Genetic Circuits for Feedback Control of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Biosynthesis in Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Media, and Inducers
2.2. Construction of GABA Production Plasmids
2.3. Construction of the gabTP Deletion in EcN
2.4. GABA Production Assays
2.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.6. Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Growth Conditions on GABA Production
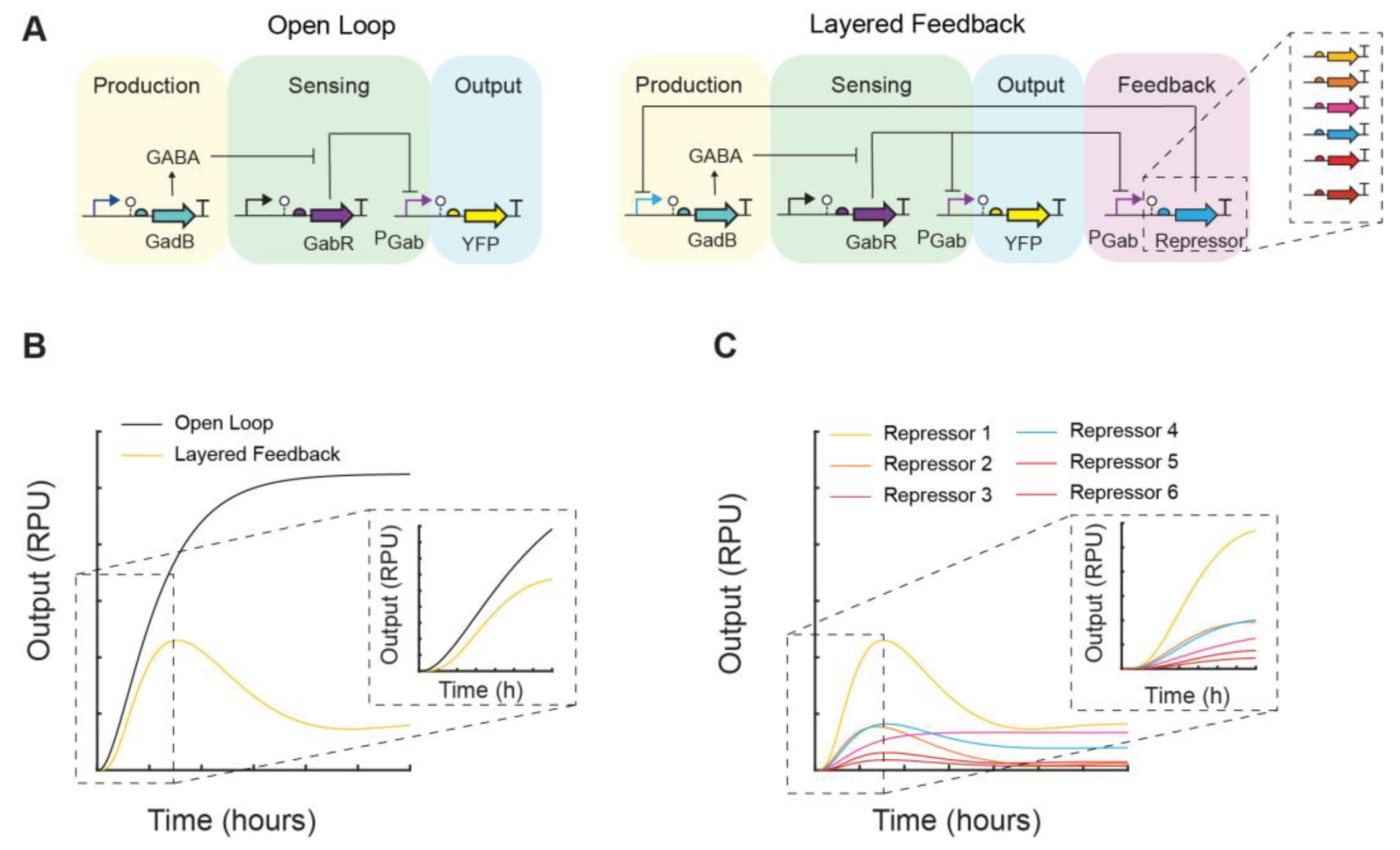
3.2. Feedback Control of GABA Production Rate
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strandwitz, P.; Kim, K.H.; Terekhova, D.; Liu, J.K.; Sharma, A.; Levering, J.; McDonald, D.; Dietrich, D.; Ramadhar, T.R.; Lekbua, A.; et al. GABA-Modulating Bacteria of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Gutiérrez, L.; San Vicente, L.; Barrón, L.J.R.; del Carmen Villarán, M.; Chávarri, M. Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Probiotics: Multiple Health Benefits and Their Future in the Global Functional Food and Nutraceuticals Market. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, E.; Steinmann, M.E. Structure, Function, and Modulation of GABAA Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40224–40231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Nutt, D.J. Role of GABA in Anxiety and Depression. Depress. Anxiety 2007, 24, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Lang, Y.; Shu, H.; Shao, J.; Cui, L. Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Epilepsy: A Review on Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 742449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus Strain Regulates Emotional Behavior and Central GABA Receptor Expression in a Mouse via the Vagus Nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, B.P.; Tabor, J.J. Engineering Diagnostic and Therapeutic Gut Bacteria. In Bugs as Drugs; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 331–361. ISBN 978-1-68367-080-3. [Google Scholar]
- Rottinghaus, A.G.; Amrofell, M.B.; Moon, T.S. Biosensing in Smart Engineered Probiotics. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 1900319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruis, W. Maintaining Remission of Ulcerative Colitis with the Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 Is as Effective as with Standard Mesalazine. Gut 2004, 53, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henker, J.; Laass, M.; Blokhin, B.M.; Bolbot, Y.K.; Maydannik, V.G.; Elze, M.; Wolff, C.; Schulze, J. The Probiotic Escherichia coli Strain Nissle 1917 (EcN) Stops Acute Diarrhoea in Infants and Toddlers. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2007, 166, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabella, V.M.; Ha, B.N.; Castillo, M.J.; Lubkowicz, D.J.; Rowe, S.E.; Millet, Y.A.; Anderson, C.L.; Li, N.; Fisher, A.B.; West, K.A.; et al. Development of a Synthetic Live Bacterial Therapeutic for the Human Metabolic Disease Phenylketonuria. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triassi, A.J.; Fields, B.D.; Monahan, C.E.; Means, J.M.; Park, Y.; Doosthosseini, H.; Padmakumar, J.P.; Isabella, V.M.; Voigt, C.A. Redesign of an Escherichia coli Nissle Treatment for Phenylketonuria Using Insulated Genomic Landing Pads and Genetic Circuits to Reduce Burden. Cell Syst. 2023, 14, 512–524.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri-Jami, M.; Abdelhamid, A.G.; Hazaa, M.; Kakuda, Y.; Griffths, M.W. Recombinant Production of Omega-3 Fatty Acids by Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveschotinunt, P.; Duraj-Thatte, A.M.; Gelfat, I.; Bahl, F.; Chou, D.B.; Joshi, N.S. Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the Delivery of Matrix-Tethered Therapeutic Domains to the Gut. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forkus, B.; Ritter, S.; Vlysidis, M.; Geldart, K.; Kaznessis, Y.N. Antimicrobial Probiotics Reduce Salmonella Enterica in Turkey Gastrointestinal Tracts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.; March, J.C. Engineered Bacterial Communication Prevents Vibrio Cholerae Virulence in an Infant Mouse Model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11260–11264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, F. Metabolic Feedback Circuits Provide Rapid Control of Metabolite Dynamics. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Y.; Murray, R.M. Layered Feedback Control Overcomes Performance Trade-off in Synthetic Biomolecular Networks. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P.; Charpin-El Hamri, G.; Folcher, M.; Zulewski, H.; Fussenegger, M. Synthetic Gene Network Restoring Endogenous Pituitary–Thyroid Feedback Control in Experimental Graves’ Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Ye, H.; Wang, H.; Charpin-El Hamri, G.; Lormeau, C.; Saxena, P.; Stelling, J.; Fussenegger, M. β-Cell–Mimetic Designer Cells Provide Closed-Loop Glycemic Control. Science 2016, 354, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.A.K.; Der, B.S.; Shin, J.; Vaidyanathan, P.; Paralanov, V.; Strychalski, E.A.; Ross, D.; Densmore, D.; Voigt, C.A. Genetic Circuit Design Automation. Science 2016, 352, aac7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, B.C.; Nielsen, A.A.K.; Tamsir, A.; Clancy, K.; Peterson, T.; Voigt, C.A. Genomic Mining of Prokaryotic Repressors for Orthogonal Logic Gates. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebovich, M.; Zeng, M.; Andrews, L.B. Algorithmic Programming of Sequential Logic and Genetic Circuits for Recording Biochemical Concentration in a Probiotic Bacterium. ACS Synth. Biol. 2023, 12, 2632–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidani, D.; Tramonti, A.; Canosa, A.V.; Campanini, B.; Maggi, S.; Milano, T.; di Salvo, M.L.; Pascarella, S.; Contestabile, R.; Bettati, S.; et al. Study of DNA Binding and Bending by Bacillus Subtilis GabR, a PLP-Dependent Transcription Factor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 3474–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovich, M.; Andrews, L. Surveying the Genetic Design Space for Transcription Factor-Based Metabolite Biosensors: Synthetic Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Propionate Biosensors in E. coli Nissle 1917. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Vo, T.D.; Kim, T.W.; Hong, S.H. Effects of Glutamate Decarboxylase and Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Transporter on the Bioconversion of GABA in Engineered Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 35, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Ren, Q.; Wang, X.; Huang, X. Enhanced Biosynthesis of γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) in Escherichia coli by Pathway Engineering. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 141, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.K.; Taylor, N.D.; Church, G.M. Biosensor-Based Engineering of Biosynthetic Pathways. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 42, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michener, J.K.; Thodey, K.; Liang, J.C.; Smolke, C.D. Applications of Genetically-Encoded Biosensors for the Construction and Control of Biosynthetic Pathways. Metab. Eng. 2012, 14, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, G.S.; Saini, M.; Miyake, R.; Ling, H.; Chang, M.W. Genetic Biosensor Design for Natural Product Biosynthesis in Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.I.; Lennen, R.M.; Herrgård, M.J.; Nielsen, A.T. Seven Gene Deletions in Seven Days: Fast Generation of Escherichia coli Strains Tolerant to Acetate and Osmotic Stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 17874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-Step Inactivation of Chromosomal Genes in Escherichia coli K-12 Using PCR Products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, L.B.; Nielsen, A.A.K.; Voigt, C.A. Cellular Checkpoint Control Using Programmable Sequential Logic. Science 2018, 361, eaap8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennacchietti, E.; Lammens, T.M.; Capitani, G.; Franssen, M.C.R.; John, R.A.; Bossa, F.; De Biase, D. Mutation of His465 Alters the pH-Dependent Spectroscopic Properties of Escherichia coli Glutamate Decarboxylase and Broadens the Range of Its Activity toward More Alkaline pH*. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 31587–31596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitani, G.; De Biase, D.; Aurizi, C.; Gut, H.; Bossa, F.; Grütter, M.G. Crystal Structure and Functional Analysis of Escherichia coli Glutamate Decarboxylase. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4027–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belitsky, B.R.; Sonenshein, A.L. GabR, a member of a novel protein family, regulates the utilization of gamma-aminobutyrate in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormack, B.P.; Valdivia, R.H.; Falkow, S. FACS-optimized mutants of the green fluorescent protein (GFP). Gene 1996, 173, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Liu, P.; Nielsen, A.A.K.; Brophy, J.A.N.; Clancy, K.; Peterson, T.; A Voigt, C. Characterization of 582 natural and synthetic terminators and quantification of their design constraints. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lebovich, M.; Lora, M.A.; Gracia-David, J.; Andrews, L.B. Genetic Circuits for Feedback Control of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Biosynthesis in Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917. Metabolites 2024, 14, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010044
Lebovich M, Lora MA, Gracia-David J, Andrews LB. Genetic Circuits for Feedback Control of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Biosynthesis in Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917. Metabolites. 2024; 14(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleLebovich, Matthew, Marcos A. Lora, Jared Gracia-David, and Lauren B. Andrews. 2024. "Genetic Circuits for Feedback Control of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Biosynthesis in Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917" Metabolites 14, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010044
APA StyleLebovich, M., Lora, M. A., Gracia-David, J., & Andrews, L. B. (2024). Genetic Circuits for Feedback Control of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Biosynthesis in Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917. Metabolites, 14(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010044






