Cetyl Alcohol Polyethoxylates Disrupt Metabolic Health in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Care
2.3. Adipogenic Differentiation and Outcome Measurements
2.4. Zebrafish Husbandry
2.5. Zebrafish Exposures
2.6. Zebrafish Metabolic Health
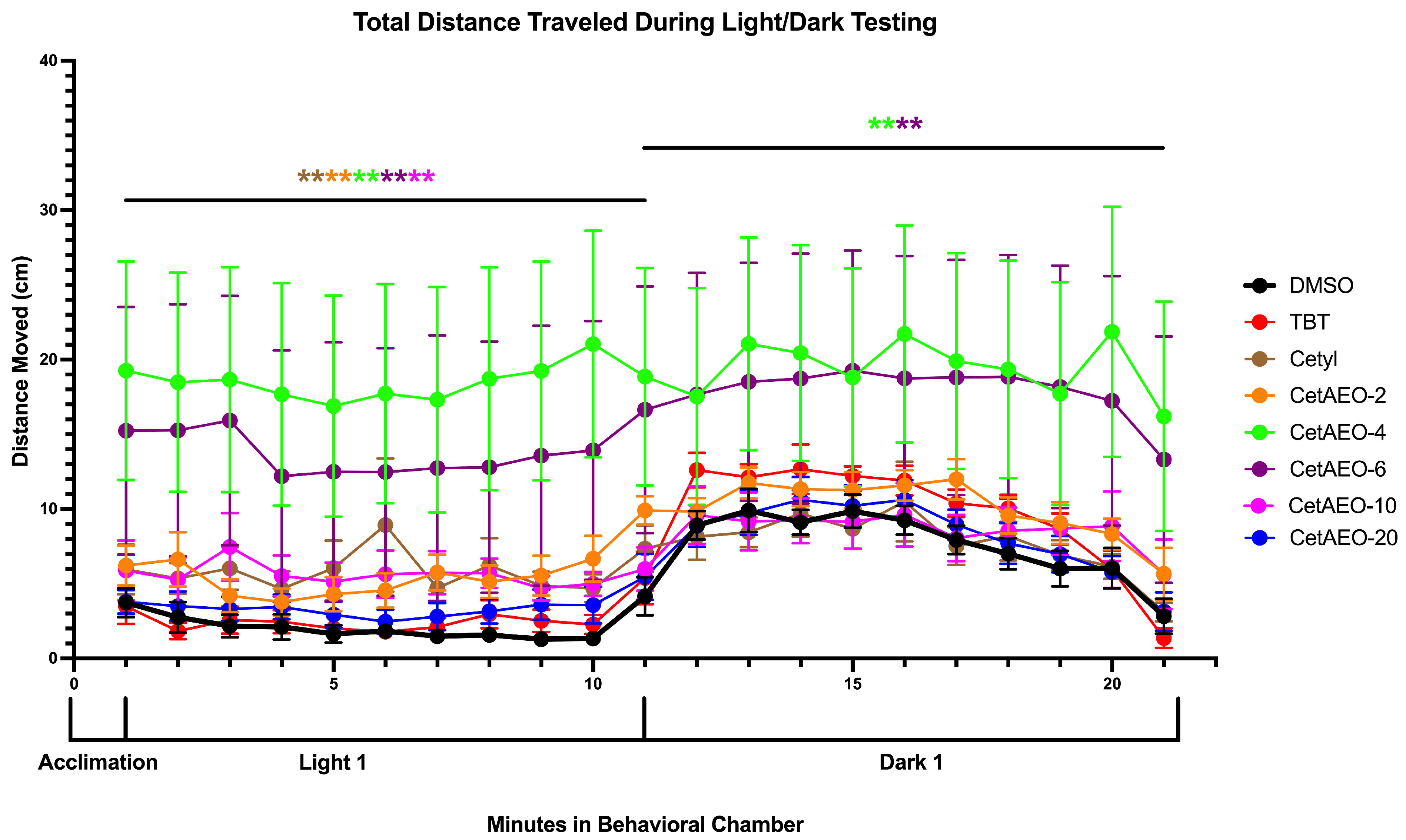
2.7. Larvae Locomotion
2.8. Morphology and Adipose Quantification
2.9. Statistical Analysis
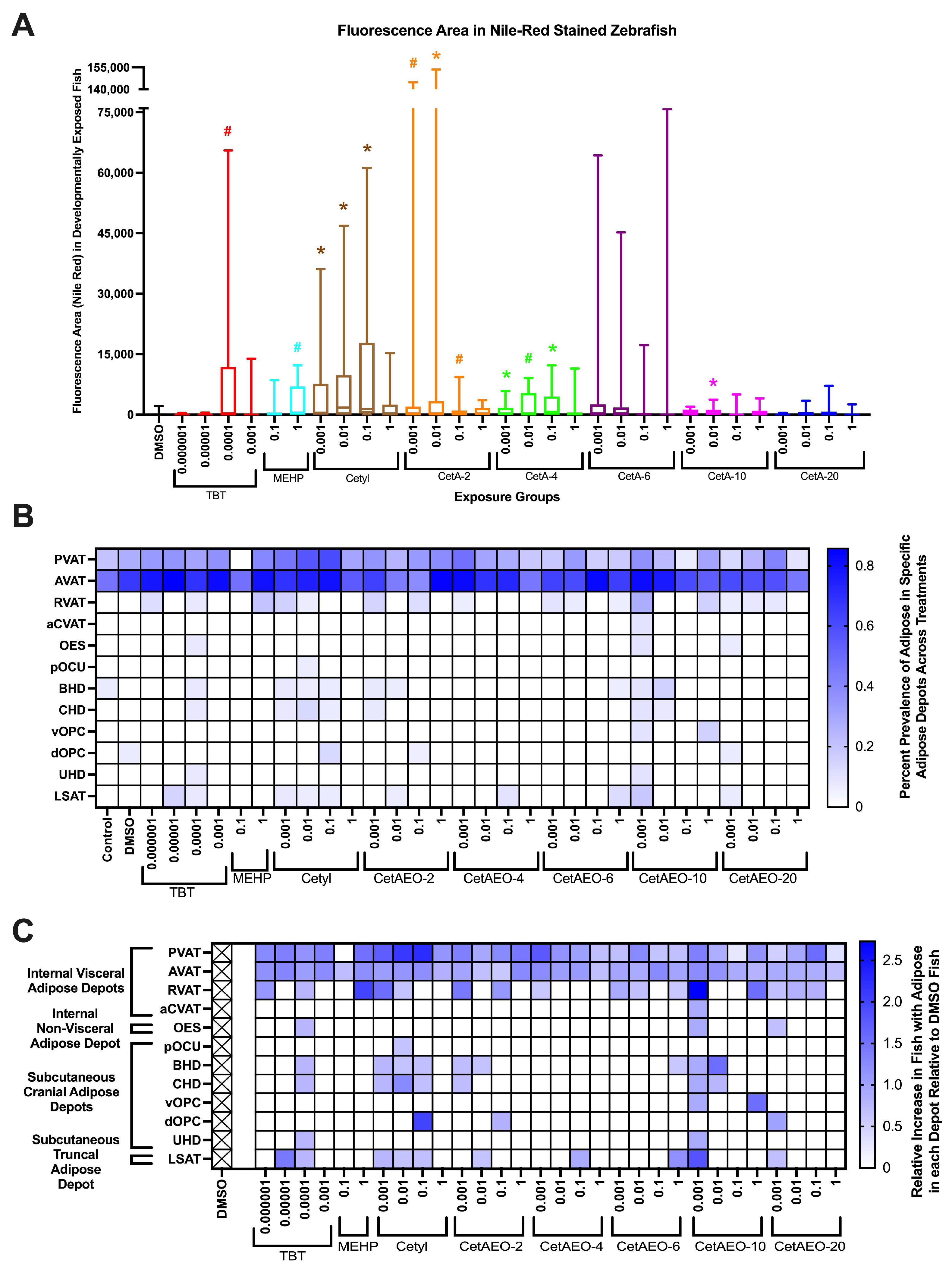
3. Results
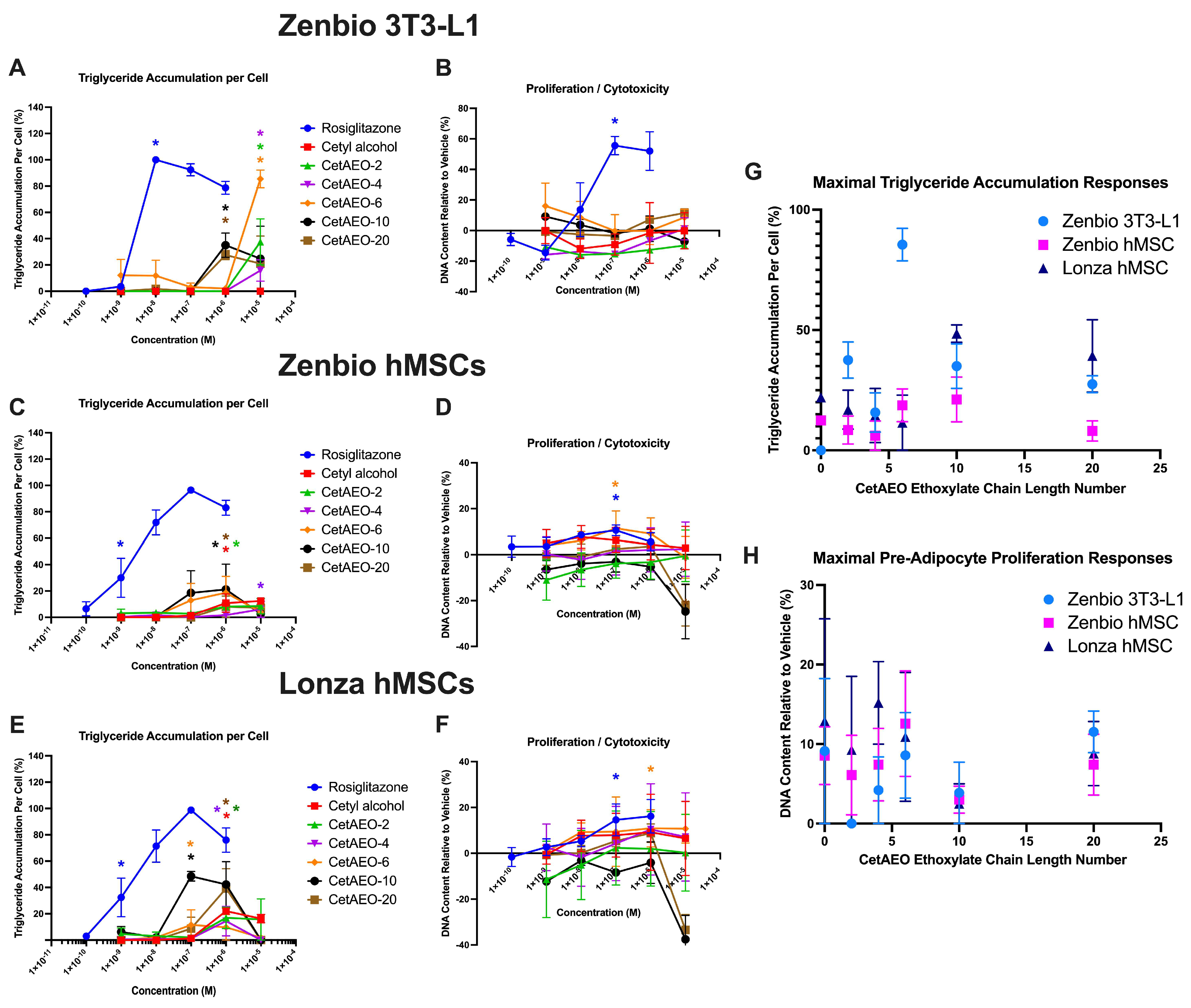
3.1. Adipogenic Activity of CetAEOs
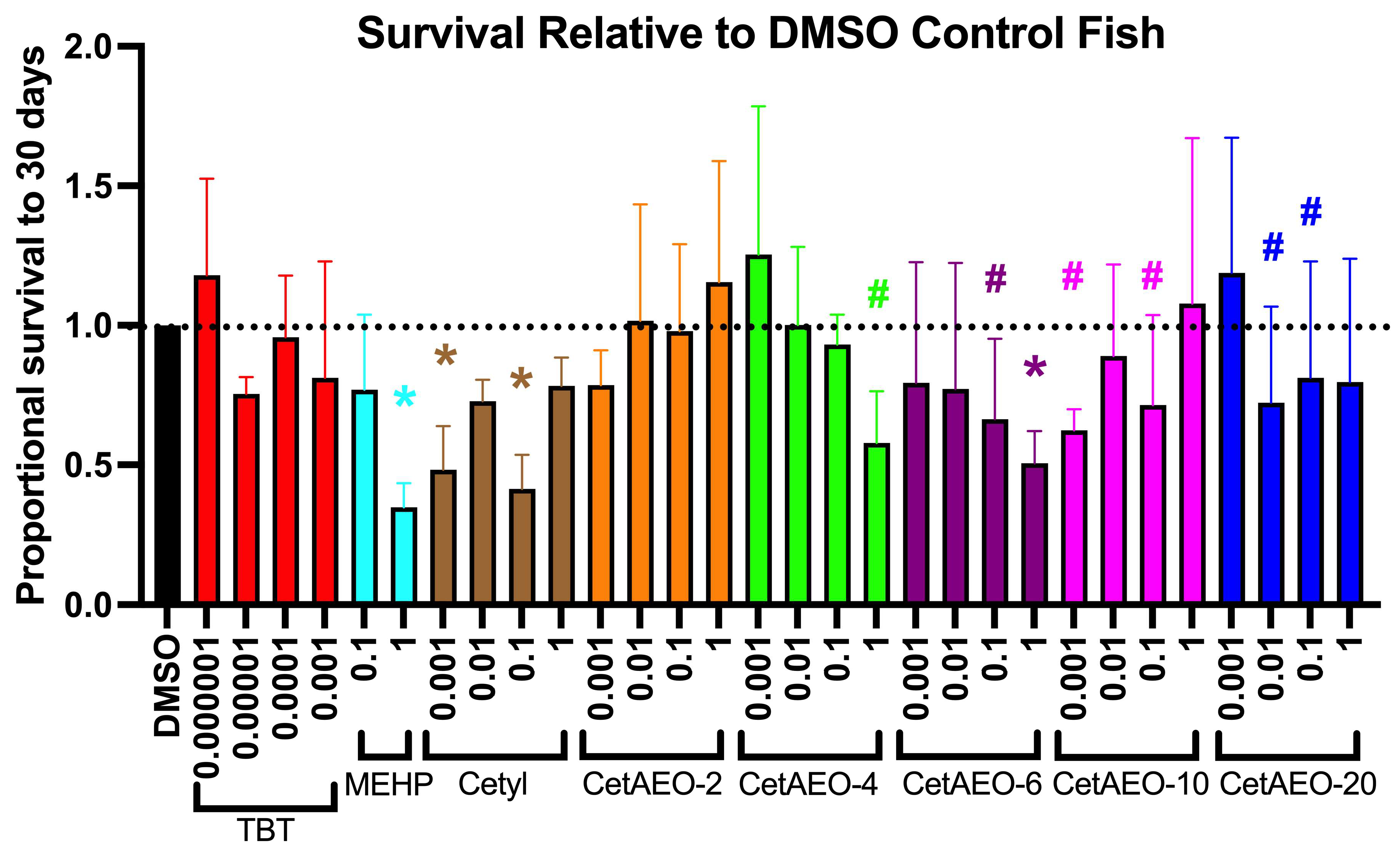
3.2. Lethality of NPEOs on Zebrafish
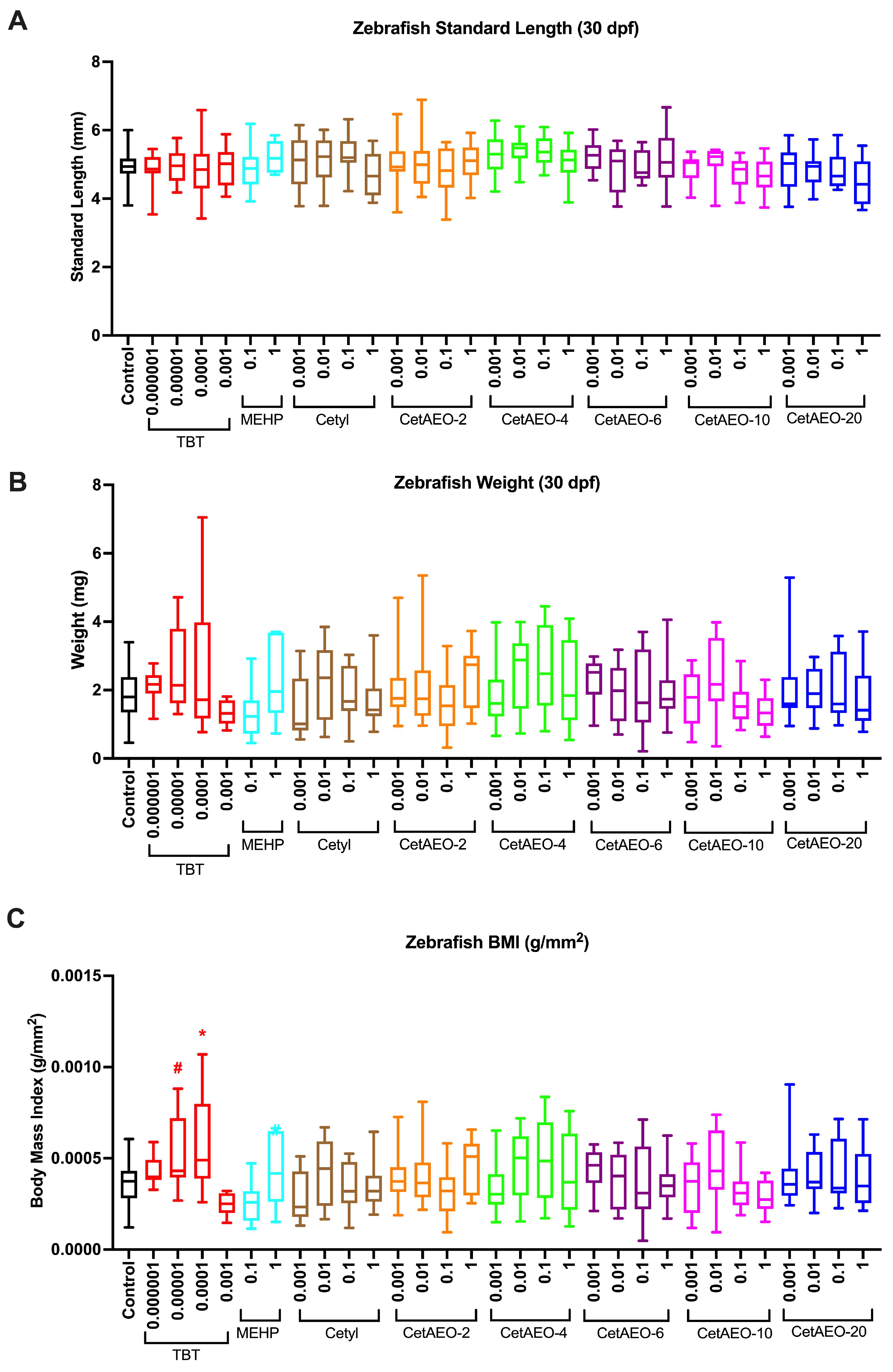
3.3. Growth Trajectory, Weights, and Adipose Deposition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- S&P Global. Chemical Economics Handbook—Detergent Alcohols; S&P Global: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.spglobal.com/commodityinsights/en/ci/products/detergent-alcohols-chemical-economics-handbook.html (accessed on 1 December 2016).
- Reznik, G.O.; Vishwanath, P.; Pynn, M.A.; Sitnik, J.M.; Todd, J.J.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Keenan, B.G.; Castle, A.B.; Haskell, R.F.; et al. Use of sustainable chemistry to produce an acyl amino acid surfactant. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresana. Market Study: Surfactants (2nd edition). Available online: http://www.ceresana.com/en/market-studies/chemicals/surfactants (accessed on 1 December 2016).
- Design for the Environment. Alternatives Assessment for Nonylphenol Ethoxylates; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Cespedes, R.; Lacorte, S.; Ginebreda, A.; Barcelo, D. Chemical monitoring and occurrence of alkylphenols, alkylphenol ethoxylates, alcohol ethoxylates, phthalates and benzothiazoles in sewage treatment plants and receiving waters along the Ter River basin (Catalonia, N.E. Spain). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, K.A.; Vejrup, K.V.; Mogensen, B.B.; Halling-Sorensen, B. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method to determine alcohol ethoxylates and alkylamine ethoxylates in soil interstitial water, ground water and surface water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 957, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, H.; van Compernolle, R.; Dyer, S.D.; Price, B.B.; Nielsen, A.M.; Selby, M.; Ferrer, D.; Stanton, K. Occurrence and risk screening of alcohol ethoxylate surfactants in three U.S. river sediments associated with wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadsforth, C.V.; Sherren, A.J.; Selby, M.A.; Toy, R.; Eckhoff, W.S.; McAvoy, D.C.; Matthijs, E. Monitoring of environmental fingerprints of alcohol ethoxylates in Europe and Canada. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 64, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgola-Grzeskowiak, A.; Grzeskowiak, T. Solid-phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction, fast derivatisation and high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis for trace determination of short-chained dodecyl alcohol ethoxylates and dodecyl alcohol in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1251, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeArmond, P.D.; DiGoregorio, A.L. Rapid liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry-based method for the analysis of alcohol ethoxylates and alkylphenol ethoxylates in environmental samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1305, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, T.; Petersen, G.; Seierø, C.; Tørsløv, J. Biodegradability and Aquatic Toxicity of Glycoside Surfactants and a Nonionic Alcohol Ethoxylate. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrall, S.W.; Dunphy, J.C.; Cano, M.L.; Evans, A.; McAvoy, D.C.; Price, B.P.; Eckhoff, W.S. Removal and environmental exposure of alcohol ethoxylates in US sewage treatment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 64, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, S.D.; Bernhard, M.J.; Cowan-Ellsberry, C.; Perdu-Durand, E.; Demmerle, S.; Cravedi, J.P. In vitro biotransformation of surfactants in fish. Part I: Linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (C12-LAS) and alcohol ethoxylate (C13EO8). Chemosphere 2008, 72, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, S.D.; Bernhard, M.J.; Cowan-Ellsberry, C.; Perdu-Durand, E.; Demmerle, S.; Cravedi, J.P. In vitro biotransformation of surfactants in fish. Part II—Alcohol ethoxylate (C16EO8) and alcohol ethoxylate sulfate (C14EO2S) to estimate bioconcentration potential. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfield, L.A.; Pottinger, T.G.; Sumpter, J.P. Exposure of female juvenile rainbow trout to alkylphenolic compounds results in modifications to growth and ovosomatic index. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servos, M.R. Review of the aquatic toxicity, estrogenic responses and bioaccumulation of alkylphenols and alkylphenol polyethoxylates. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 1999, 34, 123–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, G.; Metcalfe, C. Developmental effects in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) exposed to nonylphenol ethoxylates and their degradation products. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Filho, E.C.; Grisolia, C.K.; Paumgartten, F.J. Trans-generation study of the effects of nonylphenol ethoxylate on the reproduction of the snail Biomphalaria tenagophila. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, K.M.; Snyder, E.M.; Snyder, S.A.; Pierens, S.L.; Miles-Richardson, S.R.; Giesy, J.P. Effects of nonylphenol ethoxylate exposure on reproductive output and bioindicators of environmental estrogen exposure in fathead minnows Pimephales promelas. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2001, 20, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoller, U. Estuarine and coastal zone marine pollution by the nonionic alkylphenol ethoxylates endocrine disrupters: Is there a potential ecotoxicological problem? Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmage, S.S. Environmental and Human Safety of Major Surfactants: Alcohol Ethoxylates and Alkylphenol Ethoxylates; The Soap and Detergent Association: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; p. 374. [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, A.M.; Bowers, R.R.; Magaletta, M.E.; Holshouser, S.; Maggi, A.; Ciana, P.; Guillette, L.J.; Bowden, J.A.; Kucklick, J.R.; Baatz, J.E.; et al. Effects of Crude Oil/Dispersant Mixture and Dispersant Components on PPARgamma Activity and: Identification of Dioctyl Sodium Sulfosuccinate (DOSS.; C.AS #577-11-7) as a Probable Obesogen. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, R.R.; Temkin, A.M.; Guillette, L.J.; Baatz, J.E.; Spyropoulos, D.D. The commonly used nonionic surfactant Span 80 has RXRalpha transactivation activity, which likely increases the obesogenic potential of oil dispersants and food emulsifiers. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 238, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Kollitz, E.M.; Ferguson, P.L.; Stapleton, H.M. Nonionic ethoxylated surfactants induce adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2018, 162, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassotis, C.D.; LeFauve, M.K.; Chiang, Y.T.; Knuth, M.M.; Schkoda, S.; Kullman, S.W. Nonylphenol Polyethoxylates Enhance Adipose Deposition in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish. Toxics 2022, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, L.; Maddison, L.A.; Chen, W. Zebrafish as a Model for Obesity and Diabetes. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Zang, L.; Hirano, M.; Shimada, Y.; Wang, Z.; Umemoto, N.; Kuroyanagi, J.; Nishimura, N.; Tanaka, T. Diet-induced obesity in zebrafish shares common pathophysiological pathways with mammalian obesity. BMC Physiol. 2010, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Broeder, M.J.; Moester, M.J.B.; Kamstra, J.H.; Cenijn, P.H.; Davidoiu, V.; Kamminga, L.M.; Ariese, F.; de Boer, J.F.; Legler, J. Altered Adipogenesis in Zebrafish Larvae Following High Fat Diet and Chemical Exposure Is Visualised by Stimulated Raman Scattering Microscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, K.; Schuster, S.; Meusel, A.; Garten, A.; Riemer, T.; Schleinitz, D.; Kiess, W.; Korner, A. Short-term overfeeding of zebrafish with normal or high-fat diet as a model for the development of metabolically healthy versus unhealthy obesity. BMC Physiol. 2017, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riu, A.; McCollum, C.W.; Pinto, C.L.; Grimaldi, M.; Hillenweck, A.; Perdu, E.; Zalko, D.; Bernard, L.; Laudet, V.; Balaguer, P.; et al. Halogenated bisphenol-A analogs act as obesogens in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2014, 139, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyssimachou, A.; Santos, J.G.; Andre, A.; Soares, J.; Lima, D.; Guimaraes, L.; Almeida, C.M.; Teixeira, C.; Castro, L.F.; Santos, M.M. The Mammalian “Obesogen” Tributyltin Targets Hepatic Triglyceride Accumulation and the Transcriptional Regulation of Lipid Metabolism in the Liver and Brain of Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerger, A.N.; Schmidt, J.; Chase, A.; Paixao, C.; Patel, T.N.; Brumback, B.A.; Kane, A.S.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Bisesi, J.H., Jr. Examining the responses of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) gastrointestinal system to the suspected obesogen diethylhexyl phthalate. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouadah-Boussouf, N.; Babin, P.J. Pharmacological evaluation of the mechanisms involved in increased adiposity in zebrafish triggered by the environmental contaminant tributyltin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 294, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Qin, J.; Wang, W.; Tian, H.; Ru, S. Bisphenol S induces obesogenic effects through deregulating lipid metabolism in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.J.; Hoyo, C.; Mattingly, C.J.; Luo, Y.; Tzeng, J.Y.; Murphy, S.K.; Buchwalter, D.B.; Planchart, A. Cadmium exposure increases the risk of juvenile obesity: A human and zebrafish comparative study. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tingaud-Sequeira, A.; Ouadah, N.; Babin, P.J. Zebrafish obesogenic test: A tool for screening molecules that target adiposity. J. Lipid. Res. 2011, 52, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minchin, J.E.; Rawls, J.F. In vivo imaging and quantification of regional adiposity in zebrafish. Methods Cell Biol. 2017, 138, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, E.J., 3rd; Trent, C.M.; Rawls, J.F. Ontogeny and nutritional control of adipogenesis in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Lipid. Res. 2009, 50, 1641–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchin, J.E.N.; Rawls, J.F. A classification system for zebrafish adipose tissues. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro-Garcia, R.; Sahu, M.; Abbey, R.J.; Laude, J.; Pham, N.; Blumberg, B. Transgenerational inheritance of increased fat depot size, stem cell reprogramming, and hepatic steatosis elicited by prenatal exposure to the obesogen tributyltin in mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoucri, B.M.; Martinez, E.S.; Abreo, T.J.; Hung, V.T.; Moosova, Z.; Shioda, T.; Blumberg, B. Retinoid X Receptor Activation Alters the Chromatin Landscape To Commit Mesenchymal Stem Cells to the Adipose Lineage. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3109–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Blumberg, B.; Bovolin, P.; Calamandrei, G.; Ceresini, G.; Cohn, B.A.; Fabbri, E.; Gioiosa, L.; Kassotis, C.; et al. Parma consensus statement on metabolic disruptors. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2015, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janesick, A.S.; Blumberg, B. Obesogens: An emerging threat to public health. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 214, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, R.H.; Collier, D.; Kassotis, C.; Roepke, T.A.; Kim, M.J.; Blanc, E.; Barouki, R.; Bansal, A.; Cave, M.C.; Chatterjee, S.; et al. Obesity I: Overview and molecular and biochemical mechanisms. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 199, 115012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Vom Saal, F.S.; Babin, P.J.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D.; Le Mentec, H.; Blumberg, B.; Mohajer, N.; Legrand, A.; Munic Kos, V.; Martin-Chouly, C.; et al. Obesity III: Obesogen assays: Limitations, strengths, and new directions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 199, 115014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Howard, S.; Agay-Shay, K.; Arrebola, J.P.; Audouze, K.; Babin, P.J.; Barouki, R.; Bansal, A.; Blanc, E.; Cave, M.C.; et al. Obesity II: Establishing causal links between chemical exposures and obesity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 199, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017–2018; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2020.
- Kassotis, C.D.; Masse, L.; Kim, S.; Schlezinger, J.J.; Webster, T.F.; Stapleton, H.M. Characterization of adipogenic chemicals in three different cell culture systems: Implications for reproducibility based on cell source and handling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Kollitz, E.M.; Hoffman, K.; Sosa, J.A.; Stapleton, H.M. Thyroid Receptor Antagonism as a Contributory Mechanism for Adipogenesis Induced by Environmental Mixtures in 3T3-L1 Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Hoffman, K.; Phillips, A.L.; Zhang, S.; Cooper, E.M.; Webster, T.F.; Stapleton, H.M. Characterization of adipogenic, PPARgamma, and TRbeta activities in house dust extracts and their associations with organic contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 758, 143707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Hoffman, K.; Volker, J.; Pu, Y.; Veiga-Lopez, A.; Kim, S.M.; Schlezinger, J.J.; Bovolin, P.; Cottone, E.; Saraceni, A.; et al. Reproducibility of adipogenic responses to metabolism disrupting chemicals in the 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte model system: An interlaboratory study. Toxicology 2021, 461, 152900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filer, D.; Hoffman, K.; Sargis, R.M.; Trasande, L.; Kassotis, C.D. On the Utility of ToxCast-Based Predictive Models to Evaluate Potential Metabolic Disruption by Environmental Chemicals. Under Rev. 2022, 130, 057005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, R.M.; D’Aquila, A.L.; Biga, P.R. The validation of a sensitive, non-toxic in vivo metabolic assay applicable across zebrafish life stages. Comp. Biochem. Physiology. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2018, 208, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noldus, L.P.; Spink, A.J.; Tegelenbosch, R.A. EthoVision: A versatile video tracking system for automation of behavioral experiments. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 2001, 33, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Wong, K.; Cachat, J.; Gaikwad, S.; Kyzar, E.; Wu, N.; Hart, P.; Piet, V.; Utterback, E.; Elegante, M.; et al. Zebrafish models to study drug abuse-related phenotypes. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 22, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.A.; Konemann, S.; Krumpelmann, L.; Zupanic, A.; Vom Berg, C. Approaches to Test the Neurotoxicity of Environmental Contaminants in the Zebrafish Model: From Behavior to Molecular Mechanisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2021, 40, 989–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuth, M.M.; Mahapatra, D.; Jima, D.; Wan, D.; Hammock, B.D.; Law, M.; Kullman, S.W. Vitamin D deficiency serves as a precursor to stunted growth and central adiposity in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renquist, B.J.; Zhang, C.; Williams, S.Y.; Cone, R.D. Development of an assay for high-throughput energy expenditure monitoring in the zebrafish. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asmakh, M.; Majdalawieh, A.F.; Abdullah, A.M.; Younes, N.; Da’as, S.I.; Radwan, A.B.; Sliem, M.H.; Ech-Cherif, H.; Nasrallah, G.K. AEO-7 surfactant is “super toxic” and induces severe cardiac, liver and locomotion damage in zebrafish embryos. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Jung, S.K. High-throughput toxicity study of lubricant emulsions and their common ingredients using zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-H.; Jung, S.-K. Toxicity evaluation of household detergents and surfactants using zebrafish. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2021, 26, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellini, P.; Ometto, L. Teratogenic and toxic effects of alcohol ethoxylate and alcohol ethoxy sulfate surfactants on Xenopus laevis embryos and tadpoles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2001, 48, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, W.T.; Stocker, R.K. Toxicity of 19 adjuvants to juvenile Lepomis macrochirus (bluegill sunfish). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2003, 22, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizotte, R.E., Jr.; Wong, D.C.; Dorn, P.B.; Rodgers, J.H., Jr. Effects of a homologous series of linear alcohol ethoxylate surfactants on fathead minnow early life stages. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, W.B., Jr.; Steinriede, R.W.; Rodgers, J.H., Jr.; Dorn, P.B.; Wong, D.C.L. Chronic toxicity of a homologous series of linear alcohol ethoxylate surfactants to Daphnia magna in 21 day flow-through laboratory exposures. Environ. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.C.L.; Dorn, P.B.; Chai, E.Y. Acute toxicity and structure-activity relationships of nine alcohol ethoxylate surfactants to fathead minnow and Dapnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.T.; Zehnder, A.J.; Escher, B.I. Membrane toxicity of linear alcohol ethoxylates. Environ. Chem. 2009, 18, 2767–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, E.; Fernandez-Serrano, M.; Nunez-Olea, J.; Luzon, G.; Lechuga, M. Acute toxicity and relationship between metabolites and ecotoxicity during the biodegradation process of non-ionic surfactants: Fatty-alcohol ethoxylates, nonylphenol polyethoxylate and alkylpolyglucosides. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2009, 59, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.X.; Pang, X.Y.; Zhang, P.; Lin, J.; Li, X.X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, F.; Mu, W. Alcohol ethoxylates significantly synergize pesticides than alkylphenol ethoxylates considering bioactivity against three pests and joint toxicity to Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, S.R.; Appel, A.G. Linear alcohol ethoxylates: Insecticidal and synergistic effects on German cockroaches (Blattodea: Blattellidae) and other insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, M.; van Egmond, R. The use of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo for the acute toxicity testing of surfactants, as a possible alternative to the acute fish test. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2010, 38, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herkert, N.J.; Kassotis, C.D.; Zhang, S.; Han, Y.; Pulikkal, V.F.; Sun, M.; Ferguson, P.L.; Stapleton, H.M. Characterization of Per- and Polyfluorinated Alkyl Substances Present in Commercial Anti-fog Products and Their In Vitro Adipogenic Activity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imrie, D.; Sadler, K.C. White adipose tissue development in zebrafish is regulated by both developmental time and fish size. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 3013–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Chemical | Acronym | CAS # | Manufacturer | Catalog # | Avg MW | Molecular Formula | Conc. Tested |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohols/ethoxylates | |||||||
| cetyl alcohol | CetAEO (0) | 36653-82-4 | Chem Service | N-11416-1G | 242.5 | C16H33OH | 1 nM–10 μM (vitro) 1 nM–1 μM (vivo) |
| cetyl alcohol ethoxylate (1–2) | CetAEO (2) | N/A | Sigma | 388831-100G | 330 | C16H33(OCH2CH2)2OH | 1 nM–10 μM (vitro) 1 nM–1 μM (vivo) |
| cetyl alcohol ethoxylate (4) | CetAEO (4) | N/A | Parchem | Ceteth-4 | 419 | C16H33(OCH2CH2)4OH | 1 nM–10 μM (vitro) 1 nM–1 μM (vivo) |
| cetyl alcohol ethoxylate (6) | CetAEO (6) | N/A | Barnet | BC-5.5 | 507 | C16H33(OCH2CH2)6OH | 1 nM–10 μM (vitro) 1 nM–1 μM (vivo) |
| cetyl alcohol ethoxylate (10) | CetAEO (10) | N/A | Barnet | BC-10 | 683 | C16H33(OCH2CH2)10OH | 1 nM–10 μM (vitro) 1 nM–1 μM (vivo) |
| cetyl alcohol ethoxylate (20) | CetAEO (20) | N/A | Chem Service | NG-S317-1G | 1123 | C16H33(OCH2CH2)20OH | 1 nM–10 μM (vitro) 1 nM–1 μM (vivo) |
| Control chemicals | |||||||
| Tributyltin chloride | TBT | 1461-22-9 | Sigma | 442869 | 325.5 | [CH3(CH2)3]3SnCl | 1 pM–1 nM (vivo) |
| Mono(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate | MEHP | 4376-20-9 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-396467 | 278.3 | C16H22O4 | 0.1–1 μM (vivo) |
| Dimethylsulfoxide | DMSO | 67-68-5 | Sigma | 34869-100mL | 78.1 | (CH3)2SO | 0.1% as vehicle |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
LeFauve, M.K.; Bérubé, R.; Heldman, S.; Chiang, Y.-T.T.; Kassotis, C.D. Cetyl Alcohol Polyethoxylates Disrupt Metabolic Health in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish. Metabolites 2023, 13, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030359
LeFauve MK, Bérubé R, Heldman S, Chiang Y-TT, Kassotis CD. Cetyl Alcohol Polyethoxylates Disrupt Metabolic Health in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish. Metabolites. 2023; 13(3):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030359
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeFauve, Matthew K., Roxanne Bérubé, Samantha Heldman, Yu-Ting Tiffany Chiang, and Christopher D. Kassotis. 2023. "Cetyl Alcohol Polyethoxylates Disrupt Metabolic Health in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish" Metabolites 13, no. 3: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030359
APA StyleLeFauve, M. K., Bérubé, R., Heldman, S., Chiang, Y.-T. T., & Kassotis, C. D. (2023). Cetyl Alcohol Polyethoxylates Disrupt Metabolic Health in Developmentally Exposed Zebrafish. Metabolites, 13(3), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030359










