Pursuing Experimental Reproducibility: An Efficient Protocol for the Preparation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Samples for NMR-Based Metabolomics and Analysis of Sample Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. CSF Collection
3.3. Preparation of Model Solution and CSF Samples for NMR Studies
3.3.1. Model Solution
3.3.2. CSF Samples
3.4. NMR Spectroscopy
3.5. Chemometric Analysis
3.5.1. Metabolic Fingerprinting and Profiling
3.5.2. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milhorat, T.H.; Hammock, M.K. Cerebrospinal fluid as reflection of internal milieu of brain. In Neurobiology of Cerebrospinal Fluid, 1st ed.; Wood, J.H., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1983; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, E.; Tsang, T.M.; Huang, J.T.J.; Leweke, F.M.; Koethe, D.; Gerth, C.W.; Nolden, B.M.; Gross, S.; Schreiber, D.; Nicholson, J.K.; et al. Metabolic profiling of CSF: Evidence that early intervention may impact on disease progression and outcome in schizophrenia. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, N.W.; Cozzone, P.J. Metabolic profiling in multiple sclerosis and other disorders by quantitative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco, H.; Nadal-Desbarats, L.; Pradat, P.-F.; Gordon, P.H.; Antar, C.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Moreau, C.; Devos, D.; Mavel, S.; Emond, P.; et al. Untargeted 1H-NMR metabolomics in CSF: Toward a diagnostic biomarker for motor neuron disease. Neurology 2014, 82, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öhman, A.; Forsgren, L. NMR metabonomics of cerebrospinal fluid distinguishes between Parkinson’s disease and controls. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 594, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A.J.; Viant, M.R.; Ball, A.K.; Burdon, M.A.; Walker, E.A.; Stewart, P.M.; Rauz, S.; Young, S.P. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid and serum in neurological diseases–A diagnostic tool? NMR Biomed. 2009, 23, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, H.; Corcia, P.; Moreau, C.; Veau, S.; Fournier, C.; Vourc’h, P.; Emond, P.; Gordon, P.; Pradat, P.F.; Praline, J.; et al. 1H-NMR-Based Metabolomic Profiling of CSF in Early Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, V.G.; Bhattachayya, S.; Besser, M.; Rae, C.; Griffin, J.L. Metabolites from cerebrospinal fluid in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage correlate with vasospasm and clinical outcome: A pattern-recognition 1H NMR study. NMR Biomed. 2005, 18, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueras, L.; Gonzalo, H.; Jové, M.; Sol, J.; Gil-Sanchez, A.; Hervás, J.V.; Valcheva, P.; Gonzalez-Mingot, C.; Solana, M.J.; Peralta, S.; et al. Lipid profile of cerebrospinal fluid in multiple sclerosis patients: A potential tool for diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyer, A.; Boudah, S.; Broudin, S.; Junot, C.; Colsch, B. Annotation of the human cerebrospinal fluid lipidome using high resolution mass spectrometry and a dedicated data processing workflow. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinkohl, I.; Schipke, C.G.; Kruppa, J.; Menne, F.; Winterer, G.; Pischon, T.; Peters, O. Plasma Amyloid concentration in alzheimer’s disease: Performance of a high-throughput amyloid assay in distinguishing alzheimer’s disease cases from controls. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 74, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, O.A.C.; Yu, R.K.; Ogino, T. High-Resolution Proton Magnetic Resonance Analysis of Human Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Neurochem. 1986, 47, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenling, T.; Stoop, M.P.; Smolinska, A.; Muilwijk, B.; Coulier, L.; Shi, S.; Dane, A.; Christin, C.; Suits, F.; Horvatovich, P.L.; et al. The impact of delayed storage on the measured proteome and metabolome of human cerebrospinal fluid. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, T.; Balayssac, S.; Gilard, V.; Martino, R.; Vincent, C.; Pariente, J.; Malet-Martino, M. 1H NMR analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from alzheimer’s disease patients: An example of a possible misinterpretation due to non-adjustment of pH. Metabolites 2014, 4, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewczuk, P.; Kornhuber, J.; Wiltfang, J. The German competence net dementias: Standard operating procedures for the neurochemical dementia diagnostics. J. Neural Transm. 2006, 113, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, J.A.; Brennan, L.; Broadhurst, D.; Fiehn, O.; Cascante, M.; Dunn, W.B.; Schmidt, M.A.; Velagapudi, V. Preanalytical processing and biobanking procedures of biological samples for metabolomics research: A white paper, community perspective (for “Precision Medicine and Pharmacometabolomics Task Group”—The Metabolomics Society Initiative). Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1158–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, C.E. A consensus protocol for the standardization of cerebrospinal fluid collection and biobanking. Neurology 2009, 73, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterji, T.; Singh, S.; Sen, M.; Singh, A.K.; Maurya, P.K.; Husain, N.; Srivastava, J.K.; Mandal, S.K.; Roy, R. Comprehensive 1H NMR metabolic profiling of body fluids for differentiation of meningitis in adults. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.; Reinecke, C.J.; Solomons, R.; Wevers, R.A.; Engelke, U.F.H. 1H NMR spectral identification of medication in cerebrospinal fluid of pediatric meningitis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 143, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielman, R.; Postma, R.; Verhoeven, A.; Bakels, F.; van Oosterhout, W.P.; Meissner, A.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Terwindt, G.M.; Mayboroda, O.A.; Ferrari, M.D. Metabolomic changes in CSF of migraine patients measured with 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 3674–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, A.; van der Plas, A.A.; van Dasselaar, N.T.; Deelder, A.M.; van Hilten, J.J.; Mayboroda, O.A. 1H-NMR metabolic profiling of cerebrospinal fluid in patients with complex regional pain syndrome–related dystonia. Pain 2014, 155, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskevich, S.I.; Molchanov, M.V.; Timchenko, M.A.; Kutyshenko, V.P. Sample pretreatment of brain tissues and cerebrospinal fluid for NMR investigations. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 68, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kork, F.; Gentsch, A.; Holthues, J.; Hellweg, R.; Jankowski, V.; Tepel, M.; Zidek, W.; Jankowski, J. A biomarker for severity of Alzheimer’s disease: 1H-NMR resonances in cerebrospinal fluid correlate with performance in mini-mental-state-exam. Biomarkers 2012, 17, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.H.; Shen, Y.C.; Shiao, Y.J.; Kuo, C.H.; Lu, C.K.; Lin, T.Y.; Ku, W.C.; Lin, Y.L. Combined proteomic and metabolomic analyses of cerebrospinal fluid from mice with ischemic stroke reveals the effects of a Buyang Huanwu decoction in neurodegenerative disease. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Jeong, I.H.; Hyun, J.S.; Kong, B.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.J. Metabolomic profiling of CSF in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder by nuclear magnetic resonance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Du, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; Jia, H.; Xing, A.; Sun, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. Cerebrospinal fluid metabolomic profiling in tuberculous and viral meningitis: Screening potential markers for differential diagnosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 466, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, E.; Larkin, J.R.; Claridge, T.D.; Talbot, K.; Sibson, N.R.; Turner, M.R. The longitudinal cerebrospinal fluid metabolomic profile of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2015, 16, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelke, U.F.H.; Tangerman, A.; Willemsen, M.A.A.P.; Moskau, D.; Loss, S.; Mudd, S.H.; Wevers, R.A. Dimethyl sulfone in human cerebrospinal fluid and blood plasma confirmed by one-dimensional 1H and two-dimensional 1H-13C NMR. NMR Biomed. 2005, 18, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.; van Furth, A.M.; Mienie, L.J.; Engelke, U.F.; Wevers, R.A.; Solomons, R.; Reinecke, C.J. A hypothetical astrocyte–microglia lactate shuttle derived from a 1H NMR metabolomics analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from a cohort of South African children with tuberculous meningitis. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 822–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercier, P.; Lewis, M.J.; Chang, D.; Baker, D.; Wishart, D.S. Towards automatic metabolomic profiling of high-resolution one-dimensional proton NMR spectra. J. Biomol. NMR 2011, 49, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, F.; Lorefice, L.; Poddighe, S.; Giuseppe, F.; Secci, M.A.; Marrosu, M.G.; Cocco, E.; Atzori, L. Multi-platform characterization of cerebrospinal fluid and serum metabolome of patients affected by relapsing–Remitting and primary progressive multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.T.; Cheng, M.L.; Lo, C.J.; Lin, G.; Lin, S.F.; Yeh, J.T.; Ho, H.Y.; Lin, J.R.; Liu, F.C. 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)-based cerebrospinal fluid and plasma metabolomic analysis in type 2 diabetic patients and risk prediction for diabetic microangiopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, A.; Paciotti, S.; Tenori, L.; Eusebi, P.; Biscetti, L.; Chiasserini, D.; Scheltens, P.; Turano, P.; Teunissen, C.; Luchinat, C.; et al. Fingerprinting alzheimer’s disease by 1 H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of cerebrospinal fluid. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jääskeläinen, O.; Hall, A.; Tiainen, M.; van Gils, M.; Lötjönen, J.; Kangas, A.J.; Helisalmi, S.; Pikkarainen, M.; Hallikainen, M.; Koivisto, A.; et al. Metabolic profiles help discriminate mild cognitive impairment from dementia stage in alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 74, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podlecka-Piętowska, A.; Kacka, A.; Zakrzewska-Pniewska, B.; Nojszewska, M.; Zieminska, E.; Chalimoniuk, M.; Toczylowska, B. Altered cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of hydrophobic and hydrophilic compounds in early stages of multiple sclerosis—Metabolic profile analyses. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukarainen, N.M.; Korhonen, S.P.; Laakso, M.P.; Korolainen, M.; Niemitz, M.; Soininen, P.; Tuppurainen, K.; Vepsäläinen, J.; Pirttilä, T.; Laatikainen, R. Quantification of 1H NMR spectra of human cerebrospinal fluid: A protocol based on constrained total-line-shape analysis. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, C.D.; Willoughby, R.E.; Pan, A.; Wong, S.J.; Foley, J.F.; Wheat, L.J.; Fernandez, J.; Encarnacion, R.; Ondrush, J.M.; Fatteh, N.; et al. NMR metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid differentiates inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0007045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, W.; Lang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Chen, J.; Cui, L. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolic profiling of cerebrospinal fluid to identify metabolic features and markers for tuberculosis meningitis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 68, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterji, T.; Singh, S.; Sen, M.; Singh, A.K.; Agarwal, G.R.; Singh, D.K.; Srivastava, J.K.; Singh, A.; Srivastava, R.N.; Roy, R. Proton NMR metabolic profiling of CSF reveals distinct differentiation of meningitis from negative controls. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 469, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siesjö, B.K. The regulation of cerebrospinal fluid pH. Kidney Int. 1972, 1, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunniffe, J.G.; Whitby-Strevens, S.; Wilcox, M.H. Effect of pH changes in cerebrospinal fluid specimens on bacterial survival and antigen test results. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 49, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.; Panchalingam, K.; McClure, R.J.; Gershon, S.; Pettegrew, J.W. Stability of CSF metabolites measured by proton NMR. J. Neural Transm. 2000, 107, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoop, M.P.; Coulier, L.; Rosenling, T.; Shi, S.; Smolinska, A.M.; Buydens, L.; Ampt, K.; Stingl, C.; Dane, A.; Muilwijk, B.; et al. Quantitative proteomics and metabolomics analysis of normal human cerebrospinal fluid samples. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2010, 9, 2063–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska, A.; Attali, A.; Blanchet, L.; Ampt, K.; Tuinstra, T.; van Aken, H.; Suidgeest, E.; van Gool, A.J.; Luider, T.; Wijmenga, S.S.; et al. NMR and Pattern Recognition Can Distinguish Neuroinflammation and Peripheral Inflammation. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 4428–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ventrella, D.; Laghi, L.; Barone, F.; Elmi, A.; Romagnoli, N.; Bacci, M.L. Age-Related 1H NMR Characterization of Cerebrospinal Fluid in Newborn and Young Healthy Piglets. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dujmovic, I.; Deisenhammer, F. Stability of cerebrospinal fluid/serum glucose ratio and cerebrospinal fluid lactate concentrations over 24 h: Analysis of repeated measurements. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwaest, K.A.; Vu, T.N.; Laukens, K.; Clemens, L.E.; Nguyen, H.P.; van Gasse, B.; Martins, J.C.; van der Linden, A.; Dommisse, R. 1H NMR based metabolomics of CSF and blood serum: A metabolic profile for a transgenic rat model of Huntington disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckonert, O.; Keun, H.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Bundy, J.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Lewis, M.J.; Morrissey, J.A.; Flegel, M.D.; Jeroncic, K.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, D.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; Tzur, D.; et al. The human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 871, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Chaudhary, K.K.; Liu, P.; Yallou, F.S.; Dong, E.; Aziat, F.; Wishart, D.S. Multi-platform characterization of the human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome: A comprehensive and quantitative update. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Hao, F.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. An optimized buffer system for NMR-based urinary metabonomics with effective pH control, chemical shift consistency and dilution minimization. Analyst 2009, 134, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. Eliminating the dication-induced intersample chemical-shift variations for NMR-based biofluid metabonomic analysis. Analyst 2012, 137, 4209–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, S.; Vion-Dury, J.; Confort-Gouny, S.; Nicoli, F.; Lutz, N.W.; Viout, P.; Cozzone, P.J. Experimental protocol for clinical analysis of cerebrospinal fluid by high resolution proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Brain Res. Protoc. 1998, 3, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alum, M.F.; Shaw, P.A.; Sweatman, B.C.; Ubhi, B.K.; Haselden, J.N.; Connor, S.C. 4,4-Dimethyl-4-silapentane-1-ammonium trifluoroacetate (DSA), a promising universal internal standard for NMR-based metabolic profiling studies of biofluids, including blood plasma and serum. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, S.A.; Schober, D.; Atherton, H.J.; Fiehn, O.; Jenkins, H.; Rocca-Serra, P.; Rubtsov, D.V.; Spasic, I.; Soldatova, L.; Taylor, C.; et al. Ontology working group members metabolomics standards initiative: Ontology working group work in progress. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sar, S.A.; Zielman, R.; Terwindt, G.M.; van den Magdenberg, A.M.; Deelder, A.M.; Mayboroda, O.A.; Meissner, A.; Ferrari, M.D. Ethanol contamination of cerebrospinal fluid during standardized sampling and its effect on 1H-NMR metabolomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 4835–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, B.; Wikoff, W.R.; Patti, G.J.; Woo, H.K.; Kalisiak, E.; Heideker, J.; Siuzdak, G. Variability analysis of human plasma and cerebral spinal fluid reveals statistical significance of changes in mass spectrometry-based metabolomics data. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8538–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloarec, O.; Dumas, M.E.; Craig, A.; Barton, R.H.; Trygg, J.; Hudson, J.; Blancher, C.; Gauguier, D.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; et al. Statistical total correlation spectroscopy: An exploratory approach for latent biomarker identification from metabolic 1H NMR data sets. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesi, A.; Rondanelli, M.; D’Eril, G.M. Stability of neuroactive amino acids in cerebrospinal fluid under various conditions of processing and storage. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 2359–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

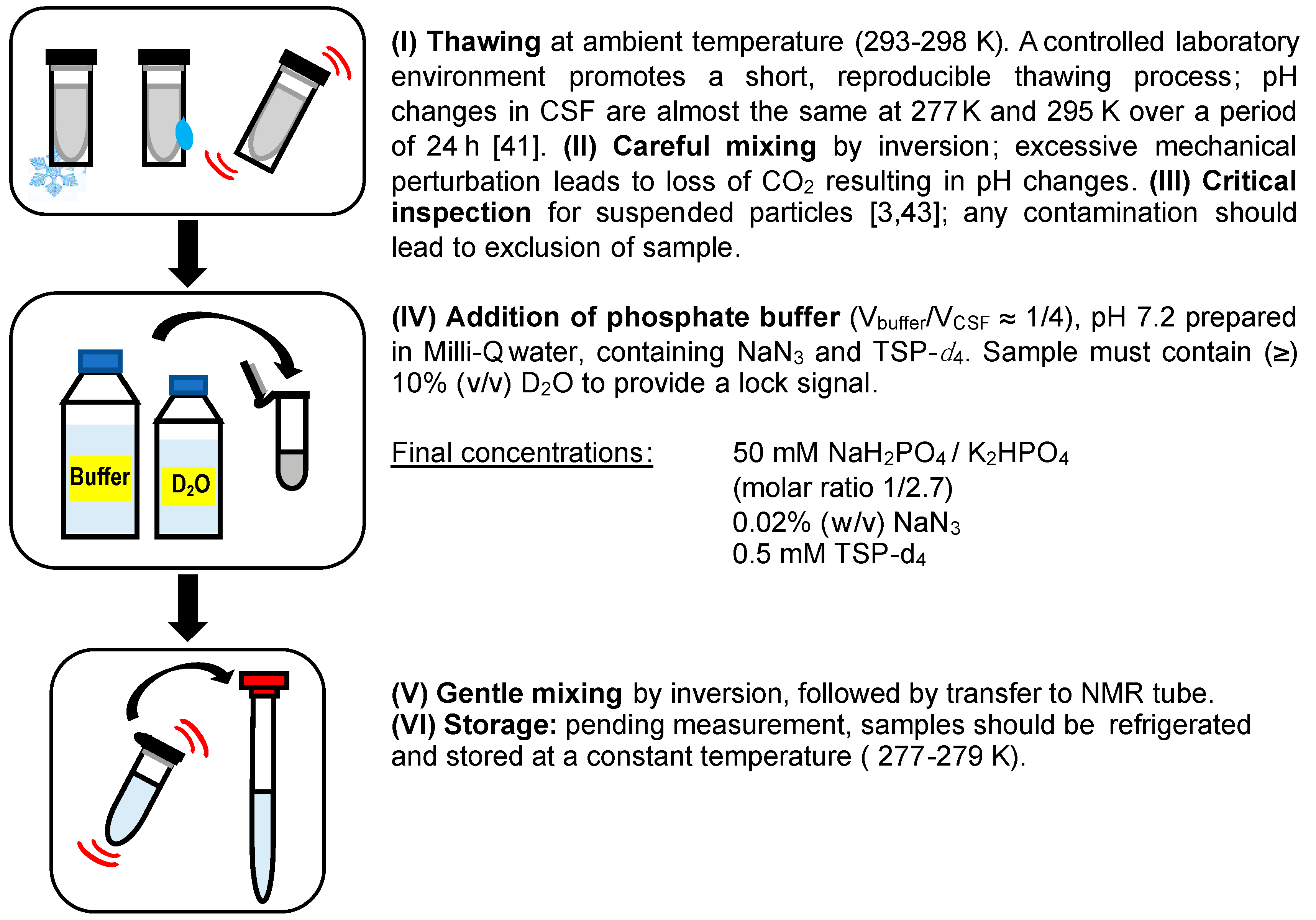

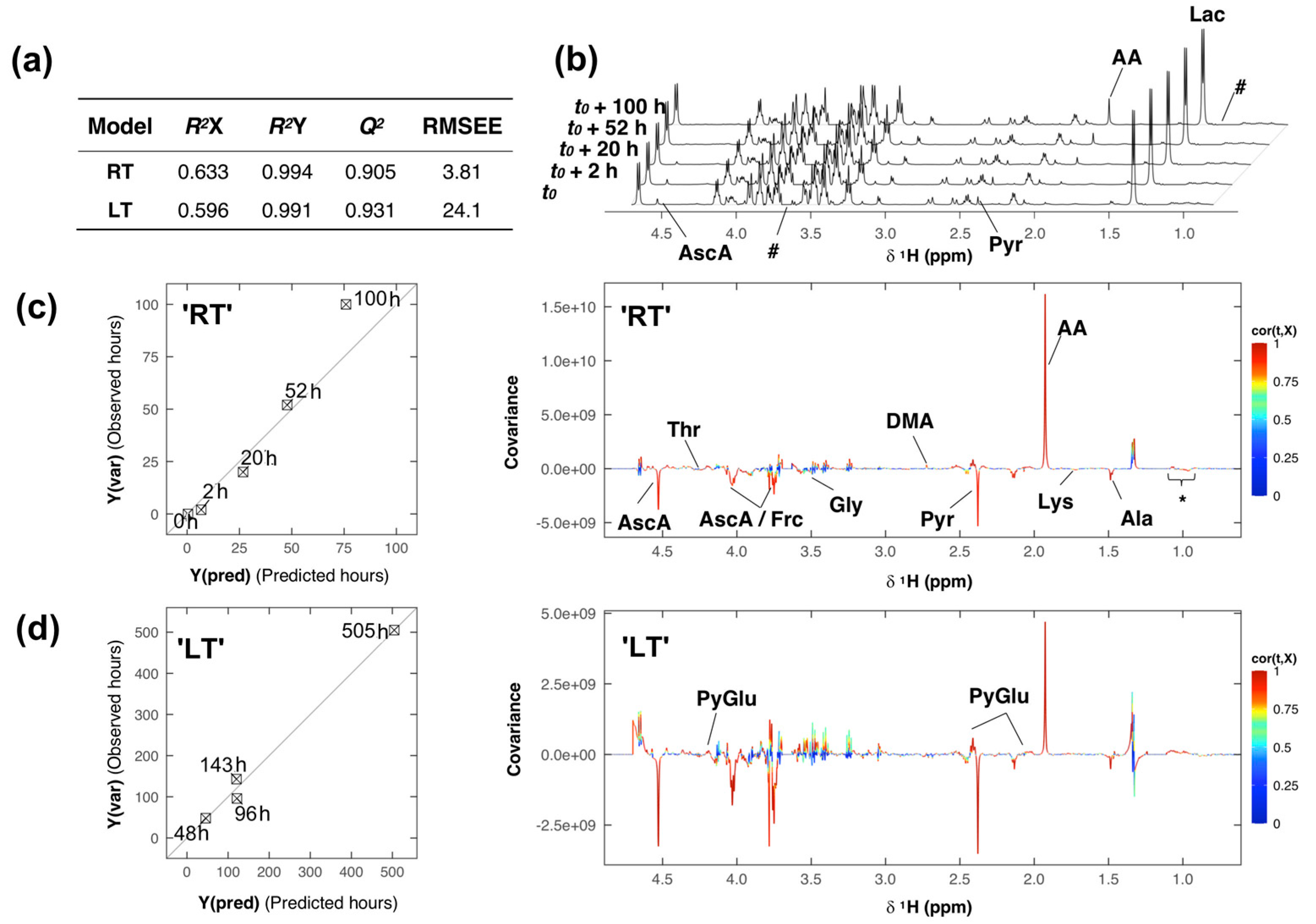
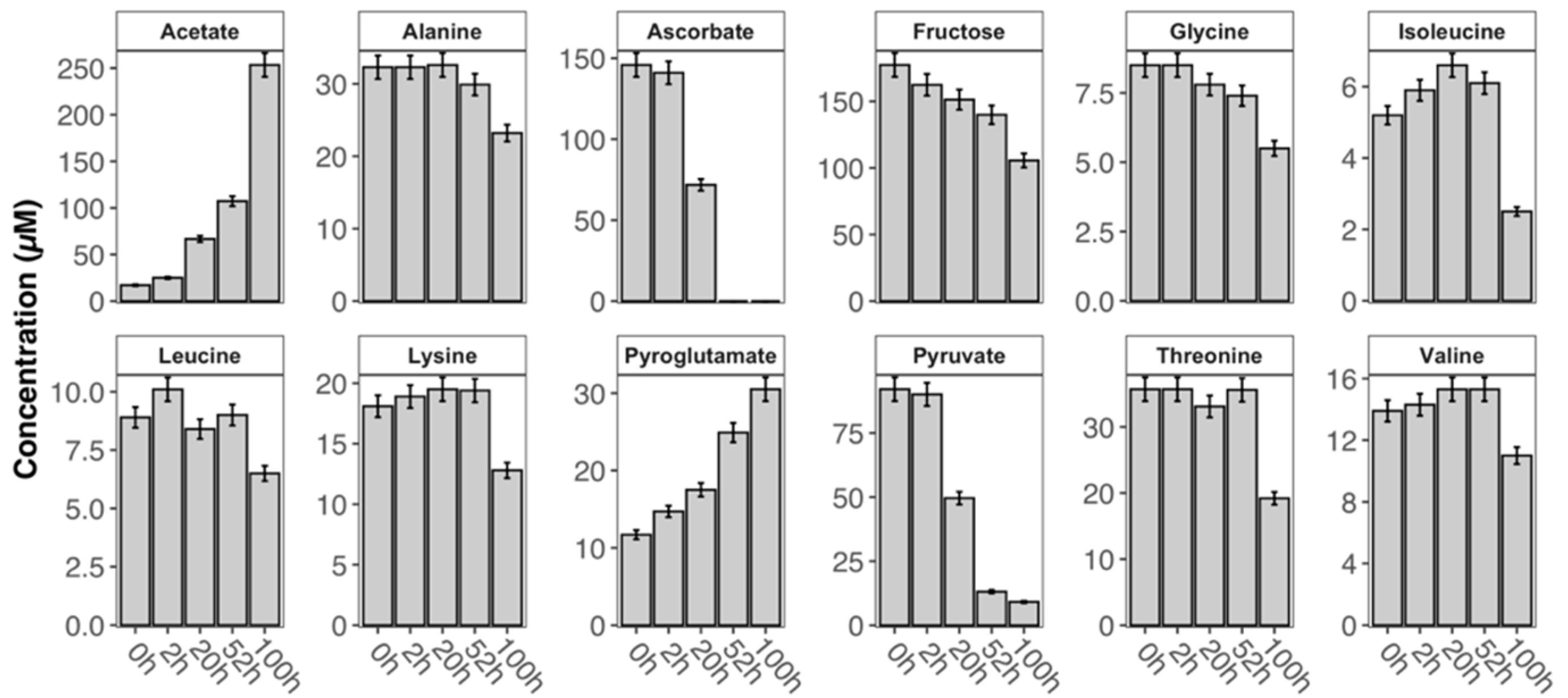
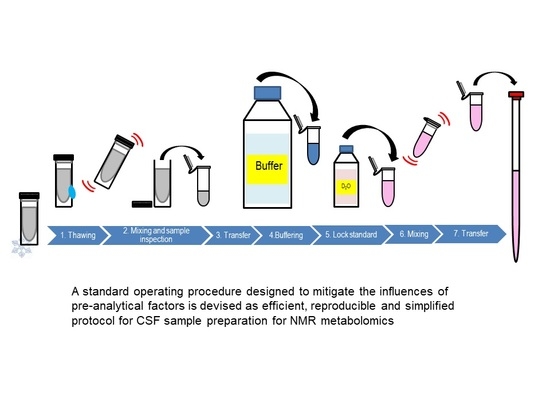
| Pre-Analytical Factor | Preparation Step | Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Volume | Variations of native sample volume. Sometimes native samples are lyophilized [22,31,36,42] and reconstituted and/or diluted [22,31,36,42,43,44]. | Available native CSF volume ranges from 40–570 µL. Depending on experimental setup/objective, samples may be reconstituted/diluted with H2O/D2O. |
| Ionic Strength | Ionic strength buffering is rarely addressed [5,6,21,38]. | Osmotic properties of buffer solutions vary (combinations of sodium/potassium phosphates/chlorides at varying concentrations) |
| Sample pH | Either adjusted with buffer solution [5,6,13,18,20,21,25,27,31,33,34,38,39], by adding HCl/NaOH solution [4,7,19,28,29,35,37], or ignored [8,23,24,26,32,36]. | Adjusted sample pH range from 2.5–10. Buffer solutions with sodium/potassium phosphate concentration in the range of 35–166 mM. |
| Sample Solution Homogeneity | Mixing, centrifugation [4,6,7,26,38] and filtration [19,28,29,37] in order to homogenize samples and remove high MW compounds and cellular material. | Vortexing, mixing (e.g., by inversion), centrifugation, filtering, and deproteinization by precipitation are found. |
| Chemical Shift Reference and Internal Standard Lock Signal | TSP-d4 or DSS(-d6). Samples contain between 10% and 100% D2O as lock standard. | Typical concentration of reference compound is 0.5–1.25 mM in the final sample. Deuterated solvent is either used for reconstitution, as part of buffer solution, or added separately. |
| Storage and Stability | After preparation, while queued for acquisition, samples are stored under suitable conditions to maintain sample integrity. | Samples were either frozen (253 K) [45], typically stored in a cooled (277–279 K) environment [37,38,46], or sometimes kept at ambient temperature (294 K) [47]. |
| Entry | Compound | Code | Concentration (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2-Hydroxybutyrate | aHBA | 18.4 ± 0.9 |
| 2 | 2-Hydroxyisovalerate | bHMB | 4.4 ± 0.2 |
| 3 | Acetate | AA | 34.3 ± 1.7 |
| 4 | Acetoacetate | AcA | 4.3 ± 0.2 |
| 5 | Acetone | Ac | 7.4 ± 0.4 |
| 6 | Alanine | Ala | 25.2 ± 1.3 |
| 7 | Ascorbate | AacA | 109.9 ± 5.5 |
| 8 | Caffeine | TMX | 9.7 ± 0.5 |
| 9 | Choline | CHO | 2.3 ± 0.1 |
| 10 | Citrate | Cit | 90.9 ± 0.4 |
| 11 | Creatine | Cr | 27 ± 1.4 |
| 12 | Creatinine | Cre | 55.1 ± 2.8 |
| 13 | Dimethylamine | DMA | 1.5 ± 0.1 |
| 14 | Dimethyl sulfone | DMS | 7.2 ± 0.4 |
| 15 | Ethanol | EtOH | 1934.8 ± 96.7 |
| 16 | Formate | FA | 19.3 ± 1.0 |
| 17 | Fructose | Frc | 130.2 ± 6.5 |
| 18 | Glucose | Glc | 2013.3 ± 100.7 |
| 19 | Glutamine | Gln | 246.0 ± 12.3 |
| 20 | Glycine | Gly | 5.5 ± 0.3 |
| 21 | Histidine | His | 8.2 ± 0.4 |
| 22 | Hypoxanthine | HX | 3.7 ± 0.2 |
| 23 | Isoleucine | Ile | 3.5 ± 0.2 |
| 24 | Isopropanol | iPrOH | 224.1 ± 11.2 |
| 25 | Lactate | Lac | 907.7 ± 45.4 |
| 26 | Leucine | Leu | 7.8 ± 0.4 |
| 27 | Lysine | Lys | 16.2 ± 0.8 |
| 28 | Mannose | Man | 28.6 ± 1.4 |
| 29 | Methanol | MeOH | 45.4 ± 2.3 |
| 30 | myo-Inositol | MIOL | 66.3 ± 3.3 |
| 31 | Phenylalanine | Phe | 5.7 ± 0.3 |
| 32 | Pyroglutamate | pyGlu | 12.8 ± 0.6 |
| 33 | Pyruvate | Pyr | 12.8 ± 0.6 |
| 34 | Threonine | Thr | 31.0 ± 1.6 |
| 35 | Trimethylamine N-oxide | TMAO | 1.2 ± 0.1 |
| 36 | Tyrosine | Tyr | 8.2 ± 0.4 |
| 37 | Valine | Val | 11.1 ± 0.6 |
| 38 | Xanthine | XAN | 4.5 ± 0.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albrecht, B.; Voronina, E.; Schipke, C.; Peters, O.; Parr, M.K.; Díaz-Hernández, M.D.; Schlörer, N.E. Pursuing Experimental Reproducibility: An Efficient Protocol for the Preparation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Samples for NMR-Based Metabolomics and Analysis of Sample Degradation. Metabolites 2020, 10, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060251
Albrecht B, Voronina E, Schipke C, Peters O, Parr MK, Díaz-Hernández MD, Schlörer NE. Pursuing Experimental Reproducibility: An Efficient Protocol for the Preparation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Samples for NMR-Based Metabolomics and Analysis of Sample Degradation. Metabolites. 2020; 10(6):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060251
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbrecht, Benjamin, Elena Voronina, Carola Schipke, Oliver Peters, Maria Kristina Parr, M. Dolores Díaz-Hernández, and Nils E. Schlörer. 2020. "Pursuing Experimental Reproducibility: An Efficient Protocol for the Preparation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Samples for NMR-Based Metabolomics and Analysis of Sample Degradation" Metabolites 10, no. 6: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060251
APA StyleAlbrecht, B., Voronina, E., Schipke, C., Peters, O., Parr, M. K., Díaz-Hernández, M. D., & Schlörer, N. E. (2020). Pursuing Experimental Reproducibility: An Efficient Protocol for the Preparation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Samples for NMR-Based Metabolomics and Analysis of Sample Degradation. Metabolites, 10(6), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060251