Low Birth Weight Intensifies Changes in Markers of Hepatocarcinogenesis Induced by Fructose Consumption in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Analysis of Blood Parameters
2.3. Analysis of Tissue Parameters
2.4. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
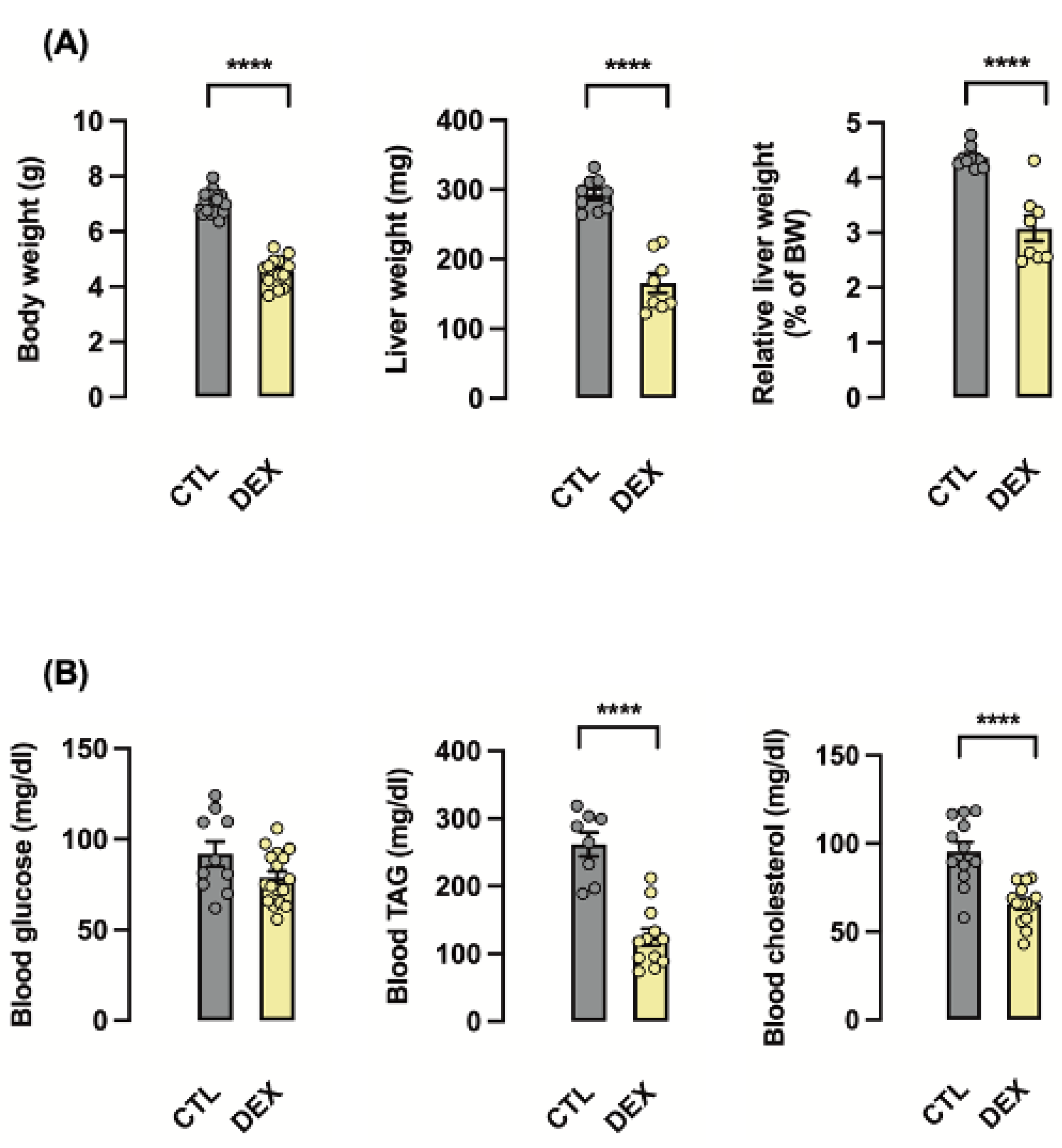
3.1. Rats Born to DEX-Treated Mothers Display Reduced Liver Weight at the First Day of Life
3.2. Rats Born to DEX-Treated Mothers Display Lower Corticosterone Levels and Increased Hepatic ERK1/2 Phosphorylation
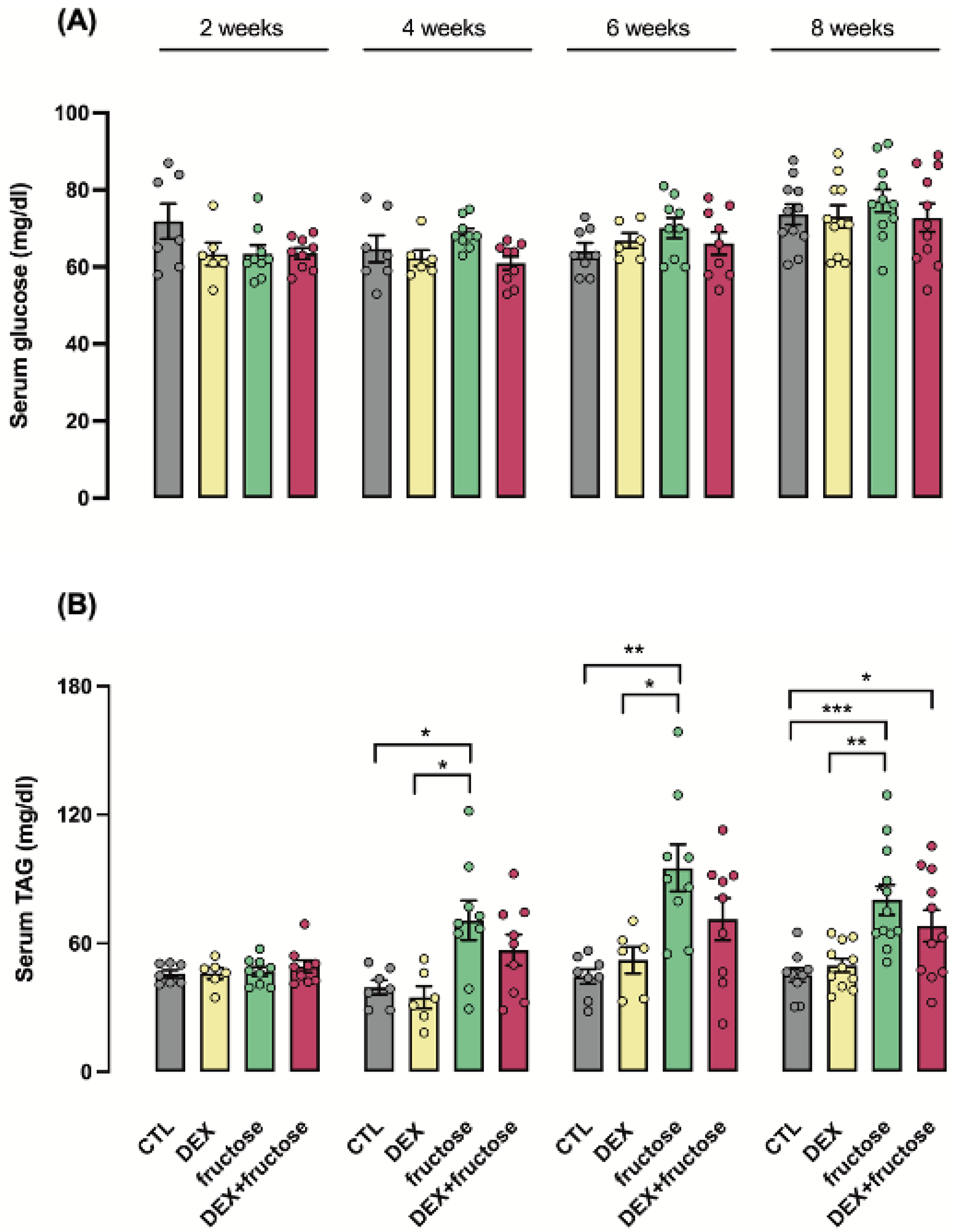
3.3. Exposure to DEX during Fetal Life Retards the Increase in Circulating TAG Induced by Fructose in Adult Rats
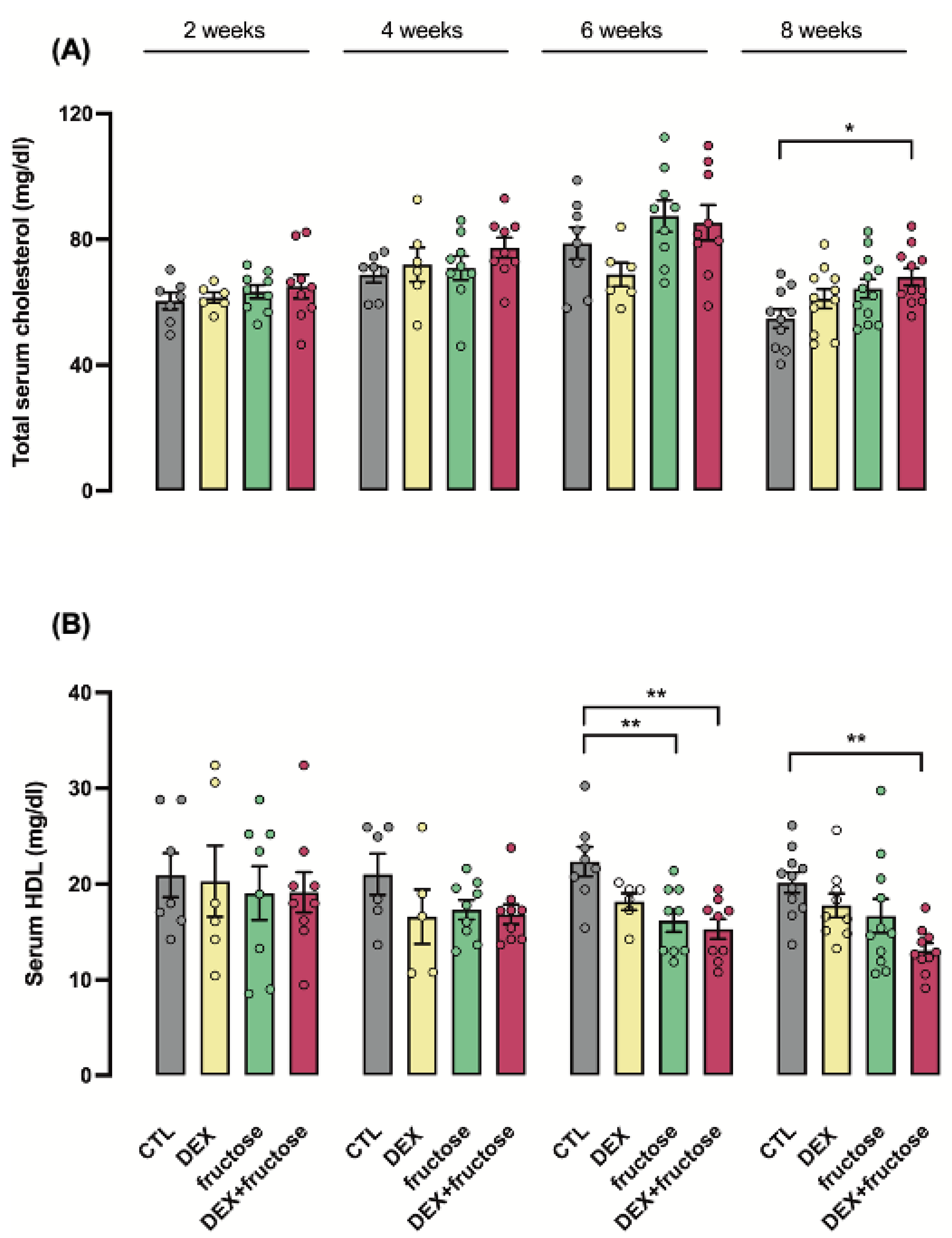
3.4. Exposure to DEX during Fetal Life Interacts with Fructose Treatment to Reduce HDL Cholesterol in Adult Rats
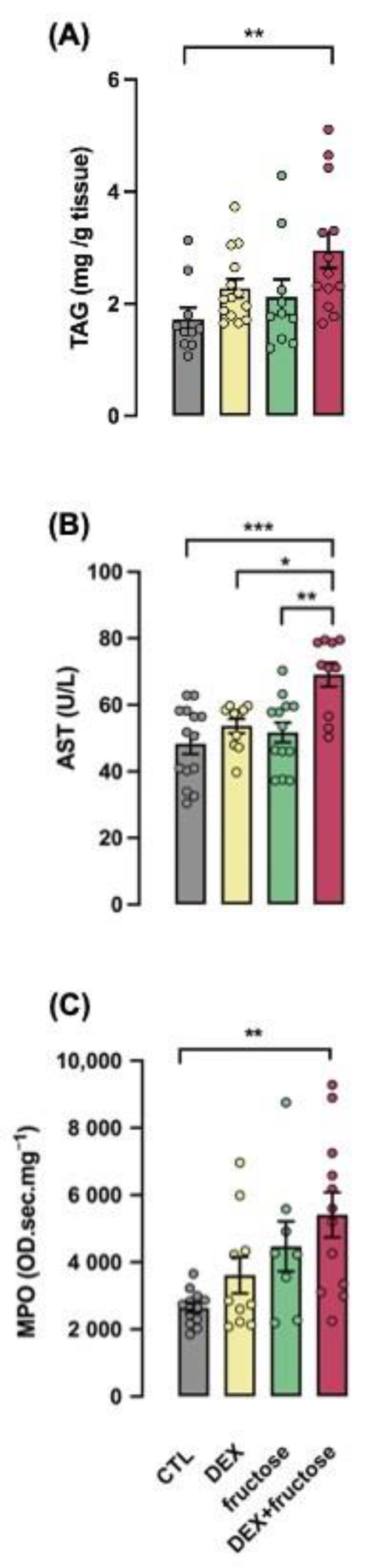
3.5. Exposure to DEX during Fetal Life Interacts with Fructose Treatment to Stimulate Parameters of NASH
3.6. Signaling Pathways Involved in Cell Proliferation Are Exclusively Increased in Fructose-Treated Rats Exposed to DEX in Utero
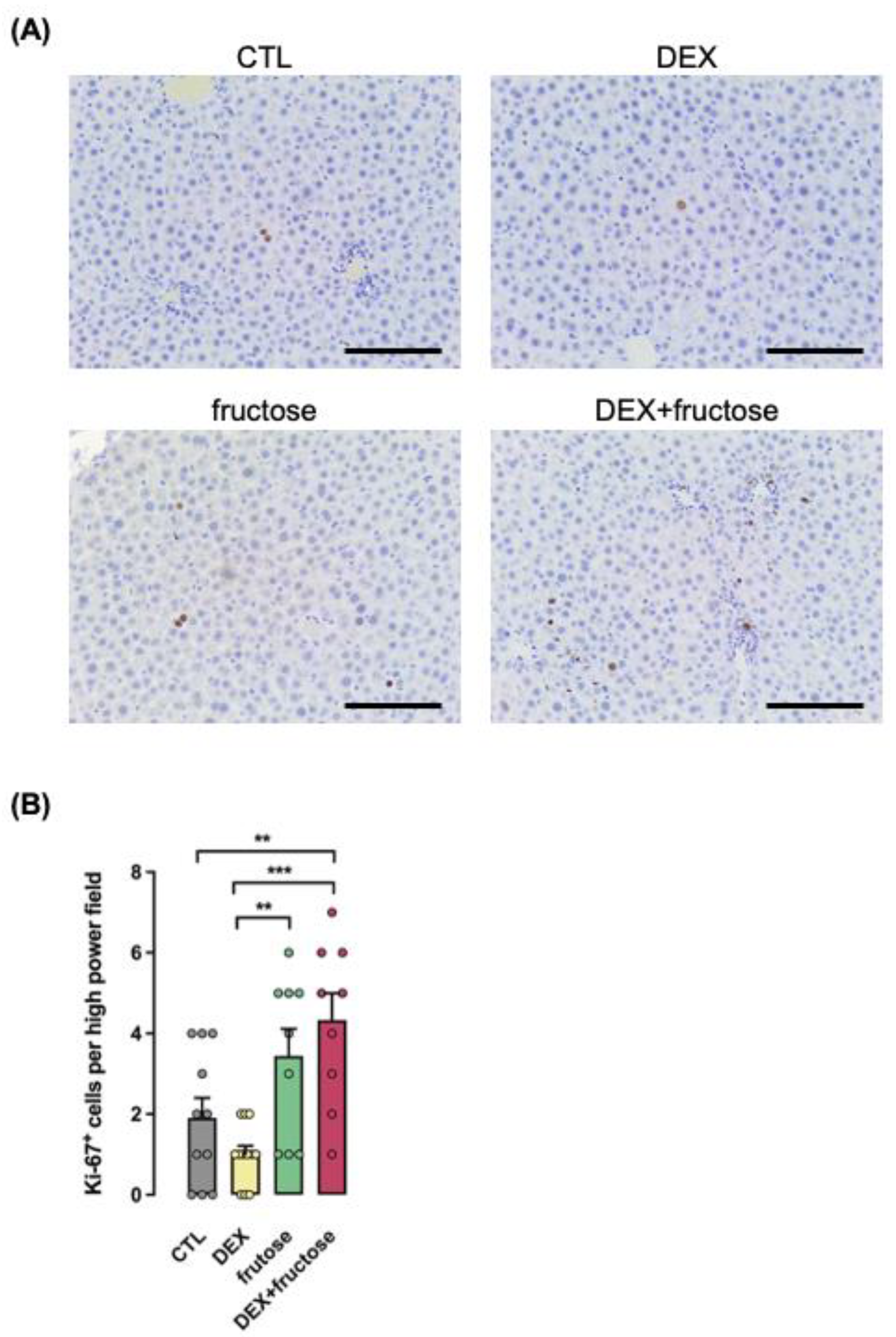
3.7. Markers Associated with HCC Are Exclusively Increased in Fructose-Treated Rats Exposed to DEX in Utero
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Margini, C.; Dufour, J.F. The story of HCC in NAFLD: From epidemiology, across pathogenesis, to prevention and treatment. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, D.M.; Harrison, S.A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and noncirrhotic hepatocellular carcinoma: Fertile soil. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baffy, G.; Brunt, E.M.; Caldwell, S.H. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging menace. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.; Torbenson, M.; Wu, T.T.; Yeh, M.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease contributes to hepatocarcinogenesis in non-cirrhotic liver: A clinical and pathological study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Nitzan-Kaluski, D.; Goldsmith, R.; Webb, M.; Blendis, L.; Halpern, Z.; Oren, R. Long term nutritional intake and the risk for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A population based study. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.; Taha, O.; Nseir, W.; Farah, R.; Grosovski, M.; Assy, N. Soft drink consumption is associated with fatty liver disease independent of metabolic syndrome. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assy, N.; Nasser, G.; Kamayse, I.; Nseir, W.; Beniashvili, Z.; Djibre, A.; Grosovski, M. Soft drink consumption linked with fatty liver in the absence of traditional risk factors. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 22, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronowski, C.; Akhanov, V.; Chan, D.; Catic, A.; Finegold, M.; Sahin, E. Fructose Causes Liver Damage, Polyploidy, and Dysplasia in the Setting of Short Telomeres and p53 Loss. Metabolites 2021, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattapuram, N.; Zhang, C.; Muyyarikkandy, M.S.; Surugihalli, C.; Muralidaran, V.; Gregory, T.; Sunny, N.E. Dietary Macronutrient Composition Differentially Modulates the Remodeling of Mitochondrial Oxidative Metabolism during NAFLD. Metabolites 2021, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, V.B.; Pioli, M.R.; de Souza, D.N.; Teixeira, C.J.; Murata, G.M.; Santos-Silva, J.C.; Hecht, F.B.; Vicente, J.M.; Bordin, S.; Anhê, G.F. Agomelatine reduces circulating triacylglycerides and hepatic steatosis in fructose-treated rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.P.; Feldman, H.S.; Chambers, C.D.; Wilson, L.; Behling, C.; Clark, J.M.; Molleston, J.P.; Chalasani, N.; Sanyal, A.J.; Fishbein, M.H.; et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network (NASH CRN). Low and High Birth Weights Are Risk Factors for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children. J. Pediatr. 2017, 187, 141–146.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadou, C.; Nabi, O.; Serfaty, L.; Lacombe, K.; Boursier, J.; Mathurin, P.; Ribet, C.; de Ledinghen, V.; Zins, M.; Charles, M.A. Association between birth weight, preterm birth, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a community-based cohort. Hepatology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelezang, S.; Santos, S.; Toemen, L.; Oei, E.H.G.; Felix, J.F.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Associations of Fetal and Infant Weight Change with General, Visceral, and Organ Adiposity at School Age. JAMA Netw. Open. 2019, 2, e192843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaleão, L.C.; Murata, G.; Teixeira, C.J.; Payolla, T.B.; Santos-Silva, J.C.; Duque-Guimaraes, D.E.; Sodré, F.S.; Lellis-Santos, C.; Vieira, J.C.; de Souza, D.N.; et al. Prolonged fasting elicits increased hepatic triglyceride accumulation in rats born to dexamethasone-treated mothers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payolla, T.B.; Teixeira, C.J.; Sato, F.T.; Murata, G.M.; Zonta, G.A.; Sodré, F.S.; Campos, C.V.; Mesquita, F.N.; Anhê, G.F.; Bordin, S. In Utero Dexamethasone Exposure Exacerbates Hepatic Steatosis in Rats That Consume Fructose During Adulthood. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.J.; Santos-Silva, J.C.; de Souza, D.N.; Rafacho, A.; Anhe, G.F.; Bordin, S. Dexamethasone during pregnancy impairs maternal pancreatic β-cell renewal during lactation. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.V.; Teixeira, C.J.; Payolla, T.B.; Crisma, A.R.; Murata, G.M.; Amaral, A.G.; Pantaleão, L.C.; Sodré, F.S.; Onari, M.M.; Almeida, L.d.S.; et al. Changes in PGC-1α-Dependent Mitochondrial Biogenesis Are Associated with Inflexible Hepatic Energy Metabolism in the Offspring Born to Dexamethasone-Treated Mothers. Livers 2021, 1, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Wang, Y.; Qi, L.; Williams, G.M.; Gao, B.; Song, G.; Burdick, J.F.; Sun, Z. Pharmacological Mobilization of Endogenous Bone Marrow Stem Cells Promotes Liver Regeneration after Extensive Liver Resection in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, D.N.; Teixeira, C.J.; Veronesi, V.B.; Murata, G.M.; Santos-Silva, J.C.; Hecht, F.B.; Vicente, J.M.; Bordin, S.; Anhê, G.F. Dexamethasone programs lower fatty acid absorption and reduced PPAR-γ and fat/CD36 expression in the jejunum of the adult rat offspring. Life Sci. 2021, 265, 118765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Silva, J.C.; da Silva, P.M.R.; de Souza, D.N.; Teixeira, C.J.; Bordin, S.; Anhê, G.F. In utero exposure to dexamethasone programs the development of the pancreatic β- and α-cells during early postnatal life. Life Sci. 2020, 255, 117810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobili, V.; Marcellini, M.; Marchesini, G.; Vanni, E.; Manco, M.; Villani, A.; Bugianesi, E. Intrauterine growth retardation, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2638–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, A.; Ebrahim, S.; Smith, G.D.; Lawlor, D.A. The associations between birthweight and adult markers of liver damage and function. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2008, 22, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Sullivan, S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Green, M.; Roncal, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Kuwabara, M.; Sato, Y.; Kang, D.H.; et al. Fructose and sugar: A major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddin, M.; Loomba, R. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Indications for liver biopsy and noninvasive biomarkers. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 1, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Jiang, T.; Wen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, K.; Xu, D.; et al. Prenatal dexamethasone exposure-induced a gender-difference and sustainable multi-organ damage in offspring rats via serum metabolic profile analysis. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 316, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Yun, H.; Moon, S.; Cho, Y.E.; Gao, B. Role of Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 751802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensen, S.S.; Slaats, Y.; Nijhuis, J.; Jans, A.; Bieghs, V.; Driessen, A.; Malle, E.; Greve, J.W.; Buurman, W.A. Increased hepatic myeloperoxidase activity in obese subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, A.C.; Thiele, N.D.; Steins, D.; Michaëlsson, E.; Wehmeyer, M.; Scheja, L.; Steglich, B.; Huber, S.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; Lohse, A.W.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of Myeloperoxidase Attenuates NASH in Mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1441–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Takahashi, S.; Hu, X.; Lu, Y.; Fujimori, N.; Golla, S.; Fang, Z.Z.; Aoyama, T.; Krausz, K.W.; Gonzalez, F.J. Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45α protects against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis induced by methionine- and choline-deficient diet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 3170–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, M.C.; Kovalsky, O.; Salvador, J.M.; Kim, K.E.; Patterson, A.D.; Haines, D.C.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. Dimethylbenzanthracene carcinogenesis in Gadd45a-null mice is associated with decreased DNA repair and increased mutation frequency. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2487–2491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, K.; Sha, X.; Magimaidas, A.; Maifrede, S.; Skorski, T.; Bhatia, R.; Hoffman, B.; Liebermann, D.A. Gadd45a deficiency accelerates BCR-ABL driven chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 10809–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, S.; Marais, R.; Zhu, A.X. The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4989–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Herzig, S.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Montminy, M. TRB3: A tribbles homolog that inhibits Akt/PKB activation by insulin in liver. Science 2003, 300, 1574–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.; Lorente, M.; García-Taboada, E.; Pérez Gómez, E.; Dávila, D.; Zúñiga-García, P.; María Flores, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Hegedus, Z.; Mosén-Ansorena, D.; et al. Loss of Tribbles pseudokinase-3 promotes Akt-driven tumorigenesis via FOXO inactivation. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, M.; Chi, J.G.; Lee, H. Expressions of HSP70 and HSP27 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2005, 20, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, S.; Kanematsu, M.; Imai, H.; Goshima, S. Clinical significance of serum HGF and c-Met expression in tumor tissue for evaluation of properties and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 2008, 55, 544–549. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.W.; Lee, K.T.; Yeh, Y.T.; Soon, M.S.; Wang, C.L.; Yu, M.L.; Wang, S.N. Association of circulating insulin-like growth factor 1 with hepatocellular carcinoma: One cross-sectional correlation study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2010, 24, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.A.; Sodré, F.S.; Murata, G.M.; Amaral, A.G.; Payolla, T.B.; Campos, C.V.; Sato, F.T.; Anhê, G.F.; Bordin, S. Fructose Consumption by Adult Rats Exposed to Dexamethasone in Utero Changes the Phenotype of Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Exacerbates Intestinal Gluconeogenesis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoric, J.; Di Caro, G.; Reibe, S.; Henstridge, D.C.; Green, C.R.; Vrbanac, A.; Ceteci, F.; Conche, C.; McNulty, R.; Shalapour, S.; et al. Fructose stimulated de novo lipogenesis is promoted by inflammation. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbraio, M.A.; Reibe, S.; Shalapour, S.; Ooi, G.J.; Watt, M.J.; Karin, M. Preclinical Models for Studying NASH-Driven HCC: How Useful Are They? Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida, L.d.S.; Teixeira, C.J.; Campos, C.V.; Casaloti, L.G.; Sodré, F.S.; Capetini, V.C.; Amaral, A.G.; Payolla, T.B.; Pantaleão, L.C.; Anhê, G.F.; et al. Low Birth Weight Intensifies Changes in Markers of Hepatocarcinogenesis Induced by Fructose Consumption in Rats. Metabolites 2022, 12, 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100886
Almeida LdS, Teixeira CJ, Campos CV, Casaloti LG, Sodré FS, Capetini VC, Amaral AG, Payolla TB, Pantaleão LC, Anhê GF, et al. Low Birth Weight Intensifies Changes in Markers of Hepatocarcinogenesis Induced by Fructose Consumption in Rats. Metabolites. 2022; 12(10):886. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100886
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida, Lorena de Souza, Caio Jordão Teixeira, Carolina Vieira Campos, Laís Guadalupe Casaloti, Frhancielly Shirley Sodré, Vinícius Cooper Capetini, Andressa Godoy Amaral, Tanyara Baliani Payolla, Lucas Carminatti Pantaleão, Gabriel Forato Anhê, and et al. 2022. "Low Birth Weight Intensifies Changes in Markers of Hepatocarcinogenesis Induced by Fructose Consumption in Rats" Metabolites 12, no. 10: 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100886
APA StyleAlmeida, L. d. S., Teixeira, C. J., Campos, C. V., Casaloti, L. G., Sodré, F. S., Capetini, V. C., Amaral, A. G., Payolla, T. B., Pantaleão, L. C., Anhê, G. F., & Bordin, S. (2022). Low Birth Weight Intensifies Changes in Markers of Hepatocarcinogenesis Induced by Fructose Consumption in Rats. Metabolites, 12(10), 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100886







