A Preliminary Metabolomic Study of Yorkshire Terrier Enteropathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Animal Characteristics
2.2. Metabolomics
2.3. Data Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Multivariate Analysis
2.3.2. Univariate Analysis
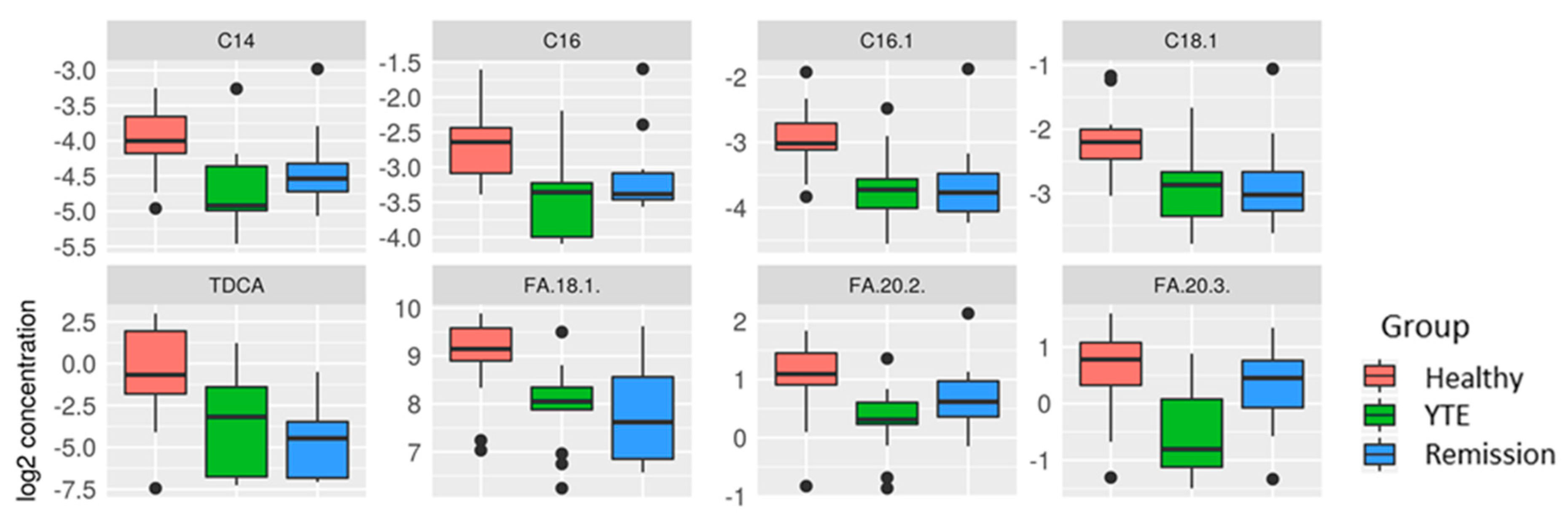
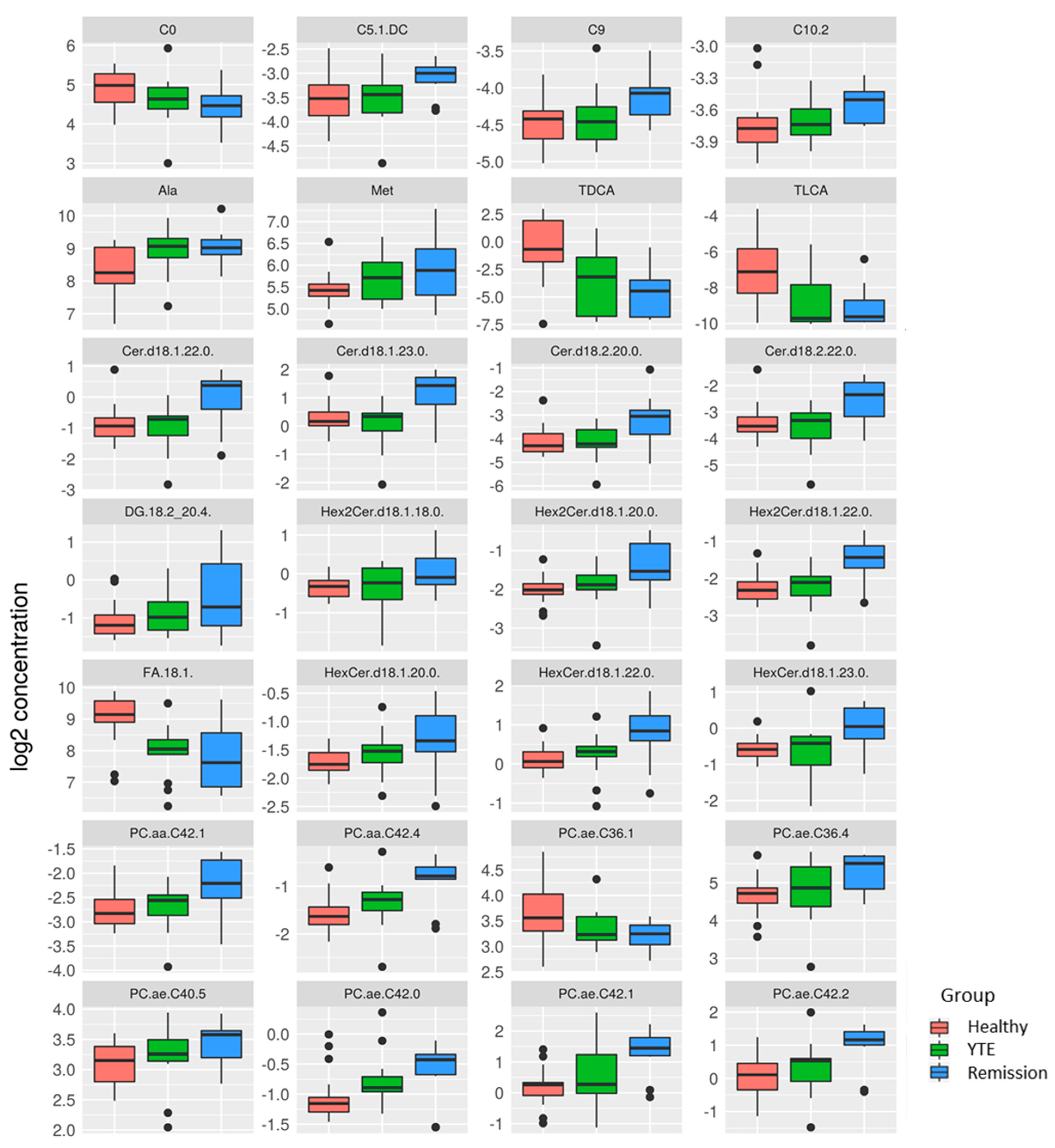
YTE Versus Healthy Dogs
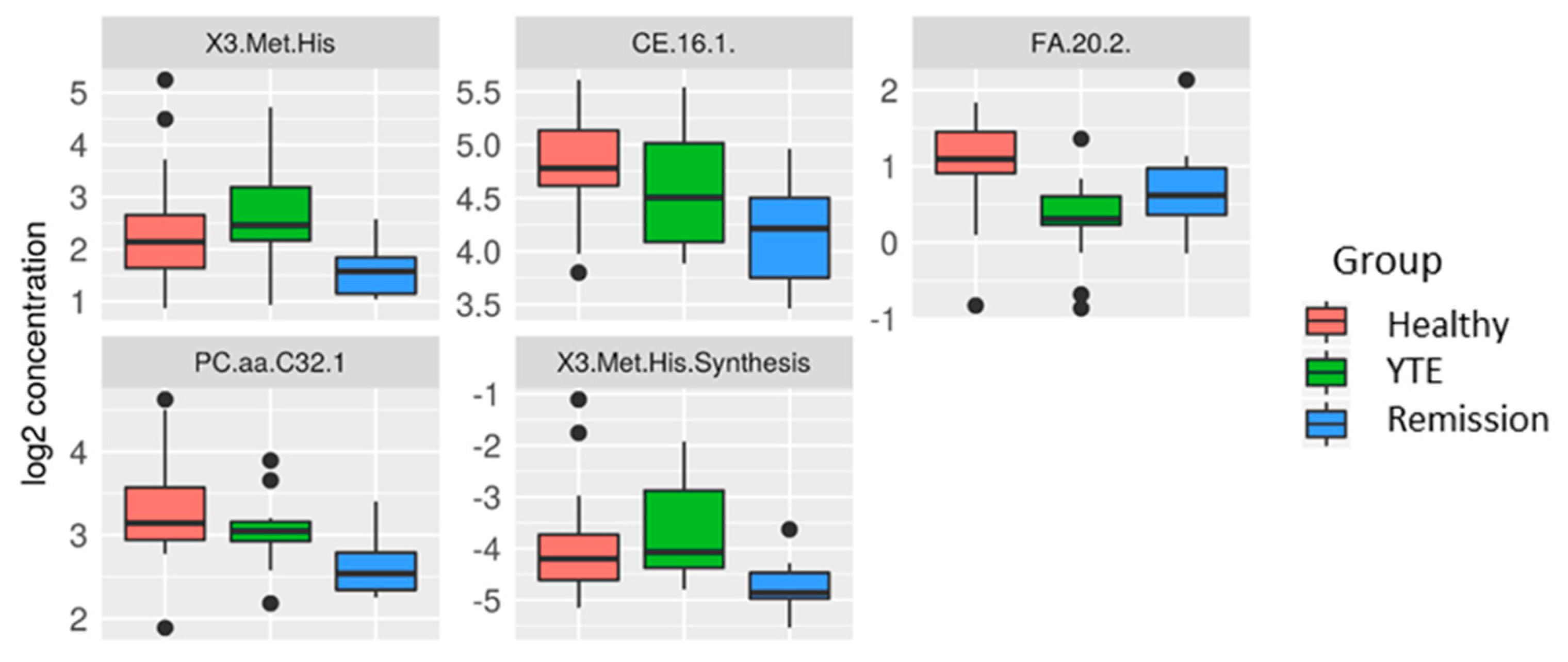
YTE Remission Versus Healthy Controls
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cases and Control Dogs
4.2. Sampling
4.3. Metabolite Analysis
4.4. Statistics
4.4.1. Data Cleaning and Imputation
4.4.2. Univariate and Multivariate Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craven, M.; Simpson, J.W.; Ridyard, A.E.; Chandler, M.L. Canine inflammatory bowel disease: Retrospective analysis of diagnosis and outcome in 80 cases (1995–2002). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washabau, R.J.; Day, M.J.; Willard, M.D.; Hall, E.J.; Jergens, A.E.; Mansell, J.; Minami, T.; Bilzer, T.W. Endoscopic, biopsy, and histopathologic guidelines for the evaluation of gastrointestinal inflammation in companion animals. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, R.B. Mechanisms of disease: Pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 3, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, R.J.; Podolsky, D.K. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2007, 448, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, J.H.; Le Bourhis, L.; Magalhaes, J.G.; Philpott, D.J. Innate immune recognition at the epithelial barrier drives adaptive immunity: APCs take the back seat. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brant, S.R. Promises, delivery, and challenges of inflammatory bowel disease risk gene discovery. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamias, G.; Arseneau, K.O.; Cominelli, F. Mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease for investigating mucosal immunity in the intestine. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 33, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathrani, A.; Allenspach, K.; Fascetti, A.J.; Larsen, J.A.; Hall, E.J. Alterations in serum amino acid concentrations in dogs with protein-losing enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benvenuti, E.; Pierini, A.; Gori, E.; Bartoli, F.; Erba, P.; Ruggiero, P.; Marchetti, V. Serum amino acid profile in 51 dogs with immunosuppressant-responsive enteropathy (IRE): A pilot study on clinical aspects and outcomes. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, Y.; Ohta, H.; Kagawa, Y.; Osuga, T.; Morishita, K.; Sasaki, N.; Takiguchi, M. Plasma amino acid profiles in dogs with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honneffer, J.B. Untargeted metabolomics reveals disruption within bile acid, cholesterol, and tryptophan metabolic pathways in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Gasteroentrology 2015, 148, S-715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, Y.; Otoni, C.C.; Steelman, S.M.; Büyükleblebici, O.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Alteration of the fecal microbiota and serum metabolite profiles in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Verbrugghe, A.; Lourenço, M.; Janssens, G.P.; Liu, D.J.; Van de Wiele, T.; Eeckhaut, V.; Van Immerseel, F.; Van de Maele, I.; Niu, Y.; et al. Does canine inflammatory bowel disease influence gut microbial profile and host metabolism? Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasquini, A.; Luchetti, E.; Cardini, G. Plasma lipoprotein concentrations in the dog: The effects of gender, age, breed and diet. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lange, K.M.; Moutsianas, L.; Lee, J.C.; Lamb, C.A.; Luo, Y.; Kennedy, N.A.; Jostins, L.; Rice, D.L.; Gutierrez-Achury, J.; Ji, S.G.; et al. Genome-wide association study implicates immune activation of multiple integrin genes in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGovern, D.P.; Kugathasan, S.; Cho, J.H. Genetics of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1163–1176.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimmel, S.E.; Waddell, L.S.; Michel, K.E. Hypomagnesemia and hypocalcemia associated with protein-losing enteropathy in Yorkshire terriers: Five cases (1992–1998). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 217, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmerson, S.M.; Armstrong, P.J.; Wünschmann, A.; Jessen, C.R.; Crews, L.J.; Washabau, R.J. Clinical features, intestinal histopathology, and outcome in protein-losing enteropathy in Yorkshire Terrier dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dijkstra, M.; Kraus, J.S.; Bosje, J.T.; Den Hertog, E. Protein-losing enteropathy in Rottweilers. Tijdschr. Diergeneeskd. 2010, 135, 406–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wildgrube, H.J.; Stockhausen, H.; Petri, J.; Füssel, U.; Lauer, H. Naturally occurring conjugated bile acids, measured by high-performance liquid chromatography, inhuman, dog, and rabbit bile. J. Chromatogr. 1986, 353, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisamatsu, T.; Okamoto, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Muramatsu, T.; Andou, A.; Uo, M.; Kitazume, M.T.; Matsuoka, K.; Yajima, T.; Inoue, N.; et al. Novel, objective, multivariate biomarkers composed of plasma amino acid profiles for the diagnosis and assessment of inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawiskiba, T.; Deja, S.; Mulak, A.; Zabek, A.; Jawien, E.; Pawełka, D.; Banasik, M.; Mastalerz-Migas, A.; Balcerzak, W.; Kaliszewski, K.; et al. Serum and urine metabolomic fingerprinting in diagnostics of inflammatory bowel diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Fan, P.; Wang, Y. Lipidomics in Health and Diseases—Beyond the Analysis of Lipids. Glycom. Lipidom. 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinaldo, P.; Matern, D.; Bennett, M.J. Fatty acid oxidation disorders. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2002, 64, 477–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agouridis, A.P.; Elisaf, M.; Milionis, H.J. An overview of lipid abnormalities in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2011, 24, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, F.; Mundra, P.A.; Fang, L.; Galvin, A.; Moore, X.L.; Weir, J.M.; Wong, G.; White, D.A.; Chin-Dusting, J.; Sparrow, M.P.; et al. Lipidomic profiling in inflammatory bowel disease: Comparison between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romanato, G.; Scarpa, M.; Angriman, I.; Faggian, D.; Ruffolo, C.; Marin, R.; Zambon, S.; Basato, S.; Zanoni, S.; Filosa, T.; et al. Plasma lipids and inflammation in active inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, F.; Iida, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Aoyagi, K.; Kanamoto, K.; Fujishima, M. Serum n3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are depleted in Crohn’s disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Xue, J.; Liu, C.W.; Gao, B.; Chi, L.; Tu, P.; Lu, K.; Ru, H. Serum Metabolomics Identifies Altered Bioenergetics, Signaling Cascades in Parallel with Exposome Markers in Crohn’s Disease. Molecules 2019, 24, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalenyak, K.; Heilmann, R.M.; van de Lest, C.H.A.; Brouwers, J.F.; Burgener, I.A. Comparison of the systemic phospholipid profile in dogs diagnosed with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease or food-responsive diarrhea before and after treatment. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoro-Huguet, M.A.; Belloc, B.; Domínguez-Cajal, M. Small and Large Intestine (I): Malabsorption of Nutrients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimerl, S.; Moehle, C.; Zahn, A.; Boettcher, A.; Stremmel, W.; Langmann, T.; Schmitz, G. Alterations in intestinal fatty acid metabolism in inflammatory bowel disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1762, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrillo, C.; Cavia Mdel, M.; Alonso-Torre, S. Role of oleic acid in immune system; mechanism of action; a review. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sergeant, S.; Rahbar, E.; Chilton, F.H. Gamma-linolenic acid, Dihommo-gamma-linolenic, eicosanoids and inflammatory processes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 15, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.J.; Chuang, L.T.; Chen, S.N. Incorporation of eicosatrienoic acid exerts mild anti-inflammatory properties in murine RAW264.7 cells. Inflammation 2015, 38, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Soh, H.; Sando, K.; Wasa, M.; Takagi, Y.; Okada, A. Beneficial effects of n-9 eicosatrienoic acid on experimental bowel lesions. Surg. Today 2003, 33, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.E.; Evans, A.M. Carnitine and acylcarnitines: Pharmacokinetic, pharmacological and clinical aspects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcken, B.; Wiley, V.; Hammond, J.; Carpenter, K. Screening newborns for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bene, J.; Komlósi, K.; Gasztonyi, B.; Juhász, M.; Tulassay, Z.; Melegh, B. Plasma carnitine ester profile in adult celiac disease patients maintained on long-term gluten-free diet. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 6671–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bene, J.; Komlósi, K.; Havasi, V.; Talián, G.; Gasztonyi, B.; Horváth, K.; Mózsik, G.; Hunyady, B.; Melegh, B.; Figler, M. Changes of plasma fasting carnitine ester profile in patients with ulcerative colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.A.; Ogawa, S.A.; Chau, L.; Whelan, K.A.; Hamilton, K.E.; Chen, J.; Tan, L.; Chen, E.Z.; Keilbaugh, S.; Fogt, F.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease alters intestinal epithelial metabolism of hepatic acylcarnitines. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e133371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, J.A.; Wargo, M.J. Carnitine in bacterial physiology and metabolism. Microbiology 2015, 161, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, Y.; Minamoto, T.; Isaiah, A.; Sattasathuchana, P.; Buono, A.; Rangachari, V.R.; McNeely, I.H.; Lidbury, J.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Fecal short-chain fatty acid concentrations and dysbiosis in dogs with chronic enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walters, J.R.; Pattni, S.S. Managing bile acid diarrhoea. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2010, 3, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giaretta, P.R.; Rech, R.R.; Guard, B.C.; Blake, A.B.; Blick, A.K.; Steiner, J.M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Cook, A.K.; Hanifeh, M.; Spillmann, T.; et al. Comparison of intestinal expression of the apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter between dogs with and without chronic inflammatory enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1918–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duboc, H.; Rajca, S.; Rainteau, D.; Benarous, D.; Maubert, M.A.; Quervain, E.; Thomas, G.; Barbu, V.; Humbert, L.; Despras, G.; et al. Connecting dysbiosis, bile-acid dysmetabolism and gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut 2013, 62, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, G.H.; Münzing, W.; von Ritter, C.; Paumgartner, G. Bile acid malabsorption as a cause of chronic diarrhea: Diagnostic value of 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one in serum. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1999, 44, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, A.C.; Cross, G.; Taylor, D.R.; Sherwood, R.A.; Watson, P.J. Measurement of serum 7alphahydroxy-4-cholesterin-3-one as a marker of bile acid malabsorption in dogs with chronic diarrhoea: A pilot study. Vet. Rec. 2016, 3, e000163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijayvargiya, P.; Camilleri, M. Current practice in the diagnosis of bile acid diarrhea. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, A.F. The continuing importance of bile acids in liver and intestinal disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, M.; Takamine, F.; Imamura, T.; Benno, Y. Clostridium hiranonis sp. nov., a human intestinal bacterium with bile acid 7alpha-dehydroxylating activity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guard, B.C.; Honneffer, J.B.; Jergens, A.E.; Jonika, M.M.; Toresson, L.; Lawrence, Y.A.; Webb, C.B.; Hill, S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; et al. Longitudinal assessment of microbial dysbiosis, fecal unconjugated bile acid concentrations, and disease activity in dogs with steroid-responsive chronic inflammatory enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AlShawaqfeh, M.K.; Wajid, B.; Minamoto, Y.; Markel, M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Serpedin, E.; Suchodolski, J.S. A dysbiosis index to assess microbial changes in fecal samples of dogs with chronic inflammatory enteropathy. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blake, A.B.; Guard, B.C.; Honneffer, J.B.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Altered microbiota, fecal lactate, and fecal bile acids in dogs with gastrointestinal disease. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, F.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y. Functions and signaling pathways of amino acids in intestinal inflammation. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9171905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, C.A. Therapeutic potential of amino acids in inflammatory bowel disease. Nutrients. 2017, 9, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.J.; Kovacs-Nolan, J.A.; Yang, C.; Archbold, T.; Fan, M.Z.; Mine, Y. l-Tryptophan exhibits therapeutic function in a porcine model of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettenworth, D.; Nowacki, T.M.; Ross, M.; Kyme, P.; Schwammbach, D.; Kerstiens, L.; Thoennissen, G.B.; Bokemeyer, C.; Hengst, K.; Berdel, W.E.; et al. Nicotinamide treatment ameliorates the course of experimental colitis mediated by enhanced neutrophil-specific antibacterial clearance. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1474–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochlik, B.; Gerbracht, C.; Grune, T.; Weber, D. The Influence of Dietary Habits and Meat Consumption on Plasma 3-Methylhistidine-A Potential Marker for Muscle Protein Turnover. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1701062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosini, Y.M.; Neuber, S.; Borcherding, D.; Seo, Y.J.; Segarra, S.; Glanemann, B.; Garden, O.A.; Müller, U.; Adam, M.G.; Dang, V.; et al. Treatment With Hydrolyzed Diet Supplemented With Prebiotics and Glycosaminoglycans Alters Lipid Metabolism in Canine Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Hadi, L.; Di Vito, C.; Riboni, L. Fostering inflammatory bowel disease: Sphingolipid strategies to join forces. Res. Article Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 3827684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gersemann, M.; Wehkamp, J.; Stange, E.F. Innate immune dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 271, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.D.; Nilsson, A. Metabolism of sphingolipids in the gut and its relation to inflammation and cancer development. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 8, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ontsouka, E.C.; Burgener, I.A.; Luckschander-Zeller, N.; Blum, J.W.; Albrecht, C. Fish-meal diet enriched with omega-3 PUFA and treatment of canine chronic enteropathies. Eur. J. Lipid. Sci. Technol. 2012, 114, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeusette, I.C.; Lhoest, E.T.; Istasse, L.P.; Diez, M.O. Influence of obesity on plasma lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 66, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kramer, N.; Pratscher, B.; Meneses, A.M.C.; Tschulenk, W.; Walter, I.; Swoboda, A.; Kruitwagen, H.S.; Schneeberger, K.; Penning, L.C.; Spee, B.; et al. Generation of Differentiating and Long-Living Intestinal Organoids Reflecting the Cellular Diversity of Canine Intestine. Cells 2020, 9, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allenspach, K.; Wieland, B.; Gröne, A.; Gaschen, F. Chronic enteropathies in dogs: Evaluation of risk factors for negative outcome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooperberg, C.; Stone, C.J. Logspline Density Estimation for Censored Data. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1992, 1, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galler, A.I.; Klavins, K.; Burgener, I.A. A Preliminary Metabolomic Study of Yorkshire Terrier Enteropathy. Metabolites 2022, 12, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030264
Galler AI, Klavins K, Burgener IA. A Preliminary Metabolomic Study of Yorkshire Terrier Enteropathy. Metabolites. 2022; 12(3):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030264
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaller, Alexandra I., Kristaps Klavins, and Iwan A. Burgener. 2022. "A Preliminary Metabolomic Study of Yorkshire Terrier Enteropathy" Metabolites 12, no. 3: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030264
APA StyleGaller, A. I., Klavins, K., & Burgener, I. A. (2022). A Preliminary Metabolomic Study of Yorkshire Terrier Enteropathy. Metabolites, 12(3), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030264





