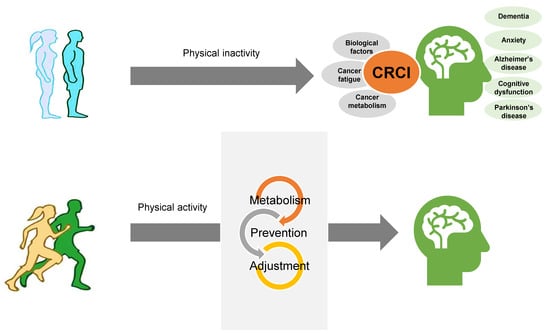
Exercise May Affect Metabolism in Cancer-Related Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CI in Cancer Patients
3. Biological Drivers of CRCI
4. The Interrelationship between CRCI and Alterations in Metabolism
5. Role of Exercise in CRCI
6. The Effects of Exercise on Cancer Metabolism and Its Associated Signaling Pathways
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jongsiriyanyong, S.; Limpawattana, P. Mild Cognitive Impairment in Clinical Practice: A Review Article. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Demen 2018, 33, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robb, C.; Boulware, D.; Overcash, J.; Extermann, M. Patterns of care and survival in cancer patients with cognitive impairment. Crit Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2010, 74, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios, H.; Narciso, S.; Guerreiro, M.; Maroco, J.; Logsdon, R.; de Mendonca, A. Quality of life in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Aging Ment. Health 2013, 17, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Chen, T.F.; Chiu, M.J. From mild cognitive impairment to subjective cognitive decline: Conceptual and methodological evolution. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, M.; Sachdev, P.; Brodaty, H. Reader response: Practice guideline update summary: Mild cognitive impairment: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2018, 91, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannock, I.F.; Ahles, T.A.; Ganz, P.A.; Van Dam, F.S. Cognitive impairment associated with chemotherapy for cancer: Report of a workshop. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezden, C.B.; Phillips, K.A.; Abdolell, M.; Bunston, T.; Tannock, I.F. Cognitive function in breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 2695–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falleti, M.G.; Sanfilippo, A.; Maruff, P.; Weih, L.; Phillips, K.A. The nature and severity of cognitive impairment associated with adjuvant chemotherapy in women with breast cancer: A meta-analysis of the current literature. Brain Cogn. 2005, 59, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.E.; Beckjord, E.; Bovbjerg, D.H.; Low, C.A.; Posluszny, D.M.; Lowery, A.E.; Dew, M.A.; Nutt, S.; Arvey, S.R.; Rechis, R. Prevalence of perceived cognitive dysfunction in survivors of a wide range of cancers: Results from the 2010 LIVESTRONG survey. J. Cancer Surviv. 2016, 10, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Licaj, I.; Clarisse, B.; Humbert, X.; Grellard, J.M.; Tron, L.; Joly, F. Cognitive complaints in cancer survivors and expectations for support: Results from a web-based survey. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2654–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelsins, M.C.; Kesler, S.R.; Ahles, T.A.; Morrow, G.R. Prevalence, mechanisms, and management of cancer-related cognitive impairment. Int Rev. Psychiatr. 2014, 26, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrigoroaei, S.; Lachman, M.E. Cognitive functioning in midlife and old age: Combined effects of psychosocial and behavioral factors. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci Soc. Sci. 2011, 66 Suppl 1, i130–i140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Joly, F.; Vardy, J.; Ahles, T.; Dubois, M.; Tron, L.; Winocur, G.; De Ruiter, M.B.; Castel, H. Cancer-related cognitive impairment: An update on state of the art, detection, and management strategies in cancer survivors. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1925–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahles, T.A.; Root, J.C.; Ryan, E.L. Cancer- and cancer treatment-associated cognitive change: An update on the state of the science. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, K.; Roukema, J.A.; Sitskoorn, M.M. Review of recent studies on interventions for cognitive deficits in patients with cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2012, 12, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, F.; Heutte, N.; Duclos, B.; Noal, S.; Leger-Hardy, I.; Dauchy, S.; Longato, N.; Desrues, L.; Houede, N.; Lange, M.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of the Impact of Antiangiogenic Treatment on Cognitive Functions in Metastatic Renal Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2016, 2, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.L.; Zadravec, K.; Bland, K.A.; Chesley, E.; Wolf, F.; Janelsins, M.C. The Effect of Exercise on Cancer-Related Cognitive Impairment and Applications for Physical Therapy: Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phys. Ther. 2020, 100, 523–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witlox, L.; Schagen, S.B.; de Ruiter, M.B.; Geerlings, M.I.; Peeters, P.H.M.; Koevoets, E.W.; van der Wall, E.; Stuiver, M.; Sonke, G.; Velthuis, M.J.; et al. Effect of physical exercise on cognitive function and brain measures after chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer (PAM study): Protocol of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winocur, G.; Johnston, I.; Castel, H. Chemotherapy and cognition: International cognition and cancer task force recommendations for harmonising preclinical research. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 69, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, S.L.; Helms, R.S.; Dreau, D. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme activities and tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkaya, H.; Liu, S.; Wicha, M.S. Breast cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor microenvironment. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 3804–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, A.C.; Vance, D.E.; Slater, L.Z.; Crowe, M. The impact of inflammation on cognitive function in older adults: Implications for healthcare practice and research. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2012, 44, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomykala, K.L.; Ganz, P.A.; Bower, J.E.; Kwan, L.; Castellon, S.A.; Mallam, S.; Cheng, I.; Ahn, R.; Breen, E.C.; Irwin, M.R.; et al. The association between pro-inflammatory cytokines, regional cerebral metabolism, and cognitive complaints following adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Brain Imaging Behav. 2013, 7, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, D.E.; Cohen, R.; Chen, H.; Kelly, D.L.; McCain, N.L.; Starkweather, A.; Ahn, H.; Sturgill, J.; Jackson-Cook, C.K. Relationship of systemic cytokine concentrations to cognitive function over two years in women with early stage breast cancer. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 301, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, Y.T.; Ng, T.; Shwe, M.; Ho, H.K.; Foo, K.M.; Cham, M.T.; Lee, J.A.; Fan, G.; Tan, Y.P.; Yong, W.S.; et al. Association of proinflammatory cytokines and chemotherapy-associated cognitive impairment in breast cancer patients: A multi-centered, prospective, cohort study. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, P.A.; Bower, J.E.; Kwan, L.; Castellon, S.A.; Silverman, D.H.; Geist, C.; Breen, E.C.; Irwin, M.R.; Cole, S.W. Does tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) play a role in post-chemotherapy cerebral dysfunction? Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 30, S99–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelsins, M.C.; Mustian, K.M.; Palesh, O.G.; Mohile, S.G.; Peppone, L.J.; Sprod, L.K.; Heckler, C.E.; Roscoe, J.A.; Katz, A.W.; Williams, J.P.; et al. Differential expression of cytokines in breast cancer patients receiving different chemotherapies: Implications for cognitive impairment research. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launer, L.J. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and Alzheimer disease: What’s next? JAMA 2003, 289, 2865–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluise, C.D.; St Clair, D.; Vore, M.; Butterfield, D.A. In vivo amelioration of adriamycin induced oxidative stress in plasma by gamma-glutamylcysteine ethyl ester (GCEE). Cancer Lett. 2009, 282, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangpong, J.; Cole, M.P.; Sultana, R.; Estus, S.; Vore, M.; St Clair, W.; Ratanachaiyavong, S.; St Clair, D.K.; Butterfield, D.A. Adriamycin-mediated nitration of manganese superoxide dismutase in the central nervous system: Insight into the mechanism of chemobrain. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, J.T.; Swomley, A.M.; Forster, S.; Harris, J.L.; Sultana, R.; Butterfield, D.A. Apolipoprotein A-I: Insights from redox proteomics for its role in neurodegeneration. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2013, 7, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, K.; Onodera, K.; Shinkai, T.; Suzuki, S.; Urano, S. Impairment of learning and memory in rats caused by oxidative stress and aging, and changes in antioxidative defense systems. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2001, 928, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Kapoor, A.; Gu, Y.; Chow, M.J.; Peng, J.; Zhao, K.; Tang, D. Contributions of DNA Damage to Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Gu, Y.; Tang, D. BMI1, ATM and DDR. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 665–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myung, N.H.; Zhu, X.; Kruman, I.I.; Castellani, R.; Petersen, R.B.; Siedlak, S.L.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Lee, H.G. Evidence of DNA damage in Alzheimer disease: Phosphorylation of histone H2AX in astrocytes. Age (Dordr) 2008, 30, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, N.M.; Evans, M.D.; Mao, W.; Nana, A.L.; Seeley, W.W.; Adame, A.; Rissman, R.A.; Masliah, E.; Mucke, L. Early neuronal accumulation of DNA double strand breaks in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, L.; Miller, D.K.; McGloin, J.M.; Freeman, M.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Magaziner, J.; Studenski, S. Recruitment and retention of older adults in aging research. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 2340–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelsins, M.C.; Roscoe, J.A.; Berg, M.J.; Thompson, B.D.; Gallagher, M.J.; Morrow, G.R.; Heckler, C.E.; Jean-Pierre, P.; Opanashuk, L.A.; Gross, R.A. IGF-1 partially restores chemotherapy-induced reductions in neural cell proliferation in adult C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Invest. 2010, 28, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Yang, Y.M.; Dietrich, J.; Luebke, A.; Mayer-Proschel, M.; Noble, M. Systemic 5-fluorouracil treatment causes a syndrome of delayed myelin destruction in the central nervous system. J. Biol. 2008, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladurner, A.G. Rheostat control of gene expression by metabolites. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Chandel, N.S. Fundamentals of cancer metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroughs, L.K.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Metabolic pathways promoting cancer cell survival and growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, A.; Malvi, P.; Wajapeyee, N. Oncogene-directed alterations in cancer cell metabolism. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, E.G.; Barbas, C. Metabolomics in cancer biomarker discovery: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 87, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.A.; Zhang, S.; Gu, H.; Asiago, V.; Shanaiah, N.; Raftery, D. Metabolomics-based methods for early disease diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn 2008, 8, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitter, B.; Lundgren, S.; Bathen, T.F.; Halgunset, J.; Fjosne, H.E.; Gribbestad, I.S. Comparison of HR MAS MR spectroscopic profiles of breast cancer tissue with clinical parameters. NMR Biomed. 2006, 19, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkert, C.; Budczies, J.; Kind, T.; Weichert, W.; Tablack, P.; Sehouli, J.; Niesporek, S.; Konsgen, D.; Dietel, M.; Fiehn, O. Mass spectrometry-based metabolic profiling reveals different metabolite patterns in invasive ovarian carcinomas and ovarian borderline tumors. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10795–10804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, M.G.; Vigneron, D.B.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Males, R.G.; Schmitt, L.; Carroll, P.R.; James, J.K.; Hurd, R.E.; Kurhanewicz, J. Proton HR-MAS spectroscopy and quantitative pathologic analysis of MRI/3D-MRSI-targeted postsurgical prostate tissues. Magn Reson Med. 2003, 50, 944–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, K.; Cavenee, W.K.; Mischel, P.S. mTORC2 in the center of cancer metabolic reprogramming. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masui, K.; Cavenee, W.K.; Mischel, P.S. mTORC2 dictates Warburg effect and drug resistance. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1053–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, L.M.; Yeung, S.C.; Lee, M.H. Cancer metabolic reprogramming: Importance, main features, and potentials for precise targeted anti-cancer therapies. Cancer Biol. Med. 2014, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, G.; Pouyssegur, J. Tumor cell metabolism: Cancer’s Achilles’ heel. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.M.; Sheaff, M.T.; Szlosarek, P.W. Targeting Arginine-Dependent Cancers with Arginine-Degrading Enzymes: Opportunities and Challenges. Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 45, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maze, I.; Noh, K.M.; Soshnev, A.A.; Allis, C.D. Every amino acid matters: Essential contributions of histone variants to mammalian development and disease. Nature reviews. Genetics 2014, 15, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulten, H.J. Pleiotropic Effects of Metformin on Cancer. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Goncalves, M.D.; Cantley, L.C. Obesity and Cancer Mechanisms: Cancer Metabolism. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4277–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuder, A.J. Exercise stimulates beneficial adaptations to diminish doxorubicin-induced cellular toxicity. Am. J. Physiol. Regul Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2019, 317, R662–R672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Holsinger, R.M.D. Exercise-induced brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression: Therapeutic implications for Alzheimer’s dementia. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 48, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krcmery, V.; Cepcek, P. [Side effects and toxicity of new quinolones]. Bratisl. Lek Listy 1991, 92, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hillman, C.H.; Erickson, K.I.; Kramer, A.F. Be smart, exercise your heart: Exercise effects on brain and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapogiannis, D.; Mattson, M.P. Disrupted energy metabolism and neuronal circuit dysfunction in cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarmeas, N.; Stern, Y.; Mayeux, R.; Manly, J.J.; Schupf, N.; Luchsinger, J.A. Mediterranean diet and mild cognitive impairment. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craft, S. The role of metabolic disorders in Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia: Two roads converged. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorens-Martin, M.; Torres-Aleman, I.; Trejo, J.L. Mechanisms mediating brain plasticity: IGF1 and adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Neuroscientist 2009, 15, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Tuszynski, M.H. Potential therapeutic uses of BDNF in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suji, G.; Sivakami, S. Glucose, glycation and aging. Biogerontology 2004, 5, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J. Leptin regulation of neuronal excitability and cognitive function. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenreich, C.M.; Neilson, H.K.; Farris, M.S.; Courneya, K.S. Physical Activity and Cancer Outcomes: A Precision Medicine Approach. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4766–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahart, I.M.; Metsios, G.S.; Nevill, A.M.; Carmichael, A.R. Physical activity, risk of death and recurrence in breast cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M.; Mizuta, C.; Yamada, Y.; Okayama, Y.; Nakamura, E. Constructing an index of physical fitness age for Japanese elderly based on 7-year longitudinal data: Sex differences in estimated physical fitness age. Age (Dordr) 2012, 34, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, K.H.; Courneya, K.S.; Matthews, C.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Galvao, D.A.; Pinto, B.M.; Irwin, M.L.; Wolin, K.Y.; Segal, R.J.; Lucia, A.; et al. American College of Sports Medicine roundtable on exercise guidelines for cancer survivors. Med. Sci Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1409–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, K.I.; Kramer, A.F. Aerobic exercise effects on cognitive and neural plasticity in older adults. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, E.; Hsiung, G.R.; Liu-Ambrose, T. The role of exercise in mitigating subcortical ischemic vascular cognitive impairment. J. Neurochem. 2018, 144, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, C.; Hooghiemstra, A.M.; Raijmakers, P.G.; van Berckel, B.N.; Scheltens, P.; Scherder, E.J.; van der Flier, W.M.; Ossenkoppele, R. The effect of physical activity on cognitive function in patients with dementia: A meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 25, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee Submits Scientific Report. Available online: https://health.gov/news/blog-bayw/2018/03/2018-physical-activity-guidelines-advisory-committee-submits-scientific-report/ (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Ashcraft, K.A.; Peace, R.M.; Betof, A.S.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Jones, L.W. Efficacy and Mechanisms of Aerobic Exercise on Cancer Initiation, Progression, and Metastasis: A Critical Systematic Review of In Vivo Preclinical Data. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4032–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, L.; Idorn, M.; Olofsson, G.H.; Lauenborg, B.; Nookaew, I.; Hansen, R.H.; Johannesen, H.H.; Becker, J.C.; Pedersen, K.S.; Dethlefsen, C.; et al. Voluntary Running Suppresses Tumor Growth through Epinephrine- and IL-6-Dependent NK Cell Mobilization and Redistribution. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyn, P.; Abreu, B.C.; Ottenbacher, K.J. The effects of exercise training on elderly persons with cognitive impairment and dementia: A meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil 2004, 85, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojman, P.; Gehl, J.; Christensen, J.F.; Pedersen, B.K. Molecular Mechanisms Linking Exercise to Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.C.; Lee, I.M.; Weiderpass, E.; Campbell, P.T.; Sampson, J.N.; Kitahara, C.M.; Keadle, S.K.; Arem, H.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Hartge, P.; et al. Association of Leisure-Time Physical Activity With Risk of 26 Types of Cancer in 1.44 Million Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasso, J.P.; Eves, N.D.; Christensen, J.F.; Koelwyn, G.J.; Scott, J.; Jones, L.W. A framework for prescription in exercise-oncology research. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2015, 6, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.W.; Alfano, C.M. Exercise-oncology research: Past, present, and future. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.I.; Scherer, R.W.; Geigle, P.M.; Berlanstein, D.R.; Topaloglu, O.; Gotay, C.C.; Snyder, C. Exercise interventions on health-related quality of life for cancer survivors. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, G.; Schmidt-Supprian, M.; Rad, R.; Saur, D. Tissue-specific tumorigenesis: Context matters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulczak, A.; Souza, A.O.; Ferrari, G.D.; Azzolini, A.; Pereira-da-Silva, G.; Alberici, L.C. Moderate Exercise Modulates Tumor Metabolism of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platten, M.; von Knebel Doeberitz, N.; Oezen, I.; Wick, W.; Ochs, K. Cancer Immunotherapy by Targeting IDO1/TDO and Their Downstream Effectors. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, P.; Schmidt, M.E.; Prentzell, M.T.; Berdel, B.; Wiskemann, J.; Kellner, K.H.; Debus, J.; Ulrich, C.; Opitz, C.A.; Steindorf, K. Resistance Exercise Reduces Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, S.; Dyar, K.A.; Ciciliot, S.; Blaauw, B.; Sandri, M. Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and atrophy. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4294–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, H.J.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, Z. Candidate mechanisms accounting for effects of physical activity on breast carcinogenesis. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahid, M.; Kim, J. Exercise May Affect Metabolism in Cancer-Related Cognitive Impairment. Metabolites 2020, 10, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10090377
Shahid M, Kim J. Exercise May Affect Metabolism in Cancer-Related Cognitive Impairment. Metabolites. 2020; 10(9):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10090377
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahid, Muhammad, and Jayoung Kim. 2020. "Exercise May Affect Metabolism in Cancer-Related Cognitive Impairment" Metabolites 10, no. 9: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10090377
APA StyleShahid, M., & Kim, J. (2020). Exercise May Affect Metabolism in Cancer-Related Cognitive Impairment. Metabolites, 10(9), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10090377