Anti-Proliferative Potential of Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Theonella sp.: Moving from Correlation toward Causation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
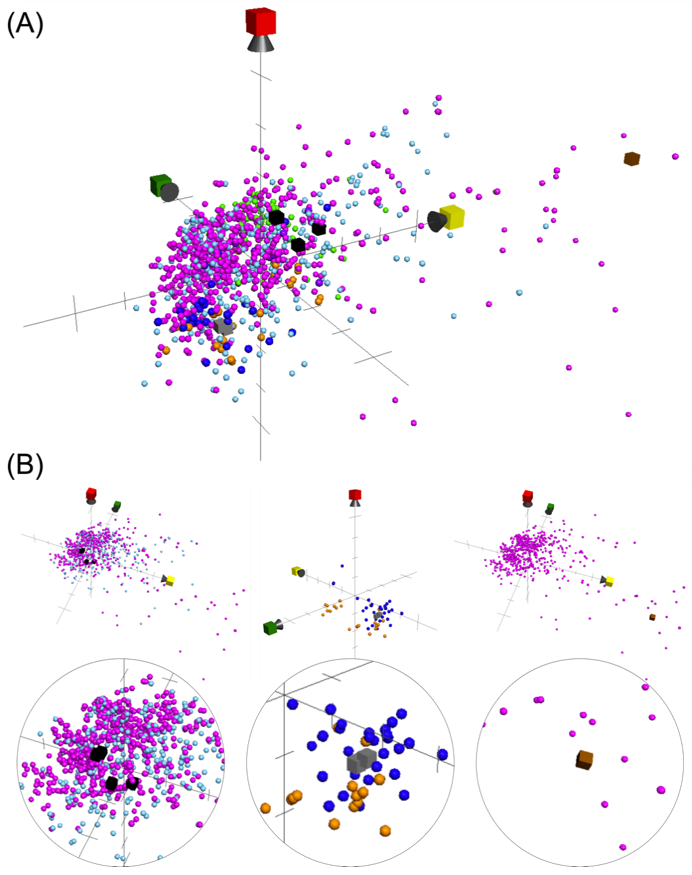
3.5. ChemGPS-NP Prediction for the Possible Mode of Actions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dahiya, R.; Dahiya, S.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.V.; Dahiya, S.; Kumar, S.; Saharan, R.; Basu, P.; Mitra, A.; Sharma, A.; et al. Structural and biological aspects of natural bridged macrobicyclic peptides from marine resources. Arch. Der Pharm. 2021, e2100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.-R.; Lai, K.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Su, J.-H.; Huang, Y.M.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lu, M.-C.; Yu, S.S.-F.; Duh, C.-Y.; Sung, P.-J. Probing anti-proliferative 24-homoscalaranes from a sponge Lendenfeldia sp. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran, A.A.; Miljkovic, M.; Prasad, V. Analysis of estimated clinical benefit of newly approved drugs for US patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2020, 96, 106420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, C.A.; Faulkner, D.J. Lithistid sponges: Star performers or hosts to the stars. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2162–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-K.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Lu, M.-C.; Chang, W.-B.; Su, J.-H. 4-Methylenesterols from a sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichiba, T.; Nakao, Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sata, N.U.; Kelly-Borges, M. Kumusine, a chloroadenine riboside from a sponge, Theonella sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 3977–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humisto, A.; Jokela, J.; Liu, L.; Wahlsten, M.; Wang, H.; Permi, P.; Machado, J.P.; Antunes, A.; Fewer, D.P.; Sivonen, K. The swinholide biosynthesis gene cluster from a terrestrial cyanobacterium, Nostoc sp. strain UHCC 0450. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02321-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinisi, A.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Dien, H.A.; Zampella, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Isoswinholide B and swinholide K, potently cytotoxic dimeric macrolides from Theonella swinhoei. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 5332–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, S.; Festa, C.; D’Auria, M.V.; Cresteil, T.; Debitus, C.; Zampella, A. Swinholide J, a potent cytotoxin from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelio, K.; Espiritu, R.; Hanashima, S.; Todokoro, Y.; Malabed, R.; Kinoshita, M.; Matsumori, N.; Murata, M.; Nishimura, S.; Kakeya, H.; et al. Theonellamide A, a marine-sponge-derived bicyclic peptide, binds to cholesterol in aqueous DMSO: Solution NMR-based analysis of peptide-sterol interactions using hydroxylated sterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, K.; Takada, K.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Nazumazoles D-F, cyclic pentapeptides that inhibit chymotrypsin, from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, K.; Takada, K.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Nazumazoles A-C, cyclic pentapeptides dimerized through a disulfide bond from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2646–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranaga, T.; Enomoto, A.; Tan, H.; Fujita, K.; Wakimoto, T. Total synthesis of theonellapeptolide Id. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1366–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, A.S.; Bugni, T.S.; Feng, X.; Harper, M.K.; Skalicky, J.J.; Mohammed, K.A.; Andjelic, C.D.; Barrows, L.R.; Ireland, C.M. Theopapuamide, a cyclic depsipeptide from a Papua New Guinea lithistid sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusetani, N.; Warabi, K.; Nogata, Y.; Nakao, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; van Soest, R.R.M. Koshikamide A1, a new cytotoxic linear peptide isolated from a marine sponge, Theonella sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 4687–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.C.S.; Barbosa, C.D.S.; Oliveira, J.T.; Moreira, N.C.D.S.; Martins, N.R.D.M.; Gomes, G.K.A.; Caldeira, C.A.; e Costa, M.L.A.; Guimarães, D.S.M.; Guimaraes, L.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of the mutagenicity of 3-alkylpyridine marine alkaloid analogues with anticancer potential. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2018, 825, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Jimenez, C.; Blanco, M.; Tarazona, G.; Fernandez, R.; Cuevas, C. Lanesoic acid: A cytotoxic zwitterion from Theonella sp. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5832–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, Y.Y.; Tang, J.; Sun, F.; Lin, H.W. New 4-methylidene sterols from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Fitoterapia 2018, 127, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, P.C.; Wilke, D.V.; Branco, P.C.; Bauermeister, A.; Rezende-Teixeira, P.; Gaudencio, S.P.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Enriching cancer pharmacology with drugs of marine origin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youssef, D.T.; Mooberry, S.L. Hurghadolide A and swinholide I, potent actin-microfilament disrupters from the Red Sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubb, M.R.; Spector, I.; Bershadsky, A.D.; Korn, E.D. Swinholide A is a microfilament disrupting marine toxin that stabilizes actin dimers and severs actin filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 3463–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Marino, S.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Debitus, C.C.; Zampella, A. Theonellasterols and conicasterols from Theonella swinhoei—Novel marine natural ligands for human nuclear receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, E.; Imagawa, D.K.; Rohmer, M.; Kashman, Y.; Djerassi, C. Sterols in marine invertebrates. 22. Isolation and structure elucidation of conicasterol and theonellasterol, two new 4-methylene sterols from the Red Sea sponges Theonella conica and Theonella swinhoei. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 46, 1836–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.; Kasinathan, G.; Leal-Cortijo, I.; Musso-Buendia, A.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Ruiz-Pérez, L.M.; Johansson, N.G.; González-Pacanowska, D.; Gilbert, I.H. Deoxyuridine triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase as a potential antiparasitic drug target. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5942–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Wu, M.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Dai, C.-F.; Sheu, J.-H. Metabolites with cytotoxic activity from the formosan soft coral Cladiella australis. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2006, 53, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, M.; Ishida, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kitagawa, I. Molecular conformation of swinholide A, a potent cytotoxic dimeric macrolide from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella swinhoei: X-ray crystal structure of its diketone derivative. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 56, 3629–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaio, A.; Notaro, G.; Piccialli, V.; Sica, D. Minor 5,6-secosterols from the marine sponge Hippospongia communis—Solation and synthesis of (7Z,22E,24R)-24-methyl-5,6-secocholesta-7,22-diene-3β,5β,6-triol. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 53, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Faulkner, D.J. 7α-Hydroxytheonellasterol, a cytotoxic 4-methylene sterol from the Philippines sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, J.; Gottfries, J.; Muresan, S.; Backlund, A. ChemGPS-NP: Tuned for navigation in biologically relevant chemical space. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J.; Lovgren, A.; Kogej, T.; Muresan, S.; Gottfries, J.; Backlund, A. ChemGPS-NP(Web): Chemical space navigation online. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2009, 23, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliakis, G.; Bryant, P.E. Effects of the nucleoside analogues alpha-ara A, beta-ara A and beta-ara C on cell growth and repair of both potentially lethal damage and DNA double strand breaks in mammalian cells in culture. Anticancer Res. 1983, 3, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

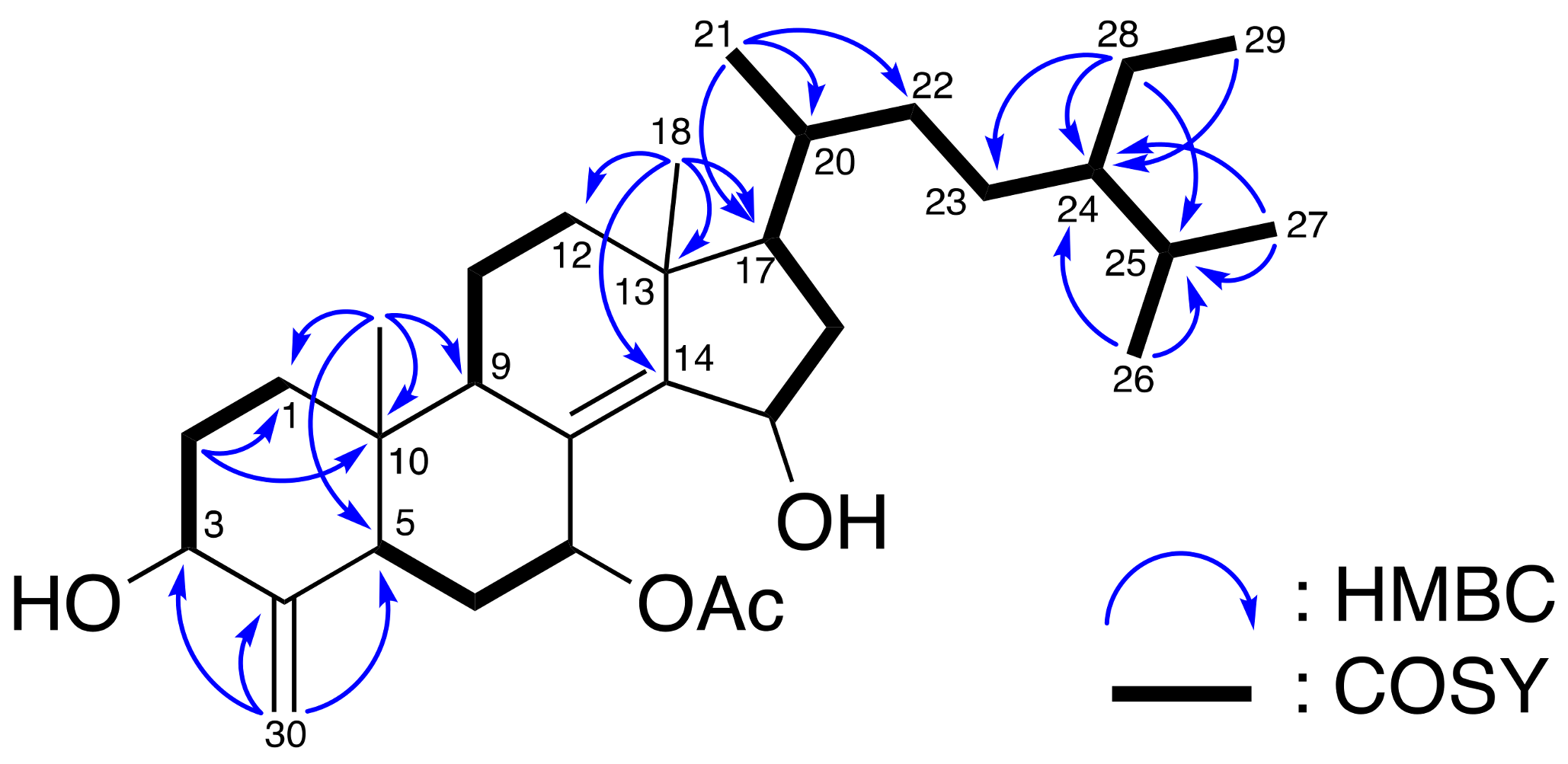
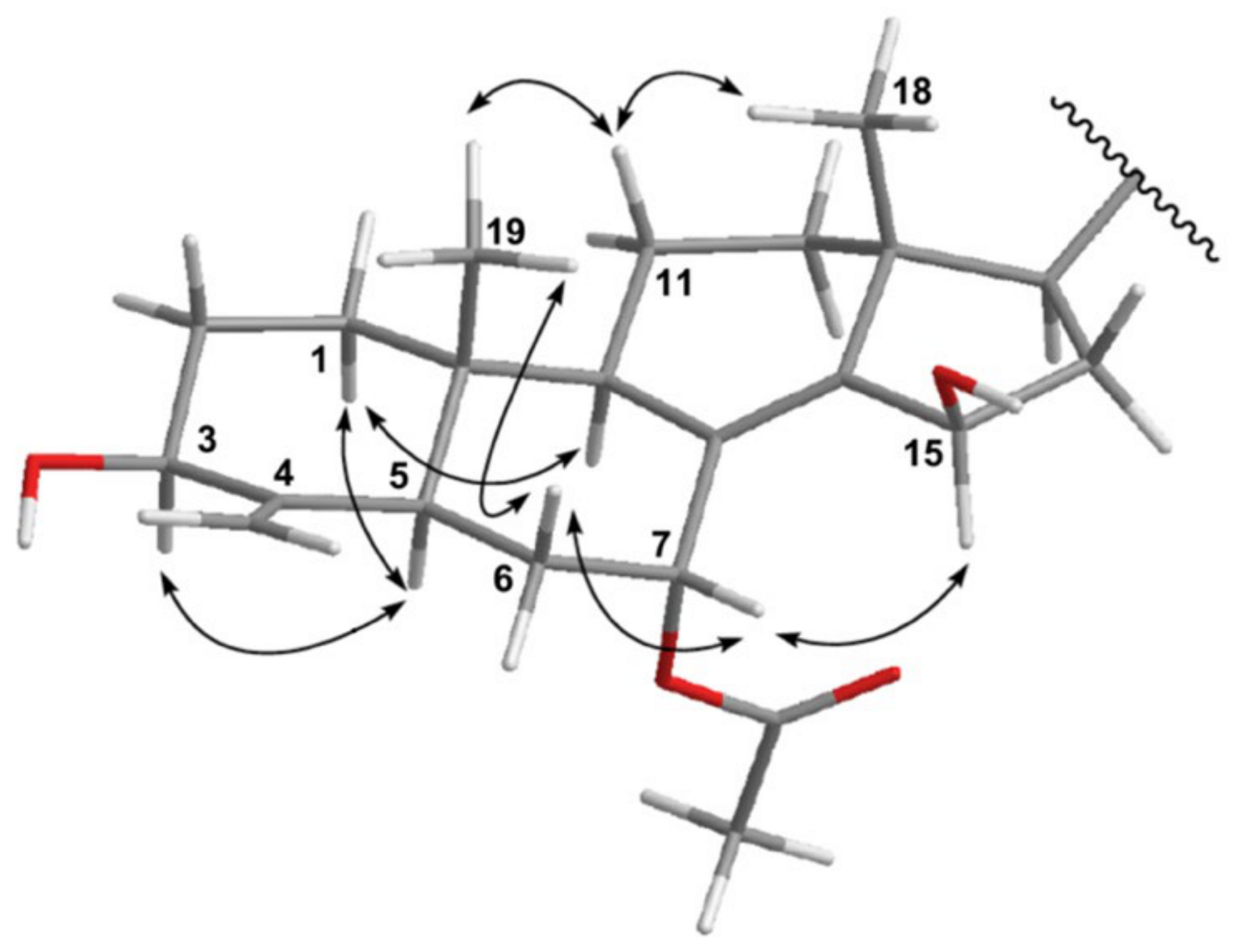
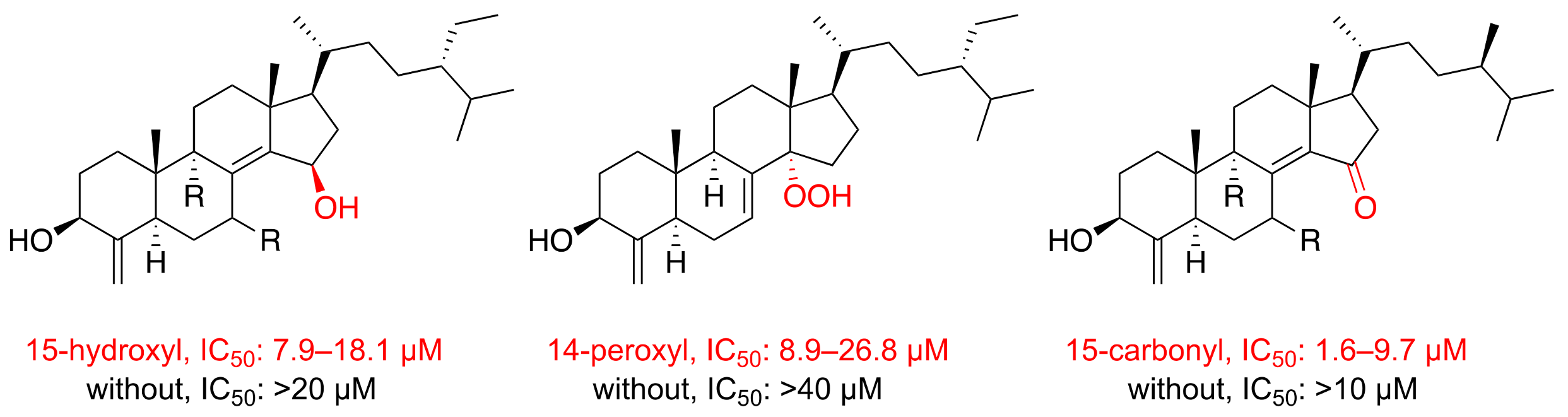
| Position | δH (J in Hz) a | δC (Mult.) b | 1H–1H COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.40 m; 1.78 m | 36.2 (CH2) d | H-2 | |
| 2 | 1.39 m; 2.05 m | 32.8 (CH2) | H-1, H-3 | C-1, C-10 |
| 3 | 4.06 m | 73.1 (CH) | H-2 | |
| 4 | 151.9 (C) | |||
| 5 | 2.27 m | 43.1 (CH) | H-6 | |
| 6 | 1.68 m; 1.88 m | 30.1 (CH2) | H-5, H-7 | |
| 7 | 5.93 br s | 70.8 (CH) | H-6 | |
| 8 | 129.8 (C) | |||
| 9 | 2.32 t (8.5) c | 44.6 (CH) | H-11 | |
| 10 | 40.2 (C) | |||
| 11 | 1.53 m; 1.72 m | 19.9 (CH2) | H-9, H-12 | |
| 12 | 1.30 m; 1.98 m | 36.7 (CH2) | H-11 | |
| 13 | 43.8 (C) | |||
| 14 | 154.1 (C) | |||
| 15 | 4.80 d (6.0) | 69.2 (CH) | H-16 | |
| 16 | 1.72 m; 1.86 m | 38.6 (CH2) | H-15, H-17 | |
| 17 | 1.58 m | 53.0 (CH) | H-16, H-20 | |
| 18 | 0.84 s | 18.9 (CH3) | C-12, C-13, C-14, C-17 | |
| 19 | 0.65 s | 12.8 (CH3) | C-1, C-5, C-9, C-10 | |
| 20 | 1.42 m | 34.1 (CH) | H-17, H-21, H-22 | |
| 21 | 0.96 d (6.5) | 19.2 (CH3) | H-20 | C-17, C-20, C-22 |
| 22 | 1.02 m; 1.42 m | 33.8 (CH2) | H-20, H-23 | |
| 23 | 1.04 m; 1.34 m | 26.6 (CH2) | H-22, H-24 | |
| 24 | 0.94 m | 46.1 (CH) | H-23, H-25, H-28 | |
| 25 | 1.68 m | 28.9 (CH) | H-24, H-26, H-27 | |
| 26 | 0.82 d (7.0) | 18.9 (CH3) | H-25 | C-24, C-25 |
| 27 | 0.83 d (6.5) | 19.6 (CH3) | H-25 | C-24, C-25 |
| 28 | 1.14 m; 1.32 m | 22.9 (CH2) | H-24, H-29 | C-23, C-24, C-25 |
| 29 | 0.86 t (7.5) | 12.3 (CH3) | H-28 | C-24 |
| 30 | 4.60 s; 5.12 s | 103.3 (CH2) | C-3, C-4, C-5 | |
| 7-OAc | 2.04 s | 21.8 (CH3) | ||
| 171.2 (C) |
| Compounds | Cell Lines (IC50 μM) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 | MDA-MB-231 | t-47D | HCT-116 | DLD-1 | K562 | Molt4 | |
| 1 | – a | – a | – a | – a | – a | 17.60 | 18.06 |
| 2 | – a | – a | – a | – a | – a | – a | – a |
| 3 | – a | – a | – a | 13.36 | – a | 7.87 | 14.14 |
| 4 | – a | – a | – a | – a | – a | – a | – a |
| 5 | – a | – a | 18.08 | – a | 2.50 | 10.93 | 8.61 |
| 6 | – a | 5.98 | – a | – a | – a | – a | – a |
| 7 | 1.03 | – a | 0.65 | 0.78 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Doxorubicin b | 1.10 | 1.16 | 0.61 | 0.27 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, K.-H.; Peng, B.-R.; Su, C.-H.; El-Shazly, M.; Sun, Y.-L.; Shih, M.-C.; Huang, Y.-T.; Yen, P.-T.; Wang, L.-S.; Su, J.-H. Anti-Proliferative Potential of Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Theonella sp.: Moving from Correlation toward Causation. Metabolites 2021, 11, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080532
Lai K-H, Peng B-R, Su C-H, El-Shazly M, Sun Y-L, Shih M-C, Huang Y-T, Yen P-T, Wang L-S, Su J-H. Anti-Proliferative Potential of Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Theonella sp.: Moving from Correlation toward Causation. Metabolites. 2021; 11(8):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080532
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Kuei-Hung, Bo-Rong Peng, Chun-Han Su, Mohamed El-Shazly, Yi-Long Sun, Ming-Cheng Shih, Yu-Ting Huang, Pei-Tzu Yen, Lung-Shuo Wang, and Jui-Hsin Su. 2021. "Anti-Proliferative Potential of Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Theonella sp.: Moving from Correlation toward Causation" Metabolites 11, no. 8: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080532
APA StyleLai, K.-H., Peng, B.-R., Su, C.-H., El-Shazly, M., Sun, Y.-L., Shih, M.-C., Huang, Y.-T., Yen, P.-T., Wang, L.-S., & Su, J.-H. (2021). Anti-Proliferative Potential of Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Theonella sp.: Moving from Correlation toward Causation. Metabolites, 11(8), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080532









