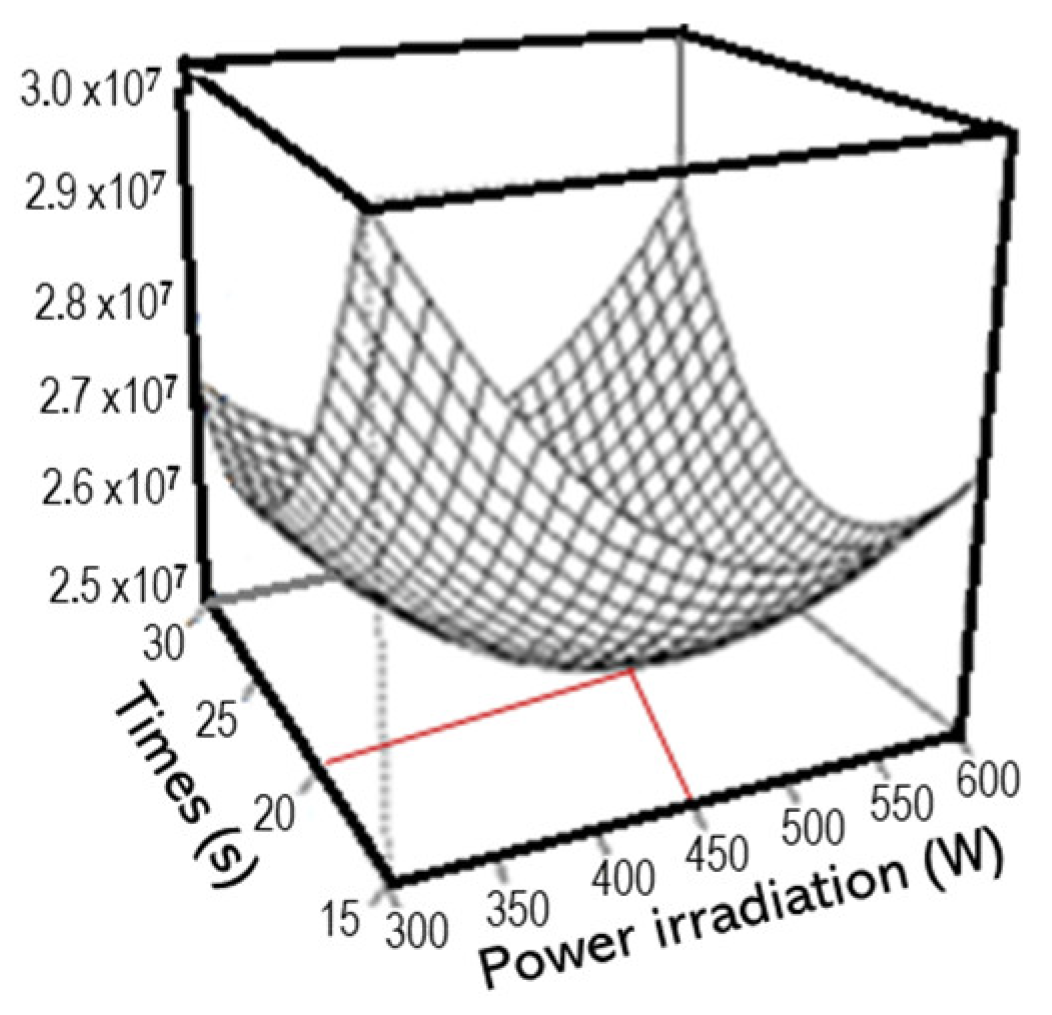
3.1. Optimizing Hydrophilic Metabolite Extraction with MAE
3.2. Validation of an HILIC-Based Method for the Separation and Quantification of Major Polar Metabolites from Plants
3.2.1. Selectivity
3.2.2. Limits of Detection and Quantification, and Linearity
3.2.3. Precision
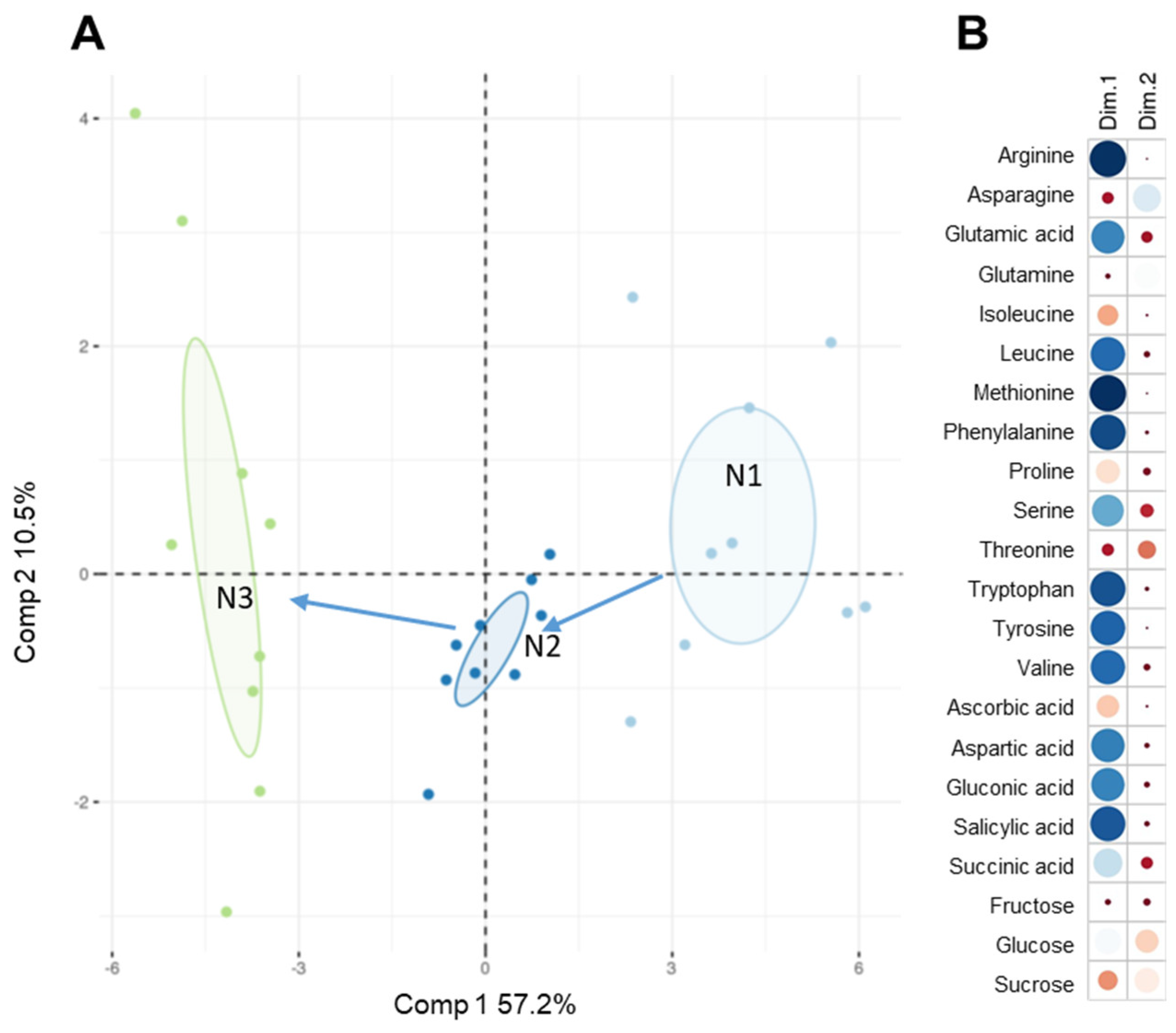
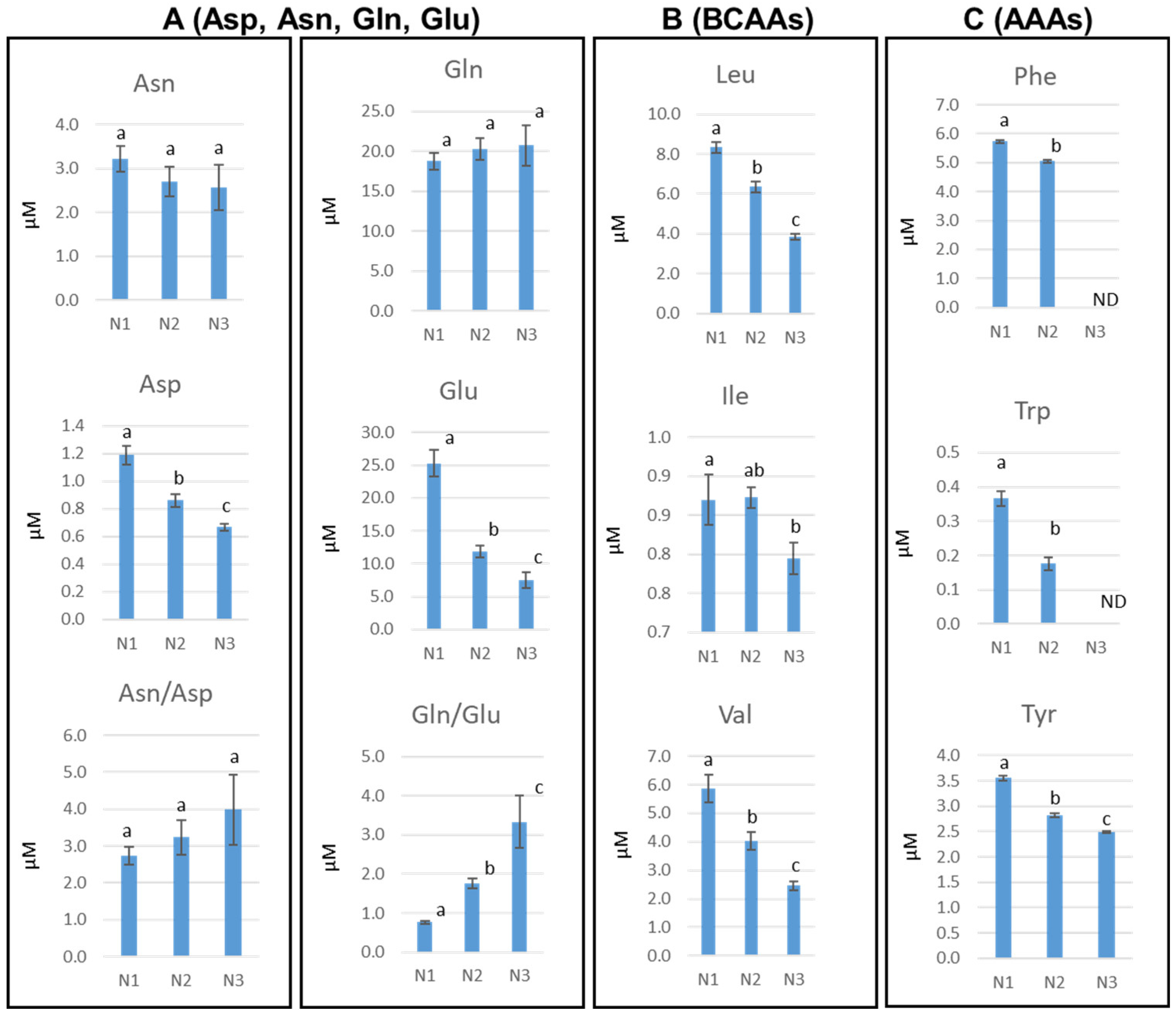
3.3. Water-Based MAE Combined with HILIC Chromatography Applied to the Analysis of the Polar Metabolome in Rosette Leaves of Arabidopsis at Distinct Developmental Stages
4. Discussion
4.1. UAE and MAE Mechanisms Comparison
4.2. Combination of Water-Based MAE with HILIC-HRMS for Efficient Characterization of Polar Metabolites in Plant Tissues
4.3. Application of the MAE /HILIC-HRMS Method to the Analysis of the Polar Metabolome of Arabidopsis Rosette Leaves
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugimoto, N.; Jones, A.J.; Beaudry, R. Changes in Free Amino Acid Content in ‘Jonagold’ Apple Fruit as Related to Branched-chain Ester Production, Ripening, and Senescence. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2011, 136, 429–440. [Google Scholar]
- Ilc, T.; Halter, D.; Miesch, L.; Lauvoisard, F.; Kriegshauser, L.; Ilg, A.; Baltenweck, R.; Hugueney, P.; Werck-Reichhart, D.; Duchene, E.; et al. A grapevine cytochrome P450 generates the precursor of wine lactone, a key odorant in wine. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yusuke, I.; Takahiro, S.; Kentaro, H.; Akihito, O.; Yuri, T.; Kyohei, N.; Rie, I.; Koichi, S.; Hiroyuki, N. Separation Technique for the Determination of Highly Polar Metabolites in Biological Samples. Metabolites 2012, 2, 496–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, A.G.; Garden, K.E.; Anderson, S.E.; Lobley, G.E. Quantitation of blood and plasma amino acids using isotope dilution electron impact gas chromatography/mass spectrometry with U- 13 C amino acids as internal standards. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 2080–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.L.; Khan, M.A.; Moskal, J.R. Neurochemical analysis of amino acids, polyamines and carboxylic acids: GC-MS quantitation of tBDMS derivatives using ammonia positive chemical ionization. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 831, 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Husek, P.; Simek, P. Alkyl chloroformates in sample derivatization strategies for GC analysis. Review on a decade use of the reagents as esterifying agents. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2006, 2, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monton, M.R.N.; Soga, T. Metabolome analysis by capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 2007, 1168, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, T.; Heiger, D.N. Amino acid analysis by capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Petritis, K.; Chaimbault, P.; Elfakir, C.; Dreux, M. Parameter optimization for the analysis of underivatized protein amino acids by liquid chromatography and ionspray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 2000, 896, 253–263. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.; Chen, W.; Luo, G.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Ling, Z.; Chen, G. Rapid determination of underivatized pyroglutamic acid, glutamic acid, glutamine and other relevant amino acids in fermentation media by LC-MS-MS. Analyst 2002, 127, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Piraud, M.; Vianey-Saban, C.; Petritis, K.; Elfakir, C.; Steghens, J.P.; Bouchu, D. Ion-pairing reversed phase liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometric analysis of 76 underivatized amino acids of biological interest: A new tool for the diagnosis of inherited disorders of amino acid metabolism. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. Int. J. Devoted Rapid Dissem. Up-Minute Res. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1587–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar, H.; Dettmer, K.; Gronwald, W.; Oefner, P.J. Automated GC-MS analysis of free amino acids in biological fluids. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 870, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimbo, K.; Oonuki, T.; Yahashi, A.; Hirayama, K.; Miyano, H. Precolumn derivatization reagents for high-speed analysis of amines and amino acids in biological fluid using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2009, 23, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl-Lassen, R.; Jan van, H.; Henning, J.; Christian, B.; Birgit, A.; Jan, K.S. High-throughput analysis of amino acids in plant materials by single quadrupole mass spectrometry. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao-Quan, T.; Li, Z.; Xiao-Xing, Y.; Choon-Nam, O. HILIC-MS for metabolomics: An attractive and complementary approach to RPLC-MS. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 574–600. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaolong, Z.; Hongyan, C.; Dawei, W.; Wei, G.; Xiao, S.; Jian, C.; Qinan, W. Determination of Free Amino Acids in Three Species of Duckweed (Lemnaceae). J. Food Qual. 2018, 2018, 7673652. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.S.; Jessica, J.; Krzysztof, B.; Patrick, G. Protocol: A fast, comprehensive and reproducible one-step extraction method for the rapid preparation of polar and semi-polar metabolites, lipids, proteins, starch and cell wall polymers from a single sample. Plant Methods 2016, 12, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Aghdase, S.; Vahid, H.; Behnam, K. Microwave assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from Food: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Eng. 2017, 7, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tiago, F.J.; Joao, A.R.; Camila, C.; Romy, S.; van Dongen, J.; Thomas-Oates, J.; Antonio, C. Mass Spectrometry-Based Plant Metabolomics: Metabolite Reponses to Abiotic Stress. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 620–649. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, T.S.; Mallikarjunan, P.; Zhou, K.; O’Keefe, S. Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic antioxidant compounds from peanut skins. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.; Yusoff, R.; Ngoh, G.; Kung, F.W. Microwave-assisted extraction of active ingredients from plants–A review. J. Chromat. A 2011, 1218, 6213–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Malah, M.H.; Mahmound, M.H.; Areif, M.H.; Al-Amrousi, E.F. Utilization of Egyptian tomato waste as a potential source of natural antioxidants using solvents, microwave and ultrasound extraction methods. Am. J. Foot Technol. 2015, 10, 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera, C.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, A.; Palma, M.; Barroso, C.G. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of amino acids from grapes. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2015, 22, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masclaux-Daubresse, C.; Reisdorf-Cren, M.; Orsel, M. Leaf nitrogen remobilization for plant development and grain filling. Plant Biol. 2008, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutterer, J.; Zinck, E. Quick-and-clean article figures with Figure. J. Microsc. 2013, 252, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Karakas, E.; Ferrante, P.; Schafleitner, R.; Giuliano, G.; Fernie, A.R.; Alseekh, S. Plant Sample Collection and Shipment for Multi-omic Analyses and Phytosanitary Evaluation. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Balazadeh, S.; Tohge, T.; Erban, A.; Giavalisco, P.; Kopka, J.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Fernie, A.R.; Hoefgen, R. Comprehensive dissection of spatiotemporal metabolic shifts in primary, secondary, and lipid metabolism during developmental senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 1290–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanojia, A.; Shrestha, D.K.; Dijkwel, P.P. Primary metabolic processes as drivers of leaf ageing. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6351–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, J.A. Physiology of Plants and Their Cells; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shrikaar, K.; Jia, L.; Bradley, S.E.; Doug, K.A. Accurate and efficient amino acid analysis for protein quantification using hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled tandem mass spectrometry. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Alireza, I.; Nazila, N.; Ali, D. Cooperative and robust object handling by multiple manipulators based on the differential equation approximator. ISA Trans. 2022, 128, 68–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt, T.M.; Nesi, A.N.; Araùjo, W.L.; Braun, H.-P. Amino acid catabolism in plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar]
- Avila-Ospina, L.; Clément, G.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Metabolite profiling for leaf senescence in Braley reveals decreases in amino acids an glycolysis intermediates. Agronomy 2017, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudrun, W.; Christopher, D.T.; Maurizio, T.; Giuseppe, F.; Dietmar, F. Physiological implications of arginine metabolism in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 534–548. [Google Scholar]
- Ravanel, S.; Block, M.A.; Rippert, P.; Jabrin, S.; Curien, G.; Rebeille, F.; Douce, R. Methionine Metabolism in Plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 21, 22548–22557. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, W.L.; Ishizaki, K.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Larson, T.R.; Tohge, T.; Krahnert, I.; Witt, S.; Obata, T.; Schauer, N.; Graham, I.A. Identification of the 2-hydroxyglutarate and isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenases as alternative electron donors linking lysine catabolism to the electron transport chain of Arabidopsis mitochondria. Plant Cell. 2010, 22, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, W.L.; Tohge, T.; Ishizaki, K.; Leaver, C.J.; Fernie, A.R. Protein degradation: An alternative respiratory substrate for stressed plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 489–498. [Google Scholar]
- Pichersky, E.; Noel, J.P.; Dudareva, N. Biosynthesis of plant volatiles: Nature’s diversity and ingenuity. Science 2006, 311, 808–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkina, L.G. Phenylpropanoids as naturally occurring antioxidants: From plant defense to human health. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 53, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart, A.A.; Joy, K.W. Use of phloem exudate technique in the study of amino acid transport in pea plants. Plant Physiol. 1981, 68, 750–754. [Google Scholar]
| Compounds | RT (min) | (m/z) | Accuracy (ppm) | Regression Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Range (µM) | R2 Value | LOQ (µM) | LOD (µM) | RSD (%) | ||||
| Arginine | 4.49 | 173.1035 | 0.238 | 2.9–338.0 | 0.9922 | 2.90 | 0.95 | 3.6 |
| Asparagine | 5.09 | 131.0454 | 0.281 | 0.1–445.6 | 0.9968 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 1.4 |
| Cysteine | 5.03 | 120.0115 | 1.286 | 0.8–486.1 | 0.9978 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 0.9 |
| Glutamine | 5.04 | 145.0608 | 0.011 | 0.7–402.9 | 0.9951 | 0.70 | 0.22 | 2.5 |
| Leucine * | 4.24 | 132.102 | 0.793 | 1.5–449.0 | 0.9972 | 1.50 | 0.70 | 3.7 |
| Lysine | 4.56 | 145.0973 | 1.418 | 2.1–402.9 | 0.9918 | 2.10 | 1.80 | 6.4 |
| Methionine | 4.48 | 148.0429 | 1.717 | 1.3–394.8 | 0.9990 | 1.30 | 0.70 | 3.6 |
| OH-proline | 5.15 | 130.0502 | 0.32 | 0.8–56.5 | 0.9976 | 0.80 | 0.25 | 3.9 |
| Phenylalanine | 4.57 | 164.0709 | 1.919 | 1.2–356.5 | 0.9928 | 1.20 | 0.40 | 2.9 |
| Proline * | 4.86 | 116.0707 | 1.162 | 4.3–511.5 | 0.9912 | 4.30 | 2.10 | 0.3 |
| Serine | 5.11 | 104.0342 | 0.13 | 0.1–70.5 | 0.9929 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 4.2 |
| Threonine * | 5.03 | 118.0498 | 0.03 | 0.8–123.5 | 0.9961 | 0.80 | 0.25 | 3.1 |
| Tryptophan * | 4.31 | 205.0972 | 0.662 | 0.5–18 | 0.9985 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 4.6 |
| Tyrosine | 4.49 | 180.0658 | 1.946 | 1.1–325.0 | 0.9980 | 1.10 | 0.50 | 5.6 |
| Valine | 4.42 | 116.0707 | 1.076 | 1.7–251.3 | 0.9970 | 1.70 | 0.80 | 5.5 |
| Glutamic acid | 5.25 | 146.0448 | 0.046 | 0.3–402.9 | 0.9934 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 4.8 |
| Gluconic acid | 5.67 | 195.0503 | 2.209 | 3.05–196 | 0.9986 | 3.05 | 0.90 | 7.0 |
| Malic acid | 5.64 | 133.0132 | 0.754 | 4.5–287.3 | 0.9893 | 4.50 | 2.40 | 8.1 |
| Salicylic acid | 3.23 | 137.0234 | 0.945 | 0.7–69.6 | 0.9954 | 0.70 | 0.04 | 9.6 |
| Succinic acid | 2 | 117.0184 | 1.067 | 2.1–162.7 | 0.9938 | 2.10 | 1.80 | 7.8 |
| Tartaric acid | 5.67 | 149.0082 | 1.045 | 4.0–512.7 | 0.9972 | 4.00 | 1.50 | 5.1 |
| Fructose | 4.53 | 179.0553 | 2.097 | 0.7–92.6 | 0.9959 | 0.70 | 0.03 | 4.3 |
| Glucose | 4.62 | 179.0553 | 1.818 | 0.7–92.6 | 0.9994 | 0.70 | 0.03 | 6.2 |
| Sucrose | 5.03 | 341.1086 | 2.44 | 0.1–97.5 | 0.9946 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 5.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Louis, A.; Chich, J.F.; Chepca, H.; Schmitz, I.; Hugueney, P.; Maia-Grondard, A. Green Extraction Method: Microwave-Assisted Water Extraction Followed by HILIC-HRMS Analysis to Quantify Hydrophilic Compounds in Plants. Metabolites 2025, 15, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040223
Louis A, Chich JF, Chepca H, Schmitz I, Hugueney P, Maia-Grondard A. Green Extraction Method: Microwave-Assisted Water Extraction Followed by HILIC-HRMS Analysis to Quantify Hydrophilic Compounds in Plants. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040223
Chicago/Turabian StyleLouis, Alexandra, Jean François Chich, Hadrien Chepca, Isabelle Schmitz, Philippe Hugueney, and Alessandra Maia-Grondard. 2025. "Green Extraction Method: Microwave-Assisted Water Extraction Followed by HILIC-HRMS Analysis to Quantify Hydrophilic Compounds in Plants" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040223
APA StyleLouis, A., Chich, J. F., Chepca, H., Schmitz, I., Hugueney, P., & Maia-Grondard, A. (2025). Green Extraction Method: Microwave-Assisted Water Extraction Followed by HILIC-HRMS Analysis to Quantify Hydrophilic Compounds in Plants. Metabolites, 15(4), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040223





