Integrating Radiology and Metabolic Risk: DEXA-Based Characterization of Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Assessments
2.3. Bone Mineral Density Measurement Protocol
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Classification of Bone Status
3.2. Descriptive and Correlation Analyses
3.3. Multivariable Regression Analyses
3.4. Summary of Key Determinants
4. Discussion
4.1. BMI and Skeletal Protection in T2DM
4.2. Glycemic Control and the Diabetic Bone Paradox
5. Limitations
6. Clinical Implications and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bentz, J.A.; Hancock-Howard, R.; Press, Z.; Brundisini, F.; Berglas, S. Living with Type 2 Diabetes: CADTH Health Technology Review. 2023. Available online: https://europepmc.org/books/nbk596303 (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Mangoulia, P.; Milionis, C.; Vlachou, E.; Ilias, I. The interrelationship between diabetes mellitus and emotional well-being: Current concepts and future prospects. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.R. Financial Toxicity in Diabetes: The State of What We Know. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2025, 25, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IDF-Annual-Report-2023.pdf. Available online: https://idf.org/media/uploads/2024/06/IDF-Annual-Report-2023.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- El-Kebbi, I.M.; Bidikian, N.H.; Hneiny, L.; Nasrallah, M.P. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in the Middle East and North Africa: Challenges and call for action. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1401–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohieldein, A.; Baig, H.A.; Elhabiby, M.; Almushawwah, A.; Mahfouz, M.S.; Khirelsied, A.H.; Abdelmarouf, N.; Modawe, G. Prediabetes in adult Saudis: A systematic review & meta-analysis of prevalence studies (2000–2024). PeerJ. 2025, 13, e19778. [Google Scholar]
- Aldukhayel, A. Prevalence and patterns of bone mineral density disorders among women in Buraidah, KSA. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2023, 18, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry: Beyond Bone Mineral Density Determination. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugh, M.; Langaker, M.D. Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. 2018. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk519042 (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Lewiecki, E.M.; Binkley, N.; Morgan, S.L.; Shuhart, C.R.; Camargos, B.M.; Carey, J.J.; Gordon, C.M.; Jankowski, L.G.; Lee, J.-K.; Leslie, W.D.; et al. Best practices for dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry measurement and reporting: International Society for Clinical Densitometry Guidance. J. Clin. Densitom. 2016, 19, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slart, R.H.J.A.; Punda, M.; Ali, D.S.; Bazzocchi, A.; Bock, O.; Camacho, P.; Carey, J.J.; Colquhoun, A.; Compston, J.; Engelke, K.; et al. Updated practice guideline for dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025, 52, 539–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Guideline for Non-Surgical Management of Chronic Primary Low Back Pain in Adults in Primary and Community Care Settings. 2023. Available online: https://books.google.com/books?hl=ar&lr=&id=EngOEQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR7&dq=World+Health+Organization.+(2023).+Scientific+group+on+the+assessment+of+osteoporosis+at+the+primary+health+care+level&ots=9bzSqlvP2u&sig=0lsSAXyn5XKvRX11p4kdQMZE29U (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Chen, W.; Mao, M.; Fang, J.; Xie, Y.; Rui, Y. Fracture risk assessment in diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 961761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, S.B.; Cenarruzabeitia, N.V.; San Martin, J.E.; Canelas, A.C. The diabetic paradox: Bone mineral density and fracture in type 2 diabetes. Endocrinol. Nutr. Engl. Ed. 2016, 63, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cui, W. Decoding the diabetic bone paradox: How AGEs sabotage skeletal integrity. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeriau, F.; Amsellem-Jager, J.; Bouhours-Nouet, N.; Donzeau, A.; Rouleau, S.; Rerat, S.; Labarre, E.; Levaillant, L.; Coutant, R. Insufficient bone mineralization to sustain mechanical load of weight in obese boys: A Cross-Sectional study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniec, U.T.; Turner, R.T. Influence of body weight on bone mass, architecture and turnover. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, R115–R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, P.; Sheu, A. Bone health in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Endocr. Soc. 2024, 8, bvae112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.R.; Long, F.; Zemel, B.S.; Kindler, J.M. Glycemic Control and Bone in Diabetes. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2022, 20, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.A.; Schousboe, J.T.; Broy, S.B.; Engelke, K.; Leslie, W.D. Executive summary of the 2015 ISCD position development conference on advanced measures from DXA and QCT: Fracture prediction beyond BMD. J. Clin. Densitom. 2015, 18, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes: Standards of care in diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47 (Suppl. S1), S20–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzucchi, S.E. Diagnosis of Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarnath, S.S.; Kumar, V.; Das, S.L. Classification of Osteoporosis. Indian J. Orthop. 2023, 57 (Suppl. S1), 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, M.L.; Overman, R.A.; Fine, J.P.; Crandall, C.J.; Robbins, J.; Schousboe, J.T.; Ensrud, K.E.; LeBlanc, E.S.; Gass, M.L.; Johnson, K.C.; et al. Time to clinically relevant fracture risk scores in postmenopausal women. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 862.e15–862.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Assessment of Fracture Risk and Its Application to Screening for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: Report of a WHO Study Group [Meeting Held in Rome from 22 to 25 June 1992]. 1994. Available online: https://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/pt/who-39142 (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Alkhunizan, M.; Almasoud, N.; Abdulmowla, M.M.; Khalid, Z. The prevalence of osteoporosis and osteopenia among older adults in a community-based setting in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2022, 14, e32765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Armamento-Villareal, R. Obesity and skeletal fragility. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, e466–e477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassio, A.; Idolazzi, L.; Rossini, M.; Gatti, D.; Adami, G.; Giollo, A.; Viapiana, O. The obesity paradox and osteoporosis. Eat. Weight. Disord. 2018, 23, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, A.F.; O’Connor, S.; Morin, S.N.; Gibbs, J.C.; Willie, B.M.; Jean, S.; Gagnon, C. Association between obesity and risk of fracture, bone mineral density and bone quality in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, A.; Tuccinardi, D.; Defeudis, G.; Watanabe, M.; D’Onofrio, L.; Lauria Pantano, A.; Napoli, N.; Pozzilli, P.; Manfrini, S. BMI and BMD: The potential interplay between obesity and bone fragility. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.F.; Zhao, P.P.; Xiao, W.J.; Karasik, D.; Xu, Y.J.; Zheng, H.F. The paradox of bone mineral density and fracture risk in type 2 diabetes. Endocrine 2024, 85, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Díaz, C.; Duarte-Montero, D.; Gutiérrez-Romero, S.A.; Mendivil, C.O. Diabetes and Bone Fragility. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhao, C.; Han, T.; Shan, H.; Cui, G.; Li, S.; Xie, Z.; Wang, J. Advanced Glycation End Products, Bone Health, and Diabetes Mellitus. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2022, 130, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Vashishth, D. Advanced glycation and glycoxidation end products in bone. Bone 2023, 176, 116880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sugimoto, T. Advanced Glycation End Products, Diabetes, and Bone Strength. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2016, 14, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShomar, A.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Ahmad, Q.S.; Alharbi, M.S.; Alkhiari, R.; Hamad, E.M.; Rasheed, Z. Assessment of osteoporosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A study from the central region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2023, 44, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, A.; Knapstein, P.R.; Jiang, S.; Baranowsky, A.; Ballhause, T.M.; Frosch, K.H.; Keller, J. Glucose metabolism in osteoblasts in healthy and pathophysiological conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Xiao, E.; Graves, D.T. Diabetes and Its Effect on Bone and Fracture Healing. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2015, 13, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samakkarnthai, P.; Sribenjalak, D.; Wattanachanya, L.; Pongchaiyakul, C. Prevalence of vertebral fractures and associated factors in thai diabetic postmenopausal women. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbhogue, V.V.; Mitchell, D.M.; Rosen, C.J.; Bouxsein, M.L. Type 2 diabetes and the skeleton: New insights into sweet bones. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Liefde, I.I.; Van Der Klift, M.; De Laet, C.E.D.H.; Van Daele, P.L.A.; Hofman, A.; Pols, H.A.P. Bone mineral density and fracture risk in type-2 diabetes mellitus: The Rotterdam Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2005, 16, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleh, Y.; Sulimani, R.; Sabico, S.; Alshahrani, F.M.; Fouda, M.A.; Almohaya, M.; Alaidarous, S.B.; Alkhawashki, H.M.; Alshaker, M.; Alrayes, H.; et al. Diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Saudi Arabia: 2023 key updates from the Saudi Osteoporosis Society. Arch. Osteoporos. 2023, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, L.F.; Benajiba, N.; Jambi, L.K.; Alshedi, A.F. Lifestyle Factors Related to Femoral and Spinal Bone Density in Young Saudi Adult Women. J. Women’s Health Dev. 2024, 7, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A. Bone mineral density among postmenopausal Saudi women in Riyadh city—A primary care level cross-sectional survey. J. Musculoskelet. Surg. Res. 2019, 3, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Total (n = 89) | Females (n = 73) | Males (n = 16) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.1 ± 12.1 | 60.6 ± 11.5 | 63.3 ± 15.1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.1 ± 6.7 | 32.7 ± 6.9 | 29.5 ± 5.2 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.6 ± 1.8 | 6.6 ± 1.9 | 6.6 ± 1.4 |
| T-score lumbar spine | −1.76 ± 1.51 | −1.81 ± 1.51 | −1.55 ± 1.51 |
| T-score femoral neck | −1.08 ± 1.30 | −1.15 ± 1.34 | −0.76 ± 1.10 |
| T-score total hip | −0.53 ± 1.25 | −0.62 ± 1.31 | −0.12 ± 0.86 |
| Variable | n | Normal BMD n (%) | Osteopenia n (%) | Osteoporosis n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 89 | 29 (32.6%) | 39 (43.8%) | 21 (23.6%) |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 73 | 20 (27.4%) | 33 (45.2%) | 20 (27.4%) |
| Male | 16 | 9 (56.3%) | 6 (37.4%) | 1 (6.3%) |
| Age group | ||||
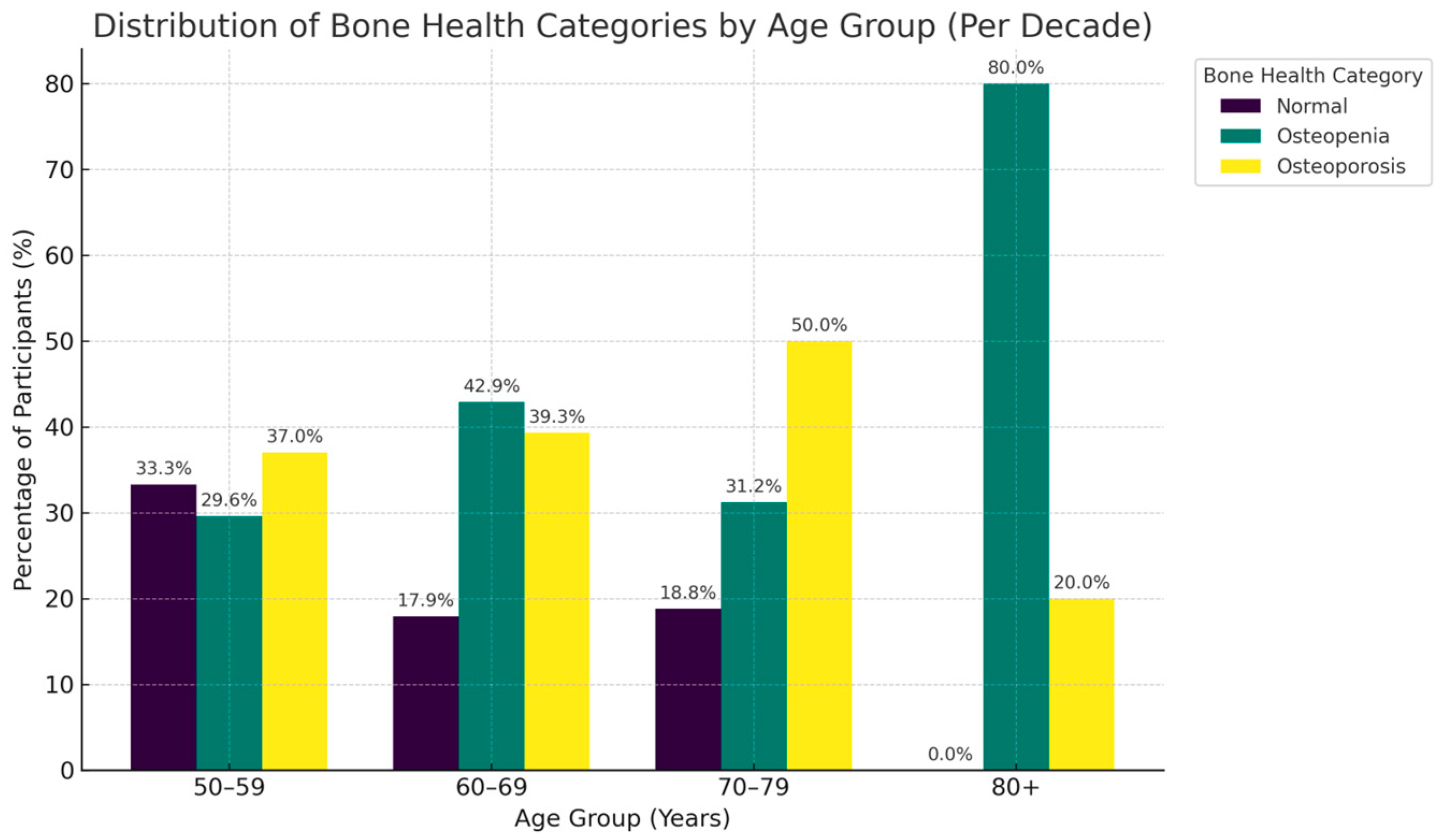
| 40–49 years | 10 | 1 (10.0%) | 8 (80.0%) | 1 (10.0%) |
| 50–59 years | 27 | 9 (33.3%) | 8 (29.6%) | 10 (37.0%) |
| 60–69 years | 28 | 5 (17.9%) | 12 (42.9%) | 11 (39.3%) |
| 70–79 years | 16 | 3 (18.8%) | 5 (31.2%) | 8 (50.0%) |
| 80+ | 5 | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (80.0%) | 1 (20.0%) |
| BMI category | ||||
| <25 kg/m2 | 12 | 2 (16.7%) | 5 (41.7%) | 5 (41.7%) |
| 25–29.9 kg/m2 | 28 | 6 (21.4%) | 15 (53.6%) | 7 (25.0%) |
| ≥30 kg/m2 | 49 | 21 (42.9%) | 19 (38.8%) | 9 (18.4%) |
| HbA1c category | ||||
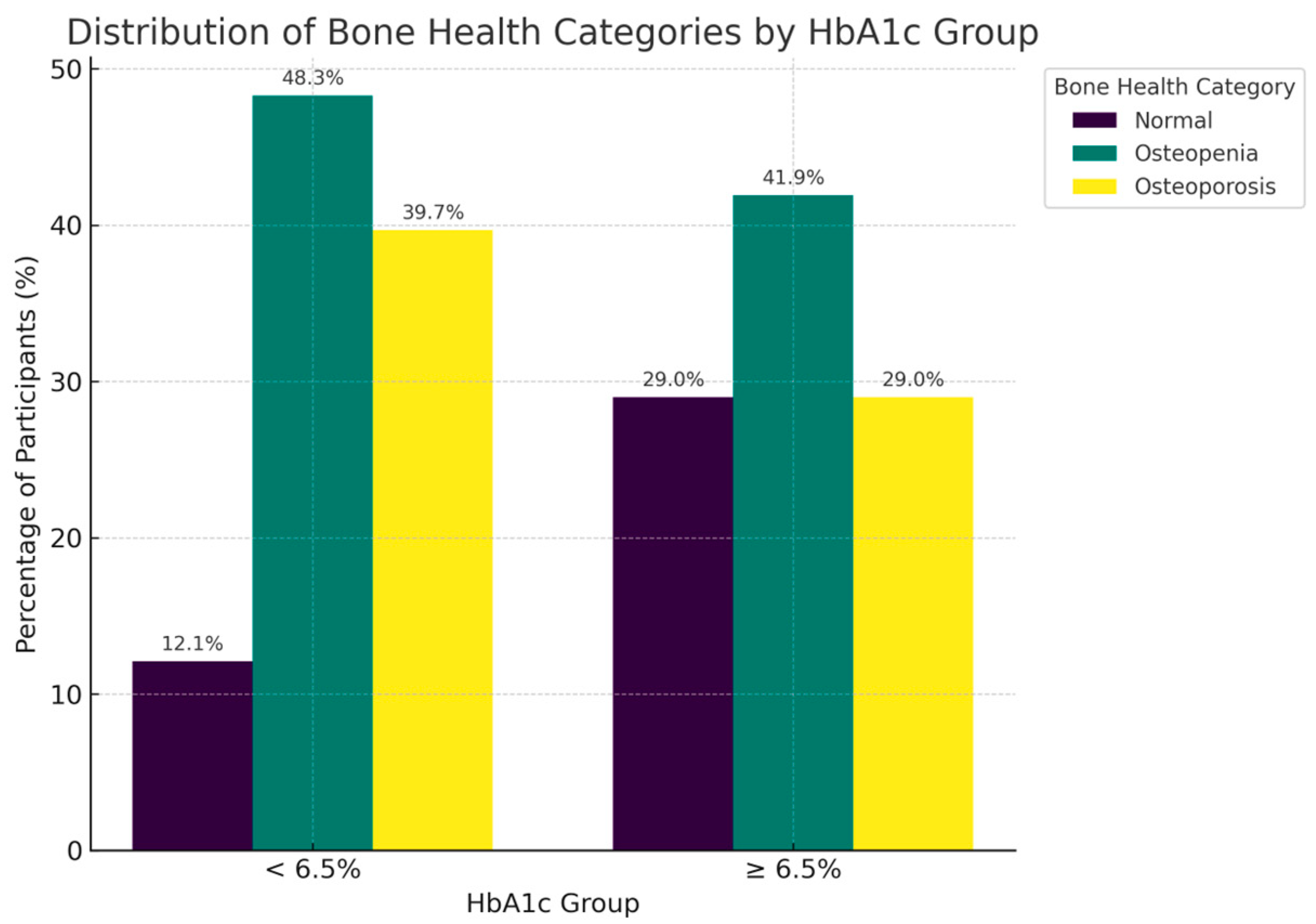
| <6.5% | 58 | 7 (12.1%) | 28 (48.3%) | 23 (39.7%) |
| ≥6.5% | 31 | 9 (29.0%) | 13 (41.9%) | 9 (29.0%) |
| Variable | Age | BMI | HbA1c | T-Score (L-Spine) | T-Score (Femoral Neck) | T-Score (Total Hip) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.01 | −0.21 | −0.16 |
| BMI | 1 | 0.18 | 0.27 * | 0.32 ** | 0.26 * | |
| HbA1c | 1 | 0.16 | 0.28 ** | 0.37 *** | ||
| T-score (Spine) | 1 | 0.65 *** | 0.53 *** | |||
| T-score (Neck) | 1 | 0.77 *** | ||||
| T-score (Hip) | 1 |
| Outcome | Predictor | β (95% CI) | p-Value | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lumbar spine | Female (1) | −0.46 (−1.28, 0.36) | 0.27 | 0.10 (0.06) |
| Age (per year) | −0.004 (−0.03, 0.02) | 0.76 | ||
| BMI (per kg/m2) | 0.061 (0.013, 0.109) | 0.013 | ||
| HbA1c (per %) | 0.096 (−0.078, 0.270) | 0.28 | ||
| Femoral neck | Female (1) | −0.66 (−1.31, −0.01) | 0.045 | 0.26 (0.22) |
| Age | −0.030 (−0.050, −0.009) | 0.0048 | ||
| BMI | 0.061 (0.024, 0.099) | 0.0017 | ||
| HbA1c | 0.189 (0.052, 0.326) | 0.0075 | ||
| Total hip | Female (1) | −0.71 (−1.32, −0.10) | 0.023 | 0.28 (0.24) |
| Age | −0.025 (−0.045, −0.006) | 0.010 | ||
| BMI | 0.045 (0.010, 0.081) | 0.013 | ||
| HbA1c | 0.250 (0.120, 0.380) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alghamdi, A.H.; Alanazi, M.A.; Bukhari, S.; Alsumaira, R.A.; Alenzi, R.H.; Aljuhani, A.S.; Alharbi, S.S.; Alsheikh, M.A. Integrating Radiology and Metabolic Risk: DEXA-Based Characterization of Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites 2025, 15, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15120766
Alghamdi AH, Alanazi MA, Bukhari S, Alsumaira RA, Alenzi RH, Aljuhani AS, Alharbi SS, Alsheikh MA. Integrating Radiology and Metabolic Risk: DEXA-Based Characterization of Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites. 2025; 15(12):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15120766
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlghamdi, Ali H., Mansuor A. Alanazi, Salwa Bukhari, Reham A. Alsumaira, Razan H. Alenzi, Abeer S. Aljuhani, Saud S. Alharbi, and Mohammed A. Alsheikh. 2025. "Integrating Radiology and Metabolic Risk: DEXA-Based Characterization of Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes" Metabolites 15, no. 12: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15120766
APA StyleAlghamdi, A. H., Alanazi, M. A., Bukhari, S., Alsumaira, R. A., Alenzi, R. H., Aljuhani, A. S., Alharbi, S. S., & Alsheikh, M. A. (2025). Integrating Radiology and Metabolic Risk: DEXA-Based Characterization of Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites, 15(12), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15120766






