Evaluation of Metabolic Profiles of Patients with Anorexia Nervosa at Inpatient Admission, Short- and Long-Term Weight Regain—Descriptive and Pattern Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Anorexia Nervosa
1.2. Metabolomics
2. Results
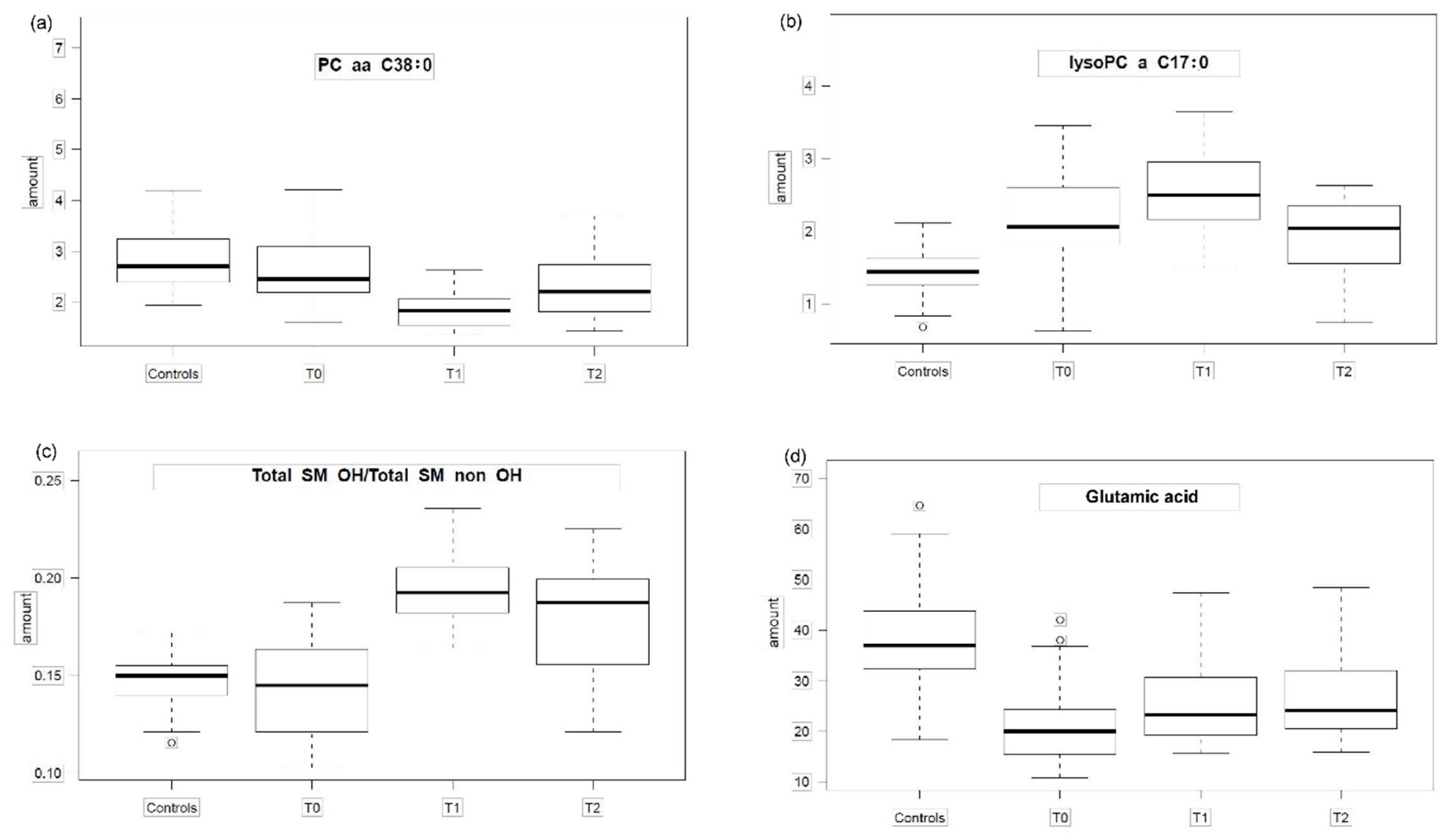
2.1. Group Comparisons
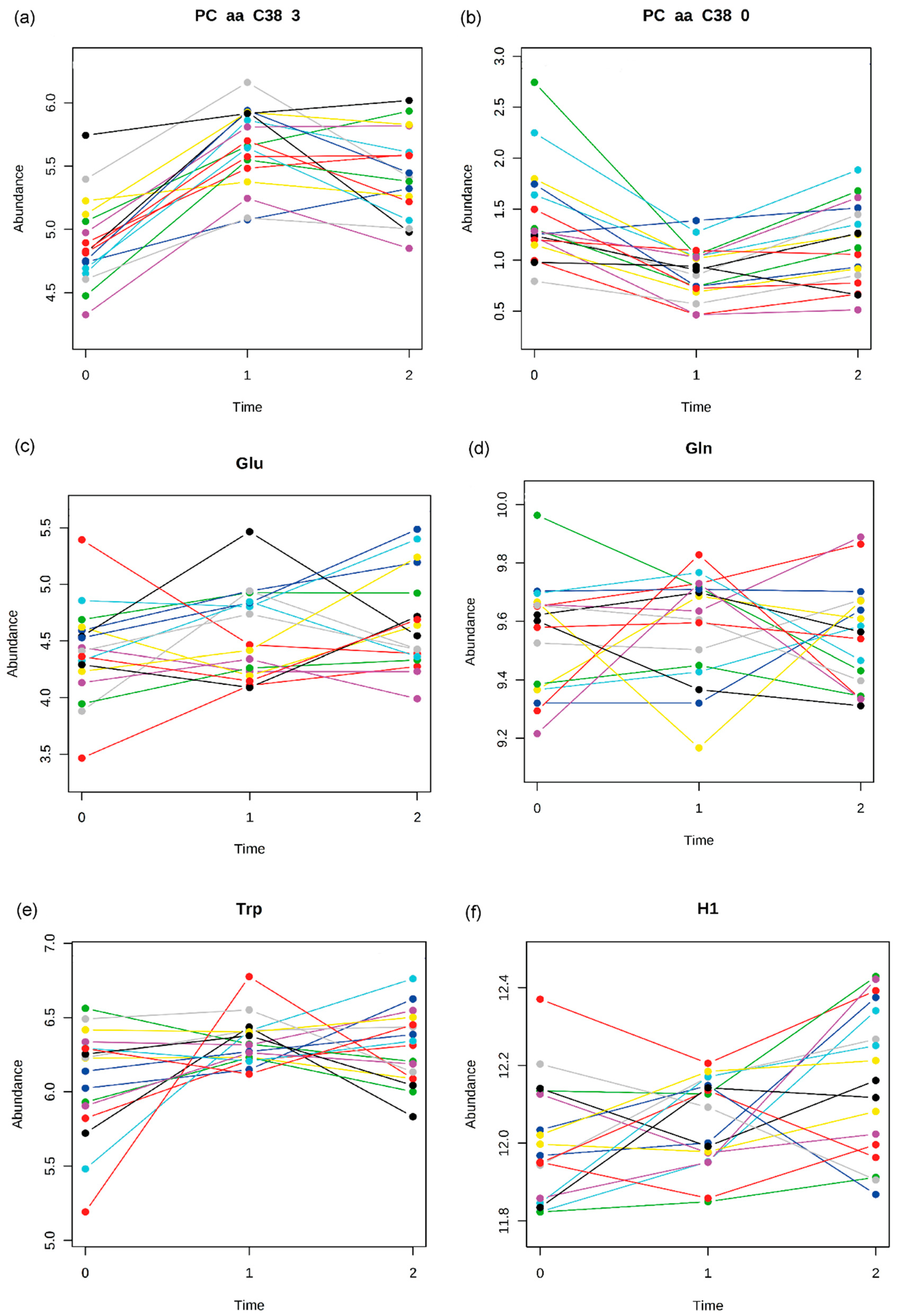
2.2. Pattern Hunter

| Pattern Group | Pattern Description | Pattern Tested | N | Best Fitting Analyte (Metabolites, Ratios, Sums) with a Correlation Coefficient > 0.5 | r | p | Second-Best Fitting Analyte (Metabolites, Ratios, Sums) With a Correlation Coefficient > 0.5 | r | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The level of metabolites in HC and in T0 is comparable. For T1 the level rises and is in T2 higher or like than in controls. | 1-1-3-2 | 12 | Total SM OH/ Total SM non OH | 0.68 | 7.10 × 10−16 | lysoPC a C14:0 | 0.65 | 4.41 × 10−14 |
| 2-1-4-3 | 11 | lysoPC a C14:0 | 0.65 | 4.37 × 10−14 | Total SMOH/ Total SM non OH | 0.65 | 4.37 × 10−14 | ||
| 2-1-3-2 | 10 | lysoPC a C14:0 | 0.63 | 4.39 × 10−13 | PC aa C32:2 | 0.61 | 3.92 × 10−12 | ||
| 2 | Metabolite levels in T1 (or together with T2) have the lowest values. For T2 the level is the same as in HC or slightly lower. | 2-2-1-1 | 3 | SMC24:1 | 0.53 | 3.6 × 10−9 | PC aa C38:0 | 0.53 | 3.90 × 10−9 |
| 3-2-1-2 | 2 | PC aa C38:0 | 0.56 | 3.73 × 10−10 | PC ae C38:5 | 0.51 | 2.07 × 10−8 | ||
| 2-2-1-2 | 1 | PC aa C38:0 | 0.53 | 3.00 × 10−9 | |||||
| 3-2-1-3 | 0 | ||||||||
| 3 | Metabolite level in T0 and T1 are higher than in HC. For T2 the level approaches that of HC. | 1-3-3-2 | 1 | lysoPC a C17:0 | 0.54 | 1.22 × 10−9 | |||
| 1-3-2-1 | 0 | ||||||||
| 1-3-3-1 | 0 | ||||||||
| 4 | The level of metabolites in T0 is much lower than in HC. It rises in T1 and T2. | 3-1-2-2 | 1 | Glu | 0.54 | 1.30 × 10−9 | |||
| 3-1-1-3 | 0 | ||||||||
| 3-1-2-3 | 0 | ||||||||
| 5 | The level of metabolites is higher in T0 than in HC, in T1 it is lower or like than in HC. In T2 it approaches those of controls | 2-3-1-2 | 0 | ||||||
| 1-2-1-1 | 0 | ||||||||
| 6 | Theoretically linear increase/decrease assumed. Not observed. | 1-2-3-4 | 1 | Total SM OH/ Total SM non OH | 0.53 | 3.63 × 10−9 | |||
| 4-3-2-1 | 0 | - |
2.3. Time Course Analysis
3. Discussion
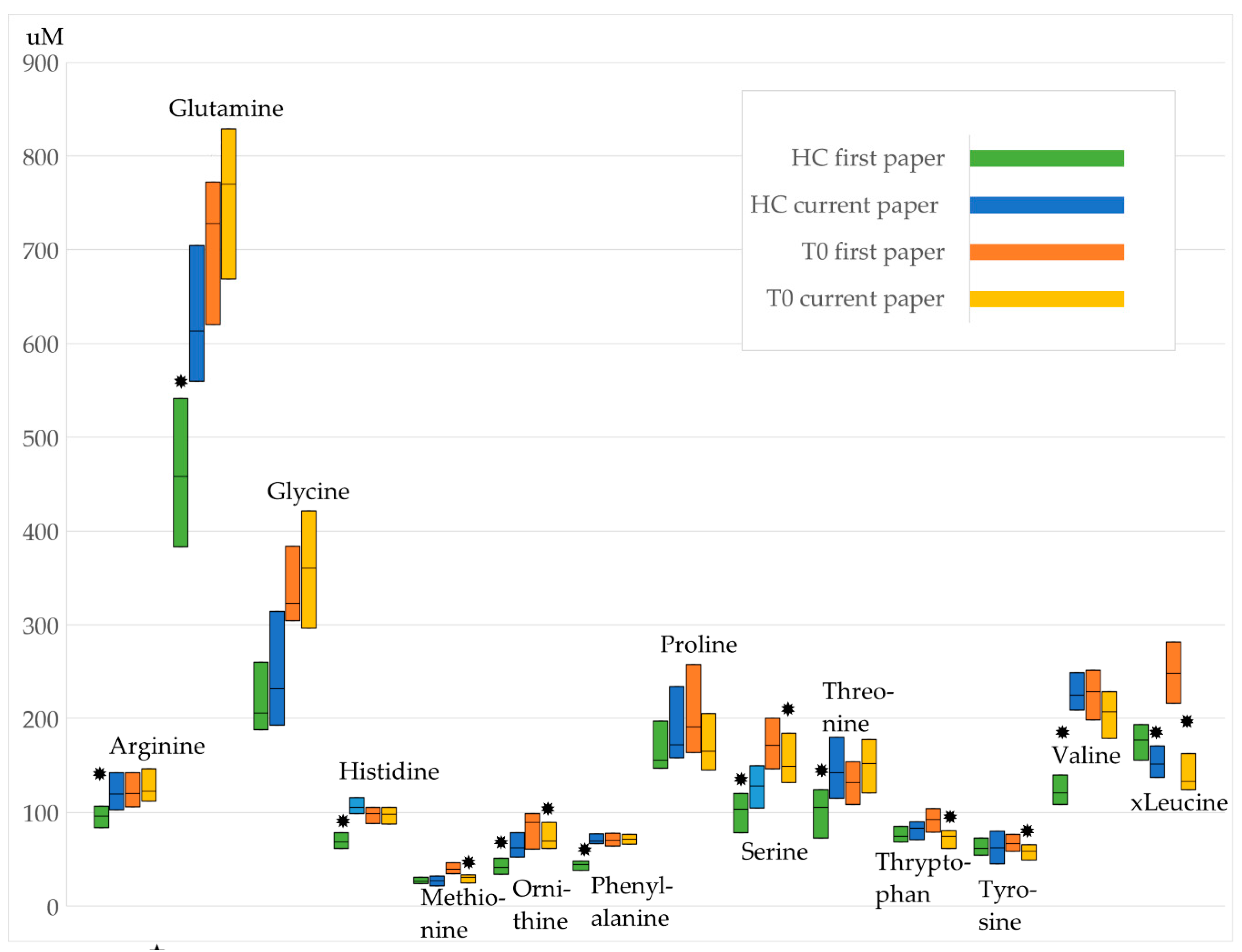
3.1. Comparison to the Previous Study
3.2. State Markers
3.3. Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Sample
4.2. Anthropometric Assessments
4.3. Sampling, Biochemical Measures and Metabolite Measurement
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.4.1. Group Comparisons
4.4.2. Pattern Hunter
4.4.3. Time Course Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zipfel, S.; Giel, K.E.; Bulik, C.M.; Hay, P.; Schmidt, U. Anorexia nervosa: Aetiology, assessment, and treatment. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcelus, J.; Mitchell, A.J.; Wales, J.; Nielsen, S. Mortality rates in patients with anorexia nervosa and other eating disorders. A meta-analysis of 36 studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focker, M.; Knoll, S.; Hebebrand, J. Anorexia nervosa. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2013, 22, S29–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Schwanenflug, N.; Muller, D.K.; King, J.A.; Ritschel, F.; Bernardoni, F.; Mohammadi, S.; Geisler, D.; Roessner, V.; Biemann, R.; Marxen, M.; et al. Dynamic changes in white matter microstructure in anorexia nervosa: Findings from a longitudinal study. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, M.; Klibanski, A. Endocrine consequences of anorexia nervosa. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G., Jr.; Olson, D.P. Central nervous system control of metabolism. Nature 2012, 491, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, G.F., Jr. Fuel metabolism in starvation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumida, Y.; Yahagi, N.; Takeuchi, Y.; Nishi, M.; Shikama, A.; Takarada, A.; Masuda, Y.; Kubota, M.; Matsuzaka, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; et al. Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, H.J.; Yilmaz, Z.; Thornton, L.M.; Hubel, C.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Gaspar, H.A.; Bryois, J.; Hinney, A.; Leppa, V.M.; Mattheisen, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies eight risk loci and implicates metabo-psychiatric origins for anorexia nervosa. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B. Metabolomics and metabolic diseases: Where do we stand? Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. The role of metabolomics in brain metabolism research. J. Neuroimmune Pharm. 2015, 10, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinones, M.P.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R. Metabolomics tools for identifying biomarkers for neuropsychiatric diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 35, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, V.R.; Oommen, A.M.; Varma, S.; Casanova, R.; An, Y.; Andrews, R.M.; O’Brien, R.; Pletnikova, O.; Troncoso, J.C.; Toledo, J.; et al. Brain and blood metabolite signatures of pathology and progression in alzheimer disease: A targeted metabolomics study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, R.M.; Quinones, M.; Marballi, K.; Gao, X.; Valdez, C.; Ahuja, S.S.; Velligan, D.; Walss-Bass, C. Metabolomic profiling of schizophrenia patients at risk for metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Wang, D.; Pan, Z.; McIntyre, R.S.; Brietzke, E.; Subramanieapillai, M.; Nozari, Y.; Wang, J. Metabolic profiling for water-soluble metabolites in patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls in a Chinese population: A case-control study. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 21, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Zhou, C.J.; Zheng, P.; Cheng, K.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, L.; Xie, P. Differential urinary metabolites related with the severity of major depressive disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 332, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, N.; Shinoda, K.; Sato, H.; Sasaki, K.; Suzuki, M.; Yamaki, K.; Fujimori, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Osei-Hyiaman, D.; Ohashi, Y. Plasma metabolome analysis of patients with major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 72, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, M.; Milaneschi, Y.; Al-Shehri, T.; Amin, N.; Garmaeva, S.; Onderwater, G.L.J.; Pool, R.; Thesing, C.S.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Vogelzangs, N.; et al. Metabolomics profile in depression: A pooled analysis of 230 metabolic markers in 5283 cases with depression and 10,145 controls. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focker, M.; Timmesfeld, N.; Scherag, S.; Knoll, N.; Singmann, P.; Wang-Sattler, R.; Buhren, K.; Schwarte, R.; Egberts, K.; Fleischhaker, C.; et al. Comparison of metabolic profiles of acutely ill and short-term weight recovered patients with anorexia nervosa reveals alterations of 33 out of 163 metabolites. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 46, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, E.; Wolk, S.; Cooper, T.; Glasofer, D.; Walsh, B.T. Plasma tryptophan during weight restoration in patients with anorexia nervosa. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, S.; Franke, L.; Schneider, N.; Salbach-Andrae, H.; Schott, R.; Craciun, E.M.; Pfeiffer, E.; Uebelhack, R.; Lehmkuhl, U. Aromatic amino acids in weight-recovered females with anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2009, 42, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyano, D.; Vilaseca, M.A.; Artuch, R.; Lambruschini, N. Plasma amino acids in anorexia nervosa. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 52, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazato, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Schmidt, U.; Tchanturia, K.; Campbell, I.C.; Collier, D.A.; Iyo, M.; Treasure, J. Serum glutamine, set-shifting ability and anorexia nervosa. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palova, S.; Charvat, J.; Masopust, J.; Klapkova, E.; Kvapil, M. Changes in the plasma amino acid profile in anorexia nervosa. J. Int. Med. Res. 2007, 35, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.; Vecka, M.; Tvrzicka, E.; Hruby, M.; Novak, F.; Papezova, H.; Lubanda, H.; Vesela, L.; Stankova, B. Composition of plasma fatty acids and non-cholesterol sterols in anorexia nervosa. Physiol. Res. 2005, 54, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Zak, A.; Vecka, M.; Tvrzicka, E.; Novak, F.; Papezova, H.; Hruby, M.; Lubanda, H.; Stankova, B. Lipid metabolism in anorexia nervosa. Casopis lekaru ceskych 2003, 142, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Holman, R.T.; Adams, C.E.; Nelson, R.A.; Grater, S.J.; Jaskiewicz, J.A.; Johnson, S.B.; Erdman, J.W., Jr. Patients with anorexia nervosa demonstrate deficiencies of selected essential fatty acids, compensatory changes in nonessential fatty acids and decreased fluidity of plasma lipids. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, A.P. The clinical biochemistry of anorexia nervosa. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 49, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haluzikova, D.; Dostalova, I.; Kavalkova, P.; Roubicek, T.; Mraz, M.; Papezova, H.; Haluzik, M. Serum concentrations of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein in patients with anorexia nervosa. Physiol. Res. 2009, 58, 577–581. [Google Scholar]
- Lanfranco, F.; Gianotti, L.; Picu, A.; Giordano, R.; Daga, G.A.; Mondelli, V.; Malfi, G.; Fassino, S.; Ghigo, E.; Arvat, E. Effects of free fatty acids on ACTH and cortisol secretion in anorexia nervosa. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 154, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heruc, G.A.; Little, T.J.; Kohn, M.R.; Madden, S.; Clarke, S.D.; Horowitz, M.; Feinle-Bisset, C. Effects of starvation and short-term refeeding on gastric emptying and postprandial blood glucose regulation in adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E565–E573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenne, I.; Gustafsson, J. Endogenous glucose production and lipolysis in anorexia nervosa-a study using stable isotope-labelled compounds. Acta Paediatr. 2004, 93, 1446–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curatola, G.; Camilloni, M.A.; Vignini, A.; Nanetti, L.; Boscaro, M.; Mazzanti, L. Chemical-physical properties of lipoproteins in anorexia nervosa. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 34, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulant, J.; Hill, M.; Velikova, M.; Yamamotova, A.; Martasek, P.; Papezova, H. Changes of BMI, steroid metabolome and psychopathology in patients with anorexia nervosa during hospitalization. Steroids 2020, 153, 108523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, P.B. Integrating multi-omics biomarkers and postprandial metabolism to develop personalized treatment for anorexia nervosa. Prostaglandins Lipid Mediat. 2017, 132, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, P.B.; Yang, J.; Morisseau, C.; German, J.B.; Zeeland, A.A.; Armando, A.M.; Quehenberger, O.; Bergen, A.W.; Magistretti, P.; Berrettini, W.; et al. Dysregulation of soluble epoxide hydrolase and lipidomic profiles in anorexia nervosa. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shih, P.B. Fasting and postprandial soluble epoxide hydrolase-associated eicosanoids of remitted patients with eating disorder. Data Brief. 2018, 17, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Ferreira, D.L.; Hubel, C.; Herle, M.; Abdulkadir, M.; Loos, R.J.F.; Bryant-Waugh, R.; Bulik, C.M.; de Stavola, B.L.; Lawlor, D.A.; Micali, N.; et al. Associations between blood metabolic profile at 7 years old and eating disorders in adolescence: Findings from the avon longitudinal study of parents and children. Metabolites 2019, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, A.M.; Troisi, J.; Fasano, A.; Dalle Grave, R.; Marciello, F.; Serena, G.; Calugi, S.; Scala, G.; Corrivetti, G.; Cascino, G.; et al. Multi-omics data integration in anorexia nervosa patients before and after weight regain: A microbiome-metabolomics investigation. Clin. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, P.; Monteleone, A.M.; Troisi, J.; Dalle Grave, R.; Corrivetti, G.; Calugi, S.; Scala, G.; Patriciello, G.; Zanetti, A.; Maj, M. Metabolomics signatures of acutely ill and short-term weight recovered women with anorexia nervosa. Mol. Psychiatry 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, A.S.; Kurth, B.M.; Stolzenberg, H.; Ellert, U.; Neuhauser, H. Body mass index percentiles for children and adolescents in Germany based on a nationally representative sample (KiGGS 2003–2006). Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillesheim, E.; Brennan, L. Metabotyping and its role in nutrition research. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2019, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.M.; King, J.J.; West, P.R.; Ludwig, M.A.; Donley, E.L.R.; Burrier, R.E.; Amaral, D.G. Amino acid dysregulation metabotypes: Potential biomarkers for diagnosis and individualized treatment for subtypes of autism spectrum disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koen, N.; Du Preez, I.; Loots du, T. Metabolomics and personalized medicine. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2016, 102, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpertz, S.; Fichter, M.M.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Hilbert, A.; Tuschen-Caffier, B.; Vocks, S.; Zeeck, A. Joint German Guideline Diagnosis and Treatment of Eating Disorders; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.A.; Hubel, C.; Hindborg, M.; Lindkvist, E.; Kastrup, A.M.; Yilmaz, Z.; Stoving, R.K.; Bulik, C.M.; Sjogren, J.M. Increased lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in anorexia nervosa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2019, 52, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittchen, H.U.; Lachner, G.; Wunderlich, U.; Pfister, H. Test-retest reliability of the computerized DSM-IV version of the Munich-composite international diagnostic interview (M-CIDI). Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 1998, 33, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Weiß, R.H. CFT 20-R mit WS/ZF-R Grundintelligenztest Skala 2-Revision (CFT 20-R) mit Wortschatztest und Zahlenfolgentest-Revision (WS/ZF-R); Hogrefe Publishing Group: Göttingen, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.J.; Green, P.J. Smoothing reference centile curves: The LMS method and penalized likelihood. Stat. Med. 1992, 11, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskos, A.P.; Jain, P.; Romisch-Margl, W.; Bennett, M.; Achaintre, D.; Asad, Y.; Marney, L.; Richardson, L.; Koulman, A.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Interlaboratory reproducibility of a targeted metabolomics platform for analysis of human serum and plasma. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHMP. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation; Commitee for Medicinal Products for Human use (CHMP): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zukunft, S.; Sorgenfrei, M.; Prehn, C.; Möller, G.; Adamski, J. Targeted metabolomics of dried blood spot extracts. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastenmuller, G.; Romisch-Margl, W.; Wagele, B.; Altmaier, E.; Suhre, K. MetaP-server: A web-based metabolomics data analysis tool. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Using MetaboAnalyst 3.0 for comprehensive metabolomics data analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 55, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.C.; Speed, T.P. A multivariate empirical bayes statistic for replicated microarray time course data. Ann. Stat. 2006, 34, 2387–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for comprehensive and integrative metabolomics data analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter (SD) | T0 | T1 | T2 | HC | T0 * | T1 * | T2 * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients/HCs | 35 | 26 | 22 | 25 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| Duration of illness (months) | 11.47 (8.87) | - | - | - | 8.82 (4.05) | - | - |
| Number of weeks between T0 and T1 | 8.05 (2.82) | 8.65 (2.24) | |||||
| Number of weeks between T1 and T2 (N = 17) | 26.04 (30.58) | 26.04 (30.58) | |||||
| Age (years) a | 15.4 (1.4) | 15.5 (1.5) | 16.0 (1.78) | 16.6 (1.8) | 15.1 (1.4) | 15.3 (1.6) | 15.8 (1.8) |
| Height (cm) b | 163.14 (6.60) | 163.84 (6.95) | 163.85 (6.79) | 166.54 (6.00) | 163.55 (6.96) | 163.64 (7.10) | 163.99 (7.20) |
| Weight (kg) c | 40.68 (5.17) | 46.01 (5.64) | 49.84 (5.83) | 57.46 (6.45) | 41.32(4.77) | 46.19(5.02) | 49.59 (6.22) |
| BMI (kg/m2) d | 15.24 (1.17) | 17.05 (1.15) | 18.51 (1.20) | 20.70 (1.86) | 15.41 (1.03) | 17.16 (1.03) | 18.38 1.28) |
| BMI percentile + | 0.98 (1.59) | 6.86 (6.50) | 16.69 (11.09) | 39.03 (22.10) | 1.30 (1.96) | 7.66 (6.91) | 16.80 (12.31) |
| BMI-SDS +e | −3.04 (1.23) | −1.78 (0.79) | −1.09 (0.53) | −0.32 (0.62) | −2.72 (0.87) | −1.61 (0.52) | −1.11 (0.58) |
| Analytes | (a) Mann-Whitney Test p-Values | (b) Friedman Test p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC vs. T0 | HC vs. T1 | HC vs. T2 | T0-T1-T2 | T0 vs. T1 * | T0 vs. T2 * | T1 vs. T2 * | |
| Acylcarnitines | |||||||
| C10 | 0.989 | 4.16 × 10−5 | 0.153 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 1.000 | 0.030 |
| C10:1 | 0.691 | 1.81 × 10−5 | 0.197 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.006 |
| C12:1 | 0.834 | 4.89 × 10−5 | 0.337 | 0.005 | 0.018 | 1.000 | 0.011 |
| C14:1 | 0.822 | 8.68 × 10−6 | 0.0536 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.910 | 0.030 |
| C14:2 | 0.708 | 7.55 × 10−6 | 0.0919 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 1.000 | 0.049 |
| C5-DC (C6-OH) | 0.105 | 0.00117 | 0.856 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.077 | 0.435 |
| C7-DC | 0.248 | 5.86 × 10−7 | 0.224 | 3.62 × 10−4 | 0.008 | 1.000 | 0.001 |
| C8 | 0.857 | 9.09 × 10−6 | 0.153 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 1.000 | 0.077 |
| Amino acids | |||||||
| Glutamic acid (Glu) | 2.49 × 10−7 | 1.08 × 10−4 | 0.001 | 0.039 | 0.310 | 0.039 | 1.000 |
| Lysophosphatidylcholines | |||||||
| lysoPC a C14:0 | 0.031 | 3.03 × 10−8 | 0.034 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.510 | 0.049 |
| lysoPC a C16:1 | 0.251 | 1.87 × 10−6 | 0.007 | 2.81 × 10−4 | 0.000 | 0.690 | 0.018 |
| lysoPC a C17:0 | 2.51 × 10−5 | 1.01 × 10−8 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.310 | 0.510 | 0.008 |
| lysoPC a C20:3 | 0.092 | 8.52 × 10−5 | 0.040 | 1.20 × 10−5 | 0.000 | 0.077 | 0.039 |
| lysoPC a C28:0 | 0.030 | 0.002 | 0.311 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.510 | 0.178 |
| Phosphatidylcholines | |||||||
| PC aa C28:1 | 0.893 | 2.09 × 10−7 | 0.008 | 2.10 × 10−4 | 0.000 | 0.119 | 0.119 |
| PC aa C30:0 | 0.168 | 2.84 × 10−6 | 0.048 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.259 | 0.259 |
| PC aa C32:1 | 0.056 | 9.12 × 10−4 | 0.103 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.049 | 0.510 |
| PC aa C32:2 | 4.63 × 10−4 | 0.003 | 0.241 | 6.90 × 10−5 | 0.000 | 0.011 | 0.510 |
| PC aa C32:3 | 0.040 | 0.004 | 0.359 | 9.80 × 10−5 | 0.000 | 0.049 | 0.178 |
| PC aa C34:3 | 0.110 | 0.006 | 0.354 | 9.80 × 10−5 | 0.000 | 0.049 | 0.178 |
| PC aa C34:4 | 1.48 × 10−4 | 0.166 | 0.915 | 1.03 × 10−4 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.910 |
| PC aa C38:0 | 0.192 | 2.44 × 10−8 | 0.003 | 6.90 × 10−5 | 0.000 | 0.510 | 0.011 |
| PC aa C38:3 | 1.99 × 10−5 | 0.152 | 0.551 | 2.00 × 10−6 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| PC aa C38:6 | 0.156 | 2.71 × 10−6 | 0.054 | 6.90 × 10−5 | 0.000 | 0.510 | 0.011 |
| PC aa C42:0 | 0.631 | 2.65 × 10−5 | 0.394 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.435 | 0.146 |
| PC aa C42:1 | 0.958 | 1.97 × 10−5 | 0.418 | 4.87 × 10−4 | 0.000 | 0.795 | 0.024 |
| PC ae C30:0 | 0.449 | 3.68 × 10−9 | 0.008 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.910 | 0.119 |
| PC ae C34:0 | 0.822 | 1.25 × 10−7 | 0.0252 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.910 | 0.119 |
| PC ae C34:1 | 0.267 | 1.16 × 10−6 | 0.277 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 1.000 | 0.018 |
| PC ae C36:1 | 0.380 | 1.17 × 10−6 | 0.130 | 1.39 × 10−4 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.003 |
| PC ae C36:2 | 0.078 | 2.15 × 10−6 | 0.0207 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 1.000 | 0.006 |
| PC ae C38:2 | 0.591 | 0.49 × 10−7 | 0.004 | 4.00 × 10−4 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.011 |
| PC ae C38:3 | 0.004 | 5.09 × 10−5 | 0.296 | 4.00 × 10−6 | 0.000 | 0.018 | 0.077 |
| PC ae C38:5 | 0.079 | 6.54 × 10−7 | 8.74 × 10−5 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 1.000 |
| PC ae C38:6 | 0.202 | 6.98 × 10−6 | 0.0313 | 0.080 | |||
| PC ae C40:3 | 0.205 | 1.77 × 10−4 | 0.228 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.510 | 0.049 |
| PC ae C42:5 | 0.205 | 1.87 × 10−6 | 0.015 | 1.76 × 10−4 | 0.000 | 0.030 | 0.368 |
| (a) Mann-Whitney Test p-Values | (b) Friedman Test p-Values | ||||||
| HC vs. T0 | HC vs. T1 | HC vs. T2 | T0-T1-T2 | T0 vs. T1 * | T0 vs. T2 * | T1 vs. T2 * | |
| Sphingomyelines | |||||||
| SMOHC22:1 | 0.025 | 0.023 | 0.522 | 6.90 × 10−5 | 0.000 | 0.011 | 0.510 |
| SMC24:1 | 0.277 | 3.69 × 10−4 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.018 | 1.000 |
| Sums | |||||||
| Carbohydrates | |||||||
| H1 | 2.43 × 10−5 | 7.97 × 10−4 | 0.237 | 0.010 | 1.000 | 0.011 | 0.077 |
| Ratios | |||||||
| PUFA PC/SFA PC | 1.04 × 10−5 | 2.96 × 10−6 | 0.002 | 0.465 | |||
| Total lysoPC/Total PC | 6.85 × 10−5 | 0.001 | 0.133 | 0.007 | 0.119 | 0.006 | 0.910 |
| Total SM/Total SM PC | 6.12 × 10−4 | 0.376 | 0.515 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.062 | 0.595 |
| Total SM/Total PC | 6.46 × 10−4 | 0.322 | 0.509 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.077 | 0.435 |
| Total SMOH/Total SM non OH | 0.467 | 2.56 × 10−8 | 5.09 × 10−4 | 5.00 × 10−6 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.510 |
| Metabolite | MEBA Hotellings T2 | ANOVA F-Value | ANOVA p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC aa C38:3 | 67.85 | 48.276 | 2.17 × 10−10 |
| PC ae C38:3 | 55.56 | 31.016 | 3.24 × 10−08 |
| lysoPC a C20:3 | 52.51 | 26.866 | 1.42 × 10−07 |
| PC aa C34_4 | 48.73 | 23.604 | 5.04 × 10−07 |
| PC aa C32_1 | 44.95 | 16.260 | 1.34 × 10−05 |
| PC aa C30:0 | 42.83 | 15.564 | 1.90 × 10−05 |
| PC aa C32:2 | 42.58 | 24.885 | 3.03 × 10−07 |
| PC aa C28:1 | 40.21 | 23.351 | 5.58 × 10−07 |
| PC ae C30:0 | 38.78 | 13.202 | 6.60 × 10−05 |
| PC aa C34:3 | 38.01 | 19.997 | 2.32 × 10−06 |
| C7-DC | 37.37 | 13.471 | 5.70 × 10−05 |
| PC aa C36:3 | 36.61 | 27.150 | 1.28 × 10−07 |
| PC aa C38:6 | 36.22 | 17.798 | 6.36 × 10−06 |
| PC aa C40:5 | 35.41 | 21.125 | 1.42 × 10−06 |
| PC ae C34:0 | 34.41 | 11.609 | 1.62 × 10−04 |
| PC aa C36:5 | 33.53 | 11.192 | 2.06 × 10−04 |
| PC aa C32:3 | 32.76 | 17.760 | 6.48 × 10−06 |
| PC ae C36:1 | 31.86 | 14.801 | 2.81 × 10−05 |
| PC aa C36:6 | 29.82 | 18.329 | 4.96 × 10−06 |
| LysoPC a C16:1 | 27.61 | 15.147 | 2.35 × 10−05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Föcker, M.; Cecil, A.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; Albrecht, M.; Adams, F.; Hinney, A.; Libuda, L.; Bühlmeier, J.; Hebebrand, J.; et al. Evaluation of Metabolic Profiles of Patients with Anorexia Nervosa at Inpatient Admission, Short- and Long-Term Weight Regain—Descriptive and Pattern Analysis. Metabolites 2021, 11, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010007
Föcker M, Cecil A, Prehn C, Adamski J, Albrecht M, Adams F, Hinney A, Libuda L, Bühlmeier J, Hebebrand J, et al. Evaluation of Metabolic Profiles of Patients with Anorexia Nervosa at Inpatient Admission, Short- and Long-Term Weight Regain—Descriptive and Pattern Analysis. Metabolites. 2021; 11(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleFöcker, Manuel, Alexander Cecil, Cornelia Prehn, Jerzy Adamski, Muriel Albrecht, Frederike Adams, Anke Hinney, Lars Libuda, Judith Bühlmeier, Johannes Hebebrand, and et al. 2021. "Evaluation of Metabolic Profiles of Patients with Anorexia Nervosa at Inpatient Admission, Short- and Long-Term Weight Regain—Descriptive and Pattern Analysis" Metabolites 11, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010007
APA StyleFöcker, M., Cecil, A., Prehn, C., Adamski, J., Albrecht, M., Adams, F., Hinney, A., Libuda, L., Bühlmeier, J., Hebebrand, J., Peters, T., & Antel, J. (2021). Evaluation of Metabolic Profiles of Patients with Anorexia Nervosa at Inpatient Admission, Short- and Long-Term Weight Regain—Descriptive and Pattern Analysis. Metabolites, 11(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010007