2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Regulates the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells by Modulating Cholesterol Homeostasis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
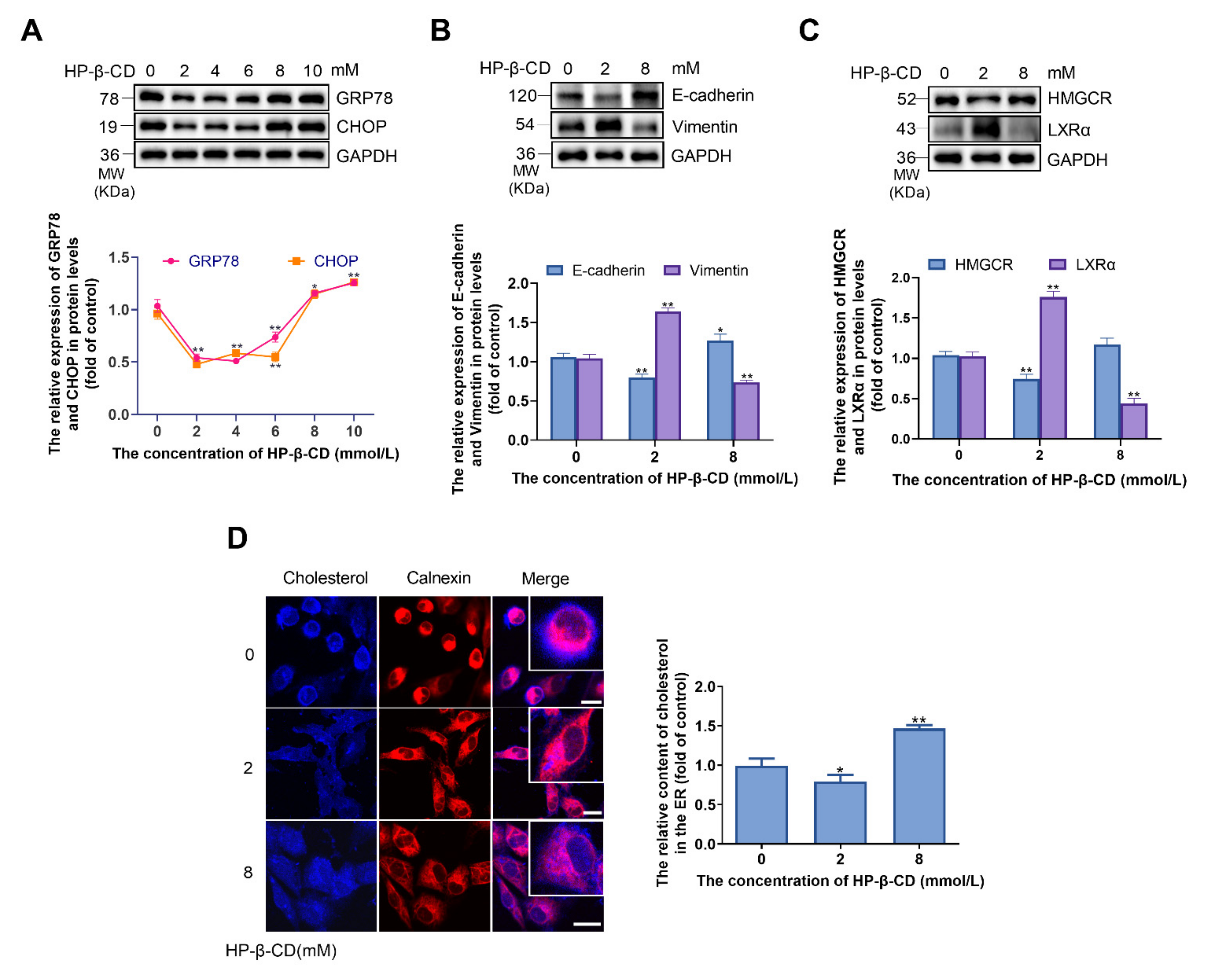
2.1. HP-β-CD Decreases the Efflux of Cholesterol by Inhibiting the Expression of LXRα
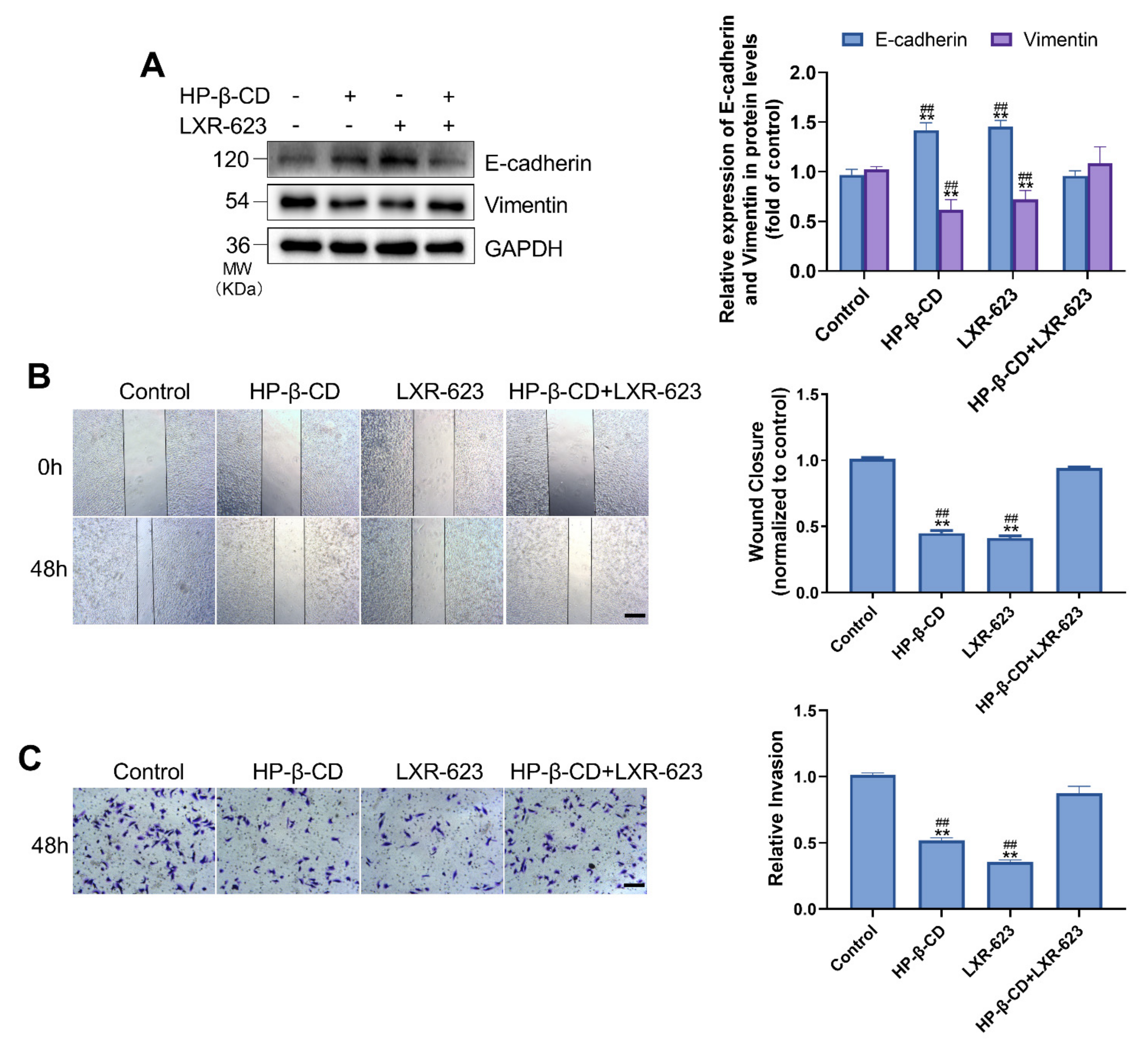
2.2. Disruption of Cholesterol Efflux Inhibits the Invasion and Migration of MDA-MB-231 Cells
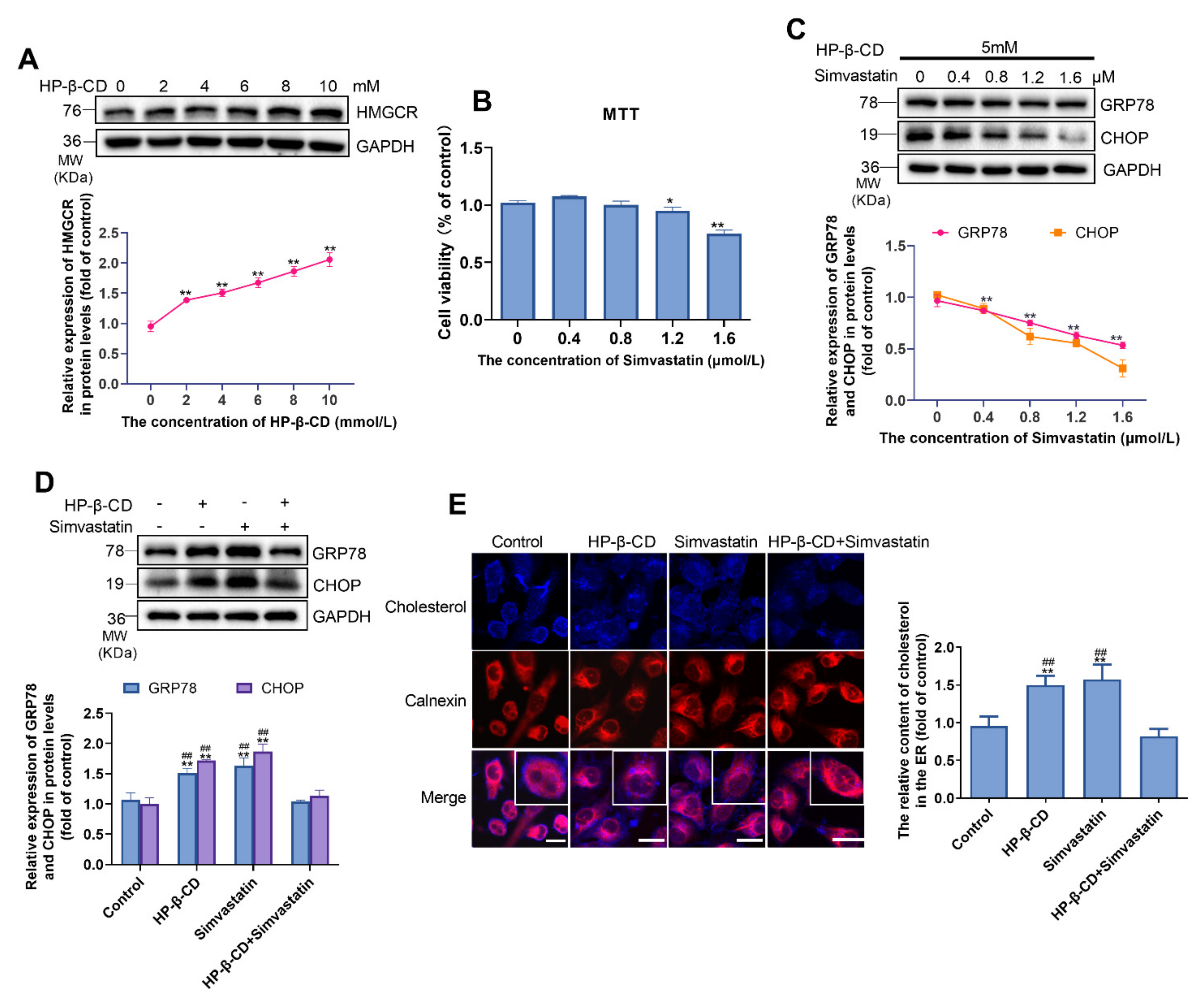
2.3. HP-β-CD Induces ER Stress by Inducing the Expression of HMGCR and Increasing the Synthesis of Cholesterol
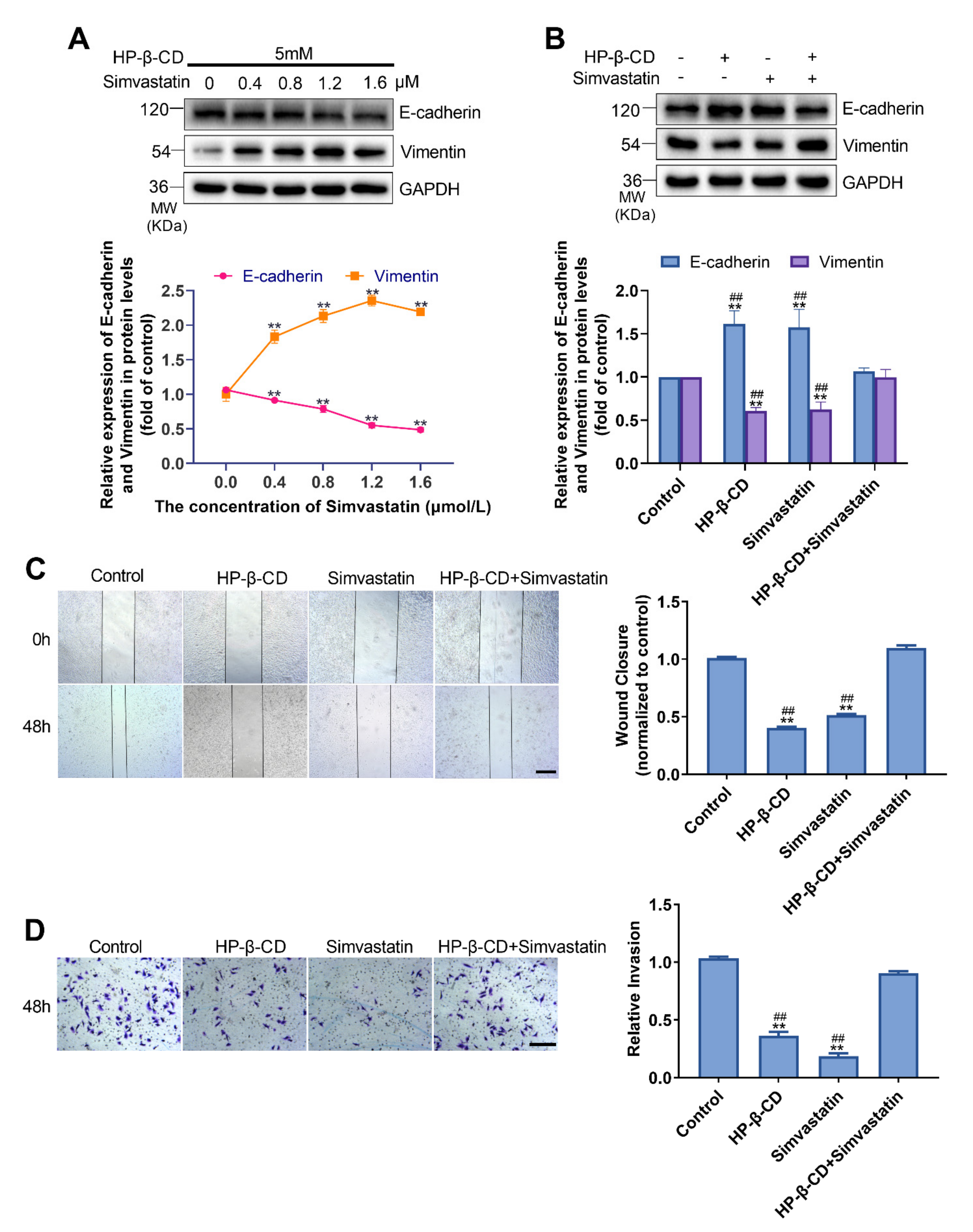
2.4. Disruption of Cholesterol Synthesis Inhibits EMT in MDA-MB-231 Cells
2.5. Lower Concentrations of HP-β-CD Promote TGF-β/Smad Pathway-Induced EMT in MDA-MB-231 Cells
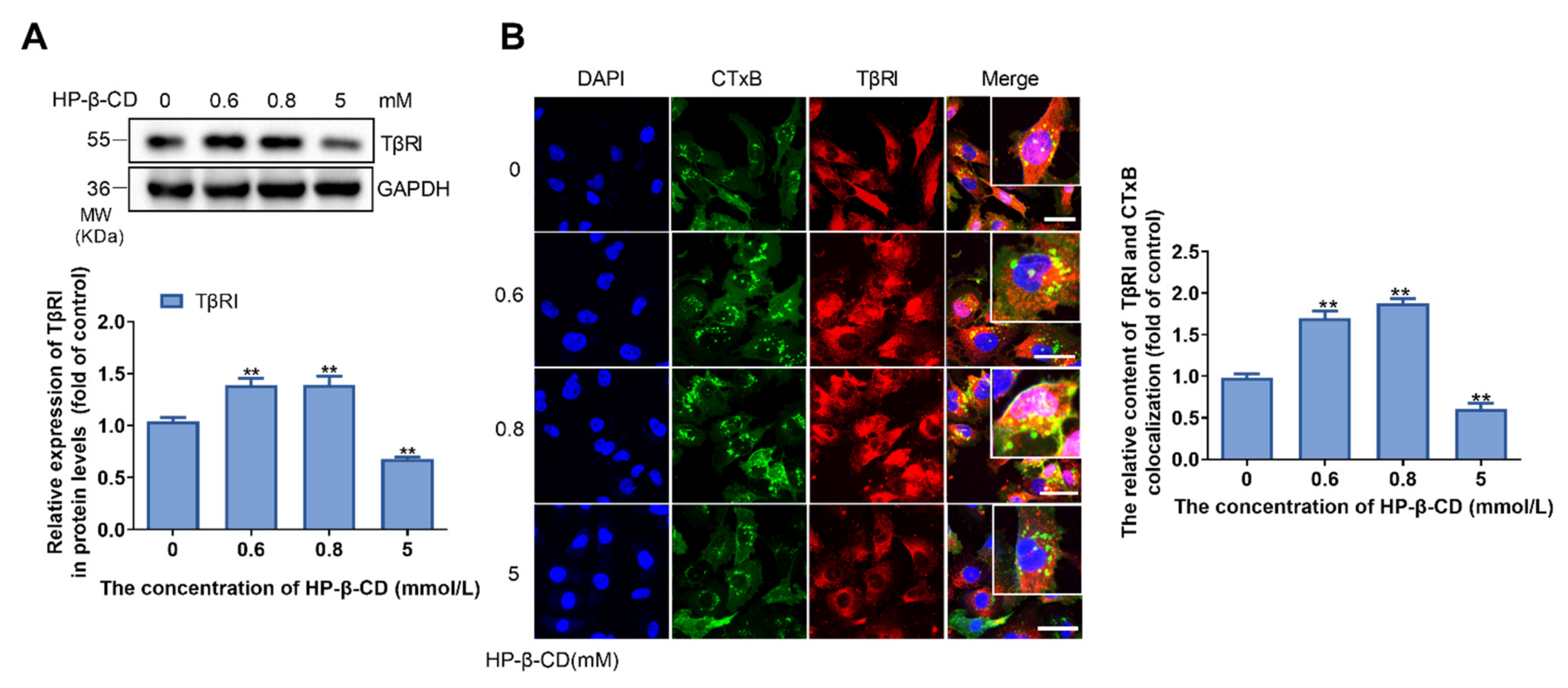
2.6. Effects of HP-β-CD on the Expression and Distribution of TβRI
2.7. ER Stress Inhibits the TGF-β/Smad Pathway in MDA-MB-231 Cells
2.8. High Concentrations of HP-β-CD Disrupt Cholesterol Metabolism in BT-549 Breast Cancer Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. Transwell Assay
4.4. Would Healing Closure
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Filipin Staining and Immunofluorescence
4.7. Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, A.P.; Wilson, J.J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: An arising target for metal-based anticancer agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8113–8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Kaufman, R.J. The role of ER stress in lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, W.J.; Park, J.W. The role of sphingolipids in endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 3632–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozaykut, P.; Ekren, R.; Sezerman, O.U.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Ozer, N.K. High-throughput profiling reveals perturbation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes in atherosclerosis induced by high-cholesterol diet and the protective role of vitamin E. Biofactors 2020, 46, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteng, A.B.; Kersten, S. Mechanisms of Action of trans Fatty Acids. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Watkins, S.M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. The role of endoplasmic reticulum in hepatic lipid homeostasis and stress signaling. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; Yu, Y.; Jia, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Affects Lipid Metabolism in Atherosclerosis Via CHOP Activation and Over-Expression of miR-33. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1995–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; He, X.; Liu, M.; Hua, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Yan, N. Simvastatin Attenuates H2O2-Induced Endothelial Cell Dysfunction by Reducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, L.; Wu, N.; Zhao, R.; He, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; He, Z.; Yu, L.; Yan, N. Sphingomyelin Synthase 2 Promotes Endothelial Dysfunction by Inducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santamaria, P.G.; Mazon, M.J.; Eraso, P.; Portillo, F. UPR: An Upstream Signal to EMT Induction in Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavernier, Q.; Legras, A.; Didelot, A.; Normand, C.; Gibault, L.; Badoual, C.; Le Pimpec-Barthes, F.; Puig, P.L.; Blons, H.; Pallet, N. High expression of spliced X-Box Binding Protein 1 in lung tumors is associated with cancer aggressiveness and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska, M.; Zielinska, W.; Halas-Wisniewska, M.; Mikolajczyk, K.; Grzanka, A. The cytotoxic effect of oxymatrine on basic cellular processes of A549 non-small lung cancer cells. Acta. Histochem. 2019, 121, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Zheng, D.; Liu, Y. Endoplasmic reticulum stress regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human lens epithelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steeg, P.S. Targeting metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenais, B.; Cornec, M.; Dumont, S.; Marchand, J.; Blanckaert, V. Transcriptomic Response of Breast Cancer Cells MDA-MB-231 to Docosahexaenoic Acid: Downregulation of Lipid and Cholesterol Metabolism Genes and Upregulation of Genes of the Pro-Apoptotic ER-Stress Pathway. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Hao, D.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, H.; Gardner, K.; et al. CtBP promotes metastasis of breast cancer through repressing cholesterol and activating TGF-beta signaling. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2076–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, H.; Ren, G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance in breast cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Du, J.; Mi, Y.; Li, T.; Gong, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Hou, Y. Long Non-coding RNAs Contribute to the Inhibition of Proliferation and EMT by Pterostilbene in Human Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaw-On, P.; Pompimon, W.; Banjerdpongchai, R. Goniothalamin Induces Necroptosis and Anoikis in Human Invasive Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.; He, Z.; Wang, T.; Wan, L.; Chen, L.; Yan, N. Hydroxypropylbetacyclodextrin attenuates the epithelialtomesenchymal transition via endoplasmic reticulum stress in MDAMB231 breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abi-Mosleh, L.; Infante, R.E.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Cyclodextrin overcomes deficient lysosome-to-endoplasmic reticulum transport of cholesterol in Niemann-Pick type C cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19316–19321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crumling, M.A.; King, K.A.; Duncan, R.K. Cyclodextrins and Iatrogenic Hearing Loss: New Drugs with Significant Risk. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singhal, A.; Szente, L.; Hildreth, J.E.K.; Song, B. Hydroxypropyl-beta and -gamma cyclodextrins rescue cholesterol accumulation in Niemann-Pick C1 mutant cell via lysosome-associated membrane protein 1. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, M.A.; O’Connor Butler, E.S.; Hinzey, A.; Sliman, S.; Kotha, S.R.; Marsh, C.B.; Uppu, R.M.; Parinandi, N.L. A simple method for effective and safe removal of membrane cholesterol from lipid rafts in vascular endothelial cells: Implications in oxidant-mediated lipid signaling. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 610, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittkowski, K.M.; Dadurian, C.; Seybold, M.P.; Kim, H.S.; Hoshino, A.; Lyden, D. Complex polymorphisms in endocytosis genes suggest alpha-cyclodextrin as a treatment for breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerra, F.S.; Sampaio, L.d.S.; Konig, S.; Bonamino, M.; Rossi, M.I.D.; Costa, M.L.; Fernandes, P.; Mermelstein, C. Membrane cholesterol depletion reduces breast tumor cell migration by a mechanism that involves non-canonical Wnt signaling and IL-10 secretion. Transl. Med. Commun. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghu, H.; Sodadasu, P.K.; Malla, R.R.; Gondi, C.S.; Estes, N.; Rao, J.S. Localization of uPAR and MMP-9 in lipid rafts is critical for migration, invasion and angiogenesis in human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoo, M.; Kubota, Y.; Motoyama, K.; Higashi, T.; Taniyoshi, M.; Tokumaru, H.; Nishiyama, R.; Tabe, Y.; Mochinaga, S.; Sato, A.; et al. 2-Hydroxypropyl-beta-Cyclodextrin Acts as a Novel Anticancer Agent. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaspar, J.; Mathieu, J.; Alvarez, P. 2-Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HPbetaCD) reduces age-related lipofuscin accumulation through a cholesterol-associated pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, B.; Agnihotri, N. Role of cholesterol homeostasis and its efflux pathways in cancer progression. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 191, 105377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.J.; Zelenko, Z.; Neel, B.A.; Antoniou, I.M.; Rajan, L.; Kase, N.; LeRoith, D. Elevated tumor LDLR expression accelerates LDL cholesterol-mediated breast cancer growth in mouse models of hyperlipidemia. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6462–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulman, I.G. Liver X receptors link lipid metabolism and inflammation. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 2978–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widenmaier, S.B.; Snyder, N.A.; Nguyen, T.B.; Arduini, A.; Lee, G.Y.; Arruda, A.P.; Saksi, J.; Bartelt, A.; Hotamisligil, G.S. NRF1 Is an ER Membrane Sensor that Is Central to Cholesterol Homeostasis. Cell 2017, 171, 1094–1109.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leussink, S.; Aranda-Pardos, I.; Noelia, A.G. Lipid metabolism as a mechanism of immunomodulation in macrophages: The role of liver X receptors. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 53, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coisne, C.; Hallier-Vanuxeem, D.; Boucau, M.C.; Hachani, J.; Tilloy, S.; Bricout, H.; Monflier, E.; Wils, D.; Serpelloni, M.; Parissaux, X.; et al. beta-Cyclodextrins Decrease Cholesterol Release and ABC-Associated Transporter Expression in Smooth Muscle Cells and Aortic Endothelial Cells. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sozen, E.; Yazgan, B.; Tok, O.E.; Demirel, T.; Ercan, F.; Proto, J.D.; Ozer, N.K. Cholesterol induced autophagy via IRE1/JNK pathway promotes autophagic cell death in heart tissue. Metabolism 2020, 106, 154205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J. Shuttle/sink model composed of beta-cyclodextrin and simvastatin-loaded discoidal reconstituted high-density lipoprotein for enhanced cholesterol efflux and drug uptake in macrophage/foam cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guan, J.; Wang, W.; Hou, C.; Zhou, L.; Ma, J.; Cheng, Y.; Jiao, S.; Zhou, Z. TRAF3-interacting JNK-activating modulator promotes inflammation by stimulating translocation of Toll-like receptor 4 to lipid rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 2744–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.L.; Huang, S.S.; Huang, J.S. Cholesterol modulates cellular TGF-beta responsiveness by altering TGF-beta binding to TGF-beta receptors. J. Cell Physiol. 2008, 215, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, A.; Sawant, M.A.; Kavishwar, G.; Lavhale, M.; Sitasawad, S. AECHL-1 targets breast cancer progression via inhibition of metastasis, prevention of EMT and suppression of Cancer Stem Cell characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, S.; Chawla, A.; Corvera, S. TGF beta receptor internalization into EEA1-enriched early endosomes: Role in signaling to Smad2. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 158, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Liu, X.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Q.; Tong, Z.; et al. Cholesterol Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Prostate Cancer Cells by Suppressing Degradation of EGFR through APMAP. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Prijic, S.; Urban, B.C.; Tisza, M.J.; Zuo, Y.; Li, L.; Tan, Z.; Chen, X.; Mani, S.A.; Chang, J.T. Candidate Antimetastasis Drugs Suppress the Metastatic Capacity of Breast Cancer Cells by Reducing Membrane Fluidity. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2037–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.G. Endocytic regulation of TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Guglielmo, G.M.; Le Roy, C.; Goodfellow, A.F.; Wrana, J.L. Distinct endocytic pathways regulate TGF-beta receptor signalling and turnover. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Ijaz, M.; Shi, Y. Tunicamycin potentiates paclitaxel-induced apoptosis through inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways in breast cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, L.P.; Voilquin, L.; Kobayashi, T.; Tomasetto, C.; Alpy, F. Intracellular and Plasma Membrane Cholesterol Labeling and Quantification Using Filipin and GFP-D4. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1949, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Actis Dato, V.; Chiabrando, G.A. Activated Alpha-2 Macroglobulin Improves Insulin Response via LRP1 in Lipid-Loaded HL-1 Cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolte, S.; Cordelieres, F.P. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 224, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingione, A.; Pivari, F.; Plotegher, N.; Dei Cas, M.; Zulueta, A.; Bocci, T.; Trinchera, M.; Albi, E.; Maglione, V.; Caretti, A.; et al. Inhibition of Ceramide Synthesis Reduces alpha-Synuclein Proteinopathy in a Cellular Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; He, L.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L.; Yan, N. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Regulates the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells by Modulating Cholesterol Homeostasis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Metabolites 2021, 11, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080562
Zhao Y, He L, Wang T, Zhu L, Yan N. 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Regulates the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells by Modulating Cholesterol Homeostasis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Metabolites. 2021; 11(8):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080562
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yiyang, Linkang He, Tian Wang, Lifang Zhu, and Nianlong Yan. 2021. "2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Regulates the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells by Modulating Cholesterol Homeostasis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress" Metabolites 11, no. 8: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080562
APA StyleZhao, Y., He, L., Wang, T., Zhu, L., & Yan, N. (2021). 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Regulates the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells by Modulating Cholesterol Homeostasis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Metabolites, 11(8), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080562






