Accumulation Characteristics of Natural Ophiocordyceps sinensis Metabolites Driven by Environmental Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Soil Factor Determination and Meteorological Factor Data Download
2.3. Sample Pretreatment and Metabolite Separation
2.4. UPLC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Metabolite Identification and Data Analysis
3. Results
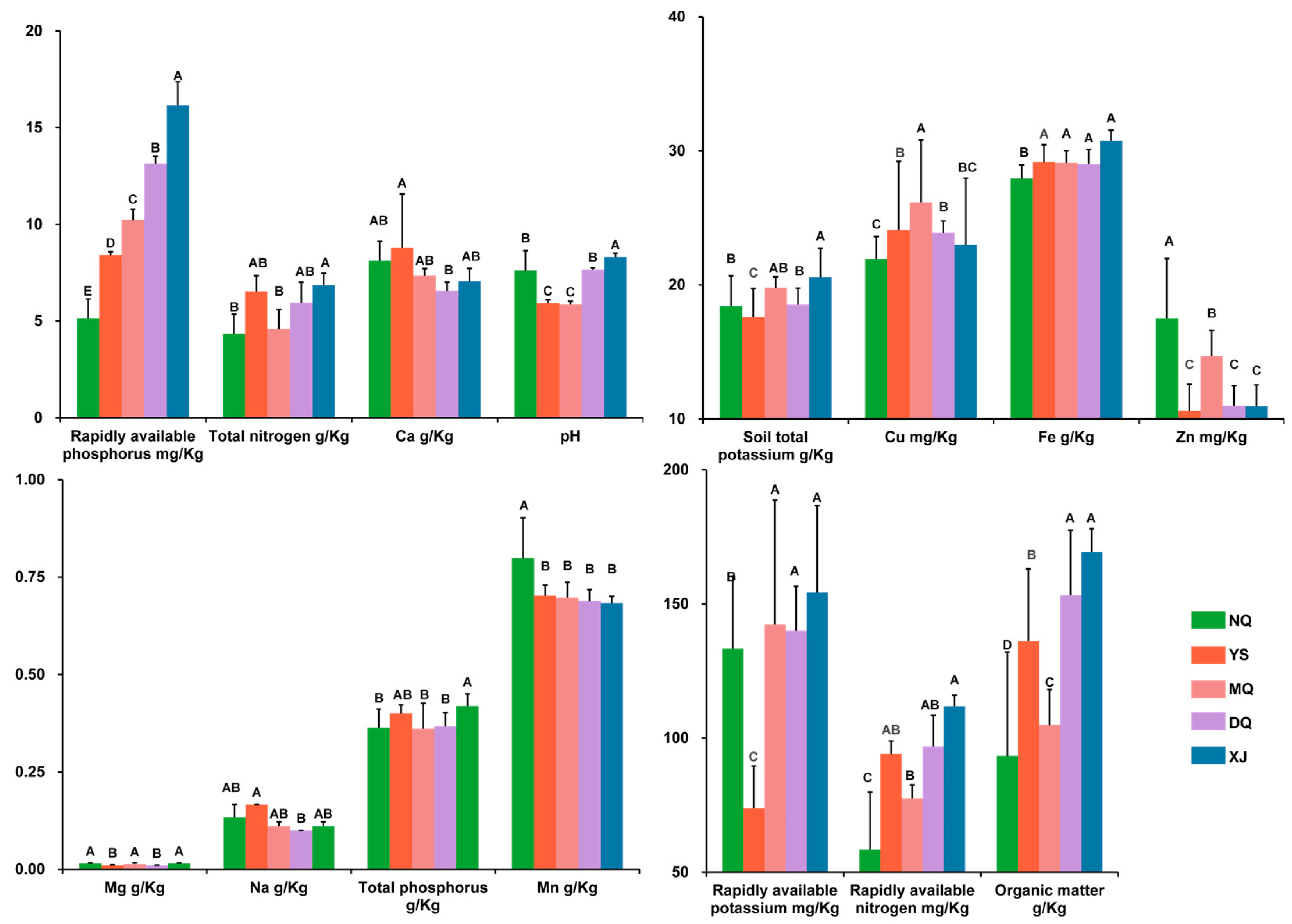
3.1. Environmental Factor Analysis
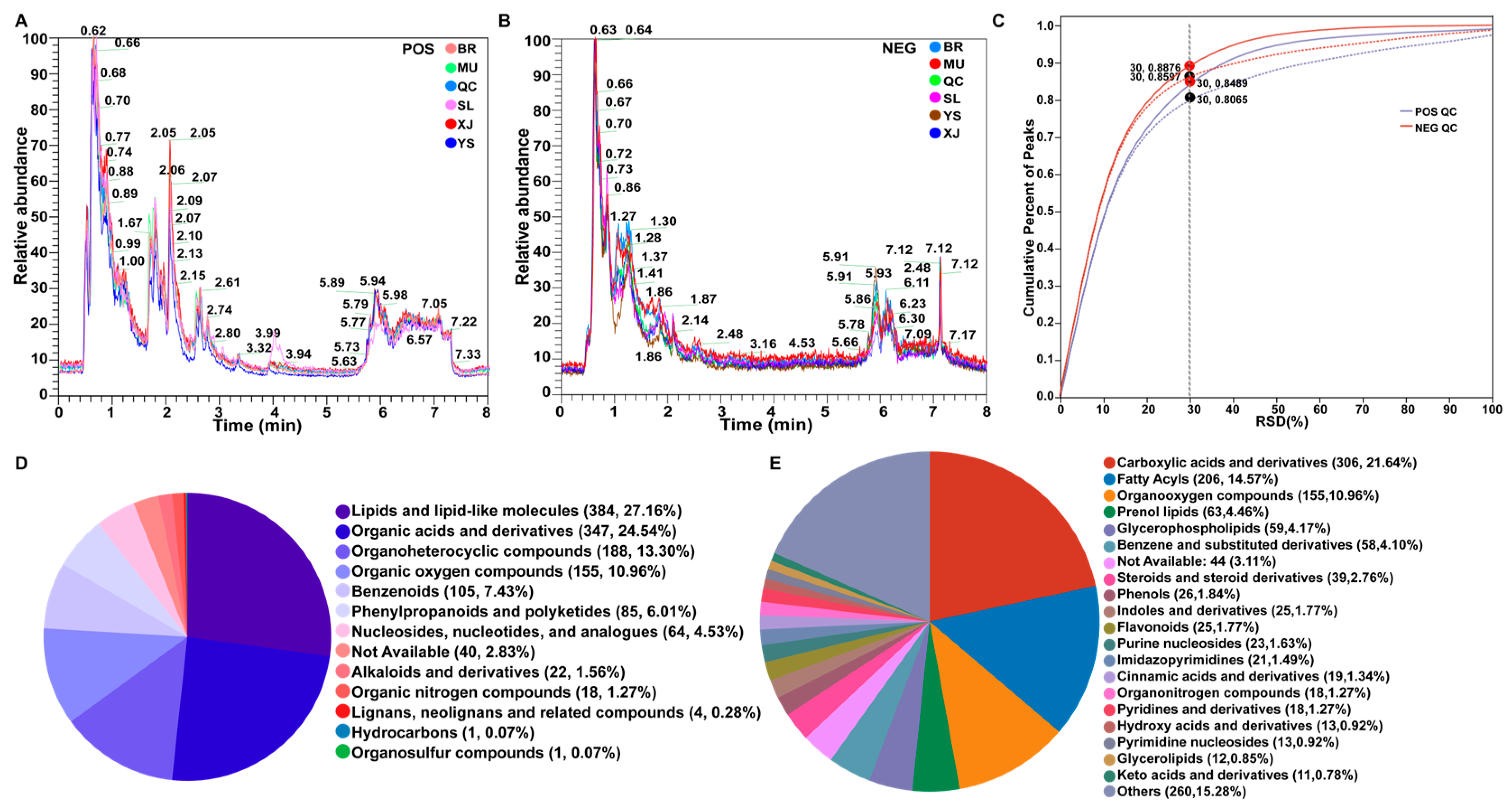
3.2. Total Metabolic Spectrum Structure of O. sinensis
3.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis and DAMs Identification
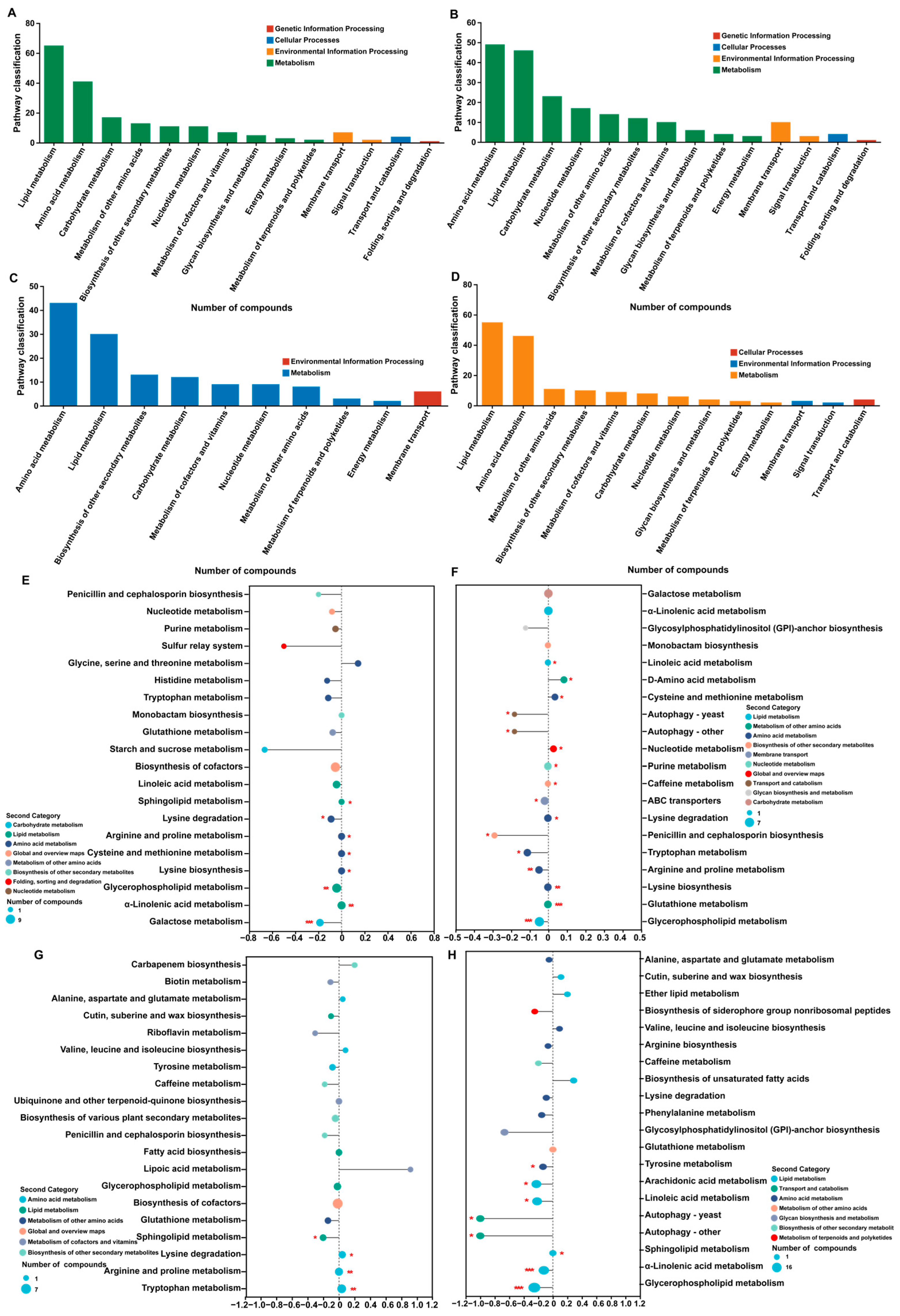
3.4. KEGG Enrichment Analysis
3.5. Association Analysis between Environmental Factors and DAMs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.P.; Yang, F.Q.; Tsim, K.W.K. Quality control of Cordyceps sinensis, a valued traditional Chinese medicine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 1571–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.W.; Gong, Z.H.; Su, Y.; Lin, J.; Tang, K.X. Cordyceps fungi: Natural products, pharmacological functions and developmental products. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalik, R.S.; Maan, B.R.; Zuzana, M.; Liang, E.Y. Habitat ecology of Ophiocordyceps sinensis in western nepal. Mt. Res. Dev. 2017, 37, 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Li, X.Z.; Chen, J.B.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.L. Suitability and regionalization of Chinese cordyceps in Qinghai Province, Northwest China. Mycosystema 2022, 41, 1772–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, M.; Pan, X.; He, Q.; Chen, W.; Zeng, G.; Li, M. Characteristics of grassland plant community change with elevation and its relationship with environmental factors in the burqin forest region of the altai mountains. Diversity 2023, 15, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, D.; Castel, T.; Pohl, B.; Richard, Y. Influence of spatial information resolution on the relation between elevation and temperature. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 5677–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Sharma, G.; Dambire, C.; Marquez, J.; Carlos, A.B.; Proaño, K.; Holdsworth, M.J. An oxygen-sensing mechanism for angiosperm adaptation to altitude. Nature 2022, 606, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proutsos, N.; Alexandris, S.; Liakatas, A.; Nastos, P.; Tsiros, I.X. PAR and UVA composition of global solar radiation at a high altitude Mediterranean forest site. Atmos. Res. 2020, 269, 106039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shik, J.Z.; Arnan, X.; Cristela, S.O.; Cerdá, X.; Boulay, R. Evidence for locally adaptive metabolic rates among ant populations along an elevational gradient. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senda, R.; Francisco, J.; Zamora, C.; Gregorio, M.R. The lizard Psammodromus algirus (Squamata: Lacertidae) is darker at high altitudes. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 112, 132–141. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, S.; Thakur, S.; Majeed, A.; Bhardwaj, P. Adaptability of Rhododendrons in high altitude habitats. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, L.; Qi, D. Variation in leaf traits at different altitudes reflects the adaptive strategy of plants to environmental changes. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 8166–8175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.S.; Liu, B.L.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Lam, M.; Law, K.; Chen, H.B. Studies on macroscopic and microscopic identification of Cordyceps sinensis and its counterfeits. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2011, 36, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, C.; Luo, J.; Xie, C.; Wei, J.; Pan, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C. Characterization and biological activities of melanin from the medicinal fungi Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerardo, S.V.; Francisco, F.M.; Paul, M.L.; Nohemi, G.O.; Octavio, L. DOPA-melanin, component and tolerance factor to heat and UV-B radiation in the conidia of two species of Cordyceps. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 437–454. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Xue, Z.Y.; Cao, J.; Peng, C.; Guo, J.L. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals genes related to altered color of artificially cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis. PeerJ 2023, 30, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.K.; Wang, W.Q.; Ma, H.L.; Wu, J.Y. Sulfation and enhanced antioxidant capacity of an exopolysaccharide produced by the medicinal fungus Cordyceps sinensis. Molecules 2013, 18, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.V.; Tran, V.K.; Le, L.S.; Tran, T.M.; Nguyen, D.G.; Trinh, T.K.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Nguyen, C.C.; Le, T.H. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of Ophiocordyceps Sobolifera extract for renal injury prevention. Process Biochem. 2022, 121, 322–329. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Yang, L.; Ren, B.; Guo, D. Metabolite profiling and antioxidant capacity of natural Ophiocordyceps gracilis and its cultures using LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics: Comparison with Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Phytochem. Anal. 2024, 35, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Mou, D.; Luo, L.; Zhong, W.; Duan, L.; Zou, X. Different cultivation environments affect the yield, bacterial community and metabolites of Cordyceps cicadae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.C.; Qin, Z.; Lesi, C.; Jiang, W.; Lu, Y.; Sun, S.Q.; Liang, H.D.; Li, Z.P. Investigation into the content change and distribution of active components in Cordyceps sinensis with growth cycle by direct TOF-SIMS detection. Microchem. J. 2022, 177, 107303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Hao, L.F.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J.Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.F. Integration of transcriptome, volatile and non-volatile metabolite profile reveals characteristic aroma formation in Toona sinensis. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Xiang, L.; Zhou, Z.J.; Dai, Y.; Han, K.H.; Zhu, T.H. Biological characteristics of four generation artificial swift moth adults (Hepialus Xiaojinensis). J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2014, 42, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.B.; Li, X.Z.; Xu, C.T.; Liang, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, T.; He, H.; Cao, Z.F.; Li, Y.L. Soil ecological stoichiometry in the excavated and non-excavated areas of Chinese Cordyceps in Qinghai province. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2023, 31, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger, F.; Baltensweiler, A.; Ginzler, C.; Roth, T.; Braunisch, V.; Bugmann, H.; Bollmann, K. Environmental predictors of species richness in forest landscapes: Abiotic factors versus vegetation structure. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Dai, Q.; Zhu, L.; Ding, P.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, H. Influence of vegetation types on the c, n, and p stoichiometric characteristics of litter and soil and soil enzyme activity in karst ecosystems. Forests 2023, 14, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, X. Plant allometric growth enhanced by the change in soil stoichiometric characteristics with depth in an alpine meadow under climate warming. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 860980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.F.; Chen, S.Y.; Shi, S.R.; Qi, M.J.; Liu, X.H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.X.; Jiang, C.Q. Effects of different management approaches on the stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N, and P in a mature Chinese fir plantation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.L.; Qian, Z.M.; Tian, W.S.; Xu, X.Q.; Yan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Lu, S.M.; Li, W.J.; Guo, D.A. Profiling and identification of aqueous extract of Cordyceps sinensis by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Wei, X.; Li, L.; Cheng, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y. A metabolomics approach for authentication of Ophiocordyceps sinensis by liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.J.; He, J.S.; Yang, R.H.; Wu, H.J.; Wang, X.L.; Jiao, L.; Tang, Z.Y.; Yao, Y.J. Range shifts in response to climate change of Ophiocordyceps sinensis, a fungus endemic to the Tibetan Plateau. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 206, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.N.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, X.L.; Lu, T.T.; Yu, C.H.; He, L.Y. Evidence-based study to compare daodi traditional Chinese medicinal material and non-daodi traditional Chinese medicinal material. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 36, 6763130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Guo, S.; Xie, D.; Li, S.; Hu, H.K. Lipidomic profiling of wild cordyceps and its substituents by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 165, 113497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.H.; Lim, S.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Cho, S.Y. Antioxidant and immunostimulating activities of the fruiting bodies of paecilomyces japonica, a new type of Cordyceps sp. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 928, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.F.; Zhou, X.B.; Zhou, H.X.; Yang, Z.F.; Jiang, H.M.; Wu, X.; Li, W.J.; Qiu, J.J.; Mi, J.N.; Chen, M.; et al. Novel Fatty Acid in Cordyceps Suppresses influenza a (H1N1) virus-induced proinflammatory response through regulating innate signaling pathways. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.P.; Li, W.J.; Qiu, J.J.; Qiao, Y.L.; Wu, F.; Huo, X.K.; An, Y.; et al. Nucleosides and amino acids, isolated from Cordyceps sinensis, protected against cyclophosphamide-induced myelosuppression in mice. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 6056–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.H.; Wu, F.F.; Zou, Z.C.; Mao, L.Y.; Lin, S. Discovery of the chemical constituents, structural characteristics, and pharmacological functions of Chinese caterpillar fungus. Open Chem. 2022, 21, 0337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Zhang, J.H.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, G.L.; Li, M.M.; Wu, P.P.; Shu, R.H.; Gao, X.X.; Guo, L.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis of the orchestrated molecular mechanisms underlying fruiting body initiation in Chinese cordyceps. Gene 2020, 763, 145061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachael, M.K.; John, C.P.; Tessa, P.; Loreta, G.S.; Norman, P.A.H. Adaptation and acclimation of photosynthetic microorganisms to permanently cold environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 222–252. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Z.; Sun, C.Y.; Xie, B.J.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.W.; Chen, X.L.; Huang, Q.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Li, T.H.; Deng, W.Q. Cordyceps guangdongensis lipid-lowering formula alleviates fat and lipid accumulation by modulating gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in high-fat diet mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1038740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asomadu, R.O.; Ezeorba, T.P.C.; Ezike, T.C.; Uzoechina, J. Exploring the antioxidant potential of endophytic fungi: A review on methods for extraction and quantification of total antioxidant capacity (TAC). 3 Biotech 2024, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, E.; Sigdel, S.R.; Liu, B.; Camarero, J.J. The coupling of treeline elevation and temperature is mediated by non-thermal factors on the Tibetan Plateau. Forests 2017, 8, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.A.J.; Anas, A.H.; Heba, E.H.; Abdulhakeem, D.H.; Mohammed, J.M.; Mohammad, A.A.; Ali, H.A.; Farhan, S.; Ekhlas, A.B. Comprehensive review on the Bis–heterocyclic compounds and their anticancer efficacy. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1271, 133970. [Google Scholar]
- Zahra, H.; Ali, R.; Nima, R.A. Anti-cancer nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018, 22, 2256–2279. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wei, G.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z. A Nucleoside/nucleobase-rich extract from Cordyceps Sinensis inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition and protects against renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Molecules 2019, 24, 4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Dong, Z.; Li, N.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, A.; Zhu, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z. Nucleosides isolated from Ophiocordyceps sinensis inhibit cigarette smoke extract-induced inflammation via the SIRT1–nuclear factor-κB/p65 pathway in RAW264.7 macrophages and in COPD mice. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 2821–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Xia, J.; Ni, J.; Li, K.; Hou, Y.; Hu, J.; Wei, L.F.; Wu, K.; Xia, H.J.; et al. TiP-Leaf: A dataset of leaf traits across vegetation types on the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaventura, H.A.; Quintela, E.D.; Santos, E.N.; Silva, J.F.A.; Humber, R.A. Susceptibility of All Nymphal Stages of Bemisia tabaci Biotype B (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) to Three Brazilian Isolates of Cordyceps sp. (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) in a Screenhouse Under Variable Temperature and Moisture Conditions. Neotrop. Entomol. 2021, 50, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, R.; Camarero, J.J. Moisture mediates temperature-growth couplings of high-elevation shrubs in the Tibetan plateau. Trees 2022, 36, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.T.; Zhu, W.Q.; Chen, G.S.; Jiang, N.; Fan, D.Q.; Zhang, D.H. Continuous but diverse advancement of spring-summer phenology in response to climate warming across the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, R.R.; Chen, Z.H.; Xia, Y.X.; Sun, Q.J. Changes of five compounds in the germination stage of Chinese cordyceps. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2023, 60, 883–892. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Accumulation Characteristics of Natural Ophiocordyceps sinensis Metabolites Driven by Environmental Factors. Metabolites 2024, 14, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080414
Wang T, Tang C, Chen J, Liang J, Li Y, Li X. Accumulation Characteristics of Natural Ophiocordyceps sinensis Metabolites Driven by Environmental Factors. Metabolites. 2024; 14(8):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080414
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tao, Chuyu Tang, Jianbo Chen, Jing Liang, Yuling Li, and Xiuzhang Li. 2024. "Accumulation Characteristics of Natural Ophiocordyceps sinensis Metabolites Driven by Environmental Factors" Metabolites 14, no. 8: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080414
APA StyleWang, T., Tang, C., Chen, J., Liang, J., Li, Y., & Li, X. (2024). Accumulation Characteristics of Natural Ophiocordyceps sinensis Metabolites Driven by Environmental Factors. Metabolites, 14(8), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080414








