Double-Weighted Bayesian Model Combination for Metabolomics Data Description and Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Pretreatment
2.3. Ensemble Machine Learning
2.4. Hyperparameter Optimization and Feature Selection
3. Results
3.1. Study 1: NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling for Diagnostic and Prognostic Purposes in Critically Ill Children (Grauslys et al. [12])
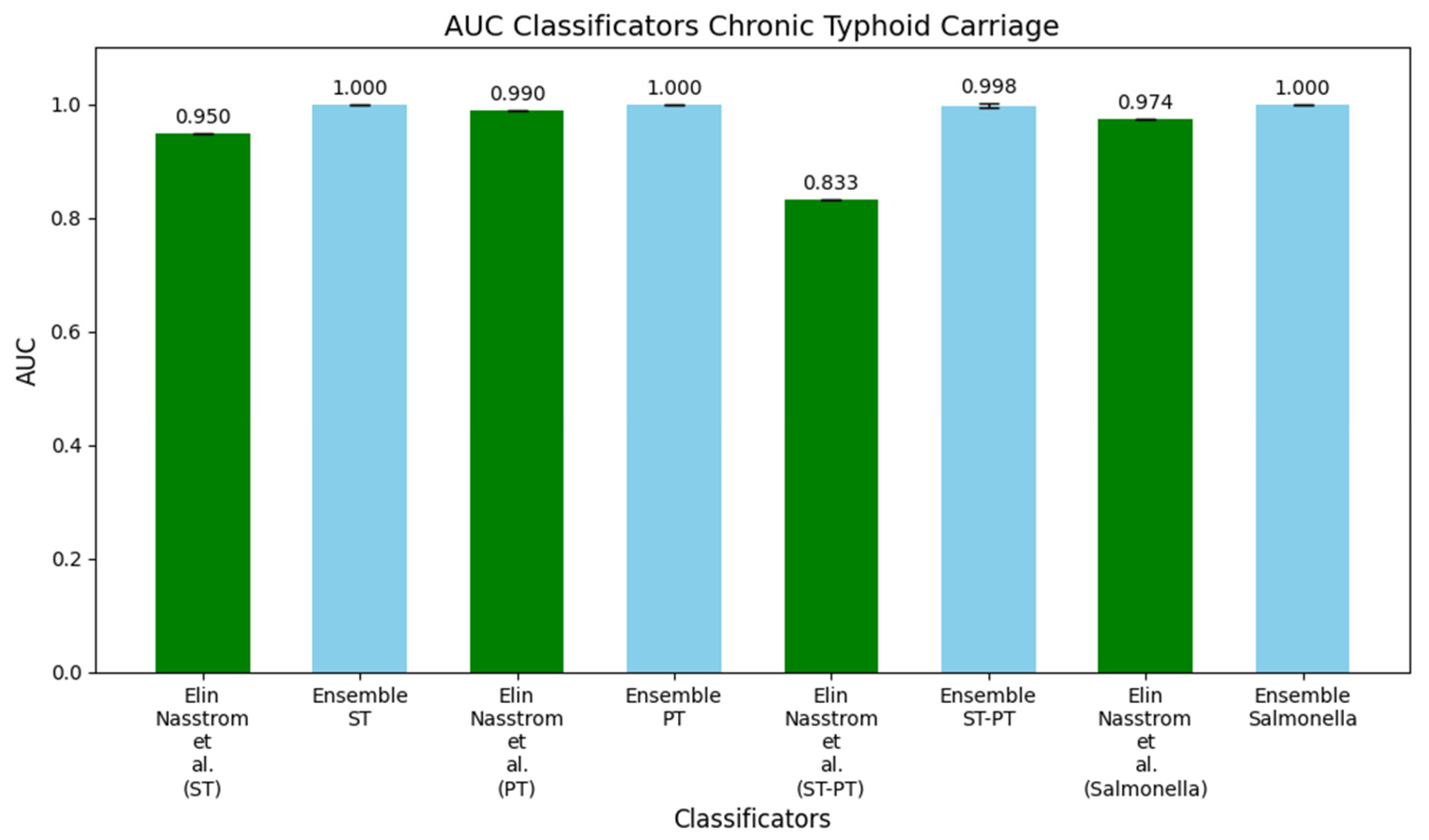
3.2. Study 2: Diagnostic Metabolite Biomarkers of Chronic Typhoid Carriage (Näsström et al. [13])
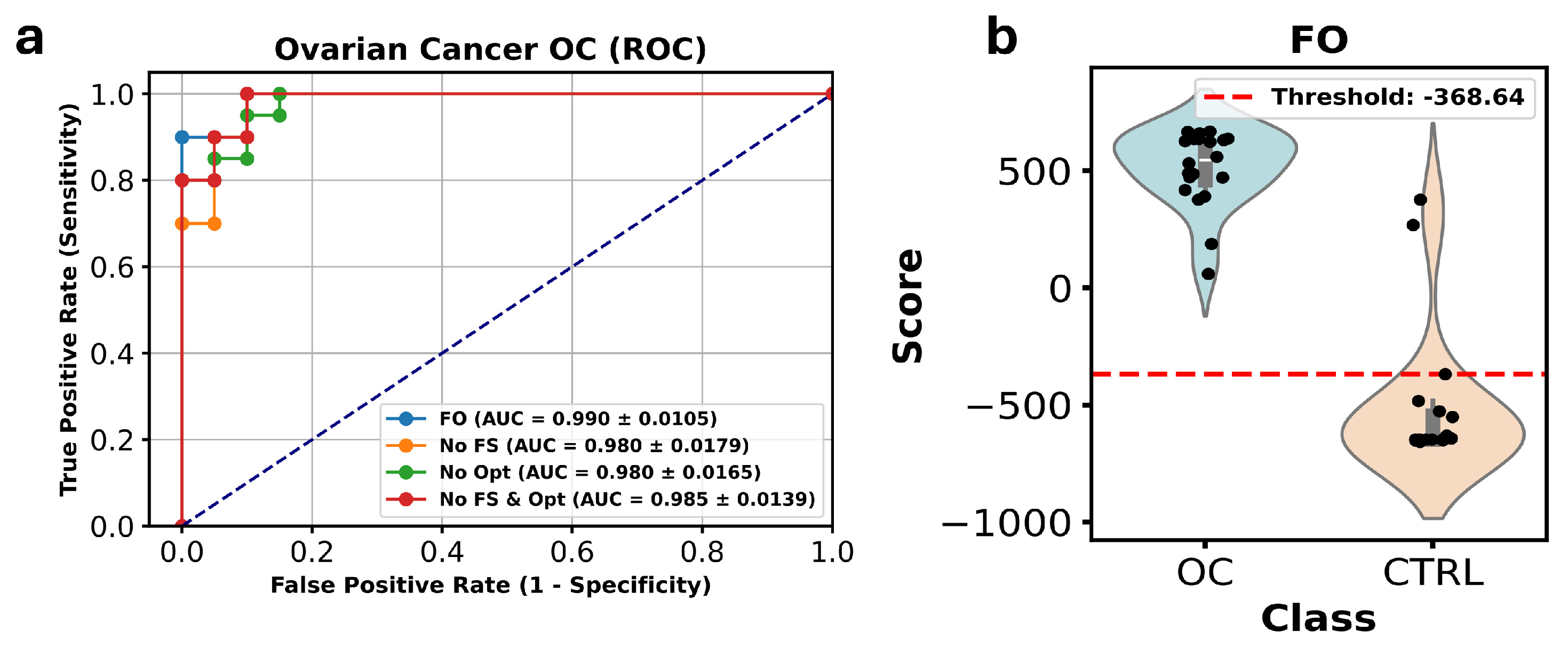
3.3. Study 3: Profiling the Metabolome of Uterine Fluid for Early Detection of Ovarian Cancer (Pan Wang et al. [14])
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruggeman, F.J.; Westerhoff, H.V. The Nature of Systems Biology. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J. Systems Biology of Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 245–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Systems Biology: A Brief Overview. Science 2002, 295, 1662–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, A.; Foroozan, E.; Tahmasebi, A.; Taghizadeh, M.S.; Bolhassani, M.; Jafari, M. System Network Analysis of Rosmarinus Officinalis Transcriptome and Metabolome—Key Genes in Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond Biomarkers and towards Mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; EBSCOhost (Eds.) Metabolomics Perspectives: From Theory to Practical Application; Academic Press: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-0-323-85062-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, M.; Lopata, A.L.; Dasouki, M.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. Metabolomics toward Personalized Medicine. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2019, 38, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Richards, S.M.; Scala, G.; Landolfi, A. Chapter 7—Approaches in Untargeted Metabolomics. In Metabolomics Perspectives; Troisi, J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 237–262. ISBN 978-0-323-85062-9. [Google Scholar]
- Szymańska, E.; Saccenti, E.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A. Double-Check: Validation of Diagnostic Statistics for PLS-DA Models in Metabolomics Studies. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromski, P.S.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Turner, M.L.; Goodacre, R. A Tutorial Review: Metabolomics and Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis—A Marriage of Convenience or a Shotgun Wedding. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habehh, H.; Gohel, S. Machine Learning in Healthcare. Curr. Genom. 2021, 22, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauslys, A.; Phelan, M.M.; Broughton, C.; Baines, P.B.; Jennings, R.; Siner, S.; Paulus, S.C.; Carrol, E.D. NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling Provides Diagnostic and Prognostic Information in Critically Ill Children with Suspected Infection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näsström, E.; Jonsson, P.; Johansson, A.; Dongol, S.; Karkey, A.; Basnyat, B.; Tran Vu Thieu, N.; Trinh Van, T.; Thwaites, G.E.; Antti, H.; et al. Diagnostic Metabolite Biomarkers of Chronic Typhoid Carriage. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Ma, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gu, X.; Wu, Y.; Dong, S.; Guo, H.; et al. Profiling the Metabolome of Uterine Fluid for Early Detection of Ovarian Cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Li, W.; Tang, Z. ASN-SMOTE: A Synthetic Minority Oversampling Method with Adaptive Qualified Synthesizer Selection. Complex. Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 2247–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluss, R.; Faraggi, D.; Reiser, B. Estimation of the Youden Index and Its Associated Cutoff Point. Biom. J. J. Math. Methods Biosci. 2005, 47, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.D.; Wittmann, B.M.; Evans, A.M.; Miller, L.A.D.; Toal, D.R.; Lonergan, S.; Elsea, S.H.; Pappan, K.L. Metabolomics in the Clinic: A Review of the Shared and Unique Features of Untargeted Metabolomics for Clinical Research and Clinical Testing. J. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 53, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Singla, J.; Nkenyereye, L.; Jha, S.; Prashar, D.; Joshi, G.P.; El-Sappagh, S.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, S.M.R. Medical Diagnostic Systems Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) Algorithms: Principles and Perspectives. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 228049–228069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, L.; Ding, L.; Jenik, B.; Reimer, B. Arguing Machines: Human Supervision of Black Box AI Systems That Make Life-Critical Decisions. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1335–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Asakura, T.; Date, Y.; Kikuchi, J. Application of Ensemble Deep Neural Network to Metabolomics Studies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1037, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edeh, M.O.; Dalal, S.; Dhaou, I.B.; Agubosim, C.C.; Umoke, C.C.; Richard-Nnabu, N.E.; Dahiya, N. Artificial Intelligence-Based Ensemble Learning Model for Prediction of Hepatitis C Disease. Front. Public. Health 2022, 10, 892371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, P.; Uddin, S.; Hajati, F.; Moni, M.A. Ensemble Learning for Disease Prediction: A Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ShahrjooiHaghighi, A.; Frigui, H.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Shi, B.; McClain, C.J. Ensemble Feature Selection for Biomarker Discovery in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. In Proceedings of the 34th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium on Applied Computing, Limassol, Cyprus, 8–12 April 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Shahrjooihaghighi, A.; Frigui, H.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Shi, B.; Trabelsi, A. An Ensemble Feature Selection Method for Biomarker Discovery. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Bilbao, Spain, 18–20 December 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Huang, J.; Foppiano, F.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; Suhre, K.; Li, Y.; Matullo, G.; Schliess, F.; Gieger, C.; et al. TIGER: Technical Variation Elimination for Metabolomics Data Using Ensemble Learning Architecture. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, M.; Hanser, F.; Breit, M.; Weinberger, K.M.; Baumgartner, C.; Baumgarten, D. Ensemble Based Approach for Time Series Classification in Metabolomics. Stud. Health Technol. Inf. 2019, 260, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Geddes, T.A.; Yang, J.Y.H.; Yang, P. Ensemble Deep Learning in Bioinformatics. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yee, H.Y.; Zhou, B.; Zomaya, A.Y. A Review of Ensemble Methods in Bioinformatics. Curr. Bioinform. 2010, 5, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Colucci, A.; Cavallo, P.; Richards, S.; Symes, S.; Landolfi, A.; Scala, G.; Maiorino, F.; Califano, A.; Fabiano, M.; et al. A Serum Metabolomic Signature for the Detection and Grading of Bladder Cancer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Tafuro, M.; Lombardi, M.; Scala, G.; Richards, S.M.; Symes, S.J.K.; Ascierto, P.A.; Delrio, P.; Tatangelo, F.; Buonerba, C.; et al. A Metabolomics-Based Screening Proposal for Colorectal Cancer. Metabolites 2022, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Raffone, A.; Travaglino, A.; Belli, G.; Belli, C.; Anand, S.; Giugliano, L.; Cavallo, P.; Scala, G.; Symes, S.; et al. Development and Validation of a Serum Metabolomic Signature for Endometrial Cancer Screening in Postmenopausal Women. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2018327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Sarno, L.; Landolfi, A.; Scala, G.; Martinelli, P.; Venturella, R.; Di Cello, A.; Zullo, F.; Guida, M. Metabolomic Signature of Endometrial Cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Mollo, A.; Lombardi, M.; Scala, G.; Richards, S.M.; Symes, S.J.K.; Travaglino, A.; Neola, D.; de Laurentiis, U.; Insabato, L.; et al. The Metabolomic Approach for the Screening of Endometrial Cancer: Validation from a Large Cohort of Women Scheduled for Gynecological Surgery. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Cavallo, P.; Richards, S.; Symes, S.; Colucci, A.; Sarno, L.; Landolfi, A.; Scala, G.; Adair, D.; Ciccone, C. Noninvasive Screening for Congenital Heart Defects Using a Serum Metabolomics Approach. Prenat. Diagn. 2021, 41, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Landolfi, A.; Sarno, L.; Richards, S.; Symes, S.; Adair, D.; Ciccone, C.; Scala, G.; Martinelli, P.; Guida, M. A Metabolomics-Based Approach for Non-Invasive Screening of Fetal Central Nervous System Anomalies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Sarno, L.; Martinelli, P.; Di Carlo, C.; Landolfi, A.; Scala, G.; Rinaldi, M.; D’Alessandro, P.; Ciccone, C.; Guida, M. A Metabolomics-Based Approach for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Chromosomal Anomalies. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Lombardi, M.; Scala, G.; Cavallo, P.; Tayler, R.S.; Symes, S.J.K.; Richards, S.M.; Adair, D.C.; Fasano, A.; McCowan, L.M.; et al. A Screening Test Proposal for Congenital Defects Based on Maternal Serum Metabolomics Profile. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 228, 342.e1–342.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Configuration | Ensemble | NB | GLM | LR | FLM | DL | DT | RF | GBT | SVM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy CB Model | FO | 92.9% | - | 96.7% | - | 73.3% | 83.3% | 70.0% | 60.0% | 86.7% | - |
| No FS | 90.5% | - | 93.3% | 60.0% | 80.0% | 80.0% | - | 63.3% | 60.0% | 80.0% | |
| No Opt | 88.1% | - | 83.3% | - | 73.3% | 83.3% | - | - | 76.7% | 73.3% | |
| No FS and Opt | 95.2% | - | 93.3% | 60.0% | 70.0% | 80.0% | 63.3% | 90.0% | 73.3% | 90.0% | |
| Accuracy CV Model | FO | 88.1% | 73.3% | 86.7% | - | 86.7% | 76.7% | 70.0% | 63.3% | 60.0% | 73.3% |
| No FS | 81% | 70% | 73.3% | - | 73.3% | 86.7% | 70.0% | 73.3% | 63.3% | 73.3% | |
| No Opt | 85.7% | 73.3% | 73.3% | - | 66.7% | 76.7% | 73.3% | 80.0% | 70.0% | - | |
| No FS and Opt | 83.3% | 70% | 73.3% | - | 76.7% | 86.7% | 73.3% | 70.0% | 63.3% | 80.0% | |
| Accuracy CB-CV Model | FO | 92.5% | 86.7% | 78.7% | - | 96.7% | 79.3% | 72.7% | 72.7% | 78.7% | 86.0% |
| No FS | 90% | 68% | 93.3% | - | 90.0% | 90.0% | 83.3% | 68.7% | 78.7% | 82.7% | |
| No Opt | 90% | 86.7% | 86.7% | - | 90.0% | 83.3% | - | - | 79.3% | 79.3% | |
| No FS and Opt | 92.5% | 68% | 93.3% | - | 86.7% | 90.0% | 76.7% | 75.3% | 78.7% | 93.3% |
| Configuration | Ensemble | NB | GLM | LR | FLM | DL | DT | RF | GBT | SVM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy ST Model | FO | 100.0% | 90.0% | 96.7% | - | 93.3% | 89.3% | 90.0% | 100.0% | 93.3% | 100.0% |
| No FS | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 96.7% | 100.0% | 96.7% | 93.3% | 96.7% | 90.0% | 100.0% | |
| No Opt | 97.5% | 90.0% | 96.7% | 89.3% | - | 100.0% | 93.3% | 93.3% | 90.0% | - | |
| No FS and Opt | 97.6% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 96.7% | 90.0% | 96.7% | 93.3% | 93.3% | 90.0% | - | |
| Accuracy PT Model | FO | 92.9% | - | 96.7% | - | 73.3% | 83.3% | 70.0% | 60.0% | 86.7% | - |
| No FS | 90.5% | - | 93.3% | 60.0% | 80.0% | 80.0% | - | 63.3% | 60.0% | 80.0% | |
| No Opt | 88.1% | - | 83.3% | - | 73.3% | 83.3% | - | - | 76.7% | 73.3% | |
| No FS and Opt | 95.2% | - | 93.3% | 60.0% | 70.0% | 80.0% | 63.3% | 90.0% | 73.3% | 90.0% | |
| Accuracy ST-PT Model | FO | 88.1% | 73.3% | 86.7% | - | 86.7% | 76.7% | 70.0% | 63.3% | 60.0% | 73.3% |
| No FS | 81% | 70% | 73.3% | - | 73.3% | 86.7% | 70.0% | 73.3% | 63.3% | 73.3% | |
| No Opt | 85.7% | 73.3% | 73.3% | - | 66.7% | 76.7% | 73.3% | 80.0% | 70.0% | - | |
| No FS and Opt | 83.3% | 70% | 73.3% | - | 76.7% | 86.7% | 73.3% | 70.0% | 63.3% | 80.0% | |
| Accuracy Salmonella Model | FO | 92.5% | 86.7% | 78.7% | - | 96.7% | 79.3% | 72.7% | 72.7% | 78.7% | 86.0% |
| No FS | 90% | 68% | 93.3% | - | 90.0% | 90.0% | 83.3% | 68.7% | 78.7% | 82.7% | |
| No Opt | 90% | 86.7% | 86.7% | - | 90.0% | 83.3% | - | - | 79.3% | 79.3% | |
| No FS and Opt | 92.5% | 68% | 93.3% | - | 86.7% | 90.0% | 76.7% | 75.3% | 78.7% | 93.3% |
| Configuration | Ensemble | NB | GLM | LR | FLM | DL | DT | RF | GBT | SVM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy OC Model | FO | 95.0% | 93.3% | 96.0% | - | 90.0% | 88.7% | 72.7% | 96.7% | 96.7% | 96.7% |
| No FS | 95.0% | 75.3% | 93.3% | 90.0% | 89.3% | 96.7% | 81.3% | 90.0% | 85.3% | 96.7% | |
| No Opt | 92.5% | 75.3% | 96.0% | - | 86.0% | 92.7% | 88.7% | 86.0% | 68.7% | 92.7% | |
| No FS & Opt | 95.0% | 75.3% | 93.3% | 90.0% | 89.3% | 96.7% | 84.7% | 96.7% | 72.0% | 96.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Troisi, J.; Lombardi, M.; Trotta, A.; Abenante, V.; Ingenito, A.; Palmieri, N.; Richards, S.M.; Symes, S.J.K.; Cavallo, P. Double-Weighted Bayesian Model Combination for Metabolomics Data Description and Prediction. Metabolites 2025, 15, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040214
Troisi J, Lombardi M, Trotta A, Abenante V, Ingenito A, Palmieri N, Richards SM, Symes SJK, Cavallo P. Double-Weighted Bayesian Model Combination for Metabolomics Data Description and Prediction. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040214
Chicago/Turabian StyleTroisi, Jacopo, Martina Lombardi, Alessio Trotta, Vera Abenante, Andrea Ingenito, Nicole Palmieri, Sean M. Richards, Steven J. K. Symes, and Pierpaolo Cavallo. 2025. "Double-Weighted Bayesian Model Combination for Metabolomics Data Description and Prediction" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040214
APA StyleTroisi, J., Lombardi, M., Trotta, A., Abenante, V., Ingenito, A., Palmieri, N., Richards, S. M., Symes, S. J. K., & Cavallo, P. (2025). Double-Weighted Bayesian Model Combination for Metabolomics Data Description and Prediction. Metabolites, 15(4), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040214









