A Comprehensive Mass Spectrometry-Based Workflow for Clinical Metabolomics Cohort Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Biospecimen Choice
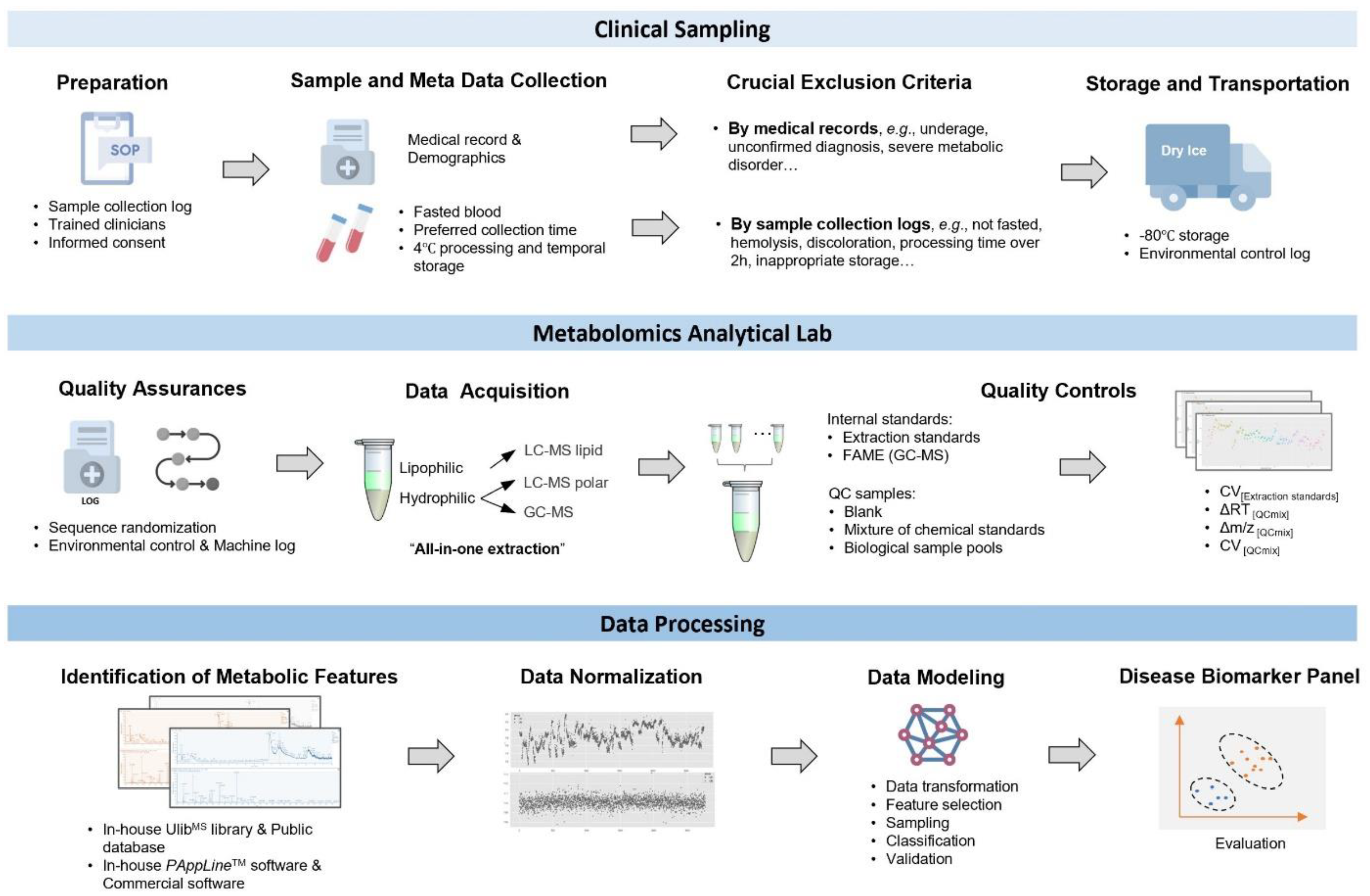
2.2. Clinical Sample Collection, Processing, and Storage
2.3. Metabolomics Sample Preparation
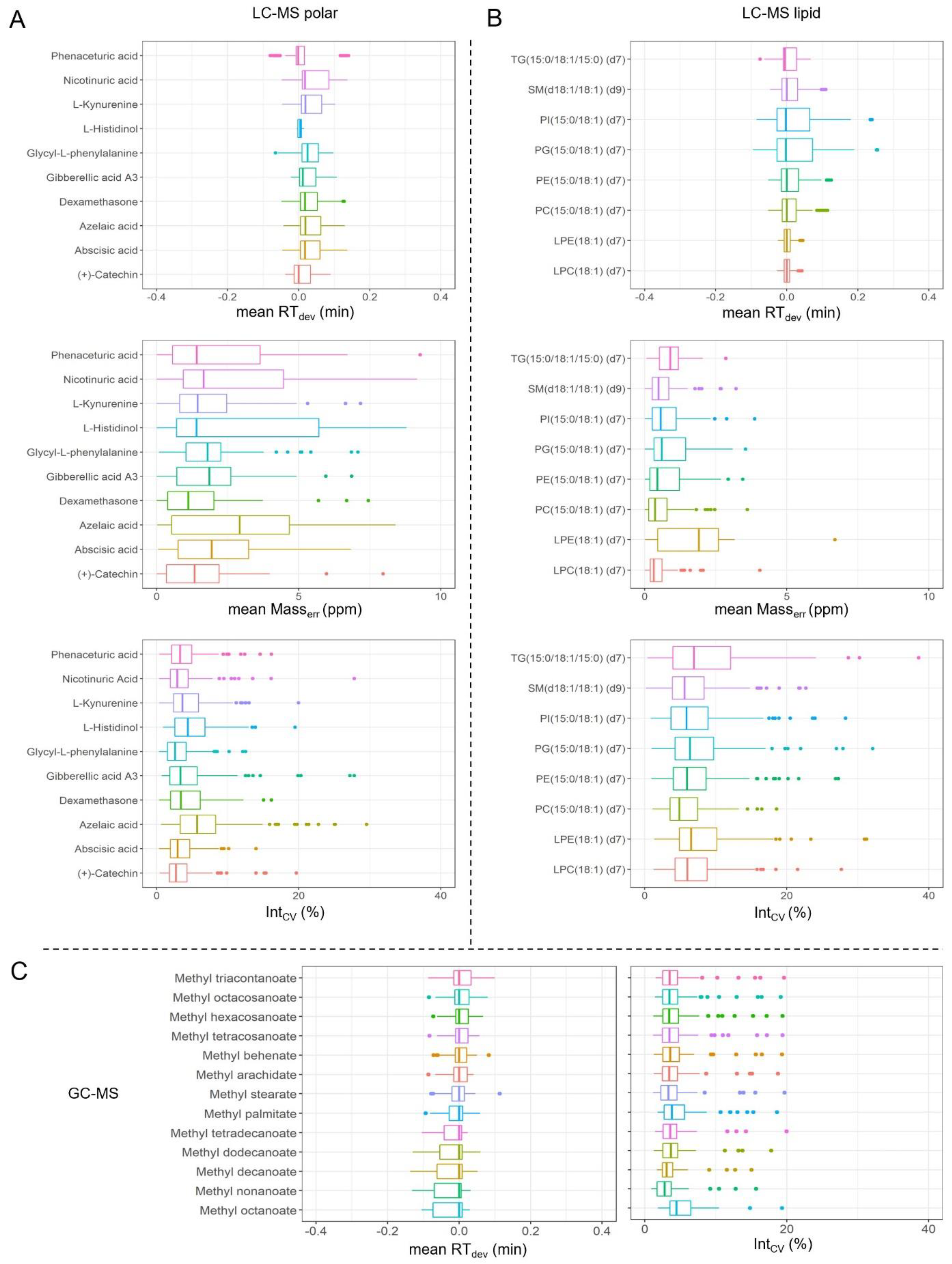
2.4. Quality Control (QC) Settings
2.5. GC-MS and UPLC-MS Detection
2.6. Mass Spectrometry Data Processing
2.7. Data Normalization
2.8. Data Analysis with Machine Learning
3. Results
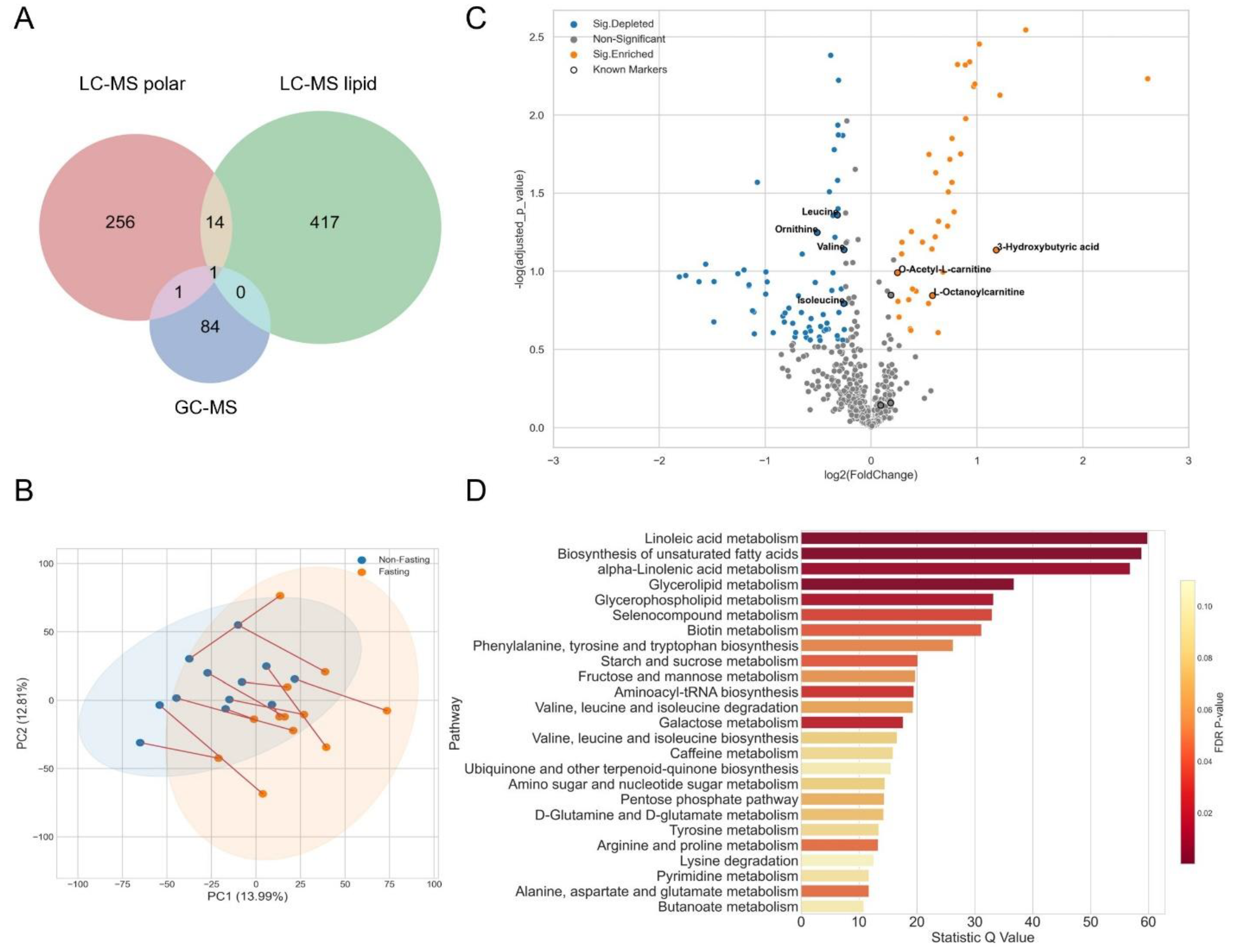
3.1. Fasting for Blood Sampling
3.2. A Cancer Pilot Study
3.3. Metabolomics Analysis and Quality Control
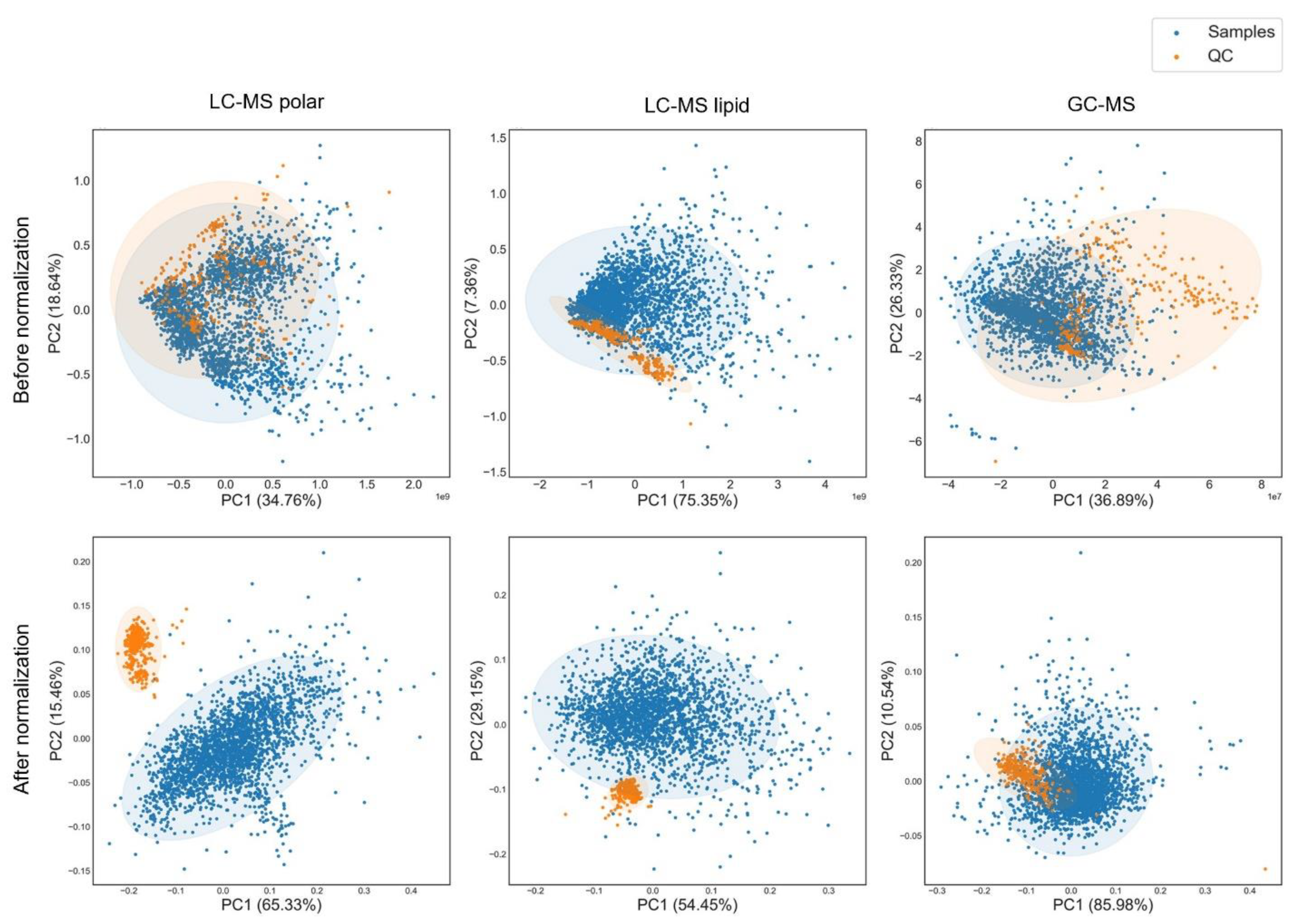
3.4. Data Normalization
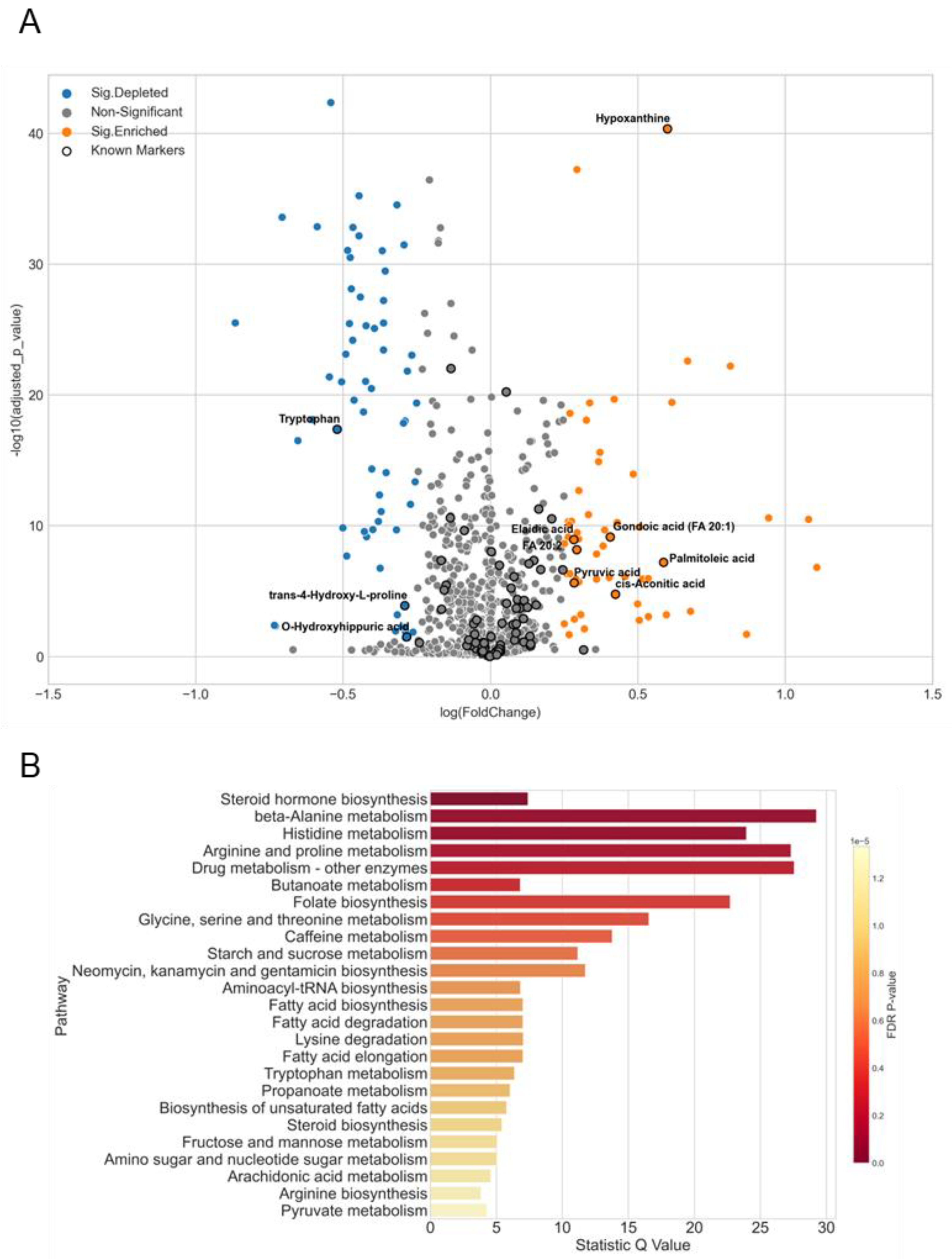
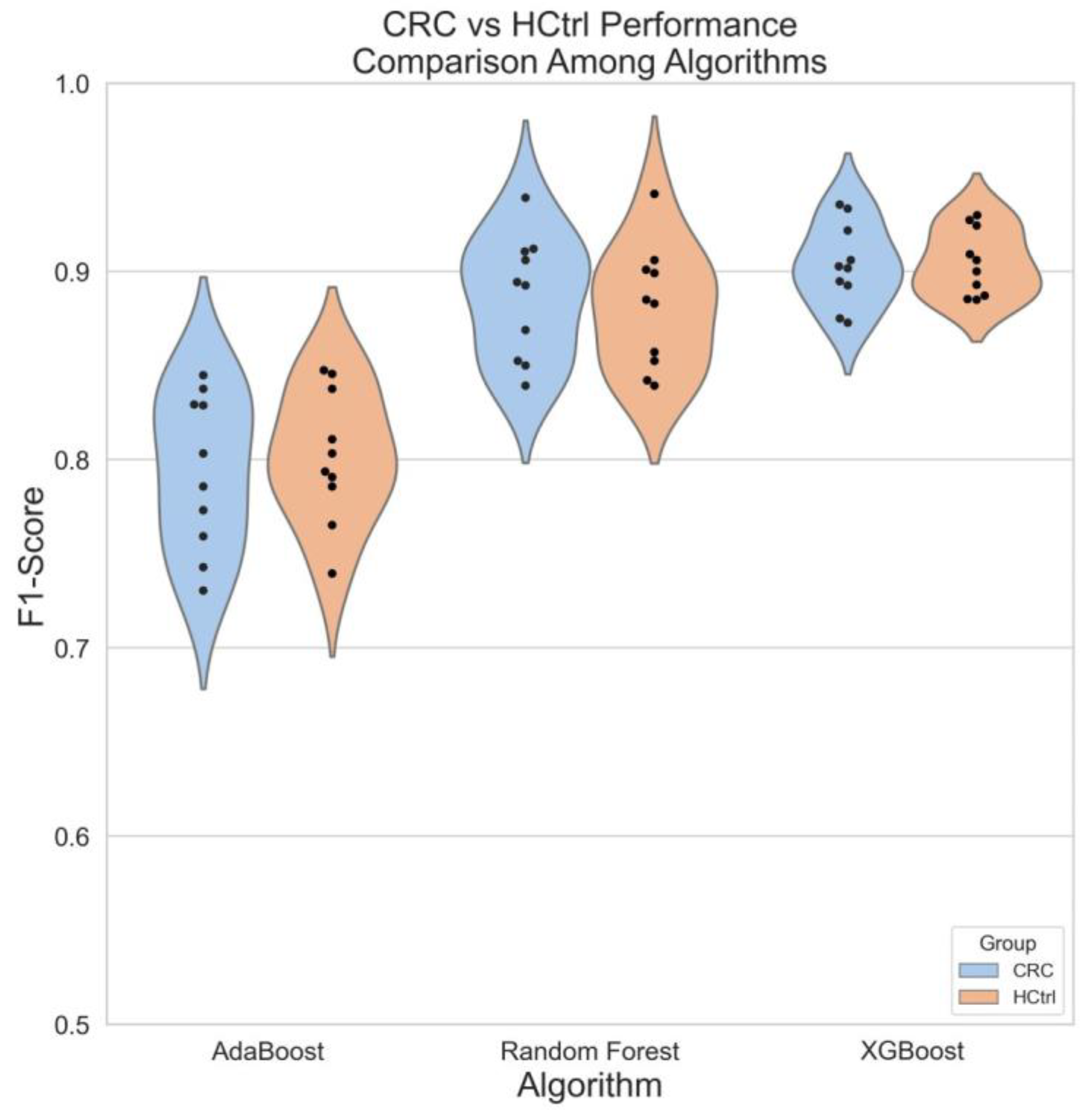
3.5. A Case Study of Colorectal Cancer Sub-Cohort
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors That May Influence Plasma Metabolomics Analysis
4.2. Good Practices for Large-Scale Data Acquisition and Processing
4.3. Biomarker Evaluation
4.4. Limitations and Outlook
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Muthubharathi, B.C.; Gowripriya, T.; Balamurugan, K. Metabolomics: Small molecules that matter more. Mol. Omics 2021, 17, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramautar, R.; Berger, R.; van der Greef, J.; Hankemeier, T. Human metabolomics: Strategies to understand biology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collino, S.; Martin, F.-P.J.; Rezzi, S. Clinical metabolomics paves the way towards future healthcare strategies. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clish, C.B. Metabolomics: An emerging but powerful tool for precision medicine. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2015, 1, a000588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shayota, B.J.; Donti, T.R.; Xiao, J.; Gijavanekar, C.; Kennedy, A.D.; Hubert, L.; Rodan, L.; Vanderpluym, C.; Nowak, C.; Bjornsson, H.T.; et al. Untargeted metabolomics as an unbiased approach to the diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism of the non-oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020, 131, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Emerging role and recent applications of metabolomics biomarkers in obesity disease research. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14966–14973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, P.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Metabolomics in diagnosis and biomarker discovery of colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Suzuki, I.; Nakamura, T.; Bernier, F.; Aoshima, K.; Oda, Y. Identification of a new plasma biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease using metabolomics technology. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhee, E.P.; Gerszten, R.E. Metabolomics and Cardiovascular Biomarker Discovery. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lazar, L.; Fang, Z.; Tang, C.; Zhao, J. Metabolomics workflow for lung cancer: Discovery of biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 495, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Cebrián, N.; Rojas-Benedicto, A.; Albors-Vaquer, A.; López-Guerrero, J.A.; Pineda-Lucena, A.; Puchades-Carrasco, L. Metabolomics Contributions to the Discovery of Prostate Cancer Biomarkers. Metabolites 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, D.R.; Patel, R.; Kirsch, D.G.; Lewis, C.A.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Locasale, J.W. Metabolomics in cancer research and emerging applications in clinical oncology. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 333–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinping, Z.; Kaiqiang, W.; Yuefei, W.; Kefeng, L. Precautions for study design and data interpretation of clinical metabolomics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2118654119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betsou, F.; Barnes, R.; Burke, T.; Coppola, D.; DeSouza, Y.; Eliason, J.; Glazer, B.; Horsfall, D.; Kleeberger, C.; Lehmann, S.; et al. Human Biospecimen Research: Experimental Protocol and Quality Control Tools. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salem, M.A.; Jüppner, J.; Bajdzienko, K.; Giavalisco, P. Protocol: A fast, comprehensive and reproducible one-step extraction method for the rapid preparation of polar and semi-polar metabolites, lipids, proteins, starch and cell wall polymers from a single sample. Plant Methods 2016, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simón-Manso, Y.; Lowenthal, M.S.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Sampson, M.L.; Telu, K.H.; Rudnick, P.A.; Mallard, W.G.; Bearden, D.W.; Schock, T.B.; Tchekhovskoi, D.V.; et al. Metabolite profiling of a NIST standard reference material for human plasma (SRM 1950): GC-MS, LC-MS, NMR, and clinical laboratory analyses, libraries, and web-based resources. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11725–11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: Combined targeted and untargeted profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 30.4.1–30.4.32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broadhurst, D.; Goodacre, R.; Reinke, S.N.; Kuligowski, J.; Wilson, I.D.; Lewis, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. Guidelines and considerations for the use of system suitability and quality control samples in mass spectrometry assays applied in untargeted clinical metabolomic studies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisec, J.; Schauer, N.; Kopka, J.; Willmitzer, L.; Fernie, A.R. Gas chromatography mass spectrometry–based metabolite profiling in plants. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Lee, D.Y.; Lu, Y.; Palazoglu, M.; Shahbaz, S.; Fiehn, O. FiehnLib: Mass Spectral and Retention Index Libraries for Metabolomics Based on Quadrupole and Time-of-Flight Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 10038–10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuadros-Inostroza, Á.; Caldana, C.; Redestig, H.; Kusano, M.; Lisec, J.; Peña-Cortés, H.; Willmitzer, L.; Hannah, M.A. TargetSearch—A Bioconductor package for the efficient preprocessing of GC-MS metabolite profiling data. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giavalisco, P.; Li, Y.; Matthes, A.; Eckhardt, A.; Hubberten, H.-M.; Hesse, H.; Segu, S.; Hummel, J.; Köhl, K.; Willmitzer, L. Elemental formula annotation of polar and lipophilic metabolites using 13C, 15N and 34S isotope labelling, in combination with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Plant J. 2011, 68, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavalisco, P.; Köhl, K.; Hummel, J.; Seiwert, B.; Willmitzer, L. 13C Isotope-Labeled Metabolomes Allowing for Improved Compound Annotation and Relative Quantification in Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-based Metabolomic Research. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6546–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Z.; Tan, Q.; Cao, L.; Zhang, L.; Deng, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Z.-J.; Li, Z.; Li, K. NormAE: Deep Adversarial Learning Model to Remove Batch Effects in Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Data. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 5082–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate Analysis in Metabolomics. Curr. Metab. 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamate, D.; Kim, M.; Proitsi, P.; Westwood, S.; Baird, A.; Nevado-Holgado, A.; Hye, A.; Bos, I.; Vos, S.J.; Vandenberghe, R.; et al. A metabolite-based machine learning approach to diagnose Alzheimer-type dementia in blood: Results from the European Medical Information Framework for Alzheimer disease biomarker discovery cohort. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019, 5, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Carayol, M.; Licaj, I.; Achaintre, D.; Sacerdote, C.; Vineis, P.; Key, T.J. Reliability of Serum Metabolites over a Two-Year Period: A Targeted Metabolomic Approach in Fasting and Non-Fasting Samples from EPIC. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 135437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina, S.; Domínguez-Perles, R.; Ferreres, F.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á. The effects of the intake of plant foods on the human metabolome. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 52, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giskeødegård, G.F.; Andreassen, T.; Bertilsson, H.; Tessem, M.B.; Bathen, T.F. The effect of sampling procedures and day-to-day variations in metabolomics studies of biofluids. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1081, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, H.; Teruya, T.; Yanagida, M. Metabolomics of human fasting: New insights about old questions. Open Biol. 2022, 10, 200176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, E.; Wulff, M.W.M. A Comparison of Various Normalization Methods for LC/MS Metabolomics Data. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norris, J.; Cornett, D.S.; Mobley, J.; Andersson, M.; Seeley, E.; Chaurand, P.; Caprioli, R.M. Processing MALDI mass spectra to improve mass spectral direct tissue analysis. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 260, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mármol, I.; Sánchez-de-Diego, C.; Pradilla Dieste, A.; Cerrada, E.; Rodriguez Yoldi, M.J. Colorectal Carcinoma: A General Overview and Future Perspectives in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Sauer, A.G.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thanikachalam, K.; Khan, G. Colorectal Cancer and Nutrition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Deng, K.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Ma, L.; Openkova, M.S.; Hou, Y.; Li, K. Metabolomics for biomarker discovery in the diagnosis, prognosis, survival and recurrence of colorectal cancer: A systematic review. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 35460–35472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hand, D.J.; Christen, P.; Kirielle, N. F*: An interpretable transformation of the F-measure. Mach. Learn. 2021, 110, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alseekh, S.; Fernie, A.R. Metabolomics 20 years on: What have we learned and what hurdles remain? Plant J. 2018, 94, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alseekh, S.; Aharoni, A.; Brotman, Y.; Contrepois, K.; D’Auria, J.; Ewald, J.; Ewald, J.C.; Fraser, P.D.; Giavalisco, P.; Hall, R.D.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: A guide for annotation, quantification and best reporting practices. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner-Golbs, A.; Neuber, S.; Kamlage, B.; Christiansen, N.; Bethan, B.; Rennefahrt, U.; Schatz, P.; Lind, L. Effects of long-term storage at −80 °C on the human plasma metabolome. Metabolites 2019, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinto, J.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Galhano, E.; Pita, C.; Almeida, M.D.C.; Carreira, I.M.; Gil, A.M. Human plasma stability during handling and storage: Impact on NMR metabolomics. Analyst 2014, 139, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paglia, G.; Del Greco, F.M.; Sigurdsson, B.B.; Rainer, J.; Volani, C.; Hicks, A.A.; Pramstaller, P.P.; Smarason, S.V. Influence of collection tubes during quantitative targeted metabolomics studies in human blood samples. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 486, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskos, A.P.; Jain, P.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Bennett, M.; Achaintre, D.; Asad, Y.; Marney, L.; Richardson, L.; Koulman, A.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Interlaboratory Reproducibility of a Targeted Metabolomics Platform for Analysis of Human Serum and Plasma. Anal. Chem. 2016, 89, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sysi-Aho, M.; Katajamaa, M.; Yetukuri, L.; Orešič, M. Normalization method for metabolomics data using optimal selection of multiple internal standards. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Livera, A.M.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Jacob, L.; Gagnon-Bartsch, J.A.; Castillo, S.; Simpson, J.A.; Speed, T.P. Statistical Methods for Handling Unwanted Variation in Metabolomics Data. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3606–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barri, T.; Holmer-Jensen, J.; Hermansen, K.; Dragsted, L.O. Metabolic fingerprinting of high-fat plasma samples processed by centrifugation- and filtration-based protein precipitation delineates significant differences in metabolite information coverage. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 718, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Lamichhane, S.; Mathema, V.B.; McGlinchey, A.; Dickens, A.M.; Khoomrung, S.; Orešič, M. Deep learning meets metabolomics: A methodological perspective. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 22, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres, L.B.; Gomez, F.J.; Linton, J.R.; Silva, M.F.; Garcia, C.D. Taking the leap between analytical chemistry and artificial intelligence: A tutorial review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1161, 338403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Blennow, K.; Hansson, O. Increasing the reproducibility of fluid biomarker studies in neurodegenerative studies. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teruya, T.; Chaleckis, R.; Takada, J.; Yanagida, M.; Kondoh, H. Diverse metabolic reactions activated during 58-hr fasting are revealed by non-targeted metabolomic analysis of human blood. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whelan, J.; Fritsche, K. Linoleic Acid. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinclair, A.J.; Attar-Bashi, N.M.; Li, D. What is the role of alpha-linolenic acid for mammals? Lipids 2002, 37, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.A.A.; Rahim, S.A.; Suddin, L.S.; Saman, M.S.A.; Mazlan, M. Global serum metabolomics profiling of colorectal cancer (Review). Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishiumi, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Ikeda, A.; Yoshie, T.; Kibi, M.; Izumi, Y.; Okuno, T.; Hayashi, N.; Kawano, S.; Takenawa, T.; et al. A Novel Serum Metabolomics-Based Diagnostic Approach for Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusof, H.M.; Ab-Rahim, S.; Suddin, L.S.; Saman, M.S.A.; Mazlan, M. Metabolomics Profiling on Different Stages of Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 25, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
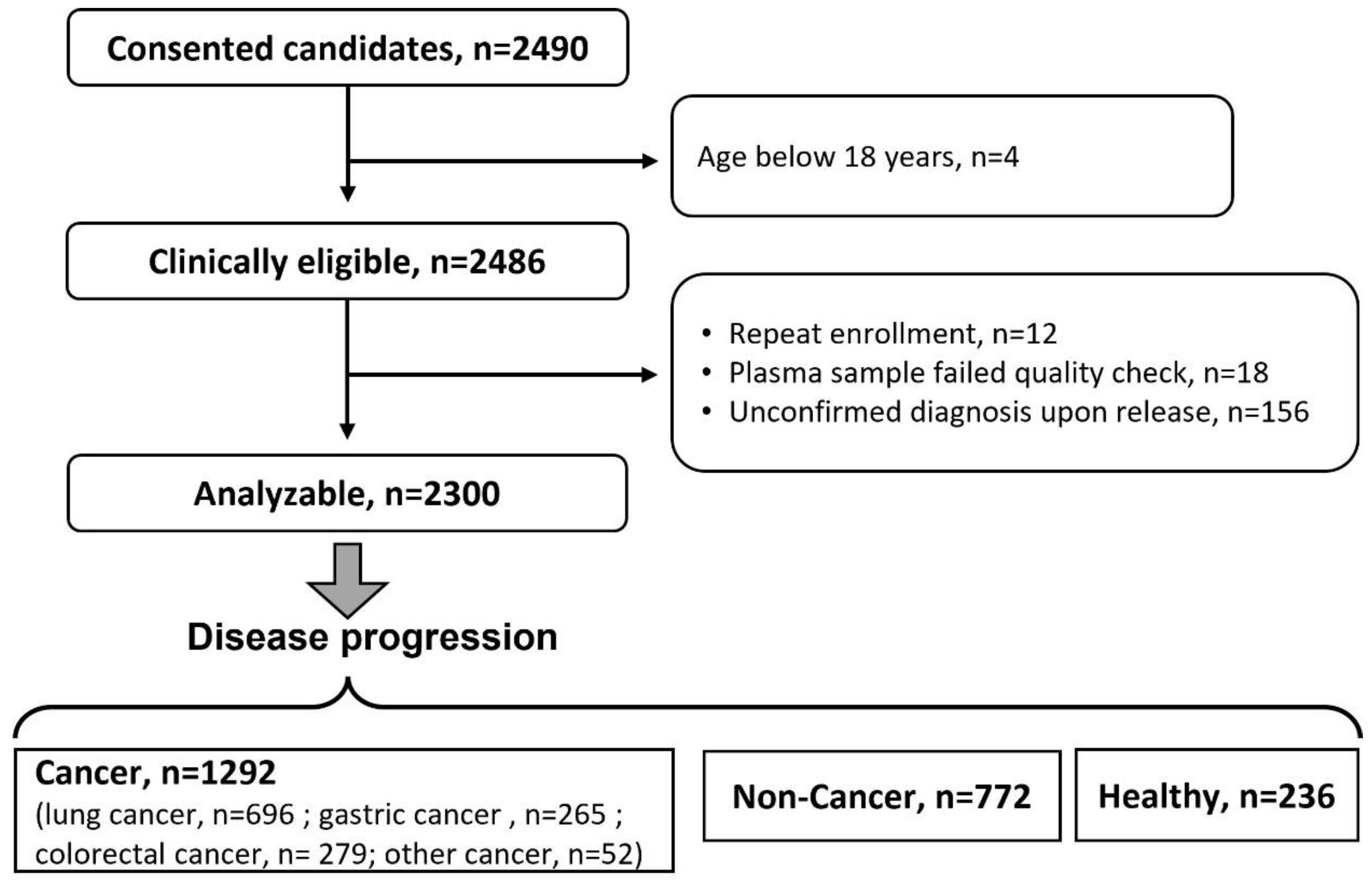
| Group | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer |
|
|
| Non-cancer |
| |
| Healthy |
|
|
| Demographics | HCtrl | Cancers | Non-Cancer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 236 | 1292 | 772 | |
| Hospital, n (%) | TJH | - | 57 (4.4) | 50 (6.5) |
| NCH | 128 (54.2) | 852 (65.9) | 591 (76.6) | |
| XYH | 108 (45.8) | 383 (29.6) | 131 (17.0) | |
| Mean age (SD) | 45.6 (13.4) | 60.9 (10.9) | 54.6 (13.6) | |
| Female (%) | 124 (52.5) | 469 (36.3) | 309 (40.0) | |
| Diabetes (%) | - | 80 (6.2) | 37 (4.9) | |
| Hypertension (%) | - | 319 (24.8) | 123 (16.1) | |
| Smoking History (%) | Never | 171 (72.5) | 789 (61.9) | 533 (70.0) |
| Current | 57 (24.2) | 317 (24.9) | 166 (21.8) | |
| Used to | 8 (3.4) | 169 (13.3) | 62 (8.1) | |
| Alcohol-drinking History (%) | Never | 153 (64.8) | 1027 (81.1) | 599 (78.9) |
| Current | 83 (35.2) | 213 (16.8) | 147 (19.4) | |
| Used to | - | 27 (2.1) | 13 (1.7) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, C.; Kang, X.; Xu, X.; Xia, Z.; Qing, B.; Yuan, Y.; et al. A Comprehensive Mass Spectrometry-Based Workflow for Clinical Metabolomics Cohort Studies. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12121168
Shi Z, Li H, Zhang W, Chen Y, Zeng C, Kang X, Xu X, Xia Z, Qing B, Yuan Y, et al. A Comprehensive Mass Spectrometry-Based Workflow for Clinical Metabolomics Cohort Studies. Metabolites. 2022; 12(12):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12121168
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhan, Haohui Li, Wei Zhang, Youxiang Chen, Chunyan Zeng, Xiuhua Kang, Xinping Xu, Zhenkun Xia, Bei Qing, Yunchang Yuan, and et al. 2022. "A Comprehensive Mass Spectrometry-Based Workflow for Clinical Metabolomics Cohort Studies" Metabolites 12, no. 12: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12121168
APA StyleShi, Z., Li, H., Zhang, W., Chen, Y., Zeng, C., Kang, X., Xu, X., Xia, Z., Qing, B., Yuan, Y., Song, G., Caldana, C., Hu, J., Willmitzer, L., & Li, Y. (2022). A Comprehensive Mass Spectrometry-Based Workflow for Clinical Metabolomics Cohort Studies. Metabolites, 12(12), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12121168






