Evaluation of Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities of Soybean Meal Products Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum FPS 2520 and Bacillus subtilis N1 in Rats Fed with High-Fat Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
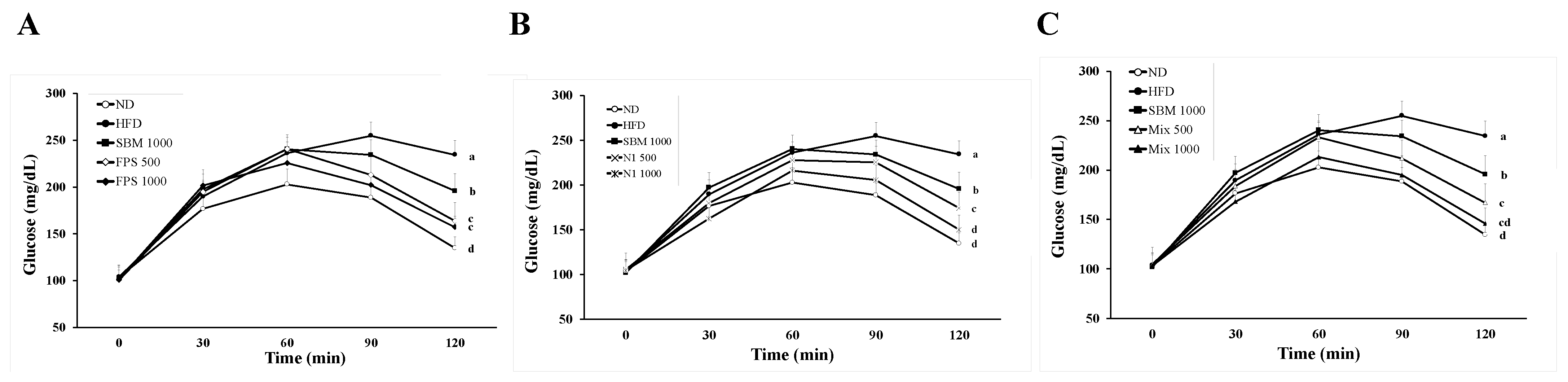
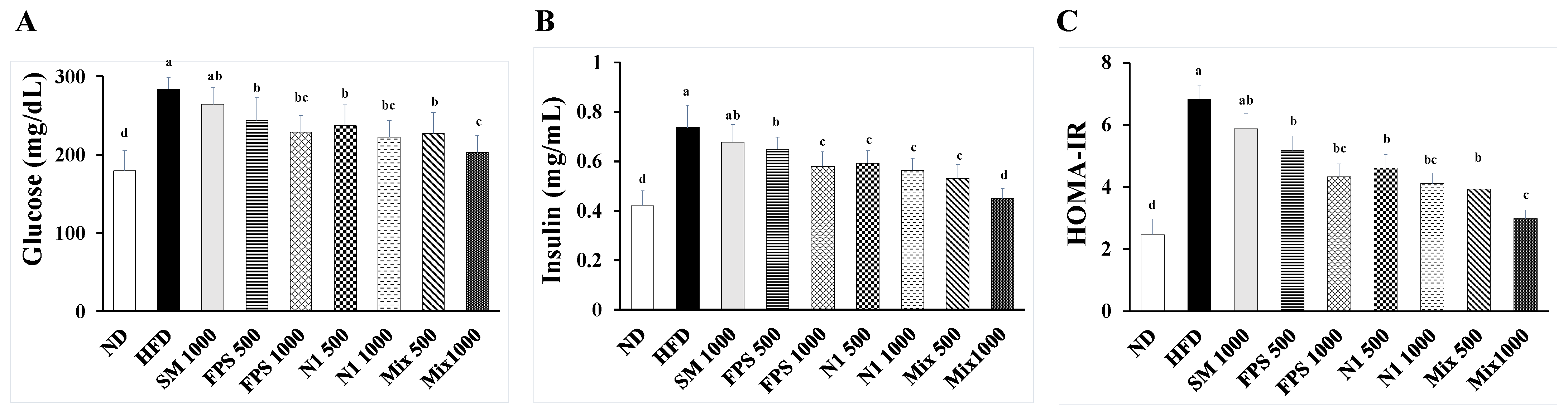
2.1. Daily Supplementation with Fermented SBM Ameliorated Hyperglycemia and Insulin Resistance in HFD-Induced Obese Rats
2.2. Daily Fed with Fermented SBM Attenuated HFD-Induced Hepatic and Nephritic Oxidative Damage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Reagents, Soybean Meal, and Rodent Diets
4.2. SBM Fermentation Culture
4.3. Extraction and Analysis of Isoflavones
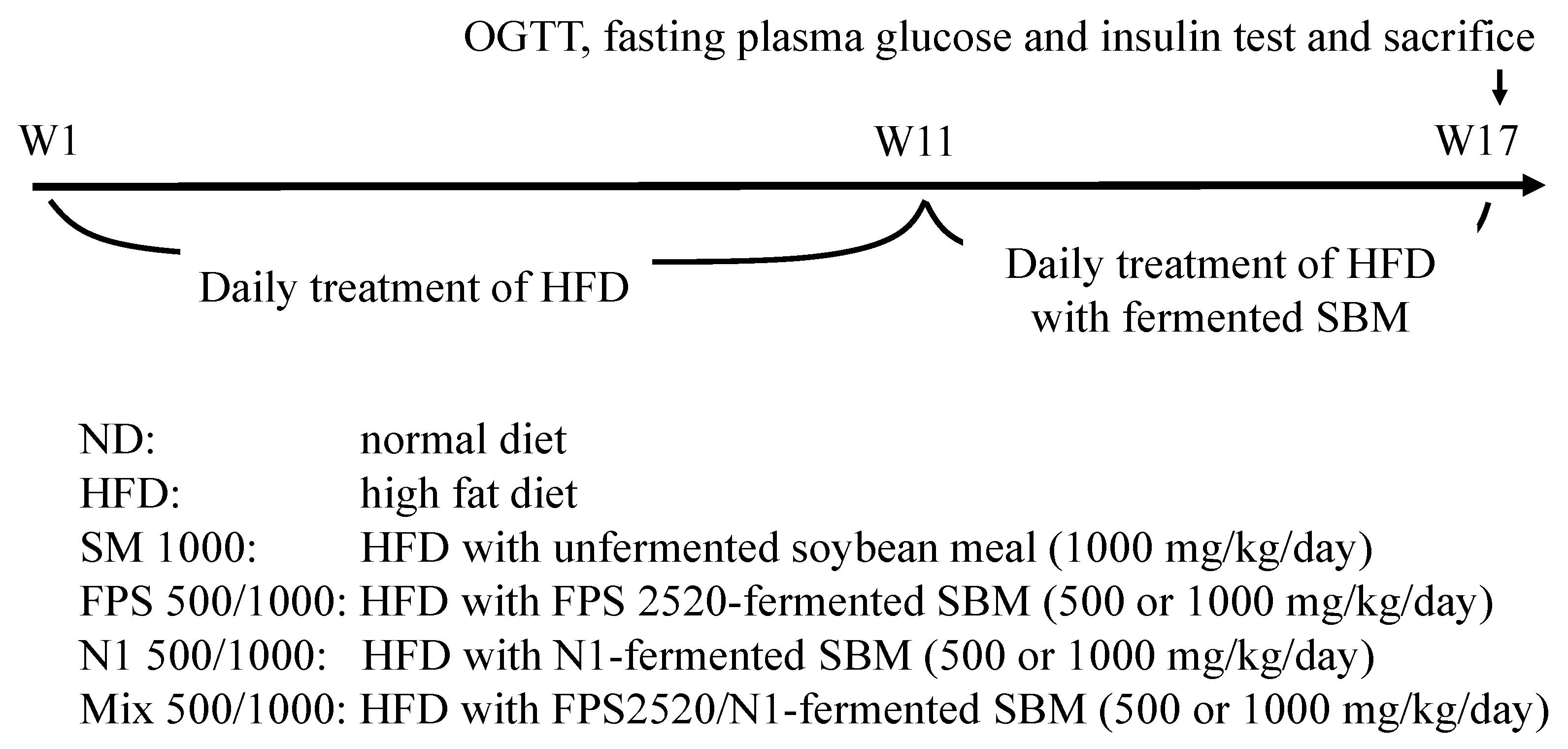
4.4. Animals and Experimental Design
4.5. Biochemistry Test for the Plasma Levels of Glucose, Insulin, AST, ALT, Creatinine and Uric Acid
4.6. Evaluation of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels in the Plasma and Liver
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirai, K. Obesity as the core of the metabolic syndrome and the management of coronary heart disease. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004, 20, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caterson, I.D.; Hubbard, V.; Bray, G.A.; Grustein, R.; Hansen, B.C.; Hong, Y.; Labarthe, D.; Seidell, J.C.; Smith, S.C. Prevention Conference VII: Obesity, a worldwide epidemic related to heart disease and stroke: Group III: Worldwide comorbidities of obesity. Circulation 2004, 110, e476–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, B.B.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesilbursa, D.; Serdar, Z.; Serdar, A.; Sarac, M.; Coskun, S.; Jale, C. Lipid peroxides in obese patients and effects of weight loss with orlistat on lipid peroxides levels. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Yu, R.C.; Chou, C.C. Antioxidative activities of soymilk fermented with lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgaard, A.; Jensen, L. The effects of soy isoflavones on obesity. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 1066–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiers, J.L.; Van Laeken, A.E.; Rombouts, F.M.; Nout, M.J. In vitro digestibility of bacillus fermented soya bean. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 60, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Effects of soy protein and genistein on blood glucose, antioxidant enzyme activities, and lipid profile in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, L.-C.; Wu, R.-Y.; Lee, K.-T. A process for high-efficiency isoflavone deglycosylation using Bacillus subtilis natto NTU-18. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, H. Enhanced biotransformation of soybean isoflavone from glycosides to aglycones using solid-state fermentation of soybean with effective microorganisms (EM) strains. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Taki, T.; Nakamoto, A.; Shuto, E.; Tsutsumi, R.; Toshimitsu, T.; Makino, S.; Ikegami, S. Lactobacillus plantarum OLL2712 regulates glucose metabolism in C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2013, 59, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouari, R.; Abdallah-Kolsi, R.B.; Hamden, K.; Feki, A.E.; Chaabouni, K.; Makni-Ayadi, F.; Sallemi, F.; Ellouze-Chaabouni, S.; Ghribi-Aydi, D. Assessment of the antidiabetic and antilipidemic properties of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Biopolymers 2015, 104, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Li, D.; Niu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Q. Antioxidant activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from traditional Chinese fermented foods. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabbene, O.; Karkouch, I.; Elkajoui, S.; Cosette, P.; Mangoni, M.-L.; Jouenne, T.; Limam, F. A new antibacterial and antioxidant S07-2 compound produced by Bacillus subtilis B38. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 303, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazza, J.A.; LeBlanc, J.G.; de Giori, G.S.; Garro, M.S. Soymilk fermented with Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL981 ameliorates hyperglycemia, lipid profiles and increases antioxidant enzyme activities in diabetic mice. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1848–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.Y.; Daily, J.W., III; Kim, H.J.; Park, S. Antidiabetic effects of fermented soybean products on type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Chen, C.L.; Chang, S.H.; Tsai, G.J. Evaluation of anti-obesity activity of soybean meal products fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum FPS 2520 and Bacillus subtilis N1 in rats fed with high-fat diet. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, E.J.; Magliano, D.; Shaw, J.E. Insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion determined by homeostasis model assessment and risk of diabetes in a multiethnic cohort of women: The Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study: Response to Song et al. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, e110–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Choi, J.H.; Pichiah, P.B.; Kim, M.J.; Cha, Y.S. Cheonggukjang, a soybean paste fermented with B. licheniformis-67 prevents weight gain and improves glycemic control in high fat diet induced obese mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2016, 59, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Aravinthan, A.; Park, Y.S.; Hwang, K.Y.; Seong, S.I.; Hwang, K. Supplementation of a fermented soybean extract reduces body mass and prevents obesity in high fat diet-induced C57BL/6J obese mice. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 21, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, M.; Okouchi, R.; Iwagaki, Y.; Asano, M.; Du, M.X.; Yamamoto, K.; Tsuduki, T. Fermented soybean suppresses visceral fat accumulation in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1701054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Ahn, N.; Jung, S.; Ju, Y.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.; Jeong, Y. Effects of resistance exercise and fermented soybean consumption on glucose tolerance and expressions of immune senescence-related myokines in middle-aged obese rats. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 27, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, B.; Park, H.; Ji, Y.; Holzapfel, W.; Kim, D.-Y.; Hyun, C.-K. Long-term fermented soybean paste improves metabolic parameters associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Yu, O.K.; Byun, M.S.; Cha, Y.S. Okara, a soybean by-product, prevents high fat diet-induced obesity and improves serum lipid profiles in C57BL/6J mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okouchi, R.; Sakanoi, Y.; Tsuduki, T. Miso (fermented soybean paste) suppresses visceral fat accumulation in mice, especially in combination with exercise. Nutrients 2019, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaneza, P.; Gonzalez, C.; Fernandez-Inarrea, J.; Alonso, A.; Diaz, F.; Perez-Lopez, F.R. Soy isoflavones improve insulin sensitivity without changing serum leptin among postmenopausal women. Climacteric 2012, 15, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrazek, H.M.A.; Mahmoud, M.M.A.; Tag, H.M.; Greish, S.M.; Eltamany, D.A.; Soliman, M.T.A. Soy Isoflavones ameliorate metabolic and immunological alterations of ovariectomy in female wistar rats: Antioxidant and estrogen sparing potential. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 5713606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Cheng, D.; Ma, W.; Xia, Y.; Liu, W.; Vhen, Z. Soy isoflavones improve the spermatogenic defects in diet-induced obesity rats through Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, G.A.; Park, S. Antioxidant action of soy isoflavones on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activities in exercised rats. Nutr Res. Pract. 2014, 8, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapbamrer, R.; Pinta, K.; Tantipaiboonwong, P. Isoflavones and anti-oxidant activities of soybean in Thailand. Res. J. Phytochem. 2012, 6, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, A.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. Soybean soluble polysaccharides enhance bioavailability of genistein and its prevention against obesity and metabolic syndrome of mice with chronic high fat consumption. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4153–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, E.; Cipriani, S.; Chiaffarino, F.; Malvezzi, M.; Parazzini, F. Effects of soy isoflavones and genistein on glucose metabolism in perimenopausal and postmenopausal non-Asian women: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Menopause 2010, 17, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.-B.; Chen, A.-L.; Lu, W.; Zhuo, S.-Y.; Liu, J.; Guan, J.-H.; Deng, W.-P.; Fang, S.; Li, Y.-B.; Chen, Y.-M. Daidzein and genistein fail to improve glycemic control and insulin sensitivity in Chinese women with impaired glucose regulation: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Igarashi, M.; Li, X.; Nakatani, A.; Miyamoto, J.; Inaba, Y.; Sutou, A.; Saito, T.; Sato, T.; Tachibana, N.; et al. Dietary soybean protein ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity by modifying the gut microbiota-dependent biotransformation of bile acids. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, T.W.; Lee, S.S. Effects of soybean supplementation on blood glucose, plasma lipid levels, and erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2008, 2, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Gu, X.; Stebbins, N.; Crandall, P.; Ricke, S.; Lee, S.-O. Effects of soybean pectin on blood glucose and insulin responses in healthy men. FASEB J. 2015, 596, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-J.; Kim, J.-I.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Kim, J.C.; Cha, I.-J. Pinitol from soybeans reduces postprandial blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, H.; Pang, X.; Hao, H. Hypoglycemic effects of space-induced Lactobacillus plantarum SS18-5 on type 2 diabetes in a rat model. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Wang, J.; Abdullah; Hafeez, M.A.; Guan, R.; Feng, F. Lactobacillus plantarum ZJUFB2 prevents high fat diet-induced insulin resistance in association with modulation of the gut microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2021, 14, 754222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Song, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Suo, H. Inhibitory effect and potential mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum YE4 against dipeptidyl peptidase-4. Foods 2021, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, N.; Yin, B.; Fang, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus plantarum X1 with α-glucosidase inhibitory activity ameliorates type 2 diabetes in mice. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 63536–63547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, D.; Park, G.-S.; Ko, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kang, J. Lactobacillus plantarum HAC01 ameliorates type 2 diabetes in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice in association with modulating the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6363–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mello, F.C.B.C.; Zaia, C.T.B.V.; Celligoi, M.A.P.C. Levan from Bacillus subtilis Natto: Its effects in normal and in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-S.; Park, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, K.-D.; Hwang, K.-Y.; Seong, S.I. Hypoglycemic effect of culture broth of Bacillus subtilis S10 producing 1-deoxynojirimycin. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 37, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, M.; Mihara, M. Determination of malonaldehyde precusor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Shieh, C.-C.; Chang, S.-H.; Tsai, G.-J. Evaluation of Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities of Soybean Meal Products Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum FPS 2520 and Bacillus subtilis N1 in Rats Fed with High-Fat Diet. Metabolites 2022, 12, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050442
Huang C-H, Chen C-L, Shieh C-C, Chang S-H, Tsai G-J. Evaluation of Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities of Soybean Meal Products Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum FPS 2520 and Bacillus subtilis N1 in Rats Fed with High-Fat Diet. Metabolites. 2022; 12(5):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050442
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chung-Hsiung, Chun-Lung Chen, Chen-Che Shieh, Shun-Hsien Chang, and Guo-Jane Tsai. 2022. "Evaluation of Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities of Soybean Meal Products Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum FPS 2520 and Bacillus subtilis N1 in Rats Fed with High-Fat Diet" Metabolites 12, no. 5: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050442
APA StyleHuang, C.-H., Chen, C.-L., Shieh, C.-C., Chang, S.-H., & Tsai, G.-J. (2022). Evaluation of Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities of Soybean Meal Products Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum FPS 2520 and Bacillus subtilis N1 in Rats Fed with High-Fat Diet. Metabolites, 12(5), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050442






