Effect of Fluid Intake on Acute Changes in Plasma Volume: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Pilot Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Assessment of Eligibility
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Study Visits
2.4.1. Screening (V1) and Fluid Consumption (V2–5)
2.4.2. Optimized Carbon-Monoxide Rebreathing Method (V6)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
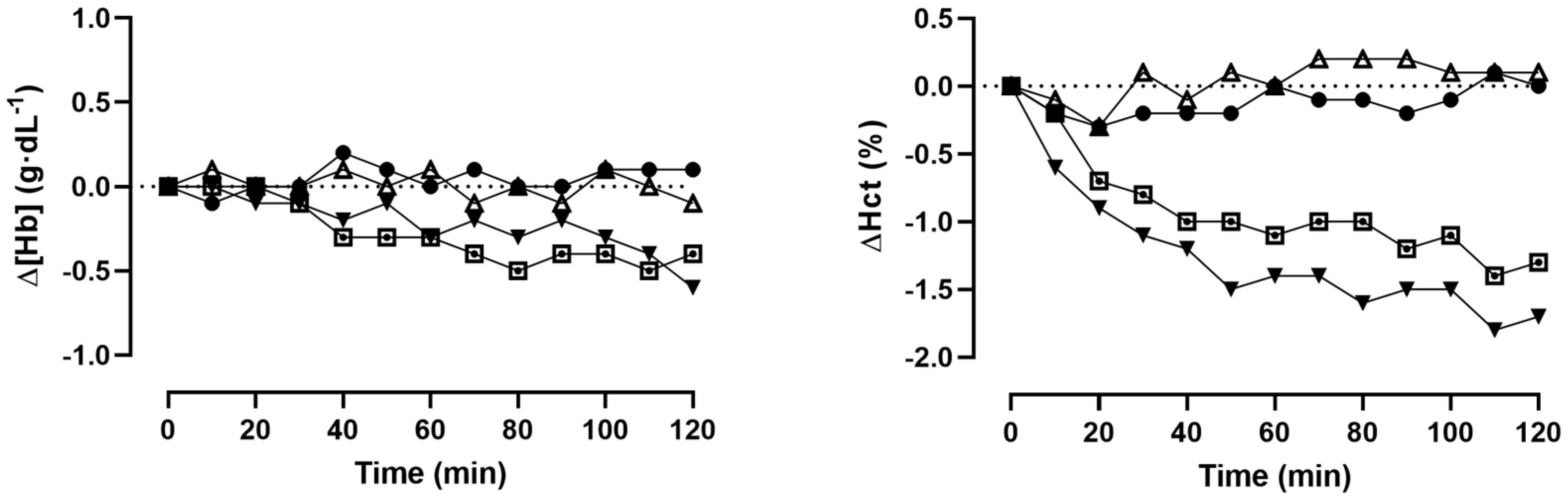
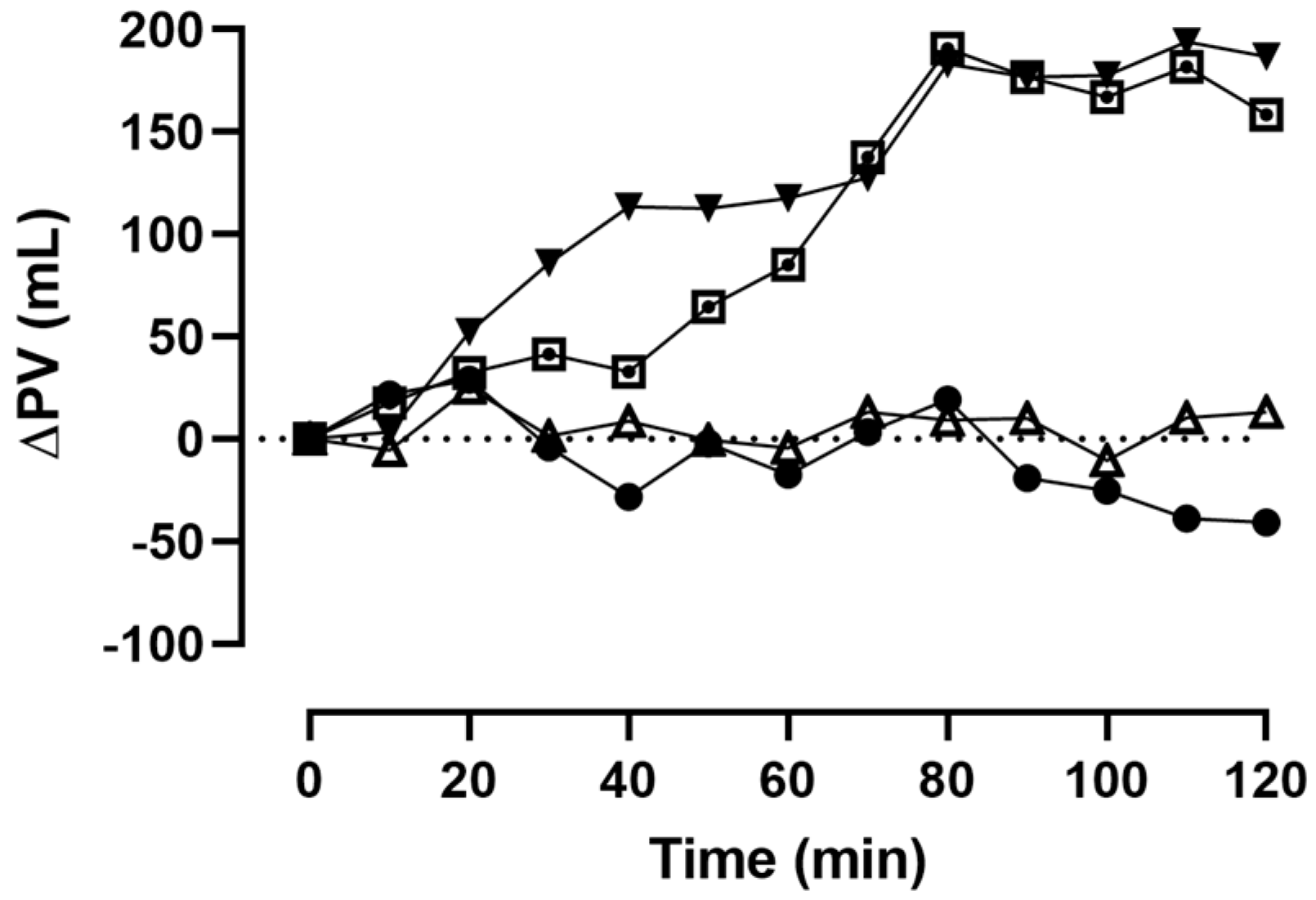
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basu, D.; Kulkarni, R. Overview of blood components and their preparation. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierbauer, J.; Ficher, S.; Zimmermann, P.; Wachsmuth, N.B.; Schmidt, W.F.J. Cardiac stroke volume in females and its correlation to blood volume and cardiac dimensions. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 895805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierbauer, J.; Hoffmeister, T.; Treff, G.; Wachsmuth, N.B.; Schmidt, W.F.J. Effect of Exercise-Induced Reductions in Blood Volume on Cardiac Output and Oxygen Transport Capacity. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 679232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skattebo, Ø.; Johansen, E.S.; Capelli, C.; Hallén, J. Effects of 150- and 450-mL Acute Blood Losses on Maximal Oxygen Uptake and Exercise Capacity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinicke, K.; Wolfarth, B.; Winchenbach, P.; Biermann, B.; Schmid, A.; Huber, G.; Friedmann, B.; Schmidt, W. Blood volume and hemoglobin mass in elite athletes of different disciplines. Int. J. Sports Med. 2001, 22, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plumb, J.O.M.; Kumar, S.; Otto, J.; Schmidt, W.; Richards, T.; Montgomery, H.E.; Grocott, M.P.W. Replicating measurements of total hemoglobin mass (tHb-mass) within a single day: Precision of measurement; feasibility and safety of using oxygen to expedite carbon monoxide clearance. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivarnik, J.M.; Goetting, M.P.; Senay, L.C. The effects of body position and exercise on plasma volume dynamics. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1986, 55, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, S.D.R.; Maughan, R.J. The effects of substrate and fluid provision on thermoregulatory and metabolic responses to prolonged exercise in a hot environment. J. Sports Sci. 2000, 18, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robach, P.; Lundby, C.; Schultz, H.; Powell, F. Plasma volume contraction at altitude: Where does the plasma go? J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 1013–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, S.; Byrnes, W.; Fleck, S. Plasma Volume during Weight Lifting. Int. J. Sports Med. 2008, 29, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, E.M.R.; Schmahl, R.M.; Senden, J.M.G.; Brouns, F. Effect of High and Low Rates of Fluid Intake on Post-exercise Rehydration. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2002, 12, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawka, M.; Convertino, V.; Eichner, E.; Schnieder, S.; Young, A. Blood Volume. Importance and Adaptations to Exercise Training, Environmental Stresses and Trauma/Sickness. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.; Prommer, N. The optimised CO-rebreathing method: A new tool to determine total haemoglobin mass routinely. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 95, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, C.; Melin, B.; Koulmann, N.; Allevard, A.M.; Launay, J.C.; Savourey, G. Plasma volume changes during and after acute variations of body hydration level in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1999, 80, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierbauer, J.R.; Günther, S.; Haupt, S.; Zimmer, R.T.; Zunner, B.E.M.; Zimmermann, P.; Wachsmuth, N.B.; Eckstein, M.L.; Aberer, F.; Sourij, H.; et al. Accuracy of Real Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring during Different Liquid Solution Challenges in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Controlled Cross-Over Trial. Sensors 2022, 22, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, G.C.; Plous, S. Research Randomizer (Version 4.0) [Computer Software]. Available online: https://randomizer.org/%0Aabout/ (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Prommer, N.; Schmidt, W. Loss of CO from the intravascular bed and its impact on the optimised CO-rebreathing method. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 100, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, C.J.; Bourdon, P.C.; Woolford, S.M.; Ostler, L.M.; Eastwood, A.; Scroop, G.C. Time and Sample Site Dependency of the Optimized CO-Rebreathing Method. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hütler, M.; Beneke, R.; Böning, D. Determination of circulating hemoglobin mass and related quantities by using capillary blood. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.J.; Wesley, R.; Leitman, S.F.; Bryant, B.J. Capillary versus venous haemoglobin determination in the assessment of healthy blood donors. Vox Sang. 2013, 104, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, G. On the behavior of the cell factor during physical work. Determinations with T-1824 (Evans blue) and radioactive chromate. Cardiologia 1965, 47, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, A.; Hopkins, W.G.; Bourdon, P.C.; Withers, R.T.; Gore, C.J. Stability of hemoglobin mass over 100 days in active men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 982–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, E.; Saunders, P.; Pyne, D.; Gore, C.; Anson, J. Effectiveness of intermittent training in hypoxia combined with live high/train low. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, R.; Bjerknes, C.; Rathgeb, I.; Altszuler, N. Glucose Uptake and Production During the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. Diabetes 1968, 17, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazi, R.C.; Dustan, H.P.; Frohlich, E.D.; Gifford, R.W.; Hoffman, G.C. Plasma Volume and Chronic Hypertension: Relationship to Arterial Pressure Levels in Different Hypertensive Diseases. Arch. Intern. Med. 1970, 125, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibblin, G.; Bergentz, S.E.; Bjure, J.; Wilhelmsen, L. Hematocrit, plasma protein, plasma volume, and viscosity in early hypertensive disease. Am. Heart J. 1966, 72, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, S.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Perreto, S.; Barberato, S.H.; Stinghen, A.E.M.; Lima, E.G.A.; Fuerbringer, R.; Sauthier, S.M.; Riella, M.C. Associations between renal function, volume status and endotoxaemia in chronic kidney disease patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 2788–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, J.L.; Finkelmeyer, A.; Petrides, G.; Frith, J.; Hodgson, T.; Maclachlan, L.; MacGowan, G.; Blamire, A.M. Reduced cardiac volumes in chronic fatigue syndrome associate with plasma volume but not length of disease: A cohort study. Open Heart 2016, 3, e000381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, H.J.; Carter, S.; Grant, S.; Tupling, R.; Coates, G.; Ali, M. Vascular volumes and hematology in male and female runners and cyclists. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1999, 79, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.A.; Rozenek, R.; DeCicco, D.M.; Carizzi, M.T.; Pham, P.H. Effect of plasma volume loss during graded exercise testing on blood lactate concentration. J. Physiol. Sci. 2007, 57, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, J.K.; Wynn, V. Effects of posture on plasma volume and some blood constituents. J. Clin. Pathol. 1960, 13, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, M.; Gledhill, N.; Jamnik, V. High VO2max with no history of training is primarily due to high blood volume. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, T. Endurance Athletes’ Stroke Volume Response to Progressive Exercise. A Critical Review. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberholzer, L.; Montero, D.; Robach, P.; Siebenmann, C.; Ryrsøe, C.K.; Bonne, T.C.; Andersen, A.B.; Bejder, J.; Karlsen, T.; Edvardsen, E.; et al. Determinants and reference values for blood volume and total hemoglobin mass in women and men. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomazo-Ravnik, T.; Jakopič, V. Changes in total body water and body fat in young women in the course of menstrual cycle. Int. J. Anthropol. 2006, 21, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Giustiniani, P.; Galloway, S.D.R. Influence of Peak Menstrual Cycle Hormonal Changes on Restoration of Fluid Balance After Induced Dehydration. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sodium-Chloride | Ringer | 5% Glucose | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium (mmol∙L−1) | 154 | 147 | 0 |
| Chloride (mmol∙L−1) | 154 | 156 | 0 |
| Potassium (mmol∙L−1) | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Calcium (mmol∙L−1) | 0 | 2.2 | 0 |
| Glucose (g∙L−1) | 0 | 0 | 50 |
| Osmotically active particles (mOsm∙L−1) | 308 | 309 | 278 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schierbauer, J.; Sanfilippo, S.; Grothoff, A.; Fehr, U.; Wachsmuth, N.; Voit, T.; Zimmermann, P.; Moser, O. Effect of Fluid Intake on Acute Changes in Plasma Volume: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Pilot Trial. Metabolites 2024, 14, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14050263
Schierbauer J, Sanfilippo S, Grothoff A, Fehr U, Wachsmuth N, Voit T, Zimmermann P, Moser O. Effect of Fluid Intake on Acute Changes in Plasma Volume: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Pilot Trial. Metabolites. 2024; 14(5):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14050263
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchierbauer, Janis, Sabrina Sanfilippo, Auguste Grothoff, Ulrich Fehr, Nadine Wachsmuth, Thomas Voit, Paul Zimmermann, and Othmar Moser. 2024. "Effect of Fluid Intake on Acute Changes in Plasma Volume: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Pilot Trial" Metabolites 14, no. 5: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14050263
APA StyleSchierbauer, J., Sanfilippo, S., Grothoff, A., Fehr, U., Wachsmuth, N., Voit, T., Zimmermann, P., & Moser, O. (2024). Effect of Fluid Intake on Acute Changes in Plasma Volume: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Pilot Trial. Metabolites, 14(5), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14050263







