Abstract
Recently, the role of trace elements in the pathophysiology of obesity, insulin resistance (IR), and metabolic diseases has been explored. In this cross-sectional study, we aimed to assess the association of overweight, obesity, and cardiometabolic traits with serum copper (Cu) levels in 346 Mexican adults. Serum Cu level was measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Anthropometrical data were collected, and biochemical parameters were measured. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index was used as a surrogate marker to evaluate IR. Overweight and obesity status was positively associated with the serum Cu level (β = 19.434 ± 7.309, p = 0.008). Serum Cu level was observed to have a positive association with serum triglycerides level (β = 0.160 ± 0.045, p < 0.001) and TyG (β = 0.001 ± 0.001, p < 0.001). Additionally, high serum Cu level was positively associated with overweight and obesity status (odds ratio [OR] = 1.9, 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 1.1–3.4, p = 0.014), hypertriglyceridemia (OR = 3.0, 95% CI 1.7–5.3, p < 0.001), and IR (OR = 2.6, 95% CI 1.4–4.6, p = 0.001). In conclusion, our results suggest that overweight, obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, and IR are positively associated with serum Cu levels in Mexican adults.
1. Introduction
Regardless of ethnicity, socioeconomic status, age, and sex, the prevalence of overweight and obesity has increased worldwide [1]. It is even estimated that if these trends continue, half of the global population may be individuals that are overweight or obesity by 2035 [2]. In Mexico, the last National Survey of Health and Nutrition reported a combined prevalence of overweight and obesity of 75.2% in the adult population [3]. Due to its high association with the development of metabolic diseases (insulin resistance [IR], type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases), the study of risk factors related to overweight and obesity is considered of high importance to improve its prevention and treatment [4].
Recently, the role of trace elements such as iron, manganese, selenium, iodine, zinc, chromium, copper (Cu), iron, and boron in the pathophysiology of obesity, IR, and metabolic diseases has been explored [5,6]. These reports indicate that the deficiency or overload of these trace elements may negatively affect systemic homeostasis related to energy metabolism [7]. In this way, high serum Cu levels have been associated with abnormal glucose homeostasis in the U.S. adult population [5] and positively associated with overweight and obesity in Mexican children [8].
Although it is known that Cu plays an important role in the human antioxidant system because it is a central component of superoxide dismutase, an antioxidant enzyme [9], its implications in the physiological dysregulation related to metabolic diseases are not entirely clear. The deficient concentration of Cu is associated with impaired ATP synthesis and decreased insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells [10,11]. On the other hand, excessive levels have been associated with an increase in reactive oxygen species, leading to oxidative stress and the progression of IR and diabetes [10,12].
IR is physiologically defined as the inability of target tissues to respond to the action of insulin and is the pathogenic trigger for type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and atherosclerosis [13]. In recent years, IR diagnosis has increased to evaluate the risk of developing more serious complications related to overweight and obesity. However, because the reference method for quantifying IR is invasive, and the most commonly used alternative methods may be expensive, the determination of IR does not frequently occur in clinical practice at the first level of care of developing populations. Although the hyperinsulinaemic euglycemic clamp has been considered as the reference method to determine IR, it requires the infusing of insulin and dextrose to evaluate correct glucose metabolism [14]. On the other hand, the commonly used methods, the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and the quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI), may be less invasive than the reference method. However, these methods involve the measurement of serum insulin, which for some populations in developing countries (people without health insurance and/or with low income), could still represent a high cost and effort to obtain an IR diagnosis [15]. For this reason, in the last years, different methods have been proposed as surrogate markers of IR [15]. One of these is the triglycerides/glucose index, which comes from the arithmetic calculation: Ln (fasting triglycerides (mg/dL) × fasting blood glucose (mg/dL)/2) [16]. The rationale for using the TyG index is that high levels of serum glucose and triglycerides are highly related to elevated levels of circulating free fatty acids, chronic low-grade inflammation, and oxidative stress, which together are characteristic conditions of the pathophysiology of IR [17,18,19]. The risk of IR measured by the TyG index has been used to evaluate harmful long-term cardiovascular events in recent follow-up studies of large cohorts [20].
The obesity pathophysiology implies a state of oxidative stress and chronic low-grade inflammation that is highly related to the dysfunction of insulin signaling and lipid metabolism [21]. In this way, the Mexican adult population could be considered at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia due to their high prevalence of overweight and obesity. Furthermore, although its physiological mechanism is not yet fully described, the association between Cu and metabolic health is acknowledged. For this reason, our study hypothesizes that being overweight and obesity or having any cardiometabolic traits will be related to high serum Cu levels. Hence, the present study aimed to analyze the association of overweight and obesity status and cardiometabolic traits (serum levels of fasting plasma glucose [FPG], TC, TG, and TyG index) with serum Cu levels in a sample of Mexican adults.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample
A total of 346 Mexican adults (214 women and 132 men) between 22 and 57 years from 4 Provinces (San Luis Potosi, Tlaxcala, Chiapas, and Mexico City) were randomly selected and invited to participate in this cross-sectional study between 2018 and 2020. This study population was composed of university students, university professors, and potters. Exclusion criteria for the study included men and women over 60 years of age, subjects with renal disease, hypo- and hyperthyroidism, cancer, hypertension, liver disease, and those individuals with FPG concentrations higher than 126 mg/dL.
2.2. Ethical Approval
The data analyzed in the present study are part of protocols that were conducted according to the guidelines established in the Declaration of Helsinki and based on the Regulations of the General Health Law on Health Research in Mexico, based on articles 14 and 16. The Ethics Committees that approved the research protocols were: Bioethics Committee of the National School of Biological Sciences, IPN (Approval register: ENCB/CEI/064/202); Institutional Review Board of the Tapachula School Medicine of UNACH (Approval register: 03/MHT/RPR/087/17); Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Nursing and Nutrition, UASLP (Approval register: 2014–092); and Ethics Committee of the Mexican Social Security Institute (Approval register: CONBIOETICA-09-CEI-009-20160601). In addition, all subjects were asked to approve their written consent.
2.3. Anthropometric and Biochemicals Measurements
Weight and height were measured using a digital scale (Seca, Hamburg, Germany) and a portable stadiometer (Seca 225, Hamburg, Germany). Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight (kg)/height (m)2.
After 8 to 12 h of fasting, blood samples were collected from each participant. Subsequently, the blood samples were centrifugated (1600× g for 10 min) to obtain serum. Finally, the serum was stored at −80 °C until analysis of Cu levels and cardiometabolic traits. To determine FPG, TG, and TC, a clinical chemistry analyzer (ILAB 300, Instrumentation Laboratory, Barcelona, Spain) was used. TyG index was calculated and used as a surrogate quantification of IR [16,22].
2.4. Definition of Binary Cardiometabolic Traits
According to the criteria put forth by the World Health Organization, normal weight, overweight, and obesity status were considered as having BMI < 25 kg/m2, ≥ 25 BMI < 30 kg/m2, and BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, respectively. To obtain a better visualization of the effect of body weight on serum Cu levels, we proposed an overweight + obesity (OW + OB) variable by arithmetically adding the frequency of overweight individuals plus the frequency of individuals with obesity. According to the reference values suggested in previous reports in the literature, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertriglyceridemia were considered as having FPG ≥ 100 mg/dL, TC ≥ 200 mg/dL, and TG ≥ 150 mg/dL, respectively [23,24,25]. Due to the lack of consensus regarding the reference value for IR measured by the TyG index in Mexicans, for this study, we created groups of low, medium, and high TyG index (according to the tertiles of the row data: Low ≤ 8.5; Medium = 8.5–8.9; High ≥ 8.9). We considered individuals with IR as those who presented the highest values of the TyG index in the study, which corresponds to the third tertile of TyG index values (TyG ≥ 8.9).
2.5. Serum Cu Quantification by ICP-MS
Serum Cu level quantification was carried out with Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS iCAP Q, Thermo Scientific, Bremen, Germany) in the kinetic energy discrimination (KED) mode. The amount of volume analyzed was 200 μL of serum following the protocol proposed by Rios-Lugo et al. [22]. The destruction of the organic matter in the sample was performed using acid digestion in a microwave system (MARS6 CEM, Matthews, NC, USA). All samples were recovered and diluted to 10 mL with 2% v/v high-purity HNO3 for Cu analysis by ICP-MS. Finally, Cu quantification was realized by an external calibration curve of Cu (10, 25, 50, 100, 150, 200, 500, and 1000 μg L−1). For total serum, the Cu concentration obtained considered the final volume, serum volume, blanks of samples, and recovery of an internal standard of indium (1 μg L−1). Concentrated high-purity nitric acid (Milestone Duopur system Milestonesrl, Sorisole, Italia) and high-purity water with >18 MΩ cm (Milli-Q® system Millipore, Mexico City, Mexico) were used in all processes. The Cu standard used in this study was obtained from the High-Purity Standards.
2.6. Statically Analysis
The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to evaluate normality in the continuous data [26] and the rank-based inverse normal transformation was used to transform the variables without normal distribution (BMI, serum levels of FPG, TC, TG, Cu, and TyG index; Appendix A). Student’s t- and Chi-square tests were used to compare continuous data and frequencies between individuals with normal weight and individuals that were overweight and obese. To evaluate the association of overweight and obesity status with serum Cu levels, a linear regression model adjusted for age, sex, and locality was employed. The association of cardiometabolic traits as continue variable (BMI, FPG, TC, TG, and TyG index) with serum Cu level was evaluated with linear regression in two models. Model 1: adjusted for age, sex, and locality. Model 2: adjusted for age, sex, locality, and overweight and obesity status. A logistic regression model adjusted for age, sex, locality, overweight and obesity status, was used to evaluate the association of binary cardiometabolic traits (overweight and obesity status, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and IR) with high serum Cu levels. The association analysis of overweight and obesity status with high serum Cu levels only was adjusted for age, sex, and locality. Based on the raw data, we created tertiles of serum Cu (Tertile 1 ≤ 69.418 µg dL−1; Tertile 2 = 69.418–129.397 µg dL−1; Tertile 3 ≥ 129.397 µg dL−1). Individuals in the tertile 3 (≥129.397 µg dL−1) were considered with high serum Cu levels. The software SPSS (version 22.0, IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used to perform the statistical analysis and a two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Description of the Study Samples
Table 1 shows the general characteristics of 346 Mexican adults, 107 (30.9%) with normal weight and 239 (69.1%) with overweight and obesity. The variables, BMI, FPG, TC, TG, and TyG index were significantly higher in the overweight and obesity group with respect to the normal weight group (p ≤ 0.007). The frequency of women and age were no different between groups (p ≥ 0.264).

Table 1.
General characteristics of study participants according to body weight status.
3.2. Association of Overweight and Obesity Status with Serum Cu Level
The mean serum Cu level was higher in subjects with overweight and obesity (137.755 ± 68.455 μg dL−1) compared with the normal weight group (113.366 ± 52.214 μg dL−1; p = 0.001; Figure 1). In a linear regression model adjusted for age, sex, and locality, overweight and obesity status were positively associated with serum Cu levels (β = 19.434 ± 7.309, p = 0.008, Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Association of overweight and obesity with serum Cu levels. Analysis by linear regression model adjusted for age, sex, and location. Abbreviations: Cu, copper; NW, normal weight; OW + OB, overweight and obesity status. Sample size: NW = 107; OW + OB = 239.
3.3. Association between Serum Cu Level and Cardiometabolic Traits
The association analysis between cardiometabolic traits and serum Cu levels, before and after adjustment for overweight and obesity status, is presented in Table 2. No significant association was found between BMI, FPG, TC, and serum Cu levels, before (p ≥ 0.055) and after (p ≥ 0.175) adjustment for overweight and obesity status. The TG level and TyG index were significantly associated with increased serum Cu level (TG: β = 0.188 ± 0.045, p < 0.001; TyG: β = 0.002 ± 0.001, p < 0.001). The positive association of the TG level and TyG index with serum Cu level remained significant after adjustment for overweight and obesity status (TG: β = 0.160 ± 0.045, p < 0.001; TyG: β = 0.001 ± 0.001, p < 0.001).

Table 2.
Association between serum Cu level and cardiometabolic traits.
3.4. Association of Binary Cardiometabolic Traits with High Serum Cu Level
We assessed the association of binary cardiometabolic traits (overweight and obesity status, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and IR) with high serum Cu level (Figure 2). No significant association was found between hyperglycemia (p = 0.337), hypercholesterolemia (p = 0.675), and high serum Cu level (Figure 2). However, overweight and obesity status (odds ratio [OR] = 1.9, 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 1.1–3.4, p = 0.014), hypertriglyceridemia (OR = 3.0, 95% CI 1.7–5.3, p <0.001), and IR (OR = 2.6, 95% CI 1.4–4.6, p = 0.001) were positively associated with high serum Cu levels (Figure 2).
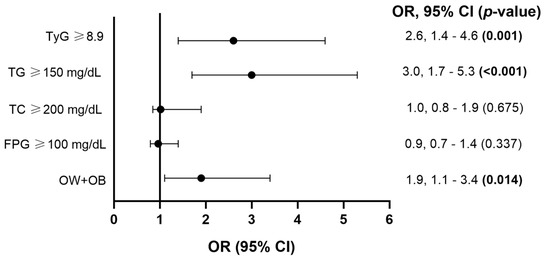
Figure 2.
Association of binary cardiometabolic traits (overweight and obesity status [OW + OB], hyperglycemia [FPG ≥ 100 mg/dL], hypercholesterolemia [TC ≥ 200 mg/dL], hypertriglyceridemia [TG ≥ 150 mg/dL], and IR [TyG ≥ 8.9]) with high serum Cu level. Abbreviations: FPG, fasting plasma glucose; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; TyG, triglycerides glucose index; OR, odds ratio, 95% CI, 95% confidence interval. Analysis by logistic regression model adjusted for age, sex, locality, and overweight and obesity status. Significant p-values (<0.05) are represented in bold. The association analysis of overweight and obesity status with high serum Cu level only was adjusted for age, sex, and locality.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we evaluated the association of overweight and obesity status and cardiometabolic traits with serum Cu levels. Our results suggest that overweight and obesity status, hypertriglyceridemia, and IR are positively associated with high serum Cu levels.
Cu is a trace element with an important role in antioxidant action and cellular metabolism, and according to balance studies, a requirement of 1.3 mg/day has been suggested for the adult population [27]. In this way, while a deficiency in Cu is associated with anemia and leukopenia, high Cu is associated with liver damage, abdominal pain, cramps, nausea, and diarrhea [27,28]. However, little has been described about the information related to the variation of Cu in serum related to the pathophysiology of metabolic diseases itself.
The results regarding the association of overweight and obesity status with serum Cu levels observed in our study are supported by previous evidence [29,30,31,32,33,34]. As an example, studies in children and adolescents have reported elevated serum Cu levels in obesity compared to normal weight groups [29,30,31]. In adults, it has been seen that individuals with obesity showed higher Cu levels in comparison to normal weight individuals [32]. As well, a positive correlation between serum Cu level and BMI has also been found [33]. These findings are consistent with a meta-analysis where it was reported that excess body mass is associated with elevated serum Cu levels [34].
To understand the relationship between overweight, obesity, and serum Cu levels, it is important to keep in mind that most of the Cu levels in serum are associated with Cu-proproteins [35], of which, semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO) and ceruloplasmin (Cp) are highly related to the pathophysiology of obesity [36,37]. Although SSAO is a Cu-dependent amine oxidase expressed in adipose tissue and involved in the uptake and storage of glucose and fatty acids [38], its increase in serum has been reported in association with obesity and hyperlipidemia [36]. A recent study evaluated the SSAO activity and Cu concentration in serum and adipose tissue of individuals that were a normal weight and obese [33]. This study reported that SSAO activity positively correlates with BMI and that Cu concentration in adipose tissue and serum correlates directly with SSO activity [33], which could suggest that the increase in adiposity that obesity involves, implies an elevation of SSAO activity in adipose tissue and serum, and consequently an elevation of Cu concentration in serum. In the case of Cp, it is an acute-phase plasma protein secreted by the liver in response to immune cells and has previously been reported in association with obesity in adult and children populations [37,39]. Nevertheless, there is evidence that obesity increases the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines from excess adiposity, especially the concentration of interleukin-6 (IL-6), which elevates the synthesis and secretion of Cp secreted by the liver [40]. Additionally, in previous studies, it has been reported that gene expression of Cp in adipose tissue is most enriched in obesity compared to individuals without obesity [41]. The case of the association of hypertriglyceridemia with the high level of serum Cu may also be explained by the serum concentration of the Cu-proproteins SSAO and Cp since both have been reported in positive association fasting plasma triglycerides in adults with metabolic syndrome [42] and in non-insulin-dependent patients with type 2 diabetes [36]. With this evidence, it may be possible to relate elevated Cu levels as another consequence of the pathophysiology of obesity.
Evidence of association between triglycerides and Cu concentration in serum or dietary Cu intake is scarce. However, our results are consistent with those reported in Chinese adult women where it was observed that the serum Cu level was positively associated with the serum triglyceride concentration [43]. Another study in children and adolescents from the U.S. reported that higher dietary Cu intake increases the risk of hypertriglyceridemia [44]. Until now, the biological mechanism to explain the relationship between serum Cu levels and hypertriglyceridemia is still unclear. Nevertheless, previous studies have suggested that the higher levels of Cu may act as pro-oxidants that affect proper lipid metabolism. Excessive Cu concentration has been observed in association with excessive Cu chelate, which is directly related to inhibiting GSH reductase, reducing GSH levels, and impaired lipid metabolism [45,46].
Although high serum Cu level is widely associated with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome [47,48,49], there is little evidence related to the association with IR. However, previous studies have shown a positive association between serum Cu levels and IR in children and adult populations [50,51]. Furthermore, in experimental animals with diabetes, has been seen that treatment with Cu chelators improves the metabolic condition and avoids metabolic complications related to this disease [52]. A possible mechanism that explains the association between IR and high serum Cu levels may be linked to the pro-oxidant effect of Cu. In an animal model, the serum Cu level has been reported in positive correlation with total reactive oxygen species level [52], which are widely related to the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and release of free fatty acids (FFA) [53], lending to IR and the risk to develop cardiovascular diseases [54]. Elevated FFA concentrations in circulation are related to increased diacylglycerols which activate signaling pathways that block insulin receptor substrate (IRS) phosphorylation, inhibiting insulin signaling and action [55]. Moreover, FFA can bind to Toll-like receptors 4 (TLR-4) in immune cells during obesity and activate the canonical nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, promoting the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines that activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) impeding the binding of IRS 1/2 to the insulin receptor and disrupting insulin signaling [56,57]. FFA can also activate NADPH oxidase (NOX), triggering the formation of reactive oxygen species, followed by the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that collectively promote an environment of inflammation and oxidative stress that induces IR [58].
Our study is one of the first reports of the association of overweight and obesity status, hypertriglyceridemia, and IR with serum Cu levels. However, these results are the product of an observational design. For this reason, we think it will be important to further evaluate the physiological mechanisms involved in these associations. Within the limitations of our study, we can mention that we analyzed individuals with overweight and obesity as a single group. Moreover, due to the high variability of the cut-off values to determine RI by TyG index, in the literature, it is still suggested to conduct more studies in populations with different ethnicities to consider the TyG index as a predictor of cardiovascular disease risk in particular populations. However, the TyG index has been used in different studies as a prognostic marker of cardiovascular disease. As an example, the TyG index has been reported in association with anthropometric markers related to overweight and obesity status (visceral fat and BMI) [59] and hypertriglyceridemia [60]. Regarding IR, the TyG index is widely used as a methodology for determining it. Such is the case in which the highest values of this index have been reported in association with harmful long-term cardiovascular events and estimated mortality risk from these causes, in important follow-up studies (123-month median follow-up) of large cohorts (16,613 individuals) [20]. Additionally, we are aware of the lack of homogeneity of our study sample (university students, professors, and potters). Studying different populations could represent different socioeconomic status that could influence the observed associations. Nevertheless, to avoid the possible effect of the socioeconomic status represented by the type of population, all association analyses in the study were adjusted by location, which is the same as the type of population. Another important limitation of our study is the lack of data related to dietary Cu intake. Previous studies describe that dietary Cu intake is directly related to serum Cu concentration. In this way, it will be interesting to evaluate in future studies whether the association of overweight and obesity status, hypertriglyceridemia, and IR with high serum Cu levels are replicated with dietary Cu intake in the Mexican population. Finally, the importance of our findings and future studies could help to understand the molecular mechanisms and treatment of metabolic diseases such as overweight and obesity status and their association with Cu. It would be important to perform follow-up studies with larger cohorts that can give us more clarity on the implications of Cu on obesity, IR, and cardiometabolic traits.
5. Conclusions
Our results suggest a positive association of overweight and obesity status, hypertriglyceridemia, and IR with high serum Cu levels (≥129.397 µg dL−1) in the sample of Mexican adults studied. This observational study contributes to the knowledge related to the understanding of the factors associated with the pathophysiology of metabolic diseases in the Mexican population. However, it is important to perform further epidemiological and molecular studies to confirm the effects of Cu on metabolic diseases and understand its role as one of the possible markers of IR pathophysiology that could be intervened to improve insulin signaling.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R.-C., M.J.R.-L., H.H.-M. and M.V.-M.; Data curation, C.J.-R., H.H.-M. and M.V.-M.; Formal analysis, A.R.-C., M.C., H.H.-M. and M.V.-M.; Funding acquisition, J.S.-S., C.A.J.-P. and H.H.-M.; Investigation, A.R.-C., M.J.R.-L., J.S.-S., C.A.J.-P., A.C.-L., C.J.-R., C.C.-R., M.C., H.H.-M. and M.V.-M.; Methodology, A.R.-C., M.J.R.-L., J.S.-S., C.A.J.-P., A.C.-L., C.J.-R., C.C.-R., M.C., H.H.-M. and M.V.-M.; Project administration, M.J.R.-L., J.S.-S., A.C.-L., C.J.-R., C.C.-R. and M.V.-M.; Resources, C.C.-R.; Supervision, M.C., H.H.-M. and M.V.-M.; Validation, H.H.-M.; Visualization, A.R.-C.; Writing—original draft, A.R.-C., M.J.R.-L., H.H.-M. and M.V.-M.; Writing—review and editing, J.S.-S., C.A.J.-P., A.C.-L., C.J.-R., C.C.-R. and M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Humanidades Ciencias y Tecnologías (CONAHCYT): Laboratorio Nacional de Ciencia, Tecnología y Gestión Integrada del Agua (Project: 315880-CONAHCYT); Instituto Politécnico Nacional, México (SIP-20220083); Laboratorio del Agua y Monitoreo Ambiental (Project: FAI-2019); CONAHCYT: Unidad de Investigación de Salud en el trabajo-IMSS (Project: PRONACE-CONAHCYT, F003-319003). Armando Ramirez-Cruz was supported by PhD fellowships from the CONAHCYT (Fellowship number 638428). Unidad de Investigación de Salud en el trabajo-IMSS: Reactivación de Protocolos de Fondo de Investigación en Salud FIS-2022, R-2017-785-052 (Project: F-CNIC-2017-36).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The data analyzed in the present study are part of protocols that were conducted according to the guidelines established in the Declaration of Helsinki and based on the Regulations of the General Health Law on Health Research in México, based on articles 14 and 16. The Ethics Committees that approved the research protocols were: Bioethics Committee of the National School of Biological Sciences, IPN (Approval register: 2022; ENCB/CEI/064/2021), Institutional Review Board of the Tapachula School Medicine of UNACH (Approval register: 2016; 03/MHT/RPR/087/17), Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Nursing and Nutrition, UASLP (Approval register: 2014; 2014–092), and Ethics Committee of the Mexican Social Security Institute (Approval register: 2016; CONBIOETICA-09-CEI-009-20160601).
Informed Consent Statement
All subjects were asked to approve their written consent.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Normality evaluation.
Table A1.
Normality evaluation.
| Trait | Shapiro–Wilk Test (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|
| Untransformed | Rank-Based Inverse Normal Transformation | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | <0.001 | 0.999 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 0.01 | 0.941 |
| TC (mg/dL) | <0.001 | 0.992 |
| TG (mg/dL) | <0.001 | 0.994 |
| TyG index | <0.001 | |
| Cu (µg dL−1) | <0.001 | 0.999 |
Shapiro–Wilk tests were performed on metabolic outcomes before and after rank-based inverse normal transformation to determine whether they were normally distributed. Significant p-values (<0.05) are represented in bold. Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; TyG index, triglycerides glucose index; Cu, copper.
References
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladher, N.; Hinton, R.; Veitch, E. Challenges of obesity and type 2 diabetes require more attention to food environment. BMJ 2023, 383, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Nonato, I.; Galvan-Valencia, O.; Hernandez-Barrera, L.; Oviedo-Solis, C.; Barquera, S. Prevalencia de obesidad y factores de riesgo asociados en adultos mexicanos: Resultados de la Ensanut 2022. Salud Publica Mex. 2023, 65, s238–s247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigeyre, M.; Yazdi, F.T.; Kaur, Y.; Meyre, D. Recent progress in genetics, epigenetics and metagenomics unveils the pathophysiology of human obesity. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 943–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattan, V.; Chang Villacreses, M.M.; Karnchanasorn, R.; Chiu, K.C.; Samoa, R. Daily Intake and Serum Levels of Copper, Selenium and Zinc According to Glucose Metabolism: Cross-Sectional and Comparative Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, P.; Thakur, V.; Chattopadhyay, M. Role of Minerals and Trace Elements in Diabetes and Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zou, Y.; Shen, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, S. Trace Elements, PPARs, and Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Moreno, M.; Sandoval-Castillo, M.; Rios-Lugo, M.J.; Klunder-Klunder, M.; Cruz, M.; Martinez-Navarro, I.; Romero-Guzman, E.T.; Victoria-Campos, C.I.; Vilchis-Gil, J.; Hernandez-Mendoza, H. Overweight and Obesity Are Positively Associated with Serum Copper Levels in Mexican Schoolchildren. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 2744–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, E.M.; da Rosa Franchi Santos, L.F.; Scavuzzi, B.M.; Iriyoda, T.M.V.; Peixe, T.S.; Lozovoy, M.A.B.; Reiche, E.M.V.; Dichi, I.; Simao, A.N.C.; Santos, M.J. Trace Elements Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Insulin Resistance. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 191, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.Y.; Soma Roy, M. Dietary copper and selenium are associated with insulin resistance in overweight and obese Malaysian adults. Nutr. Res. 2021, 93, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, D.; Barrientos, A. Mitochondrial copper metabolism and delivery to cytochrome c oxidase. IUBMB Life 2008, 60, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorklund, G.; Dadar, M.; Pivina, L.; Dosa, M.D.; Semenova, Y.; Aaseth, J. The Role of Zinc and Copper in Insulin Resistance and Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 6643–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, C.S. Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, J.J. [Methods for the measurement of insulin resistance. Hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp]. Presse Med. 1995, 24, 730–734. [Google Scholar]
- Bastard, J.P.; Lavoie, M.E.; Messier, V.; Prud’homme, D.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. Evaluation of two new surrogate indices including parameters not using insulin to assess insulin sensitivity/resistance in non-diabetic postmenopausal women: A MONET group study. Diabetes Metab. 2012, 38, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Simental-Mendia, L.E.; Gonzalez-Ortiz, M.; Martinez-Abundis, E.; Ramos-Zavala, M.G.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, S.O.; Jacques-Camarena, O.; Rodriguez-Moran, M. The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3347–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzoni, R.; Gortan Cappellari, G.; Ragni, M.; Nisoli, E. Insulin resistance in obesity: An overview of fundamental alterations. Eat. Weight. Disord. 2018, 23, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, G.; Benozzi, S.F.; Perruzza, F.; Pennacchiotti, G.L. Triglycerides and glucose index: A useful indicator of insulin resistance. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2014, 61, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdas Nayak, V.K.; Satheesh, P.; Shenoy, M.T.; Kalra, S. Triglyceride Glucose (TyG) Index: A surrogate biomarker of insulin resistance. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2022, 72, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ding, S.; Tu, J.; Xiao, G.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, R.; Liao, Y. Association between the insulin resistance marker TyG index and subsequent adverse long-term cardiovascular events in young and middle-aged US adults based on obesity status. Lipids Health Dis. 2023, 22, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Sultana, R.; Greene, M.W. Adipose tissue and insulin resistance in obese. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Lugo, M.J.; Madrigal-Arellano, C.; Gaytan-Hernandez, D.; Hernandez-Mendoza, H.; Romero-Guzman, E.T. Association of Serum Zinc Levels in Overweight and Obesity. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 198, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001, 285, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2004, 27 (Suppl. 1), S5–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic syndrome—A new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, N.M.; Wah, Y.B. Power comparisons of Shapiro-Wilk, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Lilliefors and Anderson-Darling tests. J. Stat. Model. Anal. 2011, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Turnlund, J.R. Copper nutriture, bioavailability, and the influence of dietary factors. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1988, 88, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.; Aigner, E.; Weghuber, D.; Paulmichl, K. The Potential Role of Iron and Copper in Pediatric Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 287401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Li, X.; Xiang, W.; Jiang, X. The Relationship Between Serum Copper and Overweight/Obesity: A Meta-analysis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayir, Y.; Cayir, A.; Turan, M.I.; Kurt, N.; Kara, M.; Laloglu, E.; Ciftel, M.; Yildirim, A. Antioxidant status in blood of obese children: The relation between trace elements, paraoxonase, and arylesterase values. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 160, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, S.F.; Saleh, S.H.; Elsaeed, W.F.; Elshafie, M.A.; Sherief, L.M.; Esh, A.M. Serum trace elements in obese Egyptian children: A case-control study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2014, 40, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerlikaya, F.H.; Toker, A.; Aribas, A. Serum trace elements in obese women with or without diabetes. Indian. J. Med. Res. 2013, 137, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Liu, C.N.; Wolf, R.M.; Ralle, M.; Dev, S.; Pierson, H.; Askin, F.; Steele, K.E.; Magnuson, T.H.; Schweitzer, M.A.; et al. Obesity is associated with copper elevation in serum and tissues. Metallomics 2019, 11, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, W.; Nitschke, K.; Krajewska, N.; Mongiallo, W.; Matuszak, O.; Muszynski, J.; Skrypnik, D. The Association between Excess Body Mass and Disturbances in Somatic Mineral Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Agui, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Sato, M.; Matsumoto, K. Inhibition of the copper incorporation into ceruloplasmin leads to the deficiency in serum ceruloplasmin activity in Long-Evans cinnamon mutant rat. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8965–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, Z.; Szombathy, T.; Raimondi, L.; Karadi, I.; Romics, L.; Magyar, K. Elevated serum semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase activity in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Correlation with body mass index and serum triglyceride. Metabolism 1999, 48, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignarelli, M.; DePergola, G.; Picca, G.; Sciaraffia, M.; Pannacciulli, N.; Tarallo, M.; Laudadio, E.; Turrisi, E.; Giorgino, R. Relationship of obesity and body fat distribution with ceruloplasmin serum levels. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1996, 20, 809–813. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Ralle, M.; Wolfgang, M.J.; Dhawan, N.; Burkhead, J.L.; Rodriguez, S.; Kaplan, J.H.; Wong, G.W.; Haughey, N.; Lutsenko, S. Copper-dependent amino oxidase 3 governs selection of metabolic fuels in adipocytes. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnberg, J.; Nova, E.; Moreno, L.A.; Romeo, J.; Mesana, M.I.; Ruiz, J.R.; Ortega, F.B.; Sjostrom, M.; Bueno, M.; Marcos, A.; et al. Inflammatory proteins are related to total and abdominal adiposity in a healthy adolescent population: The AVENA Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, M.; Rhodes, D.H.; Fantuzzi, G. Hematological and acute-phase responses to diet-induced obesity in IL-6 KO mice. Cytokine 2011, 56, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arner, E.; Forrest, A.R.; Ehrlund, A.; Mejhert, N.; Itoh, M.; Kawaji, H.; Lassmann, T.; Laurencikiene, J.; Ryden, M.; Arner, P.; et al. Ceruloplasmin is a novel adipokine which is overexpressed in adipose tissue of obese subjects and in obesity-associated cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e80274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, C.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Chung, Y.E.; Lee, M.S.; Hong, S.K.; Lee, K.U. Elevated serum ceruloplasmin levels in subjects with metabolic syndrome: A population-based study. Metabolism 2002, 51, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lan, C.; An, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, Q.; Ge, S.; Yu, Y.; Shen, G.; Pan, B.; Xu, Y.; et al. Potential interference on the lipid metabolisms by serum copper in a women population: A repeated measurement study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, H.; Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, X.; Li, P. Associations between dietary copper intake and hypertriglyceridemia among children and adolescents in the US. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.B.; Kang, J.H. Lipid peroxidation induced by the Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase and hydrogen peroxide system. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1999, 47, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, R.; Wember, M. Hydroxylation and O-acetylation of N-acetylneuraminic acid bound to glycoproteins of isolated subcellular membranes from porcine and bovine submaxillary glands. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 1971, 352, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, W.; Wu, J.; Liang, M. Copper in Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Plasma and Serum Studies. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 177, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.W.; Lee, Y.C.; Kuo, C.S.; Chiang, C.H.; Chang, H.H.; Huang, K.C. Association of Serum Levels of Zinc, Copper, and Iron with Risk of Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Shao, Y.; Yan, K.; Yao, T.; Liu, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y. The Link between Trace Metal Elements and Glucose Metabolism: Evidence from Zinc, Copper, Iron, and Manganese-Mediated Metabolic Regulation. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dominguez, A.; Millan-Martinez, M.; Dominguez-Riscart, J.; Mateos, R.M.; Lechuga-Sancho, A.M.; Gonzalez-Dominguez, R. Altered Metal Homeostasis Associates with Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Impaired Glucose Metabolism, and Dyslipidemia in the Crosstalk between Childhood Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouresmaeil, V.; Al Abudi, A.H.; Mahimid, A.H.; Sarafraz Yazdi, M.; Es-Haghi, A. Evaluation of Serum Selenium and Copper Levels with Inflammatory Cytokines and Indices of Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, X.K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, L. The role of zinc, copper and iron in the pathogenesis of diabetes and diabetic complications: Therapeutic effects by chelators. Hemoglobin 2008, 32, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luc, K.; Schramm-Luc, A.; Guzik, T.J.; Mikolajczyk, T.P. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Cao, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, W. Urinary copper, systemic inflammation, and blood lipid profiles: Wuhan-Zhuhai cohort study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lair, B.; Laurens, C.; Van Den Bosch, B.; Moro, C. Novel Insights and Mechanisms of Lipotoxicity-Driven Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suren Garg, S.; Kushwaha, K.; Dubey, R.; Gupta, J. Association between obesity, inflammation and insulin resistance: Insights into signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 200, 110691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Manabe, I. Toll-like receptor, lipotoxicity and chronic inflammation: The pathological link between obesity and cardiometabolic disease. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2014, 21, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, G. Obesity, insulin resistance and free fatty acids. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2011, 18, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; He, D.; Yang, G.; Ban, B.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F. Serum triglyceride glucose index is a valuable predictor for visceral obesity in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Gurrola, G.; Simental-Mendia, L.E.; Castellanos-Juarez, F.X.; Salas-Pacheco, J.M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. The triglycerides and glucose index is associated with cardiovascular risk factors in metabolically obese normal-weight subjects. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).