Overweight or Obesity Rate and Risk Factors in First-Episode and Drug-Naïve Patients with Major Depressive Disorder with Comorbid Abnormal Lipid Metabolism: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
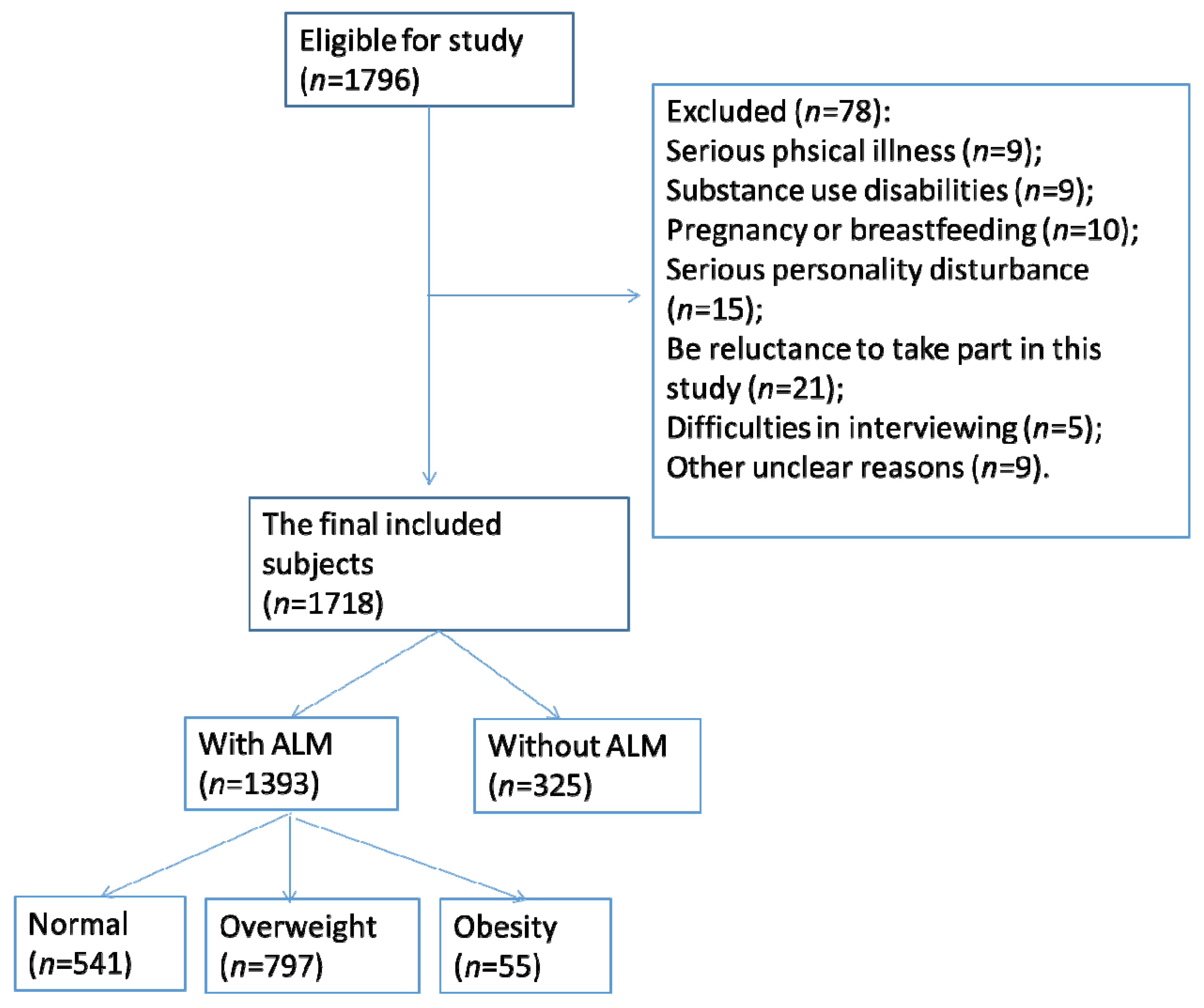
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Socio-Demographic Information Collection
2.3. Serum Assays
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Rate of Overweight and Obesity in MDD Patients with Comorbid ALM
3.2. Demographic and Clinical Variables in Overweight and Obesity in MDD Patients with Comorbid ALM
4. Discussion
5. Limitation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Ma, C.; Xu, G.; Yin, H.; Xu, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Prevalence of depressive disorders and treatment in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennis, M.; Gerritsen, L.; van Dalen, M.; Williams, A.; Cuijpers, P.; Bockting, C. Prospective biomarkers of major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homorogan, C.; Nitusca, D.; Enatescu, V.; Schubart, P.; Moraru, C.; Socaciu, C.; Marian, C. Untargeted Plasma Metabolomic Profiling in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2021, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyszkiewicz-Nwafor, M.; Jowik, K.; Dutkiewicz, A.; Krasinska, A.; Pytlinska, N.; Dmitrzak-Weglarz, M.; Suminska, M.; Pruciak, A.; Skowronska, B.; Slopien, A. Neuropeptide Y and Peptide YY in Association with Depressive Symptoms and Eating Behaviours in Adolescents across the Weight Spectrum: From Anorexia Nervosa to Obesity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, M.; Porras-Segovia, A.; Rovira, P.; Molina, E.; Gutiérrez, B.; Cervilla, J. Associations of major depressive disorder with chronic physical conditions, obesity and medication use: Results from the PISMA-ep study. Eur. Psychiatry 2019, 60, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottino, C.; Strippoli, M.P.F.; Gholam, M.; Lasserre, A.M.; Vandeleur, C.L.; Vollenweider, P.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Clair, C.; Preisig, M. Short-term and long-term effects of major depressive disorder subtypes on obesity markers and impact of sex on these associations. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 297, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.F.; Wang, L.; Pan, A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigerio, G.; Favero, C.; Savino, D.; Mercadante, R.; Albetti, B.; Dioni, L.; Vigna, L.; Bollati, V.; Pesatori, A.C.; Fustinoni, S. Plasma Metabolomic Profiling in 1391 Subjects with Overweight and Obesity from the SPHERE Study. Metabolites 2021, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Gili, M.; Visser, M.; Penninx, B.W.; Brouwer, I.A.; Montaño, J.J.; Pérez-Ara, M.Á.; García-Toro, M.; Watkins, E.; Owens, M.; et al. Soft Drinks and Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety in Overweight Subjects: A Longitudinal Analysis of an European Cohort. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F.B. The Epidemiology of Obesity: A Big Picture. Pharmacoeconomics 2015, 33, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, S.B.; Winters, K.P.; Dubbert, P.M. Overweight and obesity: Prevalence, consequences, and causes of a growing public health problem. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 331, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, R.B.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Zuckerman, H.; Park, C.; Iacobucci, M.; Lee, Y.; Tuineag, M.; Hawco, C.; Frey, B.N.; Rasgon, N.; et al. Effort-based decision-making is affected by overweight/obesity in major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 256, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.W.; Zong, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.W.; An, F.R.; Jackson, T.; Ungvari, G.S.; Xiang, Y.; Su, Y.Y.; D’Arcy, C.; Xiang, Y.T. Obesity increases the risk of depression in children and adolescents: Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 267, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, W.R.; Schienkiewitz, A.; Du, Y.; Hapke, U.; Otte, C.; Michalski, N. Comorbid depression and obesity among adults in Germany: Effects of age, sex, and socioeconomic status. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 299, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Teopiz, K.M.; McIntyre, R.S.; Chen, H. Interventions targeting comorbid depression and overweight/obesity: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 314, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patist, C.M.; Stapelberg, N.J.C.; Du Toit, E.F.; Headrick, J.P. The brain-adipocyte-gut network: Linking obesity and depression subtypes. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 18, 1121–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, J.D.; Moazzami, K.; Wittbrodt, M.T.; Nye, J.A.; Lima, B.B.; Gillespie, C.F.; Rapaport, M.H.; Pearce, B.D.; Shah, A.J.; Vaccarino, V. Diet, Stress and Mental Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Yuan, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhong, F.; Wu, Y.; Fan, X.; Bo, T.; et al. The Relationship Between Obesity and Depression Is Partly Dependent on Metabolic Health Status: A Nationwide Inpatient Sample Database Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 880230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, P.; Fu, X.; Ren, Z.; Cheng, J.; Lin, Z.; Tan, J.; Huang, B.; Huang, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. The effect of triglycerides in the associations between physical activity, sedentary behavior and depression: An interaction and mediation analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 295, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.P.; Jansen, K.; de Azevedo Cardoso, T.; Mondin, T.C.; da Silva Magalhaes, P.V.; Kapczinski, F.; de Mattos Souza, L.D.; da Silva, R.A.; Oses, J.P.; Wiener, C.D. Metabolic syndrome in subjects with bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder in a current depressive episode: Population-based study: Metabolic syndrome in current depressive episode. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 92, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, J.T.; Marsche, G. Obesity-Related Changes in High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ming, W.-K.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Using appropriate pre-pregnancy body mass index cut points for obesity in the Chinese population: A retrospective cohort study. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Yu, C.Q.; Li, L.M. Reliability and validity of depression scales of Chinese version: A systematic review. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2017, 38, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M. A rating scale for depression. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1960, 23, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, M.; Martinez, J.; Young, D.; Chelminski, I.; Dalrymple, K. Severity classification on the Hamilton depression rating scale. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 150, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br. J. Med. Psychol. 1959, 32, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, S.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Hui, C.L.; Lam, M.M.; Chiu, C.P.; Law, C.W.; Chung, D.W.; Tso, S.; Pang, E.P.; Chan, K.T.; Wong, Y.C.; et al. Maintenance treatment with quetiapine versus discontinuation after one year of treatment in patients with remitted first episode psychosis: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2010, 341, c4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yang, X.N.; Zhang, G.; Du, X.; Jia, Q.; Zhu, X.; Ma, Y.; Lang, X.; Luo, X.; et al. Psychotic symptoms in first-episode and drug naïve patients with major depressive disorder: Prevalence and related clinical factors. Depress. Anxiety 2020, 37, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kong, X.; Wang, W.; Fan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; et al. Association of peripheral differential leukocyte counts with dyslipidemia risk in Chinese patients with hypertension: Insight from the China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, P.; Ren, X.; Fang, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, L. Obesity and the onset of depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older adults in China: Evidence from the CHARLS. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, G.E.; Ludman, E.J.; Linde, J.A.; Operskalski, B.H.; Ichikawa, L.; Rohde, P.; Finch, E.A.; Jeffery, R.W. Association between obesity and depression in middle-aged women. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2008, 30, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shi, X.; Tan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Tang, C.; Xu, G.; Zhang, X.; Liao, H.; Mai, X.; Chen, W.; et al. Metabolic indexes of obesity in patients with common mental disorders in stable stage. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, F.d.C.; Pereira, F.E.F.; Pereira, A.F.; Ribeiro, B.G. Overweight or obesity and abdominal obesity and their association with cardiometabolic risk factors in Brazilian schoolchildren: A cross-sectional study. Nutrition 2020, 78, 110780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klop, B.; Elte, J.W.F.; Cabezas, M.C. Dyslipidemia in obesity: Mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1218–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Guo, P.; Liu, A.; Ares, I.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Wang, X.; Anadón, A.; Martínez, M.A. The role of long noncoding RNA in lipid, cholesterol, and glucose metabolism and treatment of obesity syndrome. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 1751–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.M.; Kuang, H.Y.; Duan, B.H.; Liu, D.N.; Yu, X.Y. Effects of thyroid hormone and depression on common components of central obesity. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Du, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Mei, J.; Wu, W.; et al. High fat diet-induced obesity leads to depressive and anxiety-like behaviors in mice via AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 348, 113949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazereel, V.; Detraux, J.; Vancampfort, D.; van Winkel, R.; De Hert, M. Impact of Psychotropic Medication Effects on Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome in People With Serious Mental Illness. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 573479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drivsholm, A.; Lund, M.A.V.; Hedley, P.L.; Jespersen, T.; Christiansen, M.; Hansen, T.; Holm, J.C. Associations between thyroid-stimulating hormone, blood pressure and adiponectin are attenuated in children and adolescents with overweight or obesity. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 32, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laclaustra, M.; Moreno-Franco, B.; Lou-Bonafonte, J.M.; Mateo-Gallego, R.; Casasnovas, J.A.; Guallar-Castillon, P.; Cenarro, A.; Civeira, F. Impaired Sensitivity to Thyroid Hormones Is Associated With Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, K.; Sieminska, L. Obesity and Thyroid Axis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, T.; Yang, K.; Lang, X.; Dong, X.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Qu, M. Prevalence and risk factors of overweight and obesity in Chinese patients with first-episode drug-naïve major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 286, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Yin, Z.; Wang, L.; Peng, L. The association between depression and metabolic syndrome and its components: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, Y.; Albatineh, A.N.; Mahmoodi, H.; Gheshlagh, R.G. The relationship between depression and risk of metabolic syndrome: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.P.; Jansen, K.; Cardoso, T.A.; Mondin, T.C.; Vieira, I.S.; Magalhães, P.V.D.S.; Kapczinski, F.; Souza, L.D.M.; Silva, R.A.; Oses, J.P.; et al. Metabolic syndrome, depression and anhedonia among young adults. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 271, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, A.M.; Lahortiga-Ramos, F.; Sayon-Orea, C.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Sánchez-Villegas, A. Depression and metabolic syndrome in participants of the “Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra” (SUN) cohort study. J. Affect Disord. 2021, 284, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazziti, D.; Arone, A.; Palermo, S.; Annuzzi, E.; Cappellato, G.; Chiarantini, I.; Prete, L.D.; Dell’Osso, L. The Wicked Relationship between Depression and Metabolic Syndrome. Clin. Neuropsychiatry 2023, 20, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
| With ALM (n = 1393) | Without ALM (n = 325) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year, mean ± SD a | 35.2 (12.5) | 33.5 (11.9) | 0.028 |
| Age of onset, year, mean ± SD a | 35 (12.4) | 33.3 (11.9) | 0.031 |
| Duration of illness, year, mean ± SD a | 6.5 (4.11) | 5 (4.8) | 0.002 |
| Sex, n (%) c | 0.255 | ||
| Male | 468 (33.6) | 120 (36.9) | |
| Female | 925 (66.4) | 205 (63.1) | |
| Education, n (%) c | 0.717 | ||
| Junior high school | 342 (24.6) | 71 (21.8) | |
| Senior high school | 615 (44.1) | 145 (44.6) | |
| College | 358 (25.7) | 91 (28) | |
| Postgraduate | 78 (5.6) | 18 (5.5) | |
| Marry status, n (%) c | 999 (71.7) | 217 (66.8) | 0.077 |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean ± SD a | 24.4 (2) | 24.1 (1.7) | 0.002 |
| BMI grouping, n (%) c | 0.034 | ||
| Normal | 541 (38.8) | 151 (46.5) | |
| Overweight | 797 (57.2) | 165 (50.8) | |
| Obesity | 55 (3.9) | 9 (2.8) | |
| HAMD, mean ± SD a | 30.7 (2.8) | 28.5 (2.7) | <0.001 |
| HAMA, mean ± SD a | 21(3.5) | 19.7 (3.3) | <0.001 |
| PANSS, median [IQR] b | 7 (7.9) | 7 (7.7) | <0.001 |
| Normal (n = 541) | Overweight (n = 797) | Obesity (n = 55) | p-Value | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal vs. Overweight | Normal vs. Obesity | Overweight vs. Obesity | |||||
| Age, year, median [IQR] b | 32 (21, 45) | 36 (25, 46) | 33 (26, 43) | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.997 | 0.349 |
| Duration of illness, year, median [IQR] b | 5 (3, 8) | 6 (3, 8.5) | 5 (3, 9) | 0.014 | 0.004 | 0.705 | 0.822 |
| Age of onset, year, median [IQR] b | 32 (21, 45) | 36 (25, 46) | 32 (26, 42) | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.998 | 0.343 |
| Sex, n (%) c | 0.165 | 0.989 | 0.066 | 0.062 | |||
| Male | 179 (33.1) | 264 (33.1) | 25 (45.5) | ||||
| Female | 362 (66.9) | 533 (66.9) | 30 (54.5) | ||||
| Education, n (%) c | 0.337 | 0.476 | 0.405 | 0.151 | |||
| Junior high school | 125 (23.1) | 205 (25.7) | 12 (21.8) | ||||
| Senior high school | 239 (44.2) | 357 (44.8) | 19 (34.5) | ||||
| College | 143 (26.4) | 196 (24.6) | 19 (34.5) | ||||
| Postgraduate | 34 (6.3) | 39 (4.9) | 5 (9.1) | ||||
| Marry status, n (%) c | 365 (67.5) | 592 (74.3) | 42 (76.4) | 0.019 | 0.007 | 0.177 | 0.732 |
| BMI, kg/m2, median [IQR] b | 23.1 (22.1, 23.5) | 25.4 (24.5, 26.2) | 28.3 (28.1, 28.6) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| HAMD, mean ± SD a | 30.7 (2.9) | 30.7 (2.8) | 31.4 (2.4) | 0.255 | 0.98 | 0.107 | 0.104 |
| HAMA, mean ± SD a | 21 (3.2) | 21 (3.6) | 21.2 (3.4) | 0.975 | 0.967 | 0.837 | 0.822 |
| PANSS, median [IQR] b | 7 (7, 8) | 7 (7, 9) | 7 (7, 10) | 0.436 | 0.608 | 0.2 | 0.285 |
| CGI, median [IQR] b | 6 (5, 7) | 6 (5, 7) | 6 (6, 7) | 0.479 | 0.651 | 0.228 | 0.3 |
| A-TG, IU/Ml, median [IQR] b | 22.3 (15.1, 49.8) | 21.7 (14.4, 49) | 22.2 (14.5, 52.5) | 0.327 | 0.135 | 0.715 | 0.814 |
| A-TPO, IU/Ml, median [IQR] b | 18.9 (12.7, 35.9) | 16.7 (12, 36.2) | 17.6 (12.2, 32.7) | 0.118 | 0.399 | 0.605 | 0.769 |
| TSH, mIU/L, mean ± SD a | 4.9 (2.7) | 5.7 (2.4) | 6.4 (1.6) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.063 |
| FT3, pmol/L, mean ± SD a | 4.9 (0.7) | 4.9 (0.7) | 4.9 (0.7) | 0.454 | 0.241 | 0.87 | 0.526 |
| FT4, pmol/L, median [IQR] b | 16.4 (14.5, 18.8) | 16.5 (14.5, 18.6) | 17.6 (14.2, 19.5) | 0.154 | 0.648 | 0.085 | 0.053 |
| Blood glucose, mean ± SD a | 5.4 (0.6) | 5.5 (0.7) | 5.5 (0.6) | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.109 | 0.882 |
| TC, mmol/L, mean ± SD a | 5.4 (1.1) | 5.5 (1.1) | 5.8 (0.8) | 0.023 | 0.369 | 0.006 | 0.015 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L, mean ± SD a | 3.1 (0.9) | 3.1 (0.9) | 3.5 (1.1) | 0.005 | 0.857 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L, median [IQR] b | 1.23 (0.98, 1.44) | 1.21 (0.95, 1.37) | 1.22 (0.9, 1.4) | 0.049 | 0.015 | 0.827 | 0.926 |
| TG, mmol/L, median [IQR] b | 2.2 (1.6, 2.9) | 2.3 (1.8, 2.9) | 2.3 (1.4, 2.9) | 0.54 | 0.265 | 0.761 | 0.971 |
| SBP, mmHg, mean ± SD a | 118.5 (11.4) | 121.4 (10.4) | 123.4 (8.4) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.169 |
| DBP, mmHg, mean ± SD a | 75.7 (7) | 76.7 (6.7) | 76.7 (6.4) | 0.02 | 0.006 | 0.272 | 0.992 |
| Suicide attempt, n (%) c | 124 (22.9) | 164 (20.6) | 14 (25.5) | 0.467 | 0.306 | 0.671 | 0.389 |
| Anxiety, n (%) c | 55 (10.2) | 116 (14.6) | 9 (16.4) | 0.047 | 0.018 | 0.157 | 0.714 |
| Exhibiting psychotic symptoms, n (%) c | 54 (10.0) | 96 (12) | 8 (14.5) | 0.377 | 0.24 | 0.291 | 0.584 |
| Variable | Unadjusted Model | Model Ⅰ | Model Ⅱ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | |
| Duration of illness | 1.007 (0.983–1.032) | 0.573 | 1.007 (0.982–1.032) | 0.611 | 1.006 (0.981–1.031) | 0.667 |
| TSH | 1.156 (1.083–1.233) | <0.001 | 1.157 (1.083–1.236) | <0.001 | 1.158 (1.081–1.24) | <0.001 |
| Blood glucose | 1.121 (0.923–1.361) | 0.249 | 1.124 (0.926–1.365) | 0.238 | 1.125 (0.927–1.367) | 0.233 |
| TC | 0.879 (0.767–1.008) | 0.064 | 0.879 (0.767–1.008) | 0.064 | 0.878 (0.766–1.007) | 0.062 |
| HDL-C | 0.942 (0.633–1.401) | 0.768 | 0.941 (0.632–1.399) | 0.763 | 0.949 (0.638–1.413) | 0.798 |
| LDL-C | 0.905 (0.77–1.052) | 0.193 | 0.905 (0.78–1.052) | 0.194 | 0.905 (0.779–1.051) | 0.191 |
| SBP | 1.009 (0.995–1.022) | 0.21 | 1.008 (0.993–1.023) | 0.292 | 1.008 (0.993–1.023) | 0.299 |
| Married | 1.269 (0.964–1.672) | 0.09 | 1.262 (0.913–1.746) | 0.159 | 1.25 (0.903–1.731) | 0.179 |
| TSH Level (mIU/L) | Unadjusted Model | Model Ⅰ | Model Ⅱ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p Value | OR (95%CI) | p Value | OR (95%CI) | p Value | |
| <4.5 | Reference | |||||
| ≥4.5 | 2.332 (1.862–2.921) | <0.001 | 2.213 (1.76–2.783) | <0.001 | 2.176 (1.726–2.743) | <0.001 |
| <2.1 | Reference | |||||
| 2.1–3.55 | 3.951 (2.721–5.736) | <0.001 | 3.913 (2.693–5.687) | <0.001 | 3.845 (2.635–5.612) | <0.001 |
| 3.56–4.49 | 2.981 (1.854–4.794) | <0.001 | 3.042 (1.888–4.899) | <0.001 | 2.958 (1.825–4.792) | <0.001 |
| ≥4.5 | 1.59 (1.025–2.469) | 0.039 | 1.598 (1.028–2.484) | 0.037 | 1.596 (1.027–2.482) | 0.038 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X. Overweight or Obesity Rate and Risk Factors in First-Episode and Drug-Naïve Patients with Major Depressive Disorder with Comorbid Abnormal Lipid Metabolism: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolites 2024, 14, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010026
Huang X, Sun Y, Zhang X. Overweight or Obesity Rate and Risk Factors in First-Episode and Drug-Naïve Patients with Major Depressive Disorder with Comorbid Abnormal Lipid Metabolism: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolites. 2024; 14(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiao, Yuan Sun, and Xiangyang Zhang. 2024. "Overweight or Obesity Rate and Risk Factors in First-Episode and Drug-Naïve Patients with Major Depressive Disorder with Comorbid Abnormal Lipid Metabolism: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study" Metabolites 14, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010026
APA StyleHuang, X., Sun, Y., & Zhang, X. (2024). Overweight or Obesity Rate and Risk Factors in First-Episode and Drug-Naïve Patients with Major Depressive Disorder with Comorbid Abnormal Lipid Metabolism: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolites, 14(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010026







