In Vitro Evaluation Reveals Effect and Mechanism of Artemether against Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Host Cells and Parasite Culture
2.2. Drug Compounds
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Anti-T. gondii Activity of Artemether Evaluated by a Plaque Assay
2.5. Effects of Artemether on Intracellular T. gondii
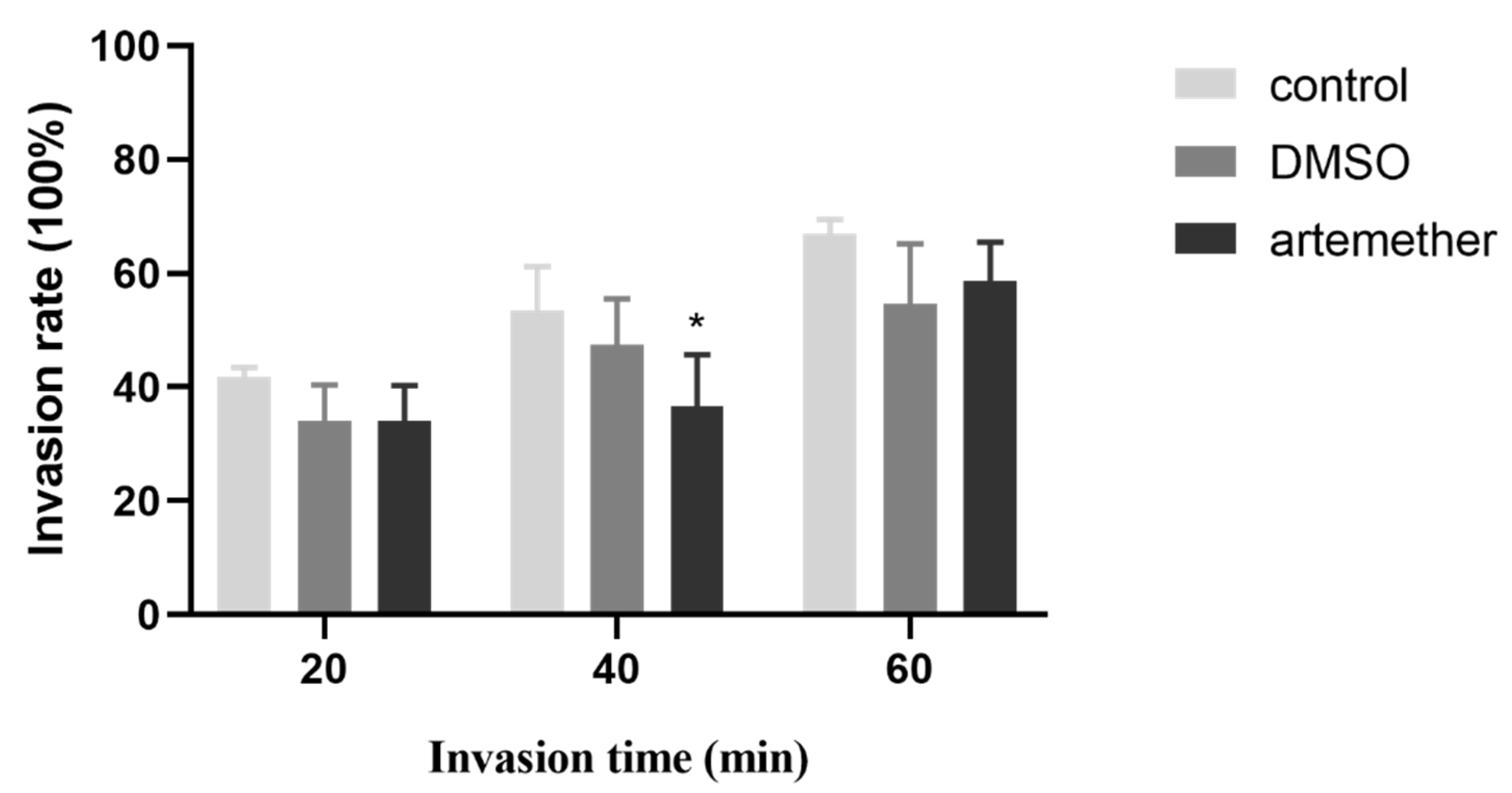
2.6. Invasion Assay
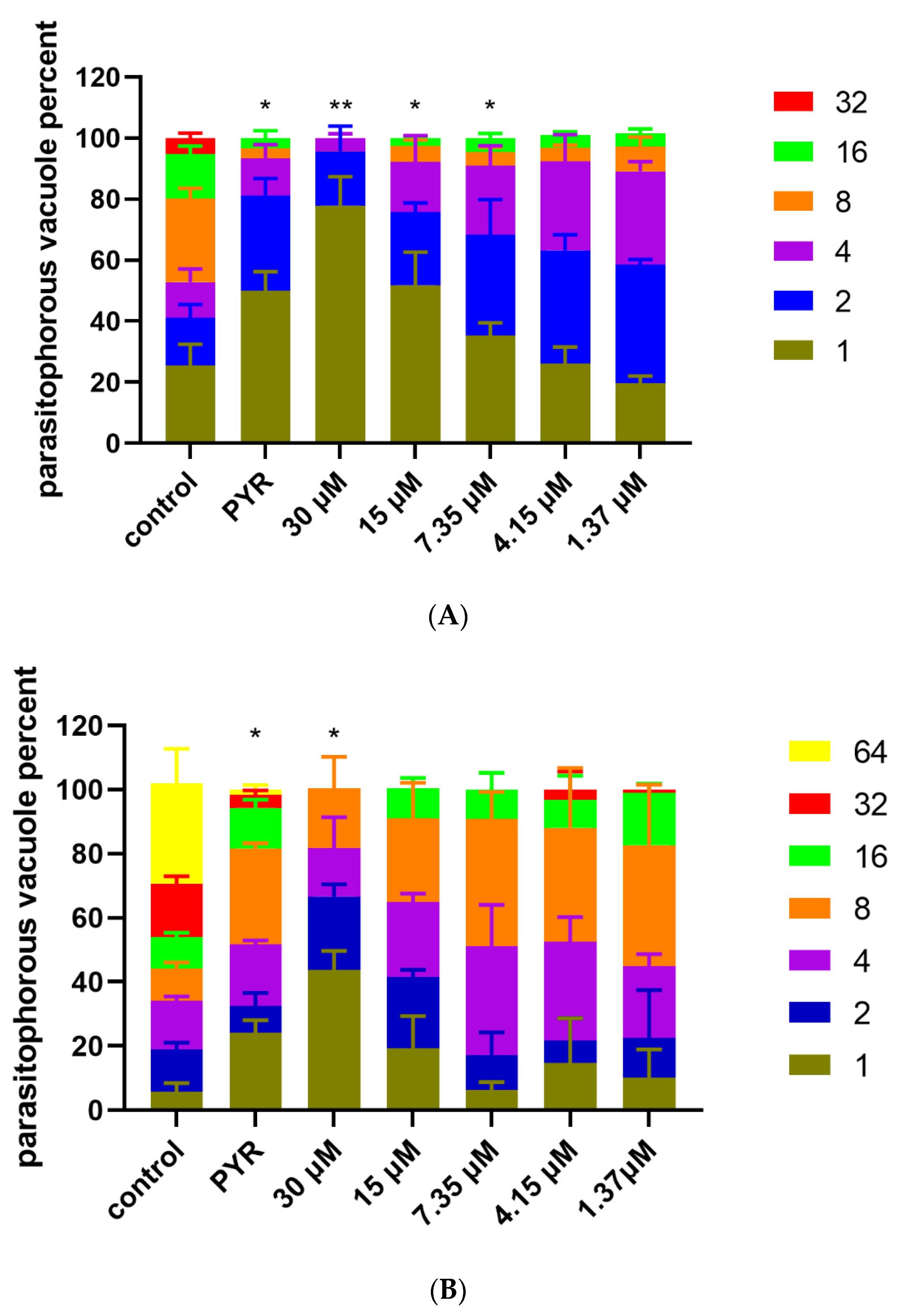
2.7. Intracellular Proliferation Assay
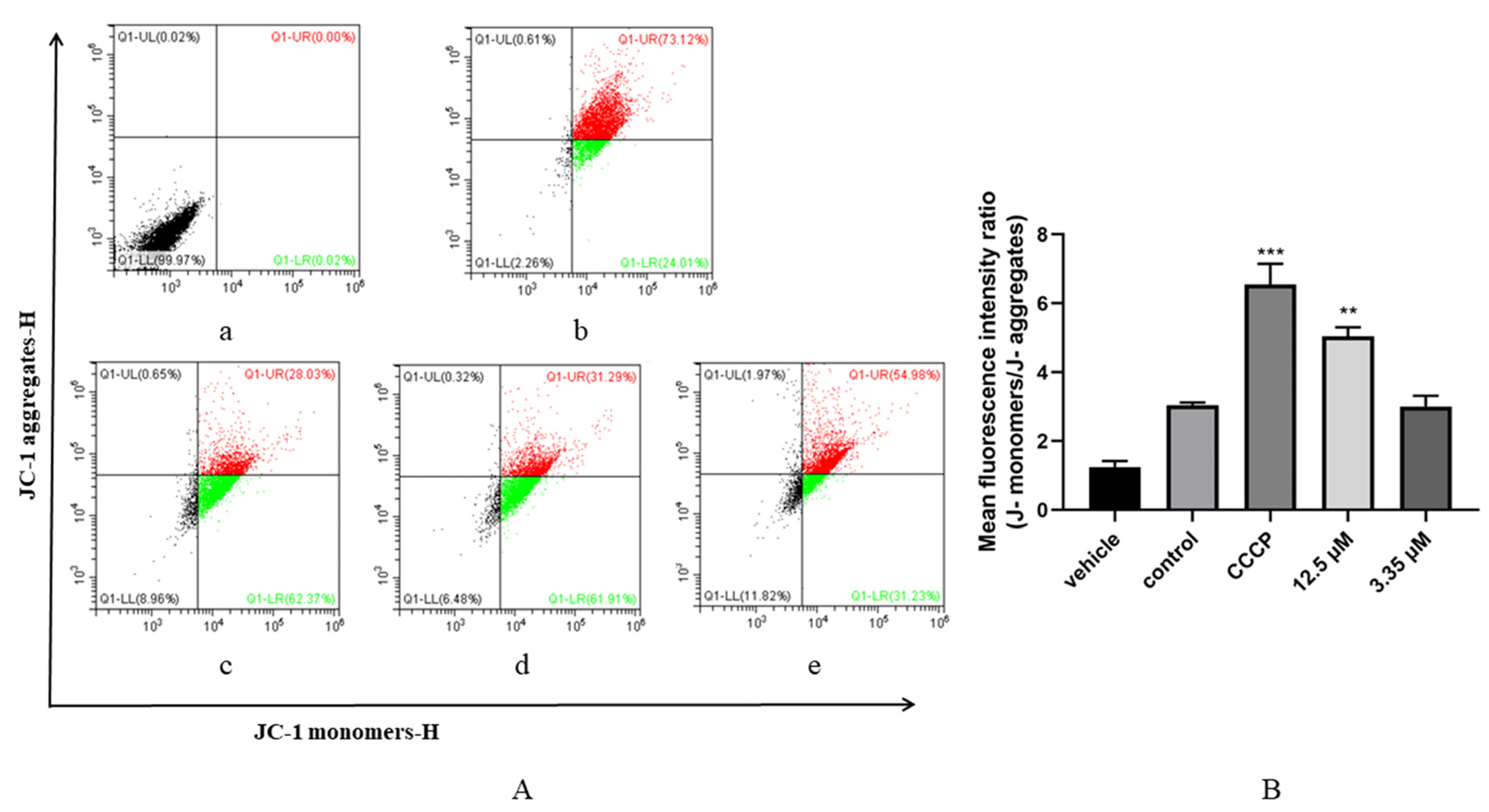
2.8. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential of Tachyzoites
2.9. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
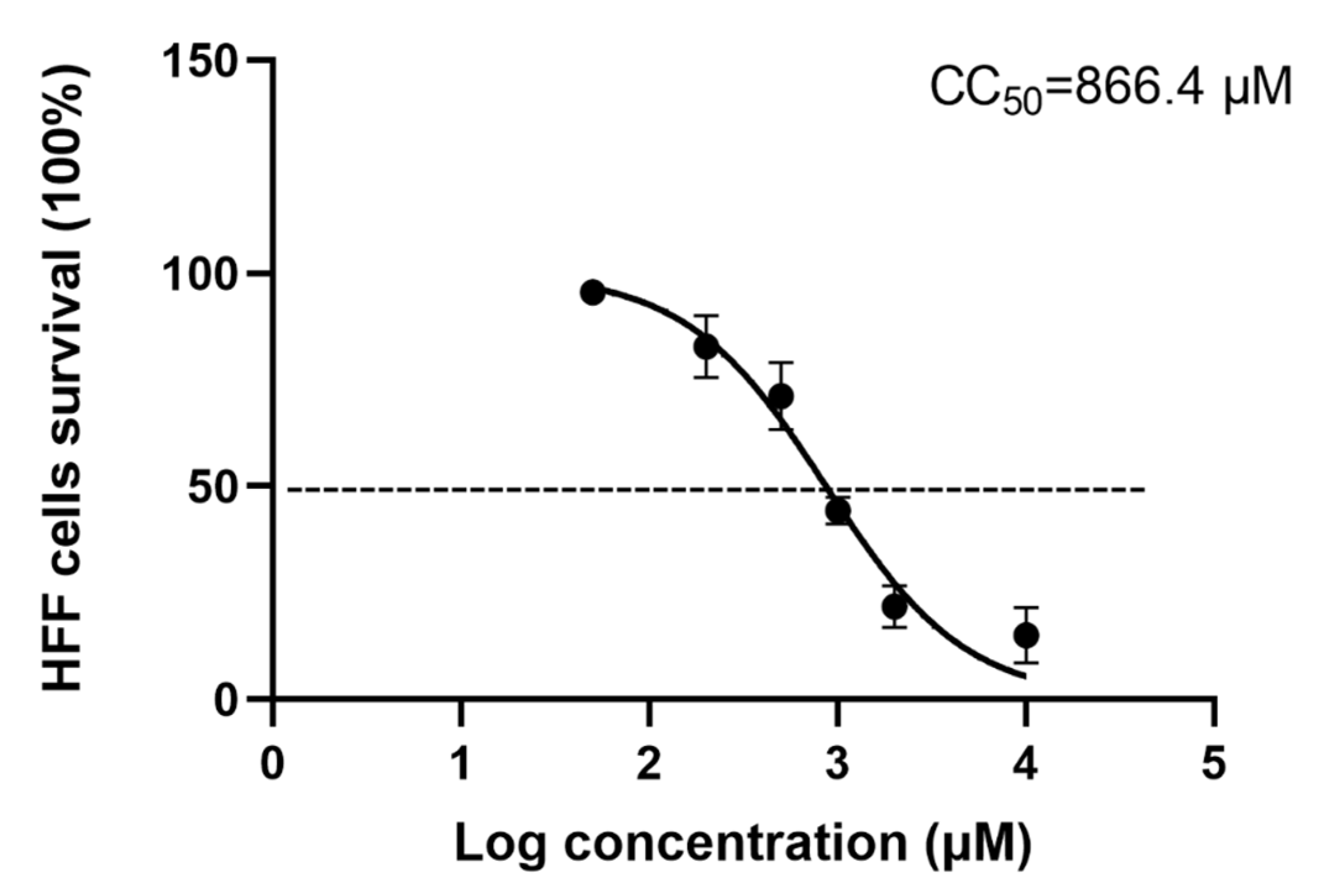
3.1. Cytotoxicity of Artemether
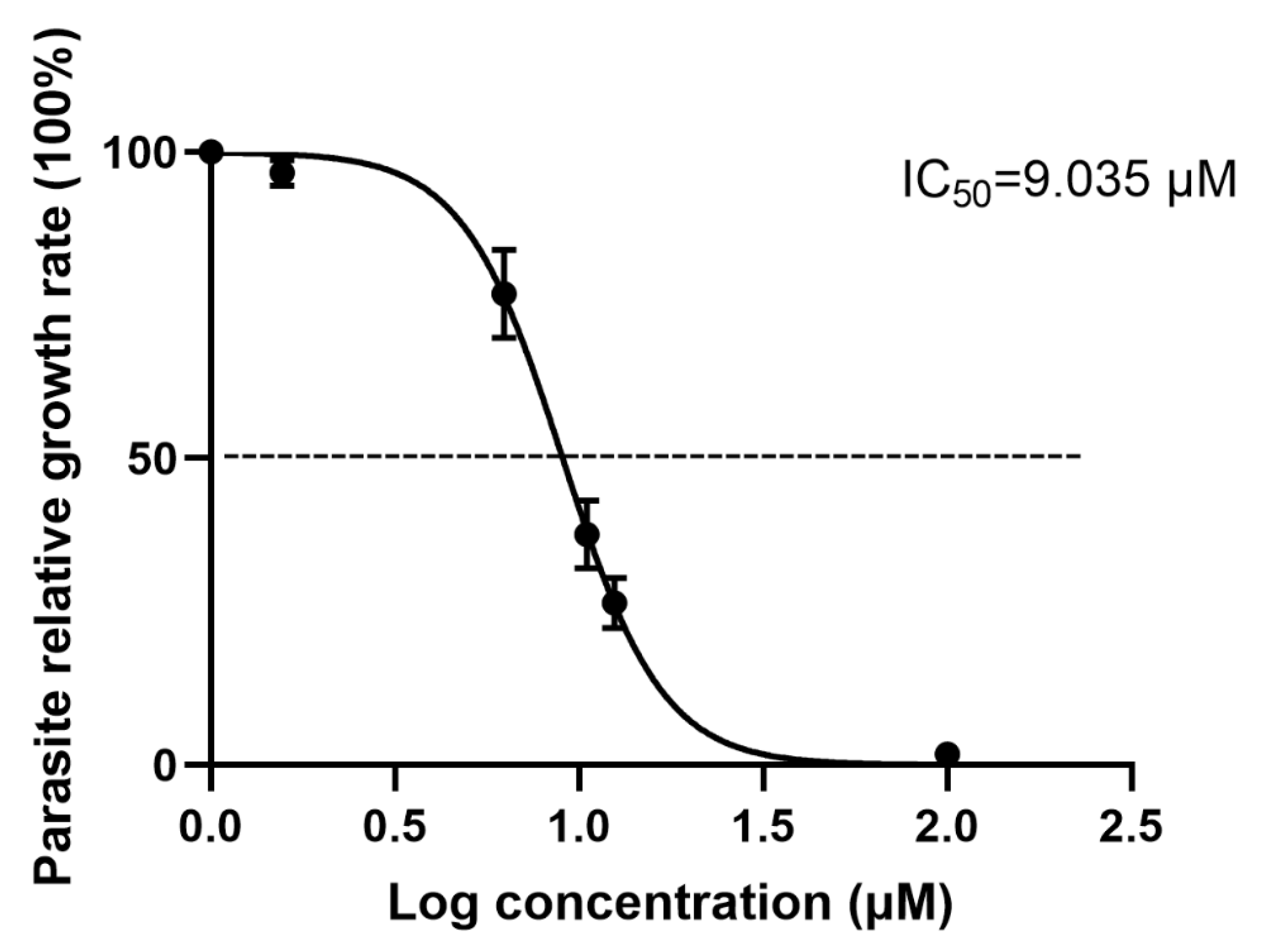
3.2. Antiparasitic Activity of Artemether In Vitro
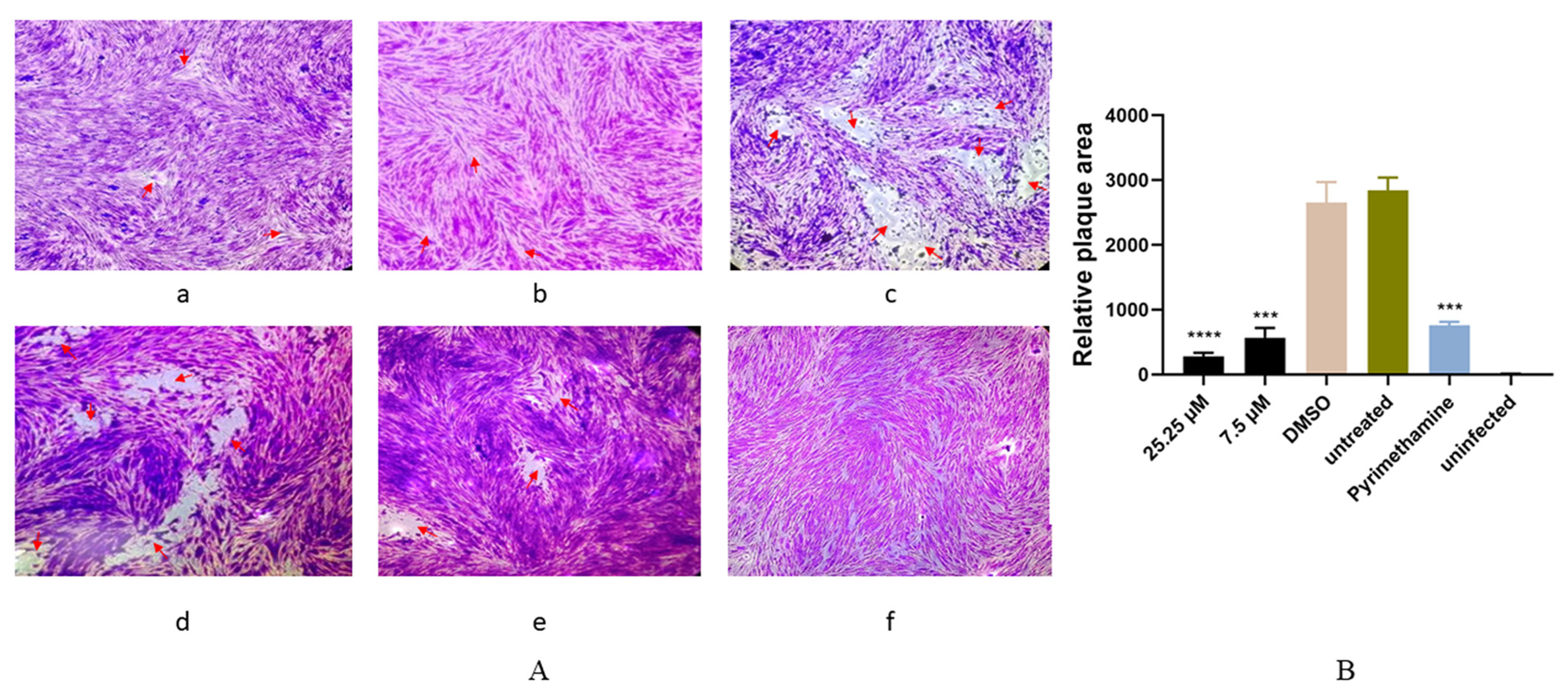
3.3. Effect of Artemether on the T. gondii Invasion
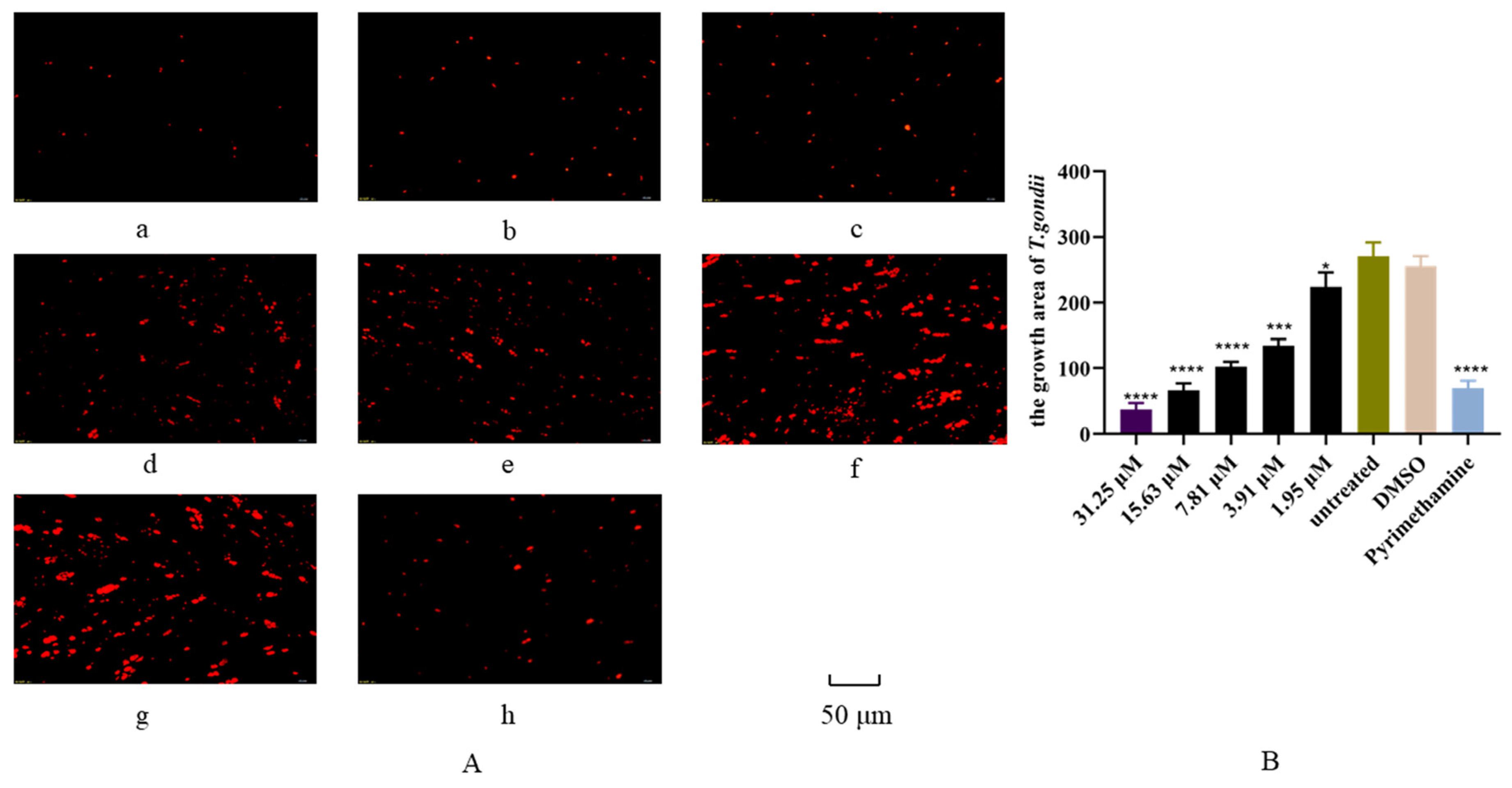
3.4. Inhibition of Artemether on T. gondii Intracellular Proliferation
3.5. Artemether Impaired Mitochondrial Membrane Potential of T. gondii
3.6. Artemether Increased ROS Production of T. gondii
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reese, M.L.; Zeiner, G.M.; Saeij, J.P.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Boyle, J.P. Polymorphic family of injected pseudokinases is paramount in Toxoplasma virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9625–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feitosa, T.F.; Costa, F.T.R.; Ferreira, L.C.; Silva, S.S.; Santos, A.; Silva, W.I.; Brasil, A.W.L.; Vilela, V.L.R. High rate of feline immunodeficiency virus infection in cats in the Brazilian semiarid region: Occurrence, associated factors and coinfection with Toxoplasma gondii and feline leukemia virus. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 79, 101718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R.; Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of Toxoplasmosis: Historical Perspective, Animal Models, and Current Clinical Practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00057-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.A.; Fernandes, M.D.; Machado, A.S.; Reis-Cunha, J.L.; Bartholomeu, D.C.; Almeida Vitor, R.W. Efficacy of sulfadiazine and pyrimetamine for treatment of experimental toxoplasmosis with strains obtained from human cases of congenital disease in Brazil. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 202, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, B.D.; Kruszon-Moran, D.; Jones, J.L. The Relationship Between Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Mood Disorders in the Third National Health and Nutrition Survey. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari, P.; Yavari, M.; Adibi, P.; Asghari, G.; Ghanadian, S.M.; Dida, G.O.; Khamesipour, F. Medicinal Properties and Active Constituents of Dracocephalum kotschyi and Its Significance in Iran: A Systematic Review. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 9465309. [Google Scholar]
- Slezakova, S.; Ruda-Kucerova, J. Anticancer Activity of Artemisinin and its Derivatives. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 5995–6003. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaalizadeh, B.; Sharif, M.; Daryani, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Zargari, M.; Sarvi, S.; Mehrzadi, S.; Rahimi, M.T.; Mirabediny, Z.; Golpour, M.; et al. Effects of Aloe vera and Eucalyptus methanolic extracts on experimental toxoplasmosis in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 192, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Filho, A.A.; Cunha, M.M.; Alves Stanton, M.; Fumiko Yamaguchi, L.; Jorge Kato, M.; Martins-Duarte, É.S. In Vitro Activity of Essential Oils from Piper Species (Piperaceae) against Tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii. Metabolites 2023, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Xu, Q.; He, J.K.; Pan, M.; Hou, Z.F.; Liu, D.D.; Tao, J.P.; Huang, S.Y. Evaluation of Origanum vulgare Essential Oil and Its Active Ingredients as Potential Drugs for the Treatment of Toxoplasmosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 793089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. The discovery of artemisinin (Qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boateng-Marfo, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ng, W.K.; Lin, H.S. Artemether-Loaded Zein Nanoparticles: An Innovative Intravenous Dosage Form for the Management of Severe Malaria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makanga, M.; Krudsood, S. The clinical efficacy of artemether/lumefantrine (Coartem). Malar. J. 2009, 8 (Suppl. 1), S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buragohain, P.; Surineni, N.; Barua, N.C.; Bhuyan, P.D.; Boruah, P.; Borah, J.C.; Laisharm, S.; Moirangthem, D.S. Synthesis of a novel series of fluoroarene derivatives of artemisinin as potent antifungal and anticancer agent. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3338–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.K.; Xu, C.; Kalesh, K.A.; He, Y.; Lin, Q.; Wong, W.S.F.; Shen, H.M.; Wang, J. Artemisinin as an anticancer drug: Recent advances in target profiling and mechanisms of action. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 1492–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yan, P.; Zou, C.; Wong, Y.K.; Shu, Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Zhang, C.; Yang, N.D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Targeting autophagy enhances the anticancer effect of artemisinin and its derivatives. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2172–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Xue, Y.X.; Yao, Y.L.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.H. Artemether combined with shRNA interference of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 significantly inhibited the malignant biological behavior of human glioma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, O.Y.; Krug, E.C.; Marr, J.J.; Berens, R.L. Inhibition of growth of Toxoplasma gondii by qinghaosu and derivatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 1961–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaeiloo, H.; Ghaffarifar, F.; Dalimi, A.; Sharifi, Z.; Hassan, Z.M. Apoptotic activity and anti-Toxoplasma effects of artemether on the tachyzoites and experimental infected Vero and J774 cell lines by Toxoplasma gondii. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhao, X.; Sang, X.; Yang, N.; Feng, Y.; Chen, R.; Chen, Q. Dihydroartemisinin regulates the immune system by promotion of CD8+ T lymphocytes and suppression of B cell responses. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J. The osteoprotective effects of artemisinin compounds and the possible mechanisms associated with intracellular iron. A review of in vivo and in vitro studies. Env. Toxicol. Pharm. 2020, 76, 103358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooko, E.; Saeed, M.E.; Kadioglu, O.; Sarvi, S.; Colak, M.; Elmasaoudi, K.; Janah, R.; Greten, H.J.; Efferth, T. Artemisinin derivatives induce iron-dependent cell death (ferroptosis) in tumor cells. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2015, 22, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yamaoka, Y.; Feng, Y.; Chi, Z.; Xue, S.; Kong, F. Co-Expression of Lipid Transporters Simultaneously Enhances Oil and Starch Accumulation in the Green Microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii under Nitrogen Starvation. Metabolites 2023, 13, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Lee, Y.M.; Feng, G.; Lim, T.K.; Shen, H.M.; Lin, Q.; Liu, B. Mechanism-Guided Design and Synthesis of a Mitochondria-Targeting Artemisinin Analogue with Enhanced Anticancer Activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 13770–13774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Wong, Y.K.; Lee, Y.M.; Zhou, C.; Wu, G.; Zhao, T.; Yang, L.; Lu, L.; et al. Artesunate-induced mitophagy alters cellular redox status. Redox Biol. 2018, 19, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, K.H.; Wu, M.Y.; Lin, L.T.; Wen, Z.H.; Li, Y.H.; Chu, P.Y.; Li, C.J. Disruption of mitochondrial homeostasis with artemisinin unravels anti-angiogenesis effects via auto-paracrine mechanisms. Theranostics 2019, 9, 6631–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheiner, L.; Vaidya, A.B.; McFadden, G.I. The metabolic roles of the endosymbiotic organelles of Toxoplasma and Plasmodium spp. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Xiang, Y.T.; Li, Q.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, Z.C.; Hao, S.S.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.L.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, D.G.; et al. The effect of artemether on psychotic symptoms and cognitive impairment in first-episode, antipsychotic drug-naive persons with schizophrenia seropositive to Toxoplasma gondii. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 53, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, D.A.; Ramos, G.A.; Zamora-Vélez, A.; Gallego-López, G.M.; Rocha-Roa, C.; Gómez-Marin, J.E.; Cortes, E. In vitro evaluation of new 4-thiazolidinones on invasion and growth of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug. Resist. 2021, 16, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striepen, B.; Soldati, D.; Garcia-Reguet, N.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Roos, D.S. Targeting of soluble proteins to the rhoptries and micronemes in Toxoplasma gondii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2001, 113, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.S.Y.; Chua, K.H.; Nölke, G.; Spiegel, H.; Goh, W.L.; Chow, S.C.; Kee, B.P.; Fischer, R.; Schillberg, S.; Othman, R.Y. Plant-derived chimeric antibodies inhibit the invasion of human fibroblasts by Toxoplasma gondii. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakavuk, M.; Can, H.; Gül, A.; Döşkaya, A.D.; Alak, S.E.; Ün, C.; Gürüz, A.Y.; Döşkaya, M. GRA8 DNA vaccine formulations protect against chronic toxoplasmosis. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryani, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Ahmadpour, E.; Edalatian, S.; Esboei, B.R.; Sarvi, S. Anti-Toxoplasma activities of methanolic extract of Sambucus nigra (Caprifoliaceae) fruits and leaves. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2015, 63, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamesipour, F.; Pourmohammad, A.; Jafarian-Dehkordi, M. Anti-Toxoplasma Effects of Dracocephalum polychaetum Essential Oil. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2022, 2022, 6091834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shan, N.N.; Sui, X.H. Research Progress on Artemisinin and Its Derivatives against Hematological Malignancies. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 26, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, N.S.; Long, X.; Wong, J.W.; Griffin, R.C.; Doery, J.C.G. Artemisinin and its derivatives: A potential treatment for leukemia. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2019, 30, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, P.J.; Dien, T.K. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic potential of artemisinin and its derivatives in the treatment of malaria. Drugs 1996, 52, 818–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, E.; Tarantino, M.; Bergamini, M.; Castelluccio, V.; Coricello, A.; Falcicchio, M.; Lorusso, E.; Collina, S. Artemisinin and its derivatives; ancient tradition inspiring the latest therapeutic approaches against malaria. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 1443–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, J.B.; Burrows, J.N.; Goldberg, D.E.; Sibley, L.D. Evaluation of Current and Emerging Antimalarial Medicines for Inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii Growth in Vitro. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, M.K.; Compton, H.L.; Roos, D.S.; Tilney, L.G. Microtubules, but not actin filaments, drive daughter cell budding and cell division in Toxoplasma gondii. J. Cell. Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 7, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zubaidi, U.; Liu, J.; Cinar, O.; Robker, R.L.; Adhikari, D.; Carroll, J. The spatio-temporal dynamics of mitochondrial membrane potential during oocyte maturation. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 25, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Lv, K.; Li, B.; Yan, B.; Gai, L.; Shi, C.; Wang, X.; Si, H.; Zhang, J. Myrislignan Induces Redox Imbalance and Activates Autophagy in Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 730222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, K.; Miyamoto, L.; Hamano, S.; Morimoto, Y.; Kangawa, Y.; Fukue, C.; Kagawa, Y.; Horinouchi, Y.; Xu, W.; Ikeda, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of the pH- and Oxygen-Dependent Oxidation Activities of Artesunate. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial ROS promote mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation in ischemic acute kidney injury by disrupting TFAM-mediated mtDNA maintenance. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1845–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, A.M.; Ayariga, J.A.; Napier, A.; Robertson, B.K.; Abugri, D.A. Inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii Growth by Dihydroquinine and Its Mechanisms of Action. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 852889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejpongsa, P.; Yeh, E.T. Prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: Challenges and opportunities. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Balta, V.A.; West, R.; Newlin, K.N.; Miljanić, O.; Sullivan, D.J.; Vekilov, P.G.; Rimer, J.D. A second mechanism employed by artemisinins to suppress Plasmodium falciparum hinges on inhibition of hematin crystallization. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Duan, Y.-Y.; Pan, M.; Jin, Q.-W.; Tao, J.-P.; Huang, S.-Y. In Vitro Evaluation Reveals Effect and Mechanism of Artemether against Toxoplasma gondii. Metabolites 2023, 13, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040476
Xu Q, Duan Y-Y, Pan M, Jin Q-W, Tao J-P, Huang S-Y. In Vitro Evaluation Reveals Effect and Mechanism of Artemether against Toxoplasma gondii. Metabolites. 2023; 13(4):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040476
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qiong, Yin-Yan Duan, Ming Pan, Qi-Wang Jin, Jian-Ping Tao, and Si-Yang Huang. 2023. "In Vitro Evaluation Reveals Effect and Mechanism of Artemether against Toxoplasma gondii" Metabolites 13, no. 4: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040476
APA StyleXu, Q., Duan, Y.-Y., Pan, M., Jin, Q.-W., Tao, J.-P., & Huang, S.-Y. (2023). In Vitro Evaluation Reveals Effect and Mechanism of Artemether against Toxoplasma gondii. Metabolites, 13(4), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040476





