Research in the Field of Exercise and Metabolomics: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Number of Citations, Number of Publications
2.2. Analysis of Periodicals
2.3. Analysis of Country/Region
2.4. Analysis of Research Direction
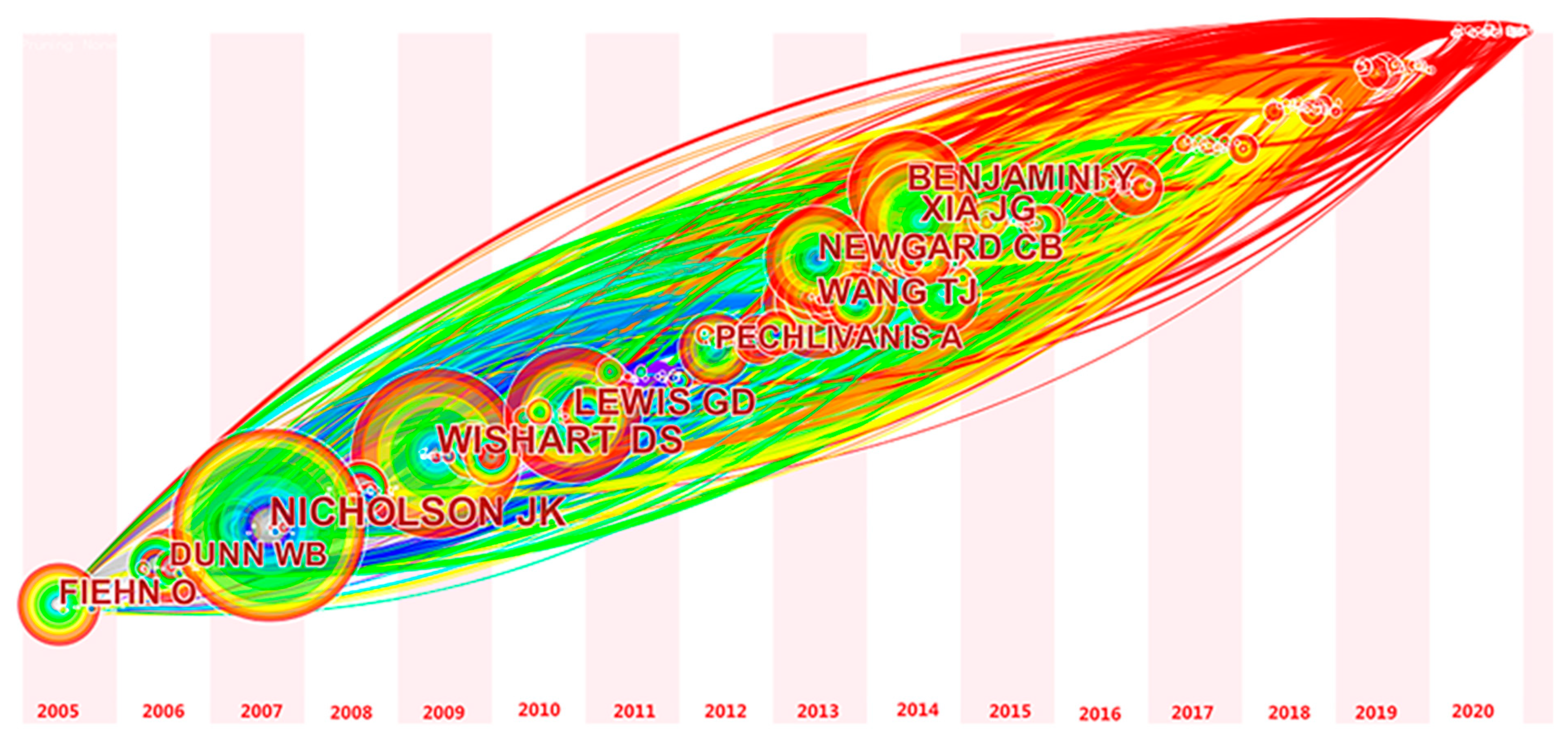
2.5. Analysis of Author
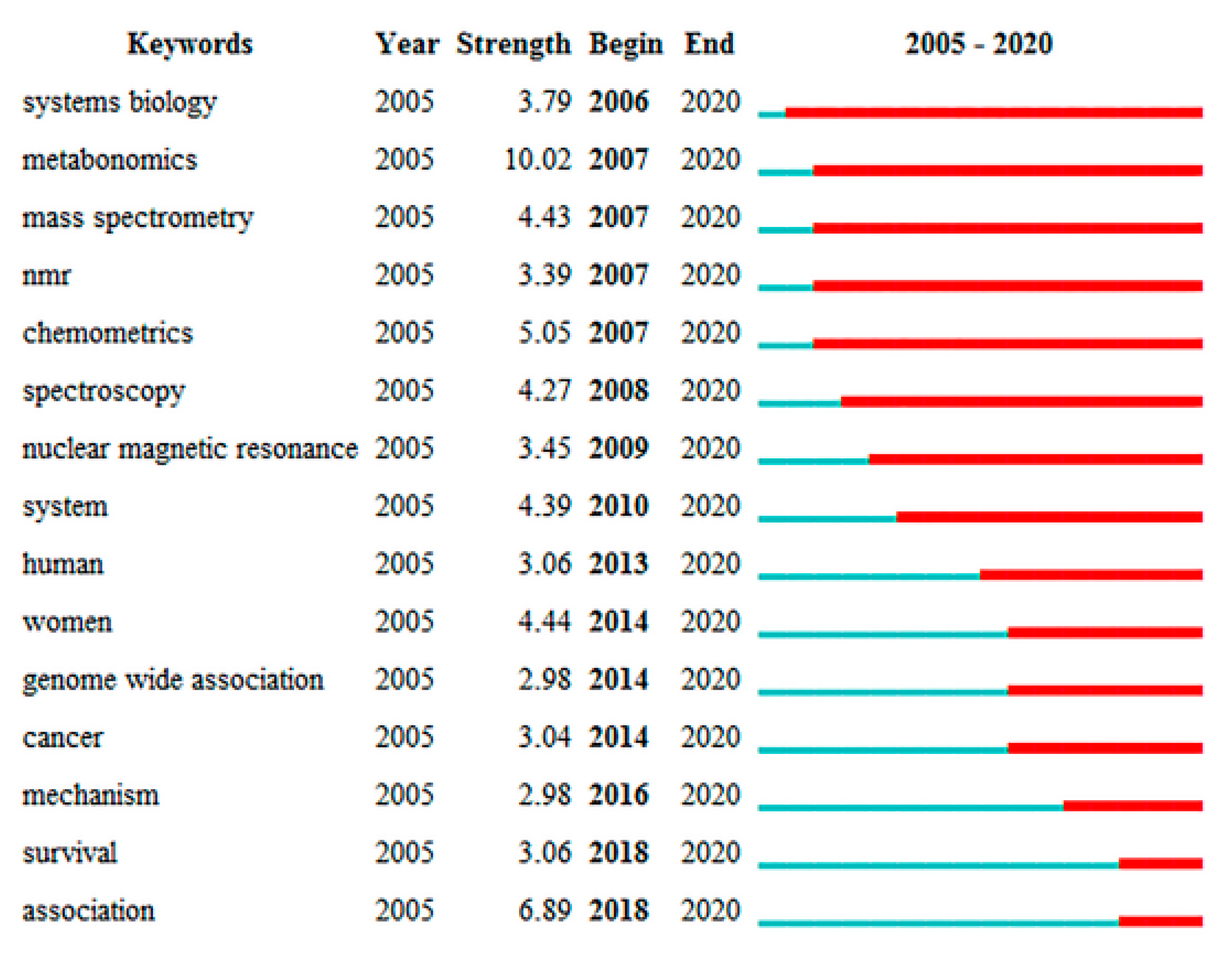
2.6. Analysis of Explicit Frontier
2.7. Analysis of Implicit Frontier
2.8. Analysis of Dynamic Development Trend
3. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
- (1)
- The search strategy was limited to the Web of Science Core Database and only articles were searched. Therefore, these factors may lead to publication bias.
- (2)
- Co-citation analysis, as well as the geospatial visualization in CiteSpace, were not used but had no effect on the final analysis results.
- (3)
- The search time was not comprehensive enough, resulting in four articles from the Web of Science Core Database before 2005 not being included in the analysis, but this did not affect the final analysis results.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Search Strategy
4.2. Analysis Tools
4.3. Data Extraction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. ‘Metabonomics’: Understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.-R.; Wang, Y.-L. Metabonomics: A Revolution in Progress5. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 33, 401–417. [Google Scholar]
- Heaney, L.M.; Deighton, K.; Suzuki, T. Non-targeted metabolomics in sport and exercise science. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Shanely, R.A.; Luo, B.; Meaney, M.P.; Dew, D.A.; Pappan, K.L. Metabolomics approach to assessing plasma 13-and 9-hydroxy-octadecadienoic acid and linoleic acid metabolite responses to 75-km cycling. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 307, R68–R74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieman, D.C.; Gillitt, N.D.; Henson, D.A.; Sha, W.; Shanely, R.A.; Knab, A.M.; Cialdella-Kam, L.; Jin, F. Bananas as an energy source during exercise: A metabolomics approach. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Gui, Y.-H.; Lin, D.-H. Metabolomics: A Novel Tool for Sports and Exercise Science. China Sport Sci. 2011, 31, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-J. Survey of approaches to research front detection. Data Anal. Knowl. Discov. 2009, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Fu, J.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-H. Study on Recognition of Research Fronts Based on a Method which Fuses Patent Bibliographic Coupling and Co-Citation in the field of Brain-Computer Interface. J. China Soc. Sci. Tech. Inf. 2016, 35, 971–979. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, L. Recognize the Fronts and Trends of Biology and Medical Research domain; Academy of Military Medical Sciences: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wallin, J.A. Bibliometric methods: Pitfalls and possibilities. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 97, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Weng, L.-M.; Peng, M.-S.; Wang, X.-Q. Exercise for low back pain: A bibliometric analysis of global research from 1980 to 2018. J. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 52, jrm00052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-W. Metabolomics: Methods and Applications; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C.M.; Liu, Z.Y.; Luan, C.; Hu, Z.; Wang, X. The methodology function of CiteSpace mapping knowledge domains. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2015, 33, 242–253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Visualization analysis of the development trajectory of knowledge sharing in virtual communities based on CiteSpace. J. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 29643–29657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamler, J.; Vaccaro, O.; Neaton, J.D.; Wentworth, D. Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonora, E.; Targher, G.; Branzi, P.; Zenere, M.; Saggiani, F.; Zenti, M.G.; Travia, D.; Tonoli, M.; Muggeo, M.; Cigolini, M. Cardiovascular risk profile in 38-year and 18-year-old men. Contribution of body fat content and regional fat distribution. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 1996, 20, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannucci, E.; Michaud, D. The role of obesity and related metabolic disturbances in cancers of the colon, prostate, and pancreas. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2208–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, G.E.; Hittel, D.S.; Sensen, C.W.; Weljie, A.M.; Vogel, H.J.; Shearer, J. Metabolomic response to exercise training in lean and diet-induced obese mice. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 110, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glynn, E.L.; Piner, L.W.; Huffman, K.M.; Slentz, C.A.; Penry, L.E.; AbouAssi, H.; White, P.J.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; et al. Impact of combined resistance and aerobic exercise training on branched-chain amino acid turnover, glycine metabolism and insulin sensitivity in overweight humans. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2324–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Yde, C.C.; Arnberg, K.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Larnkjær, A.; Bertram, H.C. NMR-based metabolomic profiling of overweight adolescents: An elucidation of the effects of inter-/intraindividual differences, gender, and pubertal development. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criswell, D.; Powers, S.; Dodd, S.; Lawler, J.; Edwards, W.; Renshler, K.; Grinton, S. High intensity training-induced changes in skeletal muscle antioxidant enzyme activity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1993, 25, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finaud, J.; Lac, G.; Filaire, E. Oxidative stress. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 327–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.K.; Jackson, M.J. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1243–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambert, G. Stress-induced gastrointestinal barrier dysfunction and its inflammatory effects. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, E101–E108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Oliveira, E.P.; Burini, R.C.; Jeukendrup, A. Gastrointestinal complaints during exercise: Prevalence, etiology, and nutritional recommendations. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssenduijghuijsen, L.M.; Mensink, M.; Lenaerts, K.; Fiedorowicz, E.; van Dartel, D.A.M.; Mes, J.J.; Luiking, Y.C.; Keijer, J.; Wichers, H.J.; Witkamp, R.F. The effect of endurance exercise on intestinal integrity in well-trained healthy men. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannoni, A.; Pietra, M.; Gaspardo, A.; Accorsi, P.A.; Barone, M.; Turroni, S.; Laghi, L.; Zhu, C.; Brigidi, P.; Forni, M. Non-invasive assessment of fecal stress biomarkers in hunting dogs during exercise and at rest. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chorell, E.; Svensson, M.B.; Moritz, T.; Antti, H. Physical fitness level is reflected by alterations in the human plasma metabolome. Mol. BioSyst. 2012, 8, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBalsi, K.L.; Wong, K.E.; Koves, T.R.; Slentz, D.H.; Seiler, S.E.; Wittmann, A.H.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; Stevens, R.D.; Perry, C.G.R.; Lark, D.S.; et al. Targeted metabolomics connects thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) to mitochondrial fuel selection and regulation of specific oxidoreductase enzymes in skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 8106–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couto, M.; Barbosa, C.; Silva, D.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Delgado, L.; Moreira, A.; Rocha, S.M. Oxidative stress in asthmatic and non-asthmatic adolescent swimmers—A breathomics approach. Pediatric Allergy Immunol. 2017, 28, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, D.; Arend, E.; Rocha, S.M.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Delgado, S.; Moreira, A.; Carvalho, J. The impact of exercise training on the lipid peroxidation metabolomic profile and respiratory infection risk in older adults. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoi, M.; Percival, M.; Nemr, C.; Li, A.; Gibala, M.; Britz-McKibbin, P. Characterization of the human skeletal muscle metabolome for elucidating the mechanisms of bicarbonate ingestion on strenuous interval exercise. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4709–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khelaifi, F.; Diboun, I.; Donati, F.; Botre, F.; Alsayrafi, M.; Georgakopoulos, C.; Suhre, K.; Yousri, N.A.; Elrayess, M.A. A pilot study comparing the metabolic profiles of elite-level athletes from different sporting disciplines. Sports Med.-Open 2018, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, N.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Peng, D.-Y. Research on Frontier Prediction Based on Citation Relation and Lexical Analysis—Taking the Field of Artificial Intelligence as an Example. J. Intell. 2020, 39, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Leng, F.-H. Development of Theoretical Studies of Co-Word Analysis. J. Libr. Sci. China 2006, 2, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, O. The intellectual base and research fronts of JASIS 1986–1990. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1994, 45, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazine L a I, S. Development and Innovation if Metrology Research; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]



| Serial Number | Source Publication Name | Number of Posts Issued | Percentage of Published Articles in Total Retrieved Articles (%) | 5 Year Impact Factor | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Metabolomics | 41 | 5.081 | 3.625 | United States |
| 2 | Journal of Proteome Research | 35 | 4.337 | 3.946 | United States |
| 3 | Metabolites | 33 | 4.089 | Switzerland | |
| 4 | Plosone | 29 | 3.594 | 3.227 | United States |
| 5 | Scientific Reports | 23 | 2.85 | 4.576 | Germany |
| 6 | Analytical Chemistry | 22 | 2.726 | 6.642 | United States |
| 7 | Analytic and Bioanalytical Chemistry | 12 | 1.487 | 3.444 | Germany |
| 8 | Amercan Journal of Clinical Nutrition | 9 | 1.115 | 7.831 | United Kingdom |
| 9 | Frontiers in Physiology | 9 | 1.115 | 3.697 | Switzerland |
| 10 | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry | 8 | 0.991 | 4.290 | United States |
| Country/Region | Number of Posts Issued | Percentage of Total Retrieved Articles (%) |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 275 | 34.077 |
| China | 154 | 19.083 |
| England | 104 | 12.887 |
| Germany | 88 | 10.905 |
| Canada | 60 | 7.435 |
| Italy | 50 | 6.196 |
| Spain | 50 | 6.196 |
| Japan | 42 | 5.204 |
| France | 38 | 4.709 |
| Australia | 36 | 4.461 |
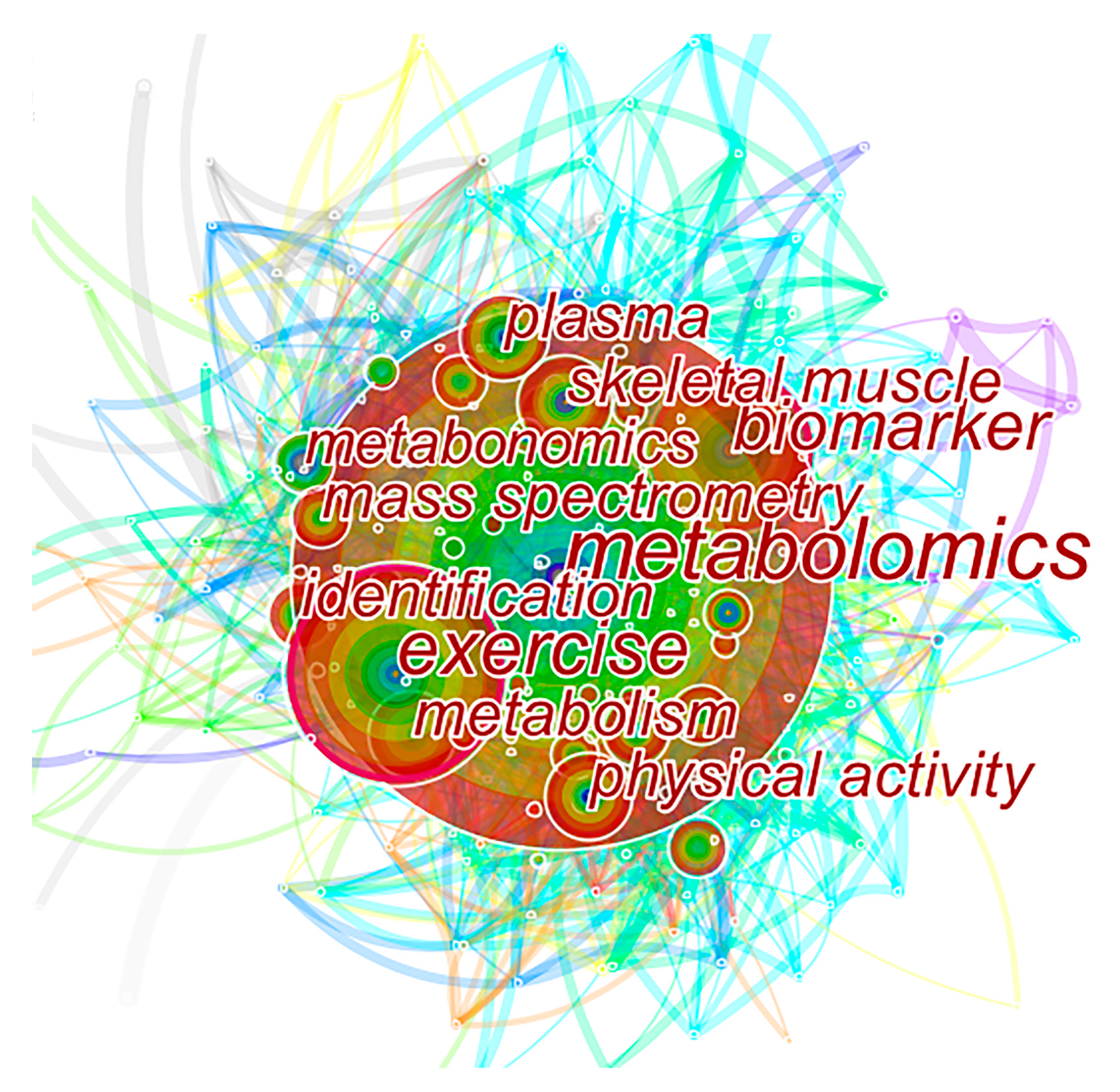
| Serial Number | High-Frequency Keywords | Frequency | Serial Number | Highly Central Keywords | Centrality Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Metabolomics | 430 | 1 | Exercise | 0.16 |
| 2 | Exercise | 197 | 2 | Biomarker | 0.11 |
| 3 | Biomarker | 148 | 3 | Metabolism | 0.09 |
| 4 | Metabolism | 86 | 4 | Acid | 0.07 |
| 5 | Skeletal muscle | 86 | 5 | Profile | 0.07 |
| 6 | Plasma | 83 | 6 | Metabolomics | 0.06 |
| 7 | Physical activity | 78 | 7 | Skeletal Muscle | 0.06 |
| 8 | Mass spectrometry | 76 | 8 | Physical activity | 0.06 |
| 9 | Identification | 74 | 9 | Mass spectrometry | 0.06 |
| 10 | Metabonomics | 68 | 10 | Amino acid | 0.06 |
| 11 | Obesity | 66 | 11 | Urine | 0.06 |
| 12 | Insulin resistance | 64 | 12 | Inflammation | 0.06 |
| 13 | Risk | 60 | 13 | Cardiovascular disease | 0.06 |
| 14 | Metabolite | 56 | 14 | Response | 0.06 |
| 15 | Serum | 55 | 15 | Disease | 0.05 |
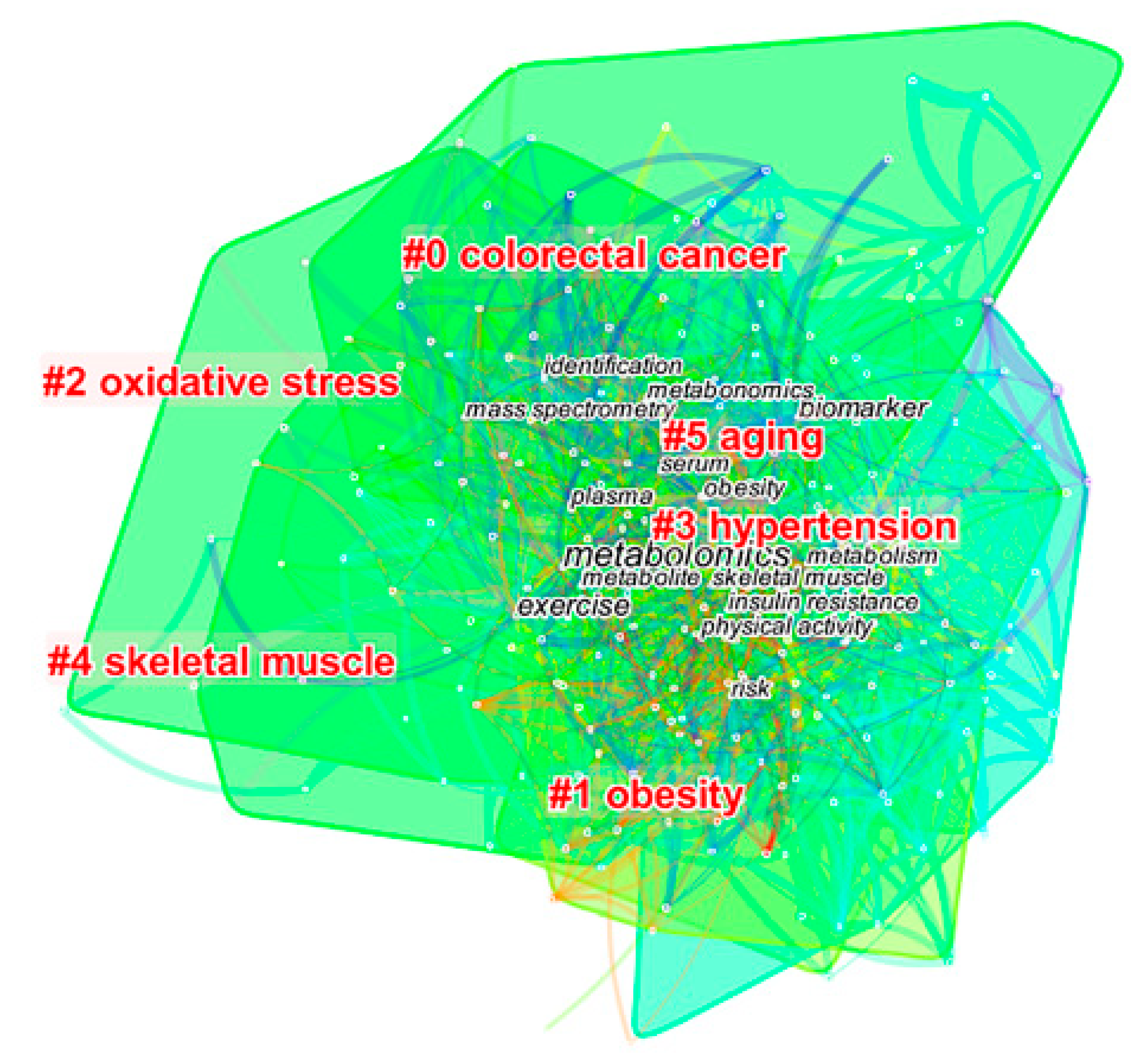
| Clustering | Number of Nodes | Contour Value | Year of Formation | Label Words | Keywords in Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 55 | 0.761 | 2012 | colorectal cancer | metabolomics, biomarkers, plasma, mass spectrometry, identification, metabonomics, serum, acid, profile, expression, urine, nuclear magnetic resonance, cancer, spectroscopy, chemometrics, system |
| 1 | 53 | 0.745 | 2014 | obesity | physical activity, obesity, insulin resistance, risk, disease, amino acid, diet, health, inflammation, association, fatty acid, cardiovascular disease, risk factor, mechanism, human, woman, genome wide association |
| 2 | 36 | 0.649 | 2013 | oxidative stress | performance, oxidative stress, muscle, metabolome, model, response, physical exercise, systems biology, stress, liver, mice, brain |
| 3 | 33 | 0.677 | 2014 | hypertension | protein, supplementation, NMR spectroscopy, mortality, nutrition, pathway, survival, body mass index, proteomics, magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| 4 | 33 | 0.793 | 2011 | skeletal muscle | exercise, metabolism, skeletal muscle, glucose, validation, gene expression, database, capacity, oxidation, gene, lactate |
| 5 | 28 | 0.670 | 2015 | aging | metabolite, rat, blood, prediction, age, gut microbiota, aging, carnitine, lipidomics, targeted metabolomics, Phosphatidylcholine, acylcarnitine |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, Z.; Gong, Z.-G.; Xu, Y.-J. Research in the Field of Exercise and Metabolomics: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060542
Lv Z, Gong Z-G, Xu Y-J. Research in the Field of Exercise and Metabolomics: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis. Metabolites. 2022; 12(6):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060542
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Zhen, Zhi-Gang Gong, and Yong-Jiang Xu. 2022. "Research in the Field of Exercise and Metabolomics: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis" Metabolites 12, no. 6: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060542
APA StyleLv, Z., Gong, Z.-G., & Xu, Y.-J. (2022). Research in the Field of Exercise and Metabolomics: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis. Metabolites, 12(6), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060542






