Oxidative Stress and Cirrhosis Severity: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Predictive and Interactive Effects with Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Data
2.3. Definitions of Variables and Indices
- NLR = neutrophil count/lymphocyte count.
- PLR = platelet count/lymphocyte count.
- MLR = monocyte count/lymphocyte count.
- SII = (platelet count × neutrophil count)/lymphocyte count.
- SIRI = (neutrophil count × monocyte count)/lymphocyte count.
- Oxidative stress markers included:
- Malondialdehyde (MDA), measured as a byproduct of lipid peroxidation and expressed in ng/mL.
- 8-epi-prostaglandin F2α (8-epi-PGF2α), a stable F2-isoprostane reflecting oxidative stress–induced lipid peroxidation, expressed in pg/mL.
2.4. Measurement of Oxidative Stress Markers
2.4.1. Assays and Specificity
- MDA (Catalog No: E-EL-0060; sensitivity: 18.75 ng/mL; detection range: 31.25–2000 ng/mL);
- 8-epi-PGF2α (Catalog No: E-EL-0041; sensitivity: 9.38 pg/mL; detection range: 15.63–1000 pg/mL).
2.4.2. Pre-Analytical Handling
2.4.3. Analytical Limitations and Quality Controls
2.4.4. Test Principle
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Predictive Performance of Individual Markers
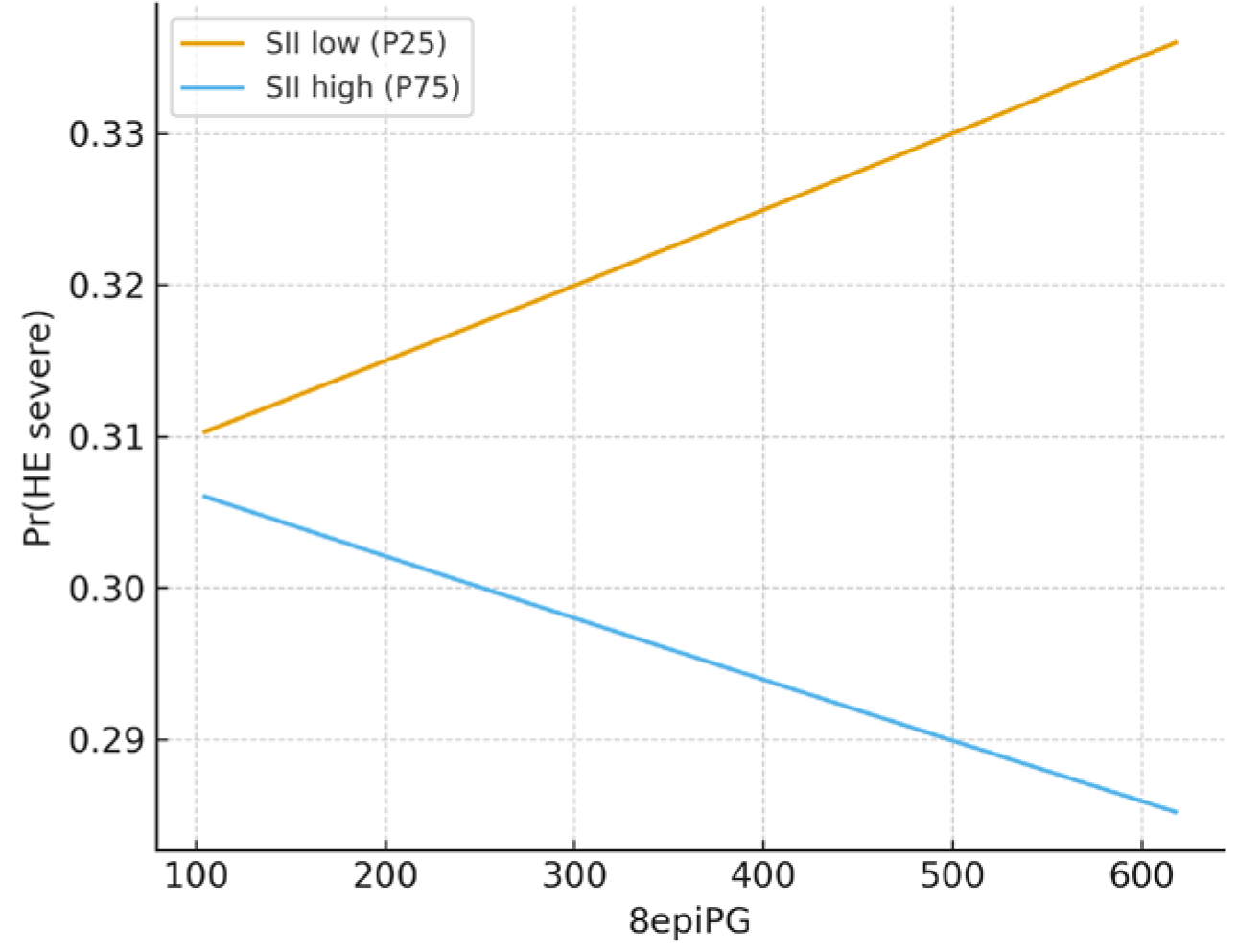
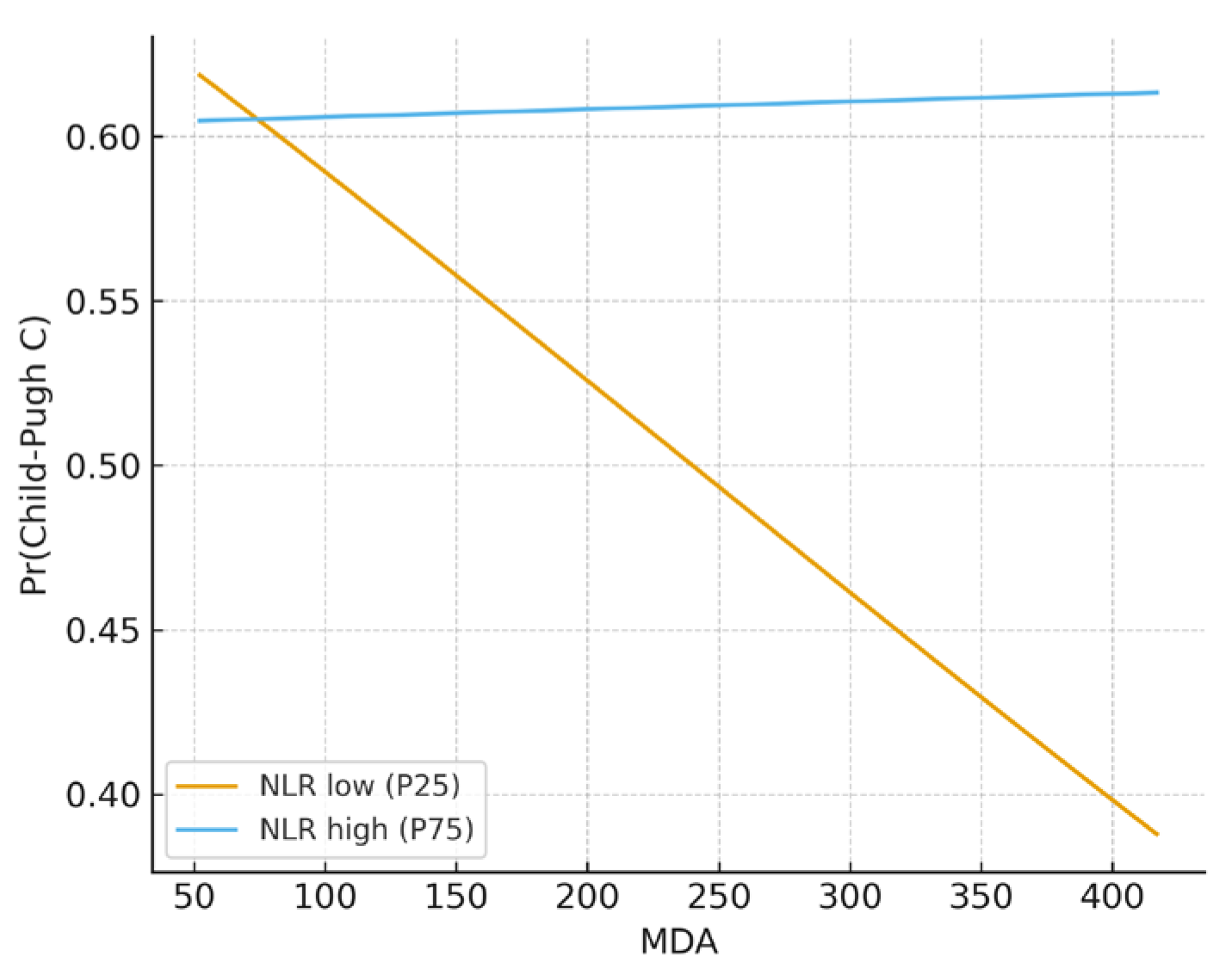
3.3. Regression, Interaction, and Exploratory Analyses
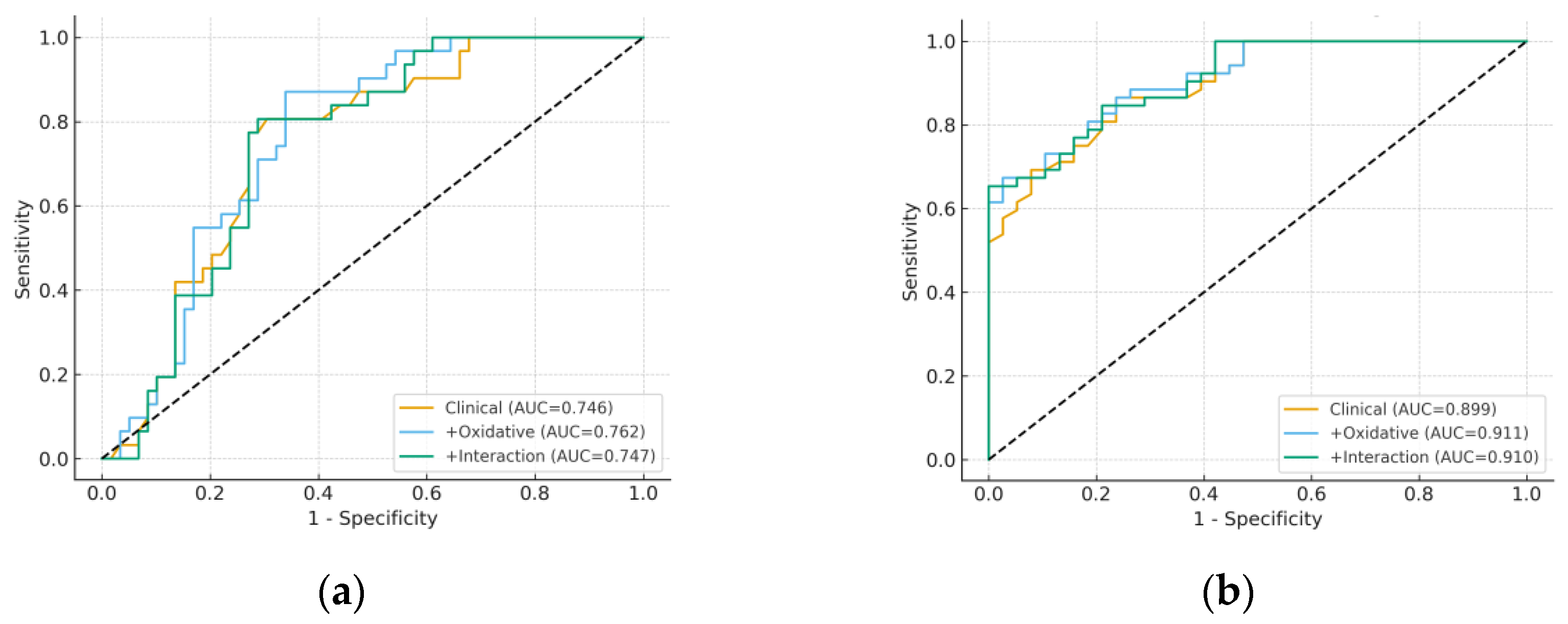
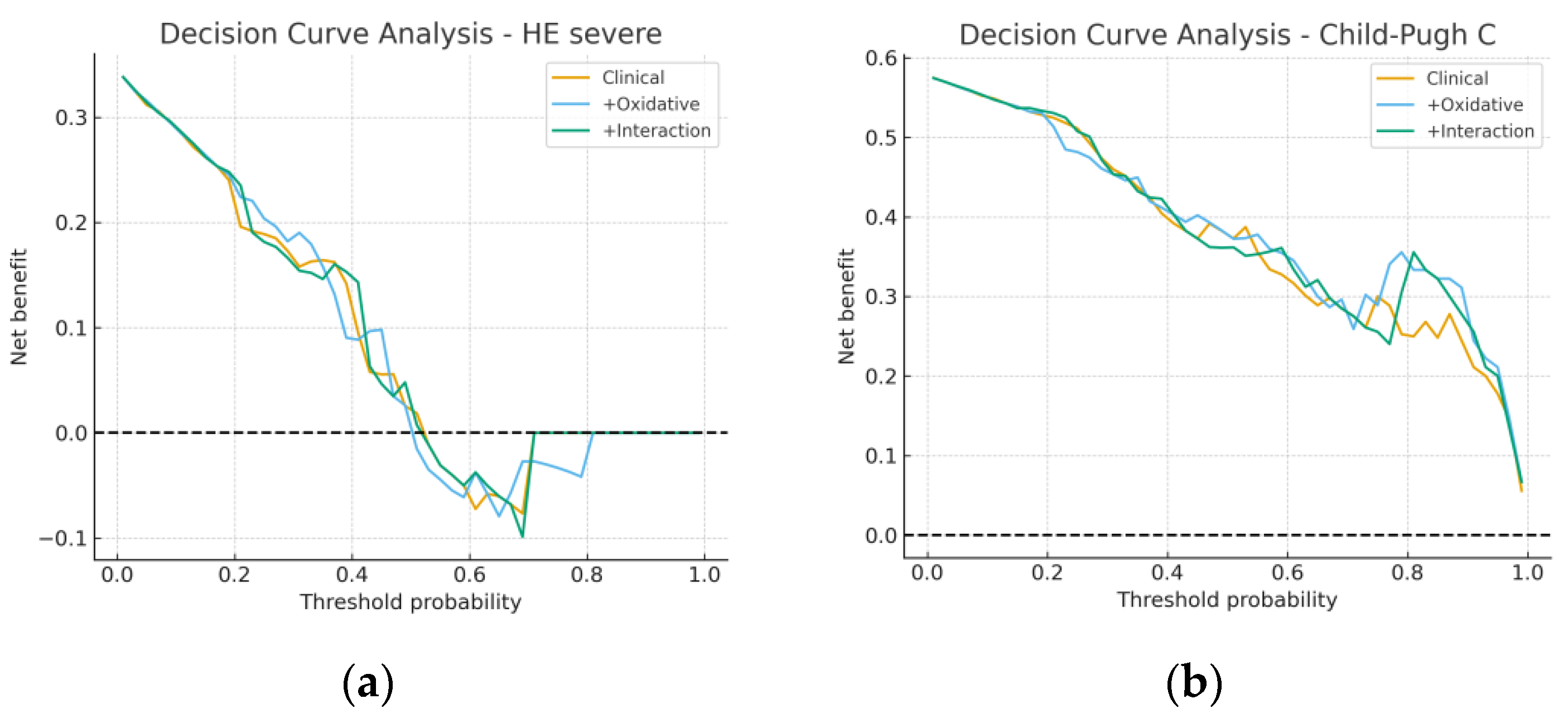
3.4. Model Performance and Incremental Value
3.5. Sensitivity and Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HE | Hepatic encephalopathy |
| CP | Child-Pugh (liver disease severity classification) |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde (ng/mL) |
| 8-epi-PGF2α | 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α (pg/mL) |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| SII | Systemic immune–inflammation index = (platelets × neutrophils)/lymphocytes |
| SIRI | Systemic inflammation response index = (neutrophils × monocytes)/lymphocytes |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the ROC curve |
| NRI | Net reclassification improvement |
| IDI | Integrated discrimination improvement |
| DCA | Decision curve analysis |
| EPV | Events per variable |
| VIF | Variance inflation factor |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| OR | Odds ratio |
References
- Leal-Mercado, L.; Panduro, A.; José-Abrego, A.; Roman, S. Genome-Based Mexican Diet Bioactives Target Molecular Pathways in HBV, HCV, and MASLD: A Bioinformatic Approach for Liver Disease Prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederbaum, A.I.; Lu, Y.; Wu, D. Role of oxidative stress in alcohol-induced liver injury. Arch. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 519–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhilarasan, D. Oxidative stress is bane in chronic liver diseases: Clinical and experimental perspective. Arab. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 19, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.C.; Zhang, Q.B.; Qiao, L. Pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7312–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruoma, O.I. Characterization of drugs as antioxidant prophylactics. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 675–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.W.; Feng, Y. The role of oxidative stress antioxidants in liver diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, G. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: Role of oxidative stress. Mol. Asp. Med. 2000, 21, 49–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Chaudhuri, P.S.; Joshi, Y.K. Superoxide dismutase and total anti-oxidant levels in various forms of liver diseases. Hepatol. Res. 2002, 23, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hong, M.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. Insights into the role and interdependence of oxidative stress and inflammation in liver diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 4234061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Li, D.; Wu, D.; Zhang, N. The relationship between hematological indices and autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs), a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabawa, I.P.Y.; Bhargah, A.; Liwang, F.; Tandio, D.A.; Tandio, A.L.; Lestari, A.A.W.; Budiana, I.N.G.; Manuaba, I.B.A.P. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as a predictive value of hematological markers in cervical cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fest, J.; Ruiter, R.; Ikram, M.A.; Voortman, T.; van Eijck, C.H.J.; Stricker, B.H. Reference values for white blood-cell-based inflammatory markers in the Rotterdam Study: A population-based prospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartal, O.; Kartal, A.T. Value of neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to lymphocyte ratios in pneumonia. Bratisl. Lekárske Listy 2017, 118, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angkananard, T.; Anothaisintawee, T.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J.; Thakkinstian, A. Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio and cardiovascular disease risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2703518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberski, P.S.; Szewczyk, M.; Krzych, L.J. Haemogram-derived indices for screening and prognostication in critically Ill septic shock patients: A case-control study. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, R.J.; Fisher-Wellman, K.H. Blood Oxidative Stress Biomarkers: Influence of Sex, Exercise Training Status, and Dietary Intake. Gend. Med. 2008, 5, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kander, M.C.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Z. Gender Difference in Oxidative Stress: A New Look at the Mechanisms for Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viña, J.; Gambini, J.; Garcia-Garcia, F.J.; Rodriguez-Mañas, L.; Borrás, C. Role of Oestrogens on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Ageing. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2013, 16, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jia, Z.; Misra, H.; Li, Y.R. Oxidative stress and redox signaling mechanisms of alcoholic liver disease: Updated experimental and clinical evidence. J. Dig. Dis. 2012, 13, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.Y.; Ahmad, I.M.; Spitz, D.R.; Schmidt, W.N.; Britigan, B.E. Hepatitis Cvirus-core non structural proteins lead to different effects on cellular antioxidant defenses. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 76, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brault, C.; Lévy, P.; Duponchel, S.; Michelet, M.; Sallé, A.; Pécheur, E.I.; Plissonnier, M.L.; Parent, R.; Véricel, E.; Ivanov, A.V.; et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4 is reversibly induced by HCV to control lipid peroxidation and to increase virion infectivity. Gut 2016, 65, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, L.; Vaziri, N.D.; Ichii, H. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis: Effect of antioxidant therapy. Pancreat. Disord. Ther. 2013, 3, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tache, D.E.; Stănciulescu, C.E.; Baniţă, I.M.; Purcaru, Ş.O.; Andrei, A.M.; Comănescu, V.; Pisoschi, C.G. Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression (iNOS) in chronic viral hepatitis and its correlation with liver fibrosis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2014, 55 (Suppl. S2), S539–S543. [Google Scholar]
- Choghakhori, R.; Abbasnezhad, A.; Hasanvand, A.; Amani, R. Inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress biomarkers in irritable bowel syndrome: Association with digestive symptoms and quality of life. Cytokine 2017, 93, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avci, B.Ş.; Avci, A.; Dönmez, Y.; Kaya, A.; Gülen, M.; Özer, A.İ.; Bulut, A.; Koç, M.; Nazik, H.; Satar, S. The effectiveness of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in predicting In-hospital mortality in Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Emerg. Med. Int. 2020, 2020, 8718304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, Z.; Han, J.; Dong, W. Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios predict post-stroke depression with acute ischemic stroke. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S.; Deng, H.; Zhong, B. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) are associated with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wan, G.; Sang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zeng, H. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: A novel predictor for short-term prognosis in acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orum, M.H.; Kara, M.Z. Platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in alcohol use disorder. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2020, 41, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.; Dodge, J.L.; Bambha, K.M.; Bajaj, J.S.; Reddy, K.R.; Gralla, J.; Ganapathy, D.; Mitrani, R.; Reuter, B.; Palecki, J.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio associates independently with mortality in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1786–1791.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | B (Median [IQR]) | C (Median [IQR]) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.0 [51.3–66.0] | 58.0 [50.0–66.0] | 0.248 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.95 [2.73–3.40] | 2.50 [2.20–2.60] | <0.001 |
| INR | 1.22 [1.16–1.41] | 1.60 [1.40–1.82] | <0.001 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.97 [0.63–2.02] | 4.80 [3.76–6.60] | <0.001 |
| Direct bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.43 [0.28–0.87] | 3.25 [2.30–4.30] | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.03 [0.95–1.21] | 1.30 [1.04–1.60] | 0.003 |
| MDA (ng/mL) | 129.4 [66.5–278.7] | 114.4 [60.9–149.1] | 0.331 |
| 8-epi-PGF2α (pg/mL) | 251.7 [211.3–411.0] | 242.2 [208.4–406.8] | 0.784 |
| NLR | 1.57 [1.19–3.13] | 1.57 [1.40–1.89] | 0.791 |
| SII | 7590.8 [2620.7–267,241.4] | 75,185.7 [1926.9–105,999.9] | 0.345 |
| Variable | HE1 (Median [IQR]) | HE2 (Median [IQR]) | HE3 (Median [IQR]) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62.0 [55.0–66.0] | 59.5 [49.3–66.0] | 57.0 [51.0–66.0] | 0.233 * |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.00 [2.80–3.40] | 2.60 [2.20–2.70] | 2.50 [2.35–2.50] | <0.001 * |
| INR | 1.18 [1.14–1.41] | 1.53 [1.40–1.64] | 1.60 [1.40–1.81] | <0.001 * |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.98 [0.63–2.36] | 4.50 [2.40–5.73] | 5.71 [3.90–7.78] | <0.001 * |
| Direct bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.46 [0.28–1.23] | 2.60 [1.73–3.35] | 3.30 [2.35–5.00] | <0.001 * |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.05 [0.90–1.36] | 1.08 [1.00–1.30] | 1.30 [1.07–1.60] | 0.009 ** |
| MDA (ng/mL) | 131.0 [66.9–301.1] | 72.0 [55.8–118.2] | 123.4 [107.6–248.4] | 0.021 * |
| 8-epi-PGF2α (pg/mL) | 258.8 [218.0–424.3] | 254.1 [215.5–402.6] | 233.4 [198.5–277.2] | 0.395 * |
| NLR | 1.52 [1.24–3.41] | 1.56 [1.31–2.28] | 1.62 [1.42–1.89] | 0.882 * |
| SII | 7590.8 [2620.7–267,241.4] | 65,378.9 [3348.9–113,733.2] | 78,252.6 [1881.2–107,221.8] | 0.552 * |
| Model | Marker | AUC (95% CI) | Cut-Off (Youden) | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE severe (grade 3 vs. 1–2) | Albumin | 0.74 (0.62–0.83) | 2.7 g/dL | 0.71 | 0.72 |
| INR | 0.72 (0.60–0.82) | 1.4 | 0.68 | 0.70 | |
| MDA | 0.58 (0.44–0.70) | 118 ng/mL | 0.55 | 0.60 | |
| 8-epi-PGF2α | 0.56 (0.43–0.69) | 250 pg/mL | 0.50 | 0.63 | |
| NLR | 0.55 (0.41–0.68) | 1.6 | 0.53 | 0.59 | |
| Child-Pugh C vs. B | Albumin | 0.90 (0.83–0.96) | 2.6 g/dL | 0.84 | 0.86 |
| INR | 0.88 (0.80–0.94) | 1.4 | 0.80 | 0.83 | |
| MDA | 0.60 (0.47–0.72) | 115 ng/mL | 0.58 | 0.61 | |
| 8-epi-PGF2α | 0.57 (0.45–0.69) | 245 pg/mL | 0.54 | 0.59 | |
| NLR | 0.59 (0.47–0.71) | 1.7 | 0.55 | 0.60 |
| Panel A. Simple models (age, albumin, MDA, 8-epi-PGF2α) | ||||||
| Model | Variable | Coef | OR | OR_Low | OR_High | p-Value |
| HE severe (grade 3 vs. 1–2) | Age | 0.0084 | 1.009 | 0.963 | 1.056 | 0.721 |
| Albumin | −2.927 | 0.054 | 0.010 | 0.292 | 0.0007 | |
| MDA | 0.0017 | 1.002 | 0.998 | 1.005 | 0.362 | |
| 8-epi-PGF2α | 0.0000 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 1.003 | 0.994 | |
| Child-Pugh C vs. B | Age | 0.0450 | 1.046 | 0.981 | 1.115 | 0.167 |
| Albumin | −7.664 | 0.0005 | 0.000 | 0.017 | <0.001 | |
| MDA | −0.0016 | 0.998 | 0.994 | 1.003 | 0.478 | |
| 8-epi-PGF2α | 0.0023 | 1.002 | 0.999 | 1.006 | 0.222 | |
| Panel B. Interaction models | ||||||
| Model | Variable | Coef | OR | OR_Low | OR_High | p-Value |
| HE severe (8-epi-PGF2α × SII) | z_age | 0.074 | 1.077 | 0.667 | 1.740 | 0.761 |
| z_albumin | −1.136 | 0.321 | 0.155 | 0.665 | 0.0022 | |
| z_8-epi-PGF2α | −0.493 | 0.611 | 0.121 | 3.089 | 0.551 | |
| z_SII | −4.344 | 0.013 | 0.000 | 9552.6 | 0.529 | |
| 8-epi-PGF2α × SII | −3.205 | 0.041 | 0.000 | 1028.1 | 0.536 | |
| Child-Pugh C (MDA × NLR) | z_age | 0.406 | 1.500 | 0.793 | 2.836 | 0.212 |
| z_albumin | −3.169 | 0.042 | 0.009 | 0.188 | <0.001 | |
| z_MDA | 1.521 | 4.575 | 0.153 | 136.78 | 0.380 | |
| z_NLR | 5.991 | 399.74 | 0.001 | 1.2 × 108 | 0.353 | |
| MDA × NLR | 8.883 | 7209.7 | 0.000 | 1.9 × 1011 | 0.309 | |
| Outcome | Model | AUC | Brier | HL Statistic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE severe | Clinical (Age + Albumin) | 0.746 | 0.192 | 8.572 |
| + Oxidative (MDA, 8-epi-PGF2α) | 0.762 | 0.190 | 15.791 | |
| + Interaction (8-epi-PGF2α × SII) | 0.747 | 0.190 | 8.959 | |
| Child-Pugh C | Clinical (Age + Albumin) | 0.899 | 0.128 | 9.211 |
| + Oxidative (MDA, 8-epi-PGF2α) | 0.911 | 0.124 | 8.860 | |
| + Interaction (MDA × NLR) | 0.910 | 0.125 | 5.919 |
| Outcome | Extended Model | ΔAUC | NRI | IDI | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE severe | +MDA | +0.01 | +0.03 | +0.01 | Minimal gain |
| +8-epi-PGF2α | +0.00 | +0.02 | +0.00 | Not significant | |
| Child-Pugh C | +MDA | +0.01 | +0.04 | +0.02 | Minimal gain |
| +8-epi-PGF2α | +0.01 | +0.02 | +0.01 | Not significant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pădureanu, V.; Boldeanu, L.; Pîrșcoveanu, D.F.V.; Dop, D.; Cioboată, R.; Bobîrcă, A.; Rădulescu, V.M. Oxidative Stress and Cirrhosis Severity: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Predictive and Interactive Effects with Inflammation. Metabolites 2025, 15, 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110711
Pădureanu V, Boldeanu L, Pîrșcoveanu DFV, Dop D, Cioboată R, Bobîrcă A, Rădulescu VM. Oxidative Stress and Cirrhosis Severity: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Predictive and Interactive Effects with Inflammation. Metabolites. 2025; 15(11):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110711
Chicago/Turabian StylePădureanu, Vlad, Lidia Boldeanu, Denisa Floriana Vasilica Pîrșcoveanu, Dalia Dop, Ramona Cioboată, Anca Bobîrcă, and Virginia Maria Rădulescu. 2025. "Oxidative Stress and Cirrhosis Severity: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Predictive and Interactive Effects with Inflammation" Metabolites 15, no. 11: 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110711
APA StylePădureanu, V., Boldeanu, L., Pîrșcoveanu, D. F. V., Dop, D., Cioboată, R., Bobîrcă, A., & Rădulescu, V. M. (2025). Oxidative Stress and Cirrhosis Severity: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Predictive and Interactive Effects with Inflammation. Metabolites, 15(11), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110711









