Differential Metabolic Analysis of Rhizomes in Shancigu Based on Widely Targeted Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.3. Metabolite Detection Parameters
2.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.5. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
2.6. Differential Metabolites Selected
2.7. KEGG Annotation and Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
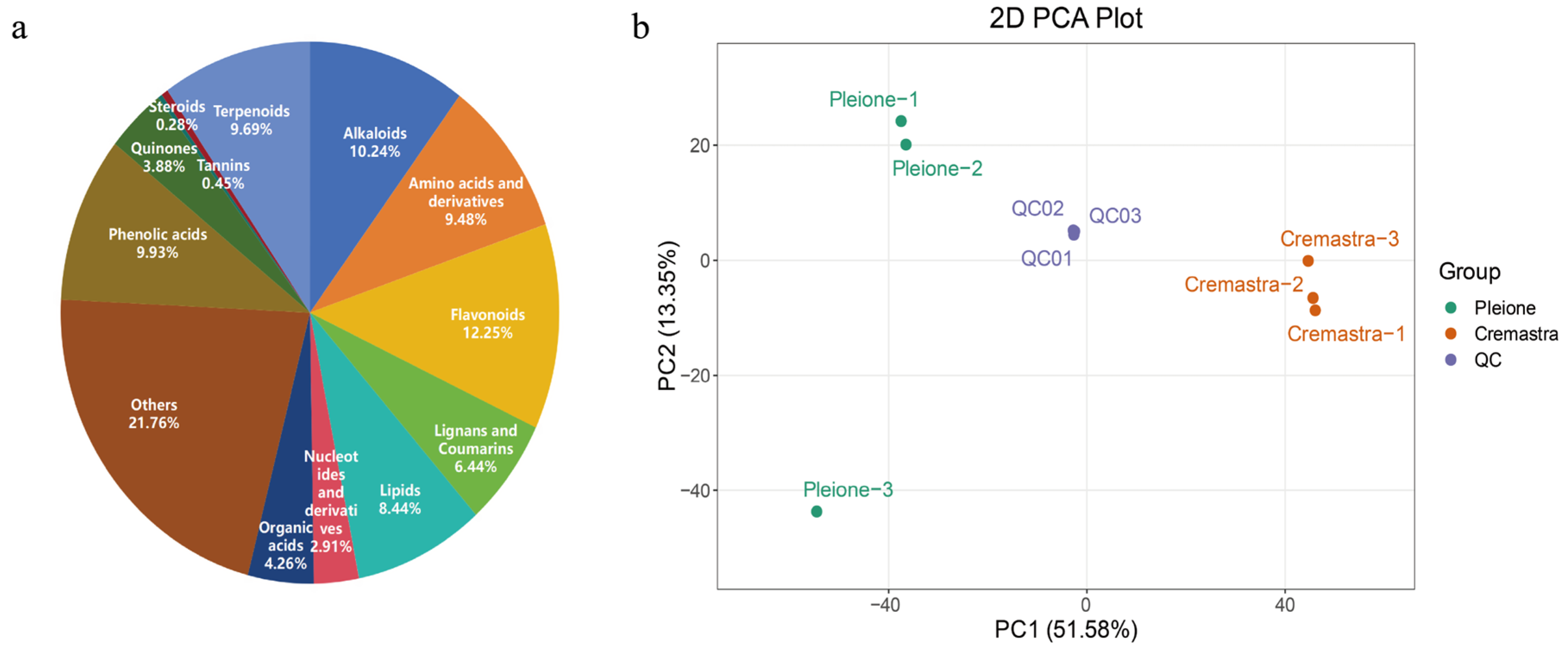
3.1. UPLC-MS/MS Metabolic Profile Analysis
3.2. Establishment of the Shancigu Metabolomics Database
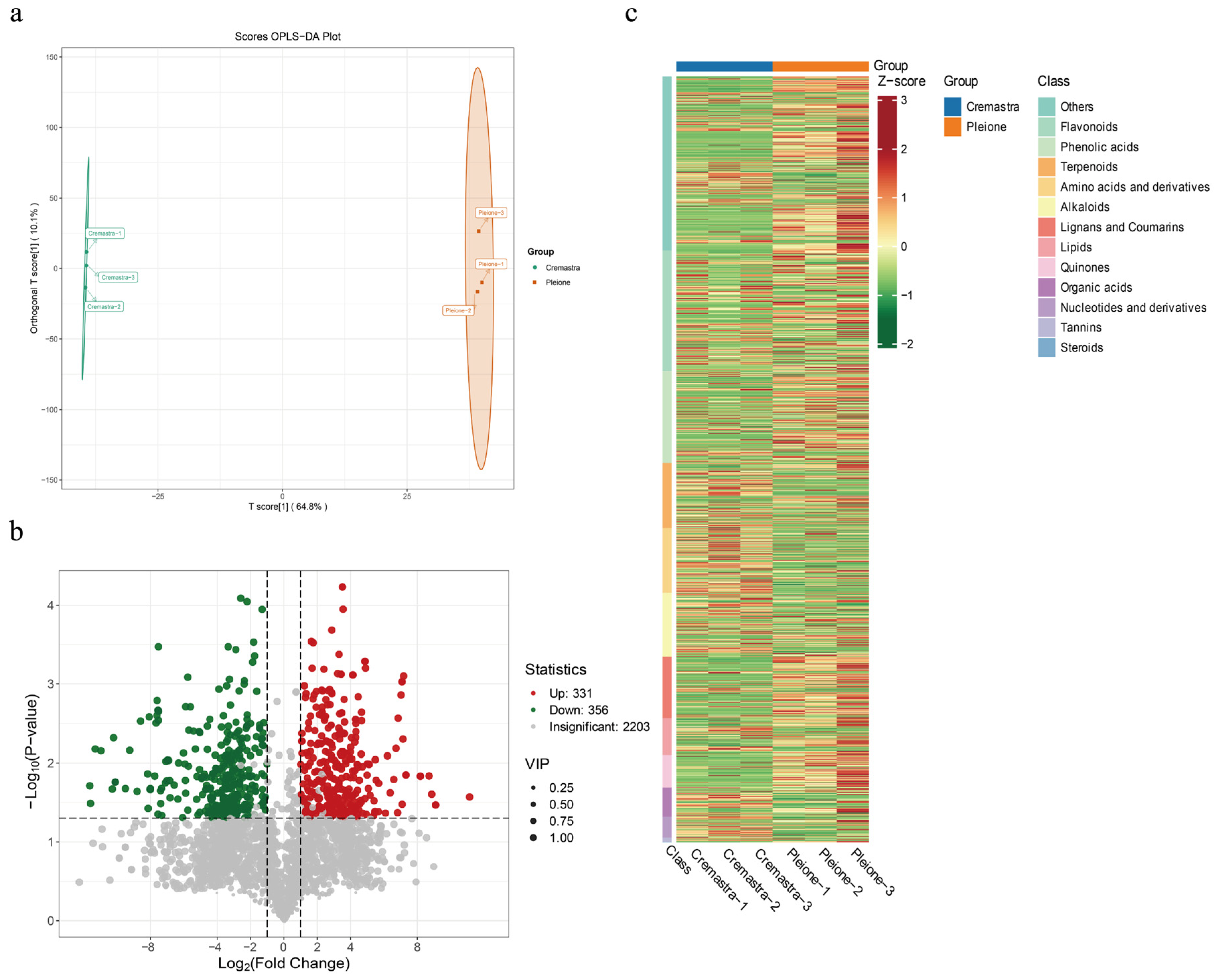
3.3. Statistical Analysis of LC-MS/MS Analytical Results
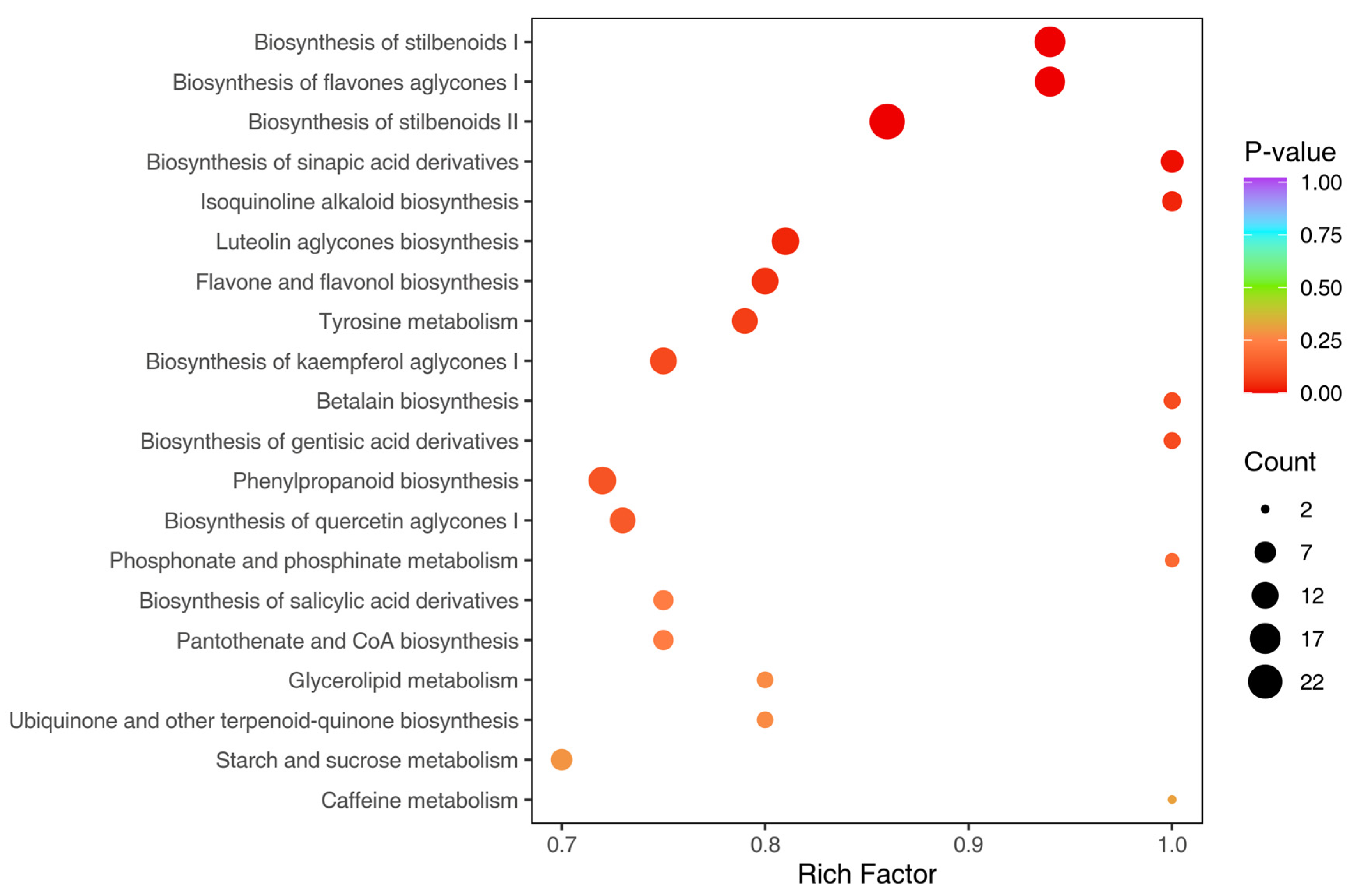
3.4. Metabolic Pathway Enrichment Analysis
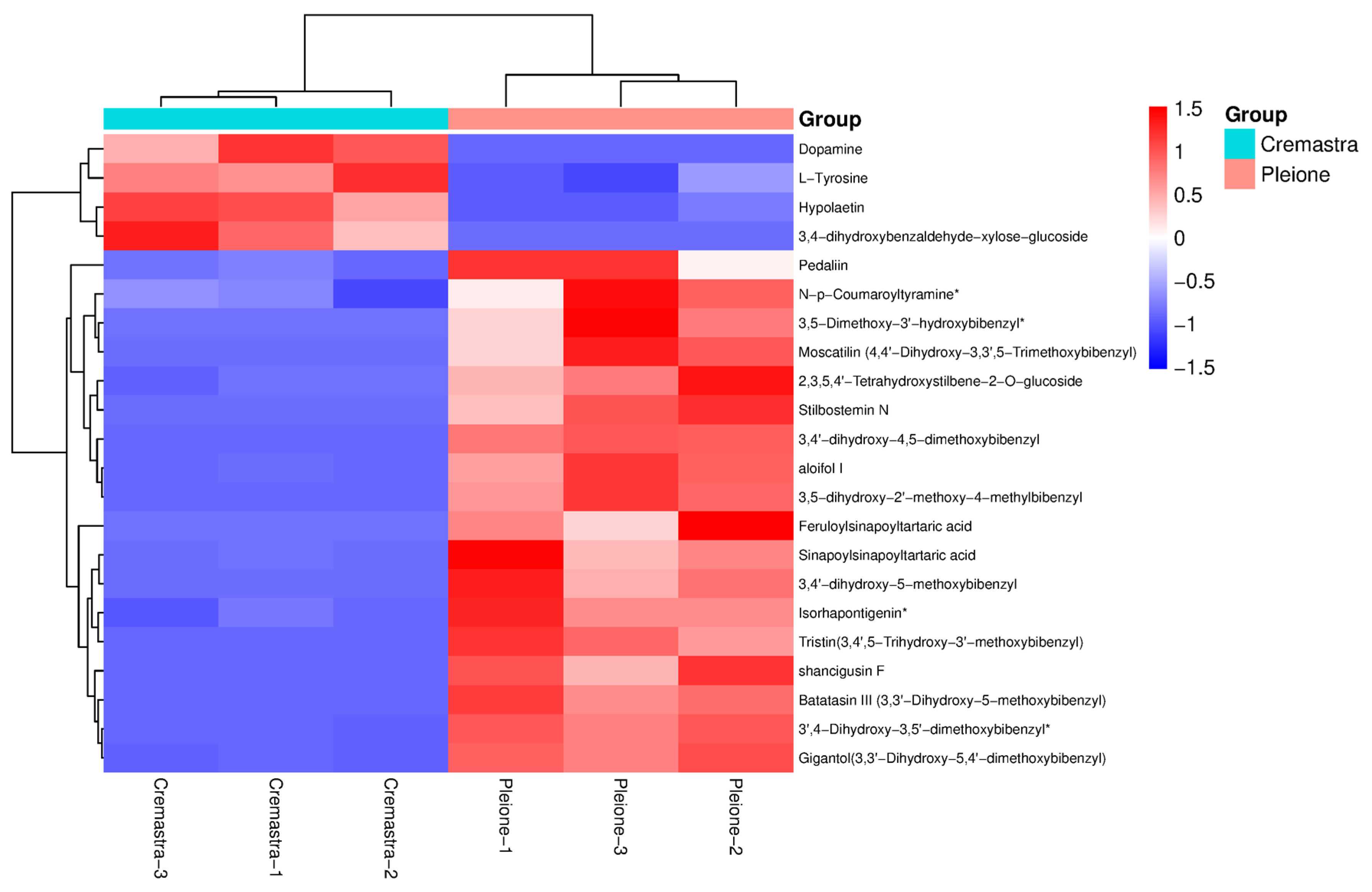
3.5. Identification and Screening of Differential Metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.Y.; Luo, B.; Wu, P.; Guo, J.X.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, M.Q.; Zhang, Z.L. Textual Research on the Cremastrae Pseudobulbus/Pleiones Pseudobulbus Based on the Evaluation of Commodity Specification and Grade. World Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 2336–2344+2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-Q.; Li, W.; Chen, J.-X.; Zhai, J.-W.; Xu, H.-Y.; Ni, L.; Wu, S.-S. Chemical Constituents and Biological Activity Profiles on Pleione (Orchidaceae). Molecules 2019, 24, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.L.; Guo, S.X.; Wang, C.L.; Yang, J.S.; Xiao, P.G. Advances in studies on chemical constituents in plants of Pseudobulbus Cremastrae seu Pleiones and their pharmacological activities. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2007, 38, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, Q.Z.; Zhang, B.G. The botanical identification of Shancigu in Chinese ancient literature. J. Syst. Evol. 2008, 46, 785–792. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.J. Investigation on the Origin and Evolution of Shancigu. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2009, 32, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Cui, B.S.; Wang, C.; Li, S. Chemical constituents from Pleione yunnanensis. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2014, 39, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Song, X.; Han, B.; Fang, S. Evolution of the origin of strain of Shancigu (Rhizoma pleionis). Chin. J. Med. Hist. 2015, 45, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Yu, D.H.; Liu, S.M. Herbal textual research and modern research progress of arrowhead mushroom. China Pharm. 2020, 31, 3055–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.Z.; Cao, Y.X.; Liu, M.M.; Xue, J.W.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Y.F.; Shi, J.L. Quality differences of different commercial specifications of Cremastrae Pseudobulbus Pleiones Pseudobulbus based on HPLC fingerprint, multi-index component determination and chemometrics. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2023, 54, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, Y.J.; Sun, Q.H.; Guo, Y.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Rong, R.; Zhao, D.T. Construction of a Phytochemical Repository for Shancigu. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2024, 47, 3165–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, C.; Tang, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Qin, X.; Jin, S. A review of Cremastra appendiculata (D.Don) Makino as a traditional herbal medicine and its main components. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 114357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.L. Research Progress on Pharmacological Action and Clinical Application of Shancigu (Cremastrae Pseudobulbus Pleiones Pseudobulbus). Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 41, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwiński, T.; Kowalczyk, T.; Sitarek, P.; Kolanowska, M. Orchidaceae-Derived Anticancer Agents: A Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Ge, C.Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Chu, H.Y.; Jing, Y.; Xu, Z.M.; Xie, G.Y.; Yuan, J. Physicochemical properties, structural analysis, and activity of Shancigu polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 298, 140071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, K.; Wang, M.; Zeng, L.; Sun, E.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Z. Exploring the mechanism of Cremastra Appendiculata (SUANPANQI) against breast cancer by network pharmacology and molecular docking. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2021, 94, 107396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.-H.; Zhu, S.; Duan, W.-J.; Ma, X.; Luo, X.; Liu, B.; He, R.-R. “Shanghuo” increases disease susceptibility: Modern significance of an old TCM theory. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 250, 112491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaili, S.; Qu, Y.; Fougère, L.; Colas, C.; Desneux, N.; Lavoir, A.; Michel, T. Untargeted metabolomic and molecular network approaches to reveal tomato root secondary metabolites. Phytochem. Anal. 2021, 32, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Shi, T.; Yin, H.; Sun, D.; Hao, Y.; Chen, W. Metabolite-based genome-wide association study enables dissection of the flavonoid decoration pathway of wheat kernels. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1722–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Xiao, J.; Chen, S.; Yu, Y.; Ma, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, R. Metabolite signatures of diverse Camellia sinensis tea populations. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannu, N.; Bhatnagar, A. Resveratrol: From enhanced biosynthesis and bioavailability to multitargeting chronic diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2237–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basolo, A.; Matrone, A.; Elisei, R.; Santini, F. Effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on thyroid function and thyroid hormone metabolism. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 79, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, A.M.; Tanabe, A.; Iwahori, Y. A systematic review of the effect of L-tryptophan supplementation on mood and emotional functioning. J. Diet. Suppl. 2021, 18, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, T.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. Functions of dopamine in plants: A review. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1827782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Gao, T.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, C.; Chen, Q.; Wei, Z.; Ma, F. Effects of Exogenous Dopamine on the Uptake, Transport, and Resorption of Apple Ionome Under Moderate Drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, X.-K.; Chang, C.; Jia, D.; Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Ma, F. Dopamine alleviates salt-induced stress in Malus hupehensis. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 153, 584–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Yi, Z.; Han, Y.; Xie, Q.; Xiu, H.; Yao, F.; Guo, N.; Yu, Y. The comparative study of the efficacy of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide combined with vasoactive medications for elderly patients with heart failure and hypotension receiving injections. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025, 25, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Romero, Y.; Rojas, J.-I.; Castillo, R.; Rojas, A.; Mata, R. Spasmolytic Effects, Mode of Action, and Structure—Activity Relationships of Stilbenoids from Nidema boothii. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-L.; Munyao Mutie, F.; Xu, Y.-B.; Saleri, F.D.; Hu, G.-W.; Guo, M.-Q. Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory Activities and Polyphenol Profile of Rhamnus prinoides. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, H.; Solla, P.; Sechi, L.A. Current Advancement of Immunomodulatory Drugs as Potential Pharmacotherapies for Autoimmunity Based Neurological Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtar, F.A.; Ahmed, M.; Al Dhanhani, A.S.; Elbehairi, S.E.I.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Shati, A.A.; Fakhry, A.M. Distribution, Phytochemical Insights, and Cytotoxic Potential of the Sesbania Genus: A Comprehensive Review of Sesbania grandiflora, Sesbania sesban, and Sesbania cannabina. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.-Y.; Yang, Y.-B.; Liu, L.-C.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.-B.; Zhou, Q. Differential Metabolic Analysis of Rhizomes in Shancigu Based on Widely Targeted Metabolomics. Metabolites 2025, 15, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15100667
Gao Z-Y, Yang Y-B, Liu L-C, Li X, Huang Y-B, Zhou Q. Differential Metabolic Analysis of Rhizomes in Shancigu Based on Widely Targeted Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2025; 15(10):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15100667
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zhu-Yi, Yi-Bo Yang, Li-Cheng Liu, Xue Li, Yan-Bo Huang, and Qiang Zhou. 2025. "Differential Metabolic Analysis of Rhizomes in Shancigu Based on Widely Targeted Metabolomics" Metabolites 15, no. 10: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15100667
APA StyleGao, Z.-Y., Yang, Y.-B., Liu, L.-C., Li, X., Huang, Y.-B., & Zhou, Q. (2025). Differential Metabolic Analysis of Rhizomes in Shancigu Based on Widely Targeted Metabolomics. Metabolites, 15(10), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15100667





