Glucocorticoid-Induced Hyperinsulinism in a Preterm Neonate with Inherited ABCC8 Variant
Abstract
1. Introduction
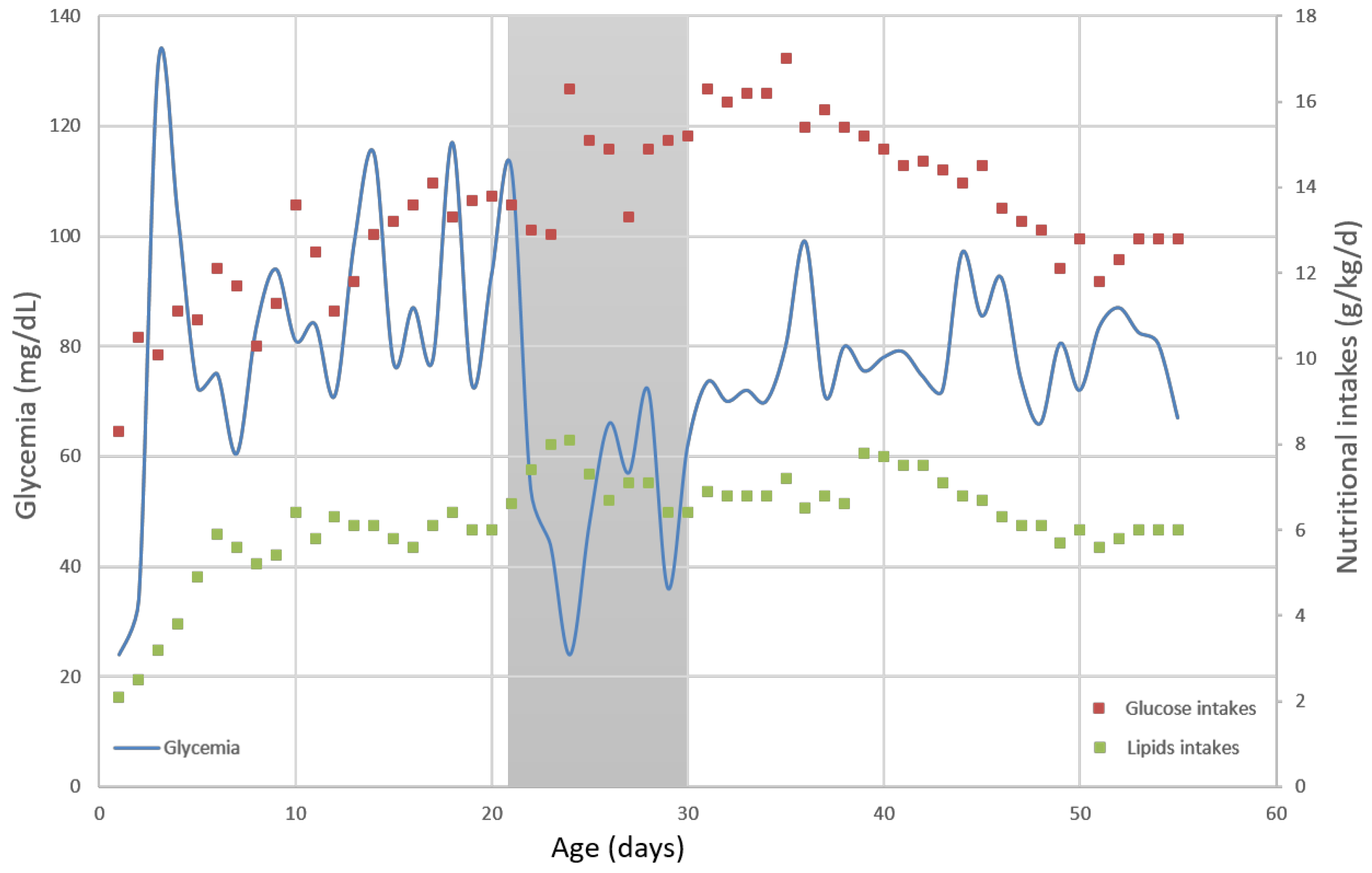
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beardsall, K. Real time continuous glucose monitoring in neonatal intensive care. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 138, 104844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitanchez, D.; Yzydorczyk, C.; Siddeek, B.; Boubred, F.; Benahmed, M.; Simeoni, U. The offspring of the diabetic mother—Short- and long-term implications. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2015, 29, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billionnet, C.; Mitanchez, D.; Weill, A.; Nizard, J.; Alla, F.; Hartemann, A.; Jacqueminet, S. Gestational diabetes and adverse perinatal outcomes from 716,152 births in France in 2012. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacko, S.K.; Ordonez, J.; Sauer, P.J.J.; Sunehag, A.L. Gluconeogenesis is not regulated by either glucose or insulin in extremely low birth weight infants receiving total parenteral nutrition. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitanchez-Mokhtari, D.; Lahlou, N.; Kieffer, F.; Magny, J.F.; Roger, M.; Voyer, M. Both relative insulin resistance and defective islet beta-cell processing of proinsulin are responsible for transient hyperglycemia in extremely preterm infants. Pediatrics 2004, 113 Pt 1, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evagelidou, E.N.; Giapros, V.I.; Challa, A.S.; Kiortsis, D.N.; Tsatsoulis, A.A.; Andronikou, S.K. Serum adiponectin levels, insulin resistance, and lipid profile in children born small for gestational age are affected by the severity of growth retardation at birth. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 156, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salis, E.R.; Reith, D.M.; Wheeler, B.J.; Broadbent, R.S.; Medlicott, N.J. Hyperglycaemic preterm neonates exhibit insulin resistance and low insulin production. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2017, 1, e000160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Doyle, L.W.; Davis, P.G.; Morley, C.J.; McPhee, A.; Carlin, J.B.; DART Study Investigators. Low-dose dexamethasone facilitates extubation among chronically ventilator-dependent infants: A multicenter, international, randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCastro, M.; El-Khoury, N.; Parton, L.; Ballabh, P.; LaGamma, E.F. Postnatal betamethasone vs. dexamethasone in premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A pilot study. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihatsch, W.A.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN working group on pediatric parenteral nutrition. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37 Pt B, 2303–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGoldrick, E.; Stewart, F.; Parker, R.; Dalziel, S.R. Antenatal corticosteroids for accelerating fetal lung maturation for women at risk of preterm birth. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 12, CD004454. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Marmiesse, A.; Salas, A.; Vega, A.; Fernández-Lorenzo, J.R.; Barreiro, J.; Carracedo, A. Mutation spectra of ABCC8 gene in Spanish patients with Hyperinsulinism of Infancy (HI). Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinney, S.E.; MacMullen, C.; Becker, S.; Lin, Y.W.; Hanna, C.; Thornton, P.; Ganguly, A.; Shyng, S.L.; Stanley, C.A. Clinical characteristics and biochemical mechanisms of congenital hyperinsulinism associated with dominant KATP channel mutations. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macmullen, C.M.; Zhou, Q.; Snider, K.E.; Tewson, P.H.; Becker, S.A.; Aziz, A.R.; Ganguly, A.; Shyng, S.L.; Stanley, C.A. Diazoxide-unresponsive congenital hyperinsulinism in children with dominant mutations of the β-cell sulfonylurea receptor SUR1. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huopio, H.; Otonkoski, T.; Vauhkonen, I.; Reimann, F.; Ashcroft, F.M.; Laakso, M. A new subtype of autosomal dominant diabetes attributable to a mutation in the gene for sulfonylurea receptor 1. Lancet 2003, 361, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Männikkö, R.; Flanagan, S.E.; Sim, X.; Segal, D.; Hussain, K.; Ellard, S.; Hattersley, A.T.; Ashcroft, F.M. Mutations of the same conserved glutamate residue in NBD2 of the sulfonylurea receptor 1 subunit of the KATP channel can result in either hyperinsulinism or neonatal diabetes. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Havinga, R.; Bloks, V.W.; Baller, J.F.; van der Leij, F.R.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Sauer, P.J.J.; Kuipers, F. Postnatal treatment with dexamethasone perturbs hepatic and cardiac energy metabolism and is associated with a sustained atherogenic plasma lipid profile in suckling rats. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 61, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, C.L.; Kim, J. Neonatal Glucose Homeostasis. Clin. Perinatol. 2022, 49, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, M.E.; Brown, S.J.; Satrom, K.M.; Scheurer, J.M.; Ramel, S.E.; Rao, R.B. Long-Term Outcomes after Early Neonatal Hyperglycemia in VLBW Infants: A Systematic Review. Neonatology 2021, 118, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, A.; Kuzuya, N. On the role of glucocorticoid in glucose-induced insulin secretion. Horm. Metab. Res. 1977, 9, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, M.; Weber, T.; Wrange, O.; Nielsen, D.A.; Matthieu, M.; Steiner, D.F. Regulation of insulin gene expression by dexamethasone, Ca2+ and a phorbol ester. Biomed. Biochim. Acta 1988, 47, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Townsend, S.F.; Rudolph, C.D.; Rudolph, A.M. Cortisol induces perinatal hepatic gluconeogenesis in the lamb. J. Dev. Physiol. 1991, 16, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawai, Y.; Arinze, I.J. Glucocorticoid regulation of G-protein subunits in neonatal liver. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 1993, 90, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambillotte, C.; Gilon, P.; Henquin, J.C. Direct glucocorticoid inhibition of insulin secretion. An in vitro study of dexamethasone effects in mouse islets. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardsall, K.; Vanhaesebrouck, S.; Ogilvy-Stuart, A.L.; Vanhole, C.; Palmer, C.R.; Ong, K.; van Weissenbruch, M.; Midgley, P.; Thompson, M.; Thio, M.; et al. Prevalence and determinants of hyperglycemia in very low birth weight infants: Cohort analyses of the NIRTURE study. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 715–719.e1–e.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte-Signoret, E.; Shankar-Aguilera, S.; Brailly-Tabard, S.; Soreze, Y.; Dell Orto, V.; Ben Ammar, R.; De Luca, D.; Boileau, P. Small for Gestational Age Preterm Neonates Exhibit Defective GH/IGF1 Signaling Pathway. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 711400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, N.; Shoji, H.; Kitamura, T.; Suganuma, H.; Yoshikawa, N.; Suzuki, M.; Lee, T.; Hisata, K.; Shimizu, T. IGF-I, leptin and active ghrelin levels in very low birth weight infants during the first 8 weeks of life. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.; Hindmarsh, P.; Aynsley-Green, A. Neonates with symptomatic hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia generate inappropriately low serum cortisol counterregulatory hormonal responses. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4342–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courty, E.; Besseiche, A.; Do, T.T.H.; Liboz, A.; Aguid, F.M.; Quilichini, E.; Buscato, M.; Gourdy, P.; Gautier, J.F.; Riveline, J.P.; et al. Adaptive β-Cell Neogenesis in the Adult Mouse in Response to Glucocorticoid-Induced Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2019, 68, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, N.H.F.; Doig, C.L.; Elhassan, Y.S.; Vierra, N.C.; Marchetti, P.; Bugliani, M.; Nano, R.; Piemonti, L.; Rutter, G.A.; Jacobson, D.A.; et al. Glucocorticoids Reprogram β-Cell Signaling to Preserve Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2018, 67, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.A.; Leete, P. Glucocorticoids: Novel agents to stimulate beta-cell neogenesis? Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, C.G. KATP channels as molecular sensors of cellular metabolism. Nature 2006, 440, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nessa, A.; Aziz, Q.H.; Thomas, A.M.; Harmer, S.C.; Tinker, A.; Hussain, K. Molecular mechanisms of congenital hyperinsulinism due to autosomal dominant mutations in ABCC8. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5142–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.C.; Bergamin, C.S.; Gurgel, L.C.; Moisés, R.S. Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia evolving to gestational diabetes and diabetes mellitus in a family carrying the inactivating ABCC8 E1506K mutation. Pediatric. Diabetes 2010, 11, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J.; Osmond, C.; Golding, J.; Kuh, D.; Wadsworth, M.E. Growth in utero, blood pressure in childhood and adult life, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. BMJ 1989, 298, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.N.; Barker, D.J. The thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Br. Med. Bull. 2001, 60, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age | Days | D23 | D28 | D40 | D53 | D76 | D337 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMA | Weeks | 30 + 2 | 31 + 0 | 32 + 5 | 34 + 4 | 38 + 0 | 11 mo |
| Glycaemia | mmol/L mg/dL | 1.2 21 | 4.2 76 | 3.6 65 | 3.6 65 | 4.2 76 | 4.3 77 |
| Cortisol | µg/dL | 0.8 | 1.3 | / | / | / | / |
| GH | mUI/L | 2.4 | 5.7 | 29.9 | / | 21.3 | 1.26 |
| IGF1 | ng/mL | 15 | 21 | 48 | 46 | 82 | 119 |
| Insulin | pmol/L | 5903 | 1625 | 194 | 226 | 82 | 15.3 |
| Peptide C | pmol/L | 5.99 | 3.4 | 0.9 | 0.93 | 0.46 | 0.36 |
| Pro-insulin | pmol/L | 159 | / | 27.7 | 28 | 16.4 | 3.5 |
| Betamethasone | mg/kg/d | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motte-Signoret, E.; Saint-Martin, C.; Bellané-Chantelot, C.; Portha, B.; Boileau, P. Glucocorticoid-Induced Hyperinsulinism in a Preterm Neonate with Inherited ABCC8 Variant. Metabolites 2022, 12, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090847
Motte-Signoret E, Saint-Martin C, Bellané-Chantelot C, Portha B, Boileau P. Glucocorticoid-Induced Hyperinsulinism in a Preterm Neonate with Inherited ABCC8 Variant. Metabolites. 2022; 12(9):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090847
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotte-Signoret, Emmanuelle, Cécile Saint-Martin, Christine Bellané-Chantelot, Bernard Portha, and Pascal Boileau. 2022. "Glucocorticoid-Induced Hyperinsulinism in a Preterm Neonate with Inherited ABCC8 Variant" Metabolites 12, no. 9: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090847
APA StyleMotte-Signoret, E., Saint-Martin, C., Bellané-Chantelot, C., Portha, B., & Boileau, P. (2022). Glucocorticoid-Induced Hyperinsulinism in a Preterm Neonate with Inherited ABCC8 Variant. Metabolites, 12(9), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090847





