Towards Extending the Detection Window of Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid—An Untargeted Metabolomics Study in Serum and Urine Following Controlled Administration in Healthy Men
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analytical and Data Processing Procedures of Samples from a Controlled Clinical Study
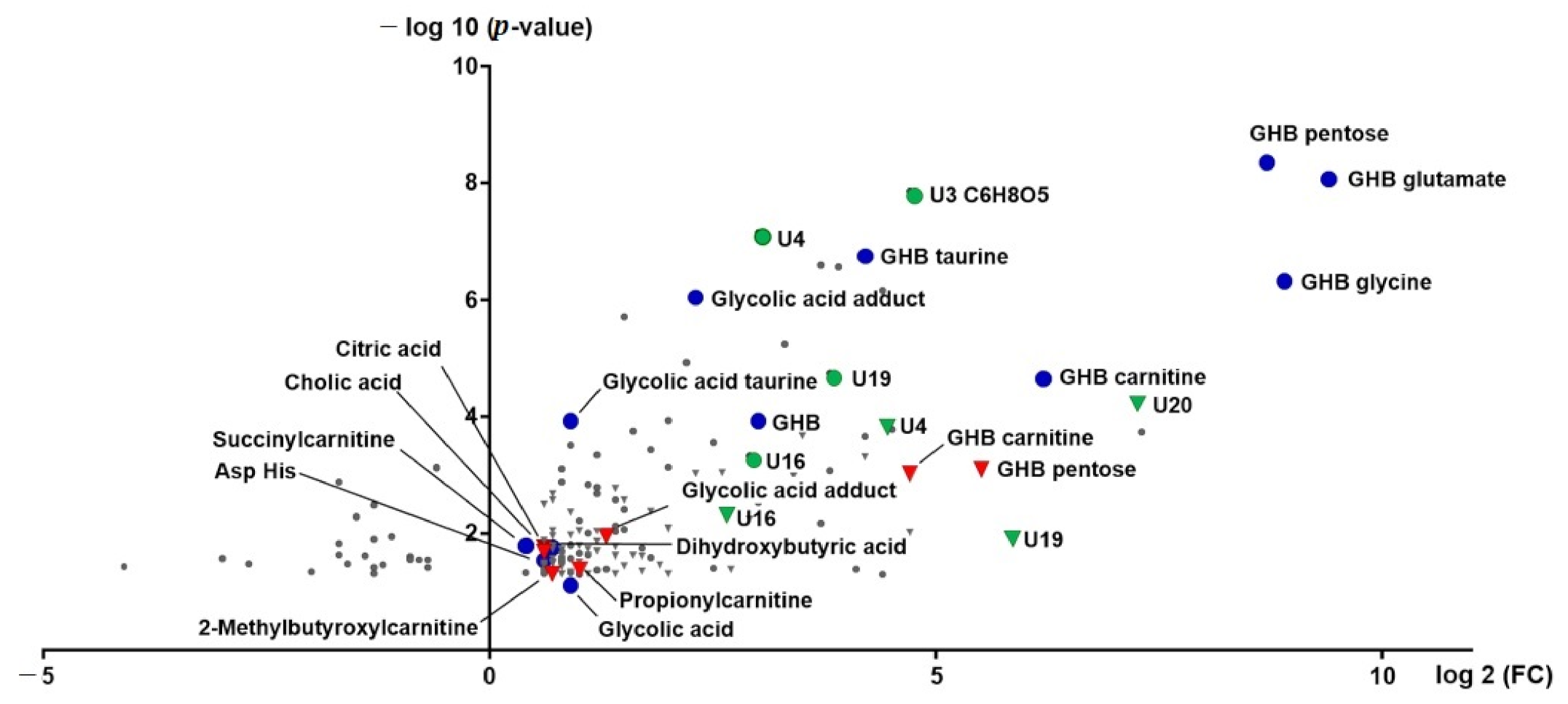
2.2. (Un)targeted Metabolomics Profiling of Urine Samples 4.5 h and 8 h Post GHB Administration
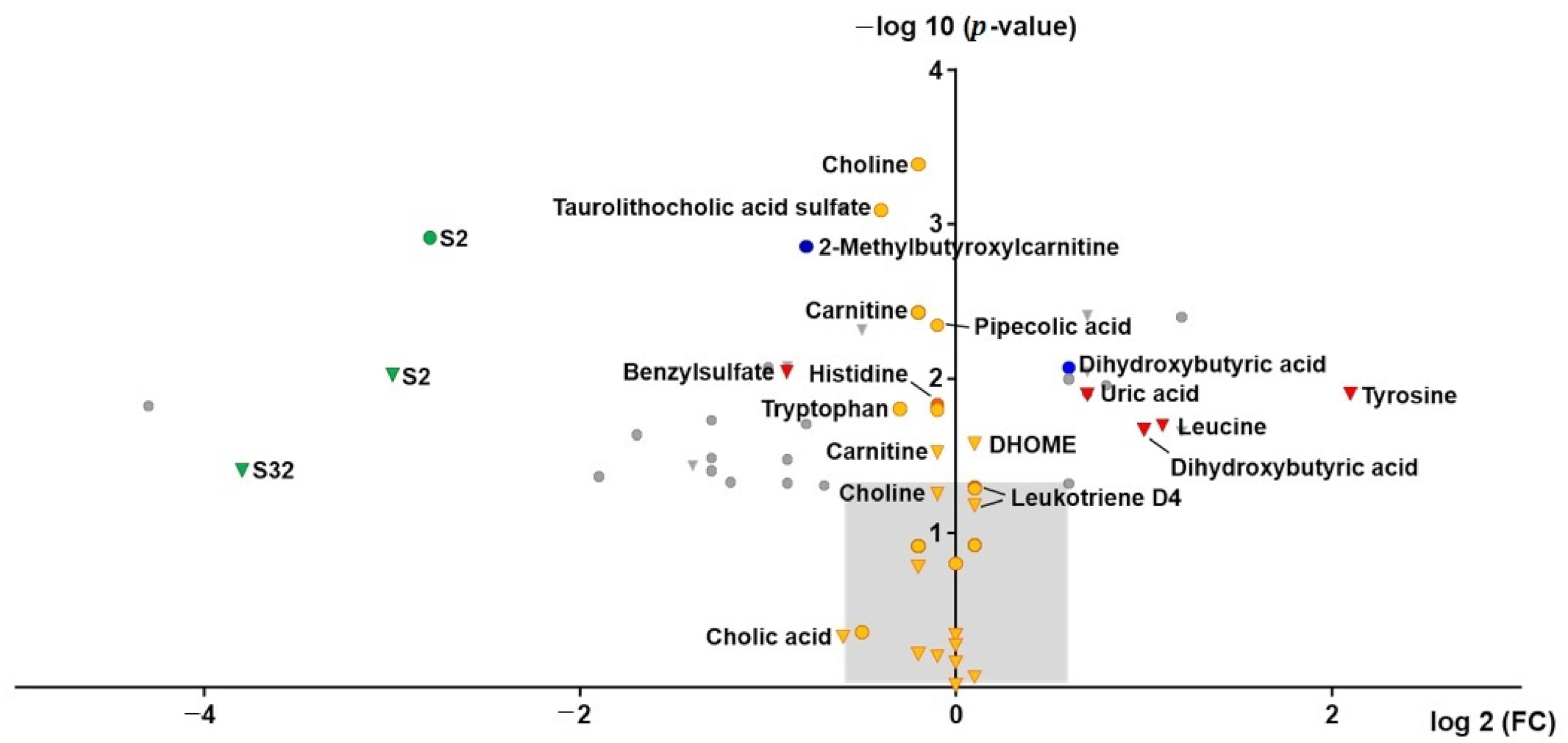
2.3. (Un)targeted Metabolomics Profiling of Serum Samples
3. Discussion
3.1. GHB Amino Acid Conjugates
3.2. Other GHB-Conjugates, GHB-Carnitine and GHB-Pentose
3.3. Unknowns Features/Feature Groups U3, U4, U16, U19, U20
3.4. Organic Acids (Glycolate, Succinylcarnitine, Dihydroxybutyrate)
3.5. Endogenous Changes of Amino Acids, Carnitines, Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Intermediates, Bile Acids, Fatty Acids
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Sample Collection
4.2. Chemicals and Reagents
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. UHPLC-HRMS
4.5. Data Pre-processing, Normalization
4.6. Statistical Analysis/Feature Selection
4.7. Compound Identification
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andresen, H.; Aydin, B.E.; Mueller, A.; Iwersen-Bergmann, S. An overview of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid: Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, toxic effects, addiction, analytical methods, and interpretation of results. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Moore, C. Drug facilitated sexual assault—A review. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2008, 15, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscolo-Berto, R.; Viel, G.; Montagnese, S.; Raduazzo, D.I.; Ferrara, S.D.; Dauvilliers, Y. Narcolepsy and effectiveness of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB): A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, E.E.; Nelson, T.; Miller, D.; Stadlan, N. Oxidation of gamma-hydroxybutyrate to succinic semialdehyde by a mitochon-drial pyridine nucleotide-independent enzyme. J. Neurochem. 1988, 51, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardò, F.P.; Jones, W.; Alan, G.H.B. Pharmacology and toxicology: Acute intoxication, concentrations in blood and urine in forensic cases and treatment of the withdrawal syndrome. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingels, A.-S.M.E.; Wille, S.M.R.; Samyn, N.; Lambert, W.E.; Stove, C.P. Screening and confirmation methods for GHB determination in biological fluids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3553–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenneisen, R.; El Sohly, M.A.; Murphy, T.P.; Passarelli, J.; Russmann, S.; Salamone, S.J.; Watson, D.E. Pharmacokinetics and excretion of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in healthy subjects. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2004, 28, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, S.; Farré, M.; Segura, M.; Pichini, S.; Pastor, A.; Pacifici, R.; Pellegrini, M.; De La Torre, R. Disposition of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in conventional and nonconventional biologic fluids after single drug administration: Issues in methodology and drug monitoring. Ther. Drug Monit. 2007, 29, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, S.; Stachel, N.; Skopp, G. A potential new metabolite of gamma-hydroxybutyrate: Sulfonated gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2015, 130, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, I.N.; Tortzen, C.; Kristensen, J.L.; Pedersen, D.S.; Breindahl, T. Identification of a new metabolite of GHB: Gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid glucuronide. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehling, L.-M.; Piper, T.; Spottke, A.; Heidbreder, A.; Young, P.; Madea, B.; Thevis, M.; Hess, C. GHB-O-β-glucuronide in blood and urine is not a suitable tool for the extension of the detection window after GHB intake. Forensic Toxicol. 2017, 35, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, T.; Mehling, L.-M.; Spottke, A.; Heidbreder, A.; Young, P.; Madea, B.; Hess, C.; Schänzer, W.; Thevis, M. Potential of GHB phase-II-metabolites to complement current approaches in GHB post administration detection. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 279, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, A.E.; Raeber, J.; Steuer, C.; Boxler, M.I.; Dornbierer, D.A.; Bosch, O.G.; Quednow, B.B.; Seifritz, E.; Kraemer, T. Identification of new urinary gamma-hydroxybutyric acid markers applying untargeted metabolomics analysis following placebo-controlled administration to humans. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomino-Schätzlein, M.; Wang, Y.; Brailsford, A.D.; Parella, T.; Cowan, D.A.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Pérez-Trujillo, M. Direct Monitoring of Exogenous γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid in Body Fluids by NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8343–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarsiah, P.; Roehrich, J.; Wyczynski, M.; Hess, C. Phase I metabolites (organic acids) of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid–validated quantification using GC–MS and description of endogenous concentration ranges. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, G.; Vienne, J.; Vaucher, A.; Jimenez, S.; Tafti, M. Central and Peripheral metabolic changes induced by gamma-hydroxybutyrate. Sleep 2015, 38, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinka, T.; Inoue, Y.; Ohse, M.; Ito, A.; Ohfu, M.; Hirose, S.; Kuhara, T. Rapid and sensitive detection of urinary 4-hydroxybutyric acid and its related compounds by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry in a patient with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficienc. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 776, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.K.; Cromby, C.H.; Manning, N.J.; Pollitt, R.J. Urinary organic acids in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency: Evidence of α-oxidation of 4-hydroxybutyric acid, interaction of succinic semialdehyde with pyruvate dehydrogenase and possible secondary inhibition of mitochondrial β-oxidation. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1987, 10, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Carvalho, F.; Duarte, J.A.; Remião, F.; Marques, A.; Santos, A.; Magalhães, T. Collection of biological samples in forensic toxicology. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2010, 20, 363–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, A.E.; Brockbals, L.; Kraemer, T. Metabolomic strategies in biomarker research—New approach for indirect identification of drug consumption and sample manipulation in clinical and forensic toxicology? Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrallah, F.A.; Maher, A.D.; Hanrahan, J.R.; Balcar, V.J.; Rae, C.D. γ-Hydroxybutyrate and the GABAergic footprint: A metabolomic approach to unpicking the actions of GHB. J. Neurochem. 2010, 115, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steuer, A.E.; Arnold, K.; Schneider, T.D.; Poetzsch, M.; Kraemer, T. A new metabolomics-based strategy for identification of endogenous markers of urine adulteration attempts exemplified for potassium nitrite. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6235–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steuer, A.E.; Kaelin, D.; Boxler, M.I.; Eisenbeiss, L.; Holze, F.; Vizeli, P.; Czerwinska, J.; Dargan, P.I.; Abbate, V.; Liechti, M.E.; et al. Comparative untargeted metabolomics analysis of the psychostimulants 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine (MDMA), amphetamine, and the novel psychoactive substance mephedrone after controlled drug administration to humans. Metabolites 2020, 10, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxler, M.I.; Schneider, T.D.; Kraemer, T.; Steuer, A.E. Analytical considerations for (un)-targeted metabolomic studies with special focus on forensic applications. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 678–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornbierer, A.D.; Boxler, M.; Voegel, C.D.; Stucky, B.; Steuer, E.A.; Binz, T.M.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Baur, D.M.; Quednow, B.B.; Kraemer, T.; et al. Nocturnal gamma-hydroxybutyrate reduces cortisol-awakening response and morning kynurenine pathway metabolites in healthy volunteers. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manier, S.K.; Meyer, M.R. Current situation of the metabolomics techniques used for the metabolism studies of new psycho-active substances. Ther. Drug. Monit. 2020, 42, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxler, M.I.; Streun, G.L.; Liechti, M.E.; Schmid, Y.; Kraemer, T.; Steuer, A.E. Human metabolome changes after a single dose of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) with special focus on steroid metabolism and inflammation processes. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2900–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, A.G. Detection times of drugs of abuse in blood, urine, and oral fluid. Ther. Drug Monit. 2004, 26, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, H.H. Analytical toxicology. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steventon, G.B. The Amino Acid conjugations. In Enzyme Systems that Metabolise Drugs and other Xenobiotics; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2001; p. 501. [Google Scholar]
- Badenhorst, C.P.S.; Erasmus, E.; Van Der Sluis, R.; Nortje, C.; Van Dijk, A.A. A new perspective on the importance of glycine conjugation in the metabolism of aromatic acids. Drug Metab. Rev. 2014, 46, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazu, T.; Yamaguchi, T. Substrate specificity for carnitine and glycine conjugation of branched side-chain and cyclic side-chain carboxylic acids in various experimental animals. Xenobiotica 2009, 39, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.W.; Zhang, D.; Halladay, J.S.; Driscoll, J.P.; Khojasteh, S.C. Going beyond common drug metabolizing enzymes: Case studies of biotransformation involving aldehyde oxidase, glutamyl transpeptidase, cathepsin B, flavin-containing monooxygenase, and ADP-ribosyltransferase. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarda, S.; Page, C.; Pickup, K.; Schulz-Utermoehl, T.; Wilson, I. Diclofenac metabolism in the mouse: Novelin vivometabolites identified by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Xenobiotica 2011, 42, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Liu, L.; Shi, J.; Yu, X.; Xiao, W.; Sun, R.; Zhou, Y.; Aa, J.; Wang, G. The metabolic impact of methamphetamine on the systemic metabolism of rats and potential markers of methamphetamine abuse. Mol. BioSyst. 2014, 10, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Liu, L.; Aa, J.; Wang, G.; Cao, B.; Li, M.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Gu, R.; et al. Metabolic phenotype of rats exposed to heroin and potential markers of heroin abuse. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013, 127, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrine, S.A.; Michaels, M.S.; Ghoddoussi, F.; Hyde, E.M.; Tancer, M.E.; Galloway, M.P. Cardiac effects of MDMA on the metabolic profile determined with 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the rat. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaveski, T.; Narvik, J.; Innos, J.; Philips, M.-A.; Ottas, A.; Plaas, M.; Haring, L.; Zilmer, M.; Vasar, E. Repeated administration of D-amphetamine induces distinct alterations in behavior and metabolite levels in 129Sv and Bl6 mouse strains. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijas, C.; Montenegro-Burke, J.R.; Domingo-Almenara, X.; Palermo, A.; Warth, B.; Hermann, G.; Koellensperger, G.; Huan, T.; Uritboonthai, W.; Aisporna, A.E.; et al. METLIN: A technology platform for identifying knowns and unknowns. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 3156–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. HMDB: The human metabolome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linstrom, P.J.; Mallard, W.G. NIST Chemistry WebBook; NIST Standard Reference Database No. 69; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2001.
- Kind, T.; Liu, K.-H.; Lee, D.Y.; DeFelice, B.; Meissen, J.K.; Fiehn, O. LipidBlast in silico tandem mass spectrometry database for lipid identification. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steuer, A.E.; Raeber, J.; Simbuerger, F.; Dornbierer, D.A.; Bosch, O.G.; Quednow, B.B.; Seifritz, E.; Kraemer, T. Towards Extending the Detection Window of Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid—An Untargeted Metabolomics Study in Serum and Urine Following Controlled Administration in Healthy Men. Metabolites 2021, 11, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030166
Steuer AE, Raeber J, Simbuerger F, Dornbierer DA, Bosch OG, Quednow BB, Seifritz E, Kraemer T. Towards Extending the Detection Window of Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid—An Untargeted Metabolomics Study in Serum and Urine Following Controlled Administration in Healthy Men. Metabolites. 2021; 11(3):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030166
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteuer, Andrea E., Justine Raeber, Fabio Simbuerger, Dario A. Dornbierer, Oliver G. Bosch, Boris B. Quednow, Erich Seifritz, and Thomas Kraemer. 2021. "Towards Extending the Detection Window of Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid—An Untargeted Metabolomics Study in Serum and Urine Following Controlled Administration in Healthy Men" Metabolites 11, no. 3: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030166
APA StyleSteuer, A. E., Raeber, J., Simbuerger, F., Dornbierer, D. A., Bosch, O. G., Quednow, B. B., Seifritz, E., & Kraemer, T. (2021). Towards Extending the Detection Window of Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid—An Untargeted Metabolomics Study in Serum and Urine Following Controlled Administration in Healthy Men. Metabolites, 11(3), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030166






