The Role of Thyroid Hormones on Skeletal Muscle Thermogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Thyroid Physiology
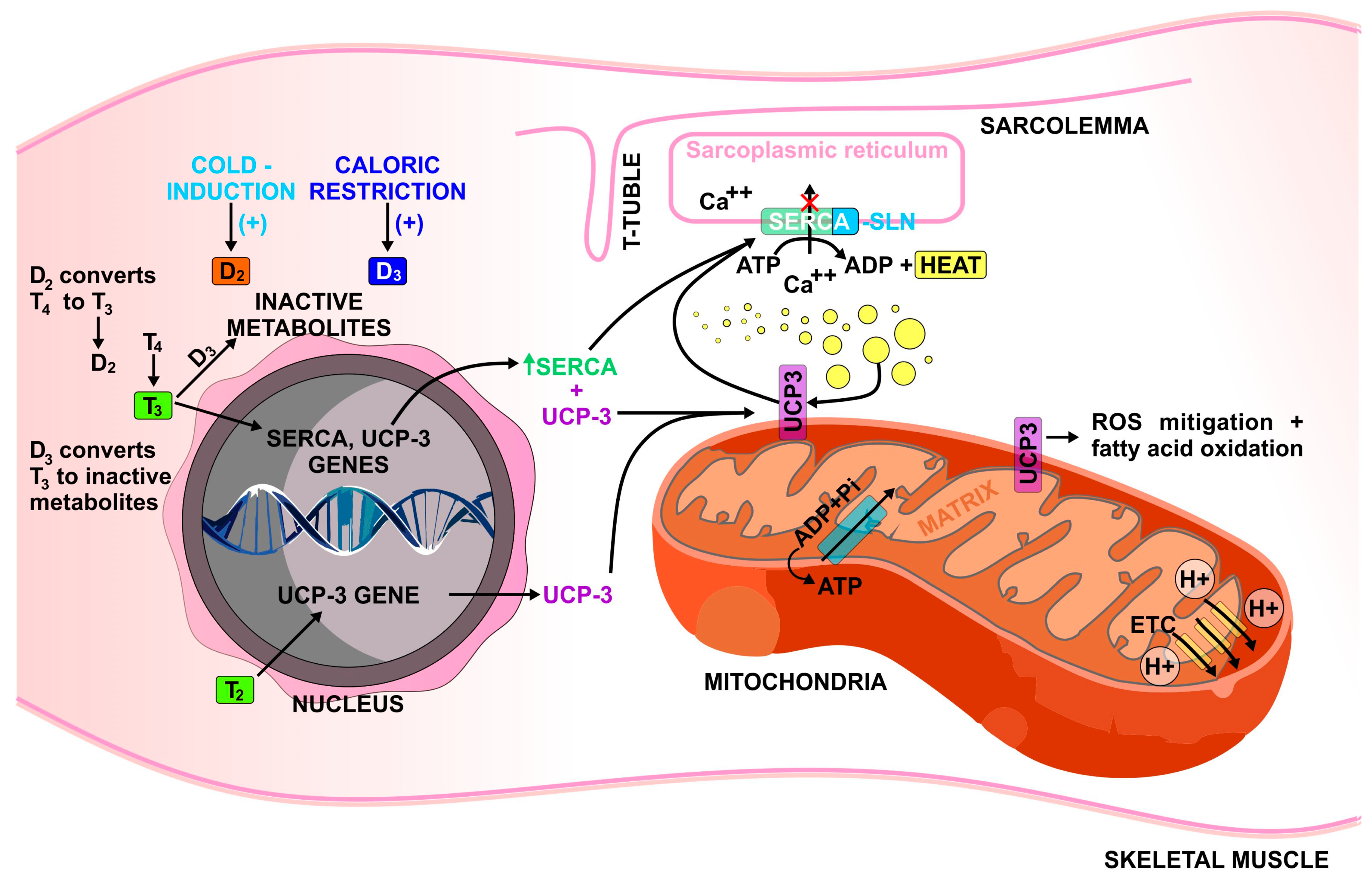
2.1. Regulation of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA)
2.2. Regulation of Mitochondrial Uncoupling Protein 3 (UCP-3)
2.3. Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Receptor Alpha 1 (TRa1)
2.4. 3,5-diiodo-L-Thyronine (T2) Effects
2.5. Role of Deiodinase Enzymes
3. Hypothyroidism
4. Sick Euthyroid Syndrome
5. Exogenous Levothyroxine
6. Hyperthyroidism
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piché, M.-E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.-P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.O.; Wyatt, H.R.; Peters, J.C. Energy Balance and Obesity. Circulation 2012, 126, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.Y.; Brychta, R.J.; Abdul Sater, Z.; Cassimatis, T.M.; Cero, C.; Fletcher, L.A.; Israni, N.S.; Johnson, J.W.; Lea, H.J.; Linderman, J.D.; et al. Opportunities and Challenges in the Therapeutic Activation of Human Energy Expenditure and Thermogenesis to Manage Obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 1926–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, A.; Yenilmez, B.; Bedard, A.H.; Henriques, F.; Liu, D.; Lee, A.; Goldstein, L.; Kelly, M.; Nicoloro, S.M.; Chen, M.; et al. Control of Adipocyte Thermogenesis and Lipogenesis through Β3-Adrenergic and Thyroid Hormone Signal Integration. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuchi, C.; Sul, H.S. Signaling Pathways Regulating Thermogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 595020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenzl, A.; Kiefer, F.W. Brown Adipose Tissue and Thermogenesis. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2014, 19, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-H.; Song, N.-J.; Choi, J.H.; Yun, U.J.; Park, K.W. Mechanisms Underlying UCP1 Dependent and Independent Adipocyte Thermogenesis. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2019, 20, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Li, L. Skeletal Muscle Non-Shivering Thermogenesis as an Attractive Strategy to Combat Obesity. Life Sci. 2021, 269, 119024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullur, R.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Brent, G.A. Thyroid Hormone Regulation of Metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 355–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, E.N. Thyroid Hormone and Obesity. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2012, 19, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangierski, A.; Ruchała, M.; Krauze, T.; Moczko, J.; Guzik, P. Treatment of Severe Thyroid Function Disorders and Changes in Body Composition. Endokrynol. Pol. 2016, 67, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geronimo, V.; Cannarella, R.; La Vignera, S. Thyroid Function and Obesity: From Mechanisms to the Benefits of Levothyroxine in Obese Patients. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Solís, P.; García, O.P.; Hernández-Puga, G.; Sánchez-Tusie, A.A.; Sáenz-Luna, C.E.; Hernández-Montiel, H.L.; Solis-S, J.C. Thyroid Hormones and Obesity: A Known but Poorly Understood Relationship. Endokrynol. Pol. 2018, 69, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.; Sieminska, L. Obesity and Thyroid Axis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsibulnikov, S.; Maslov, L.; Voronkov, N.; Oeltgen, P. Thyroid Hormones and the Mechanisms of Adaptation to Cold. Hormones 2020, 19, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payumo, A.Y.; Chen, X.; Hirose, K.; Chen, X.; Hoang, A.; Khyeam, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Powers, N.; et al. Adrenergic-Thyroid Hormone Interactions Drive Postnatal Thermogenesis and Loss of Mammalian Heart Regenerative Capacity. Circulation 2021, 144, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maushart, C.I.; Senn, J.R.; Loeliger, R.C.; Kraenzlin, M.E.; Müller, J.; Becker, A.S.; Balaz, M.; Wolfrum, C.; Burger, I.A.; Betz, M.J. Free Thyroxine Levels Are Associated with Cold Induced Thermogenesis in Healthy Euthyroid Individuals. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 666595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwen, K.A.; Oelkrug, R.; Brabant, G. Effects of Thyroid Hormones on Thermogenesis and Energy Partitioning. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 60, R157–R170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittag, J. More Than Fever—Novel Concepts in the Regulation of Body Temperature by Thyroid Hormones. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 128, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekri, Y.; Flamant, F.; Gauthier, K. Central vs. Peripheral Action of Thyroid Hormone in Adaptive Thermogenesis: A Burning Topic. Cells 2021, 10, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johann, K.; Cremer, A.L.; Fischer, A.W.; Heine, M.; Pensado, E.R.; Resch, J.; Nock, S.; Virtue, S.; Harder, L.; Oelkrug, R.; et al. Thyroid-Hormone-Induced Browning of White Adipose Tissue Does Not Contribute to Thermogenesis and Glucose Consumption. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3385–3400.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, K.J. Beige Fat, Adaptive Thermogenesis, and Its Regulation by Exercise and Thyroid Hormone. Biology 2019, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K. Novel Aspects of White Adipose Tissue Browning by Thyroid Hormones. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 128, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, W.W.; Yen, P.M. Thermogenesis in Adipose Tissue Activated by Thyroid Hormone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seale, L.A.; Ogawa-Wong, A.N.; Watanabe, L.M.; Khadka, V.S.; Menor, M.; Torres, D.J.; Carlson, B.A.; Hatfield, D.L.; Berry, M.J. Adaptive Thermogenesis in a Mouse Model Lacking Selenoprotein Biosynthesis in Brown Adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meis, L. Role of the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase on Heat Production and Thermogenesis. Biosci. Rep. 2001, 21, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, N.C.; Maurya, S.K.; Sopariwala, D.H.; Sahoo, S.K.; Gupta, S.C.; Shaikh, S.A.; Pant, M.; Rowland, L.A.; Bombardier, E.; Goonasekera, S.A.; et al. Sarcolipin Is a Newly Identified Regulator of Muscle-Based Thermogenesis in Mammals. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periasamy, M.; Herrera, J.L.; Reis, F.C.G. Skeletal Muscle Thermogenesis and Its Role in Whole Body Energy Metabolism. Diabetes Metab. J. 2017, 41, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, S.K.; Periasamy, M. Sarcolipin Is a Novel Regulator of Muscle Metabolism and Obesity. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 102, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloise, F.F.; Cordeiro, A.; Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M. Role of Thyroid Hormone in Skeletal Muscle Physiology. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 236, R57–R68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonides, W.S.; Thelen, M.H.M.; van der Linden, C.G.; Muller, A.; van Hardeveld, C. Mechanism of Thyroid-Hormone Regulated Expression of the SERCA Genes in Skeletal Muscle: Implications for Thermogenesis. Biosci. Rep. 2001, 21, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, A.P.; Oliveira, G.M.; Carvalho, D.P.; De Meis, L. Thyroid Hormones Differentially Regulate the Distribution of Rabbit Skeletal Muscle Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) Isoforms in Light and Heavy Sarcoplasmic Reticulum. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2005, 22, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaisen, T.S.; Klein, A.B.; Dmytriyeva, O.; Lund, J.; Ingerslev, L.R.; Fritzen, A.M.; Carl, C.S.; Lundsgaard, A.; Frost, M.; Ma, T.; et al. Thyroid Hormone Receptor α in Skeletal Muscle Is Essential for T3-mediated Increase in Energy Expenditure. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 15480–15491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busiello, R.A.; Savarese, S.; Lombardi, A. Mitochondrial Uncoupling Proteins and Energy Metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentis, S.C.; Oelkrug, R.; Mittag, J. Thyroid Hormones in the Regulation of Brown Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, R106–R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, J.E.; Mallett, N.M.; Rusyniak, D.E.; Mills, E. UCP3 and Thyroid Hormone Involvement in Methamphetamine-Induced Hyperthermia. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, J.E.; Yang, X.; Sommers, J.; Gilman, T.L.; Mills, E.M. Roles of Norepinephrine, Free Fatty Acids, Thyroid Status, and Skeletal Muscle Uncoupling Protein 3 Expression in Sympathomimetic-Induced Thermogenesis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, E.E.; Rupprecht, A.; Macher, G.; Hilse, K.E. Important Trends in UCP3 Investigation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, U.; Castelbou, C.; Demaurex, N. Uncoupling Protein 3 (UCP3) Modulates the Activity of Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) by Decreasing Mitochondrial ATP Production. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 32533–32541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, P.; Gauthier, K.; Sideleva, O.; Samarut, J.; Silva, J.E. Mice Lacking the Thyroid Hormone Receptor-α Gene Spend More Energy in Thermogenesis, Burn More Fat, and Are Less Sensitive to High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 6471–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senese, R.; de Lange, P.; Petito, G.; Moreno, M.; Goglia, F.; Lanni, A. 3,5-Diiodothyronine: A Novel Thyroid Hormone Metabolite and Potent Modulator of Energy Metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louzada, R.A.; Carvalho, D.P. Similarities and Differences in the Peripheral Actions of Thyroid Hormones and Their Metabolites. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, E.; Cioffi, F.; De Matteis, R.; Senese, R.; de Lange, P.; Coppola, M.; Salzano, A.M.; Scaloni, A.; Ceccarelli, M.; Goglia, F.; et al. 3,5-Diiodo-L-Thyronine Affects Structural and Metabolic Features of Skeletal Muscle Mitochondria in High-Fat-Diet Fed Rats Producing a Co-Adaptation to the Glycolytic Fiber Phenotype. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanni, A.; Moreno, M.; Lombardi, A.; Goglia, F. 3,5-Diiodo- l -Thyronine and 3,5,3′-Triiodo- l -Thyronine Both Improve the Cold Tolerance of Hypothyroid Rats, but Possibly via Different Mechanisms. Pflügers Arch. 1998, 436, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, F.; Gentile, A.; Silvestri, E.; Goglia, F.; Lombardi, A. Effect of Iodothyronines on Thermogenesis: Focus on Brown Adipose Tissue. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, A.; de Lange, P.; Silvestri, E.; Busiello, R.A.; Lanni, A.; Goglia, F.; Moreno, M. 3,5-Diiodo-l-Thyronine Rapidly Enhances Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation Rate and Thermogenesis in Rat Skeletal Muscle: AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Involvement. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E497–E502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, A.; Moreno, M.; de Lange, P.; Iossa, S.; Busiello, R.A.; Goglia, F. Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Activity by Thyroid Hormones: Focus on the “Old” Triiodothyronine and the “Emerging” 3,5-Diiodothyronine. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Teixeira, S.; Filgueira, C.; Sieglaff, D.H.; Benod, C.; Villagomez, R.; Minze, L.J.; Zhang, A.; Webb, P.; Nunes, M.T. 3,5-Diiodothyronine (3,5-T2) Reduces Blood Glucose Independently of Insulin Sensitization in Obese Mice. Acta Physiol. 2017, 220, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.C.; Kim, B.W. Deiodinases: Implications of the Local Control of Thyroid Hormone Action. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, W.; Marsili, A.; Larsen, P.R.; Zavacki, A.M.; Silva, J.E. Type-2 Iodothyronine 5′Deiodinase (D2) in Skeletal Muscle of C57Bl/6 Mice. II. Evidence for a Role of D2 in the Hypermetabolism of Thyroid Hormone Receptor α-Deficient Mice. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louzada, R.A.; Santos, M.C.S.; Cavalcanti-de-Albuquerque, J.P.A.; Rangel, I.F.; Ferreira, A.C.F.; Galina, A.; Werneck-de-Castro, J.P.S.; Carvalho, D.P. Type 2 Iodothyronine Deiodinase Is Upregulated in Rat Slow- and Fast-Twitch Skeletal Muscle during Cold Exposure. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 307, E1020–E1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Calonne, J.; Isacco, L.; Miles-Chan, J.; Arsenijevic, D.; Montani, J.-P.; Guillet, C.; Boirie, Y.; Dulloo, A.G. Reduced Skeletal Muscle Protein Turnover and Thyroid Hormone Metabolism in Adaptive Thermogenesis That Facilitates Body Fat Recovery During Weight Regain. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Munno, C.; Busiello, R.A.; Calonne, J.; Salzano, A.M.; Miles-Chan, J.; Scaloni, A.; Ceccarelli, M.; de Lange, P.; Lombardi, A.; Senese, R.; et al. Adaptive Thermogenesis Driving Catch-Up Fat Is Associated with Increased Muscle Type 3 and Decreased Hepatic Type 1 Iodothyronine Deiodinase Activities: A Functional and Proteomic Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 631176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaker, L.; Bianco, A.C.; Jonklaas, J.; Peeters, R.P. Hypothyroidism. Lancet 2017, 390, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gauthier, K.; Ho, J.P.; Lim, A.; Zhu, X.-G.; Han, C.R.; Sinha, R.A.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Yen, P.M. Thyroid Hormone Receptor α Regulates Autophagy, Mitochondrial Biogenesis, and Fatty Acid Use in Skeletal Muscle. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchala, M.; Zybek, A.; Szczepanek-Parulska, E. Serum Irisin Levels and Thyroid Function—Newly Discovered Association. Peptides 2014, 60, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zybek-Kocik, A.; Sawicka-Gutaj, N.; Wrotkowska, E.; Sowiński, J.; Ruchała, M. Time-Dependent Irisin Concentration Changes in Patients Affected by Overt Hypothyroidism. Endokrynol. Pol. 2016, 67, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maushart, C.I.; Loeliger, R.; Gashi, G.; Christ-Crain, M.; Betz, M.J. Resolution of Hypothyroidism Restores Cold-Induced Thermogenesis in Humans. Thyroid 2019, 29, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, A.P.; Ketzer, L.A.; Nigro, M.; Galina, A.; Carvalho, D.P.; de Meis, L. Cold Tolerance in Hypothyroid Rabbits: Role of Skeletal Muscle Mitochondria and Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ ATPase Isoform 1 Heat Production. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 6262–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, A.G.; Seebacher, F. Thyroid Hormone Regulates Muscle Function during Cold Acclimation in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 3514–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspari, R.R.; Reyna-Neyra, A.; Jung, L.; Torres-Manzo, A.P.; Hirabara, S.M.; Carrasco, N. The Paradoxical Lean Phenotype of Hypothyroid Mice Is Marked by Increased Adaptive Thermogenesis in the Skeletal Muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22544–22551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, C.B.; Olivares, E.L.; Bianco, A.C. Responsiveness to Thyroid Hormone and to Ambient Temperature Underlies Differences Between Brown Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle Thermogenesis in a Mouse Model of Diet-Induced Obesity. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3571–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ganesan, K.; Wadud, K. Euthyroid Sick Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Perez, A.; Palos-Paz, F.; Kaptein, E.; Visser, T.J.; Dominguez-Gerpe, L.; Alvarez-Escudero, J.; Lado-Abeal, J. Identification of Molecular Mechanisms Related to Nonthyroidal Illness Syndrome in Skeletal Muscle and Adipose Tissue from Patients with Septic Shock. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 68, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado-Abeal, J.; Romero, A.; Castro-Piedras, I.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.; Alvarez-Escudero, J. Thyroid Hormone Receptors Are Down-Regulated in Skeletal Muscle of Patients with Non-Thyroidal Illness Syndrome Secondary to Non-Septic Shock. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 163, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelen, A.; van der Spek, A.H.; Bloise, F.; de Vries, E.M.; Surovtseva, O.V.; van Beeren, M.; Ackermans, M.T.; Kwakkel, J.; Fliers, E. Tissue Thyroid Hormone Metabolism Is Differentially Regulated during Illness in Mice. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedia, R.; Lowes, A.; Gillis, S.; Markert, R.; Koroscil, T. Iatrogenic Subclinical Hyperthyroidism Does Not Promote Weight Loss. South. Med. J. 2016, 109, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriacou, A.; Kyriacou, A.; Makris, K.C.; Syed, A.A.; Perros, P. Weight Gain Following Treatment of Hyperthyroidism—A Forgotten Tale. Clin. Obes. 2019, 9, e12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.A.; Ashraf, M.A.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Thyroid Hormone. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Arruda, A.P.; da Silva, W.S.; Carvalho, D.P.; de Meis, L. Hyperthyroidism Increases the Uncoupled ATPase Activity and Heat Production by the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Biochem. J. 2003, 375, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, L.; Arruda, A.P.; Da Silva, W.S.; Reis, M.; Carvalho, D.P. The Thermogenic Function of the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ -ATPase of Normal and Hyperthyroid Rabbit. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 986, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, X. Thyrotoxic Myopathy: Research Status, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Endokrynol. Pol. 2022, 73, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.D.; Powell, C.; Kaufman, K.R.; Sun, P.C.; Bahn, R.S.; Nair, K.S. The Impact of Overt and Subclinical Hyperthyroidism on Skeletal Muscle. Thyroid 2006, 16, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riis, A.L.D.; Jørgensen, J.O.L.; Gjedde, S.; Nørrelund, H.; Jurik, A.G.; Nair, K.S.; Ivarsen, P.; Weeke, J.; Møller, N. Whole Body and Forearm Substrate Metabolism in Hyperthyroidism: Evidence of Increased Basal Muscle Protein Breakdown. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E1067–E1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka-Gutaj, N.; Zybek-Kocik, A.; Kloska, M.; Ziółkowska, P.; Czarnywojtek, A.; Sowiński, J.; Mańkowska-Wierzbicka, D.; Ruchała, M. Effect of Restoration of Euthyroidism on Visfatin Concentrations and Body Composition in Women. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zybek-Kocik, A.; Sawicka-Gutaj, N.; Domin, R.; Szczepanek-Parulska, E.; Krauze, T.; Guzik, P.; Ruchała, M. Titin and Dystrophin Serum Concentration Changes in Patients Affected by Thyroid Disorders. Endokrynol. Pol. 2021, 72, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riis, A.L.D.; Jørgensen, J.O.L.; Møller, N.; Weeke, J.; Clausen, T. Hyperthyroidism and Cation Pumps in Human Skeletal Muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E1265–E1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maushart, C.I.; Senn, J.R.; Loeliger, R.C.; Siegenthaler, J.; Bur, F.; Fischer, J.G.W.; Betz, M.J. Resting Energy Expenditure and Cold-Induced Thermogenesis in Patients with Overt Hyperthyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sawicka-Gutaj, N.; Erampamoorthy, A.; Zybek-Kocik, A.; Kyriacou, A.; Zgorzalewicz-Stachowiak, M.; Czarnywojtek, A.; Ruchała, M. The Role of Thyroid Hormones on Skeletal Muscle Thermogenesis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040336
Sawicka-Gutaj N, Erampamoorthy A, Zybek-Kocik A, Kyriacou A, Zgorzalewicz-Stachowiak M, Czarnywojtek A, Ruchała M. The Role of Thyroid Hormones on Skeletal Muscle Thermogenesis. Metabolites. 2022; 12(4):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040336
Chicago/Turabian StyleSawicka-Gutaj, Nadia, Abikasinee Erampamoorthy, Ariadna Zybek-Kocik, Angelos Kyriacou, Małgorzata Zgorzalewicz-Stachowiak, Agata Czarnywojtek, and Marek Ruchała. 2022. "The Role of Thyroid Hormones on Skeletal Muscle Thermogenesis" Metabolites 12, no. 4: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040336
APA StyleSawicka-Gutaj, N., Erampamoorthy, A., Zybek-Kocik, A., Kyriacou, A., Zgorzalewicz-Stachowiak, M., Czarnywojtek, A., & Ruchała, M. (2022). The Role of Thyroid Hormones on Skeletal Muscle Thermogenesis. Metabolites, 12(4), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040336





