Urinary Metabolomics in Young Soccer Players after Winter Training Season
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
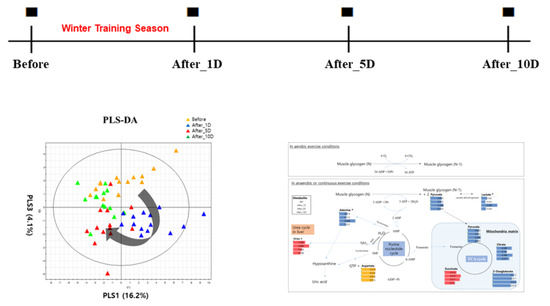
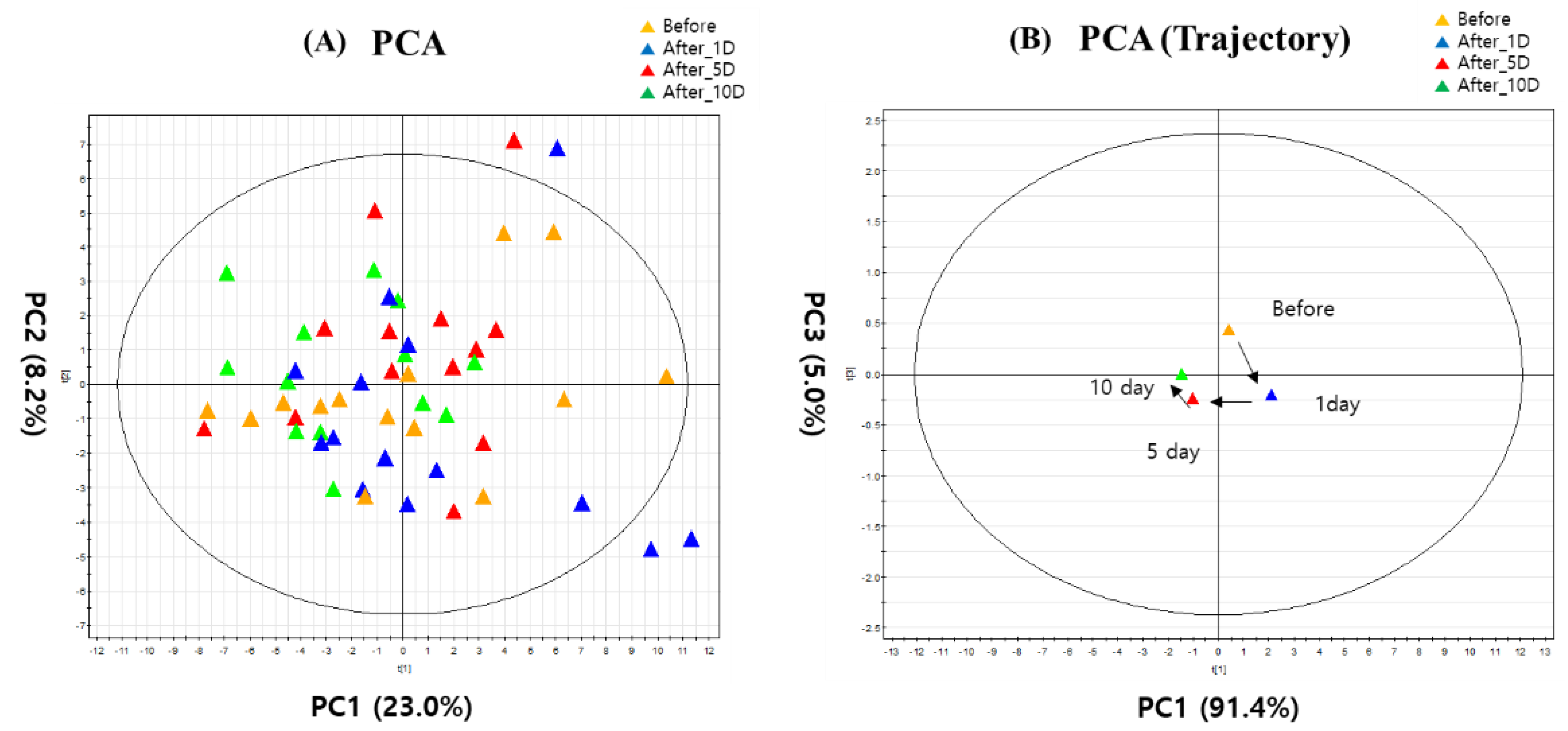
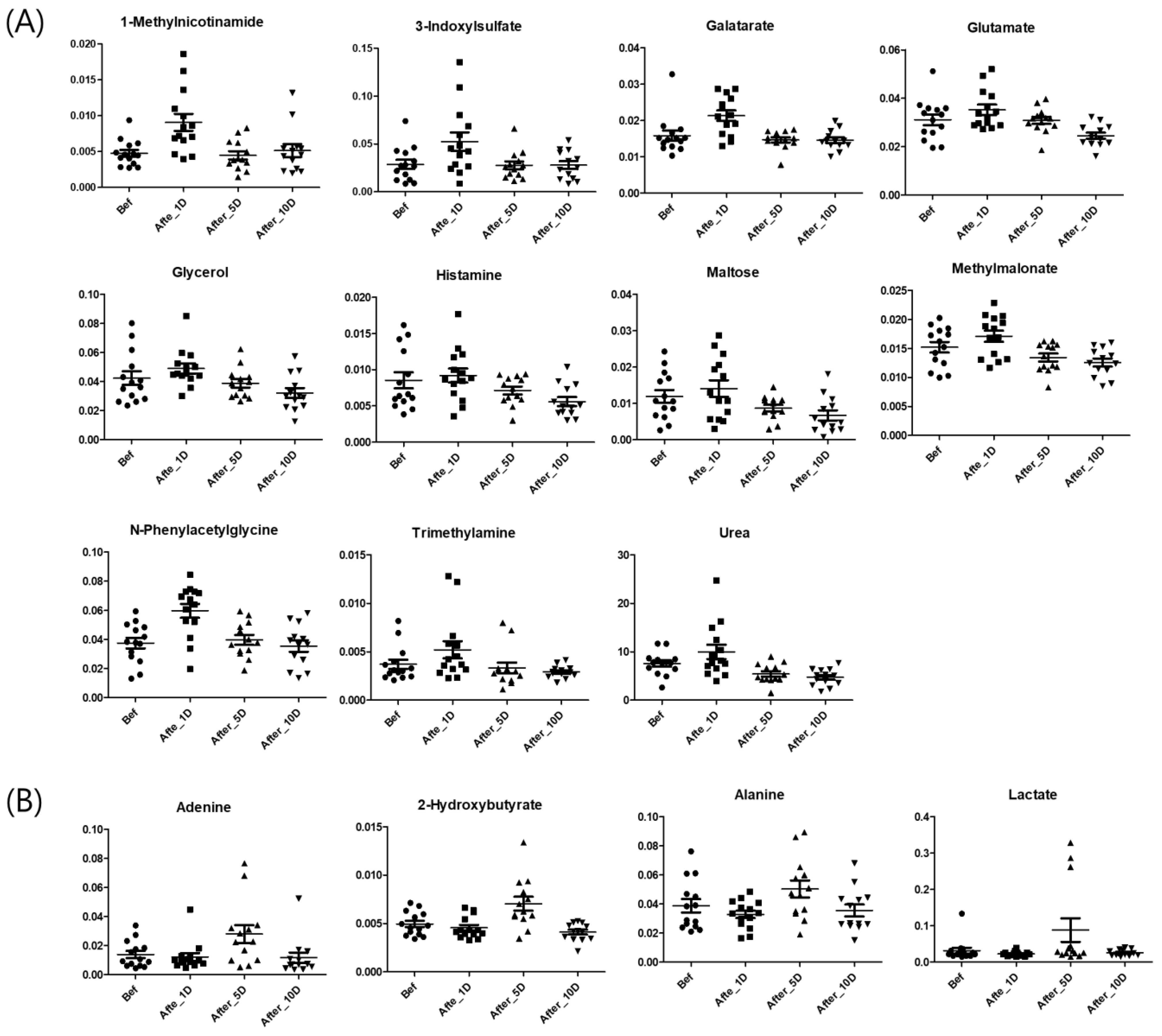
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bloomfield, J.; Polman, R.; O’Donoghue, P. Physical demands of different positions in FA Premier League soccer. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2007, 6, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Stølen, T.; Chamari, K.; Castagna, C.; Wisløff, U. Physiology of soccer: An update. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 501–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H. Effects of Winter season Physical Training on Cardiopulmonary and muscular Function of N league Professional Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 24, 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, R.S.; Oliver, J.L.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Myer, G.D.; De Ste Croix, M.B. Chronological age vs. biological maturation: Implications for exercise programming in youth. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, S.A.; Minson, C.T.; Halliwill, J.R. The cardiovascular system after exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 122, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, J.R. Potential causes, mechanisms, and implications of post exercise hypotension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwill, J.R. Mechanisms and clinical implications of post-exercise hypotension in humans. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2001, 29, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, J.J.; Oh, S.B.; Goo, H.; Cho, K.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.-B. Metabolomics approach to biomarkers of dry eye disease using 1H-NMR in rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2021, 84, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Kim, H.Y.; Kang, K.; Jeong, H.G.; Song, M.-K.; Tae, I.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, K.; Chae, S.; et al. Integration of transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics identifies biomarkers for pulmonary injury by polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate (PHMG-p), a humidifier disinfectant, in rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 887–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yoo, S.; Lee, J.-D.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.-B. A metabolomics approach to sulforaphane efficacy in secondhand smoking-induced pulmonary samage in mice. Metabolites 2022, 12, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-B.; Lee, B.-M. Metabolomics, a new promising technology for toxicological research. Toxicol. Res. 2009, 25, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate Analysis in Metabolomics. Curr. Metab. 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Renterghem, P.; Sottas, P.E.; Saugy, M.; Van Eenoo, P. Statistical discrimination of steroid profiles in doping control with support vector machines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 20, 768:41–768:48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, F.; Rossing, P. Diagnosis of diabetic kidney disease: State of the art and future perspective. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2018, 8, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Ling, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, B.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, P.; Li, L.; Wang, W. Alterations of Urinary Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Hypertension and/or Hyperlipidemia. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas, G.; Reche, X.; Sanjuan-Herráez, J.D.; Martínez, H.; Herrero, M.; Valle, X.; Masa, M.; Rodas, G. Urine metabolomic analysis for monitoring internal load in professional football players. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vike, N.L.; Bari, S.; Stetsiv, K.; Talavage, T.M.; Nauman, E.A.; Papa, L.; Slobounov, S.; Breiter, H.C.; Cornelis, M.C. Metabolomic response to collegiate football participation: Pre- and Post-season analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Ryu, H.Y.; Cha, K.S.; Sung, D.J. Exercise-induced rhabdomyolysis mechanisms and prevention: A literature review. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Lee, J.D.; Jeon, H.S.; Kim, A.R.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, K.B. Metabolic Profiling of Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Human Urine. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 34, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, P. Physical preparation for elite-level rugby union football. Strength Cond. J. 2004, 26, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternlicht, E.; Rugg, S.G.; Bernstein, M.D.; Armstrong, S.D. Electromyographical analysis and comparison of selected abdominal training devices with a traditional crunch. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargreaves, M.; Spriet, L.L. Skeletal muscle energy metabolism during exercise. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2020, 2, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutch, B.J.; Banister, E.W. Ammonia metabolism in exercise and fatigue: A review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1983, 15, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipata, P.L.; Pesi, R. Metabolic interaction between purine nucleotide cycle and oxypurine cycle during skeletal muscle contraction of different intensities: A biochemical reappraisal. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, V. Ammonia toxicity and its prevention in inherited defects of the urea cycle. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsum, H.E.; Strömme, S.B. Urea and Creatinine Production and Excretion in Urine during and after Prolonged Heavy Exercise. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1974, 33, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, J. Effect of exercise on amino acid concentrations in skeletal muscle and plasma. J. Exp. Biol. 1991, 160, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikura, K.; Ra, S.G.; Ohmori, H. Exercise-induced changes in amino acid levels in skeletal muscle and plasma. Phys. Fit. Sports Med. 2013, 2, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.; Tymianski, M. Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Pflug. Arch. 2010, 460, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainesalo, S.; Keränen, T.; Palmio, J.; Peltola, J.; Oja, S.S.; Saransaari, P. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid amino acids in epileptic patients. Neurochem. Res. 2004, 29, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miulli, D.E.; Norwell, D.Y.; Schwartz, F.N. Plasma concentrations of glutamate and its metabolites in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 1993, 93, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cairns, B.E.; Gambarota, G.; Svensson, P.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Berde, C.B. Glutamate-induced sensitization of rat masseter muscle fibers. Neuroscience 2002, 109, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.J.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, K.B.; Park, J.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Song, K.D.; Kim, S.; Cho, B.W. Analysis of metabolomic patterns in thoroughbreds before and after exercise. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibom, R.; Hultman, E.; Johansson, M.; Matherei, K.; Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Schantz, P.G. Adaptation of mitochondrial ATP production in human skeletal muscle to endurance training and detraining. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 73, 2004–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, C.M.; Arildsen, L.; Nissen, J.D.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Schousboe, A.; Maechler, P.; Ott, P.; Vilstrup, H.; Walls, A.B. Glutamate Dehydrogenase Is Important for Ammonia Fixation and Amino Acid Homeostasis in Brain During Hyperammonemia. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 646291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisanaga, S.; Ueno, N.; Inagaki, H.; Tokura, T.; Uezono, S.; Yokota, N.; Fujimoto, S.; Eto, T. Exercise-induced acute renal failure associated with renal vasoconstriction. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1999, 4, 406–412. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Gundlapalli, S.; Gaur, Y.; Rao, M.V.; Bande, S.R.; Sandhya, P. Renal Hypouricemia with Exercise Induced Acute Kidney Injury-A Case Report. Indian J. Nephrol. 2021, 31, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, M.A. Accumulation of trimethylamine and trimethylamine-N-oxide in end-stage renal disease patients undergoing haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riphagen, I.J.; Minović, I.; Groothof, D.; Post, A.; Eggersdorfer, M.L.; Kootstra-Ros, J.E.; de Borst, M.H.; Navis, G.; Muskiet, F.A.J.; Kema, I.P.; et al. Methylmalonic acid, vitamin B12, renal function, and risk of all-cause mortality in the general population: Results from the prospective Lifelines-MINUTHE study. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.H.; Thompson, G.N.; Leonard, J.V.; Bartlett, K.; Halliday, D. Contribution of amino acid catabolism to propionate production in methylmalonic acidaemia. Lancet 1989, 1, 1298–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, P.; Sklar, R.; Murrell, M.; Swanson, R.A.; Sharp, F.R. Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase induction by cerebral ischemia and neurotoxicity of the mitochondrial toxin methylmalonic acid. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 7336–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wei, F.; Vaziri, N.D.; Cheng, X.L.; Bai, X.; Lin, R.C.; Zhao, Y.Y. Metabolomics insights into chronic kidney disease and modulatory effect of rhubarb against tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Liu, L.; Fu, T.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Xiao, L.; Liu, J.; Kong, Y.; Xie, H.; Yi, F.; et al. Exercise Inducible Lactate Dehydrogenase B Regulates Mitochondrial Function in Skeletal Muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25306–25318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Nishida, Y. Effect of Lactate Accumulation during Exercise-induced Muscle Fatigue on the Sensorimotor Cortex. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2013, 25, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, G.D.; Stephenson, D.G.; Bangsbo, J.; Juel, C. Point:Counterpoint: Lactic acid accumulation is an advantage/disadvantage during muscle activity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A. The lactate shuttle during exercise and recovery. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1986, 18, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavletic, A.J.; Pao, M. Exercise-induced elevation of liver enzymes in a healthy female research volunteer. Psychosomatics 2015, 56, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, T.; Ventress, M.; Allerton, D.M.; Stansfield, S.; Tang, J.C.Y.; Fraser, W.D.; Vanhoecke, B.; Prawitt, J.; Stevenson, E. The effects of collagen peptides on muscle damage, inflammation and bone turnover following exercise: A randomized, controlled trial. Amino Acids. 2019, 51, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaas, S.; Pettersen, J.E. Clinical conditions associated with urinary excretion of 2-hydroxybutyric acid. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1975, 35, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siopi, A.; Deda, O.; Manou, V.; Kellis, S.; Kosmidis, I.; Komninou, D.; Raikos, N.; Christoulas, K.; Theodoridis, G.A.; Mougios, V. Effects of Different Exercise Modes on the Urinary Metabolic Fingerprint of Men with and without Metabolic Syndrome. Metabolites 2017, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, J.; Hindorf, U.; Persson, P.; Bengtsson, T.; Malmqvist, U.; Werkström, V.; Ekelund, M. Muscular exercise can cause highly pathological liver function tests in healthy men. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 65, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahlin, K.; Broberg, S. Adenine Nucleotide Depletion in Human Muscle During Exercise: Causality and Significance of AMP Deamination. Int. J. Sports Med. 1990, 11, S62–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, G.; Vinaixa, M.; McGovern, R.; Beltran, A.; Novials, A.; Correig, X.; McClean, C. Metabolomic Response to Acute Hypoxic Exercise and Recovery in Adult Males. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, B.H.; Karaca, T.; Al Suleimani, Y.; Al Za’abi, M.; Al Kalbani, J.; Ashique, M.; Nemmar, A. The effect of swimming exercise on adenine-induced kidney disease in rats, and the influence of curcumin or lisinopril thereon. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokozawa, T.; Zheng, P.D.; Oura, H.; Koizumi, F. Animal model of adenine-induced chronic renal failure in rats. Nephron 1986, 44, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, J.-D.; Lee, Y.-H.; Seo, S.-W.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.-B. Urinary Metabolomics in Young Soccer Players after Winter Training Season. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12121283
Kim H-Y, Lee J-D, Lee Y-H, Seo S-W, Lee H-S, Kim S, Kim K-B. Urinary Metabolomics in Young Soccer Players after Winter Training Season. Metabolites. 2022; 12(12):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12121283
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyang-Yeon, Jung-Dae Lee, Yun-Hwan Lee, Sang-Won Seo, Ho-Seong Lee, Suhkmann Kim, and Kyu-Bong Kim. 2022. "Urinary Metabolomics in Young Soccer Players after Winter Training Season" Metabolites 12, no. 12: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12121283
APA StyleKim, H.-Y., Lee, J.-D., Lee, Y.-H., Seo, S.-W., Lee, H.-S., Kim, S., & Kim, K.-B. (2022). Urinary Metabolomics in Young Soccer Players after Winter Training Season. Metabolites, 12(12), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12121283