Genome-Scale Metabolic Reconstruction, Non-Targeted LC-QTOF-MS Based Metabolomics Data, and Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Cannabis sativa Leaf Extracts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
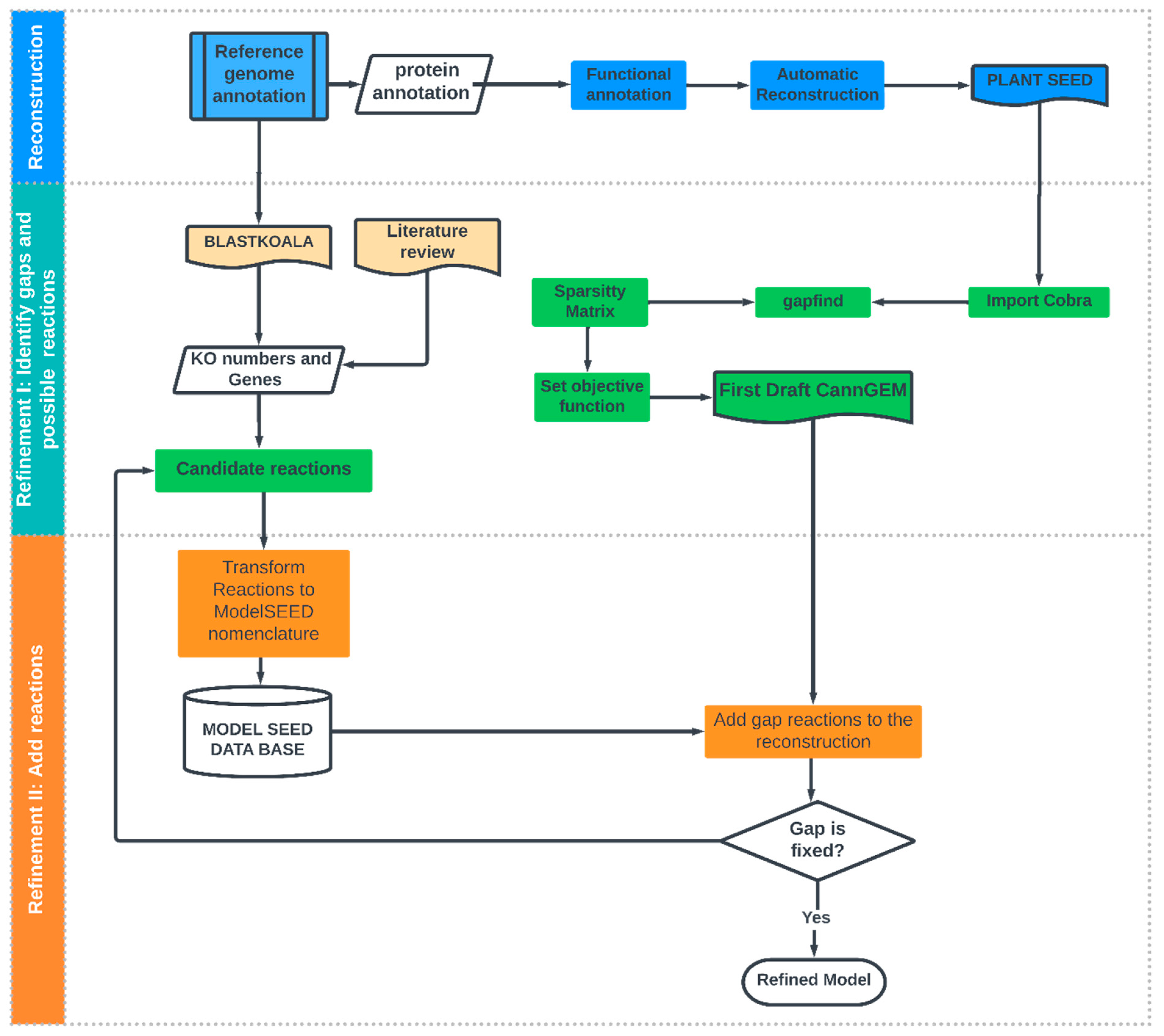
2.1. Metabolic Reconstruction
2.1.1. Functional Annotation and Automated Reconstruction
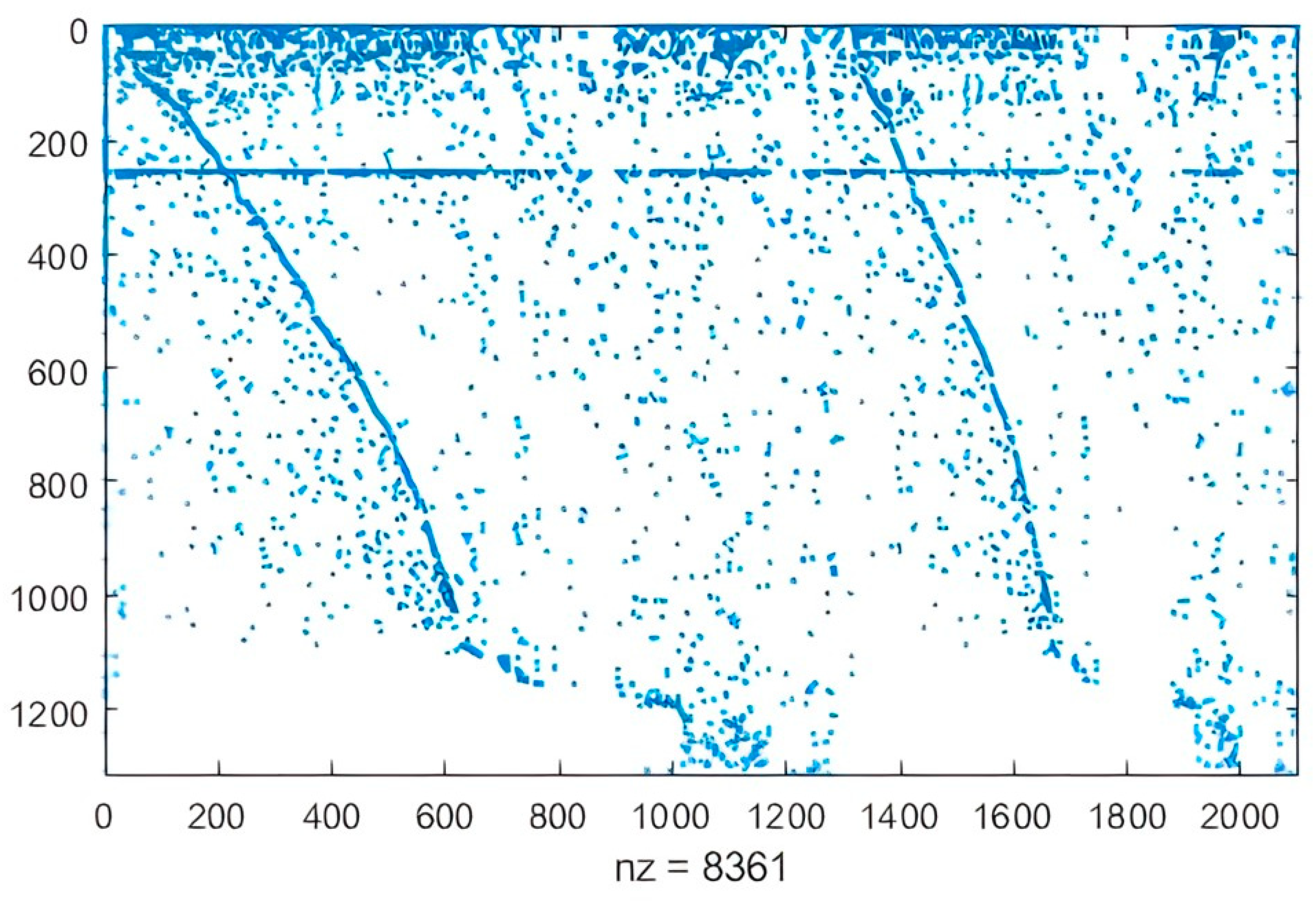
2.1.2. Refinement of Reconstruction
Identify Candidate Reactions to Fill Gaps
Add Gap Reactions to Reconstruction
2.2. Chromatographic Analysis of C. sativa Leaf: LC-PDA and RP-LC-QTOF-MS
2.2.1. Plant Material and Extraction
2.2.2. LC-PDA
2.2.3. Analysis by RP-LC-QTOF-MS
2.2.4. Data Processing
2.2.5. Cell Cytotoxicity and Anticancer Activity of C. sativa Leaf Extract
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Scale C. sativa Metabolic Reconstruction
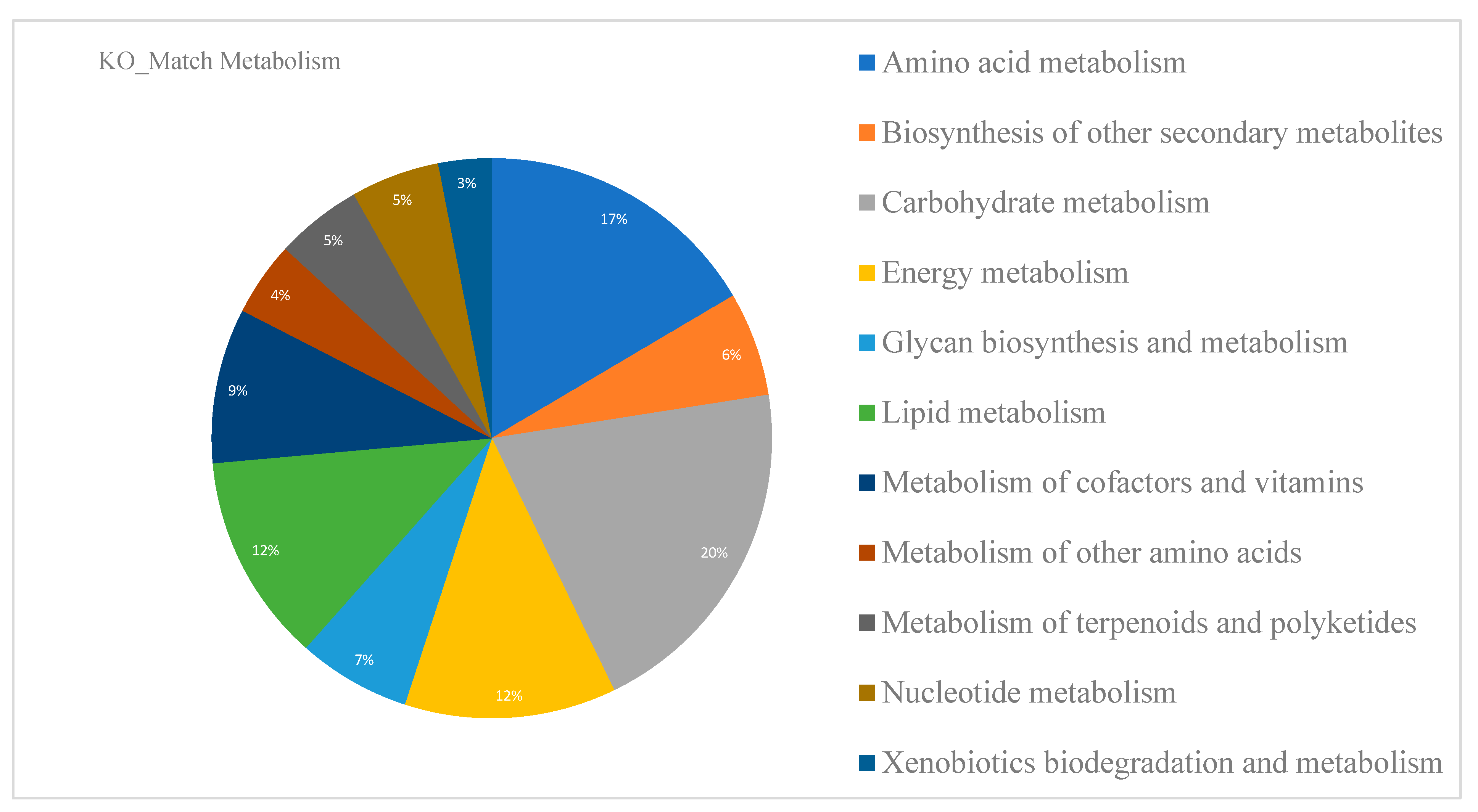
3.1.1. Functional Annotation
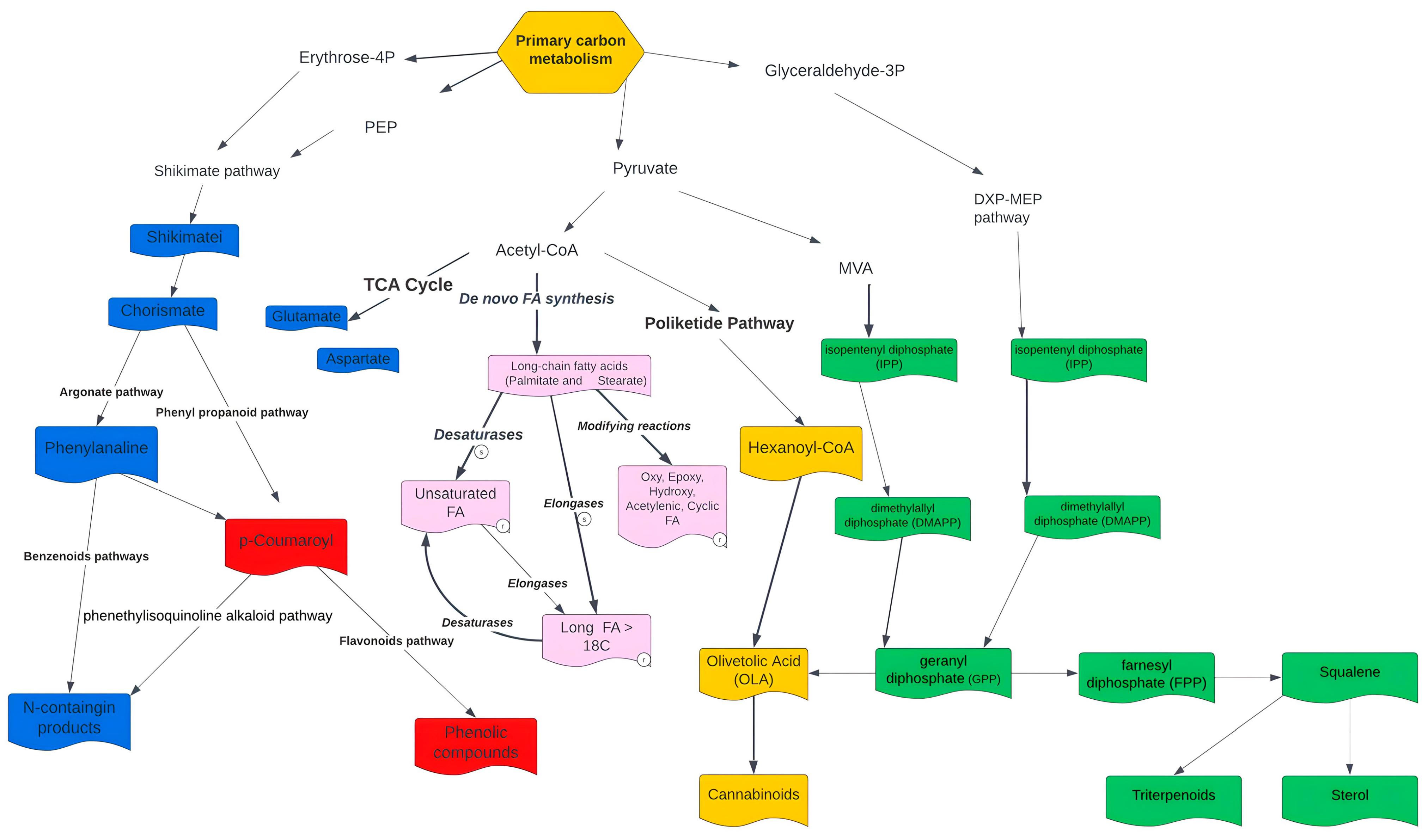
3.1.2. Secondary Metabolites Biosynthesis of C. sativa
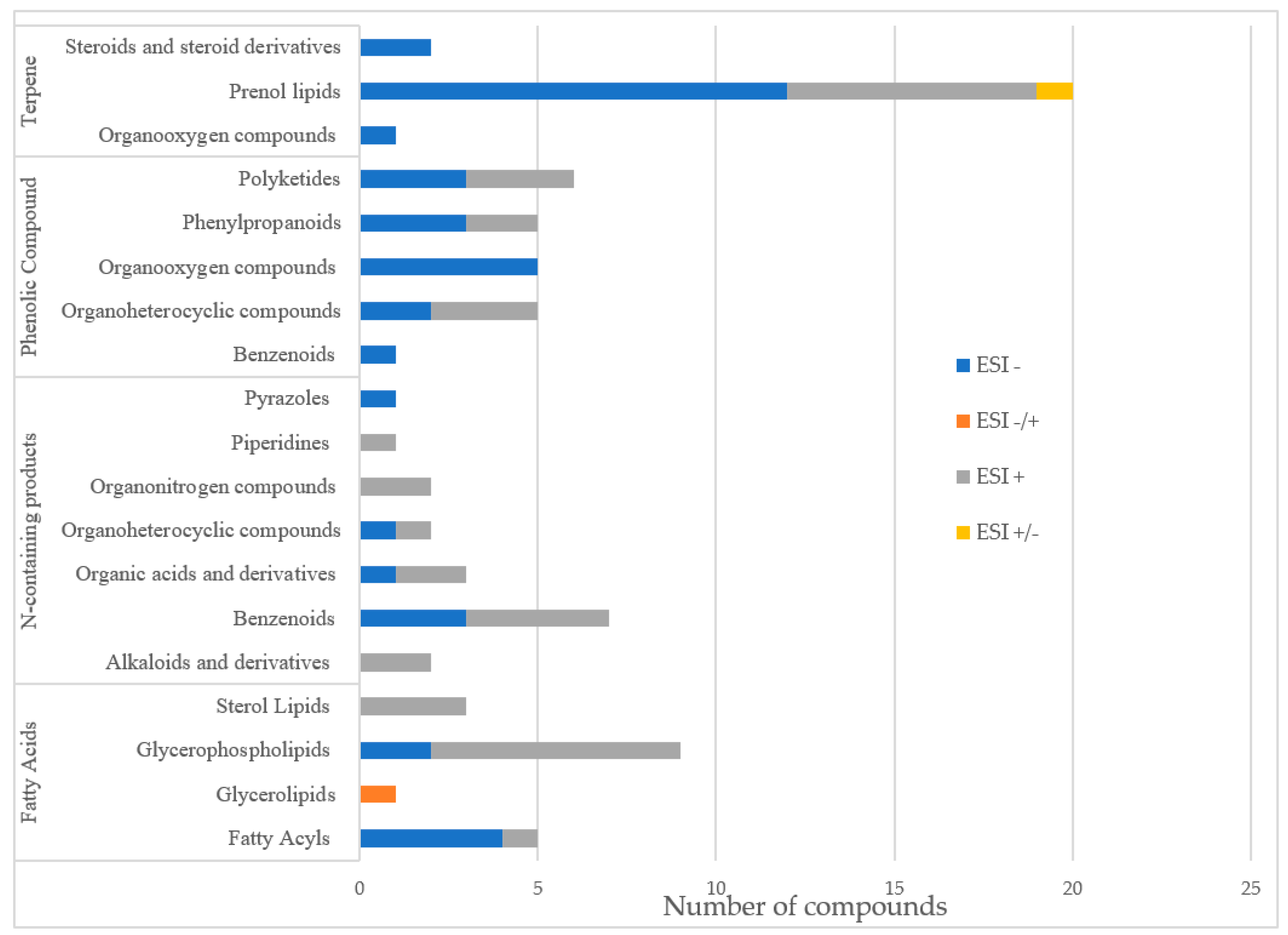
3.2. Non-Targeted LC-QTOF-MS Based Metabolomics Data
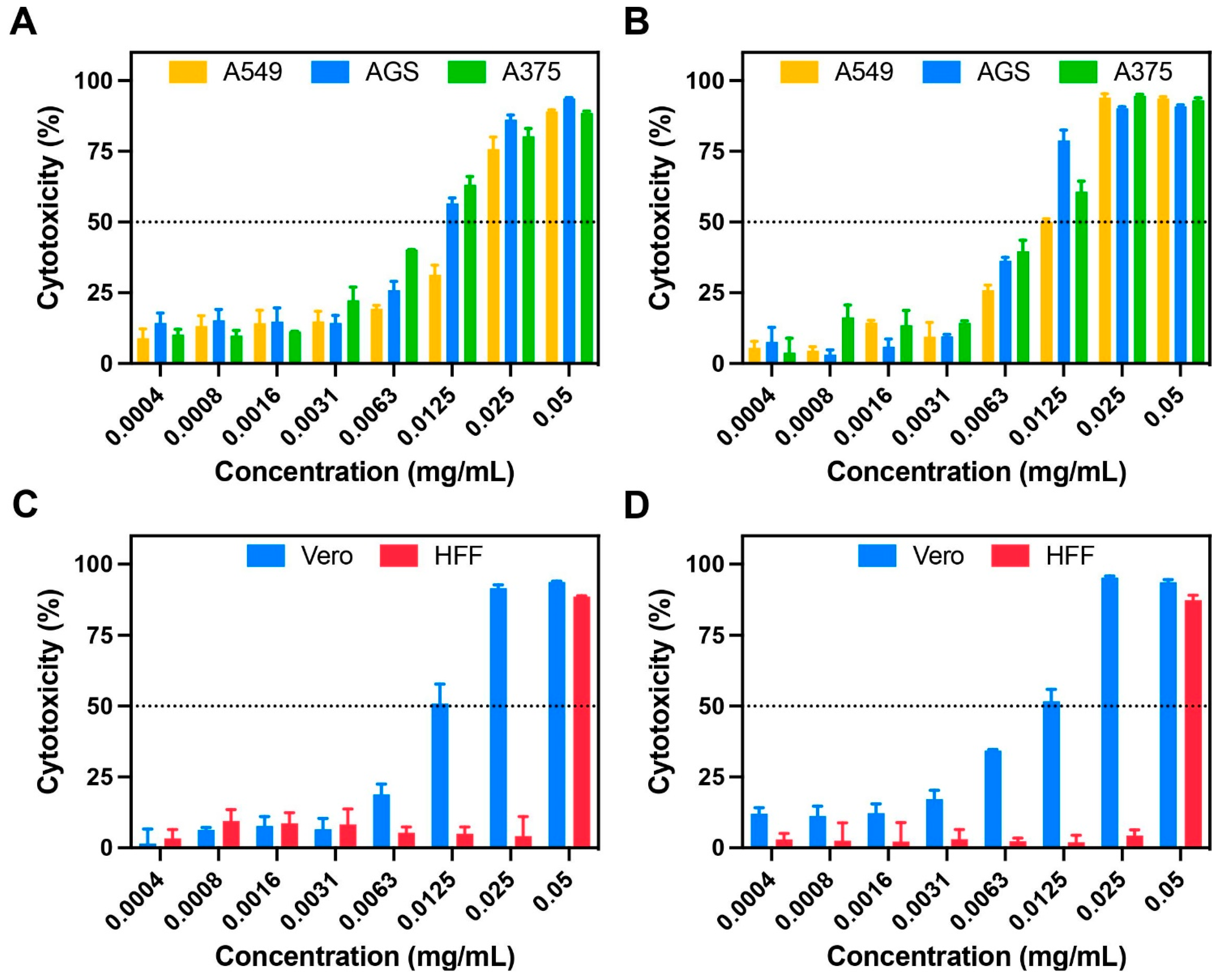
3.3. Cytotoxicity and Anticancer Activity of C. sativa Leaf Extracts
4. Discussion
4.1. GEM Reconstruction, Functional Annotation and Secondary Metabolism of C. sativa
4.2. Non-Targeted LC-QTOF-MS Based Metabolomics Data Analysis
4.2.1. N-Containing Products
4.2.2. Phenolic Compounds: Polyphenols, Phenylpropanoids, Flavonoids
4.2.3. Fatty Acids Derivates
4.2.4. Terpenes
4.3. Cytotoxicity and Anticancer Activity of C. sativa Leaf Extracts
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz, A.M.; Sanchez, F. Geografía de Los Cultivos Ilícitos y Conflicto Armado En Colombia. Doc. CEDE Sch. Econ. Univ. Andes 2004, 1, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, B.I.; Restrepo, D.; Zuleta, P.; Martínez, T. Evolución Normativa de La Industria Para Usos Médicos y Científicos En Colombia; (CESED) Centro de Estudios de Seguridad y Drogas” of the School of Economics of the Universidad de los Andes: Bogotá, Colombia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zuleta, P.; Martínez, T.; Restrepo, D.; Ramos, B. Serie Cannabis Legal: Evolución de la Normativa Mundial; (CESED) Centro de Estudios de Seguridad y Drogas” of the School of Economics of the Universidad de los Andes: Bogotá, Colombia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- González Ortiz, I.D. Resolución 315 de 2020; Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social: Bogotá, Colombia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Orejuela, W.; Molano, D.; Zea, R.; Ruiz, F.; Lombana, M.; Muñoz, V. Decreto 811 Del 23 de Julio de 2021; Presidencia de la República de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Montero, L.; Ballesteros-Vivas, D.; Gonzalez-Barrios, A.F.; Sánchez-Camargo, A. del P. Hemp Seeds: Nutritional Value, Associated Bioactivities and the Potential Food Applications in the Colombian Context. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, C.M.; Hausman, J.F.; Guerriero, G. Cannabis Sativa: The Plant of the Thousand and One Molecules. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Dai, K.; Xie, Z.; Chen, J. Secondary Metabolites Profiled in Cannabis Inflorescences, Leaves, Stem Barks, and Roots for Medicinal Purposes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3309–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Ocmín, P.G.; Marti, G.; Bonhomme, M.; Mathis, F.; Fournier, S.; Bertani, S.; Maciuk, A. Cannabinoids vs. whole metabolome: Relevance of 1 cannabinomics in analyzing Cannabis varieties. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1184, 339020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannabis Inflorescence Quality Control Monograph—American Herbal Pharmacopoeia®. Available online: https://herbal-ahp.com/collections/frontpage/products/cannabis-inflorescence-quality-control-monograph (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Lowe, H.; Steele, B.; Bryant, J.; Toyang, N.; Ngwa, W. Non-cannabinoid metabolites of cannabis sativa l. With therapeutic potential. Plants 2021, 10, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latter, H.L.; Abraham, D.J.; Turner, C.E.; Knapp, J.E.; Schiff, P.L.; Slatkin, D.J. Cannabisativine, a new alka-loid from cannabis sativa l. root. Tetrahedron Lett. 1975, 16, 2815–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, L.; Castaldo, L.; Narváez, A.; Graziani, G.; Gaspari, A.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Ritieni, A. Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Commercial Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences Using UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS. Molecules 2020, 25, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudge, E.M.; Brown, P.N.; Murch, S.J. The Terroir of Cannabis: Terpene Metabolomics as a Tool to Under-stand Cannabis sativa Selections. Planta Med. 2019, 85, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janatová, A.; Doskočil, I.; Božik, M.; Fraňková, A.; Tlustoš, P.; Klouček, P. The chemical composition of etha-nolic extracts from six genotypes of medical cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) and their selective cytotoxic activity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 353, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, J.L.; Yu, S.; Tian, L. Flavonoids in Cannabis sativa: Biosynthesis, Bioactivities, and Biotechnology. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5119–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.B. Taming THC: Potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects LINKED ARTICLES. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1344–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namdar, D.; Voet, H.; Ajjampura, V.; Nadarajan, S.; Mayzlish-Gati, E.; Mazuz, M.; Shalev, N.; Koltai, H. Terpenoids and phytocannabinoids co-produced in cannabis sativa strains show specific interaction for ell cytotoxic activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grijó, D.R.; Bidoia, D.L.; Nakamura, C.V.; Osorio, I.V.; Cardozo-Filho, L. Analysis of the antitumor activity of bioactive compounds of Cannabis flowers extracted by green solvents. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 149, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachari, A.; Piva, T.J.; Salami, S.A.; Jamshidi, N.; Mantri, N. Roles of Cannabinoids in Melanoma: Evidence from In Vivo Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltai, H.; Shalev, N. Anti-Cancer Activity of Cannabis sativa Phytocannabinoids: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential in the Fight against Ovarian Cancer and Stem Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Hudson, J.B.; Adomat, H.; Guns, E.; Cox, M.E. In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Plant-Derived Cannabidiol on Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2014, 5, 806–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, R.; Kawamura, R.; Singer, E.; Pakdel, A.; Sarma, P.; Judkins, J.; Elwakeel, E.; Dayal, S.; Martinez-Martinez, E.; Amere, M.; et al. Targeting multiple cannabinoid anti-tumour pathways with a resorcinol derivative leads to inhibition of advanced stages of breast cancer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4464–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, B.; Borrelli, F.; Pagano, E.; Cascio, M.G.; Pertwee, R.G.; Izzo, A.A. Inhibition of colon carcinogenesis by a standardized Cannabis sativa extract with high content of cannabidiol. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G.; Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E.; Alexander, S.P.H.; Di Marzo, V.; Elphick, M.R.; Greasley, P.J.; Hansen, H.S.; Kunos, G.; Mackie, K.; et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid Receptors and Their Ligands: Beyond CB 1 and CB 2. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 588–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.; Beckstead, H.D. Cannabinoid Phenotypes in Cannabis sativa. Nature 1973, 245, 5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avoxa—Mediengruppe Deutscher Apotheker GmbH, DAC/NRF: English Version, ABDA-Federal Unio. 1967. Available online: https://dacnrf.pharmazeutische-zeitung.de/ueber-uns/english-version (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Thiele, I.; Palsson, B. A protocol for generating a high-quality genome-scale metabolic reconstruction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 93–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassa, J.C. High-CBD Cannabis—BioSample—NCBI. High-CBD Cannabis. BioSample: SAMEA5040675; SRA: ERS2852417, 17 August 2017. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/biosample/SAMEA5040675 (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- McKernan, K.J.; Helbert, Y.; Kane, L.T.; Ebling, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Eaton, Z.; McLaughlin, S.; Kingan, S.; Baybayan, P.; et al. Sequence and annotation of 42 cannabis genomes reveals extensive copy number variation in cannabinoid synthesis and pathogen resistance genes. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurgobin, B.; Tamiru-Oli, M.; Welling, M.T.; Doblin, M.S.; Bacic, A.; Whelan, J.; Lewsey, M.G. Recent Advances in Cannabis sativa Genomics Research. In New Phytologist; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; Volume 230, pp. 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, D.; Huscher, E.L.; Keepers, K.G.; Givens, R.M.; Cizek, C.G.; Torres, A.; Gaudino, R.; Kane, N.C. Gene copy number is associated with phytochemistry in Cannabis sativa. AoB Plants 2019, 11, plz074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zager, J.J.; Lange, I.; Srividya, N.; Smith, A.; Lange, B.M. Gene networks underlying cannabinoid and terpenoid accumulation in cannabis. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1877–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Fasoli, E.; Boschin, G.; Lammi, C.; Zanoni, C.; Citterio, A.; Arnoldi, A. Proteomic characterization of hempseed (Cannabis sativa L.). J. Proteom. 2016, 147, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Pan, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Tang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.; Pan, G. Proanthocyanidins Alleviate Cadmium Stress in Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Plants 2022, 11, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frassinetti, S.; Moccia, E.; Caltavuturo, L.; Gabriele, M.; Longo, V.; Bellani, L.; Giorgi, G.; Giorgetti, L. Nutraceutical potential of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds and sprouts. Food Chem. 2018, 262, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Ali, V.; Khajuria, M.; Faiz, S.; Gairola, S.; Vyas, D. GC–MS based metabolomic approach to understand nutraceutical potential of Cannabis seeds from two different environments. Food Chem. 2020, 339, 128076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwonuma, C.O.; Atanu, F.O.; Okonkwo, N.C.; Egharevba, G.O.; Udofia, I.A.; Evbuomwan, I.O.; Alejolowo, O.O.; Osemwegie, O.O.; Adelani-Akande, T.; Dogunro, F.A. Evaluation of anti-malarial activity and GC–MS finger printing of cannabis: An in-vivo and in silico approach. Sci. Afr. 2022, 15, e01108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorović, J.; Joković, N.; Radulović, N.; Mihajilov-Krstev, T.; Cvetković, V.J.; Jovanović, N.; Mitrović, T.; Aleksić, A.; Stanković, N.; Bernstein, N. Antioxidant Activity of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed oil in Drosophila melanogaster Larvae under non-stress and H2O2-induced oxidative stress conditions. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal’molin, C.G.D.O.; Nielsen, L. Plant genome-scale metabolic reconstruction and modelling. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, M.; Rocha, M.; Dias, O. Exploring synergies between plant metabolic modelling and machine learning. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1885–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheunemann, M.; Brady, S.M.; Nikoloski, Z. Integration of large-scale data for extraction of integrated Arabidopsis root cell-type specific models. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Povedano, M.; Callado, C.S.-C.; Priego-Capote, F.; Ferreiro-Vera, C. Untargeted characterization of extracts from Cannabis sativa L. cultivars by gas and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry in high resolution mode. Talanta 2020, 208, 120384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassa, J.C. Cannabis sativa, Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing Project—Nucleotide—NCBI. Accession Number UZAU01000000; HARVARD OEB, Economic Herbarium of Oakes Ames, 22 Divinity Ave: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/UZAU00000000.1/ (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Seaver, S.; Lerma-Ortiz, C.; Conrad, N.; Mikaili, A.; Sreedasyam, A.; Hanson, A.D.; Henry, C.S. PlantSEED enables automated annotation and reconstruction of plant primary metabolism with improved compartmentalization and comparative consistency. Plant J. 2018, 95, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaver, S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Jeffryes, J.; Faria, J.P.; Edirisinghe, J.N.; Mundy, M.; Chia, N.; Noor, E.; Beber, M.E.; et al. The ModelSEED Database for the integration of metabolic annotations and the reconstruc-tion, com-parison, and analysis of metabolic models for plants, fungi, and microbes. bioRxiv 2020, 1, 018663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heirendt, L.; Arreckx, S.; Pfau, T.; Mendoza, S.N.; Richelle, A.; Heinken, A.; Haraldsdóttir, H.S.; Wachowiak, J.; Keating, S.M.; Vlasov, V.; et al. Creation and analysis of biochemical constraint-based models using the COBRA Toolbox v.3.0. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 639–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MathWorks, I. Matlab. Symbolic Math Toolbox 2.0; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 1–280. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Cheung, C.Y.M.; Hilbers, P.A.J.; Van Riel, N.A.W. Flux balance analysis of plant metabolism: The effect of biomass composition and model structure on model predictions. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer Protocols. Plant Metabolism Methods and Protocols Methods in Molecular Biology, 1st ed.; University of Hertfordshire: London, UK; Human Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; Available online: http://www.springer.com/series/7651 (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Kumar, V.S.; Dasika, M.S.; Maranas, C.D. Optimization based automated curation of metabolic reconstructions. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, S. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Arab. Book 2010, 8, e0137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.; Hans, J.; Matern, U. Biosynthesis of Phenylpropanoids and Related Compounds. In Biochemistry of Plant Secondary Metabolism: Second Edition; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 182–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichman, B.R. The scaffold-forming steps of plant alkaloid biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 103–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.P.; Slabas, A.R.; Rafferty, J.B. Fatty Acid Biosynthesis in Plants-Metabolic Pathways, Structure and Organization. In Lipids in Photosynthesis: Essential and Regulatory Functions; Springer Science: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ModelSEED/Model SEED Database GitHub. Github Model SEED Database/Biochemistry. Github, Inc. Available online: https://github.com/ModelSEED/ModelSEEDDatabase/tree/master/Biochemistry (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Orth, J.D.; Thiele, I.; Palsson, B.Ø. What is flux balance analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kind, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Ma, Y.; Lai, Z.; Mehta, S.S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Barupal, D.K.; Showalter, M.R.; Arita, M.; et al. Identification of small molecules using accurate mass MS/MS search. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, N.; Khan, M.N.; Ali, A.; Khadim, A.; Bin Muhsinah, A.; Uddin, J.; Musharraf, S.G. Rapid analysis of flavonoids based on spectral library development in positive ionization mode using LC-HR-ESI-MS/MS. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz-Oron, S.; Meir, S.; Malitsky, S.; Ruppin, E.; Aharoni, A.; Shlomi, T. Reconstruction of Arabidopsis metabolic network models accounting for subcellular compartmentalization and tissue-specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, S.; Haraldsdóttir, H.S.; Ahookhosh, M.; Arreckx, S.; Fleming, R.M. Structural conserved moiety splitting of a stoichiometric matrix. J. Theor. Biol. 2020, 499, 110276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershenzon, J.; Fontana, A.; Burow, M.; Wittstock, U. Mixtures of plant secondary metabolites: Metabolic origins and ecological benefits. In The Ecology of Plant Secondary Metabolites: From Genes to Global Processe; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; Available online: https://www.ebsco.com/terms-of-use (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Palsson, B.O.; Abrams, M. Systems Biology: Simulation of Dynamic Network States; Cambridge University Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, M. Introduction: Biochemistry, Physiology and Ecological Functions of Secondary Metabolites. In Biochemistry of Plant Secondary Metabolism: Second Edition; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassa, C.J.; Weiblen, G.D.; Wenger, J.P.; Dabney, C.; Poplawski, S.G.; Motley, S.T.; Michael, T.P.; Schwartz, C.J. A new Cannabis genome assembly associates elevated cannabidiol (CBD) with hemp introgressed into marijuana. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 1665–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmala, L.; Damodharan Pillai Padmini Amma, Z.; Jalaj, A.V. Plant Secondary Metabolites as Nutraceuticals. In Plant Metabolites: Methods, Applications and Prospects; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Pan, H.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, Q.; Cai, Y.; Han, B. Natural Composition and Biosynthetic Pathways of Alkaloids in Medicinal Dendrobium Species. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.T.; Mole, M.L. Chemical Components of Cannabis sativa; New York University: New York, NY, USA, 1973; Volume 225. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, M. Potential of DNA Intercalating Alkaloids and Other Plant Secondary Metabolites against SARS-CoV-2 Causing COVID-19. Diversity 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ma, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Geng, Z.; Huang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. UPLC–MS-Based Non-targeted Analysis of Endogenous Metabolite Changes in the Leaves of Scabi-osa tschiliensis Grüning Induced by 6-Benzylaminopurine and Kinetin. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeil, S.D.; Nuccio, M.L.; Ziemak, M.J.; Hanson, A.D. Enhanced synthesis of choline and glycine betaine in transgenic tobacco plants that overexpress phosphoethanolamine N -methyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10001–10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth Winter A Consumer’s Dictionary of Food Additives; Three Rivers Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 6.
- Atta-ur-Rahman, Studies in Natural Products Chemistry—Volume 37. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=SHS6K_cmJMgC&pg=PA315&dq=Pipercitine&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwiVrtaazYj4AhWUkYkEHQkPAEAQ6AF6BAgHEAI#v=onepage&q=Pipercitine&f=false (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Yoo, H.; Widhalm, J.R.; Qian, Y.; Maeda, H.; Cooper, B.R.; Jannasch, A.S.; Gonda, I.; Lewinsohn, E.; Rhodes, D.; Dudareva, N. An alternative pathway contributes to phenylalanine biosynthesis in plants via a cytosolic tyrosine:phenylpyruvate aminotransferase. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Derbassi, N.; Pedrosa, M.C.; Heleno, S.; Carocho, M.; Ferreira, I.C.; Barros, L. Plant volatiles: Using Scented molecules as food additives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 122, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.M.; Chandra, S.; Gul, S.; ElSohly, M.A. Cannabinoids, Phenolics, Terpenes and Alkaloids of Cannabis. Molecules 2021, 26, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Mi, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Cao, X.; Wan, H.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Genome-wide identification of key enzyme-encoding genes and the catalytic roles of two 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase involved in flavonoid biosynthesis in Cannabis sativa L. Microb. Cell Factories 2022, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpiński, T.; Adamczak, A.; Ożarowski, M. Antibacterial activity of apigenin, luteolin, and their C-glucosides. In Proceedings of the 5th International Electronic Conference on Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmaceuticals, Online, 1–30 November 2019; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.U. Lipid Metabolism in Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aid, F. Plant Lipid Metabolism. Adv. Lipid Metab. 2019, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, S.; Bermudez, B.; Pacheco, Y.M.; Ortega, A.; Varela, L.M.; Abia, R.; Muriana, F.J. Oleic Acid: The Main Component of Olive Oil on Postprandial Metabolic Processes. In Olives and Olive Oil in Health and Disease Prevention; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Muniz, F.J.; Bastida, S.; Benedí, J. Sunflower Oil. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Jiang, X.; Ben, S.; Yuan, Q.; Su, L.; Zhang, Z.; Christiani, D.C.; Du, M.; Wang, M. Association between circulating vitamin E and ten common cancers: Evidence from large-scale Mendelian ran-domization analysis and a longitudinal cohort study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosroi, A.; Chankhampan, C.; Kietthanakorn, B.O.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Chaikul, P.; Boonpisuttinant, K.; Sainakham, M.; Manosroi, W.; Tangjai, T.; Manosroi, J. Pharmaceutical and Cosmeceutical Biological Activities of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L var. sativa) Leaf and Seed Extracts. J. Sci. 2023, 46, 180–195. Available online: http://epg.science.cmu.ac.th/ejournal/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Schanknecht, E.; Bachari, A.; Nassar, N.; Piva, T.; Mantri, N. Phytochemical Constituents and Derivatives of Cannabis sativa; Bridging the Gap in Melanoma Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamdabsri, V.; Buaban, K.; Taechowisan, T.; Phutdhawong, W.S.; Phutdhawong, W. Chemical composition of seized cannabis and its extraction for medical purposes. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 15, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.; Kim, G.B.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, S.Y. Current Status and Applications of Genome-Scale Metabolic Models. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Strategy—Plant Seed | AraGEM | |
|---|---|---|
| Reactions | 2101 | 1567 |
| Metabolites | 1314 | 1748 |
| GPR | 1462 | 5253 |
| Transport Reactions | 143 | 148 |
| Compartments | c, d, g, v, w, x, m, n, r, e, j | c, m, p, x, plastid, v |
| Strategy II—Plant Seed | |
|---|---|
| allGaps | 228 |
| rootGaps | 100 |
| downstreamGaps | 128 |
| Compound | Formula | Mass | RT (min) | Mass Error (ppm) | Adduct | DET | ID Confidence a | Area (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaloids and derivatives | ||||||||
| Neurine | C5H13NO | 103.0997 | 1.09 | 7 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.86 |
| Cannabisativine | C21H39N3O3 | 381.2991 | 5.66 | 4 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.31 |
| Benzenoids | ||||||||
| Phenylacetaldehyde | C8H8O | 120.0575 | 3.33 | 5 | [M+H-H2O]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.43 |
| Methylstyrene | C9H10 | 118.0783 | 14.59 | 6 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 2.31 |
| Phenylpropanal | C9H10O | 134.0732 | 14.59 | 5 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.65 |
| Cyclointegrin | C21H20O6 | 368.1260 | 14.87 | 0 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.61 |
| Cresol | C7H8O | 108.0575 | 16.46 | 4 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 1.25 |
| Levomethadyl Acetate | C23H31NO2 | 353.2355 | 16.99 | 6 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 1.17 |
| Hydroxy-(pentadecatrienyl)benzoic acid | C22H30O3 | 342.2195 | 17.33 | 4 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.30 |
| Fatty Acyls | ||||||||
| Corchoionol C glucoside | C19H30O8 | 386.1941 | 6.17 | 0 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 2 | 0.46 |
| Trihydroxy-octadecadienoic acid | C18H32O5 | 328.2250 | 11.14 | 1 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 2 | 0.42 |
| Octadecatetraenoic acid | C18H28O2 | 276.2089 | 15.23 | 1 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.37 |
| Hydroxyoctadecatrienic acid | C18H30O3 | 294.2195 | 15.32 | 1 | [M-H-H2O]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 1.40 |
| Palmitoleic acid | C16H30O2 | 254.2246 | 16.89 | 5 | [M+H-H2O]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.79 |
| Glycerolipids | ||||||||
| Gingerglycolipid A | C33H56O14 | 676.3670 | 14.50 | 1 | [M-H]− | ESI −/+ | Level 3 | 0.72 |
| Glycerophospholipids | ||||||||
| LPC 16:0 | C24H50NO7P | 495.3325 | 15.94 | 6 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 2 | 0.43 |
| LPC 8:0 | C16H32NO8P | 397.1866 | 16.21 | 2 | [M+HCOOH-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.98 |
| PI 41:7 | C50H83O13P | 922.5571 | 16.03 | 7 | [M+HCOOH-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.39 |
| PS O-37:2 | C43H82NO9P | 787.5727 | 16.51 | 2 | [M+Na]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.39 |
| PE 38:5 | C43H76NO8P | 765.5309 | 16.56 | 3 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.49 |
| PA O-36:4 | C39H71O7P | 682.4937 | 16.59 | 4 | [M+Na]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.72 |
| PA O-36:6 | C39H67O7P | 678.4624 | 16.64 | 6 | [M+H-H2O]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.78 |
| LPG 16:0 | C22H45O9P | 484.2801 | 16.96 | 10 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.62 |
| PG 25:3;O3 | C31H55O13P | 666.3380 | 16.67 | 9 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.37 |
| Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||
| Alloisoleucine | C6H13NO2 | 131.0946 | 1.89 | 3 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.35 |
| Dilauryl 3.3′-thiodipropionate | C30H58O4S2 | 546.3777 | 16.74 | 3 | [M+H-H2O]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.60 |
| Gly-Tyr-Tyr-Pro-Thr | C29H38N5O9 | 600.2670 | 16.99 | 6 | [M+Na]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.61 |
| Organoheterocyclic compounds | ||||||||
| delta-9-THC | C21H30O2 | 314.2246 | 15.76 | 5 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 2 | 3.71 |
| delta-9-THC | C21H30O2 | 314.2246 | 16.47 | 5 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 2 | 5.67 |
| Geranylhydroquinone | C16H22O2 | 246.1620 | 16.46 | 0 | [M-H-H2O]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 13.35 |
| methyl-(4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)-2H-chromen-ol | C16H20O2 | 244.1463 | 16.46 | 2 | [M-H]- | ESI − | Level 3 | 3.10 |
| Dimethyl-prenylchromene -carboxylic acid | C17H20O3 | 272.1413 | 16.46 | 2 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 2 | 2.09 |
| Phaeophorbide b | C35H34N4O6 | 606.2478 | 17.19 | 4 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.55 |
| Organonitrogen compounds | ||||||||
| Tetradecylamine | C14H31N | 213.2457 | 14.11 | 6 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.79 |
| Palmitoleoyl-EA | C18H35NO2 | 297.2668 | 16.31 | 8 | [M+Na]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.34 |
| Organooxygen compounds | ||||||||
| Trehalose | C12H22O11 | 342.1162 | 1.13 | 0 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 2 | 0.93 |
| Kobusone | C14H22O2 | 222.1620 | 15.83 | 3 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 2 | 0.51 |
| Methyl-pentenone | C6H10O | 98.0732 | 16.46 | 1 | [M-H-H2O]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.75 |
| Methylpicraquassioside A | C19H24O10 | 412.1369 | 16.61 | 10 | [M+Cl]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.68 |
| (carboxymethoxy)- trihydroxyoxane-carboxylic acid | C8H12O9 | 252.0481 | 16.81 | 1 | [M+HCOOH-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.61 |
| Epoxyprogesterone | C21H28O3 | 328.2038 | 17.39 | 2 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.59 |
| Phenylpropanoids | ||||||||
| Clausarinol | C24H30O6 | 414.2042 | 14.59 | 4 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 4.45 |
| 6-{[2-(dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(dimethylocta-dien-yl)-hydroxy-(3-methylbut-2-en-yl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-6-yl]oxy}-trihydroxyoxane-carboxylic acid | C36H42O12 | 666.2676 | 15.58 | 1 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.33 |
| Nevskin | C24H32O5 | 400.2250 | 16.27 | 1 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.60 |
| Methoxy-abietatrienolide | C21H28O3 | 328.2038 | 16.48 | 1 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.47 |
| Nordihydroguaiaretic acid | C18H22O4 | 302.1518 | 16.65 | 2 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.32 |
| Piperidines | ||||||||
| Pipercitine | C23H43NO | 349.3345 | 15.91 | 5 | [M+H-H2O]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 4.88 |
| Polyketides | ||||||||
| Cannabidiolic acid | C22H30O4 | 358.2144 | 16.26 | 4 | [M+H-H2O]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 7.15 |
| Cannflavin A | C26H28O6 | 436.1886 | 16.34 | 4 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 1.84 |
| Betavulgarin | C17H12O6 | 312.0634 | 16.34 | 3 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 1.18 |
| Cannflavin A | C26H28O6 | 436.1886 | 16.41 | 4 | [M+H]+ | ESI − | Level 3 | 2.55 |
| Chlorophorin | C24H28O4 | 380.1988 | 16.46 | 8 | [M+HCOOH-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.53 |
| Quercetol B | C23H28O4 | 368.1988 | 16.51 | 3 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.67 |
| Prenol lipids | ||||||||
| Icariside B8 | C19H32O8 | 388.2097 | 6.19 | 2 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.34 |
| Capsularone | C27H38O8 | 490.2567 | 11.77 | 1 | [M+HCOOH-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.66 |
| Diterpenoid EF-D | C27H38O7 | 474.2618 | 13.60 | 1 | [M+HCOOH-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 1.13 |
| Persicachrome | C25H36O3 | 384.2664 | 14.33 | 4 | [M+H-H2O]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.72 |
| Nigellic acid | C15H20O5 | 280.1311 | 14.59 | 3 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.37 |
| Yucalexin | C20H26O4 | 330.1831 | 15.67 | 4 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.49 |
| 2-(Hydroxy-methylphenyl)-5-methyl-4-hexen-3-one | C14H18O2 | 218.1307 | 15.67 | 7 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.38 |
| Tintinnadiol | C21H32O3 | 332.2351 | 15.76 | 1 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 1.21 |
| Hydroxymethylphenyl pentanone | C12H16O2 | 192.1150 | 15.76 | 5 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 2 | 0.32 |
| Dimethylrosmanol | C22H30O5 | 374.2093 | 16.00 | 1 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 2 | 0.64 |
| hydroxy-methoxy-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)benzoic acid | C13H16O4 | 236.1049 | 16.26 | 4 | [M+H-H2O]+ | ESI + | Level 2 | 0.77 |
| Lucidone B | C24H32O5 | 400.2250 | 16.28 | 1 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 2 | 1.53 |
| Pentylresorcinol | C11H16O2 | 180.1150 | 16.46 | 3 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 2 | 2.06 |
| Hyperforin | C35H52O4 | 536.3866 | 16.46 | 1 | [M-H-H2O]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.30 |
| Hydroxymethylphenyl)pentanone | C12H16O2 | 192.1150 | 16.47 | 5 | [M+H]+ | ESI +/- | Level 2 | 0.76 |
| Curzerenone | C15H18O2 | 230.1307 | 16.48 | 3 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.54 |
| Geranyl benzoate | C17H22O2 | 258.1620 | 16.49 | 6 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.33 |
| Hydroxy- Caroten-3′-one | C40H54O | 550.4175 | 16.71 | 9 | [M+Na]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.73 |
| Trimethyl-pentadecatrien-2-one | C18H30O | 262.2297 | 17.16 | 6 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 2 | 0.82 |
| Grifolin | C22H32O2 | 328.2402 | 17.66 | 3 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 0.32 |
| Pyrazoles | ||||||||
| Glyceryl lactopalmitate | C20H16N6O2S | 404.1055 | 16.23 | 8 | [M+HCOOH-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 1.38 |
| Steroids and steroid derivatives | ||||||||
| Pregnadienedione | C21H28O2 | 312.2089 | 16.48 | 0 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 2.24 |
| Neriantogenin | C23H32O4 | 372.2301 | 17.66 | 2 | [M-H]− | ESI − | Level 3 | 2.89 |
| Sterol Lipids | ||||||||
| Rhodexin A | C29H44O9 | 536.2985 | 15.43 | 1 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.45 |
| ST 27:0;O7 | C27H48O7 | 484.3400 | 16.77 | 4 | [M+H]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.35 |
| Dihomocholic acid | C26H44O5 | 436.3189 | 17.30 | 8 | [M+Na]+ | ESI + | Level 3 | 0.53 |
| Precursor | EC Number | Is It Included in CannGEM? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthocyanin biosynthesis | BZ1; anthocyanidin 3-O-glucosyltransferase | 2.4.1.115 | No |
| 3MaT1; anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside-6″-O-malonyltransferase | 2.3.1.171 | No | |
| 3MaT2; anthocyanidin 3-O-glucoside-3″,6″-O-dimalonyltransferase | 2.3.1.- | No | |
| 3GGT; anthocyanidin 3-O-glucoside 2″-O-glucosyltransferase | 2.4.1.297 | No | |
| 5GT; cyanidin 3-O-rutinoside 5-O-glucosyltransferase | 2.4.1.116 | No | |
| AA7GT; cyanidin 3-O-glucoside 7-O-glucosyltransferase (acyl-glucose) | 2.4.1.300 | No | |
| UGT79B1; anthocyanidin 3-O-glucoside 2′″-O-xylosyltransferase | 2.4.2.51 | No | |
| 3AT; anthocyanidin 3-O-glucoside 6″-O-acyltransferase | 2.3.1.215 | No | |
| 5MaT1; anthocyanin 5-O-glucoside-6′″-O-malonyltransferase | 2.3.1.172 | No | |
| 5MaT2; anthocyanin 5-O-glucoside-4′″-O-malonyltransferase | 2.3.1.214 | No | |
| UGT75C1; anthocyanidin 3-O-glucoside 5-O-glucosyltransferase | 2.4.1.298 | No | |
| AA5GT; cyanidin 3-O-glucoside 5-O-glucosyltransferase (acyl-glucose) | 2.4.1.299 | No | |
| 5AT; anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase | 2.3.1.153 | No | |
| UGAT; cyanidin-3-O-glucoside 2″-O-glucuronosyltransferase | 2.4.1.254 | No | |
| GT1; anthocyanidin 5,3-O-glucosyltransferase | 2.4.1.- | Yes | |
| 3GT; anthocyanin 3′-O-beta-glucosyltransferase | 2.4.1.238 | No | |
| Fatty acid biosynthesis | ACACA; acetyl-CoA carboxylase | 6.4.1.2 | Yes |
| ACSF3; malonyl-CoA/methylmalonyl-CoA synthetase | 6.2.1.- | Yes | |
| FASN; fatty acid synthase, animal type | 2.3.1.85 | Yes | |
| FAS1; fatty acid synthase subunit beta, fungi type | 2.3.1.86 | Yes | |
| fas; fatty acid synthase, bacteria type | 2.3.1.- | No | |
| HT2; 3-hydroxyacyl-thioester dehydratase, animal type | 4.2.1.- | No | |
| FATB; fatty acyl-ACP thioesterase B | 3.1.2.14 | Yes | |
| FATA; fatty acyl-ACP thioesterase A | 3.1.2.14 | Yes | |
| ACSL, fad; long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase | 6.2.1.3 | Yes | |
| Fatty acid degradation | ACAT, atoB; acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase | 2.3.1.9 | Yes |
| fadA, fadI; acetyl-CoA acyltransferase | 2.3.1.16 | Yes | |
| fadB; 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase/enoyl-CoA hydratase/3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA epimerase/enoyl-CoA isomerase | 1.1.1.35 | Yes | |
| fadJ; 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase/enoyl-CoA hydratase/3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA epimerase | 1.1.1.35 | Yes | |
| HAH; 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.35 | Yes | |
| HAHA; enoyl-CoA hydratase/long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 4.2.1.17 | No | |
| E1.3.3.6, ACOX1, ACOX3; acyl-CoA oxidase | 1.3.3.6 | No | |
| ACAS, bcd; butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.3.8.1 | No | |
| ACAM, acd; acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.3.8.7 | No | |
| ACAL; long-chain-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.3.8.8 | No | |
| fadE; acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.3.99.- | No | |
| ACASB; short-chain 2-methylacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.3.8.5 | No | |
| ACAVL; very long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.3.8.9 | No | |
| GCH, gcdH; glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.3.8.6 | No | |
| ACSL, fad; long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase | 6.2.1.3 | Yes | |
| CPT1A; carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase 1, liver isoform | 2.3.1.21 | No | |
| ECI1, CI; elta3-elta2-enoyl-CoA isomerase | 5.3.3.8 | No | |
| alkB1_2, alkM; alkane 1-monooxygenase | 1.14.15.3 | No | |
| hca; 3-phenylpropionate/trans-cinnamate dioxygenase ferredoxin reductase component | 1.18.1.3 | No | |
| rubB, alkT; rubredoxin---NA+ reductase | 1.18.1.1 | No | |
| AH1_7; alcohol dehydrogenase 1/7 | 1.1.1.1 | Yes | |
| frmA, AH5, adhC; S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione dehydrogenase/alcohol dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.284 | No | |
| AH6; alcohol dehydrogenase 6 | 1.1.1.1 | Yes | |
| adhE; acetaldehyde dehydrogenase/alcohol dehydrogenase | 1.2.1.10 | No | |
| ALH; aldehyde dehydrogenase (NA+) | 1.2.1.3 | Yes | |
| ALH7A1; aldehyde dehydrogenase family 7 member A1 | 1.2.1.31 | No | |
| ALH9A1; aldehyde dehydrogenase family 9 member A1 | 1.2.1.47 | No | |
| cyp_E, CYP102A, CYP505; cytochrome P450/NAPH-cytochrome P450 reductase | 1.14.14.1 | No | |
| Fatty acid elongation | HAHB; acetyl-CoA acyltransferase | 2.3.1.16 | Yes |
| HAH; 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.35 | Yes | |
| ECHS1; enoyl-CoA hydratase | 4.2.1.17 | No | |
| PPT; palmitoyl-protein thioesterase | 3.1.2.22 | Yes | |
| ELOVL1; elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein 1 | 2.3.1.199 | No | |
| HS17B12, KAR, IFA38; 17beta-estradiol 17-dehydrogenase/very-long-chain 3-oxoacyl-CoA reductase | 1.1.1.62 | No | |
| HAC, PHS1, PAS2; very-long-chain (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase | 4.2.1.134 | No | |
| TER, TSC13, CER10; very-long-chain enoyl-CoA reductase | 1.3.1.93 | No | |
| ACOT1_2_4; acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 1/2/4 | 3.1.2.2 | Yes | |
| Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | E2.5.1.54, aroF, aroG, aroH; 3-deoxy-7-phosphoheptulonate synthase | 2.5.1.54 | Yes |
| ARO1; pentafunctional AROM polypeptide | 4.2.3.4 | Yes | |
| aroKB; shikimate kinase/3-dehydroquinate synthase | 2.7.1.71 | Yes | |
| K16305; fructose-bisphosphate aldolase/6-deoxy-5-ketofructose 1-phosphate synthase | 4.1.2.13 | Yes | |
| K11646; 3-dehydroquinate synthase II | 1.4.1.24 | No | |
| aro; 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase I | 4.2.1.10 | Yes | |
| QUIB, qa-3; quinate dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.24 | No | |
| aroE; shikimate dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.25 | Yes | |
| quiA; quinate dehydrogenase (quinone) | 1.1.5.8 | No | |
| ydiB; quinate/shikimate dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.282 | Yes | |
| aroK, aroL; shikimate kinase | 2.7.1.71 | Yes | |
| aroA; 3-phosphoshikimate 1-carboxyvinyltransferase | 2.5.1.19 | Yes | |
| K24018; cyclohexadieny/prephenate dehydrogenase/3-phosphoshikimate 1-carboxyvinyltransferase | 1.3.1.43 | No | |
| aroC; chorismate synthase | 4.2.3.5 | Yes | |
| TRP3; anthranilate synthase/indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase | 4.1.3.27 | Yes | |
| trp; anthranilate phosphoribosyltransferase | 2.4.2.18 | Yes | |
| trpF; phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase | 5.3.1.24 | Yes | |
| priA; phosphoribosyl isomerase A | 5.3.1.16 | Yes | |
| trpC; indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase | 4.1.1.48 | Yes | |
| TRP; tryptophan synthase | 4.2.1.20 | Yes | |
| E5.4.99.5; chorismate mutase | 5.4.99.5 | Yes | |
| tyrA1; chorismate mutase | 5.4.99.5 | Yes | |
| tyrA; chorismate mutase/prephenate dehydrogenase | 5.4.99.5 | Yes | |
| pheA1; chorismate mutase | 5.4.99.5 | Yes | |
| pheA; chorismate mutase/prephenate dehydratase | 5.4.99.5 | Yes | |
| AROA1, aroA; chorismate mutase | 5.4.99.5 | Yes | |
| aroH; chorismate mutase | 5.4.99.5 | Yes | |
| pheB; chorismate mutase | 5.4.99.5 | Yes | |
| tyrA2; prephenate dehydrogenase | 1.3.1.12 | No | |
| TYR1; prephenate dehydrogenase (NAP+) | 1.3.1.13 | No | |
| tyrC; cyclohexadieny/prephenate dehydrogenase | 1.3.1.43 | No | |
| tyrAa; arogenate dehydrogenase (NAP+) | 1.3.1.78 | Yes | |
| pheC; cyclohexadienyl dehydratase | 4.2.1.51 | Yes | |
| AT, PT; arogenate/prephenate dehydratase | 4.2.1.91 | Yes | |
| GOT1; aspartate aminotransferase, cytoplasmic | 2.6.1.1 | Yes | |
| TAT; tyrosine aminotransferase | 2.6.1.5 | Yes | |
| hisC; histidinol-phosphate aminotransferase | 2.6.1.9 | Yes | |
| tyrB; aromatic-amino-acid transaminase | 2.6.1.57 | Yes | |
| ARO8; aromatic amino acid aminotransferase I/2-aminoadipate transaminase | 2.6.1.57 | Yes | |
| ARO9; aromatic amino acid aminotransferase II | 2.6.1.58 | Yes | |
| pdh; phenylalanine dehydrogenase | 1.4.1.20 | No | |
| IL4I1; L-amino-acid oxidase | 1.4.3.2 | No | |
| phhA, PAH; phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | 1.14.16.1 | No | |
| hphA; benzylmalate synthase | 2.3.3.- | No | |
| hphC; 3-benzylmalate isomerase | 4.2.1.- | No | |
| hphB; 3-benzylmalate dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.- | Yes | |
| xanB2; chorismate lyase/3-hydroxybenzoate synthase | 4.1.3.40 | No | |
| fkbO, rapK; chorismatase | 3.3.2.13 | No | |
| Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis | dxs; 1-deoxy--xylulose-5-phosphate synthase | 2.2.1.7 | Yes |
| dxr; 1-deoxy--xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase | 1.1.1.267 | Yes | |
| isp; 2-C-methyl--erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase | 2.7.7.60 | Yes | |
| ispE; 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl--erythritol kinase | 2.7.1.148 | Yes | |
| ispF; 2-C-methyl--erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase | 4.6.1.12 | Yes | |
| gcpE, ispG; (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl-diphosphate synthase | 1.17.7.1 | Yes | |
| ispH, lytB; 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate reductase | 1.17.7.4 | No | |
| ACAT, atoB; acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase | 2.3.1.9 | Yes | |
| HMGCS; hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase | 2.3.3.10 | Yes | |
| HMGCR; hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NAPH) | 1.1.1.34 | Yes | |
| mvaA; hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase | 1.1.1.88 | No | |
| MVK, mvaK1; mevalonate kinase | 2.7.1.36 | Yes | |
| E2.7.4.2, mvaK2; phosphomevalonate kinase | 2.7.4.2 | Yes | |
| PMVK; phosphomevalonate kinase | 2.7.4.2 | Yes | |
| MV, mva; diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase | 4.1.1.33 | Yes | |
| pmd; phosphomevalonate decarboxylase | 4.1.1.99 | No | |
| ipk; isopentenyl phosphate kinase | 2.7.4.26 | No | |
| acnX1; mevalonate 5-phosphate dehydratase large subunit | 4.2.1.- | No | |
| K25518; trans-anhydromevalonate 5-phosphate decarboxylase | 4.1.1.- | Yes | |
| ubiX, bsdB, PA1; flavin prenyltransferase | 2.5.1.129 | No | |
| E2.7.1.185; mevalonate-3-kinase | 2.7.1.185 | No | |
| E2.7.1.186; mevalonate-3-phosphate-5-kinase | 2.7.1.186 | No | |
| E4.1.1.110; bisphosphomevalonate decarboxylase | 4.1.1.110 | No | |
| idi, II; isopentenyl-diphosphate elta-isomerase | 5.3.3.2 | Yes | |
| FPS; farnesyl diphosphate synthase | 2.5.1.1 | Yes | |
| E2.5.1.68; short-chain Z-isoprenyl diphosphate synthase | 2.5.1.68 | No | |
| ZFPS; (2Z,6Z)-farnesyl diphosphate synthase | 2.5.1.92 | No | |
| E2.5.1.86; trans, polycis-decaprenyl diphosphate synthase | 2.5.1.86 | No | |
| E2.5.1.88; trans, polycis-polyprenyl diphosphate synthase | 2.5.1.88 | No | |
| hexPS, COQ1; hexaprenyl-diphosphate synthase | 2.5.1.82 | No | |
| hexs-a; hexaprenyl-diphosphate synthase small subunit | 2.5.1.83 | No | |
| hepS; heptaprenyl diphosphate synthase component 1 | 2.5.1.30 | Yes | |
| ispB; octaprenyl-diphosphate synthase | 2.5.1.90 | No | |
| SPS, sds; all-trans-nonaprenyl-diphosphate synthase | 2.5.1.84 | Yes | |
| PSS1; decaprenyl-diphosphate synthase subunit 1 | 2.5.1.91 | No | |
| uppS; undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase | 2.5.1.31 | No | |
| NUS1; dehydrodolichyl diphosphate syntase complex subunit NUS1 | 2.5.1.87 | No | |
| uppS, cpdS; tritrans, polycis-undecaprenyl-diphosphate synthase [geranylgeranyl-diphosphate specific | Yes | ||
| chlP, bchP; geranylgeranyl diphosphate/geranylgeranyl-bacteriochlorophyllide a reductase | 1.3.1.83 | No | |
| ispS; isoprene synthase | 4.2.3.27 | No | |
| FNTA; protein farnesyltransferase/geranylgeranyltransferase type-1 subunit alpha | 2.5.1.58 | No | |
| RCE1, FACE2; prenyl protein peptidase | 3.4.22.- | No | |
| STE24; STE24 endopeptidase | 3.4.24.84 | No | |
| ICMT, STE14; protein-S-isoprenylcysteine O-methyltransferase | 2.1.1.100 | No | |
| PCME; prenylcysteine alpha-carboxyl methylesterase | 3.1.1.- | No | |
| PCYOX1, FCLY; prenylcysteine oxidase/farnesylcysteine lyase | 1.8.3.5 | No | |
| FOHSR; NAP+-dependent farnesol dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.216 | No | |
| FLH; NA+-dependent farnesol dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.354 | No | |
| FOLK; farnesol kinase | 2.7.1.216 | No | |
| K15793; acyclic sesquiterpene synthase | 4.2.3.49 | No | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camargo, F.D.G.; Santamaria-Torres, M.; Cala, M.P.; Guevara-Suarez, M.; Restrepo, S.R.; Sánchez-Camargo, A.; Fernández-Niño, M.; Corujo, M.; Gallo Molina, A.C.; Cifuentes, J.; et al. Genome-Scale Metabolic Reconstruction, Non-Targeted LC-QTOF-MS Based Metabolomics Data, and Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Cannabis sativa Leaf Extracts. Metabolites 2023, 13, 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070788
Camargo FDG, Santamaria-Torres M, Cala MP, Guevara-Suarez M, Restrepo SR, Sánchez-Camargo A, Fernández-Niño M, Corujo M, Gallo Molina AC, Cifuentes J, et al. Genome-Scale Metabolic Reconstruction, Non-Targeted LC-QTOF-MS Based Metabolomics Data, and Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Cannabis sativa Leaf Extracts. Metabolites. 2023; 13(7):788. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070788
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamargo, Fidias D. González, Mary Santamaria-Torres, Mónica P. Cala, Marcela Guevara-Suarez, Silvia Restrepo Restrepo, Andrea Sánchez-Camargo, Miguel Fernández-Niño, María Corujo, Ada Carolina Gallo Molina, Javier Cifuentes, and et al. 2023. "Genome-Scale Metabolic Reconstruction, Non-Targeted LC-QTOF-MS Based Metabolomics Data, and Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Cannabis sativa Leaf Extracts" Metabolites 13, no. 7: 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070788
APA StyleCamargo, F. D. G., Santamaria-Torres, M., Cala, M. P., Guevara-Suarez, M., Restrepo, S. R., Sánchez-Camargo, A., Fernández-Niño, M., Corujo, M., Gallo Molina, A. C., Cifuentes, J., Serna, J. A., Cruz, J. C., Muñoz-Camargo, C., & Gonzalez Barrios, A. F. (2023). Genome-Scale Metabolic Reconstruction, Non-Targeted LC-QTOF-MS Based Metabolomics Data, and Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Cannabis sativa Leaf Extracts. Metabolites, 13(7), 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070788











